#antique architectural elements
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Why Limestone Mantels from Ancient Surfaces Are Essential for Your Home
Ancient Surfaces brings history into the heart of your home with reclaimed limestone mantels sourced from ancient villas, castles, and estates. Each piece tells a story, bearing the marks of time and tradition that lend authenticity and elegance to any space. These mantels are not just architectural elements they are a seamless blend of functionality and heritage, turning your living room or…

View On WordPress
#Ancient Villas#Anique French Fireplaces#antique architectural elements#Antique Bolection Fireplaces#Antique Fireplaces#Antique Italian Fireplaces#antique limestone#Antique Reclaimed Fireplaces#Antique Stone Fireplaces#fireplace designs
0 notes
Text
Luxurious Indian Interiors Decor and Furniture
Unique architectural remnants and paintings are the focus and give a vibrant pop of color against the crisp white wall, creating a captivating visual contrast that draws the eye. Each piece tells a story, with intricate details that invite closer inspection and an appreciation for craftsmanship. A huge Carved Hope Chest sits prominently in the foyer, serving as a practical yet elegant storage…
#antique door#Antique Doors#antique furniture#Arches & Columns#architectural design#Architecture Elements#armoires#Boutique hotel Décor#carved door panel#carved door panels#carved table#carved wood#chakra door#coffee table#conscious design#console table#consoles#door panel#eclectic décor#farmhouse rustic#hall table#Hand Carved Panel#handcarved table#home décor#indian antiques#indian carved doors#indian carving#indian doors#Interior Design#interior Door
0 notes
Text
Kitchen Great Room

Example of a mid-sized french country l-shaped medium tone wood floor and wood ceiling open concept kitchen design with a farmhouse sink, recessed-panel cabinets, white cabinets, granite countertops, gray backsplash, ceramic backsplash, paneled appliances, two islands and gray countertops
#monochromatic#architectural elements#french country#antiques#exposed beams#rustic tiles#elegant antique
0 notes
Photo

Laundry Room Laundry in Vancouver Mid-sized, elegant laundry room image with a single-wall, white floor, raised-panel cabinets, turquoise cabinets, white walls, and a side-by-side washer and dryer.
0 notes
Text
Dining Room Houston

Image of a large kitchen and dining area in a French country style with medium-toned wood floors and white walls
1 note
·
View note
Note
Any tips on how to describe indoor spaces so they feel real and match the vibe of the story without throwing in too much detail?
Getting interior scenes just right is all about finding the balance between setting the mood, showing the unique personality of your story world, and keeping the plot moving. There are lots of ways you can use senses, action, and background to set a scene, all of which can work seamlessly with the type of story you want to tell. Here are some tips on how you can achieve that:
How does it look?
Lighting: does your space contain the soft glow of lamps, harsh fluorescent lights, or natural light?
Use colour and textures like peeling paint, plush velvet, or sleek marble.
Size and scale: is it claustrophobically small or impressively grand?
Architectural features: does the space have high ceilings, crown mouldings, or exposed beams?
Furnishings: are they modern, sparse, antique, or cluttered?
Style and decor: what style is represented, and how does it affect the atmosphere?
State of repair: is the space well-kept, neglected, or under renovation?
Perspective and layout: how do spaces flow into each other?
Unique design features: describe sculptural elements, or things that stand out.
Spatial relationships: describe how objects are arranged—what’s next to, across from, or underneath something else?
How does it sound?
Describe echoes in large spaces or the muffled quality of sound in carpeted or furnished rooms.
Note background noises; is there a persistent hum of an air conditioner, or the tick of a clock?
Describe the sound of footsteps; do they click, scuff, or are they inaudible?
Include voices; are they loud and echoing or soft and absorbed?
Is there music? Is it piped in, coming from a live source, or perhaps drifting in from outside?
Capture the sounds of activity; typing, machinery, kitchen noises, etc.
Describe natural sounds; birds outside the window, or the rustle of trees.
Consider sound dynamics; is the space acoustically lively or deadened?
Include unexpected noises that might be unique to the building.
Consider silence as a sound quality. What does the absence of noise convey?
How does it smell?
Identify cleaning products or air fresheners. Do they create a sterile or inviting smell?
Describe cooking smells if near a kitchen; can you identify specific foods?
Mention natural scents; does the room smell of wood, plants, or stone?
Are there musty or stale smells in less ventilated spaces?
Note the smell of new materials; fresh paint, new carpet, or upholstery.
Point out if there’s an absence of smell, which can be as notable as a powerful scent.
Consider personal scents; perfume, sweat, or the hint of someone’s presence.
Include scents from outside that find their way in; ocean air, city smells, etc.
Use metaphors and similes to relate unfamiliar smells to common experiences.
Describe intensity and layering of scents; is there a primary scent supported by subtler ones?
What can you do there?
Describe people’s actions; are they relaxing, working, hurried, or leisurely?
Does the space have a traditional use? What do people come there to do?
Note mechanical activity; elevators moving, printers printing, etc.
Include interactions; are people talking, arguing, or collaborating?
Mention solitary activities; someone reading, writing, or involved in a hobby.
Capture movements; are there servers bustling about, or a janitor sweeping?
Observe routines and rituals; opening blinds in the morning, locking doors at night.
Include energetic activities; perhaps children playing or a bustling trade floor.
Note restful moments; spaces where people come to unwind or reflect.
Describe cultural or community activities that might be unique to the space.
How is it decorated?
Describe the overall style; is it minimalist, baroque, industrial, or something else?
Note period influences; does the decor reflect a specific era or design movement?
Include colour schemes and how they play with or against each other.
Mention patterns; on wallpaper, upholstery, or tiles.
Describe textural contrasts; rough against smooth, shiny against matte.
Observe symmetry or asymmetry in design.
Note the presence of signature pieces; a chandelier, an antique desk, or a modern art installation.
Mention thematic elements; nautical, floral, astronomical, etc.
Describe homemade or bespoke items that add character.
Include repetitive elements; motifs that appear throughout the space.
What is its history?
Mention historical usage; was the building repurposed, and does it keep its original function?
Describe architectural time periods; identify features that pinpoint the era of construction.
Note changes over time; upgrades, downgrades, or restorations.
Include historical events that took place within or affected the building.
Mention local or regional history that influenced the building’s design or function.
Describe preservation efforts; are there plaques, restored areas, or visible signs of aging?
Describing indoor spaces doesn’t have to feel like a chore. Focus on the details that matter most, tie them to the mood or characters, and let your readers fill in the blanks. A well-crafted space not only sets the scene but builds your character's relationship to it. Use sensory language, background, and action beats to tie it into your narrative, and don’t be afraid to play around with motifs and contradictions, depending on who is experiencing it!
#writeblr#writers of tumblr#writing tips#writing resources#creative writing#writers#writing#writing community#creative writers#writing inspiration#writerblr#writing advice#writing reference#writers on tumblr#ask novlr#writer
378 notes
·
View notes
Text

1895 Victorian in Chicago, IL was voted Best Renovation in Chicago by Curbed Magazine. 6bds, 4.5ba, 7,000 sq ft, $1.75m.


I have never seen an entrance like this one. It has to be one-of-a-kind architecture.


