#bpmn
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Being a successful Business Analyst requires a mix of technical expertise, analytical skills, and strong communication. This cheat sheet serves as a quick reference to keep you on track and efficient in your role.
#BusinessAnalyst#BA#Agile#Waterfall#ProjectManagement#ProcessImprovement#DataAnalysis#StakeholderManagement#BPMN#SWOTAnalysis#RequirementGathering#UserStories#SQL#JIRA#PowerBI
0 notes
Text
BPMN e Automação: Transformando Processos
BPMN e automação são ferramentas essenciais para empresas que desejam otimizar seus processos e se tornar verdadeiramente data driven. Imagine um mundo onde seus fluxos de trabalho são automatizados, livres de erros e executados com máxima eficiência. Esse futuro, antes distante, está ao seu alcance, e este artigo revelará como a combinação de BPMN e automação pode transformar seus processos,…
#análise de dados#automação#BPMN#eficiência#otimização#processos contábeis#produtividade#redução de erros#transformação digital
0 notes
Video
youtube
Business Studio. Моделирование бизнес-процессов в нотации BPMN
0 notes
Text
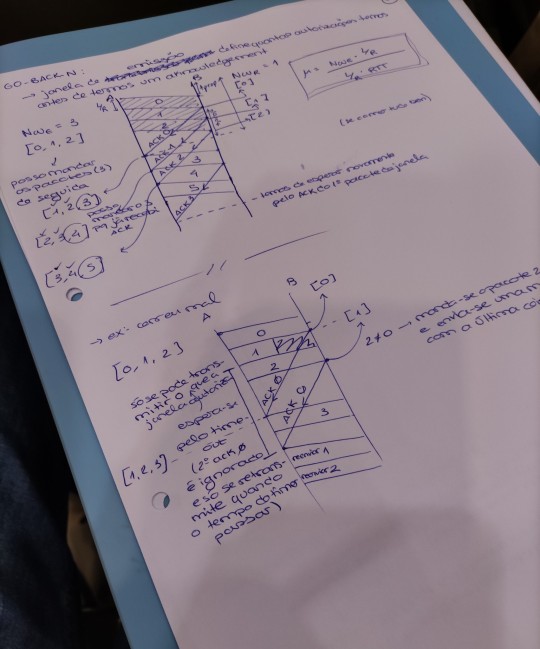

[ 28th november, 2023 • 79/145 days of uni ]
had to miss some classes to go to the doctor (just a normal volleyball hand injury, nothing's broken!)
finished my essay on The Overcoat AND my essay on R.U.R.! FINALLY! those 2 are out of my to do list once and for all!! drafted some ideas to fix the issue with my BPMN diagram and now just have to review the Archimate diagrams and finish the client side of the RC project.. those are stressing me out haha but will be done soon :))
#stargazerbibi#study#studyblr#100 dop#100 days of productivity#studygram#stem#uni#student#studyspo#studyspiration#studystudystudy#aesthetic#productivity#student life#studying#studies#study blog#study motivation#college#uniblr#uni life#university#stem studyblr#stemblr#stem girls
40 notes
·
View notes
Note
MESSAGE from SHPSHFTINGSHITHOUSE to be sent to KN0WN_FAKER
Hi, this is Jota's sister. I'd rather not be on the same side of reality as you unless it's to kill you personally, so I'm hoping he relays this message for me. With that out of the way, I only have one thing to tell you. If you even dare hurt my brother, AMSLR WMSP BYWQ, BPMN RFC BYKLCB EMB AMKNJCV, YLB QRYPR NPYWGLE, WMS CBEW UYQRC MD DSAIGLE CVGQRCLAC.
[[ Relay to KN0WN_FAKER? (y/n) ]]
[ sent it... uh. mhm, uh, oh ok. ] [ he says he doesn't care- ]
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Considering if I want a study blog while I'm brushing up my BPMN and UML, and/or a kinky aesthetic photo blog for personal pics and spicy reblogs, and/or a tarot blog.
