#autoregulation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Há dias que só queremos ficar em silêncio, bem quietinhos, só existindo.
Eu mesma, com cada vez maior frequência, prefiro esse estado silencioso e tranquilo à minha volta, o que não significa que, em mim, tudo esteja perfeitamente tranquilo, calmo e sereno! Muitas vezes, ao contrário, estou um enorme caos e preciso da solitude e silêncio ao redor para que, dentro de mim, pouco a pouco, venha a calmaria e o silêncio comece a reinar.
( Uma Sonhadora )

#pensamentos#noite#sentimentos#autocuidado#autoregulation#autoregulagem#acalmar#calmaria#cuidado#paz#silencio#silenciar#tiffany young
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Coronary Circulation |Human Physiology | Myocardial Ischemia| Infarction
Introduction: Blood circulation in the arteries and veins that supply the heart is known as ‘coronary circulation.’ The heart contains and supplies blood but cannot use it directly. Table of contents: Introduction: The coronary arteries: Normal anastomosis: Functional anastomosis Coronary Sinuses: The great cardiac vein Chemical factors: Neural control The heart is unique in nature,…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
physiology i luv u

#was explaining the concept of autoregulation to my parents (dad bcuz mum doesnt vibe with biology) and i had to reread my fav chapter#cant wait to get back to uni im so sick of these gap years
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
through a lot of reading papers and comparing those papers to what I've discussed with autistics I know irl and reading self-reports all over the place I think there is a useful distinction to make between chronically under-aroused autistics who need and seek out strong stimulus to break through the painful numbing effect of their subjective experience, and the chronically over-aroused autistics who find even normal levels of noise/touch/scent/light painful to the point of debility. and there are a lot of mixed cases too but I think the useful takeaway for everyone is that both groups are constantly attempting to achieve homeostasis which has been denied to them, and that the regulation-seeking takes up an enormous amount of time and energy that people who are autoregulated at almost all times without thinking about it just cant perceive or even empathize with, only (at best) come to understand and accept on good faith.
the regulation-seeking is also at the top of their hierarchy of needs. it is more urgent than food, shelter, or any form of social connection
i don't have any ideas about applying this information to the question of "how to suffer less" except as a framework that helps guide decisions for the autistic, and especially as a forceful redirection of the idea of "treatment" by medical workers back to addressing symptoms individually rather than trying to generalize to "treating autism" which I don't think is a real idea.
168 notes
·
View notes
Text

Had this one in my folder as a WIP, hope it isn't too much!
Why a bunny girl? idk? Its the year of the rabbit and tbh it was one of the first things that crossed my mind when I wanted to do the New Year pic, but I felt mch were too young for that(sometimes even drawing them as adults feels bad?IDK why I autoregulate myself this much I used to not care at all :_:)
#mitsucho#mitsuchou#I keep seeing mistakes but I'm the type of idiot that will ignore them so I can sleep at night at ease
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
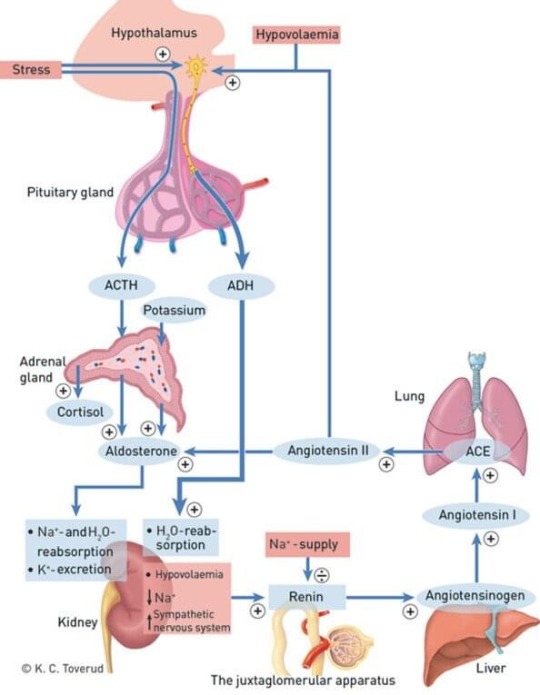
Fatigue that improves with caffeine (as it forces increased cortisol secretion) or hydrocortisone intake may suggest transient (reversible) hypoadrenalism due to excess cortisol requirement. Unfortunately, hypoadrenalism is difficult to detect in blood work and is often normal even in patients with who are severely ill, unless suffering from pituitary or supradrenal tumors, etc.
