#anarchist anthropology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
'The tendency in popular thought to view the biological world in economic terms was present at the nineteenth-century beginnings of Darwinian science.
Charles Darwin, after all, borrowed the term “survival of the fittest” from the sociologist Herbert Spencer, that darling of robber barons. Spencer, in turn, was struck by how much the forces driving natural selection in On the Origin of Species jibed with his own laissez-faire economic theories.
Competition over resources, rational calculation of advantage, and the gradual extinction of the weak were taken to be the prime directives of the universe.'
– David Graeber, What’s the Point If We Can’t Have Fun?
By the way, by contrast, the other great, independent discoverer of Evolution, Alfred Russel Wallace, was a socialist, indeed an anarchist, even if he didn't use the label.
“However, we did not talk of geography during the afternoon we spent together, but of Anarchism, of which [Élisée Reclus] was one of the most convinced advocates, and I was very anxious to ascertain his exact views, which I found were really not very different from my own. We agreed that almost all social evils — all poverty, misery, and crime — were the creation of governments and of bad social systems ; and that under a law of absolute justice, involving equality of opportunity and the best training for all, each local community would organize itself for mutual aid, and no great central governments would be needed, except as they grew up from the voluntary association of their parts for general and national purposes.”
— Alfred Russel Wallace, My life: A Record of Events and Opinions
#david graeber#anarchist anthropology#charles darwin#what is the point if we cant have fun#anarchism#alfred russel wallace
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

How Peace Came to the Rotinonshón:ni

Aiewáhtha Wampum Belt [9]
The story of the formation of the Rotinonshón:ni has been passed down by oral tradition, by reciting the Kaianere’kó:wa. This recitation has been done in at least five similar languages and translated and transcribed into English in multiple versions. There are many variations, and no definitive version. [10]
In a version of the story common at Ohswé:ken, [11] Tekanawí:ta was born under mysterious circumstances to a Wendat mother, along the Bay of Quinte. [12] After a difficult childhood, Tekanawí:ta left his community to bring the message of peace to the Iroquois. He traveled south across Kaniatarí:io, where he encountered Aiewáhtha preparing a meal. Aiewáhtha, grieving for lost loved ones, was planning to a eat a man he had slain in vengenance. Tekanawí:ta conducted a condolence ceremony for Aiewáhtha, so as to end the blood feuding. He convinced Aiewáhtha to eat only of the flesh of deer, not man. Finally, he persuaded Aiewáhtha to give up war and to help him bring peace to the Iroquois.
According to a women’s oral tradition, [13] Tekanawí:ta then approached the head clan mother, Tsikónhsase.[14] Tsikónhsase, of the Kakwa:ko (Neutral) nation, had provisioned warriors and also administered disputes. [15] She agreed to support Tekanawí:ta’s efforts for peace if he agreed to codify into the Kaianere’kó:wa several powers and responsibilities for women: matrilineality of clans, the clan as the basis of popular sovereignty, and the collective ownership of agricultural land by women. Barbara Mann, Shotinontowane’á:ka author and professor of Native American Studies, views the underlying conflict of the era in terms of the material culture of production. She describes the conflict as one between women-led agriculturists and the cannibalistic hunters, led by Thatotáhrho. Tekanawí:ta’s role was to unite the warring factions, establish both farming and hunting as modes of production, and abolish cannibalism. [16]
Tekanawí:ta, Aiewáhtha and Tsikónhsase visited a series of Iroquois communities. Having gone to the Kanien’kehá:ka and gained their support, they visited the Oneniote’á:ka, gaining their acceptance as well. Next they visited the Ononta’kehá:ka, but were rebuffed by Thatotáhrho. They then gained the support of the Kaion’kehá:ka, and finally visited the westernmost nation—the Shotinontowane’á:ka. All of the Shotinontowane’á:ka were convinced except their two principal war chiefs; these were brought into agreement and designated as the ratihnhohanónhnha, the doorkeepers, responsible for protecting the long house of the Rotinonshón:ni from enemies to the west. Having convinced all of the Shotinontowane’á:ka, they returned to the Ononta’kehá:ka, and there was a mighty struggle with Thatotáhrho.[17] Tsikónhsase devised a solution, suggesting to Tekanawí:ta that the council fire of the Rotinonshón:ni could be with the Ononta’kehá:ka, and that Thatotáhrho should become its keeper. [18]
Tekanawí:ta had several other innovations for the Rotinonshón:ni polity. The fifty men who would make decisions through consensus at the council fire were named roiá:ner, and they would wear deer horns to represent that they had forsaken war and ate only the flesh of deer, not of men. The roiá:ner were to have skins “seven spans thick”: they would be patient, not easily offended. Tekanawí:ta named each of the roiá:ner, and stated that their names would be requickened when they died (or were removed from office) and returned to the clan mothers, the iotiiá:ner. The iotiiá:ner had the responsibility of selecting new roiá:ner, though never the son of the previous roiá:ner. The iotiiá:ner would also have the authority to recall roiá:ner from office. A provision was made for further speakers to be added to the council at Ononta’kehá:ka, men who had merit and had sprung up like a Pine Tree—“Ohnkaneto:ten.” The Ohnkaneto:ten would have voices but not votes; their appointment would die with them and not be transferred. Further, the great good way, the Kaianere’kó:wa, could be amended by “adding to the rafters” of the longhouse.