The fireplaces in this home are exquisite. Isn't this is a gorgeous sitting room? The fireplace is stunning.

Very large home office. Since the 2013 restoration, the home has been impeccably maintained.


The dining room is incredible. The wood is so beautiful and look at the ceiling details. Have you ever seen built-in cabinetry like this in a Victorian dining room?


The kitchen is huge. It's modern, but so stunning. And, look at the fireplace.

The dark wood combined with the white cabinetry strikes a perfect balance of old and new. I love the marble counter on the island and the backsplash tile.

This actually looks like it could be a newer addition. Judging by the vintage part of the home, I don't think that they would've done a completely modern remodel like this.

It looks like they would've preserved anything that was original, like dark wood. However, they did put some Victorian style elements in this room, like the built-in window seat.

Maybe they decided to brighten up the bedrooms, b/c Victorian bedrooms could tend to be dark.

This bath is gigantic and combines elements of both old and new.

The original door, woodwork, and fireplace in this child's room indicate that it was renovated and brightened.

Nurseries and children's rooms really need to be cheerful.

Very chic black and white bedroom.

Super-chic matching bath. Love the sink and tile, but the gold fixtures really make it pop.

Up in the new lofted space they've got a home gym, but it can be a family room or anything the new owner would like.

How classy is the vintage looking home theater? I don't think I've ever seen one with a fireplace. Love the ceiling.

And, this looks like a renovated basement. For a room w/o windows, it's very light and bright.

What a lovely place to entertain.

They spared no expense on this bar, right down to the gold backsplash.


And, look at the wine cellar. They even have an antique wine press.

Love the terrace.


There's also a deck and the beautiful yard even has a small patio. TBH, a home like this, under $2m seems like a bargain. They really made the most of a 0.17 acre lot.

https://www.compass.com/listing/4518-south-drexel-boulevard-chicago-il-60653/1682096781908098609/
#victorian mansion#victorian renovation#victorian restoration#houses#house tours#home tour#old house dreams
131 notes
·
View notes
Text



