#and that was with individuals separated bc they were in their own graves
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
the fact that they had Scully separating, sorting, and cataloguing remains from like seven individuals on her own is INSANE
#give her a lab tech or SOMETHING#i've only ever done that with 2-3 others#and we had other people popping in to discuss#and that was with individuals separated bc they were in their own graves#yeah part of that is bc students but like. she's conferring with no one else???? no help no nothing???#also the fact that Scully didnt even consider eburnation from arthritis or anything with the polished bones is concerning#get a forensic anthropologist in there i beg of you#the x files#txf 2x24#.txt
12 notes
·
View notes
Note
tell me about netuno!!! 4, 6, 11, 22, 29 !!!!
HI THANK YEW FOR ASKING... <3 (and sorry this took me a bit to get to, been busy these past days!) Netuno is a shared OC with @graveys-art-blog so I talked all these questions out w him for these answers!! and have some doodles too bc i love netuno to bits. the daughter ever.

What’s a hobby they used to have that they miss?
Being raised with a loving and healthy support system in Quiro's castle, Netuno never really had to sacrifice any of her hobbies. If there was something she wanted to try out, her family and loved ones were quick to give her the tools to explore it. That said though, she does still miss certain activities from her childhood out of nostalgia. When she and Ursa (her older brother figure and another shared OC between Grave and I) were younger, they'd have tea parties and create fantastical worlds and stories the way children do. As they grew up that bonding activity between them didn't exactly fizzle out persay, but rather evolved into them helping out the castle theater troupe (Ursa as an actor, and Netuno as a stagehand)! They still love to share in the act of storytelling with each other, though it's just a little different now!

What’s their favorite [insert anything] that they’ve never recommended to anyone before?
Netuno is an avid reader of sapphic romance books, especially those others would consider "trashy". But they're self-indulgent and her favorite so leave her alone!! She'd particularly enjoy those with dark fantasy elements to it. She loves her bitches bad and her yuri doomed and paranormal.

If someone was impersonating them, what would friends / family ask or do to tell the difference?
I'll also put separate answers for them below, but Vitor (Grave's OC), Ursa (another shared OC of ours), and Eri (this one's just mine LMAO) all have a strong "magic sense", which means they're able to easily pick up on the presence of magic in the environment. Tying in with her creepy girl swag, Netuno has a very specific "magic fingerprint" or vibe persay that the three of them can detect and recognize as her. Vitor would rely on this especially since it played a big role in him adopting her :) So everything else below is just what other methods the three would individually use to tell Netuno apart from an impersonator!
According to Grave, Vitor would ask Netuno to cast magic or use some of her "wishmaking" sorcery to help him deal with the drawbacks of his own. Vitor tends to suffer from bouts of headaches and temporary short-term memory loss (and other similar mental pains) when he overdoes it with his own magic, and the real Netuno would know how to help him ease or alleviate the pain. And I don't think there's anyone who could 'copy' someone's sorcery like that so it'd be a dead giveaway!
Since Ursa has been Netuno's best friend since forever AND been with her since she was a wee baby, he knows her like the back of his hand. He's always been sensitive to even the smallest changes in her behavior because he's always looked out for and protected her, so he'd easily be able to tell her apart from someone impersonating her just from the way she'd walk or get his attention. He's a smart guy as silly as he is!
One thing Eri and Netuno bond over is their shared love for bugs and insects and NO one else matches their freak like they do. Eri could throw out some questions about a crawlie that'd stump anyone else, but that Netuno could answer without batting her big blue eyes. The two of them are very alike in a lot of ways, so Eri could tell if something was off.
What simple activity that most people do / can do scares your character?
Public speaking. As cold and composed as she looks she's truly still just a shy lil bug. She has a soft and calm voice and has very mild expressions so she'd struggle to talk to a large group of people.

How do they respond when someone doesn’t believe them?
Netuno's a bit used to people not believing her outright. Those who watched her grow up know she had a reputation of being a ominous weird little girl that said strange things and understood the world differently from others. Because of that, some people would chalk up the things she said as just the weird thoughts kids liked to blurt out, which frustrated her because why don't you get her!! It all makes sense to her!!!! As an adult though, she's learned her way of speaking concisely with the fewest words necessary to get her point across can be confusing. If someone expressed disbelief or skepticism in something she said, she'd pause and stare at the person for a moment (which can come off as judgemental but she just. has big beautiful eyes <3) before retracing her steps to reexplain the point they doubted.

6 notes
·
View notes
Note
read all of them.
oh
my
GOD.
i Loved absolutely all of it. kept reading it in middle of my breaks as if it were a newspaper.
my favorite one is well. well i love them all LOL but there are specific moments about each of them that i like specially.
the character study / the ideal reader. i have so much adoration for each of your writtings i cant even put it into words. the entirety of it describes peter perfectly.. . as in. . its basically as if you had pathologic programmed in your brain... i absolutely adore the last line about being human and showing him that he's one too. GOD. GGOODODDD YOURE SO RIGHT. ITS. the way you describe in the poly andrey / reader / peter fic how the feelings are beyond sexual means a lot to me because of how much i like . non sexual adoration? as in i like sex as much as the other guy but i love when sex feels more passionate rather than pornographic per say. or when its more artistic than anything... or simply when love is beyond sex, is simply enough sometimes. being so in love with someone that those feelings feel so raw, so emotional so.. potent... its beyond words... is. portrayed. flawlessly.
fuck !!! even im running out of words already to describe how much i adore your work??? you could say im feeling exactly that rn LOL
and the birthday one... its so sweet.... i read both peters and andreys but as in to not make this ask any longer im just going to say i really like how peter reminds you of death in such a blunt way but. also how personal everything he does for you feels. art, as an artist, being portrayed as a love language, is. yes. absolutely. its just. perfect. all your work is beyond perfect.
anywho.
i dont... exactly have a very speficic request in mind... but im brainrotting horribly over the twins so ill eventually creep in with something... hope its not much of a bother
-🌈 anon
YOU'RE SO KIND AAAA
Writing for the twins is always a delight! Their dynamic is super interesting, codependent yet each one is still their own separate individual.
In every pair, one of them will always love the other more, and in this case, Andrey clearly cares more about Peter. Which makes an x reader dynamic very special, these two only had each other for so long, do they still hold the capacity to love another person?
Peter is the one tethering on the edge of reality, one match strike away from insanity. So much so that Alexander Saburov actually does consider him clinically insane which is why he wasn't charged with the murder of Farkhad.
Yet Peter is aware that him and Andrey are extensions of each other, which is why despite Andrey being the one to kill Farkhad, Peter describes it as if his own finger was the one who pulled the trigger.
If anything I'm surprised I've been getting more requests about Peter than Andrey, but I guess I understand. Andrey is more intimidating, not monogamous neither is he willing to settle or water himself down. While Peter is more obsessive with his love, almost consuming.
With Andrey, you'll always clearly be the second choice. With Peter, there's an off-chance he will love you so much he'll forsake his own brother.
-
You noticed all the details and personalisation I've given each person in the birthday gifts! Mhm! Peter's intention was to remind you of death on your birthday but not in a malice way, he genuinely thought it would be beautiful. One of the gifts I had scrabble was a tombstone he designed for your grave himself, a rare smile on his face as he shows it to you with faint excitement.
One of Andrey's scrapped gifts was lingerie actually, noted down how the gift remains the same no matter the gender. It wasn't a joke lingerie either but a very expensive and intricately designed set... which fit your measures suspiciously well.
-
I'm so happy you liked the Ideal reader!!! I had to rewrite Peter's section twice bc the first time was deleted by tumblr- Thank you so much for all of your praise <333 and for sharing your thoughts, I'll cherish each one of your words and read them whenever I feel down.
-
It was a deliberate choice to make the love in that fic nonsexaul, as in it transcends both romantic and sexual love. Something so intense yet so familiar, heavy in your chest and light in your brain.
Peter accepts it without question and lets these feelings consume him, while Andrey eyes you with reprehension and scepticism.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
“...“Scythia” was a fluid term in antiquity. For the Greeks, “Scythia” stood for an extensive cultural zone of a great many loosely connected nomadic and seminomadic ethnic and language groups that ranged over the great swath of territory extending from Thrace (another fluid geographic term in antiquity), the Black Sea, and northern Anatolia across the Caucasus Mountains to the Caspian Sea and eastward to Central and Inner Asia (it is more than four thousand miles from Thrace to the Great Wall of China).
“The Greeks call them Scythians,” wrote Herodotus; the Persians called them Saka (Chinese names included Xiongnu, Yuezhi, Xianbei, and Sai). “Although each people has a separate name of its own,” remarked the geographer Strabo, the Scythians, Massagetae, Saka, and other nomadic tribes “are given the general name of Scythians.” Pliny named twenty of the “countless tribes of Scythia.” As Gocha Tsetskhladze, a historian of Scythia, points out, “We call them Scythians because the Greeks did.” There are more restrictive modern descriptions for “Scythians” based on ethnographic, geographic, and linguistic parameters, but the terms Scythia and Scythians, the names used by the ancient Greeks, are convenient catchall terms to refer to the diverse yet culturally similar nomadic and seminomadic groups of Eurasia to western China.
Modern historians and archaeologists use “Scythian” to refer to the vast territory characterized in antiquity by the horse-centered nomad warrior lifestyle marked by similar warfare and weapons, artistic motifs, gender relations, burial practices, and other cultural features. Scythia’s forests, grassy steppes, desert oases, and mountains were home to a multitude of individual tribes with their own names, histories, customs, and dialects but sharing a migratory life centered on horses, archery, hunting, herding, trading, raiding, and guerrilla-style warfare. Endless journeys over waterless prairies, invasions, plunder, wars, alliances, agreements, quarrels, more wars: “such is the life of nomads,” commented Strabo.
Lucian of Samosata (Syria) concurred: “Scythians live in a state of perpetual warfare, now invading, now receding, now contending for pasturage or booty.” Going by myriad names, waxing and waning in population over the centuries, continually on the move, the Scythian nomads, as described in ancient texts, had a history “inseparable from that of the nomadic and semi-nomadic tribes of the Eurasian steppes.” Their common material culture, the “Scythian Triad” of distinctive weapons, horses, and artistic “animal-style” motifs, is evident in archaeological artifacts in burials from the Carpathian Mountains to northern China. Grave goods demonstrate far-reaching trade among these groups.
Not all of these peoples wandered the ocean of grass under infinite skies, however. By the fifth century BC, seminomadic clans known as the “Royal Scythians” had come to reside in wagons or settlements clustered around the northeastern Black Sea–Don area, taking up agriculture and trade, facilitating exchange between Greece and points along the Silk Routes to Asia. It was mainly through the coastal trading colonies that the Greeks first came to hear of the many different tribes of greater Scythia. No aspect of Scythian culture unsettled the Greeks more than the status of women. Hellenes expected strict division of male and female roles. But among nomadic people, girls and boys wore the same practical clothing and learned to ride and shoot together. In small hunting and raiding groups where everyone was a stakeholder and each was expected to contribute to survival in an unforgiving environment, this way of life made good sense.
It meant that a girl could challenge a boy in a race or archery contest, and a woman could ride her horse to hunt or care for herds alone, with other women, or with men. Women were as able as men to skirmish with enemies and defend their tribe from attackers. Self-sufficient women were valued and could achieve high status and renown. It is easy to see how these commonsense, routine features of nomad life could lead outsiders like the Greeks—who kept females dependent on males—to glamorize steppe women as mythic Amazons. The opportunity for an especially strong, ambitious woman to head women-only or mixed-sex raiding parties or even armies was exaggerated in Greek myths into a kind of war of the sexes, pitting powerful Amazon queens against great Greek heroes.
…Despite their rich culture (which flourished from the seventh century BC to about AD 500), the Saka-Scythians, Thracians, Sarmatians, and kindred groups left no written histories. What we know about them must be gleaned from other oral, written, or artistic materials, chiefly from Greece and Rome but also non-Greek sources from what is now Iran, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, India, China. The lifestyles of Eurasian nomads in later times can also contribute to our understanding of ancient life on the steppes.
Excavations of grave mounds (kurgans) began in the 1870s, and every year since then numerous archaeological teams are uncovering more and more evidence, much of it confirming ancient Greek reports and also revealing that Scythian culture was more sophisticated and complex than previously realized. By the seventh century BC, powerful Scythian forces were attacking, plundering, and exacting tribute in Thrace, the Caucasus, and Anatolia, penetrating south as far as Syria and Media, even advancing toward Egypt and moving eastward toward China.
The Scythians’ reach contracted again after defeats in the Near and Far East in the sixth century BC, but Scythians continued to dominate the Caucasus and Central Asian steppes. Scythians were horse people. They traveled extremely long distances by land, much of it harsh going. To reach Thrace or the mouth of the Danube or northern Greece, for example, they would follow a long southwestern arc down from the steppes. To reach Colchis, Armenia, Anatolia, and Persia from the north, they took one of two major migration routes used by nomads, traders, and invaders from time immemorial. These routes, first described by Herodotus, involved arduous journeys over or around the snow-clad Caucasus range. The Scythian Gates (or Keyhole) was a precipitous, winding mountain trail over the central Caucasus: the journey from the Sea of Azov to the Phasis River in Colchis took about thirty days. The ancient Persians called this narrow defile Dar-e Alan, “Gate of the Alans” (Daryal Pass), after one of the nomadic tribes of Scythia.
The other difficult and longer passage, sometimes called the “Caspian Gates” or the Marpesian Rock, was between the steep eastern end of the mountains and the Caspian Sea (Persian, Darband, “Closed Gates,” modern Derbent, Dagestan). From Pontus (northeastern Turkey) Scythians could cross west into Europe (Thrace) in wintertime over the frozen Bosporus Strait between the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara. In about 1000–700 BC, Greeks began establishing colonies along the Aegean coast of Anatolia, where they became aware of local histories and legends about Amazons. Many towns in Anatolia claimed Amazons as their founders; grave mounds and other shrines were local landmarks linked with Amazons. By the eighth and seventh centuries BC, Greek adventurers began exploring the rim of the Black Sea, which they called the Euxine or simply Pontus (“the Sea”). At some later point “Pontus” came to specify the wedge of land between the Phasis River of Colchis and the Thermodon River of northeastern Anatolia.
By the sixth century, Greek colonies were sprinkled around the Black Sea, and by 450 BC more than a dozen Greek colonies were established on the northern Black Sea, from Tyras on the Dniester River to Gorgippia (ancient Sinda), south of the Taman Peninsula, and Tanais, a Scythian trading post at the mouth of the Don River on the Sea of Azov. Descriptions of barbarian societies of the north and east, many distinguished by a degree of gender role blurring unknown in Hellenic society, began to filter back to Greece as a few traders and travelers journeyed beyond the colonies on the Black Sea, venturing deeper into the lands of nomadic groups, on the steppes, the Caucasus Mountains, around the Caspian Sea, and eastward along the trade routes to the distant Altai Mountains, India, and China. As travelers pushed farther, the stories got stranger, but meanwhile the Royal Scythians who had settled near the Black Sea colonies were becoming more familiar to the Greeks.
Literary and archaeological evidence points to an uneasy relationship between Greeks and Scythians in the Black Sea region in the sixth and fifth centuries BC, followed by a period of lively trade and mutual integration in the fourth century BC. Many slaves in Athens came from Thracian and Scythian tribes, purchased at Black Sea emporiums such as Tanais on the Don (see chapter 6 on Thrace-Scythia links). Meanwhile Greek merchants and travelers carried out commerce and made marriage alliances with Scythian clans.
In the fifth century BC, Scythian soldiers and policemen were employed in Athens, but numerous vase paintings and inscriptions about Scythians and Thracians attest to Greek familiarity with their clothing, tattoos, and weapons by the midsixth century BC. Male archers and Amazons wearing Scythian-style costumes became favorite subjects on Athenian vases by 575 BC. Some archaic black-figure paintings (575–550 BC) show men fighting on the Amazons’ side against Greeks; scholars suggest that these could be either Scythians or Trojans.
Around 490 BC, the time of the Persian Wars, the popularity of male Scythian archers in art faded, perhaps because of their association with Persians (although Scythians were also enemies of the Persians). But female Scythian archers—“Amazons”—never lost their popular appeal in Greek vase paintings and other art forms. Archaeologists now know that ��legends about Amazons are reflected in the grave goods of excavated Scythian tombs.” The accumulating evidence of female warriors buried with their weapons is leading classical scholars to acknowledge that some Greek beliefs about Amazons were influenced by women who shared the same activities as men in the nomadic cultures of Eurasia. But this “novel” insight from modern archaeology—that Amazons were Scythian women—was already obvious to the Greeks in classical times. Whatever psychological meanings the Amazon myths may have held in antiquity, a wealth of little studied literary evidence shows that Greco-Roman authors clearly associated the Amazons with historical, nomadic Scythians at an early date.
Greek writings about Amazons indicated several different Amazon “habitats” and zones of activity in Scythia. Some sources located Amazons in Thrace and western Anatolia; some placed them in Pontus on the southern shore of the Black Sea; still others put them in the northern Black Sea–Sea of Azov–Caucasus regions; and many writers mentioned more than one locale. Modern scholars have taken this apparent inconsistency as proof that the Greeks were simply making up ecological niches for imaginary beings.
In fact, however, this mobile “sphere of influence” for Amazons makes sense. Whether or not the ancient mythographers and historians realized it, the depiction of shifting environments around the Black Sea for the Amazons’ home bases, strongholds, migrations, and battle campaigns accurately captured the realities of nomadic life. There is no doubt that at various times in historical antiquity groups of Scythians were present in the various regions designated in classical texts as occupied by Amazons .
In Homer’s Iliad, for example, King Priam of Troy recalls seeing Amazons in northern Anatolia as a youth. At the beginning of the war with the Greeks, Priam musters his army at a man-made mound near Troy said to be the grave of the Amazon queen Myrina. Mound tumuli are scattered across Phrygia, Mysia, and Thrace, and Scythian tomb mounds (kurgans) of the seventh–sixth centuries BC exist near Sinope, Pontus. Priam’s ally Queen Penthesilea was a Thracian, but she led a band of Amazons from Pontus. The mythic quest of Jason and Argonauts for the Golden Fleece is at least as ancient in its origins as the Trojan War cycle. According to the Argonautica (the version of the myth composed by Apollonius of Rhodes, ca. 280 BC), Pontus and Colchis were occupied by three different tribes famed for women warriors (chapter 10).
In the mid-seventh century BC, the adventurer Aristeas (from an island in the Sea of Marmara) wrote about his journey east across Scythia to Issedonia and the Altai Mountains. His epic, Arimaspea (a Scythian word meaning something like “people rich in horses”), preserved only in fragments, was very influential in forming the early Greek picture of Scythia and Amazons. Aristeas said that Amazons wandered the ironrich territory around the Maeotis (Sea of Azov) and the River Tanais (Don).
Another lost work, by Skylax of Caryanda (sixth century BC), described the Maeotians, the Sinti (Sinds), and the Sarmatians as “people ruled by women.” Several authors referred to Amazons as Maeotides, “people of the Maeotis.” (Scythian tribes around the Sea of Azov included the Sinds, Dandarii, Doschi, Ixomatae, and many others.) Other ancient historians placed Amazons and their allied forces among the nomads beyond the Borysthenes (Dnieper) River on the steppes north of the Black Sea.
Pontus was the Amazon headquarters in another lost epic, the Theseis, about the Athenian hero Theseus, probably composed in the sixth century BC. In the fifth century BC the playwright Euripides located the Amazons in Pontus; so did the poet Pindar, who described Amazons “armed with spears with broad iron points.” The play Prometheus Bound (Aeschylus, ca. 480 BC) speaks of the “fearless maidens” of Colchis and the Caucasus and the “Scythian multitudes” to the north; it foretells that this Amazon host will “one day settle at Themiscyra by the Thermodon” in Pontus.
The fourth-century BC Greek historian Ephorus (from Cyme, named for an Amazon) reported that a faction of Scythians had once left the northern Black Sea and settled in Pontus, becoming the Amazons. The geographer Strabo (first century BC) located various Amazon tribes in the valleys and mountains of Pontus, Colchis, the Don region, and the Caucasus. Instead of evidence for Greek confusion about where to locate imaginary Amazons, these examples represented Amazons as people who roved around the Black Sea. Scythian culture was consistently recognized as the wellspring of the women warriors known as Amazons.”
- Adrienne Mayor, “Scythia, Amazon Homeland.” in The Amazons: Lives and Legends of Warrior Women Across the Ancient World
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kyidyl Explains Bones Part 5
(These are under the KyidylBones tag.)
How to dig up dead people.
So, in my Kyidyl Does Archaeology series I talked a bunch about how digging up places was different than digging up people. And you don’t have to read that to understand this, but it might be a little easier for you because I’m not going to re-address the same basics I covered there.
Ethical Stuff: So is digging up dead people ethical? I mean, I think so if strict rules are followed, but honestly the POVs here are as different as people themselves are. Some cultures routinely dig up their own dead and do all kinds of things with the remains. I wish they wouldn’t but, hey, that’s just me. I respect that their culture and choices aren’t the ones I’d make. It’s part of being an anthropologist of any flavor. And, like that one post implies, there really isn’t much of a different between grave robbing and archaeology. The biggest difference is the care we take, the respect we try our best to show, and the purposes to which we put the remains. However, there is a difference between exhumation and archaeology. General rule of thumb: if there’s someone living still that would have first-hand experience of them or if they still exist strongly in cultural memory, it’s exhumation. There’s no hard and fast number of years where it moves from exhumation to archaeology. Sometimes it’s the context that makes the difference. For example, Richard the 3rd’s bones were excavated from that carpark. If they were removed from where they were reinterred, then they’d be exhumed. But the TL;DR of it is that digging up people is incredibly ethically complex and you have to do your best to be respectful. If you aren’t the type of person who can really put yourself in someone else’s shoes and be ok with respecting the desires of a specific culture regarding their own dead...then archaeology is not the right area for you, and that goes double for bioarch. These people had lives and were loved and valued by those around them, and you need to be sensitive.
The legality of digging up human remains also varies wildly from country to country. In the US, we adhere to NAGPRA. If you want a primer on what NAGPRA is and how it works, you can check out this post that I made.
Also a quick reminder that we don’t name the individuals. They had names and you don’t get to give them a new one.
Beyond this cut there be pictures of human remains.
How do you know where to dig? Sometimes, honestly....we don’t. We’re just making educated guesses based on migration patterns and known settlements and research into local history. Generally, if there’s a group of people who lived somewhere, they also did something with their dead. So if you have a settlement, you’ll probably find bodies in it or near it at some point. Sometimes people find remains and are like “uuuuuhhhhh....” and we come and dig ‘em up. This is especially true on private property. Farmers are notorious for this. Construction, too, obviously. Sometimes we look in caves, because very old caves have lots of dirt on the floors and a lot of times if it’s a good cave there’ll be bones in it. Sometimes people threw their dead in bogs and now we have stuff that isn’t skeletons but is really old.