The weapons of war were buried beneath the tree of peace, so that there would be no further war among the nations of the Rotinonshón:ni. [19] (The English idiom, “burying the hatchet,” originates with the Rotinonshón:ni.) The tree’s four white roots of peace stretched to the cardinal directions, spreading the good tidings. There were rules for adoption of individuals and whole nations, to follow the roots, find shelter beneath the tree of peace, and join the Rotinonshón:ni. The condolence ceremony for those who were in grief was described, as well as the use of wampum. The Rotinonshón:ni would be guided by principles of “peace, power and righteousness.” The last issue that Tekanawí:ta resolved was about hunting territory: Tekanawí:ta declared that all Rotinonshón:ni would share the hunt and “eat of one bowl.” [20]
#anthropology#first nations#indigenous#Iroquois#mohawk#history#true history#Rotinonshón:ni Polity#Rotinonshón:ni#Rotinonshon:ni Polity#us politics#us history#Native Americans#Northeastern Anarchist#Six Nations#anarchism#anarchy#anarchist society#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#resistance#autonomy#revolution#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#daily posts#libraries#leftism
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Gift Economy
Maybe we all feel something so dark and painful deep down, something off and something exhausting about living in this world, which has become so thoroughly pervaded by capitalism and the values of white christian imperialism, because life is a gift meant to be given, and we are not made to exchange one thing for another.
In many indigenous societies, instead of having a transactional economy ("barter" is a myth by the way) there exists what anthropologists call a gift economy, where the main way things get passed around is through gifts and reciprocity.
I think that life itself is a gift we have received, and it's ours to do whatever we want with it, but the best thing to do when you receive a gift is to give again, if you are able. I for one think that the meaning in my life comes from giving; giving myself to my wife, and to my work, giving gifts and sharing love with my friends, giving my heart to music and to the beauty in the world around me. Life is a gift, so I want to give it.
#anthropology#anarchism#robin wall kimmerer#braiding sweetgrass#anti capitalism#gift economy#life#life is a gift#economics#communism#feminism#I got these ideas mainly from Kimmerer's book Braiding Sweetgrass#Also influenced by David Graeber's anarchist anthropology work.#david graeber#capitalist hell#mental health
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anthropologists and philosophers have asked whether agriculture could have been the tipping point in the power balance between men and women. Agriculture needs a lot of physical strength. The dawn of farming was also when humans started to keep property such as cattle. As this theory goes, social elites emerged as some people built up more property than others, driving men to want to make sure their wealth would pass onto their legitimate children. So, they began to restrict women’s sexual freedom.
The problem with this is that women have always done agricultural work. In ancient Greek and Roman literature, for example, there are depictions of women reaping corn and stories of young women working as shepherds. United Nations data shows that, even today, women comprise almost half the world’s agricultural workforce and are nearly half of the world’s small-scale livestock managers in low-income countries. Working-class women and enslaved women across the world have always done heavy manual labour.
More importantly for the story of patriarchy, there was plant and animal domestication for a long time before the historical record shows obvious evidence of oppression based on gender. “The old idea that as soon as you get farming, you get property, and therefore you get control of women as property,” explains Hodder, “is wrong, clearly wrong.” The timelines don’t match up.
The first clear signs of women being treated categorically differently from men appear much later, in the first states in ancient Mesopotamia, the historical region around the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in what is now Iraq, Syria and Turkey. Around 5,000 years ago, administrative tablets from the Sumerian city of Uruk in southern Mesopotamia show those in charge taking great pains to draw up detailed lists of population and resources.
“Person power is the key to power in general,” explains political scientist and anthropologist James Scott at Yale University, whose research has focused on early agrarian states. The elites in these early societies needed people to be available to produce a surplus of resources for them, and to be available to defend the state—even to give up their lives, if needed, in times of war. Maintaining population levels put an inevitable pressure on families. Over time, young women were expected to focus on having more and more babies, especially sons who would grow up to fight.
The most important thing for the state was that everybody played their part according to how they had been categorised: male or female. Individual talents, needs, or desires didn’t matter. A young man who didn’t want to go to war might be mocked as a failure; a young woman who didn’t want to have children or wasn’t motherly could be condemned as unnatural.
As documented by the American historian Gerda Lerner, written records from that time show women gradually disappearing from the public world of work and leadership, and being pushed into the domestic shadows to focus on motherhood and domestic labour. This combined with the practice of patrilocal marriage, in which daughters are expected to leave their childhood homes to live with their husbands’ families, marginalised women and made them vulnerable to exploitation and abuse in their own homes. Over time, marriage turned into a rigid legal institution that treated women as property of their husbands, as were children and slaves.