Would anyone follow any of that?
Study blog would be updates about how my business analysis studies are going, study encouragement and memes, book reviews and excerpts, and achievement tracking.
Kink blog would be mostly aesthetic sexy pics of fem and androgynous bodies (including my own), hypn0/mind control nsft, bondage, a bit of objectum here and there, hornyposting, that sort of thing.
Tarot blog would be mostly free one card readings, and musings on tarot and metaphysics and such.
#this is me trying to look for new hobbies#or well#turn existing hobbies into new online occupations#I need new spaces for other parts of myself#i just...#don't wanna go at it alone#or ho at it alone I suppose -thank you autocorrect#is any of this a good idea?#disaster thoughts#kinkblr#tarotblr#studyblr
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is a Workflow Model? A Complete Guide for Modern Enterprises
Efficiency is no longer a luxury—it's a necessity. To remain competitive, modern enterprises must streamline operations, eliminate bottlenecks, and ensure teams collaborate seamlessly. This is where a workflow model becomes essential. But what exactly is a workflow model, and why should it matter to your business?

Defining a Workflow Model
A workflow model is a visual or logical representation of a business process. It outlines how tasks, data, and documents flow from one step to another to achieve a specific business goal. Think of it as a blueprint that maps out who does what, when, and how, within a defined process.
By modeling a workflow, organizations gain clarity into each stage of a task or process, helping them identify redundancies, automate repetitive tasks, and improve overall performance.
Key Components of a Workflow Model
Understanding the anatomy of a workflow model is crucial. A well-designed model typically includes:
Tasks/Activities: Specific actions that need to be completed.
Roles/Actors: The individuals or systems responsible for each task.
Decision Points: Conditions that determine which path the workflow takes.
Sequence Flow: The order in which tasks are carried out.
Start and End Points: Mark the beginning and conclusion of the process.
Types of Workflow Models
Different business needs call for different workflow structures. The three most common types are:
Sequential Workflows: Tasks are performed in a linear, step-by-step sequence.
State Machine Workflows: Processes move between states based on user or system actions.
Rules-Driven Workflows: Task progression is dictated by conditional logic and predefined rules.
Each type serves a unique purpose. For instance, a sequential workflow might work best for onboarding employees, while a rules-driven model could be ideal for processing loan applications.
Benefits of Using Workflow Models in Modern Enterprises
Implementing workflow models isn’t just about documentation—it’s a strategic move. Here’s why:
Increased Efficiency: Mapping out processes reveals inefficiencies and areas for automation.
Better Collaboration: Clear roles and responsibilities reduce confusion and foster teamwork.
Error Reduction: Standardized steps reduce the risk of mistakes and missed tasks.
Scalability: As your organization grows, models make it easier to adapt and replicate successful processes.
Improved Compliance: Workflow models help ensure that regulatory and procedural standards are met consistently.
Real-World Applications
Workflow models are used across all industries. Here are a few examples:
Healthcare: Managing patient intake and medical record updates.
Finance: Streamlining approval processes for loans and invoices.
Manufacturing: Coordinating supply chain and inventory management.
IT and Software: Managing ticketing systems and agile development cycles.
Human Resources: Onboarding, performance evaluations, and leave management.
Whether you're a tech startup or a large enterprise, workflow modeling can bring structure and visibility to complex operations.
Tools to Build Workflow Models
Today’s businesses have access to a range of tools for creating and managing workflow models. Popular platforms include:
BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) tools for standardized modeling.
Workflow automation platforms like Cavintek, Monday.com, or Kissflow.
Low-code/no-code tools that allow teams to build workflows without programming skills.
These tools not only help you design workflows visually but also enable automation and real-time monitoring.
youtube
Final Thoughts
A workflow model is more than a diagram—it's a strategic tool that empowers businesses to operate smarter, faster, and more consistently. By clearly mapping out processes, modern enterprises can unlock efficiencies, improve service delivery, and foster growth.
If your organization hasn’t yet invested in workflow modeling, now is the time. With the right approach, you can turn everyday processes into powerful engines of productivity.