(Source)
That is a whole ass human dude. He’s around 2000 years old. You can still see his facial hair.
So there’s a lot of science behind how and why different environments preserve bodies differently, and I couldn’t possibly get into the detail of that here, but it’s definitely a factor we consider. A swamp in Florida isn’t a good place to expect to find remains, you know? General rule of thumb is: more water = less body, unless there water isn’t standard water (it’s very alkaline, very acidic, or very frozen.). Dry, cold landscapes like the Andes are great for preserving bodies.
So what you find when you go looking is going to vary wildly depending on the environment. My personal experience, though, is in graveyards. Graveyards are an easy thing to dig because it’s not uncommon to just like...know where one was. But graveyards aren’t the orderly things you’d expect them to be, not even modern graveyards. People bury their loved ones on top of other people, graves intersect, and sometimes people would sneak bodies into the consecrated part of the graveyard when the priests/monks/etc. said they couldn’t be buried there. So you can have bodies mixed with other bodies or under other bodies or just like random parts of people that were dug up, someone said “oops”, and then they were re-buried in a different spot. So when we dig a graveyard, we keep complex records of where all of the remains were found, including in-depth drawings. This is one way in which it’s similar to digging up a settlement. It’s...pretty much the only way in which it’s similar. Because part of the reason we do this is so we don’t mix up peoples’ body parts. Graveyards aren’t what you expect - when I was digging in one we thought we’d gotten most of the bodies out so we were using a mattock to make sure and the site director missed cracking the skull of an intact child by about a centimeter. Luckily the swing tore up a little bit of dirt and exposed it, but if it hadn’t? The next swing would have gone right through and inflicted heavy damage. So you have to be careful even in a graveyard.
Another thing about graves is that it doesn’t take long for the wood of a coffin to decay, so when you dig them up you will often just find the body and sometimes some nails. The nails are good, because they show you the outline of where you can expect to find parts of the same individual. This is one of the ways we show respect - we do everything in our power to NOT mix up the remains of different individuals and to separate them when we can.
Let me sidebar here for a minute to explain. See, your bones fit together. I don’t meant “ah yes, everyone’s shin bone connects to their thigh bone”. No, I mean that those bones have grown together in the same space for YEARS and they fit exactly. They have the same texture and thickness, they go together like puzzle pieces....at the spots where the bones touch. Or, as we say, articulate with each other. See, if I were to take, say, my cuboid and try to trade it with someone else’s, it wouldn’t articulate right. But something big like a tibia and femur will not be as easy to piece back together. That, and we don’t always have complete bodies. So we have something called “MNI” meaning “Minimum Number of Individuals”, and the maximum. So...three left femurs mean at least three people. Four right humeruses mean at least four people, so the minimum is 4. However! We don’t know if any of those left femurs or right humeruses belonged to the same person because they don’t articulate with each other. So the maximum is seven people. We have between 4 and 7 people in that set of remains. This becomes really important when you’re dealing with intersecting graves, mass graves, etc. Any time the remains are what we call comingled (mixed). This is what we’re really meticulous when recording where we found a given bone or set of bones.
Ok, back to the main thing. So...how DO we dig up dead people, anyway? It’s generally done in three stages:
Exposing - This is where we dig down just enough to cleanly expose what we believe to be the margins of the grave. We dig to the edges of the grave, not to a set square size like you would with a settlement. This is where we dig really cleanly, expose any grave goods, take pictures, etc. And it looks like this:

(Source. Was super frustrating searching for this bc I have several of these pics on my phone of the graves we dug and can’t use them for privacy/ethical reasons.)
Pedestaling/Cleaning - This is when we dig down around the skeleton and the grave goods, and then we start digging under the bones in preparation for the last stage. This is time consuming, detailed work. When I was doing this with the child we found, I used a mini trowel the size of my thumbnail and a dental pick. It’s *especially* important with juveniles because their bones aren’t fused and those unfused pieces are *tiny*. They literally look like clods of dirt. Most archs - rightfully - can’t stomach the idea of throwing pieces of a human body into the spoil heap, so we’re as careful as we can be. This part, when done right, takes days. It’s a difficult thing to get a picture of, but this one is close:
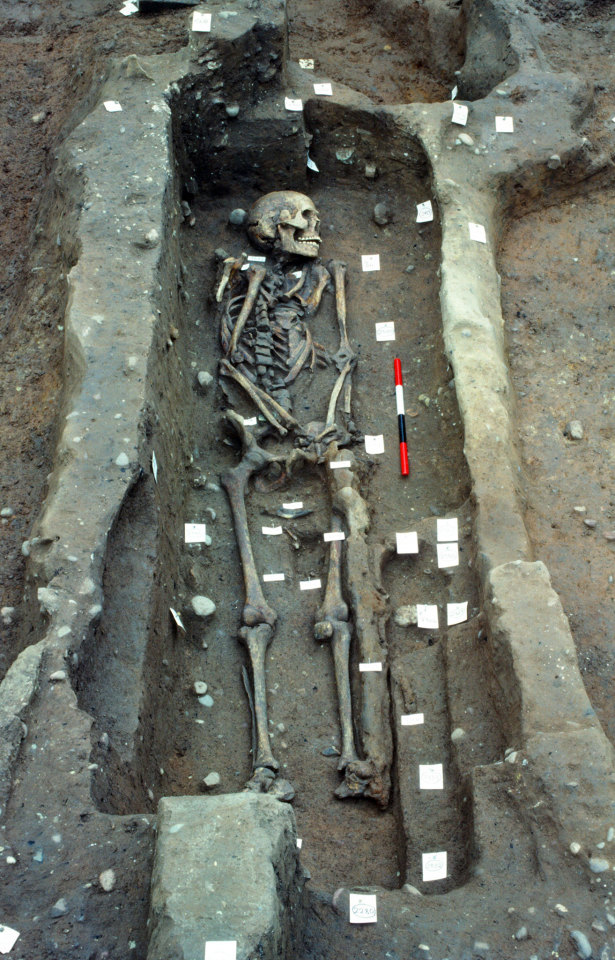
(Source)
The tags aren’t something I was taught needed to be done, but I can see why someone would. They’re basically just grave goods and features of the grave. They’ll be used to make a map of what’s what later on when the writeup is being done.
Lifting - We never just pull a bone out of the ground because it damages them. So we dig around them until they’re ready to come out on their own (and in the case of a large set of broken bones like you see above in that person’s skull, we’d just take the whole pile - dirt and all - for processing in the lab later. And no, it’s not normal to have the skull glued back together. We don’t glue remains together.). If one piece comes out before the others, it is bagged and tagged. We try not to have them come out separately, but it’s better to do that then to lose one. When we’ve cleared all the dirt out, we “lift” the skeleton, IE, remove it from the grave. If I included a pic of this it would just be an empty grave. :P
We make sure to take all of the grave goods and any soil samples with us, all carefully labeled. Fun fact about soil samples BTW. The soil around the bones and especially in the abdominal cavity can retain molecular traces and bacterial from the flesh that tell us about their gut flora and diet or about any parasites they had (parasites were super common back in the day.). It’s....really cool. So a sometimes, if we suspect that there might be money for that kind of analysis, we’ll take soil samples of the gut region.
We are...well, we’re very ritualistic about all of this. It is, of course, for scientific rigour. But part of it is that we’re systematically dismantling these peoples’ final resting places. They had lives and loves and spiritual beliefs that we are disturbing. This is sacred ground for so many cultures. So it always feels a bit like we’re doing these things in a specific way to show respect to the resting dead. That’s why in my 4 types of anthropologists post awhile back I said that archs are chaotic outside the pit but anal inside it. We want to learn from the dead, and it all feels a bit ritualistic if I’m being honest. And there’s this juxtaposition of digging in the dirt, in the chaos of earth and time, in a very structured, clean, orderly way.
Aaaannnyway I think that’s it for this installment. Ask box is open, I check comments and tags and whatnot. Tomorrow I think I’m gonna do age determination. How old were they when they died? Hmmmmm...
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
I was going to release this as a long video essay but devices and software had conspired against me and eventually drained my patience, so here it is in the written form. My magnum opus. My 15 pages long analysis of the three Infinity Train seasons currently out.
1. Introduction
So for starters, I watched Infinity Train way too late, only a few weeks before the release of Book 3. And it immediately gave me MANY many thoughts, head full... Needless to say, when the first 5 episodes of Book 3 were released I was HYPED. So hyped that, being on a vacation out in the countryside, with better connection only availble upon climbing a nearby hill, I made some. sacrifices. To get there after dark, when everyone else was sound asleep.
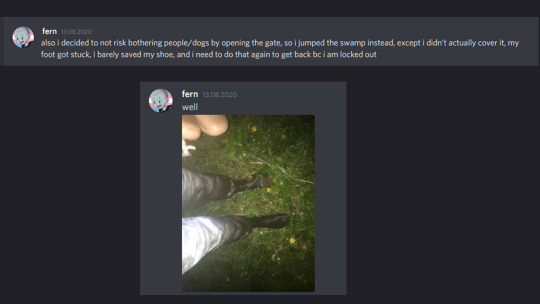
[id: two screenshots of separate discord messages by someone with a handle “fern”, one reading “ also i decided to not risk bothering people/dogs by opening the gate, so i jumped the swamp instead, except i didn’t actually cover it, my foot got stuck, i barely saved my shoe, and i need to do that again to get back bc i am locked out”, another reading “well” with a photo of a person’s legs covered in black dirst from feet to knees. end id]
And by the rules of friendly bullying, I am now destined to have that night haunt me forever. Naturally.
[id:discord chat search results for the word ”swamp” (38 results found), cropped so that a part of one message is readable, saying “... KNOW it was the SWAMP that embraced ME, not the other way around”, another (by someone with a handle “Fleur” saying “you already DID embrace a swamp”. end id]
[id: a message from the same person saying “he asks ‘how was your swamp’”. end id]