Rather than beginning in the family, then, history points instead to patriarchy beginning with those in power in the first states. Demands from the top filtered down into the family, forcing ruptures in the most basic human relationships, even those between parents and their children. It sowed distrust between those whom people might otherwise turn to for love and support. No longer were people living for themselves and those closest to them. Now, they were living in the interests of the patriarchal state.
This is interesting.
#repost of someone else’s content#article#patriarchy#adultism#statism#feminism#anarchist#anarcha-feminist#history#historiography#anthropology
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
Not me and wifey having a conversation about the foundational nature of clothing to our cultural development and the alienation and destruction that hides behind our production and distribution processes as a dying imperialist empire 😍🥰😳
#my wife is the most attractive when she talks anarchist anthropology with me 💚#it's what made me fall in love with her in the first place#get you a basketball dyke baddie who kisses you like that's the only way she can breathe#swoon
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trying to explain what the fuck just happened in Lankan politics today.
The leftist party has won 159 seats out of 218 in the Parliamentary elections. The single biggest landslide win since we broke from the British and achieved universal franchise in 1948.
Any party achieving a super majority in the executive and legislative is, objectively speaking, bad. It disables checks and balances, which is a catastrophic thing for any democracy, and the only two other times it's happened for us has irrevocably eroded the fabric of civic rights and democratic freedom. Also, the reason the NPP won the North and East is that the colonized, genocided and subjugated people there have no faith in electoralism anymore. The way this government has engaged minority issues has been utterly abysmal and now they've been rewarded for it.
On the other hand:
The winners. Are all. Grassroots. Candidates.¹
We have voted out every single career criminal that's been barnacled into the Lankan political arena since before I've been alive. The fascist party has only three seats.² The other fascists didn't win a single seat. The neoliberal legacy party won none. There are only forty people in Parliament that represent any sort of dynastic political legacy. After 76 solid years of nothing but political dynasties.
This is barely five years after the Rajapaksas swept in and absolutely glutted the Parliament with their family members and cronies end to end.
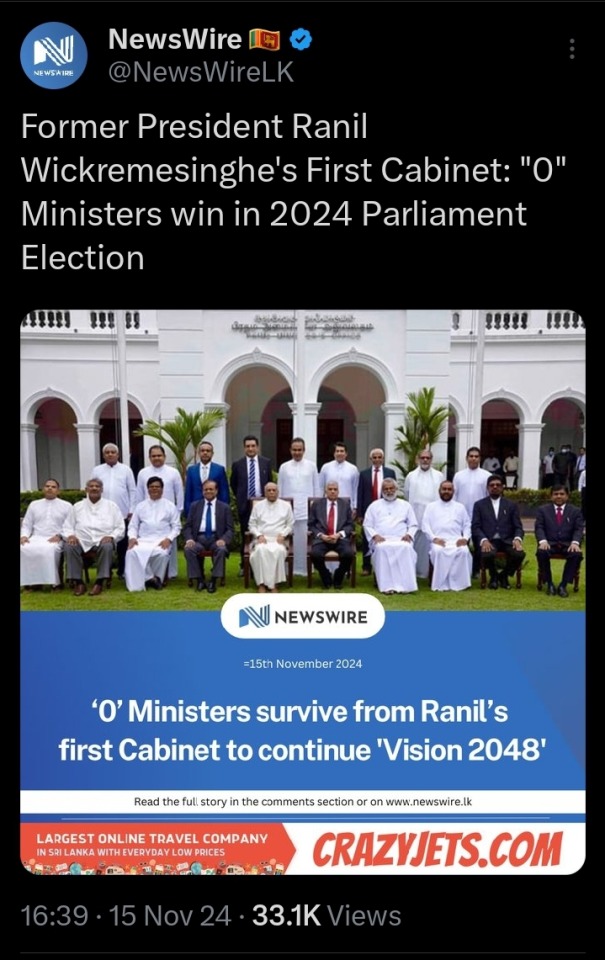
This is the illegitimate interim government we had for most of the last 18 months. We literally, physically, chased the Rajapaksas out of the country and this fucking demon set up a puppet government just so he could finally sit in that goddamn chair and be the despot he'd always dreamed of in exchange for letting them all come back. He's now gone. His entire circle is gone.
THEY ARE ALL FUCKING GONE.
In US terms, just imagine that, five years from now, when Trump's GOP has control of everything, the entire GOP and the worst of the Dems are all purged from Congress and Senate, the Green Party in control of all three branches of government under a pro-union left-wing President and an unmarried female LGBT rights activist Vice President, and the Dems reduced to barely 20% of the House.