One of the most important causes of reversible adrenal exertion symptoms in patients with chronic pain, is TOS CVH. TOS CVH causes high arterial brain pressures that lead to paradoxical systemic hypotension due to cerebral autoregulation. This will raise adrenal output to perform daily tasks, ie. raise blood pressure and cardiac output through the sympathetic system, often resulting in profound fatigue, and as a worst case scenario, myalgic encephalomyelitis, if it goes on over a longer period of time. Usually, years.
Patients who have fatigue that responds to caffine but who do not have chronic pain, should mainly look to their sleep, diet and training habits. If sleep and diet is ok, then cardiovascular health is perhaps the most important aspect. Poor cardiac compliance to physical stressors, ie. inadequate strength of the heart, will be compensated for by a raised sympathetic tone and raised adrenal output. Increasing sodium intake can also help, but this should not be done excessively, as the heart may not tolerate a greater blood volume until its strength has been increased. This patient group should stick to [no more than] one cup of coffee per day, preferably in the morning and avoiding high-carbohydrate meals in the evenings. Mental stress also influences, needless to say.
A good indication of improved heart strength is reduced resting heart rates, but also overall lower heart rates during activities. Training too hard too often will strain the adrenal system and make the problem worse than it was initially, so starting with a 45-minute brisk walk once to twice per week, then gradually "feel it out from there", can be appropriate.
#health advice#adrenals#caffeine#stress#chronic pain#cardiovascular health#Body Alive#heart strength#fitness goals
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Analgetika
Opioide

Antagonist: Naloxon (= reiner Antagonist -> blockiert auch körpereigene Opioide!)
Analgesie
Sedation
antitussiv (=Hustenhemmung)
Nebenwirkungen:
atemdepressiv
vagusstimulierend: periphere Vasodilatation u. Bradykardie (gelten bei vorsichtiger Dosierung aber als sicher; Absichern durch gemeinsame Gabe mit Parasympatholytikum/ Vagolytikum)
wird über Leber verstoffwechselt -> vor Gabe Leber checken
am wenigsten ausgeprägte (Neben)Wirkung haben partielle und Agonist-Antagonisten -> wenn starke Analgesie notwendig -> Gabe reiner Agonisten
Reine μ-Rezeptor Agonisten
= aktiviert alle Opioid-Rezeptoren
Fentanyl: stärkste sedative u. analgetische Wirkung; starke Bradykardie; kurze Wirkdauer (20min) -> meist Gabe als Dauertropf intraOP Pethidin: starke Histaminausschüttung bei i.v.-Gabe -> IMMER i.m. zB f. postOP Kältezittern; weniger Bradykardie/ Atemdepression; spasmolytisch -> gut für gastrointestinale Probleme Morphin: NICHT für Tiere zugelassen; gilt als Goldstandard; Histaminausschüttung bei i.v.-Gabe; emetisch & übelkeitserregend; Hyperthermie (außer Hd); Wirkungseintritt nach 2min, Wirkdauer 2-4 h je nach Dosierung Methadon: Bradykardie/ Atemdepression nur in hohen Dosierungen; es kann zu Erbrechen kommen; Wirkungseintritt i.v. nach 2min, Wirkdauer 2-4 h je nach Dosierung
Partielle μ-Rezeptor Agonisten
= aktiviert μ nicht komplett -> Wirkung geringer
fast nicht antagonisierbar, wegen hoher Rezeptorbindungsaffinität
Buprenorphin (=Bupaq): weniger sedierend, gut analgetisch; längere Wirkdauer (4-8h) -> gut f. postOP-Phase; Ceiling-Effekt! (Schwellenwert aber sehr hoch); Ktz: kann zu Hyperthermie kommen, Applikation sehr gut über Maulschleimhaut möglich
κ-Rezeptor Agonisten & μ- Rezeptor Antagonist
= Aktivierung κ, Blockierung μ
Butorphanol: gut sedierend, schwach analgetisch; kein Suchtgift!; Ceiling-Effekt!; antiemetisch; kurze Wirkdauer: Hd (1-2h), Ktz (45min)
NSAIDs (= nicht-steroidale Antiphlogistika)
entzündungshemmend
analgetisch
antipyretisch
Nebenwirkungen
gastrointestinale Schädigung der Schleimhaut (zB Ulcera)
Schädigung der Niere (beeinträchtigt Autoregulation) -> Akutes Problem bei Hypotension
Blutungsneigung (wg. Hemmung d. Thrombozytenaggregation)
Verstärkung der Nebenwirkungen bei gemeinsamer Gabe mit Steroiden!