SITES WE SUPPORT
AI Job Hire Flow - Weebly
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
0 notes
Text
Understanding Workflow Automation: A Technical Deep Dive
Introduction:
Today, it has become common to see more and more firms engage workflow automation to manage business operations more efficiently and minimize mistakes in their operations. Workflow automation refers to the execution of tasks, forwarding of information, or carrying out processes without human interaction with the use of technology. In addition to speeding up task completion, the automation approach assists in the delivery of consistent and accurate outcomes in a multitude of business functions.
What is Workflow Automation?
Workflow automation is the software mechanism of using the automatic flow of tasks, documents, and information across work-related activities based on defined business rules. This approach ensures that business processes are streamlined, consistent, and efficient.
Key Components of Workflow Automation Systems:
Process Definition Environment:
This is a graphical interface that allows users to model and design workflows. Tools like Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) provide standardized symbols to represent various tasks and decision points within a process.
Workflow Engine:
The core of the automation system, the workflow engine interprets the process definitions and manages the execution of tasks. It ensures that tasks are assigned, notifications are sent, and business rules are enforced.
Integration Layer:
Modern workflows often require interaction with multiple systems. The integration layer facilitates communication between the workflow engine and other enterprise applications, databases, and services through APIs or middleware.
User Interface:
A platform where users can interact with the workflow system. This interface allows users to monitor progress, provide inputs, and manage tasks assigned to them.
Technical Mechanisms Behind Workflow Automation:
Task Sequencing and Routing:
Tasks within a workflow are sequenced based on predefined rules. The routing mechanism directs tasks to the appropriate users or systems, ensuring that each step is executed in the correct order.
Event Triggers:
Workflows can be initiated or altered based on specific events, such as the receipt of a document, completion of a task, or a particular date and time. Event-driven architectures enable workflows to respond dynamically to changing conditions.
Conditional Logic:
Incorporating if-else conditions allows workflows to handle decision points, enabling different paths based on specific criteria or data inputs.
Parallel Processing:
Some workflows require multiple tasks to be executed simultaneously. Parallel processing capabilities ensure that tasks can run concurrently without causing conflicts or data inconsistencies.
Benefits of Implementing Workflow Automation:
Enhanced Efficiency:
By automating repetitive tasks, organizations can significantly reduce the time required to complete processes, allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities.
Improved Accuracy:
Automation minimizes human errors, ensuring that tasks are performed consistently and data integrity is maintained.
Scalability:
Automated workflows can be easily scaled to handle increased volumes without a proportional increase in resource requirements.
Auditability and Compliance:
Workflow systems maintain detailed logs of all actions taken, providing a clear audit trail that is essential for compliance and reporting purposes.
Challenges and Considerations
Complexity in Implementation
Designing and deploying workflow automation can be complex, requiring a thorough understanding of existing processes and potential bottlenecks.
Integration with Legacy Systemsp:
Ensuring seamless integration with existing legacy systems can pose challenges, often necessitating custom connectors or middleware solutions.
Change Management:
Transitioning to automated workflows requires careful change management to ensure user adoption and to address any resistance.
Conclusion:
Workflow automation stands at the forefront of technological advancements driving operational excellence in modern enterprises. By leveraging sophisticated workflow automation systems, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and agility, positioning themselves for sustained success in a competitive landscape.
0 notes
Text
Transforming Business Efficiency: Business Process Modelling and Enterprise Architecture in Mumbai

In today’s highly competitive business landscape, staying agile and efficient is crucial for sustained success. Companies are increasingly turning to Business Process Modelling (BPM) and Enterprise Architecture and Business Strategy to streamline operations, reduce costs, and align strategies with dynamic market demands. In Mumbai, a city known as the financial heartbeat of India, the demand for expert business management consultants and BPM services is growing rapidly.