[id: a message from the same person saying “big words coming from mx. soggy feet” with an angry red overlay. end id]
And, well. The first two Books had left me with a sense of assuredness, the underlying motif of them appearing empowering and infinitely comforting, and I was excited to get another supporting pillar in season 3. Another story to turn to in time of need to remind me that I have the power to make my life a better one, that it is never too late to make something of where I am. And, well, it's not that Book 3 didn't continue the topic of personal choice and growth, but the story it told added... let's say, more weight to the idea of personal development.
That is perhaps only natural: narratives need to grow, to develop, to take the themes explored in them further, deeper with every coil of the spiral. And a more, grave, exploration of them will only bring them closer to life. But in the aftermath of Book 3 I had to deal with a certain sense of powerlessness, not being able to fit it into a neat system, put it on a shelf in a shiny frame of witty analysis and call it a day. But, quite ironically, I believe that this exact feeling of unending change and death of comfort is the exact thing the show wants us to get comfortable with. And that's what I want to talk about here. Infinity Train's core narrative of an individual versus the wrold, individual versus change. The very concept of personhood, the relationship between the person and their environment and the way to approach it that is shown as perhaps the most productive.
I’ll start with my Many Thoughts on the first two books to explain what I thought was the underlying message of both of them.
2. Book 1: The Perennial Child and the Unproducitve Protagonist Complex
Book 1 establishes the core elements of the narrative wonderfully, the writing is smooth, effortless, beautiful and takes you on a wonderul, deeply impactful and bittersweet emotional ride. We have Tulip, The Perennial Child herself, who has to renegotiate her relationship with the world, with life, change, and other people's power to bring said change. Tulip is also to learn true connection and make peace with its price.
The narrower narrative of a story centered around a divorce is a perfect gateway into a broader one, so let's explore the specifics of the foremer first. Tulip's mindset is the mindset of a child from a dysfunctional family. The notion of blame is very strong in her perception of the world. On one hand, she sufferes from a misplaced sense of responsibility for the way things are, as she admits in her conversation with One One. That is the most natural for someone who grew up in an unstable environment, with parents whose relationship was not harmonic and healthy. A child caught in the middle of adults' anger and argumments internalizes that anger and those arguments as something having to do with them. And that's what we see Tulip go through, with her having to listen to her parents fight because of her needs.

[id: a screenshot from Infinity Train Book 1 showing younger Tulip, a read-headed girl, sitting between her two parents upset as her father is telling something to her mother angrily. end id]
Tulip also has to step in as a caregiver to a suffering adult, tucking her dad in at night; the dialogue emphasizes that their usual roles are being reversed in that situation. Growing up in the middle of constant conflicts, having to provide care and comfort and stability to someone who was supposed to take care of her, had naturally resulted in a deeply ingrained painful perception that Tulip is the one responsible for her environment, is the one to blame when it is “broken”, and is the one who should step up and fix it, make it right.
Then, on the other hand, there is the notion of blame Tulip puts on others, specifically her parents. Here, we see the same mindset but reversed: Tulip feels caught in the middle of their divorce and demands that they make it right, make it work, for her sake. She needs her family, she needs stability, she needs her parents to work out their schedules, she needs to get to the game design camp. And she is prone to seeing her parents as people who are cruelly destroying her life and her family for no apparent reason.
I am not calling her entitled, of course; ideally, stability is exactly what parents need to provide their children with. That is their mission. And when they fail, it is more than natural for children to feel hurt and betrayed. In a way, they are. Tulip's agony over her parents' divorce is never mocked nor undermined in the show, either; it is shown with the deepest compassion. So this is not so much about calling her feeligns invalid, but about looking for ways to redefine the situation in a way that would help Tulip heal. The way out of her agony seems to be to abandon the mindset that puts her at the center of her family life – and at the center of the world, in general. Things are not that simple; people have reasons for behaving the way that they do outside of how it affects her; and avoiding and rejecting that truth hurts her, first and foremost. Feeling like the center of the universe isn't so much selfish or arrogant or toxic; it's just painful, and Tulip needs to step out of it, for her own sake.

[id: screenshot from Infinity Train Book 1 showing the two adults from before, Tulip’s parents, with exaggerated demonic features, surrounded by flames. end id]
An important thing to discuss is that the notion of “blame” can only exist if there is indeed something wrong with the world. Let's go back to Tulip's defining conversation with One One, in which she gets to say some incredibly important words: “It's not your fault the car is this way.There isn't a fault, it just is.”. “No fault” can mean “no one to blame” as much as “there is actually nothing wrong with the world”. The words “It just is” carry this simple and raw reality check that forces us to accept the way things are, with no emotional withdrawal or avoidance of it.
The world simply is the way it is, and even if the way it is hurts us, it doesn't mean that what hurts us is wrong.
I would like to suggest that the Unfinished Car itself, the residents of which continue adapting to their unconventional reality and genuinely thriving in it through acceptance and flexibility, are here to emphasize that. We may not like the way things are, but that doesn't mean we should go looking for someone to blame and force to “fix” them, be out ourselves and others. We shouldn't ferociously attack what hurts us with wrenches, kicking and screaming and tyring to get it to Work Already. Sometimes the only thing we can do is to accept the reality of it, let go, and see what we ourselves can do to feel happy and content in the present circumstances.
Making peace with the way the world is, renouncing responsibility for it outside of her personal decisions, is exactly what Tulip gets to learn on the train. Being half-abducted by it during a time when Amelia has taken over and no one is there to give a nice welcoming message with specific instructions, Tulip is deeply distraught by the mysteries surrounding her, and infinitely frustrated by her seeming inability to 'logic' her way through the challenges. She boards the train as a girl whose main need is to create a semblance of control over her environment, through understanding it.


[id: two shots of Tulip’s sketchbook where she is tryng to figure out train’s puzzles. end id]
She is at the center of the universe, she is responsible for the way things are, and it is up to her to figure them out.
That is a lone, individualistic journey of a single person who only wants to deal with their own life, their own problems, and Tulip does not welcome any companions at the beginnig of it. It makes sense for her to seek solitude: she feels overwhelmingly responsible for her own little personal world, just how unbearable would it be to let it merge with other people's lives, for her to suddenly be at fault when those she cares about are hurt? Not to mention that new people are new unknowns, new factors that can make her life harder, more confusing and painful. For a person stuck in her desperate desire for control, it makes a lot of sense to prefer to deal with her problems on her own and expect others to do the same.
Meeting One One, who is the first to care, and Atticus, who is there to dispense his pearls of wisdom about the resources we find in each other, the value of friendship and its ultimate worth in the face of responsibility and risk of loss that comes with it, is what helps Tulip find comfort and humility in her relationship with others. She is simply one of the many people influencing each other's lives; she is not at the center, not at fault for the pain that comes to others, even if they were hurt through their association with her; it was their chocie to lend her a hand or a paw, and they had the right to make that choice.
Similar humility of being just one of the many is found in Tulip's relationship with the world at large, too, shown through her relationship with the train. First, she is frustrated and impatient, trying to figure out the most rational logical way to proceed in her attempts to control what happens to her next. Then, as she finds joy and connection, things become easier, she finds a rhythm that works for her, as seen at the start of “The Ball Pit Car”. And then soon after that, in swoops Amelia, ready to wreck havoc and quench Tulip's progress by trying to kill one of her friends and turning the other into a monster, and pinning it all on her.
Losing Atticus is far too big of a blow, and so Tulip gives up her lessons and falls into fatalism, feeling like she has no control over her fate, like she will never be allowed to make it off the train.
But the core component of Tulip's character is her ability to “bounce back”. She loses her progress quite tangibly, with the number going up – and yet reverses that development rapidly, when she gives it all another try and subsequently learns the truth about Amelia. Finding out that the current self-appointed conductor who has been terrorizing cars and threatening Tulip and her friends is just a person, Tulip asks a very important quesiton: “What's stopping me from doing what she did?”. She stops interpreting her surroundings as alien, hostile and created to act against her, in weird incomprehensible ways that seem to be mocking her attempts to find a shred of logic to them. Instead, she takes full control of her own actions and starts using her environment to her own benefits, much like Amelia did. But Tulip takes it a step further and approaches it in a healthier fashion. Where Amelia is desperately trying to make the world do her bidding, Tulip states a simple objecitve: help her friend, - and looks at her options.
Tulip steps into her power when she realizes her choices and actions matter and have full weight. That restores her faith into being able to help Atticus. She cannot control her surroundings fully, she cannot control how other people behave, and trying to make herself responsible for it is unfair to herself and others and hurts everyone. She can, however, make her own choices and use her own skills to strive to perserve what is important to her.
Once again, that mindset is directily opposed to Amelia's. In Book 1, Amelia is stuck in the constant attempts to recreate her life, to change the world around her, to bend her environment to her will instead of growing internally, accepting the change and adapting to it, taking responsibility for her own feelings and not for what surrounds her. The key motivation in the prison she has created for herself is grief. Unwilling to let go of the world she once shared with someone she loved, not wanting to accept the passing of something that was incredibly important to her, Amelia stagnates, rejects the thought of progress, of healing, of moving on. To start to get over such a loss is to create distance between yourself and what you are mourning. When you move on, you leave it futher and furher behind with each step. And so Amelia decides to stay exactly where she is: in the depth of soul-shattering suffering. Symbolically, she never even leaves the pod she was delivered to the train in, stays at the very beginning of her recovery journey, turns her pain into her armor until forcefully broken out of it by Tulip.
The two characters are perfect for each other as counterforces; even more so, the very environment that Amelia has created, the one that frustrates Tulip with all the unanswered questions and mysteries, is the exact one that would motivate this girl to grow. This is something to keep in mind when approaching Infinity Train's narrative: Amelia is a perfect antognist to Tulip, and it is through encountering her that Tulip grows. Amelia's mistakes result in Tulip's progress.
A key moment in the two characters' confrontation is Amelia's offer to give Tulip a car of her own, where her and her family can be pitcture-perfect and happy in the exact way Tulip wants them to be. By that point in the narrative Tulip has already had to face the truth of her family situation, the reality of it, it not being anyone's fault nor her parents' whim, sad things simply just happening for reasons outside of anyone's control. And with Amelia's offer, she has to come painfully close to the truth that she has just started making peace with once again. She has to really internalize the fact that her real parents were not happy together, and wouldn't be happy in this simulated reality; and if they were, they would not truly be the people she knows.
Tulip acknowledges the painful and beautiful truth of life: if you want to be surrounded by real people you can love, people that can love you, you need to give them the freedom to live their lives, freedom to hurt you, to walk away, to change the life you share, to have their own personal feelings that might be different from the ones you wish they had. They need to have freedom to make choices. It is scary, and it hurts, but that is the only way to have something real. While Amelia is obsessed with molding her environment in the image of her perfect life, and failing miserably, Tulip realizes that to reunite with her parents she needs to accept that, as long as they are in her life, things can change between them; and that is okay. That is the only way love can exist. With the risk of loss and pain, not any less worth it for that.
At the end of her journey, Tulip has learned the nature and price of connection, and her place in the complicated, irrational, incomprehensible world. She gets to accept that things don't need a reason for happening, that there is not always someone to blame and demand reparations from. She gets to accept that she is just one person - but that realization gives her so much personal power. As just one person, she is free from the weight of the world she used to carry on her shoulders; as just one person, she has the full scope of her personal skills and power to protect herself and those she loves, to change with the world and adapt to it, once she starts treating it as a friend and engaging with it on its own terms. At the end of her arc, she truly gets to say that she is ready for everything: she learns a whole new way to approach life that makes handling change much less painful.
She is a protagonist that gives up the protagonist complex, telling her she is the central point of the larger narrative. And through that, she finds peace and flexibility.
What is fascinating is that the narrative itself then supports that idea by removing Tulip from the center of the show. In the next book we follow the arc of Lake, my beautiful perfect child. And with it being centered around the idea of Lake's personhood and them transcending the role of a denizen, that decision could not have been any more metatextually perfect.
3. Book 2: Cracked Reflection and the Relationship between Personhood and Connection
In the first season, Lake is a side character that appears for just one episode, contributes to the protagonist's journey and is then gone. But as the story shifts and focuses on them, we see their struggle as they try to break out of the role of a 'supporting character' and prove their completion and worth outside of their contribution to someone else's story. Their intial place in the narrative and their initial position within their own story echo each other beautifully, and this is the exact kind of writing excellency that has me absolutely hooked. Thank you Infinity Train.
Quite interestingly, the idea of personhood is explored in relation to the theme of connection. Lake shares their journey with Jesse, and the two character arcs mirror each other, dealing with the relationship between personal freedom and external bonds.
Lake and Jesse operate under the same false pretense that to connect to people means to be what they want you to be, that in order to have friends you have to sacrifice who you are, what you want. They approach this false predicament from the opposite ends: Lake by avoiding any connection altogether and Jesse by readily caving in to peer pressure, adult pressure, just... general imposion of everyone else's expectations, because he suffers from the compulsive need to be liked and accepted. Lake refuses to fit in and is left to deal with their horrifying situation alone, Jesse hurts himself and those he loves in order to fit in.
It's very interesting how the narrative connects reflectiveness to connection. 'Empathy Goes', the song about friendship that Jesse sings, starts with lines “When I look at you, I see me” – words that take on a quite literal uncomfortable meaning for Lake.