The Temple of Venus in Baalbek (Heliopolis), Lebanon was built in the 200s CE to honor the goddess of love, sex and fertility. Venus was derived by the Romans from the Greek goddess Aphrodite, who herself was inspired by the Near Eastern goddess Astarte. This temple's cult likely incorporated elements of both Roman Venus and the local Astarte.
The temple itself has many novel and unique features found nowhere else in Classical architecture. Five semicircular exedrae run along the outer wall, framing arched niches decorated with carved doves and seashells that probably contained statues in ancient times. Above each niche a festoon of leaves and fruit hangs, symbolizing fertility. The pentagonal column bases are without parallel in antiquity, and no other examples are known. The interior is less well preserved, but it can be safely assumed by the lavishness of the construction that it was once sumptuously decorated with paintings, statues, colored marbles and golden ornaments.
The temple has an eventful history, being also a site of persecutions of early Christians under Julian the Apostate, the last pagan emperor of Rome. Sozomen, a late antique historian, says in his Ecclesiatical Histories:
The inhabitants of Heliopolis, near Mount Libanus, and of Arethusa in Syria, seem to have surpassed them in excess of cruelty. The former were guilty of an act of barbarity which could scarcely be credited, had it not been corroborated by the testimony of those who witnessed it. They stripped the holy virgins, who had never been looked upon by the multitude, of their garments, and exposed them in a state of nudity as a public spectacle and objects of insult. After numerous other inflictions they at last shaved them, ripped them open, and concealed in their viscera the food usually given to pigs; and since the swine could not distinguish, but were impelled by the need of their customary food, they also tore in pieces the human flesh.
I am convinced that the citizens of Heliopolis perpetrated this barbarity against the holy virgins on account of the prohibition of the ancient custom of yielding up virgins to prostitution with any chance comer before being united in marriage to their betrothed. This custom was prohibited by a law enacted by Constantine, after he had destroyed the temple of Venus at Heliopolis, and erected a church upon its ruins."
Whether Sozomen's account is an exaggeration or not, there is archaeological evidence that the temple was indeed converted into a church, dedicated to Saint Barbara. According to the (comparatively late) Christian legend, Barbara was the daughter of a Heliopolitan dignitary, Dioscorus, who still worshipped the old gods. When he learned that she had been baptized, he killed Barbara and was immediately struck by lightning. Up til the present day, Saint Barbara is invoked if people want to be protected against lightning.
Because the monument continued to be in use, the temple of Venus is comparatively well-preserved. Unbroken religious activity has continued on almost the same site since antiquity, and there's still a small mosque next to the temple of Venus. The Greek-Orthodox church of Baalbek, which is close by, is still dedicated to Saint Barbara.
235 notes
·
View notes
Note
hey!! i really love your posts and trust me when i say this but you're practically doing a work of charity by making all these synonym lists. 😩🫶
i was wondering if you could compile monument vocabulary. vocabulary to describe the intricate and exquisite designs inside historical buildings. tysm!
Some Historical Architecture & Interior Design Vocabulary
Acanthus Leaf - A leaf decoration often used on furniture, particularly on brackets and legs.
Acroterium - Originally an ornament on the roof corners of Greek temples. In classical furniture, similar ornaments applied to the top corners of secretaries, bookcases, highboys and other furniture.
Amorini - Cupid ornaments found on Italian Renaissance furniture.
Anthemion - A honeysuckle design from classical Greek decorative motifs. Term refers to any conventional flower or leaf design.
Antique - Could be anything ranging from a piece of furniture to art. The U.S. government considers any item over 100 years old to be an antique, whereas most collectors use 50 years as a benchmark.
Apothecary Chest - A low chest with small drawers that was originally used to store herbs for cooking and medicinal purposes.
Arabesque - Decorative scroll work or other intricate ornamentation consisting of foliage, vases, leaves and fruits, or fantastic human and animal figures.
Baroque - A highly ornate decorative style that originated in Italy in the 1600's. The style is characterized by irregular curves, twisted columns, elaborate scrolls and oversize moldings. The Italian equivalent of French "rococo".
Bibliotheque-Basse - A low cupboard with shelves for books. Doors are often of glass and sometimes fitted with grilles.
Bullate - Having the surface covered with irregular and slight elevations, giving a blistered appearance.
Cabriole leg - An ornamented furniture leg with a double curve structure.
Chevron - A 'zigzag' pattern characteristic of Romanesque decoration that is often carved around pillars, arches and doorways.
Chinoiserie - A European style of design that is meant to mimic elements of East Asian art.
Console table - A freestanding table, often found in the entryway of homes, that typically serves as a space for decorative elements.
Enfilade - A series of rooms that are connected via doorways that align with one another (commonplace in grand castles, like the Palace of Versailles, or even museums).
Etagere - A freestanding or hanging set of open shelves, designed to display trinkets or other decorative objects.
Gilding - A coating with a thin layer of gold or gold-like substance.
Klismos - Ancient Greek style of chair with saber shaped legs splayed at the front and back. The back legs continue up to support a shoulder-height curved back.
Laurelling - A decorative feature using the laurel leaf motif as its basis.
Lozenge - A diamond shaped decorative panel. Term comes from the Middle English word for stone.
Niche - A recess in a wall for displaying a sculpture or other accessory.
Ormulu - A metal resembling gold. Used as mounts and decorative effects on furniture.
Ovolo - A continuous ornament in the form of an egg which generally decorates the molding called the "quarter-round". Eggs are often separated from each other by pointed darts.
Passementerie - Fancy decorative trimmings such as tassels, tiebacks and ribbon.
Régence Style - This furniture style spanned from about 1715 to 1723, when France was ruled by a regent. This style of furniture design was a transition from massive straight lines to graceful curves.
Sconces - A type of light fixture that is fastened to a wall for support.
Swan-Neck Handle - A curved handle popular in the 1700's.
Trompe l’oeil - A technique used to trick the eye into thinking that something flat, like a wall, is actually three-dimensional. This is often achieved through photorealistic painting.
Victorian - An architectural style defined by highly ornamented design and grand, sweeping facades.
Wainscoting - A type of interior wall paneling that covers the lower portion of a wall.
"Traditional" Interior Design
When talking about traditional interior design, most are referencing a design style that originated in the 18th and 19th century throughout Europe. However, it’s worth noting that other cultures have their own versions of a traditional style that may not look the same as this more Western version.
Traditional Design Elements. Though not exhaustive, a traditional interior will often make use of the following elements:
Emphasis on symmetry and order
Traditional architectural details such wainscoting and crown molding
Classic decor elements such as chandeliers and bookcases
Neutral color schemes with pops of bold colors, often in jewel tones
Upholstery and textiles tend to be subtler (cotton, velvet, or wool, for example)
Furniture pieces with traditional silhouettes, though they’re often updated with modern elements or finishes
Layered window treatments and draperies; curtain valances aren’t used often
Classic patterns such as plaids, damask, or florals
Flooring tends to make use of darker wood
Sources: 1 2 3 4 ⚜ More: Notes & References ⚜ Word Lists
Previous posts that include some related words you might find useful:
Some Architecture Vocabulary
Some European Renaissance Art Vocabulary
Some Medieval Art & Architecture Vocabulary: Part 1
Some Medieval Art & Architecture Vocabulary: Part 2
Some Roman Art Vocabulary
Thanks so much for your kind words, you're really sweet! I tried to include a wide range of terminology since you didn't specify which time period you were looking for. Do go through the sources if I wasn't able to include here what you need in your writing. Hope this helps <3
#terminology#architecture#interior design#writing reference#writeblr#dark academia#spilled ink#literature#writers on tumblr#writing prompt#writing inspiration#history#writing ideas#creative writing#writing resources
73 notes
·
View notes
Text
About Hogwarts Castle's Architecture
I think the history is wrong... Like, stone castles only became a thing in Britain when the Normans brought the practice over with them from France (Norman rule was officially established in 1066). And the first stone castles in Scotland were only built around the 1100s. Hogwarts was built around the 990s... so what's up with that?
(Like, there were some fortified stone structures in Scotland pre-normans (brochs), but no one would really call them a typical castle. Also, they were built in the Iron Age (Brochs were specifically built between 400 BC and 200 AD), so not the founders' times)
Also, many of the architectural details of Hogwarts in the movies/Hogwarts Legacy/any other video games/illustrations have much later influences, what with the Gothic architecture (which only came around in the 1200s) and elements from Victorian restored castles (I'll go more about what this means later).
And I have a Watsonian theory/headcanon to make it make sense.
What I think, is that the Hogwarts castle we (and the characters) experience, has been heavily reconstructed over the past thousand years. So Hogwarts likely started as a simpler, wooden structure (as was common in Scotland around the 10th century) and it changed and grew and evolved throughout the centuries.
So we'll walk through the history of castle architecture in Scotland and explain how Hogwats evolved over the years. (Becouse I'm an architecture and history nerd, sue me).
Pre Founders
Hogwarts is legend to have been built where the founders found a pensive:
The Hogwarts Pensieve is made of ornately carved stone and is engraved with modified Saxon runes, which mark it as an artefact of immense antiquity that pre-dates the creation of the school. One (unsubstantiated) legend says that the founders discovered the Pensieve half-buried in the ground on the very spot where they decided to erect their school.
(Pottermore)
So, the location probably wasn't empty, but had some evidence of past wizarding residence there. How much is unclear, but it was a place magic was practiced in before the founders.
990s
Hogwarts is founded as a school and sanctuary. Muggles at the time didn't really believe in witchcraft (the church considers believing in witchcraft heresy). So, it's not really to protect themselves together, but more to allow wizards to build a united community.
There is an element of hiding magic from muggles:
Why didn’t we choose to produce flying barrels, flying armchairs, flying bathtubs – why brooms? Shrewd enough to see that their Muggle neighbours would seek to exploit their powers if they knew their full extent, witches and wizards kept themselves to themselves long before the International Statute of Wizarding Secrecy came into effect.
(Quidditch Through the Ages)
But it's not for the same reason as the later witch hunts. At this time, people who confessed to witchcraft would need to repent (not via execution, mind) because they'd be seen as delusional. After all, magic doesn't exist according to church doctrine at the time. and as mentioned in the book, the concern was to be bothered to help muggles with everything, not because they were hunted at the time.
Around this time there is the magical government in England at least, is the Wizard Council, also known as the Wizengamot. Due to the similar name, the muggle Wittengamot (the council of lords that chose the king of England) might be aware of their wizard equivalent, but they might also be completely unaware (explained in the next section).
Castles, in this time period in the UK, looked something like this:
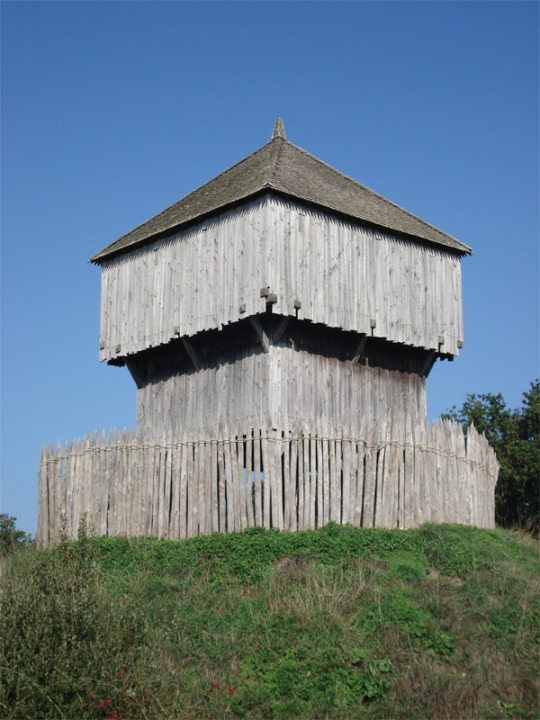