Understanding Business Process Modelling Services
Business Process Modelling Services is a structured method that visualizes the steps, workflows, and decision points within a business process. The goal is to understand, analyze, and improve these processes for maximum efficiency. By using tools like flowcharts, BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation), and simulation software, businesses can uncover bottlenecks, eliminate redundancies, and ensure smoother operations across departments.
Whether it's enhancing customer service, speeding up product delivery, or improving compliance, BPM helps organizations make data-driven decisions. Companies that invest in professional BPM services gain the ability to continuously adapt and improve — essential qualities in Mumbai's fast-paced corporate environment.
Role of Business Management Consultants in Mumbai
Mumbai is home to a diverse ecosystem of industries — from finance and real estate to IT and manufacturing. Navigating such complexity requires more than just operational knowledge; it demands strategic insight. This is where business management consultants play a vital role.
These consultants provide expert guidance to identify inefficiencies, redesign workflows, and align operations with broader business goals. They act as transformation partners, offering objective advice backed by market research, data analytics, and performance benchmarks. Businesses in Mumbai benefit from local consultants who understand regional nuances, regulatory requirements, and customer behaviors.
Business Process Architecture Mapping
A key part of BPM is Business Process Architecture Mapping. This involves documenting how various processes interact with each other, what dependencies exist, and how they contribute to organizational objectives. Think of it as creating a blueprint that links everyday tasks to the company’s strategic goals.
Process architecture mapping enables decision-makers to see the bigger picture. It supports better resource allocation, improves collaboration between departments, and forms the foundation for automation and digital transformation initiatives. It also helps in identifying gaps between current operations and future goals, allowing for more effective change management.
Aligning Enterprise Architecture with Business Strategy
Enterprise Architecture (EA) provides a holistic view of an organization’s structure, processes, information systems, and technologies. When EA is aligned with business strategy, companies can ensure that their IT infrastructure supports and enhances their goals rather than hindering them.
In Mumbai’s fast-evolving business climate, EA is crucial for companies undergoing digital transformation. It ensures that new technologies are seamlessly integrated and supports scalability, security, and compliance. Enterprise architects work closely with business strategists to develop roadmaps that bridge the gap between where the company is and where it wants to be.
Conclusion
For businesses in Mumbai aiming for operational excellence, growth, and digital transformation, combining Business Process Modelling, Process Architecture Mapping, and Enterprise Architecture is essential. Partnering with a trusted Business management consultant in Mumbai can accelerate this journey, providing the expertise needed to unlock greater efficiency, agility, and profitability in a competitive market.
0 notes
Text

📊 Struggling with #MBIS4008 Business Process Modeling?
We’ve got your back with expert assignment help!
✅ BPMN diagrams
✅ Process analysis
✅ Quality academic support
We specialize more in related courses:
MBIS4006 Information Systems Security
MBIS4008 Business Process Management
MBIS4009 Professional Practice in Information Systems
MBIS4017 Cybersecurity Risk Assessment and Strategies
MBIS4001 Information Systems Applications in Business+
MBIS4002 Database Management Systems
MBIS4003 Software Development
MBIS4004 Systems Analysis Design
Get A++ papers crafted to perfection by best experts at affordable prices!
💡 Get the grades you deserve – DM us now!
#AssignmentHelp #BPM #BusinessAnalytics #MBIS4008 #BusinessProcessModeling #MBIS4007 #BusinessInformationSystems #AustralianInstitute #HigherEducation #MBIS5014 #MBIS4006 #MBIS4002 #MBIS5015 #MBIS5013 #MBIS4017 #MBIS4009 #HomeworkHelp #BusinessInformationSystems #AustralianInstitute #HigherEducation
0 notes
Text


[ 23rd november, 2023 • 74/145 days of uni ]
-> RC, AMS, ILE and SO classes (total: 7h00)
so tired, but the AMS practical class was super interesting and i think i'm going to be comfortable enough with BPMN and the Carmunda Modeler to finish that part of the project quickly :)
#stargazerbibi#study#studyblr#100 dop#100 days of productivity#studygram#student life#student#studyspo#studyspiration#studystudystudy#aesthetic#productivity#studying#studies#study blog#study motivation#college#uni#uniblr#uni life#university
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
1 note
·
View note
Text
Business Process Mapping: A Step-by-Step Guide to Success
In today’s fast-paced business environment, optimizing efficiency is crucial for staying competitive. One of the most effective ways to enhance operations is through business process mapping. This technique allows organizations to visualize workflows, identify inefficiencies, and design solutions that streamline processes for greater success. Whether you're a small business or a large enterprise, mastering business process mapping can lead to better decision-making, reduced costs, and improved performance.