COX1 & COX 2- Hemmer
= haben grundsätzlich die meisten/ schwersten Nebenwirkungen resultierend durch die COX1-Hemmung (= nur COX2-Hemmung = weniger Nebenwirkungen)
Aspirin: Verwendung nur mehr als Blutverdünner Flunixin: sehr stark analgetisch; Gabe bei KolikPfd wenn Ursache bekannt, (Wirkungsdauer 8-12h); NIE präOP beim Kleintier -> verursacht postOP Niereninsuffizienz Ketoprofen (=Rifen): nicht beim Kleintier -> akutes Nierenversagen Phenylbutazon: NICHT bei Ktz wg. geringer therapeutischer Breite; gut antiinflammatorisch, Anreicherung in Entzündungsexsudat, lange Wirkung (12-24h)
Tolfenaminsäure
COX2-Hemmer
Carprofen (=Rimadyl) Meloxicam (=Metacam): geeignet für Langzeitbehandlung (einziges f. Ktz! ABER: entweder orale Gabe ODER einmalige parenterale Injektion -> plötzliche Todesfälle durch Mischung beider Anwendungsformen) Vedaprofen
Coxibe (=selektive COX2-Hemmer)
Cimicoxib: Hd: auch bei Niereninsuffizienz u. f. Langzeittherapie zugelassen Mavacoxib: zugelassen nur f. Hd.: für Langzeittherapie (max. 6,5 Mo.) Wirkungsdauer: 1 Monat Robenacoxib (=Onsior): Gabe nur sinnvoll wenn Entzündung bereits vorhanden (Halbwertzeit kurz, sammelt sich aber im Entzündungsbereich an und hält lokal den Wirkungsspiegel); zugelassen beim Hd. f. Langzeittherapie
Andere Analgetika
Metamizol (=Novasul): stark analgetisch, antipyretisch und spasmolytisch; zugelassen für einmalige Verwendung; maskiert Schmerzen nicht -> gut für Initialbehandlung v. KolikPfd/ Schlundverstopfung und f. Kleintier bei viszeralem Schmerz; Nebenwirkung bei mehrmaliger Gabe großer Dosen: knochenmarksdepression Paracetamol (=Mexalen): NICHT bei Ktz -> einmalige Gabe tödlich!; NUR für Hd.; kann gemeinsam mit Steroiden gegeben werden Gabapentin: für Tiere nicht zugelassen; Gabe bei chronischen/ neuropathischen Schmerzen Amantadin: für Tiere nicht zugelassen; Gabe bei chronischen/ neuropathischen Schmerzen Tramadol
0 notes
Text
The country advocates the increase of organic fertilizer, the vice minister of agriculture put forward organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer together with the use is the most scientific way of fertilization at present! So what is the difference between organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer? What are the benefits of the two collocation?
One,What are organic fertilizers and chemical fertilizers
1, organic fertilizer mainly comes from plants and/or animals, applied to the soil to provide plant nutrition as its main function of carbon-containing materials. The Production process of this kind of Fertilizer usually involves the Organic Fertilizer Production Line, which can ensure the quality and effect of organic fertilizer.
2, chemical fertilizer is through chemical research and manufacture of fertilizer, with chemical and/or physical methods made of containing one or several kinds of crop growth needs nutrient elements of fertilizer.
Two, the environment is different
1, organic fertilizer is the use of biological excreta or remains to act as fertilizer, organic matter in organic fertilizer is decomposed by microorganisms, the remaining inorganic salts into the soil is absorbed by plants, because organic fertilizer and the environment has a good compatibility, will not cause pollution to the environment.