Hogwarts, when founded, probably looked like this combination of buildings and not what we imagine as a castle.
with the Chamber of Secrets as a basement. It's canon that a Gaunt later added the pipe entrance from the bathroom, so it's original entrance lay elsewhere.
Note that this means it wasn't the founders who but the Common Rooms, Room of Requirement, or the moving staircases and that the in-universe history books are wrong.
Since Hogsmeade was founded by Hengist of Woodcroft who was a student of Helga Hufflepuff when she was alive, the village was probably founded in the century following the school's founding.
1000s-1100s
Here we get the Norman Conquest of England, and while Scotland wasn't Norman, the culture in Scotland was influenced by the changes down south. Specifically, castle architecture is something they copied from the Normans.
The reason I mentioned earlier the muggle Witengamot might've not been aware of the wizarding community is because we know William brought with him wizards in his army, like the Malfoys:
Like many other progenitors of noble English families, the wizard Armand Malfoy arrived in Britain with William the Conqueror as part of the invading Norman army. Having rendered unknown, shady (and almost certainly magical) services to King William I, Malfoy was given a prime piece of land in Wiltshire, seized from local landowners, upon which his descendants have lived for ten consecutive centuries.
(Pottermore)
But many other pureblood wizard family names we can date back to the Norman invasion. Such as: Lestrange, Peverell, Wealey, Gaunt, etc. So, it's somewhat implied William won England with the help of wizards that the local Anglo-Saxon English didn't have fighting with them.
Due to these Norman wizards clearly getting positions of influence in the wizarding community (talked a bit more about this here[]), it's likely they or even William himself wanted to improve Hogwarts to keep the wizardibg population onside.
So, around the later 1000s or early 1100 Hogwarts would've looked something like this:



So, basically, the same structure as before, but the keep (where the Great Hall is, is built from stone. The Great Hall (AKA the most defensible place in the castle everyone fell back to in the Battle of Hogwarts) was the first built.
As for the inside:
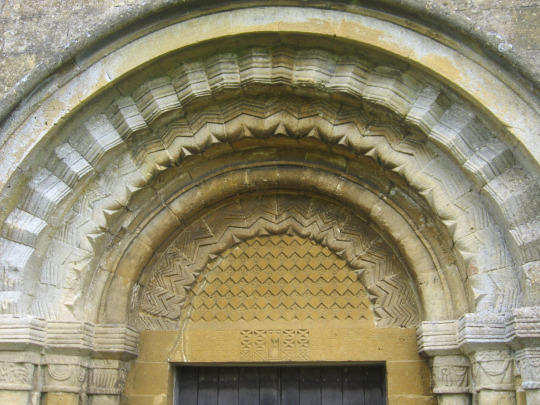



We have geometric details on the columns and archways (which are round, it's not yet the pointed gothic arches we all know and love). The walls would all be painted white and then colorful and vibrant colors over it (somewhat visible in the picture on the left).
1200s-1300s
Throughout the next two centuries, more and more wings would be added to the castle. Many of the classrooms and dorms that were outside the keep in the outer buildings moved to these new wings inside the main stone castle. The outer walls & fortifications would also be improved and extended from the former ones and a proper gatehouse would likely be built:
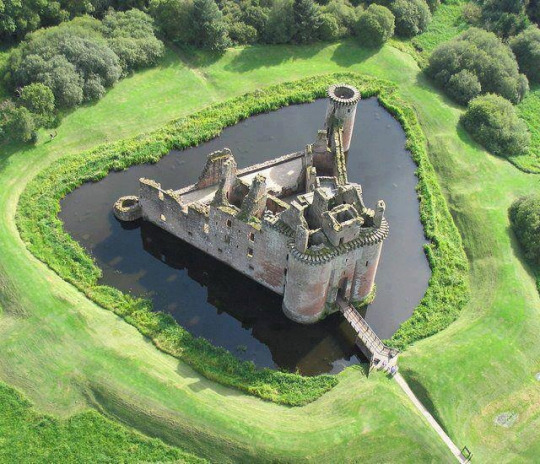