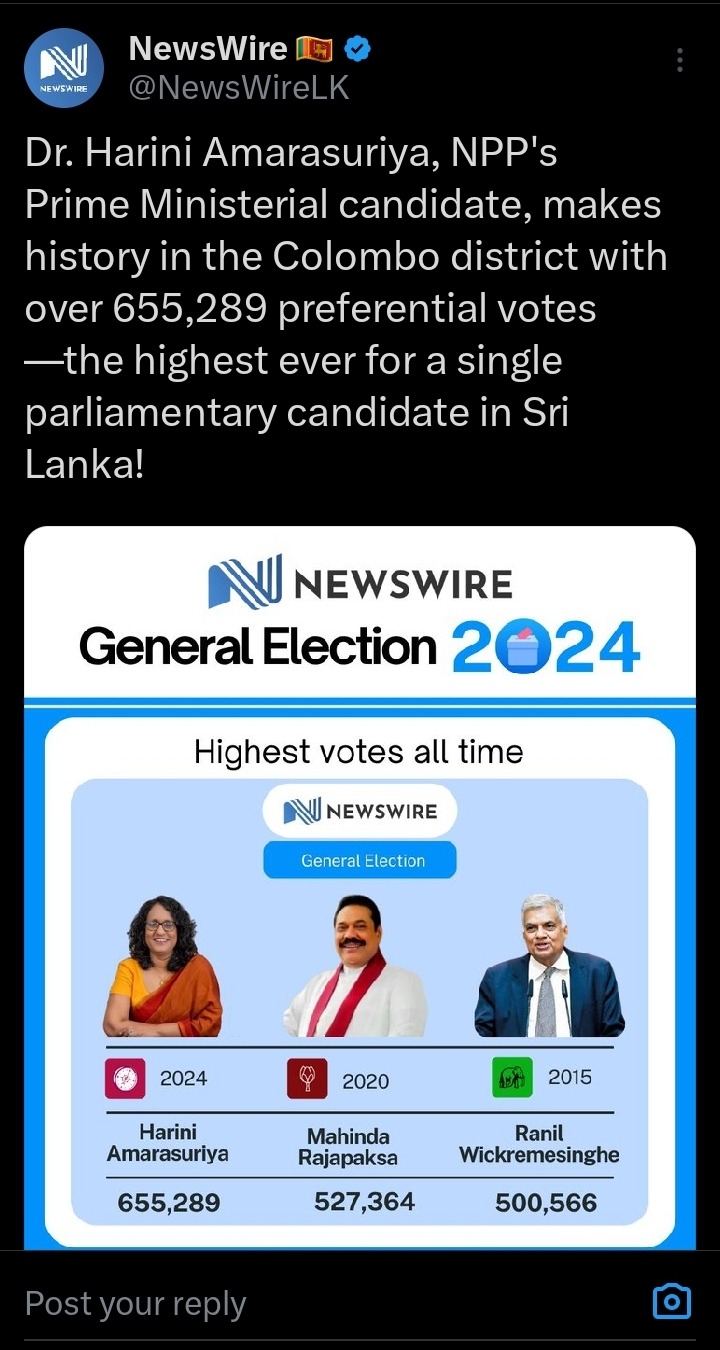
This is my anthropology professor. She joined politics from the small nascent leftist coalition to help keep the government accountable. She's now the Prime Minister and the most popular Parliamentary candidate in the nation's history. (Edit: She was knocked off first place by a dude in the final result. Boo.)
(On the other hand— the woman who helped make me a radical anarchist and literally helped write a book on political dissent and resistance...now is the state. Uh.)
But there are so many women in Parliament! We had the lowest female representation in a South Asian Parliament and some of them were from the list of seats reserved for parties rather than elected ones. Most were either anti-feminist conservative embarrassments, widows and daughters of elite politicians and neoliberal shills. It's still only an increase of a few percentage points (Edit: from the previous 5% to 10% in the final result!) but now we have elected academics, feminist advocates, activists! There Is a representative for Malaiyaha Tamils in the Central Province for the first time in history and it's a young woman! (Edit: now it's two female Malaiyaha MPS!!) This is the plantation community that still live in conditions closest to the slavery the British forced upon them two hundred years ago!
I'm like. Completely mindfucked. To be very very clear, the NPP coalition formed around the nucleus of the JVP that used to be communist but haven't been in 30 years, they're now just social democrats who are left of places like the US and UK, whose "left" is now center-right. They're only threatening to the Western mainstream media for some reason who can't stop bleating about how we have a "Marxist" government now. In reality, the actual chances for radical reform are still quite low, and the opportunity for further erosion is quite high with a super majority government regardless of affiliation.
On the other hand:
What the fuck.
Sometimes living through historical events is really damn amazing.
---
¹ Well, nearly. There are a few career politicians and a nepo baby but they aren't so bad either.
² Goddamn it, Baby Rajapaksa and Sri Lanka's answer to JD Vance have wormed their way in using the list of Constitutionally reserved party seats for non-elected members. FUCK the National List.