2, chemical fertilizer is the high purity of inorganic salts buried in the soil, these salts dissolved into the soil after the absorption of plants, because the concentration of inorganic salts is large, it is easy to cause soil acid-base balance is destroyed, harm the environment.
Three, the seven differences between organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer:
(1) Organic fertilizer contains a large amount of organic matter and has obvious effects on soil improvement and fertilization; Chemical fertilizer can only provide inorganic nutrients for crops, long-term application will cause adverse effects on the soil, so that the soil "more and more greedy".
2) Organic fertilizer contains a variety of nutrients, the nutrients contained in a comprehensive balance; However, the nutrients contained in chemical fertilizer are single, and long-term application is easy to cause nutrient imbalance in soil and food.
(3) Organic fertilizer has low nutrient content and needs to be applied in large quantities; However, chemical fertilizers have high nutrient content and low application rate.
(4) Long effective time of organic fertilizer; The fertilizing period of chemical fertilizers is short and fierce, which is easy to cause nutrient loss and pollute the environment.
(5) Organic fertilizer comes from nature, there is no chemical synthesis in fertilizer, long-term application can improve the quality of agricultural products; Chemical fertilizer is a pure chemical synthetic substance, improper application can reduce the quality of agricultural products.
(6) In the production and processing process of organic fertilizer, as long as it is fully decomposed, it can improve the drought resistance, disease resistance and insect resistance of crops after application, and reduce the use of pesticides; Long-term application of chemical fertilizer, because it reduces the immunity of plants, often requires a large number of chemical pesticides to maintain crop growth, which is easy to cause the increase of harmful substances in food.
(7) Organic fertilizer contains a large number of beneficial microorganisms, which can promote the biotransformation process in the soil and is conducive to the continuous improvement of soil fertility; Long-term and extensive application of chemical fertilizers can inhibit the activities of soil microorganisms, resulting in a decline in the ability of soil autoregulation.
Four, organic fertilizer with chemical fertilizer six benefits
1, short to take long, fertilizing soil. The nutrient of chemical fertilizer is single, high content, fast fertilizer effect, but short duration; Organic fertilizer has complete nutrients and long fertilizer effect, which can improve soil and fertilize soil fertility. The two can be used in combination, which can be replaced by short and long, fully supply the nutrients needed for crop growth, promote the healthy growth of crops, and improve the yield benefit. 2. Preserve nutrients and reduce loss. Chemical fertilizer dissolves quickly and has large solubility. After being applied to soil, the concentration of soil solution will increase soon, resulting in higher infiltration pressure of crops, affecting the absorption of nutrients and water by crops, and increasing the loss and opportunity of nutrients. The mixed use of organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer can inhibit the disadvantage of the sudden increase of soil solution. At the same time, organic fertilizer can improve the nutrient absorption conditions of crops, improve the water storage and fertilizer retention capacity of soil, avoid and reduce the loss of chemical fertilizer nutrients, and improve the utilization rate of chemical fertilizer.
3, reduce nutrient fixation, improve fertilizer efficiency. After fertilizer is applied to the soil, some nutrients will be absorbed by the soil, chelated or fixed, reducing the fertilizer efficiency. For example, superphosphate and calcium-magnesium phosphate fertilizer are directly applied to soil, which is easy to connect with iron, aluminum, calcium and other elements in soil, and generate insoluble phosphoric acid which is fixed, resulting in the loss of available nutrients. If mixed with organic fertilizer, it can not only reduce the contact surface with soil, reduce the fixed opportunity of soil and chemical fertilizer, but also make those insoluble phosphorus in phosphate fertilizer into effective phosphorus that can be used by crops, and improve the fertilizer efficiency of phosphate fertilizer. 4, improve soil structure, increase production. Long-term single application of chemical fertilizer will damage the aggregate structure of soil, cause soil adhesion and compaction, and reduce tillage performance and fertilizer supply performance. Organic fertilizer contains abundant organic matter, which can activate fluffy soil and reduce capacity; Can improve soil water, fertilizer, air, heat and other physical and chemical properties; Adjust the pH. The combination of the two can not only increase the yield, but also promote the sustainable development of agriculture. 5, reduce the amount, reduce pollution. The mixing and collocation of organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer can reduce the application amount of chemical fertilizer by 30%-50%. On the one hand, the land pollution can be reduced from the use of chemical fertilizer, and on the other hand, some organic fertilizer can degrade the residue of chemical fertilizer and pesticide in the soil.