And a few churches, since they tended to be more decorated on the outside and I want to explain this is when gothic architecture was a thing and that most of the styles we recognize for castles are from this period:



This is when the Room of Requirement, the moving staircases, the towers (the Astronomy Tower, the Headmaster's Tower, and perhaps the Owlery), and the various common rooms would be built.
(Note the castle on the left would've likely had a whitewash on all of the exterior back in the day)
At this point, the Great Hall, and the quad if we think of the typical Hogwarts castle would be built:

(Image from Hogwarts Legacy)
There would be no transfiguration courtyard area yet and no clocktower yet as they are likely later additions.
I'd also note the inside of the castle, would look something like this at this point:



The walls would be painted and colorful and vibrant. You might also see wall hangings like we see in the Gryffindor Common room in the movies, that's actually accurate (the wall tapestry/curtain things, not the furniture, the furniture is 17th and 18th century) except the stone would likely not be bear stone and instead have a whitewash over it and tapestries over the whitewashed stone. Bear stone wasn't an all that common look in this era unless they used pretty stones that were meant to be shown off (which was expensive, hence rare).
1500s-1600s
This period is still building in a style called Gothic (12th to 16th century), but we're adding more intricate detail, and the style for furniture changes quite drastically (because we've entered the Tudor area). I believe that around the 1500s and the 1600s, more wings were added, like the clocktower, the transfiguration courtyard, and the viaduct (a bridge was probably there before, but I think it was rebuilt with the new building):

The style of buildings we're looking at now would have this sort of exterior:



(Note the house on the left and castle on the white would've likely had a whitewash on all of the exterior back in the day)
And this is the interior we're talking about:



Also, up until this point, greenhouses weren't really a thing (at least not the glasshouse variety). I assume there was an Herbology Garden or that perhaps a Vegetable Patch Harry mentions exists next to the greenhouses and served as the place where they grew plants because glasshouses like we think of when we read the word "greenhouse" were only started being built in England late in the 16th century. So the Greenhouses are likely a 17th-century addition since the wizards probably adopted them a little later than the muggles.
1700s
This is when indoor plumbing was introduced to Hogwarts and the entrance to the Chamber of Secrets was changed:
When first created, the Chamber was accessed through a concealed trapdoor and a series of magical tunnels. However, when Hogwarts’ plumbing became more elaborate in the eighteenth century (this was a rare instance of wizards copying Muggles, because hitherto they simply relieved themselves wherever they stood, and vanished the evidence), the entrance to the Chamber was threatened, being located on the site of a proposed bathroom. The presence in school at the time of a student called Corvinus Gaunt – direct descendant of Slytherin, and antecedent of Tom Riddle – explains how the simple trapdoor was secretly protected, so that those who knew how could still access the entrance to the Chamber even after newfangled plumbing had been placed on top of it.
(Pottermore)
1800s
Now, back to what I mentioned in the opening paragraph about Victorian castle reconstruction. So, during the Victorian era, many rich people bought castles to restore and preserve them. Victorians in England were kinda obsessed with the Medieval period (and Ancient Egypt, but we're not talking about that right now) so they wanted to be able to walk around castles, and they had a lot of castles in the UK that fell into disrepair and just stood there empty. The thing is, the Victorian people who restored castles had no idea what Medieval castles actually looked like in the Medieval period. So all the castles you see with this sort of interior (which are most reconstructed castles, btw):


That's a Victorian reconstruction. They built how they imagined medieval castles looked like according to their own tastes and aesthetics and what they saw from more recent Todur castles, not how medieval castles actually looked like.
That being said, Hogwarts was continuously used throughout all these years, so I imagine some of these Victorian elements would make their way in, but not to the same level as these reconstructions.
Basically, different locations in the castle would look different depending on when they were built. Most furniture is likely to have been replaced more recently and would at most date back to the 1500s. So, we'll see a lot of dark wood furniture that isn't painted the way they would've painted furniture in the medieval period.
I'd also expect that some of the older walls/ceilings are still painted very vibrantly (which fits with the wizard's sense of style overall).
Basically, I think the Hogwarts we experienced in the books wasn't built in one year as a monolith by the founders. It was added to over time. Rooms that look older Medieval, and ones that look like a Tudor addition would all exist within the same castle. Areas in the older sections would have 18th-century wooden paneling because reconstruction was needed. I personally think that's the right way to go about designing Hogwarts since most castles in Britain are like that (and in the rest of Europe).
Castles changed and grew according to the needs of whoever lived there at the time and the technology available. And since, well, at some point castles weren't needed as fortified structures anymore, they lost fortifications for aesthetics. We have no surviving castles that actually look the way they did back when they were built. All the preserved ones had wings added, walls paneled with wood, and the windows replaced. And in many of them, you can actually see the patchwork in the bricks, the window style changing from one window to the next across a single wall. I think that's part of what makes castles gorgeous and it always made sense to me Hogwarts was like that too.
#harry potter#hp#hp meta#hollowedtheory#harry potter meta#wizarding world#hogwarts#hogwarts school of witchcraft and wizardry#hogwarts castle#wizarding world of harry potter#hollowedheadcanon#hp headcanon#hollowed hp redesign#historical context#wizarding history
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Soulful Beauty of Reclaimed Limestone Mantels
There’s a unique allure to a space graced by history a feeling that transcends time, where every corner whispers stories of craftsmanship, legacy, and beauty. A reclaimed limestone mantel from Ancient Surfaces embodies that essence, transforming a home into a sanctuary of timeless sophistication. Each piece, carved by hand and steeped in centuries-old history, serves as a living testament to the…