#five years ago i was working a news desk watching a band of violent ethnofascists known for genocide torture kidnappings and murder sweep in#and take control of the entire country#on the heels of the worst terrorist attack we've suffered that they orchestrated for this purpose#wondering how many of our colleagues would be safe#and watching the people that opposed them flee the country#i cannot tell you the enraging hopeless terror#and now#they're all gone#THEY'RE FUCKING GONE#sri lanka politics#sri lanka news#sri lanka protests#sri lankan parliamentary elections#sri lanka election 2024#anura kumara dissanayake#harini amarasuriya#feminism#leftism#world news#faith in humanity#power to the people#aragalaya#knee of huss#අරගලයට ජය!#අරගලයට ජය
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
this is everything actually

Meme I made in college. Is this anything
221 notes
·
View notes
Note
can you explain family abolition in a few words?
sure. there is no one unitary 'family abolitionist' perspective so be aware that i'm explaining this as a marxist and not as an anarchist or a radical feminist.
basically, "the family" is a social construct rather than a fixed self-evident truth. the family has been created and can be shaped, altered, or--indeed--abolished. this is evinced by the broad anthropological and historical record of radical transformations in what constitutes 'the family' (cf. clans, the extended family, the nuclear family). viewing the family as such opens it up to critique and also to the concept that it could be replaced with something better (in much the same way that, for communist and anarchist, refusing to accept the timelessness / naturalization of the bourgeois state opens up new horizons of political thought outside of engagement with electoral politics.)
among these critiques of the family are:
that it is a tool of patriarchal control over women and children by creating an economic dependence upon spouses / parents
ergo, that it enables and causes 'abuse' -- that child abuse, spousal abuse, and intimate partner violence are not abberations of 'the family' but in fact a natural consequence of its base premises re: power and control
that it serves as a site of invisiblised economic labour (e.g. housework)
that it is a tool of the capitalist (formerly the feudal) economy's reproduction of inequality via e.g. inheritance laws
that it serves as a site of normalization and reproduction of hegemonic ideology--i.e. that it is the site where heteronormativity, cisnormativity, gender roles, class positionality, & more are ingrained in children
among solutions family abolitionists propose to remedy it are:
the total dissolution of any legal privilege conferred by romantic or blood relationship in favour of total freedom for any group of people to form a household and cohabitate
the recognition of housework, the work of childrearing, & the general tasks of social reproduction as 'real' labour to be distributed fairly and not according to formal or informal (feminized) hierarchies
the economic and legal freedom of children--(i.e., allowing children unconditional access to food and shelter outside 'the family', allowing children the legal right to informed consent and self-determination)
similarly, the emancipation of women from economic dependence on their partners--both of these can only really be achieved via socialism (as marx put it, 'women in the workplace' only trade patriarchal dependence upon a husband for patriarchal dependence upon an employer)
communal caretaking of children, the sick, & the elderly
yeah. i know. this is a lot of words. its not few words. sorry. it's a complex topic innit. this is a few words For Me consideri ng that i've got a long-ass google doc open where i'm writing up a whole damn essay on this exact topic.
tldr: the family is not inevitable, it is constructed & can be replaced with something better. full economic freedom from dependence on interpersonal familial relationships for everybody now. check out cuba's 2022 family code for an idea of what this could look like as practical legislation.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text


FRAGMENTS OF AN ANARCHIST ANTHROPOLOGY
46 notes
·
View notes
Note
I also really like Direct Action— it’s a huge book but very readable. It’s also an ethnography so you get a really detailed look at how actual people practice anarchism, even if it’s very constrained to a particular time and place; it looks at anarchists and their allies as a cultural group, so you get a lot of insight into specific practices and terminology, at least in the time and place he was writing from (things like black blocs, spokescouncils, temporary autonomous zones etc).
I love your take on the government and how futile voting is. I want to be an anarchist and work to create change, but I honestly don't know what steps to take. Is it primarily grassroots efforts and supporting those around you? Is it protesting? Is it working towards government reform somehow? I would love your insight!
Check out the anarchist library online and read around a little! Look up a local Food Not Bombs chapter or mutual aid group and check out their efforts. Then work on forming an affinity group with 3-5 other like-minded people and start forming your own plans to make a difference in the ways that you deem best and most feasible for you. The magic of anarchy is that it entrusts people to build the solutions to our own problems, and to create the kind of world we want to see. YOU are in charge of what your anarchy means.
#also fragments of an anarchist anthropology#but mostly it’s an anthropologist talking to other anthropologists#might not be useful for non-anthropology people#but it made me feel a lot better about the discipline and a lot more hopeful about its possibilities
144 notes
·
View notes
Text
"[An anarchist social theory] would have to proceed from the assumption that, as the Brazilian folk song puts it, “another world is possible.” That institutions like the state, capitalism, racism and male dominance are not inevitable; that it would be possible to have a world in which these things would not exist, and that we’d all be better off as a result. To commit oneself to such a principle is almost an act of faith, since how can one have certain knowledge of such matters? It might possibly turn out that such a world is not possible.