6. Enhance microbial activities and increase soil nutrients. Organic fertilizer is the energy of microbial life, and chemical fertilizer is the inorganic nutrition of microbial growth. The combination of the two can promote microbial activity, and then promote the decomposition of organic fertilizer, produce a large number of carbon dioxide and organic acid, help to dissolve insoluble nutrients in soil, and supply crops for absorption. Carbon dioxide can increase the carbon nutrition of crops and improve photosynthetic efficiency. Microbial life is short, and after death, it decomposes and releases nutrients for crop absorption and utilization.
The importance of organic fertilizer granulator
In the production process of Organic Fertilizer, Organic Fertilizer Granulator plays a crucial role. It can process organic fertilizer raw materials into particles suitable for application, improving the utilization rate of fertilizer and the absorption effect of crops.
The application of Fertilizer Granules Compaction Machine
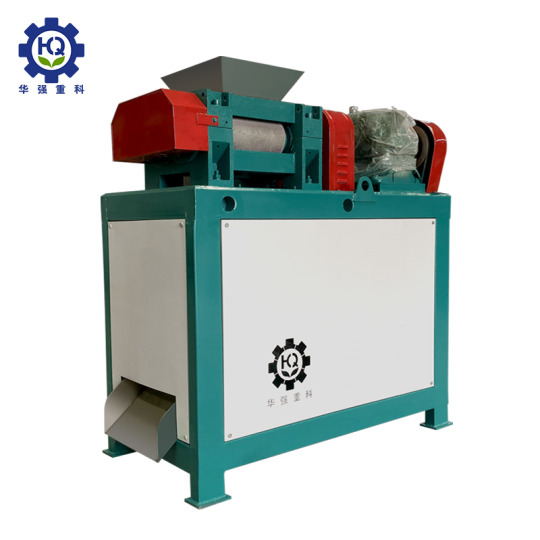

Fertilizer Granules Compaction Machine is a kind of organic fertilizer granulator. It makes raw materials into granules by means of extrusion, which is suitable for the production of a variety of organic fertilizers.
The advantages of Disc Granulator

Disc Granulator also plays an important role in the granulation process of organic fertilizer due to its efficient granulation capacity and stable product quality.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
🚨 🚨 🚨 Job - Alert #phd !
KU Leuven is looking for:
➡ Cerebrovascular autoregulation physiology in a piglet cranial window model
Apply before: 2024-04-15
Read more here:
https://www.academiceurope.com/job/?id=3540

0 notes
Text
Sleep Apnea and Eye Health: Potential Risks and Management Strategies
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, which can have far-reaching effects on various aspects of health, including eye health. At Sleep Center, we understand the importance of recognizing the potential risks of sleep apnea on eye health and implementing appropriate management strategies. Here's an overview of how sleep apnea can impact eye health and the approaches to mitigate these risks:
1. Increased Risk of Glaucoma:
Studies have shown a link between sleep apnea and an increased risk of glaucoma, a group of eye conditions characterized by damage to the optic nerve. Sleep apnea-related factors such as intermittent hypoxia, oxidative stress, and increased intraocular pressure may contribute to the development and progression of glaucoma. Regular eye examinations and early detection are crucial for managing glaucoma risk in individuals with sleep apnea.
2. Dry Eye Syndrome:
Sleep apnea can exacerbate dry eye syndrome, a common ocular condition characterized by insufficient tear production or poor tear quality. Sleep disturbances, nocturnal mouth breathing, and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy may contribute to ocular surface inflammation and evaporative dry eye. Proper hydration, humidification of CPAP therapy, and regular eye drops can help alleviate dry eye symptoms in individuals with sleep apnea.
3. Papilledema and Optic Neuropathy:
Severe untreated sleep apnea can lead to chronic oxygen desaturation and increased carbon dioxide levels, resulting in elevated intracranial pressure and cerebral blood flow dysregulation. These physiological changes may manifest as papilledema (swelling of the optic disc) and optic neuropathy (damage to the optic nerve), leading to visual disturbances and vision loss if left untreated. Timely diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea are essential for preventing optic nerve damage and preserving vision.
4. Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION):
Sleep apnea has been identified as a potential risk factor for non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), a sudden loss of vision in one eye due to inadequate blood flow to the optic nerve. Sleep apnea-related vascular abnormalities, endothelial dysfunction, and impaired autoregulation of blood flow may predispose individuals to NAION. Optimal management of sleep apnea may help reduce the risk of NAION occurrence and recurrence.
5. Management Strategies:
Effective management of sleep apnea is essential for mitigating its impact on eye health. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy remains the primary treatment for sleep apnea, improving nocturnal oxygenation and reducing respiratory events. Adherence to CPAP therapy, regular follow-up appointments, and adjustments to treatment settings as needed are essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and minimizing ocular complications.
Conclusion:
Sleep apnea can pose significant risks to eye health, ranging from glaucoma and dry eye syndrome to optic nerve damage and vision loss. By recognizing the potential ocular complications of sleep apnea and implementing appropriate management strategies, individuals can protect their eye health and preserve vision. Regular eye examinations, collaboration between sleep specialists and ophthalmologists, and adherence to recommended treatments are essential for comprehensive care.
Contact Sleep Center today to schedule a consultation and learn more about our comprehensive approach to managing sleep apnea and preserving eye health.
0 notes
Text
Research Specialist II Johns Hopkins School of Medicine See the full job description on jobRxiv: https://jobrxiv.org/job/johns-hopkins-school-of-medicine-27778-research-specialist-ii/?feed_id=70215 #Animal_models #autoregulation #biomedical #cardiovascular_disease #cerebrovascular #perfusion #ScienceJobs #hiring #research
0 notes
Text
The RgaS-RgaR two-component system promotes Clostridioides difficile sporulation through a small #RNA and the Agr1 system
by Adrianne N. Edwards, Shonna M. McBride The ability to form a dormant spore is essential for the survival of the anaerobic pathogen, Clostridioides difficile, outside of the mammalian gastrointestinal tract. The initiation of sporulation is governed by the master regulator of sporulation, Spo0A, which is activated by phosphorylation. Multiple sporulation factors control Spo0A phosphorylation; however, this regulatory pathway is not well defined in C. difficile. We discovered that RgaS and RgaR, a conserved orphan histidine kinase and orphan response regulator, function together as a cognate two-component regulatory system to directly activate transcription of several genes. One of these targets, agrB1D1, encodes gene products that synthesize and export a small quorum-sensing peptide, AgrD1, which positively influences expression of early sporulation genes. Another target, a small regulatory #RNA now known as SpoZ, impacts later stages of sporulation through a small hypothetical protein and an additional, unknown regulatory mechanism (s). Unlike Agr systems in many organisms, AgrD1 does not activate the RgaS-RgaR two-component system, and thus, is not responsible for autoregulating its own production. Altogether, we demonstrate that C. difficile utilizes a conserved two-component system that is uncoupled from quorum-sensing to promote sporulation through two distinct regulatory pathways. https://journals.plos.org/plosgenetics/article?id=10.1371%2Fjournal.pgen.1010841&utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr
1 note
·
View note
Text
Management of Cerebrovascular Steno-Occlusive Disease
Patients with steno-occlusive cerebrovascular disease are at risk of ischemic symptoms from haemodynamic insufficiency in the presence of reversible hypoperfusion, exhausted autoregulation and impaired vasodilatory reserve. Multidisciplinary management approach includes blood pressure management, antithrombotic therapy, treatment of underlying brain-body interactions targeted at optimising cerebral blood flow and oxygen delivery, and revascularisation procedures.
Patients with symptomatic stenoocclusive disease have a risk of recurrent stroke of at least 10-15 per cent within 5 years. Progressive atherosclerosis of internal carotid artery (ICA) or middle cerebral artery (MCA) is the most common cause of impaired distal cerebral perfusion with cerebral misery hypoperfusion
Cerebral Hypoperfusion & Collateral Circulation In the setting of cerebral hypoperfusion, recurrent ischaemic events occur depending on the following factors: (1) amount of collateral cerebral circulation; (2) extent of haemodynamic impairment; (3) age; (4) cardiac status; (5) presence of metabolic syndrome of hypertension, hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance; (6) factors affecting coagulation, blood oxygen carrying capacity and delivery (such as anaemia and other haematology disorders, systemic infections and sepsis, renal and hepatic disorders).