View On WordPress
#Ancient Villas#Anique French Fireplaces#antique architectural elements#Antique Bolection Fireplaces#Antique Fireplaces#Antique Italian Fireplaces#antique limestone#Antique Reclaimed Fireplaces#Antique Stone Fireplaces#fireplace designs
0 notes
Text
Elevate Your Space with Vintage Modern Spanish Farmhouse Charm
In the world of home design, few styles capture the imagination like the timeless blend of vintage carved door and modern Spanish farmhouse aesthetics. By incorporating rustic textures, intricate carvings, and bold architectural detail carved door, you can create a home that feels warm, inviting, and utterly unique. Whether you’re redesigning your living space, updating your exterior, or…
#antique carved door#antique door#Antique Doors#Antique Doors And Artistic Elements farmhouse doors#antique indian doors#architecture design#barn door#barn doors#barndoor#Bed Headboard#bedroom door#Carved Barn Door#carved door#carved door panel#Cellar Doors#custom barn door#custom door Old Doors#custom doors#Custom Size Door#customdoors#door#Double Sliding Door#eclectic décor#Entrance doors#Exterior Door#Farmhouse Barndoor#farmhouse door#farmhouse doors#Floral Carved Door#garden doors
0 notes
Text
not to beat the "sokka's misogyny" disk horse even further into the ground, but while i agree with the take that sokka being sexist logically doesn't make sense, i would go further to say that the water tribes themselves being sexist is both illogical and thematically contradictory.
the flaws of each nation in atla have always been linked to their element, and specifically what those elements represent. fire is the element of power; power, left unchecked, leads to imperialism and authoritarianism. earth is the element of substance and stability; stability, prioritized too highly, creates and justifies the rigid class system and rampant corruption of ba sing se. air is the element of freedom; freedom, taken too far, becomes irresponsibility and abandonment.
meanwhile, water is the element of change... therefore the water tribes cling to antiquated ideas about gender roles instead of adapting with the times (especially when the times involve a fucking war going on).
not only is this unrealistic, it also breaks the thematic pattern of the nations' flaws being virtues taken to extremes, and how this dovetails into the show's overall message about the importance of balance. if we're keeping with the pattern of virtue and vice being two sides of the same coin, then the flaw of the water tribes has to be related to change. and here is where some of the (badly executed) ideas in the comics and legend of korra could have come into play: change, left uncontrolled, can lead to progress... but at the cost of tradition and spirituality.
(imagine a nwt cut off from the world and forced to rely solely on itself, ingenuity and creativity flourishing out of sheer, desperate need. imagine a nwt where waterbending is nothing more than a tool, used to build and defend and maintain a fortress always at risk, its spiritual origins slowly lost to time. imagine a nwt more military than community, whose architecture and technology far exceed anything the world has ever seen, who look down upon their less advanced sister tribe, and see no need for the avatar - after all, where was he when they had no one but themselves for the last 100 years?
when warned that the fire nation is coming, they show no fear; they have held strong on their own for the last century, bolstered by their weapons and wits, and will continue to do so. you need the spirits, aang implores, and is met with derision, for there is no place for spirits in a society always chasing more, greater, better. the spirits have not helped us before, avatar. why would they now? we are all we need.
when the moon spirit falls, unprotected and forgotten in an abandoned, rundown spirit oasis - so do they.)
not only would this fit better thematically, it would also ensure that the nwt's flaw plays a role in its own downfall. where the fire nation's warmongering resulted in the poverty and suffering of its own people, and the earth kingdom's corruption led - at least in part - to the fall of ba sing se, the misogyny of the water tribes is never shown to negatively impact them in any way. the north isn't defeated by the fire nation because they relegated half the population to healing. the south doesn't suffer raids or lose their waterbenders because they (supposedly) didn't let women fight. this lack of narrative punishment means that - outside of a few girlboss moments for katara - the sexism of the nwt isn't significant to the overall story whatsoever.
furthermore, while the ba sing se arc last almosts half a season, and the fire nation's actions drive the entire show, this supposed systemic oppression of women shows up for one episode in the first season before disappearing entirely. pakku is reminded of his lost love, magically turns into a feminist, and somehow the entire tribe follows suit? no one else protests, not even the other students or the chief?
and yet, though there are still no female waterbenders other than katara, or agency for kanna in her relationship, or any indication that women stopped being forcibly betrothed - the entire issue is simply swept under the rug and never brought up ever again in the show. i understand this was a children's cartoon made in 2005, and that even having female characters openly speak about and challenge misogyny was a radical feat for the time and genre, but the reality of patriarchy is that it's structural, sustained and immensely difficult to resist - if the show was going to depict that resistance, it should have done so with greater depth and nuance, as it did for many of the other difficult topics it tackled.
ultimately, handwaving misogyny away like it never existed is far more disrespectful to katara's character, her fight against injustice, and the girls who saw themselves in her, than simply toning it down or removing it could ever be.
#atla critical#atla live action#it also always struck me as odd that sokka and katara seemed so chill with the north#when the nwt literally left the swt to fight the fire nation alone and stayed out of the war for a century#they lost their benders. their parents.#and all the while the north was sequestered away doing nothing to help#you're telling me that wouldn't have created any resentment? any anger?#plus imagine how powerful it would've been for the last southern waterbender to help the north rediscover the origins of waterbending#also the north disdaining spirits yet being saved by the ocean spirit and the avatar?#that's the exact kind of narrative irony atla does best#i'm seriously begging people to realize that the misogyny arc in atla was NOT as groundbreaking or well-developed as they think it is#and i for one am interested to see if and how netflix is going to handle it
155 notes
·
View notes
Photo
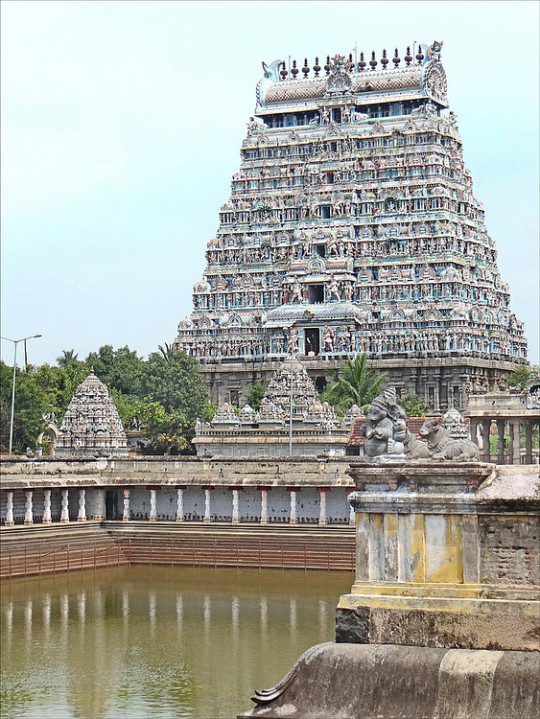