But one could also make the argument that it’s this very unavailability of absolute knowledge which makes a commitment to optimism a moral imperative: Since one cannot know a radically better world is not possible, are we not betraying everyone by insisting on continuing to justify, and reproduce, the mess we have today? And anyway, even if we’re wrong, we might well get a lot closer."
- Fragments of an Anarchist Anthropology, David Graeber (emphasis mine)
275 notes
·
View notes
Text

“We are left to answer for our women”
“Hear and listen to what we, women, shall speak, as well as the Sachems; for we are the owners of this land, AND IT IS OURS! It is we that plant it for our and their use. Hear us, therefore, for we speak things that concern us and our children; and you must not think hard of us while our men shall say more to you, for we have told them” Seneca women “We are left to answer for our women, who are to conclude what ought to be done by both Sachems and warriors. So hear what is their conclusion. The business you come on is troublesome, and we have been a long time considering it; and now the elders of our women have said that our Sachems and warriors must help you, for the good of them, and their children” Sagoyawatha “Red Jacket”, 1791[34]
Anarchist anthropologist Harold Barclay has pointed out that “Egalitarian does not… mean that there is any equality between sexes and between different age groups” and that “true sexual equality is a rarity.”[35] By contrast, the Rotinonshón:ni are often held up as an example of a matriarchy, though I disagree with the semantics of that term. While the Rotinonshón:ni are both matrilineal and matrilocal, and the women do have a role in consensual politics and in selecting and removing men from leadership positions; women do not wield power over men the way men wield power over women in a patriarchal society. Anthropological archaeologist Dean Snow, explains this very well: “Iroquois women were not matriarchs, or Amazons, or drudges. They were Iroquois women, who lived in a nonhierarchical society in which their role as food producers was properly appreciated and in which the elevation of some aspects of kinship to political significance gave them influence that they might not otherwise have had.” [36]
Another anarchist anthropologist, David Graeber, described the overlapping councils by gender:
“Longhouses were governed by councils made up entirely of women, who, since they controlled its food supplies, could evict any in-married male at will. Villages were governed by both male and female councils. Councils on the national and league level were made up of both male and female office-holders. It’s true that the higher one went in the structure, the less relative importance the female councils had—on the longhouse level, there wasn’t any male organization at all, while on the league level, the female council merely had veto power over male decisions—but it’s also true that decisions on the lower level were of much more immediate relevance to daily life. In terms of everyday affairs, Iroquois society often seems to have been about as close as there is to a documented case of a matriarchy.” [37]
Another indication of differences between the Rotinonshón:ni and European settler society comes from that same Sullivan expedition in 1779 that destroyed so many Rotinonshón:ni towns. While preparing to attack and destroy the towns, General James Clinton even remarked that the Rotinonshón:ni men never raped women, and that some measures needed to be taken to prevent American soldiers from raping. [38] Among the Rotinonshón:ni, violence against women, including spousal abuse, was harshly punished by a woman’s kin. [39] A man who abused a woman could not be selected as a roiá:ner. [40]
Divorce was easy and common, so much so that Jesuit missionary Father Jacques Bruyas, while regarding divorce as the greatest sin among the Rotinonshón:ni, explained that “There is as great ease in breaking marriages as in making them — the husband leaving his wife, and the wife her husband, at pleasure.” [41] Since the husbands lived with their wives’ kahwá:tsire (matrilineal clan), in divorce former husbands had to leave the home. While the majority of the property as it was held in common through the matrilineal clan, personal possessions were always kept distinct between a husband and wife. [42] Children remained with the mother after divorce, [43] a contrast to the paternal ownership of children which was the standard in the continent’s European settler society until it was replaced by maternal preference in custody in the 1920s. Kanatiiosh (Barbara Gray) has argued that “western law emerges with a structure based on hierarchy, which I believe is attributed, to their treatment of women as secondary citizens. Whereas, Haudenosaunee law emerges with a democratic structure based on equality and goodwill for all.” [44]
Family planning was essential to women, who had the responsibility for farming, and often chose to limit the number of children for whom they were responsible at any one time. There were many abortifacients and fertility medicines known to Rotinonshón:ni herbalists. [45] Christian missionaries, and later in the early 19th century the Shotinontowane’á:ka prophet Ganioda’yo, who codified Karihwí:io or Gaiwiio (“the good message”), preached against divorce and abortion, while emphasizing the relationship of husband and wife over that of mother and daughter. [46] Wallace, a psychological anthropologist and historian, regarded the reforms of the Karihwí:io as “the sentence of doom upon the traditional quasi-matriarchal system.” [47] Kahentinetha Horn, the editor of Mohawk Nation News, has asserted that the polity’s “structure has been modified to accommodate the Gai’wiio. For example, instead of the Clan Mothers appointing the Chiefs according to the Old Way, in the Gai’wiio the Chiefs select the Clan Mothers.” [48]