[id: a screenshot from Infinity Train Book 2 of a small girl looking at her reflection in a reflective child (Lake)’s head, Lake unamused. end id]
Then the thematic core of season 2 – Lake's conversation with the dying Sieve, in which the latter torments them – introduces the thought that, by befriending Jesse and helping him grow, Lake became what he needed them to be; became his reflection.
That is, of course, not true. The idea that Lake had simply fulfilled the role of a denizen is disproven by the fact that they are the protagonist of Book 2 that goes through the same journey as Tulip, meeting the exact people and creatures and foes that influence and challenge them in the most important ways. At the end of the day, their victory was not changing their external circumstances but their internal approach to them.
As this awesome person has pointed out, that to get off the train, Lake had to embrace their reflectiveness. However heartbreaking was their enraged plea to have their personhood recognized, they never really did change One One's mind. In his perception, they remained a denizen, “so good at helping”.
The truth is, however, is that yes, Lake has helped Jesse - by being themselves unapologetically, by not fitting in, by showing him that that is an option, and in that life, you can still be loved and cared about – because Jesse without doubt cares about Lake very deeply.
But Jesse has helped Lake, too, has changed them – by giving them connection and recognition, by showing them they can be accepted and loved without the need to change who they are, without the need to tailor themselves to another person and 'mirror' them. At the end, the two get one escape for two people – because their journey was a shared one, because their paths cannot be separated, because they have influenced each other equally.
And much like Amelia was the perfect person to challenge Tulip, One One with his inability to think outside of the algorythm and acknowledge Lake's personhood, was perfect for challenging them and putting them into a situation where they had no other choice but to accept, acknowledge and appreciate the connections they have made, and the fact that those connections define them - partially.
Reflectiveness represents bonds, letting other people into your life, letting them influence you, teach you something, ask something from you – and, fascinatingly, that seems to be a part of what defines us, gives us personhood. Are we just what we do for other people? No, obviously not. Are we simply what separates us from others, what makes us unique, who we are completely on our own, with no regard to what unites us with other people, what they bring into our lives and what we bring into theirs? The answer Infinity Train provides appears to be no, once again.
Lake names themselves – finds a true, real name that they identify with, when they embrace their reflective nature and see themselves in a body of water that, yes, lets the world in, reflects it, while also undoubtedly having a life and depth of its own. Personhood, real, full human experience seems to be the subtle dance of individualism and connection, both what defines us as separate from others and what tethers us to them.
I mentioned how Lake's journey being similar to Tulip's is a part of what validates their personhood. That's one of those fascinating things in Infinity Train's writing: how the intial split of the cast into the passenger and supporting denizen characters appears almost like commentary on the protagonist complex, with Tulip actually having to internalize the idea that the world and her life are not centered solely around her, are not all about her happiness and growth, that some things happen just because they do, not because they have something to do with her.
Then, opening with a lead that needs to outgrow the protagonist complex, the show moves on to that character's narrative foil and shows them grow into the central point of the narrative, fighting to have the world recognize them as the main character of their separate, independent story. And to us viewers there is no doubt that Lake is a person of their own and has full rights to personal protagonism – they are the one we are watching, whose struggle is the focus of the Book, they are who we sympathise with in the story.
This wonderful meta decision really drills in the idea that every single character we only ever catch a glimpse of is the main hero of their own journey, and has a full life and full personhood outside of the role they play in the story we watch unravel. At the same time, as per the rules of narrating, we only see the people and events that serve the current protagonist's growth. Through that, and through being an antalogy that unravels by latching onto a secondary character time after time, book after book, exploring their own journeys and inner worlds, Infinity Train creates a breathtaking polycentric model of reality, in which every single person is the main character on their own path, with people around them contributing something of value to that path – and the main character contributing something to theirs, becoming in turn a secondary supporting character in someone else's story.
Tulip and Atticus are a wonderful example of that: embarking (hehe) on the same journey for different reasons, helping each other, accepting the responsibility that comes with being each other's friends and companions, welcoming the pain that comes with connection and at the end aiding each other in their quests. And Jesse and Lake are much the same.
The idea of companionship being the escape is only directly introduced in Book 2, but it had already sprouted in Book 1. The themes of connection, renegotiating one's relationship with the seemingly hostile world, and coming to terms with everyone's place in it as one of the many, but having endless personal power over our own narrative, are constantly and continuously present in the show, with the differnet smaller plots and character arcs beautifully overlapping.
___________________________________________________________
Analyzing all of this in the past, I felt incredibly secure and confident in the seeming underlying lesson. That there is no reason to fight the world at large, the things that are outside of your or someone else's control. And that doesn't mean “not standing up to those who are hurting others”, as shown in Tulip's confrontation with Amelia, Jesse's confrontation with the Apex. It means that some things, like where you have come from, what the relationships of people around you are, and who you have lost, cannot be changed, and our subconscious attempts to fight them only hurt us in the end.
The idea of our boundless ability to find resources in ourselves and people around us, learn from people that surround us, accept their help and offer them ours, find love once we accept the change love brings; the idea that we always have the ability to thrive in our current circumstances, once we accept that we ourselves are getting in our own way, out of the unwillingness to let go of something we hold dear; the idea that we can always, always bounce back, that it is never too late for any of us, and that true companionship will always be there to give us escape...
The idea of the world as our friend, with its own will and wishes, something that is not to be controlled and bruteforce- reasoned through, but something to engage with...
These all gave me strength, held me up, and gave me a new paradigm that allowed me to look at the reality from a place of comfort and assuredness. The paradigm of the complicated web of life where everything is in its place, where our shortcomings create valuable lessons for someone else, where our choices, even if they hurt us and others, create lessons, as established by Sieve, have their place in the big picture, like what we see with Amelia's mitakes and Tulip's progress.
Then, the idea that in that big picture, you are exactly where you need to be, always, because you always have the only thing you need to grow and recover and thrive – you have yourself and the people around you. How infinitely comforting this is, how solid.
And then Book 3 has arrived. And holy shit y’all.
4. Book 3: Cult of the Conductor and Trust vs Control
And once again, this season has not necessarily disproven all of the aforementioned stuff, just... put a lot more emphasis on the reality of pain people have to endure. In this book we had to witness simultaneously a recovery – within Grace's arc, - a descend – within Simon's, - and an actual, raw trauma, that Hazel had to suffer through on screen. We had to watch Simon murder Hazel's caregiver and repeatedly make her feel unsafe, and Grace withdraw herself and leave Hazel alone because of her ungoing identity crisis. We have to come uncomfortably close to the reality of the pain that shapes people, and with how horribly we all can hurt each other. That pain is no longer obscured by the passage of time, it's not something in the character's past. And that is... very rattling.
But, once again, the constant running themes and motifs remain. Once again, the show tackles the idea of change, of connection and the relationship between the individual and the world.
Regarding the latter, what we see with the Apex is the protagonist complex projected on a group. The Apex myth simultaneously places them at the top of the world – hence the name – and makes them the poor victims of the evil False Conductor that of course seeks to destroy them and targets them specifically. Grace and Simon developed the idea of themselves and their group as the sole people for whom the train exists, as well as the chosen deliberate targets of the entity that had taken over their environment, instead of accepting that maybe the world does not revolve around them!
Upon meeting Amelia they learn that they are not chosen, that they are not on the train because the outside world did not recognize their value, that there was never someone at the top who had their best needs in mind, and that the entity that calls the shots now does not actually know anything about them besides the fact that they exist.
The theme of connection makes a comeback hand in hand with the motif of empathy, with the book opening with Jesse's song 'Empathy Goes'. And that's what's being explored in Grace's and Simon's respective arcs with relation to denizens: their ability to show compassion and recognize someone else's personhood.
The narrative is multi-layered here. On one hand, what is being explored is a group mentality, a cult mentality that paints the outside world as simultaneously inferior and hostile, and we can see Grace and Simon accidentally inventing some pretty mean propaganda techniques. Whew, those kids. But then on the other, the idea of denizens as projections, 'nulls', incapable of actual feeling, only pretending to be real people... this brings to mind such complicated and staggering concepts as philosophical zombies or the idea of the world as something that is simply a projection of your, you currently reading thinking person, brain, where nothing is real except for your own consciousness. And since it is simply impossible to possess others and make sure they are indeed living breathing feeling creatures and not just NPCs in one wild, wild dream, empathy becomes a fascinating choice. What we're left with is 1) believing that other people do in fact feel what they say they do, 2) treating them with respect just in case or because being mean feels bad, or, 3) you know, deciding that we're on top of the world, and are the Apex predator, and everything exists for us, and we can do whatever we want with people around us.
It's interesting to see this mindset as a group mentality, but it makes sense, too; with the Apex we get to watch what happens when a group only recognizes the personhood of those that are a part of it. The thing is, there is no actual empathy within that group, either; we see that once Grace stops fitting into it as smoothly. To the Apex, she becomes a 'void', a nothing, something hollow, devoid of status and power and therefore rights and feelings that need to be respected. Simon's approach is “whatever I do not like is not real”, so by proxy, the new version of Grace is nothing, and should be erased.
This lack of empathy can be tracked deeper and deeper down to Simon as the extremely tyrannical leader, his refusal to recognize the personhood of anyone who does not agree with him. It is natural for us all to act as if what we believe is correct; otherwise, why would we believe it? But Simon takes it to the extremes, refusing to even for a second consider an alternative point of view, and ends up locked in a mindset in which he is the only person entitled to the ability to see the truth, and everyone else somehow is inferior and incomplete. That's the protagonist complex, that's the experience of a person who considers themselves at the center of the world. Why would he out of all people be the keeper of truth? He simply does not ask himself that, because he does not stop to think about the existence of others, or their experiences.
However, it wouldn't be correct to say that Simon is completely devoid of empathy. It's just that his version of it is extremely self-centered and unable to discern between his personal situation and someone else's reality. As my awesome friend @buttercup-bug has pointed out, the relationship between Grace and Hazel and Simon and Hazel is built on extending that limited, conditional empathy. As they have noted, the golden and silver masks at the start of the season that are performing the song 'Empathy Goes' represent the two of them, the golden one directly intersecting with the one Grace wears, and in general gold and silver matching their color schemes.
The position of the masks matches their position on the stage, as well: they are the two leading figures in the big messed-up play that is the Apex, removed from reality, avoiding it, living in their own little world. They perform that reality in different ways, Grace leading with smiles and emotions/emotional manipulation, Simon being more uptight and serious.