Chidambaram
Chidambaram (Cidambaram) is an important Chola temple site in Tamil Nadu, southern India. Most of the temples at Chidambaram were built in the 12th and 13th centuries CE. The site is dominated by the huge gateway tower of the Nataraja temple but Chidambaram also boasts the first Devi or Amman shrine, the first Surya shrine with the distinctive stone chariot wheels which would adorn many subsequent temples, and the first large Siva Ganga tank. In this respect Chidambaram is something of a transitional site, linking elements of the old and new styles of Indian temple architecture.
The name Chidambaram, one of several from antiquity, derives from the Tamil Cirrambalam, meaning 'little hall'. The site was chosen because according to mythology it was the precise spot where the Hindu god Shiva had once danced in a grove of tillai trees. The dance was, in fact, a competition between Shiva and Parvati and naturally the great Shiva won. The story became a popular subject in Hindu art over the centuries.
The site is enclosed within four perimeter walls and covers a rectangular area of 55 acres. Within the compound are shrines, halls, temples, ornamental gateways, and a large ritual bathing pool, known as a Siva Ganga tank, which is surrounded by cloisters. Inscriptions claim the site was built by various Pandya kings and local rulers but none are contemporary with the dates the buildings were actually first constructed. The walls and east gopura (gateway) may be ascribed with greater certainty, and were probably built by Kulottunga III, who reigned from 1178 to 1218 CE.
The Nataraja temple was constructed between c. 1175 and c. 1200 CE. The actual temple shrine is relatively modest as by now in Indian architecture the gopuras had become the most important structures, at least in terms of aesthetics. The twin sacred chamber was, however, adorned with copper sheets covered in gold by successive Chola kings. The shrine is preceded by a dance hall and large entrance porch with columns (mandapa).
The massive granite and brick east gopura dominates the site but there are three other gopuras on the north, south and west sides (the earliest). The corbelled roofs diminish as the structures rise and are finally topped with the usual barrel-vaulted roof (sala), the eastern gopura also having a row of 13 decorative finials. The east gopura has a proper interior floor at each of its nine levels and there is an interior staircase which climbs to the very top of the building. All four gopuras have false windows on their facades, typical for this kind of structure, and pairs of pilaster columns set at regular intervals. The second floor of each gopura also has a passageway which worshippers ritually walked around. The entrance archways all have coffered ceilings decorated with relief panels.
Of particular note at Chidambaram are the thousands of sculptures adorning its buildings. In particular there are many statues of women in a wide variety of dance postures. Many statues are accompanied by quotations from Hindu literature which provide an invaluable reference for scholars. There are also figures of the four dvarapalas (guardian demons), the dikpalas (cardinal directions), many figures of Shiva performing heroic deeds, various other deities such as Vishnu, Devi, Sarasvati, and, unusually in southern architecture, river goddesses.
Finally, Chidambaram is also famous for its 17th century CE Nayaka ceiling paintings which decorate the Shivakamasundari shrine of the Nataraja Temple. More than 40 panels depict scenes from the life of the saint Manikkavachakar, a devotee of Shiva.
Continue reading...
90 notes
·
View notes
Text

Antigua Via Latina / The ancient Via Latina
In the middle of the Roman periphery, between the modern Via Appia and Via Tuscolana, a section of the 3rd mile of the ancient Via Latina is preserved in perfect condition.
It has ancient origins: the natural route, already followed in prehistoric times, was used by the Etruscans to colonise Campania in the 8th-6th centuries BC.
Definitely laid out by the Romans around the IV-III centuries B.C., it connected Rome with Capua, maintaining its importance throughout Antiquity. In fact, even in the Middle Ages, it was preferred as an access road to Naples because of its better preservation compared to the Appian Way and the presence of a number of Christian places of worship along the route..
Entering the Archaeological Park of the Tombs of the Via Latina, it is now possible to walk along a section of the original paving of the street. With a pleasant walk you can admire the rich tombs dating back to the I-II century A.D. that overlooked the route, which still have perfectly preserved polychrome decorations on the façades and inside: vaults covered with painted plaster and stucco, walls frescoed with funerary scenes and rich mosaic floors are still substantially intact in their original context.
From the street it is also possible to reach the Basilica of S. Stefano, a rare example of an early Christian building erected under the pontificate of Leo the Great in the middle of the 5th century.
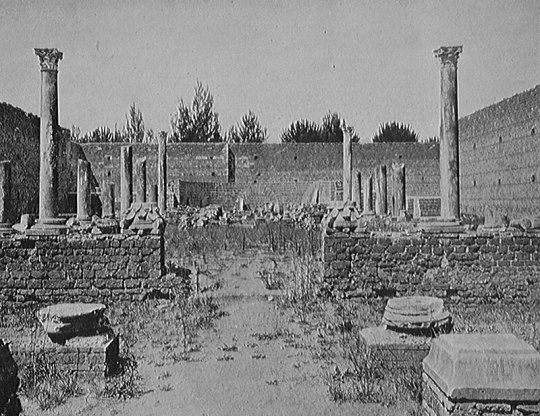

Santo Stefano en Vía Latina, restos parcialmente reconstruidos, 1911.
Santo Stefano in Via Latina, partially reconstructed remains, 1911.
The Archaeological Park of the Tombs of the Via Latina was created in 1879 following the acquisition by the State of a vast area in which important remains from Roman times had been discovered.
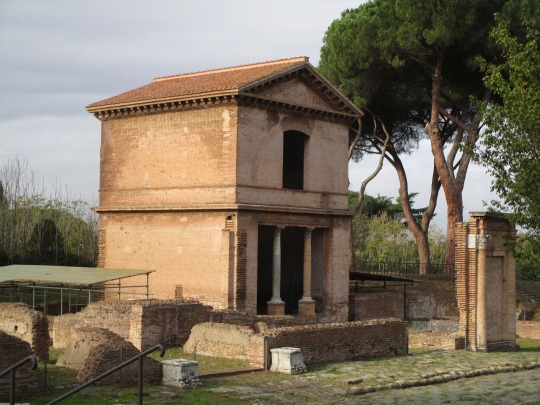
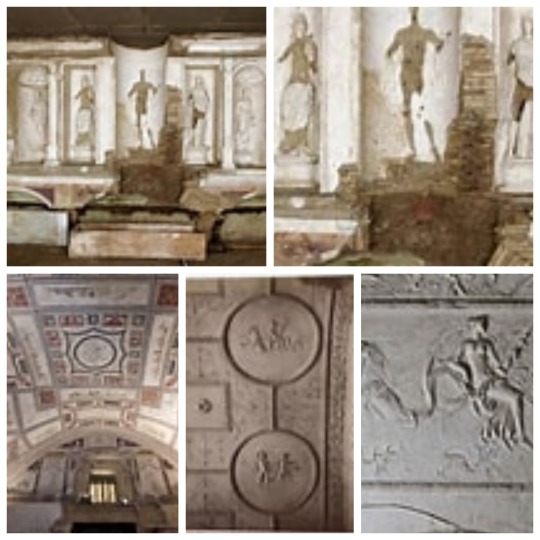
BARBERINI TOMB
The so-called Barberini Sepulchre, or Sepulchre of the Corneli. The funerary monument, dating from the 2nd century AD, consists of two above-ground floors and a hypogeum in an excellent state of preservation. The upper floor is covered by a ribbed vault completely covered with plaster painted with a red background and stucco elements. Groups of figures, winged victories on chariots, love affairs, birds, marine animals, mythological themes and architectural backgrounds can be recognised.