What is Business Process Mapping?
Business process mapping is a method of visually representing the steps, inputs, outputs, and resources involved in a business process. It helps businesses understand how work flows from one task to another and highlights areas that need improvement. By mapping these processes, businesses can make data-driven decisions, pinpoint redundancies, and create more efficient workflows.
Why is Business Process Mapping Important?
Clarity and Understanding: Visualizing processes makes them easier to comprehend. It enables team members at all levels to see how their tasks contribute to the overall goal of the organization.
Process Improvement: Mapping helps identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or areas with excessive steps. This insight allows for continuous improvements that can save time, resources, and money.
Alignment Across Teams: Business process mapping ensures all team members understand their roles, the steps they need to take, and the overall goals of the organization, reducing confusion and enhancing collaboration.
Data-Driven Decision Making: With clear visual representations, management can use process maps to make better-informed decisions about where to allocate resources and how to streamline workflows.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Business Process Mapping
1. Define the Process
The first step in business process mapping is defining the process you wish to map. This involves identifying the specific task or workflow that needs improvement. Be clear about what the process aims to achieve and the desired outcomes. For example, the process could be related to customer service, order fulfillment, or employee onboarding.
2. Identify Key Stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders who are familiar with the process, including employees, managers, and other departments that interact with it. Gather input from those directly involved to understand the process flow and its pain points.
3. List the Process Steps
Break down the process into individual steps. Each step should represent a distinct action or decision. Make sure to capture all relevant activities and avoid skipping any stages, no matter how small they seem. For example, an order fulfillment process might include order receipt, payment verification, inventory check, packaging, and shipping.
4. Choose a Mapping Method
There are several techniques to map business processes. The most common methods include flowcharts, value stream mapping, SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers) diagrams, and BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation). Choose a method based on the complexity of the process and your organization’s needs.
5. Create the Process Map
Now, start creating the process map. Use appropriate symbols for different process elements: ovals for start/end points, rectangles for actions, diamonds for decision points, and arrows for flow direction. There are various tools available to create process maps, including software like Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, or free tools like draw.io. Ensure that your process map is clear, easy to follow, and contains all necessary information.
6. Analyze the Process
Once the process map is created, analyze it to identify any inefficiencies, redundancies, or bottlenecks. Are there unnecessary steps that can be eliminated? Are there points where delays or errors frequently occur? This analysis is critical for improving the process and enhancing overall productivity.
7. Optimize the Process
With a clear understanding of the existing process, look for areas to optimize. This might involve eliminating unnecessary steps, automating repetitive tasks, or improving communication between departments. Reducing the complexity of the process can lead to significant time savings and cost reductions.
8. Test and Implement Changes
Before making widespread changes, test the new optimized process on a smaller scale. Gather feedback from stakeholders, and make any necessary adjustments. Once the new process is refined, implement the changes organization-wide.
9. Monitor and Iterate
After implementation, regularly monitor the process to ensure it remains efficient and effective. Business processes evolve over time, so it's important to update the process map and make adjustments when needed. Continuous improvement is key to maintaining success.
youtube
Conclusion
Business process mapping is a powerful tool for organizations looking to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance collaboration. By following these simple steps, businesses can map out their processes, identify pain points, and implement improvements that drive success. With a clear, visual representation of workflows, teams can work more cohesively, and businesses can achieve higher productivity and better overall performance.
SITES WE SUPPORT
Software Processes - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
1 note
·
View note