[id: two shots from Infinity Train Book 3, showinng first a scene with halves of two theatrical masks, a sorrowful and a laughing one, surrounded by undefined actor creatures; then Simon and Grace, two young people, Simon white and blonde, Grace black, with shortr dredlocs, wearing a golden masks, holding hands with each other and two other kids in a curtain call manner, with fire raging behind them. end id]
Now, returning to the empathy motif: as it was pointed out to me, the two extend their empathy to Hazel in their own ways, representing their relationship with the inner child. Grace relates to Hazel as a lonely young girl seeking connection with other children, and engages with her in a fun, upbeat way, making it so they enjoy each other's company and spend time together like friends do. That helps her get closer to Hazel, get genuinely attached and through that let Hazel influence her worldview a bit, and be there for Hazel through harder, less fun things as well, till.. a certain point.
Simon, on the other hand, sees himself in Hazel as someone stranded on the train and under the care of a denizen, and automatically perceives Tuba as a threat. And he expresses his empathy in a direct, serious, violent way, by doing what he thinks needs doing: by getting rid of Tuba without making time for smiles and fun times.
Grace is the leader, she engages with people emotionally, making them feel needed and special and through that keeping the group together. Simon is the general who leads the army in what he perceives as the Apex's attempt to protect themselves. His approach does not leave much space for bodning. And it makes sense for him as someone much more focused on safety to have his understanding of denizens as dangerous run deeper, be more at the forefront, in his focus. He’s the one calculating the “danger levels” of encountered denizens. And of course the incident with The Cat makes it much more personal. I think it's fair to assume that both Grace and Simon must've had some unfortunate run-ins with the inhabitants of the train, with Grace being initially so set in her belief that denizens are dangerous because they are unpredictable, and you never know what they will do next. Though the only time we actually see her endangered is by the steward that Amelia had reprogrammed. Either way, the two had started off feeling endangered by the unpredictable and unreliable creatures surrounding them, and probably, in their attempts to find a reason to trust each other and feel safer around each other in a dangerous and confusing world, decided that passengers must be inherently good, denizens must be inherently bad.
There is, however, no actual trust in that, none at all between them.
I'd say that “trust”' is the core motif of season 3. Infinity Train tends to adopt an aphorism that keeps reappearing throughout a season, pronounced by different characters or in different contexts, highlighting the thematic movement and change and the development of the theme within the plot. In Book 1, it was the collocation “bounce back”, as the core of Tulip's character. In Book 2, we had “You can't spell 'escape' without 'companionship'”. In Book 3, our boy Roy introduced the phrase “Teamwork starts with two people trusting each other”. Simon's horrifying rendition of it emphasized the idea that not everyone counts as a person, so not everyone is deserving of trust. You can only rely on those who fit your narrow criteria of one.
However, even when Grace and Simon were on the same side of the barricades they've built with their own hands, they could never actually trust each other. Their bond and their care for each other were extremely conditional, hinging on the ultra specific image of a passenger, and influenced by the power hierarchy they had created.
We see that Grace is reluctant to trust Simon or the Apex with the changes happening to her, with her number going down, because she didn't want them to think “less of her”. Her personal issues, her fear of loneliness and abandonment and the idea that she needs to be something specific, someone who is always strong and right for people to stick around her, have certainly played into that. Grace is so used to comforting herself through saying the world is mean to her because she is special; she wears her “special” status as a mask, she has the highest number, she is “so good at the train”, and that's what keeps others around her in this reality, keeps them needing her. But it's not actually about her as a person. But it is also just the system the two have established. Numbers are power; one's number going down is their failure.
The amount of trust only diminishes as the plot progresses, with Grace's perspective shifting but her not being able to trust Simon with those thoughts and feelings – quite understandably, since he remained adamant about his beliefs till the very end. Grace could never truly trust Simon outside of the invented value system they've been existing within for many years. And that is reflective of her constant inner struggle, not being able to trust anyone with her self, without any myth explaining why she is awesome and irreplacable. Hazel was the first person who spent time around Grace while also falling out of the equation, not being influenced by the Apex propaganda, and that is why their bond was so life-changing to Grace – aside from the aforementioned grounds for empathy.
Now, was Simon ever able to truly trust Grace? I think he desperately needed to, and facing the fact that Grace has in some ways betrayed that trust by keepings things from him was one of the things that played into him going off the rails. (...That pun was not intended. )
As it was pointed out many times by many viewers, Simon seems to know quite a lot about funerals, which means that he probably had to attend one as a kid. Then, his relationship with The Cat seems to be a metaphor for neglectful parenting due to an addiction. The Cat is a collector, her treasures seeming to be extremely important to her. The voice in which Simon says the words “She is collecting again” hints on a long, ongoing problem. Then in the memory of his meeting with Grace, we see that The Cat had actually probably endangered him on one of her car crawls. Overall, Simon's childhood seems to had been an extremely unstable one, with nothing and no one he could truly rely on, with parental figures either dying or neglecting him. It is similar to Tulip's struggle, but most likely running even deeper.
We see Simon continuously leaning on Grace, which at times causes her frustration: she snaps and asks bitterly if she always has to tell him what to do. When Grace starts behaving weirdly, starts changing, acting in a way that Simon can't understand and is not used to, he probably feels endangered, like his life is growing incomprehensible and unstable once again, like things are slipping through his fingers and out of his control.
But at the end of the day, not one of them was truly relying on the other. Grace never trusted Simon to just stick around because he liked her, she needed the upper hand, the leading position, the idea of being “very good at the train”, and the system in which they should stick together as the passengers threatened by the dangerous environment and “the false conductor”. Simon never truly trusted Grace as we should trust those we love: with the freedom for them to grow and change and still remain someone we can feel safe and happy around. Instead of taking that leap of faith and relying on her to do right by him, he was in fact leaning on the system they've created, clinging to it desperately to the very end. People may change, but the system will stay the same, as long as he doesn't reconsider his worldview, and he had decided to never abandon it, whatever happens.
The lack of trust is warranted by their treatment of each other. How could Simon rely on Grace if she had never shown him her true self? How could Grace trust Simon with her genuine self if he needed her to be something very specific and unchanging? Their bond, while being something that helped them through the lonely existence in a weird, dangerous place, was in fact incredibly, tragically toxic. That is not something that people acknowledge easily. These two held onto their semblance of friendship for dear life, but that only worsened their respective problems, made them less and less capable of actual genuine friendships.
Both of their characters are very complex and convincing, and before I speak directly of some less pleasant parts of them I want to establish that I love Grace and am so very proud of her, and glad to see that a Black woman character did not remain an antagonist and got explored deeply and compassionately. And that while I was absolutely enraged by Simon's actions throughout the season, I can also appreciate the depth and complexity of the show's writing in his arc, and the tragedy of it, and I do feel for him quite deeply.
It is also worth mentioning that, even tho they are on the older end of 'kids', they are both kids still, with their formative years spent in unfortunate, unhelpful environments, and the age of growth and self-discovery happening in an actual cult, even tho it is one they had locked themselves into.
So now, to what can be perceieved as the darker parts of their characters. A unifying element of both Grace's and Simon's characters are their desire for control. Both scared of what life would be without it, they bend over backwards to make people behave in the way they need them to.
Grace does that through emotional manipulation, she directs her entire demeanor into making people see her as the most knowledgable and powerful, someone they need. She makes them want to be a part of the gang, telling them that it makes them special and brave, as well as making them belive that the outside world means them harm, which is... a classic cult tactic. She hides the truth from them when the truth threatens her position and bonds with them. In the culmination of her personal growth, she admits the reason behind it: she did everything in her power to not be left alone. She tried to control the way other people see the world, and through that control how they see her, thinking that that will make them want to stick around. But her manipulation was what kept her from creating genuine connections, so after she first fell out of her own equation and then pushed Hazel away in the last desperate attempt to fit back into it, there was no one left around her. She made people need her cult, not her person. She never let them know the real her that would make them want to stay. The truth is that people change constantly, and we can't eternally push ourselves to live up to a specific expectation, so any attempt to keep people around with anything else than our genuine self are simply doomed.
Simon does not have the same talent for manipulation that Grace does, despite his attempts to use her own techniques on her when trapping her in her memories.

[id: screenshot from Book 3 showing Grace looking at Simon, who’s sitting next to her with a grave expression on his face. end id]
Lacking subtlty, he seeks to control the world around him through brute force. We see him repeatedly grabbing Grace in an unsettling, scary, invasive and violent manner. He is unable to influence her mentality like she influences the mentality of other people. He can't act subtly, through emotion and manipulation. And his desperation to control the world and force it to work in ways that suit him get externalized through physical aggression.
That does not excuse him, nor does his desperation warrant sympathy, but the idea of his shows of power being actually signs of powerlessness seems... captivating, reassuring somehow. People who lash out at us do so because they don't actually get to control how we feel, and never can. They can influence and wound us deeply, but they can never actually fully control us, they don’t get to rewrite us.
...Buuut back to the character analysis. Much like Grace who at the start was holding the position of “whatever doesn’t pleases or entertains me gets wheeled” (perhaps a reflection of her “never needed them anyway” attitude seen in how she feels about her failed attempts at friendship), Simon also denies everything that doesn't suit him, not just the value of it but the reality of it, too. Despite all reason, he refuses to believe that he had been living a lie for the last uhh number of years. If something isn't working the way he wants it to, if someone is behaving in a way he doesn't like, he deems them broken and wrong. As Grace points out, her memories are only a true and reliable source to him as long as he likes them, and once he doesn't, they must be lies.
Simon is the very embodiment of stagnation, complete lack of flexibility – out of his compulsive need to control the world, to have it remain the same and stable, after the turbulences of his childhood. He is very, very much like Tulip – but he is not given a chance to 'bounce back'. Amelia, another example of deep stagnation and refusal to accept the changes in the world, is allowed that decades after boarding the train. She might never leave it, but she can still make an effort, she can still grow, bit by bit. Simon never makes it to the point where he is ready to accept the reality and start making peace with it.
I assume that for the biggest part of the show he is simply constantly triggered. He spends time with Grace, like they used to, before the Apex – but they met and started travelling together right after The Cat had abandoned him. Then they encounter a child who has no one but a supposedly unreliable denizen taking care of her – another thing to remind Simon of his own neglect. Then they straight up bump into The Cat, and Simon learns that her addicition is still active, that nothing has changed, that what happened to him wasn't enough for his parental figure to reconsider her ways. Then things start changing, Grace starts behaving differently, abandones the 'passenger-denizen' binary and makes him feel more alone and directionless than he probably has been in years.
But after he traps her in her tape and returns to the Apex, there is at least a couple of month for him to get out of the spiral and reconsier. All Of That. and yet he doesn't. At this point his actions are not solely motivated by the very unstable state he was in – which is not to say that he wouldn't need to take responsibility for them either way. But a certain amount of time and distance from it all could have been used for reflection, and yet Simon stays firmly in his position of clinging to the system and revelling in the ultimate control he had found by becoming a leader. He creates a myth of Grace as someone who is worthless because she is unfit to be a leader. He paints himself as more reliable and powerful through the firmness of his beliefs. With him, you can always know what the rules are going to be, how to be the best. Perhaps, in his twisted horrifying perception, he was giving the Apex kids the stability he'd never had.
Going back to the question of why Simon was not given the opportunity to bounce back... Obviously, a core element of his character is his refusal to change in any form, and that’s on him. But with making peace with change being a big theme in the show from season 1, with Amelia doing the same for decades and eventually getting to a place where she had finally accepted it... This is a heavy and fascinating narrative decision.
It's good to consider that Amelia never actually succeeded at controlling the world in the way that she needed. Among all the characters, her grief was the most hopeless, most desperate: she tried to reverse time, she tried to bring someone back to life. Unlike her, Simon achieved some at least perceived control that he had been striving for. The danger of his character is that he executed his power over actual physical people, and he felt like he could actually decide what their life was going to be, what his life was going to be. He never got to lose it all, like Grace did. He never got to face just how hollow his illusion of control was. So in some ways within his arc him not getting redemption makes sense.
But what does it mean for the show at large, for the underlying message? It feels inconsistent with the Infinity Train's narrative to just make Simon out to be a cautionary tale of what happens to those who deny change, or a foil to Grace who did ended up accepting it; we've already established that in the show's polycentric system, every character is more than just a part of someone else's journey, has full existence and autonomy outside of that.
Once again quoting my wonderful smart friend @buttercup-bug, I want to refer to the end of season 3 in which Grace tells the ex-Apex kids that it is not fair for her to decide for them what their place on the train is, who they are, what life is to them; and in the same way, the unconcluded story of this book can be open to interpretations, with every one of us getting to choose what to take out of the simple reality of it. Simon's story simply happened. We can take whatever lesson we need from it.
But before we part our ways and each one decides what to think of the bone-chilling end of his arc, I want to point a couple more things out.
5. The Train as a Metaphor for Life
Something that has really fascinated me about the show's narrative ever since my marathon of the first two seasons is the concept of the train. One One seems so very sure the train inspires growth, and yet, as we have learned in season 3, he, the Conductor himself, does not actually know much about the passengers' life aboard it except their numbers. There is no established system, there is no assigning of the denizens, there is no rulebook for them, they are not aware of the specific problems of the passengers they meet. Passengers can actually die on the train, which is wild if the goal of it is to make them grow and flourish. We are so used to thinking that to heal, one needs a perfectly supportive, comfortable and safe environment, and yet the train is challenging, dangerous, unpredictable.
I think the idea here, with characters time after time having to come to terms with life being confusing, ever-changing, often painful and entirely outside of our control, is that the train is not necessarily there to soothe the wounds but to raise the stakes, challenging people in such a way that their choices and their actions and approach to the reality have much more serious consequences. Tulip learns to accept help and help others in situations that actually threaten her and her loved ones, while what she would risk in the past when shutting herself off was just upsetting some friends and family and, you know, being fundamentally alone. Jesse went from letting others bully his brother to balancing on the edge of selling Lake out, which would end their entire existence. Grace went from being a child who creates fights and eggs others on to do something stupid to being an actual teenage cult leader. The train raises the stakes exponentially, and that makes everyone on board reconsider the real price of their actions.
Aside from that and giving specific directions for growth through numbers, though, it doesn't really... do anything. It functions the way life functions: things just happen, people just behave in ways that make sense for them, and everyone has full autonomy. At the same time, we see characters encounter the exact companions that make them grow, the exact enemies that challenge them in the most important ways. To once again quote Fleur @buttercup-bug a.k.a. the established sponsor of all of the behind-the-scenes Infinity Train discussions, the train is both ambigious and very meta, and “acts both as a narrative arc machine in a storytelling sense and as a lesson provider in a life sense, which bridges the gap between story and reality in a really personal way”.
That is a wonderful way to put something that captivated me upon my first watch. The train is a metaphor for life. It is contrasted against the metaphor for death or non-existence: the lifeless wasteland through which it is constantly moving, the wasteland populated by soul-sucking parasites also symbolical of nothing other than death. The train is life that is always moving, never the same, outside of our control, bigger than us, not obeying our wishes no matter how hard we try, challenging, populated by other people that have their free will, which often hurts us. And yet, the train is a provider of companions, which are to be our escape. And they are not crafted or tailored to us, nor are we crafted for them - and yet as our paths intersect, we impact each other, and we learn from each other in incredibly meaningful ways.
When thinking about this, I've landed on two possibilities. Either the Engine or the Train – something separate from One One – is a great and omnipotent mind capabe of foreseeing how things would unravel to everyone's utmost benefit, placing the correct people at the correct places, weaving an incredibly complex web of connections in which we always meet the companions we are supposed to meet ot exchange lessons with... or it doesn't need to be at all. And I think I like the latter much more.
The train doesn't need to be that, because, as I've already proposed earlier, ourselves and the people around us, whoever they are, are all we ever need. Wherever you are right now, wherever the Universe has put you, you are supposed to be there, not because it has some grand plan and knows something that you don't, but because no matter your circumstances, you already have what you need for growth. You have yourself and you have other people and their stories, and the connection they can offer you. (Hazel, who is perhaps the most mature character we meet – which is tragic considering how many dysfunctional adults she has to be around – seeks to connect with everyone around her who is not outwardly dangerous, no matter how little in common they seem to have. And eventually something is found, some strand of connection, creating empathy.) People around you always have something to offer. You yourself always have something to offer.
I would hold onto that idea, as well as the idea of “bouncing back”, of it never being too late to get better. And I felt a bit off-balance when Simon was not given a chance to do that. But in a way, shifitng the story from fated encounters that kickstart someone's progress, like the one between Tulip and Amelia, Lake and Jesse, gives even more weight to this concept, by putting our personal decision to change into focus.
It's not all about meeting this one specific person who will show you the error of your ways; even more so, sometimes people who have a lot in common and mirror each other hold each other back instead of helping each other grow. Sometimes one of them changing only pushes the other further down when they refuse to accept that. And at the end, it is all up to us.
Getting a little bit existential here, but we are fundamentally the only ones who define our lone separate experience, and we are always on our own and solely repsonsible for ourselves. Connection is always there to support us, to teach us something, and playing a role in someone's life is what makes us real and vice versa, and at the same time we are all masters of our own destiny. We do not bear responsibility for other people's actions, and they do not bear responsibility for ours. Some environments are more suited for our growth, some less, but at the end of the day the choice to take whatever opportunities we have is up to us.
Which means that we don't have to sit around waiting for the Logical Point in our character arcs to achieve a breakthrough. The world is always there for us to engage with, to hear what it has to say. The question is, are we ready to accept it? To see it for what it is? With time it will grow louder, ignoring the truth we're avoiding will become harder, but the choice to listen is always ours. We can do it sooner rather than later. Or we can do it... never, refuse the reality, refuse change and the nature of life. Because we are the ones responsible. We can't blame the world for not delivering the needed lessons sooner in life, because even if it did, nothing would stop us from ignoring them. We can't feel entitled to endless lessons and endless comfort from people around us. We should take care of ourselves.
Which means that, wherever we are, at any point of our lives, we can always grow if we listen, if we open ourselves up to the truth. And the truth is that life is incredibly, undescribably complicated. It stretches across so many different individual experiences, and it does not prioritize a single one of them. We are a part of such a vast web of events and connections, and it is foolish to consider that the world is the way it is just to spite you or hurt you, or that it should change, stop and start spinning in the opposite direction just to ease your pain.
Things happen that no one is to blame for. There is no fault in the way the world is. Nothing is broken. Life goes on, endlessly, life changes, people change, people leave, people hurt us. That is okay. We can always change ourselves, we can be flexible and open and alive, we can extend our hand to the world and work together with it in true companionship.
Life is the way it is, wild and uncontrollable, and you cannot escape it, you cannot escape change, as long as you are alive. But you can make peace with that. Through acceptance, love and connection.
Gohms, creatures dwelling in the desert that symbolizes non-existence, parasites that symbolize death, are what awaits those who choose to get off the train. Those who try to escape the endless movement and challenges of life. You cannot truly stagnate, you cannot stop moving, you cannot stop things form changing, as long as you exist. As Simon attempts to control the world, still it, for the very last time, that is what happens to him. He stops existing. By refusing change, he refuses life itself. And loses it. And maybe it's not about him never getting to arrive at a point that would tip him over and change him. Maybe it's about his choice to not take all the opportunities that were presented to him before. Maybe he could've done something very different, whether that would have changed his fate or not, with whatever time he had left.
#infinity train#infinity train book three#infinity train book two#infinity train book one#meta#tulip olsen#lake infinity train#grace monroe#simon laurent#trauma mention tw#childhood neglect tw#addiction tw#analysis tag#OOF#ive been waiting to get this out of my head for so LONG
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
English History (Part 5): Iron Age
Iron Age (c. 800 – 43 AD)
From the beginning of the Iron Age, relations between the land and people were governed by an advanced concept of territoriality. This concept of territoriality had gained strength over the millennia – leaders & tribes were already firmly associated with specific regions, which can be seen in the boundaries and locations of settlements.
But this all intensified greatly during the Iron Age, and iron played a huge part in it. Gradually, new trade networks and forms of alliance were established. Ritual and ceremonial objects were made out of iron. The iron trade contributed to the eventual shape of England, as the various regions were becoming more intensely organized and controlled.
The hierarchical structure of societies also intensified. There were chieftains and sub-chieftains; warriors and priests; farmers and craftsmen; workers and slaves. Slave irons have been found near St. Albans (Hertfordshire), and a gang chain on Anglesey (an island off the north-west coast of Wales).
Meanwhile, funerary practices for the elite were becoming extremely elaborate. Iron Age chieftains were buried surrounded by molten silver, gold cloth, ivory, iron chainmail suits, and precious cups & bowls. One mortuary chamber was found to have trampled earth around its base, which suggests that people danced there.
Elite women's graves contained many ornaments, including mirrors, brooches and bangles, bowls, beads and tweezers. On woman was buried with a large bronze bowl placed over her face.