In addition to the traditional cerebral ischaemic symptomatology pertaining to the affected vascular territory (Table 2), orthostatic symptoms, syncope, transient global amnesia, episodic limb shaking and watershed infarction are possible.
In states of misery perfusion, compensatory cerebral vasodilation is not possible as the cerebral autoregulatory capacity is exhausted and, as a result, cerebral blood flow decreases proportionally with cerebral perfusion pressure (Figure 1). Possible cerebral collateral circulation routes include: (1) contralateral internal carotid artery (ICA) through anterior communicating artery; (2) posterior circulation via posterior communicating artery; (3) leptomeningeal or pial collaterals; (4) collateral circulation from external carotid artery (ECA) with retrograde flow and connections with ophthalmic artery, extracranial connections between ECA or vertebral artery (VA) branches and distal ICA; (5) collaterals through dural meningeal arteries to cortical arteries; (6) anterior cerebral artery (ACA)-posterior cerebral artery (PCA) connections via the limbic loop; and (7) anterior spinal artery collaterals with the vertebrobasilar circulation.
Medical management principles Medical management strategies are essential to treatment of cerebral ischaemic events and prevention of recurrent strokes in face of cerebral hypoperfusion. These include: (1) cautious individualised blood pressure management (usually systolic blood pressure targets of 130-160 mmHg for those with severe bilateral carotid stenoses); (2) maintenance of fluid status to maintain appropriate plasma oncotic pressures for adequate cerebral perfusion; (3) anti-platelet and anticoagulant therapies (single anti-platelet agent and anticoagulant for those with embolic strokes or in the setting of cardiac arrthymias; dual anti-platelet therapy, with laboratory evidence of responsiveness to these agents, for those with atherosclerotic disease or perforator events), (4) statin, and (5) glycaemic control.
Treatment of underlying brainbody interactions are also essential, including attention to haemodynamic stability, cardiac status, optimising cerebral oxygen delivery with avoidance of anaemia, goal-directed therapy for sepsis, optimisation of renal perfusion and avoidance of coagulopathy and encephalopathy due to underlying multi-systemic involvement, particularly renal or hepatic impairment.
Identification of surgical candidate For patients with symptomatic severe (> 70 per cent) carotid stenosis, carotid endarterectomy or angioplasty/stenting is considered. Thrombectomy is considered for patients with embolic strokes to large size cerebral vessels. For patients who have been medically optimised but are still at risk of ischaemic symptoms of haemodynamic insufficiency due to ICA/MCA stenosis/occlusion in the setting of hypotension or orthostasis, one can identify candidates with reversible hypoperfusion, exhausted autoregulation and impaired vasodilatory reserve. Consideration of extracranialintracranial bypass procedure can be reliably made to identify patients who have reasonable chances of augmentable flow-induced long-term cerebral blood flow re-organisation (collateral shift) while preventing future hypoperfusion events. Identification of these candidates is made after blood pressure management, antithrombotic therapy and treatment of underlying brainbody interactions targeted at optimising cerebral blood flow and oxygen delivery.
Investigational adjuncts In addition to clinical findings on presentation and with monitoring (Table 2), other adjunctive investigations are useful in identifying such surgical candidates. CT perfusion scans demonstrate ischaemic penumbra of increased time-to-peak (TTP, time between first arrival of CT contrast intracranially and its peak concentration), increased mean transit time (MTT, average time for blood to travel through a volume of brain), with relatively preserved cerebral blood volume (CBV) due to vasodilation and recruitment of collateral flow, and decreased cerebral blood flow (CBF). As reference, an infarcted core shows increased TTP, increased MTT, decreased CBV and decreased CBF. SPECT (single photon emission computerised tomography) scan with acetazolamide (DiamoxTM) is used to identify patients with haemodynamic insufficiency who exhibit reversible hypoperfusion and decreased cerebrovascular reactivity when challenged with acetazolamide (Figure 3a-c). In those who are in the misery perfusion stage of haemodynamic insufficiency, they are already maximally vasodilated and dysautoregulated. In this regard, they cannot further vasodilate in response to increased carbon dioxide tension from diuretic acetazolamide, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.