Sepulcro Barberini y su interior / Barberini Tomb and its interior
TOMB OF THE VALERI
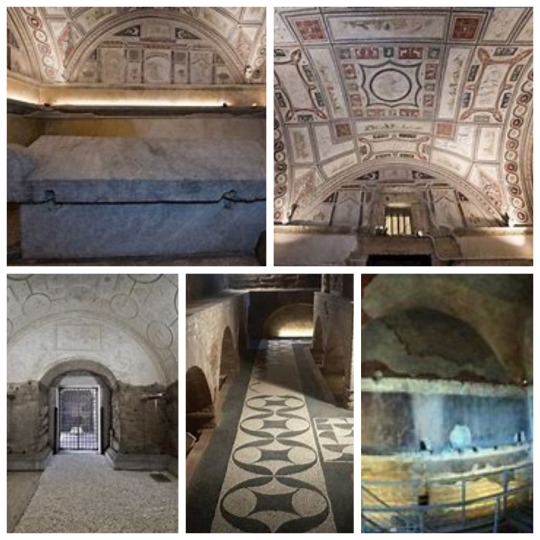
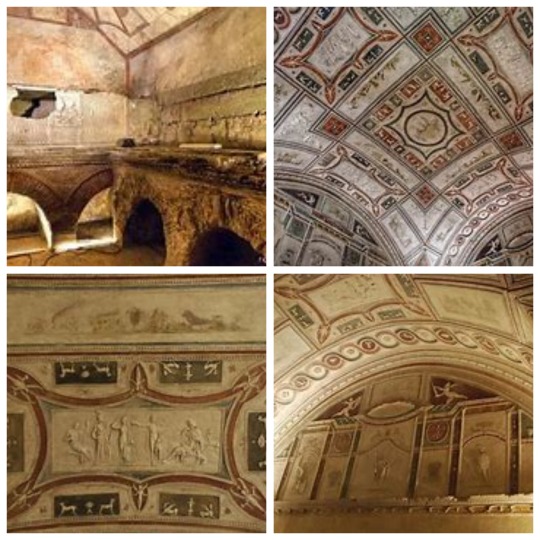
The Tomb of the Valeri. The richly decorated underground rooms dating from the mid-2nd century AD are preserved, while the elevation is a hypothetical reconstruction dating from the mid-19th century. An elaborate white stucco covering, articulated in 35 medallions and panels, adorns the lunettes and the barrel vault of the underground room. The medallions depict Dionysian themes, female figures and sea animals, while in the central tondo there is a delicate-veiled figure on the back of a griffin, representing the deceased being carried to the afterlife.


Tumba de los Valeri, exterior e interior / Tomb of the Valeri, exterior and interior
THE TOMB OF THE PANCRATII
The Tomb of the Pancratii. Much of the visible structure is a modern construction that protects the monument below by resting on the original 1st-2nd century AD walls, about a metre high. Upon entering the tomb, one can admire the beautifully decorated underground rooms, with mosaics on the floors and vaults and walls frescoed in bright colours and stucco in an excellent state of preservation. They depict mythological scenes, natural and architectural landscapes, images of women and animals. In the centre of one of the underground chambers is a large sarcophagus for two Greek marble depositions.


Sepulcro de los Pancracios, exterior e interior / Tomb of the Pancracios, exterior and interior
83 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cylinder desk and bookcase attributed to Duncan Phyfe, 1815–1820. Met.
Ornamented Grecian Style
The second phase of Phyfe’s work in the Grecian style is a bold synthesis of late English Regency and French Empire furniture design characterized by the use of opulent materials and sculptural and architectural elements derived from classical antiquity. The overall effect is one of brilliance, monumentality, and archaeological correctness, especially when compared to the suave, almost delicate character of his earlier work in the style. The transition was gradual and probably occurred sometime between 1810 and 1815 under the general influence of several important English and French design publications, including Thomas Hope’s Household Furniture and Interior Decoration (London, 1807), George Smith’s Collection of Designs for Household Furniture and Interior Decoration (London, 1808), Percier and Fontaine’s Recueil de décorations intérieures (Paris, 1812), and two important fashion magazines, Pierre de La Mésangère’s Collection de meubles et objets de goût (Paris, 1802–35) and Rudolph Ackermann’s Repository of Arts, Literature, Commerce & C. (London, 1809–29). This transition was also likely spurred by Phyfe’s most able competitor in New York, the Parisian-trained ébéniste Charles-Honoré Lannuier, who organized his manufactory to take advantage of these international trends by staffing it with ébénistes and other specialists who, like himself, had once worked in Paris, the epicenter of the opulent Greco-Roman revival under way in Europe. By 1815–20 the Grecian style as formulated by Lannuier and Phyfe was a rich mélange of French Empire and late English Regency design trends. Lannuier was in some ways more avant-garde and successful at this visually complex and technically challenging furniture, but his untimely death in 1819 cleared the field for Phyfe, who continued to refine his ornamented Grecian-style furniture. By the 1820s it was the finest available in New York.
—Peter M. Kenney and Michael K. Brown, Duncan Phyfe: Master Cabinetmaker in New York
15 notes
·
View notes