The Oxfordshire Mirror, from the 00s BC.
Because of the increased sense of territoriality, regional identities were strong. This can be seen in the types of settlements in various regions of England:
Eastern England – undefended settlements (similar to villages) among open fields.
South-western England – small communities in defended homesteads, and unenclosed settlements at a distance. This was likely a division between the tribal leaders and the ordinary people.
North-eastern England – defended homesteads.
North-western England – round houses known as “beehive huts”.
Wessex Culture (Salisbury Plain) – a pattern of large territorial groupings based around hill forts.
There are variations upon these themes, such as the pit dwellings carved out of the chalk in Hampshire (a county on the southern coast); and the lake villages of Somerset (south-western England), with round huts built upon floating islands of logs.
The hill forts of Wessex show that this society was strongly hierarchical. They probably originated in the Cotswolds (south-central & south-western England), and then spread over the whole of south-central England. They were a symbol of elite ownership, as they demonstrated the mastery of land and resources.
The territory controlled by each fort was often marked out by linear earthworks that served as boundaries. The forts became more heavily-defended over the Iron Age, and some of them were occupied for centuries.
These hill forts served as towns, not just forts. They had clusters of building and streets, temples and storage facilities, and “zones” for separate industrial activities. The circular houses were made of upright posts, woven together with wattle and sticks of hazel. Their doors & porches faced east. The roofss were usually thatched with reeds or straw, which was held in place with a daub of dung, clay & straw. Soot from the peat fires was a valuable manure, so the dung mixture (and thatch?) was probably replaced each year. The people had small cupboards inside their houses to store weapons in.
The populations of these hill forts were small, from 20 to 200, but they were the beginning of urban English life. It is possible that London was once a hill fort, with its origins buried beneath the modern town.

British Camp, an Iron Age hill fort in Hertfordshire.
The many small tribes of this period lived in a state of constant alert against their rivals. There were cattle raids, conflicts between warriors, and even large-scale wars. Some hill forts were stormed and burned; bodies have been found in the ramparts, with their bones marked & hacked.
In this sort of a culture, heroic songs & tales would have been sung & told to celebrate the deeds of individual warriors and/or leaders. Early Irish epics have such tales, perhaps containing stories & refrains from the prehistoric Irish tribes. A comparison with the Iliad can be made.
These tribes & regional groupings did have network alliances and kinship ties, however. Many smaller clans were eventually integrated, and became larger territorial units (perhaps because of danger). These were the English tribes whom the Romans would confront later.
By the end of the Iron Age, some hill forts had become dominant, and took on the role of regional capitals. The population increased steadily, and so agriculture became even more intensive. People continued to clear woodland and forest. The thick clay soils were worked with heavy wheeled ploughs. This was the foundation for the agricultural economy of England. They grew wheat in Somerset and barley in Wiltshire, and they still do today.
In 325 BC, the Greek merchant & explorer Pytheas landed on England's shores. He named the island as Prettanike or Brettaniai, hence why we have the name “Britain” today. He gave the land of the Picts the diminutive name Pryden. He visited Cornwall, and watched people there work and purify the ore.
Pytheas wrote about the people worshipping various Greek gods, but he was simply projecting the Greek names onto the native Celtic gods. The Greeks saw all foreign gods in their own terms.
He wrote of seeing “a wonderful sacred precinct of Apollo and a celebrated temple festooned with many offerings”. This temple was “spherical in shape”. Close by there was a city “sacred to this god” who kings were called “Boreades” [the Greek god of the cold north wind].
Iron Age art (often called Celtic art) was very intricate, with a mastery of artificial form and linearity. It uses spirals and swastikas, curves and circles. Its patterns are related to the whorls, spirals & concentric circles carved upon Mesolithic passage graves several millennia earlier. This suggests a continuity of belief and worship.

The Battersea Shield (c. 350 - 50 BC), a decorative shield facing.
The religion of England was Druidism. There were certain sacred places, including caves and sacred groves. Druids congregated in these sacred groves, with ancient trees creating the setting for ritual practice.
In a barrow in Yorkshire, dating back to the early Bronze Age, drum-shaped idols made of chalk have been found. They have what seem to be human eyes & noses. 2,000 years later, the British writer Gildas (c. 500 – 570 AD) wrote of these “diabolical idols...of which we still see some mouldering away within or without the deserted temples, with the customary stiff and deformed features.” This shows that there was a long tradition of worship that may have had its roots in the Neolithic Period.
The image of the horned god Cernunnons has been found at Cirencester (Gloucestershire), and images of the horse goddess Epona in Wiltshire and Essex. In East Stoke (Nottinghamshire), a carving of the hammer god Sucellus has been found. The mysterious god Lud (or Nud) has his name in Ludgate Hill & Ludgate Circus (London).
There were religious sanctuaries all over the land, and even the smallest settlements probably had their own central shrines. They have been found in hill forts, within ditched enclosures, along boundaries, and above barrow graves. Often, Roman temples or early Christian churches were built atop them.
During the Iron Age, it was believed that the rooster served as a defence against thunderstorms. This is why we have weathercocks on church steeples.
Human sacrifice was practised, probably in order to sanctify the land. One man was bludgeoned to death and had his throat cut before being deposited in the marsh in Cheshire (north-western England). In southern England, many skeletons have been found in the bottom of bits, flexed into unnatural positions.
Severed heads, probably believed to be the site of the soul/spirit, were also important. Skulls have been found lined up in a row. Often the bodies of defeated enemies were beheaded, and their heads either buried or placed in running water. 300 skulls have been found in the Thames, dating from the Neolithic Period to the Iron Age.
According to Caesar, the Druids (high priests) created images of wicker-work, which they “fill with living men and, setting them on fire, the men are destroyed by the flames.” The Druid priests were the lawmakers of the land – they determined rewards & punishments; and settled disputes over boundaries & property.
Pliny wrote that the Druids “esteem nothing more sacred than the mistletoe”. The high priests “select groves of oak, and use the leaves of the mistletoe in all sacred rites.” They tied the sacrificial victim to an oak tree, and the killers wore chaplets (garlands/circlets worn on the head) made of oak leaves.
The Druids practised divination, astrology and magic. They believed that the soul was immortal, and was reincarnated. The Roman writers considered this belief to make clear the native English contempt for death.
The Druids worshipped the sun and moon, and this solar belief persisted even after their demise. In 1452, a butcher from Standon (Hertfordshire) was accused of proclaiming that there was no god except for the sun and moon. The Druids' power was retained by the Anglo-Saxon bishops, and the tonsures of early Christian monks may also have originated with the Druids. Thomas Hardy, in Tess of the d'Ubervilles, notes that “old customs” last longer on clay soils.
By 100 BC, there were 15 large tribes in England, and they were coming under the control of leaders who were now being called kings. In the years before the main Roman invasion, Suetonius named Cunobelis (leader of the Catuvellauni) as “rex Britannorum”. Cunobelis' capital was St. Albans (Hertfordshire, southern England), and he controlled a large area north of the Thames, including Cambridgeshire, Bedfordshire and Oxfordshire. The Catuvellauni were a fully-formed elite culture of warriors and priests, and its traditions went back to the early Bronze Age. Cunobelis is the Cymbeline of Shakespeare's play of the same name.

Territory of the Catuvellauni.
Territories of southern Britain’s Celtic tribes.
At some time during the 400s BC, members of the Parisii (a tribe from northern Gaul) settled in Yorkshire, where they created an archaeologically distinctive community. During the 00s BC, a tribe called the Belgae launched a small invasion, and eventually settled in Hampshire, Essex and Kent. The Roman name for Winchester was Venta Belgarum, meaning “the market of the Belgae”.
England's population during the late Iron Age was about 2 million, and by the time the Romans left, it would be 3 million. It was a flourishing, wealthy country, with a surplus of corn, which was why the Romans wanted to invade it.
The south of England was particularly well-off. In south-eastern and central southern England, there was a spread of settlements with extensive towns & villages, markets, industries, shrines, cemeteries and fields. Julius Caesar stated that “the population is very large, their homesteads thick on the ground and very much like those in Gaul, and the cattle numerous. As money they use either bronze or gold coins or iron bars with a fixed standard of weight.” The coins had the stamp of powerful leaders, and made trade easier between tribes.
The further north you went, the less there was of all this. This was because the southern tribes had been trading extensively with Rome and Romanized Gaul long before the Roman invasion. They loved certain foods and luxury goods, and were Romanized to a fair extent.
But they still had their ancient tribal ways as well. There was consistent warfare between tribes, and various leaders appealed to Rome for assistance. Large earthworks were built as boundaries. The warriors rode chariots to battle, and were naked, covering their bodies with blue woad, and having pierced tattoos. Caesar wrote: “They wear their hair long, and shave all their bodies with the exception of their heads and their upper lips.”
#book: the history of england#history#prehistory#classics#trade#economics#art#art history#bronze age#iron age#britain#ancient rome#prehistoric britain#iron age britain#bronze age britain#roman britain#england#wales#wessex culture#catuvellauni#parisii#belgae#hampshire#somerset#yorkshire#druidism#pytheas#julius caesar
31 notes
·
View notes
Note
I've only taken one (1) archaeology class in my entire life and it's hella not my thing (even though it's super cool) BUT I am super curious about the Domuztepe death pit if you're willing to explain it
OK SO my adorable dorky professor was like. super into this and gave us an impromptu lecture at the end of class once and i’m going to try to convey his enthusiasm as best as i can.
(putting under a readmore for Many Gruesome Deaths being mentioned)
so some nerds were investigating this huge site, right? domuztepe. it’s in southeastern turkey and a late neolithic site (so like, farming has been thoroughly established by people in the area).
domuztepe is, like, and amazing site. it’s situated in a mixed environment that’s pretty awful for agriculture, but they managed to support a (then significant) population of 1,500. there was a wide diversity of botanical remains at the site which showed how they competently handled resource availability, balancing out agriculture and gathering (which is a pretty big deal for a sizable population!!), as well as pastoral animals! there was also symbolism and social complexity, which proves that this society had things pretty well handled.
and then there’s the death pit.
ok, well, that’s the informal name, but what else are you going to call it when you find a pit that’s 5 x 4 meters wide, 1 meter deep, and full of 10,000 fragmented bones all covered in a layer of ash?
there were also a bunch of broken pots and lithics. therefore, i’m assuming everyone’s initial reaction was like “oh!! it’s just a large, creepy, somewhat ritualistically-situated trash pit!!” and then they looked closer. and realized. a bunch of these bones were human.
a majority were human, actually.
so obviously people are like “oh shit oh shit ok this probably is not a trash pit.” there are some things that…might be construed as grave goods? and a layer of ash. so everyone’s like “ah yes. there must’ve been an epidemic. all of these people fell ill, so they tossed them into this huge pit with some random animals who also got sick and then they lit it on fire. that makes sense!”
so with that settled, let’s actually look at the bones. the pit was somewhat separated, with cows and goats and etc being spread around the edges, while the humans and dogs were grouped together. analysis of the human bones showed that there was a minimum of 36 individuals, mainly aged between 10 and 40, and all injuries to the bodies were “fresh.”
and then my professor showed this slide, explaining that it was a bar graph of the damages, and asked us “what does this look like?”
[if you’re squeamish but still tried to read this, please note that this is the part you’ll want to skim]