Quantitative MR angiography (q-MRA)’s non-invasive optimal vessel analysis (NOVA) is also essential to quantify and measure blood flow through large vessels of the Circle of Willis (Figure 3b). Together with formal cerebral angiography, it can be used to estimate pial and collateral flow. It gives reasonable estimates of augmentable flow to ensure appropriate blood velocity ranges after bypass, and also in anticipation of longer term collateral shift, cerebral blood flow re-organisation.
Surgical procedure Direct superficial temporal artery (STA) [donor] and middle cerebral artery (MCA) M4 cortical branch [recipient] bypass is generally preferred. Meticulous attention to blood pressure control, maintenance of intravascular volume and depth of anaesthesia are essential to avoid cerebral hypoperfusion during these cases with underlying steno-occlusive disease. Intraoperative end-to-side anastomoses are performed using 10-0 nylon sutures with indocyanine green (ICG) and intra-operative angiographic confirmation of anastomotic patency. Individualised blood pressure goals with gradual liberalisation of these parameters are done post-operatively with continuation of antithrombotic agents to maintain anastomotic patency and to avoid reperfusion-related injury.
Read More: https://www.europeanhhm.com/medical-sciences/management-of-cerebrovascular-steno-occlusive-disease
#healthcare#hospitals#health#medical care#doctors#healthy lifestyle#health and wellness#medical equipment#technologies#cerebrovascular#steno
0 notes
Text
Diabetes & Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye disease caused by diabetes mellitus and should not be taken lightly. Diabeteus acts as the main risk factor for the development and progression of diabetic retinopathy; thus it's crucial that individuals living with the condition understand its intricate relationship in order to effectively manage it and avoid vision loss in those at risk.
Diabetes, a metabolic condition marked by chronic hyperglycemia, can have serious repercussions for organs' microvasculature - including that of the retina. High blood glucose levels combined with metabolic abnormalities cause pathological changes that eventually result in diabetic retinopathy.
Hyperglycemia and Metabolic Dysfunction:
Chronic hyperglycemia plays a central role in diabetic retinopathy development. Prolonged exposure to high glucose levels results in biochemical alterations, such as advanced glycation end products (AGEs), increased oxidative stress levels, and the activation of protein kinase C (PKC) pathways; all of which disrupt retinal cell function, induce inflammation, and lead to tissue damage in retinal tissue.
Vascular Changes and Microangiopathy:
Diabetes leads to microangiopathy in the retina, an alteration affecting small blood vessels supplying it compromising both their structure and function. Endothelial cell dysfunction, impaired autoregulation of vasoconstriction mechanisms, abnormal angiogenesis processes and increased vascular permeability all play roles in its development and progression leading to diabetic retinopathy.
Breakdown of Blood-Retinal Barrier:
Individuals living with diabetes find the integrity of the blood-retinal barrier compromised. Normally protecting the retina from harmful substances and maintaining an ideal environment, it becomes vulnerable in diabetic retinopathy as chronic hyperglycemia and associated metabolic disturbances disrupt its function, allowing fluid, proteins, and lipids into retinal tissues causing leakage which contributes to retinal edema as well as further progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Chronic low-grade inflammation plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Hyperglycemia stimulates release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines from resident retinal cells to activate them further and recruit immune cells such as macrophages and T cells to the retina, further exacerbating retinal damage by producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and activating various signaling pathways.
Growth Factors and Angiogenesis:
Imbalances in the production and regulation of growth factors, specifically vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), contribute to abnormal blood vessel development in diabetic retinopathy. Hypoxia caused by impaired retinal blood flow triggers the release of VEGF which stimulates new vessel growth; however, these fragile new vessels often leakage further compromising retinal damage.
Sanjeevan Netralaya’s Advanced Ayurvedic Eye Care is known to be one of the most effective treatments for Diabetic Retinopathy and causes absolutely no side effects. Its tailor made treatments works effectively in a holistic way ensuring that the patient gets the best care.
#diabetic#eye diseases#diabetic retinopathy#eye care#eye health#sanjeevan netralaya#ayurveda#health & fitness#eyes#ayurvedic treatment#retina centers#retirement#retinacare#eyesight#ayurvedic eye treatment#india
1 note
·
View note