Over time, individual households of nuclear families replaced the traditional longhouses as residences. The situation had so changed by 1850, when Lewis Henry Morgan published his classical ethnographical study The League of the Ho-de’-no-sau-nee, or Iroquois, he observed that women, and only women, were punished for adultery by public whipping. [49] In 1924, an elected band council, rather than the traditional polity, governed Ohswé:ken; women were initially deprived of suffrage. [50] At Onondaga, Tonawanda and Tuscarora, the iakoiá:ner never lost their rights to select roiá:ner. [51]

Drawn by Joseph Keppler, “Puck”, 1914 [52]
At the same time Rotinonshón:ni rights and responsibilities were under attack, female European settlers were gaining some of those very rights. The contradiction is made even more glaring in the examination of American feminism by Women’s Studies professor Sally Roesch Wanger, who found that the gender relations among the Rotinonshón:ni were an inspiration to suffragists in the United States like Matilda Joslyn Gage, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, and Lucretia Mott. [53] While Gage had been to court for attempting to vote in U.S. elections, she pointed out that her adoption as Karonhienhá:wi into the Wolf kahwá:tsire granted her a voice in selecting roiá:ner—giving her more political representation by adoption into the Kanien’kehá:ka nation than she had in the U.S. [54]
This difference in regards to suffrage was something well known to Rotinonshón:ni. Gawasco Waneh (Arthur Parker) wrote in 1909: “Does the modern American woman [who] is a petitioner before man, pleading for her political rights, ever stop to consider that the red woman that lived in New York state five hundred years ago, had far more political rights and enjoyed a much wider liberty than the twentieth century woman of civilization?” [55]
Modern feminists might regard the traditional division of roles according to gender as less than egalitarian. Some contemporary Rotinonshón:ni would agree, and argue that traditional gender role division is obsolete, while also pointing out that some of that division had its origin in colonial gender roles imposed by European cultural imperialism. One example is the concern raised by Taiaiake Alfred:
“We cannot hold on to a concept of the warrior that is gendered in the way it once was and that is located in an obsolete view of men’s and women’s roles. The battles we are fighting are no longer primarily physical; thus, any idea of the indigenous warrior framed solely in masculine terms is outdated and must be rethought and recast from the solely masculine view of the old traditional ways to a new concept of the warrior that is freed from colonial gender constructions and articulated instead with reference to what really counts in our struggles: the qualities and actions of a person, man or woman, in battle.” [56]
#precolonial#precolonial history#first nations#indigenous#Iroquois#mohawk#history#anthropology#true history#Rotinonshón:ni Polity#Rotinonshón:ni#Rotinonshon:ni Polity#us politics#us history#Native Americans#Northeastern Anarchist#Six Nations#anarchism#anarchy#anarchist society#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#resistance#autonomy#revolution#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#daily posts
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
So, I started rewatching Community after a year or two and wow, I forgot so many things about this show:
Jeffannie started in season 1 during that debate episode and this makes me feel even more icky. Somehow I thought that this ship started at the end of season 1/beginning of season 2.
Jeffannie is so uncomfortable for me to watch. Not only is the age gap creepy, Annie is presented as this innocent girl while Jeff is Jeff. And yeah, as the series progresses, Annie matures but she's still so young and has her whole life ahead while Jeff is 40 and stuck at Greendale
Britta in season one was the best because she wasn't dumbed down and exaggerated. She had the same flaws as in later seasons (like her lack of real activism, terrible choice of boyfriends, being uncool etc.) but those flaws were believable and toned down to fit the rest of characters. I miss Britta
I forgot that they made Pierce horrible in season 2 onwards so it was a shock. In season one he has more redemptive moments
I miss season one and two of community the most. The show was still somewhat grounded and it made me think of my own college experiences (anthropology as shown in community was basically 80% of my real classes)
Senior Chang > any other Chang BUT that one episode of Guard Change is top ten for me ("Arizona backwards is Arizona!")
Abed was terrible to Troy in some episodes in season 3 (Blanket fort episode, stars doppelgangers episode) and doesn't face consequences/learn a lesson/start to appreciate Troy more. I like Abed but it still pisses me off
I feel that as the show progressed it was less about the main 7 and more about Annie and Jeff which sucks and I hate it
Also, Jeffbritta was the best. Are they toxic? Yes. Do they understand each other on a deep level and always help each other when needed? Also yes. I loved their bickering in the show and I always liked their little moments.
I forgot that Dean's Dalmatian fetish started in season one and progressed throughout the story
Paintball episodes are meh for me. Yes, all of them
"If loving worms is stupid then I don't want to be smart!" "It is and you can't!" I love this little exchange.