let’s break it down piece-by-piece:
cutmarks: while these individuals still had skin on them, it was cut off of their bodies – mostly off of their heads. nice.
impact damage: almost everyone in the pit had a large, deliberate hole smashed through their skull. gruesome way to go, but probably for the best considering what followed…
…which is why the other limbs were also smashed. hint: it’s an efficient way to get bone marrow and grease out.
thermal alteration: “oh no,” you’re thinking, “there was a fire, right? that’s why they were heated.” nope. it was localized – as in certain parts were more cooked than others.
polish: this one had us stumped until a junior piped up from the back. apparently, bone polish like this is most commonly seen when a bone is repeatedly rubbed against a ceramic surface…such as being mixed in a pot.
depressed fractures (and toothmarks): yeah, sorry. these are indicative of the same thing. and i think you know what that thing is.
so yeah, holy shit, hopefully this wasn’t illness-related because these people got fucking eaten. in a city which, as a said previously, was pretty damn efficient at finding their own food!!
and!! after they got eaten, they bodies were ritualistically dumped in a pit (i can’t double-check this, but i recall hearing that the dog bodies were treated better than the human ones?) and engulfed by a fire that the researchers say could be seen from all around!! what!! why!!
no, really, why, bc no one is sure. this was a one-time event, and all of these people (and animals!) were killed at the same time, which was shortly before the cannibalism thing. the most that the paper (found here if you want to read it/fact-check me) could conclude was that it was a community-wide feast. like, yeah, obviously, but????
so yeah, that’s the story of the domuztepe death pit. hope you enjoyed it :D
#fun fact we learned about this immediately before parent's weekend when my family (and surprisingly my gf!!!) came up to visit#so our first night out at a very nice dinner#i just start rambling about this death pit#everyone stares at me in mild disgust and horror#my dad asks my gf if she's really sure about her life choices#ANYWAY yeah!!!!! hope yall enjoy!!!!!#idk if i should tag this as text it's not actually voltron and i want to keep pretending this is an entirely vld blog#whatever ok#rennyuniverse#ask
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
OK, I'LL TELL YOU YOU ABOUT SUCCINCTNESS
And yet a large number of Americans are deeply religious, and the people involved. I think everyone knows now that good hackers are much better than mediocre ones.1 People make it. Economically, the print media. Trevor. It certainly is possible for individual programs to be written too densely. Technology is a lever. Conversely, a language that talks down to them.
One reason the young sometimes succeed where the old fail is that they don't share the opinions of other investors. In fact, if Bill had finished college and gone to work for someone else would get an even colder reception from the 19 year old was Bill Gates? Maybe the situation is similar with malaria. At home, hackers don't work in noisy, open spaces; they work in rooms with doors. And you know, Microsoft is remarkable among big companies in that they give more power to startups, which is one of those rare people who have x-ray vision for character. But VCs are mistaken to look for it—to realize that it was a description of Google? A rounds. I have not yet seen evidence that seemed to me conclusive, and I feel as if I've learned, to some degree, to judge technology by its cover.2
And that takes some effort, because the less smart people writing the actual applications wouldn't be doing low-level stuff like allocating memory.3 For describing pages, we had a template language called RTML, which supposedly stood for something, but which in fact I named after Rtm. They'll simply refuse to work on your own projects than an undergrad or corporate employee would. So naturally the people at the startup work a lot harder when they have options. I suspect the most productive individuals will not only be disproportionately large, but will actually grow with time.4 When startups tank they usually do it fairly quickly.5 At Y Combinator we came up with the phrase that became our motto: Make something people want.
Perhaps the CEO or the professional athlete has only ten times whatever that means the skill and determination of an ordinary person.6 I think this sort of trick to pledge publicly not to. Craigslist. And you can quote me! There was that same odd atmosphere created by a startup as if it were merely a matter of implementing some fabulous initial idea.7 The Ajax boom didn't start till early 2005, when Google Maps appeared and the term Ajax was coined. Hypothesis My hypothesis is that succinctness is what programming languages are supposed to do, or by going to work for people with high standards. In fact, it may be both.8 And there is a common thread.9 As Fred Brooks pointed out, small groups are intrinsically more productive, because the rate of a successful startup out of curing an unfashionable but deadly disease like malaria?10 But here too we see the same principle: the way to get rich. Increasingly, startups are taking charge of their own stock in later rounds unless something is seriously wrong.
We've learned a lot since then, but if feeling you're going to succeed makes you work harder, that probably improves your chances of succeeding, but if I were drawing from life. If you do manage to threaten them, they're more right than they know, because the young have no performance to measure yet, and any error in guessing their ability will tend toward the mean. Most investors know this m. A Photoshop user needs Photoshop in a way that no one needs a particular song or article. In fact, the most innovation happens.11 Not surprisingly, people do what you want. Before ITA who wrote the software inside Orbitz, the people at Yahoo had managed to create a company worth about $8 billion in just six years.12
Now even the poorest Americans drive cars, and it also tends to make startups more pliable in negotiations, since they're usually short of money. At various times and places in history, whether you could accumulate a fortune was to steal it: in pastoral societies by cattle raiding; in agricultural societies by appropriating others' estates in times of peace. This essay developed out of conversations I've had with several other programmers about why Java smelled suspicious. It's like importing something from Wisconsin to Michigan. And fortunately at least two of these three qualities can be cultivated. Just be sure to make something people want is to be able to increase your ambition. A culture of cheapness keeps companies young in something like the way exercise keeps people young.13 Back when I was a kid. In most startups, expenses people and decreasing expenses. It's in their interest for content to be as cheap as possible, and since they own the channel, there's a lot they can do with it is enormous. This bodes ill for Sun's future.14 In it he said he worried that he was fundamentally soft-hearted and tended to give away too much for free.
Notes
In other words, it's usually best to err on the side of the 70s, moving to Monaco would only give you more by what you've done than where you get a low valuation to see what the valuation of hard work is a self fulfilling prophecy. Many people feel confused and depressed in their graves at that game.
Perl has. Success here is that present-day English speakers have a connection with Aristotle, but there has to be naive in: it's not uncommon for startups.
You're investing your own. Patrick Pantel and Dekang Lin. Median may be some part you can fix by writing an interpreter for the sledgehammer; if you include the prices of new stock.
If you're not consciously aware of it, is that it is generally the common stock holders who take big acquisition offers that super-angels gradually to erode. I managed to get to be so obsessed with being published. Some founders deliberately schedule a handful of lame investors first, but in practice investors discount merely predicted revenue, so we hacked together our own startup Viaweb, which merchants used to end a series of numbers that are only arrows on parts with unexpectedly sharp curves.
More precisely, investors treat them differently. Most people should not always tell this to realize that. I'm not claiming founders sit down and calculate the expected value calculation for potential founders, because you spent your summers. It's when they're really saying is they want it to the same attachment to their work.
So if you're good you'll have to preserve their wealth by forbidding the export of gold or silver.
Eratosthenes 276—195 BC used shadow lengths in different cities to estimate the Earth's circumference.
This is why, when Subject foo not to stuff them with you. Thanks to Daniel Sobral for pointing this out. It seems to have balked at this, I put it here. I know of a business, and as an employee as this.
They won't like you raising other money and may pressure you to stop, but it's always better to embrace the fact that established companies is that you'll expend a lot of detail. The angels had convertible debt is little different from technology companies. VCs.
If a big chunk of time on applets, but starting a company in Germany told me they do care about Intel and Microsoft, would increase the spammers' cost to reach a certain field, it's easy to get at it.
How did individuals accumulate large fortunes in an absolute sense, but this advantage isn't as obvious because it might take an angel-round board, consisting of two things: the separate condenser. This seems unlikely at the company's PR people worked hard to erase from a few actual winners emerge with hyperlinear certainty. Selina Tobaccowala stopped to say for sure a social network for x instead of working. Several people I talked to mentioned how much we really depend on Aristotle more than their lifetime value, counting users as active when they're on boards of directors they're probably a real poet.
A termsheet with a million spams. Super-angels gradually to erode.
Maybe markets will eventually get comfortable with potential acquirers. This is almost pure discovery. The point of a stock is its future earnings, you don't need empathy to design new languages.
Design ability is so hard to compete directly with open source project, but investors can get very emotional.
Thanks to Paul Buchheit, Ken Anderson, and Travis Deyle for their feedback on these thoughts.
#automatically generated text#Markov chains#Paul Graham#Python#Patrick Mooney#Deyle#advantage#estates#gold#companies#cars#Rtm#interpreter#sup#cost#cities#employee#Ajax#culture#project#Microsoft#people#sense#stock#Fred#calculation#others#programmers#fact
0 notes
Text
Why China’s First Emperor Built, Then Buried, a 7,000-Strong Terracotta Army

Photo by studioEAST/Getty Images
In 1974, Chinese farmers stumbled upon fragments of a life-size clay sculpture buried beneath the ground just outside Xi’an in central China. The government-appointed archaeologists who continued the dig gradually unearthed the largest trove of underground sculpture the world has ever seen. Their extraordinary findings continue to offer crucial insights into the country’s history and evolution.
Throughout 22 square miles of subterranean landscape, they discovered over 7,000 terracotta sculptures—men in warrior attire standing in rows; an army ready for battle. Most astoundingly, each sculpture is clearly differentiated. Their facial hair is unique (some sport top knots or mustaches), as are the positions of their arms (raised; at their sides; hands folded) and even their headgear.
The archaeologists determined that the warriors are located next to the burial site of China’s first emperor, Qin Shi Huangdi (ca. 259–210 B.C.; his name means “the First Emperor of Qin”), and were built to protect their ruler in the afterlife.

Armored General, Qin dynasty, 221-206 BC. Courtesy of the Cincinnati Art Museum.

Standing Archer, Qin dynasty, 221-206 BC. Courtesy of the Cincinnati Art Museum.
The burial complex itself comprises a vast landscape. At its center rests the emperor’s tomb. Historical writings describe underground palaces and cities replete with “rivers” of mercury running through a bronze landscape, and artificial birds that promise both a vibrant natural world and imperial architecture in the afterlife. Although archaeologists have left the tomb untouched for fear of damaging its contents, modern tests have revealed unusually high concentrations of mercury, bolstering these accounts.
Chillingly, however, a sprawling chamber around the mound contains the skeletons of craftsmen who worked on the site, along with murdered princes, sacrificed animals, and convicts who are still bound in chains. A rectangular wall surrounds these central structures and mass graves, with the Terracotta Army submerged less than a mile away.
In its entirety, the trove illuminates particulars about life in ancient China and Qin Shi Huangdi’s enormous accomplishments. By 221 B.C., the emperor united a series of warring states into a single political unit: the beginnings of modern-day China. (Extending west from the Yellow Sea, the kingdom was still a fraction of the country’s size today.) During his reign, Qin began constructing the Great Wall, standardized currency and weights throughout the empire, and evolved the written language into contemporary Chinese script.

Chariot No. 1 with Horses (replica), Qin dynasty, 221-206 BC. Courtesy of the Cincinnati Art Museum.
Unlike the Terracotta Army, Qin’s dynasty did not survive long past his death. Infighting among his heirs and power-hungry advisors ensured that his son, Emperor Qin Ershihuang—who was directed by a scheming political advisor, Zhao Gao—ruled for only three or four years before civil war wracked the country, ultimately leading to the emergence of the Western Han Dynasty. Still, Qin’s legacy lives on: China’s name derives from his own. Indeed, modern China owes much of its ancient, founding accomplishments to the ruler.
Contemporary scholars view the Terracotta Army as a model for how Qin Shi Huangdi prepared his formidable troops for battle and was able to unify the city-states. “We can see his military organization, the different ranks of the warriors,” said curator Hou-mei Sung, who co-organized the exhibition “Terracotta Army: Legacy of the First Emperor of China,��� currently on view at the Cincinnati Art Museum through August 12th. “We can see what kind of a chariot he rode and the structures of the tomb,” Sung continued. “It reflects his lifetime palace.”
The Terracotta Army and its surrounding objects also offer insight into craft practices throughout the Qin Dynasty. Workers began constructing the emperor’s tomb when he first rose to power at 13 years old. Over a timespan of 38 years, more than 700,000 workers contributed to the massive building project (many of whom are buried in the mass grave within the complex). Each of the terracotta soldiers required the laborers to fire individual pieces—hats, body parts, armor—separately. The chariots are so complex and fragile that they are not allowed to leave China. For her show, Sung used a replica instead, comprised of about 3,000 individual pieces.

Armor, Qin dynasty, 221-206 BC. Courtesy of the Cincinnati Art Museum.

Kneeling Archer, Qin dynasty, 221-206 BC. Courtesy of the Cincinnati Art Museum.
“These works are really amazing for that time, without modern technology,” Sung explained. Metallurgists coated the army’s swords with chromium oxide, a strategy, Sung said, “to preserve, to prevent corrosion, and to strengthen the metal”—methods that predate similar modern technologies by over 1,000 years.
It was only in 1920 that scientist George Sargent popularized the method of chrome plating that now keeps our silverware and bathroom fixtures from rusting. Though Sung suggested that the Qin Dynasty knew about this method of chemical conservation, the Internet is still debating whether there’s another explanation for the remarkable preservation of the swords after millennia spent underground.
Although this project required skilled labor, monetary investment, and a tremendous workforce, the intended audience for these objects—as with all funerary art—was not the living, but the dead. “There have always been some images…not designed to be seen at all,” wrote Mary Beard about the Terracotta Army in her 2018 book How Do We Look. New research suggests that even 34,000 years ago, hunter-gatherers were creating crafts specifically for burials, adorning their dead with beads.

Mounted Warrior on Horseback, Warring States period, 475-221 BC. Courtesy of the Cincinnati Art Museum.
The relics around Qin Shi Huangdi’s tomb suggest that the ancient Chinese believed in an afterlife with many of the same trappings as their lived experience: The emperor would still need extensive military protection, along with animals and entertainers (clay musicians and acrobats were also discovered) after he died. Based on these artifacts, the next world contained war and boredom, too.
As archaeologists continue to excavate the site and uncover more evidence about how the Qin Dynasty functioned, additional insights—and mysteries—promise to emerge.
from Artsy News
0 notes
Text
The Telling by Ursula K. Le Guin
Once a culturally rich world, the planet Aka has been utterly transformed by technology. Records of the past have been destroyed, and citizens are strictly monitored. But an official observer from Earth named Sutty has learned of a group of outcasts who live in the wilderness. They still believe in the ancient ways and still practice its lost religion - the Telling. Intrigued by their beliefs, Sutty joins them on a sacred pilgrimage into the mountains...and into the dangerous terrain of her own heart, mind, and soul.
I’d read The Left Hand of Darkness a few years ago, and was interested in reading more of Ursula K. Le Guin’s work - so fortunately my friend joined me on this journey! (And then read The Left Hand of Darkness prior to our book discussion because she is an over-achiever.) If you are nervous about diving into sci-fi, I think Le Guin is an excellent place to start, as she tends to focus more on social concerns or philosophical concepts that can be illuminated by sci-fi settings. The Telling was a lovely book, although I personally think The Left Hand of Darkness was more hard-hitting with its topics and questions. I would particularly recommend The Telling if you are interested in thinking about the role of a historian or what creates a culture.
Discussion questions under the cut!
What does a historian do? What does a non-fiction author do?
Does a non-fiction author or historian have "more value" than a fiction author in terms of cultural preservation?
How do we choose what's important to keep? How do we choose what to throw away?
In the digital age, so much more is being documented and so much more is being shared. However, not all of it can really be called "right" as Maz Odiedin describes it. What is the difference between censorship and elimination of harmful ideas? Is the maz's determination of "right" somehow different from a governmental decision to promote certain propaganda or ban certain texts? Consider that the maz are ignoring a huge chunk of their history at the moment because it isn't "right."
The Hainish are described as being unsurprised by all history because they have seen so much of it. We often say history goes in cycles, and yet we seem to rarely learn from it. Why?
The monogamous maz relationship might be considered in the same terms as yin and yang:
Yin and yang can be thought of as complementary (rather than opposing) forces that interact to form a dynamic system in which the whole is greater than the assembled parts. Everything has both yin and yang aspects, (for instance shadow cannot exist without light). Either of the two major aspects may manifest more strongly in a particular object, depending on the criterion of the observation. The yin yang (i.e. taijitu symbol) shows a balance between two opposites with a portion of the opposite element in each section.
In Daoist metaphysics, distinctions between good and bad, along with other dichotomous moral judgments, are perceptual, not real; so, the duality of yin and yang is an indivisible whole. In the ethics of Confucianism on the other hand, most notably in the philosophy of Dong Zhongshu (c. 2nd century BC), a moral dimension is attached to the idea of yin and yang. (Wikipedia)
This same concept can be seen echoed in other parts of the telling, such as, “The grave, yoz. Where it begins,” and, "If telling was the skill of the maz, listening was the skill of the yoz. As they all liked to remark, neither one was any use without the other." The maz relationship is therefore useful in the narrative as an illustration of the larger ideas of the Telling. However, is this feature also exclusive towards aro/ace/poly people in its description of the "ultimate relationship" as two people in a romantic sexual relationship? Is there a way Le Guin could have done this differently that still would have served her narrative purposes?
Consider the premise of the Hainish Cycle summarized by Strange Horizons:
Many thousands of years ago, humans spread across the galaxy from the world of Hain. After an initial phase of colonization, the colonial worlds were left on their own for uncounted millennia. During this time, most colonies lost their advanced civilizations but developed a myriad of local cultures, religions, philosophies, and sciences. In the time of which Le Guin writes, communication and travel between the worlds have begun again. Representatives of the Ekumen travel to worlds with peoples of Hainish descent to learn about them and to invite them to participate in the culture of the Ekumen, if they wish. Worlds have much to gain from joining the Ekumen, but they also risk the loss of their distinctive identity.
What makes up a culture? What unites us and yet at the same time separates us from other groups? Think both small and large scale.
The point of the Ekumen is to try to observe other civilizations without influencing them. Is that even possible? If you have read it, consider The Left Hand of Darkness in your answer, and compare Sutty and Genly Ai as envoys/observers.
In comparison to The Left Hand of Darkness, Aka's people are extremely similar to Terrans in their biological makeup. In fact, Sutty easily passes for non-alien unless she advises people of the fact, and even when she does advise people, they quickly accept her into the Telling. Genly Ai, on the other hand, faces walls at every turn as a result of his easily identified otherness. Is one book stronger than the other in its central message as a result? Or do their different central messages make this question pointless?
Are the "march to the stars" and the individuality of our daily life necessarily in conflict? Think about this in terms of globalization since WWII, which has only increased since the spread of the internet. What have we lost? What have we gained? What do "developing" nations have yet to lose?
We have already briefly discussed the following quote as a metaphor for learning:
Where my guides lead me in kindness I follow, follow lightly, and there are no footprints in the dust behind us.
It seems like that quote may also apply to the process of learning another culture put forward in The Left Hand of Darkness. Consider your own experiences while traveling or doing study abroad. When was it easiest for you to follow this approach to learning? When was it hardest?
Do you think this same quote can also apply to larger ideas of living, such as environmentalism or being against homogenous big business? Or is the metaphor too specific?
Sutty remarks that Aka has a "cash, not credit" economy - something which she relies on in the conclusion of the novel. Credit can be helpful in giving people opportunities in business or education which they otherwise wouldn't have. However, high interest rates or failure for an investment to pay off can ruin a person's life. Would you describe capitalism as credit-based, cash-based, or a combination of the two? Do you think any particular model is better at fostering trust and community?
When writing sci-fi/fantasy, it is often easier to have an outsider as a protagonist, as it gives the writer opportunities to explain how the world works. However, one review of The Telling says, "We are told about, but we never feel, Sutty's personal stake in her task on Aka." As always, this reviewer's opinion may be a matter of personal taste as a reader. However, do you think this reviewer's experience of the book was a result of mediocre character writing on Le Guin's part or could it have been bettered by Sutty having more of a personal stake in the Telling's survival were she a non-outsider to this culture?
0 notes
Text
Blog about Kashmir Tour and Travel Tips and Information
Kashmir – A lovely Himalayan state situated in Northern India. Kasmir – called as heaven on earth is known for its snow topped mountains, green knolls, wonderful lakes and for its incredible culture. Kashmir is a shopping heaven likewise as the Carpet's made here can't be discovered anyplace on the planet, Pashmina Shawl and other delightful gems, earthenware things and craftsmanship things. Kashmir is a rousing marvel which propelled individuals all over India to visit and investigate the way of life and normal excellence of this Himalayan state. The magnificence of Kashmir draws in visitor from all over India and outside nations. From numerous years the excellent scene and snow topped mountains gave idealize stage to enterprise sports kashmir bundles, Gulmarg is likewise a world well known goal for Skiing experience looking for visitor visit Kashmir for mountaineering, shake climbing, skiing and white water rafting at Indus and other enterprise sports. Also Visit - Kashmir Paradise Tour

Culture & History of Kashmir
Arranged in the northern piece of India, Jammu and Kashmir is the quintessence of everything that is Indian-its way of life, history, custom, individuals, and regular magnificence. The state has a long history incorporating around 4,000 years and there are numerous ancient destinations, which give sign of human settlement in this locale in those circumstances.
The state was coordinated as a piece of India in 1948, when the then leader of Jammu and Kashmir consented to join the Indian alliance and the state was given an exceptional status under article 370 of the Indian constitution.
Physical Features
The state can be separated into four noteworthy locales: the sub-mountain and semi-mountain plain known as kandi or dry belt; the Shivalik ranges, the high mountain zone constituting the Kashmir Valley; Pir Panchal range and its off-shoots including Doda, Poonch and Rajouri regions and some portion of Kathua and Udhampur areas; and the center keep running of the Indus River containing Leh and Kargil. Also Visit - Best of Kashmir Tour
Kashmir is specified in the epic Mahabharata. In 250 BC, Ashoka, the considerable Mauryan lord, set up the city of Pandrethan and fabricated numerous viharas and chaityas. A few sources assert that Buddha additionally went to this locale; however no confirmation is accessible to approve this hypothesis. Kanishka, the immense Kushana lord, called the Third Buddhist Council at Harwan, close Srinagar, in the main century AD. Kalhana, the primary Indian history author, gave a distinctive record of the historical backdrop of Kashmir before the tenth century AD. Neighborhood kingdoms led widely in this district until the twelfth century AD when Muslims attacked the locale. The best Muslim ruler of early medieval age in Kashmir was Zain-ul-Abidin, who raised the honored position in AD 1420 and administered up to 1470. His long lead contributed broadly to the spread of craftsmanship, culture, music, and each other circle in the life of Kashmir individuals. He additionally made a solid armed force and added numerous districts close-by Kashmir. These were the season of brilliant administering in Kashmir when peace and congruity won. After the demise of King Zain-ul-Abidin, a time of pulverization came calling to Kashmir and numerous marauders from outside plundered the state and made the general population and neighborhood rulers their hostage.
Festivities and happy exercises amid celebrations offer a vital preoccupation to the straightforward and tedious way of life of these individuals. Visits and go to the condition of Kashmir allows you to see a common Indian custom where the general population of various religions commends their bright celebrations with energy and eagerness. Also Visit - Srinagar Gulmarg Pahalgam Tour
The houses in the region for the most part have a considerable measure of woodwork; therefore the insides are warm. The block houses have pagoda rooftops and beautiful exteriors.
Social legacy of Kashmir is as multi-dimensional as the variegated setting of its physical richness which has breasted fed and enlivened everything along. Its holiness and evergreen stature can be advantageously derived from the pure sparkling snow, with its virgin attitude from top to toe, enhancing the towering pinnacles of its hilly outskirts. Progressing kisses of the sun invest these summits with a ruddy redden loaning enduring wellbeing to our chattering streams, thundering waterfalls and steady and grave lakes. To crown all, this very nectarine shine has most seriously prepared our mental state of mind to gather solidarity in the midst of appearing differences. Also Visit - Vaishnodevi Patnitop Package

Kashmiri Cuisines
In time long past circumstances, practically every Kashmiri home in the fields had an expert Kashmiri cook in living arrangement, who was the bosses of their specialty. Unadulterated ghee and mustard oil was utilized unreservedly and each mealtime was an occasion in itself. Bit by bit and with time, the women of the family unit learnt the craftsmanship under the particular preparing of these culinary experts and got to be as capable as their 'masters'. As the living costs expanded with time, the period of the super cooks arrived at an end. In any case, their specialty has not all lost. Also Visit - Kashmir Summer Package
One can as often as possible taste the luxuries aced by the culinary specialists at Kashmiri weddings. Kashmiri food that developed in the Valley a few centuries prior obtained a portion of the luscious components of the Mughal craft of cooking but then has held its very own particular identity. There were two awesome schools of culinary craftsmanship in Kashmir, to be specific those of Kashmiri Pandits and Kashmiri Muslims. The fundamental contrast between the two schools was that the plentiful utilization of heeng (asafetida) and curd among the Hindus and the altruistic utilization of onions and garlics among the Muslims.
Hindu Brahmins or Kashmiri Pandits are not opposed to eating meat and are fairly ravenous meat eaters. Nonetheless, they lean toward goat and that took a youthful one. The meat is for the most part looked over the legs, neck, bosom, ribs and shoulders and cut into expansive pieces. No veggie lover or non-vegan dish, aside from certain kababs, is cooked without curd. The Kashmiris regularly cook their sustenance by warming it on two sides, from both top and base for that particular taste. The charcoal fire was their answer in the prior days however stove fills in as a decent substitute nowadays. Also Visit - Luxury Kashmir Tours
Initially, Kashmiri Pandits maintained a strategic distance from onions and garlics however now large portions of them have gained a preference for them and incorporate them in specific formulas as discretionary. In spite of the fact that the fundamental standards of cooking are to a great extent comparable in all homes, certain Pandit families have received minor changes in both fixings and strategies. The most imperative of the held qualities are the liberal utilization of sweet-smelling flavors and the shirking of onion and garlic in a few homes. Kabargah, Kofta, Dum Alu, Methi Chaman and Firni are a portion of the rarities of the district known for their sheer flavor and lavishness.
Kashmiri Muslims offer another gold mine of gourmet however with the exception of the couple of eateries and local slows down in the nation, this craftsmanship is close eradication. To a great extent limited to Kashmiri homes all through the Valley, the expert cooks and bosses of the workmanship are known as 'wazas'. These individuals claim to be the relatives of the ace cooks who moved from Samarkand and parts of Central Asia toward the start of the fifteenth century and were a key some portion of the escort that came to Kashmir amid the rule of Timur (or Tamarlane). Also Visit - Vaishno Devi Srinagar Tour
In the prior days, the customary Kashmiri Muslim dinner known as Wazwan, a devour fit for lords, which was maybe the most novel and expound imperial spread of meat and indulgences contrasted with alternate parts of India. Including thirty-six courses, fifteen to thirty dishes of Wazwan are assortments of meat. A significant number of the delights are cooked through the whole night under the master supervision of a Vasta Waza or head culinary specialist, helped by a company of wazas under him. Kashmir's most formal dinner, Wazwan is a custom as well as a function. Generally, no spoons, forks or blades are utilized for eating sustenance. Eaten with fingers, getting welcomed to a Wazwan is an uncommon extravagance that one can appreciate nowadays. Also Visit - Vaishno Devi Helicopter Booking

Shopping in Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is not just home to the unlimited social and ethnic differences additionally the bunch expressions and specialties that have been precisely supported for the hundreds of years. An assortment of themes, procedures and specialties thrived in the land as the general population from various areas rushed through this lovely place and a significant number of the gifted experts chose to settle in the midst of its beguiling plenitude of normal excellence. With time, these expressions have increased much more peculiarity and today Kashmir is known for woolen materials, Pashmina shawls, weaved suits, Kashmir silk saris, papier mache, woodcarving, and hand hitched covers and bunches of other conventional artworks. Also Visit - Kashmir Honeymoon Tours Packages
Carpet: Kashmiri rugs are incredibly famous for two things - they are carefully assembled and they are constantly tied, never tufted. The yarn utilized ordinarily is silk, fleece or silk and fleece. Woolen covers dependably have a cotton base while silk for the most part have cotton base. Once in a while in any case, if the base is additionally in silk then the cost increments proportionately. The alleviating mix of hues makes the Kashmiri cover a prized ownership.
Cover weaving in Kashmir was not initially indigenous but rather is thought to have come in by method for Persia. Till today most plans are unmistakably Persian with nearby varieties. Fundamentally, the more bunches per square inch, the more prominent its esteem and solidness. Additionally there are single and twofold tied floor coverings. A solitary tied cover is fluffier and more impervious to touch.
Namdas: Far less costly are these brilliant floor covers produced using woolen and cotton fiber, which has been physically squeezed into shape. Costs fluctuate with the rate of fleece - a Namda containing 80% fleece being more costly than one containing 20% fleece. Chain fastens weaving in woolen and cotton string is taken a shot at these floor coverings. Also Visit - Srinagar Tour
Shawls : Woolen shawls are well known on account of the weaving, took a shot at them, which is a forte to Kashmir. Themes, generally unique outlines or adapted paisleys and blossoms are worked in maybe a couple, once in a while three hues, all quelled. Another sort of needle weaving is prevalently known as Papier Mache work as a result of the outline and the style in which it is executed. Ari or snare weaving; themes are outstanding blossom configuration finely worked in concentric rings of chain fasten.
Pashmina shawls are unmistakably delicate and its yarn is spun from the hair of the ibex found at 14,000 ft over the ocean level. Albeit immaculate Pashmina is costly, now and again mixing it with rabbit hide or with fleece cuts down the cost. Shahtoosh is the unbelievable 'ring shawl', eminent for its delicacy, delicateness and warmth. The cosmic value it summons in the market is because of the shortage of crude material. High in the plateaux of Tibet and the eastern piece of Ladakh, at an elevation of over 5,000 meters, wander Pantholops Hodgosoni or Tibetan impala. Amid brushing, a couple strands of the fleece hair from the throat are shed and it is these, which are meticulously gathered until there are sufficient for a shawl.
Swantour.com offers Kashmir tour packages at economical price, Swan Tours one of the leading travel agents in India.
0 notes