Idk, I noticed that sometimes some characters from main 7 appeared for like 1 minute in the whole episode. I know that you can't always have episode with all of them equally on the screen but idk it leaves a bad taste in my mouth. Like the election episode which is basically all about Jeff and Annie. Pierce has like 5 lines and all are horrible, Troy and Abed are reduced to being announcers, Britta and Shirley basically don't exist (Britta also goes on stage and is ridiculed)
Idk they could have done more with Shirley
I also like the friendship between Britta and Shirley, the anarchist and atheist being friends with devoted Christian has so much potential
I was never fan of Troy and Britta together
Idk, on one hand Trobed is fine, but on the other hand showing a deep and profound friendship like that is also fine. I'm ok with both
Ass crack bandit song slaps and I love it
Out of all of the main seven, I don't like Annie the most (after season 2 onwards Pierce ofc). And I honestly can't tell if I don't like her that much because of the personality or because of her ship with Jeff
#community show#community nbc#britta perry#jeff winger#jeffbritta#anti jeffannie#shirley bennett#troy barnes#abed nadir#annie edison#pierce hawthorne#nbc community
86 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hcs off modern Castlevania chars? Like jobs/friends & stuff
Ask: Hcs off modern Castlevania chars? Like jobs/friends & stuff
A/N: In this, most people are living sort of happily ever after. Does that make them OOC, yes it does. Do I care? No, I don’t.
👷♂️ Modern-Day Castlevania Headcanons: Jobs 👩⚕️
I see Trevor as something of a detective/cop, but I don’t think he’d be down with working for the system. Being a P.I. or an independent security contractor of some sort would probably suit his personality better. He’s the cool kinda punk that strikes fear into the hearts of violent bigots but is also somehow seen as a safe adult to little kids. Which he doesn’t mind. He finds it useful that only those hiding something or guilty of something see him as a threat. He’s not the best with kids, but he’s nice enough to them. He was on his own a lot from a very young age- definitely a latch-key kid- so he feels a fair share of protectiveness when it comes to them.
Sypha strikes me as a natural protector/nurturer, so maybe a preschool/grade-school teacher or physical therapist? She loves learning and sharing that knowledge with others. I can absolutely see her leading workshops related to whatever it is she’s chosen to have a career in. And she’s great with everyone- adults, kids, seniors, animals- you name it, they love Sypha. (Except for assholes and Karens of course.)
Alucard is introverted by nature, and also a lifelong student like Sypha. He’s also the inheritor/keeper of his father’s money and his mother’s wisdom. For that reason, I see him as a History or Anthropology Professor- at the college level and above. Maybe even an eventual department head. He’s very serious, and doesn’t have the demeanor for working with children or amateurs; he wants to teach people who are just as committed as he is to what they’re learning. His whole life he feels like his purpose is greater than what it currently is, and because of that, he’s never quite content with the life he’s living. He feels like something or someone is missing from his journey.
I think the three of them would become friends eventually, but one like one of those friend groups that makes absolutely no sense to people outside it. Like, you wouldn’t expect a rough and tumble cop-hating anarchist, a feisty, yet kind-hearted physical therapist, and a tall skinny history academic to be besties, yet there they are.
Maybe they’d meet at a conference somewhere. Like a wellness convention/conference is taking place at Alucard’s college, Sypha’s a prominent speaker (ah! pun not intended) there, and Trevor’s company is providing extra security.
Maybe there’s some kind of snafu, and there’s like an assailant loose on campus or something. Trevor’s chasing the guy, but Alucard sees him coming and decides he’ll help out and head the bad guy off. But in the end, the two men are beaten to the quick by Sypha, who stops the guy in the most impressively timed frisbee toss they’ve ever seen. The two men insist on talking Sypha out for coffee- and getting to know her, because, let’s be honest, who wouldn't want to be friends with Sypha? The three of them get to talking and the rest is history.
Dracula is someone who just has power- he doesn’t have to amass it, it just naturally comes to him. He’s the type to gather fortune and invest it in a bunch of different properties and revolutionary pharmaceutical investment opportunities. He’s the Big Guy in the Chair. And then he just sort of, fucks off to his mansion to do whatever he wants. He’s a recluse- he deems human interaction pointless and unnecessary as a man of his stature. Who needs to leave the house when you can just pay people to do everything for you? He’d much rather be alone anyway. Of course that all changes when he meets Lisa.
Lisa, similar to her nature in the show, would be a physician of some sort. I could see her being especially interested in women’s medicine or infectious disease as it disproportionately affects those in need, and she has a very strong internal sense of justice. Maybe she seeks out Vlad because he’s the big cheese CEO of a pharmaceutical company that’s publicly refusing to lower the cost of a specific drug that would revolutionize her patients’ care. She’d find out where he lived, bang on his door, and demand he lower his profit margins right now. Of course, no one has ever had the balls to say such a thing to his face before, and Drac falls in love pretty much instantly.
The two of them are a power couple: he still maintains so much fortune and sway, but his partnership with Lisa makes him see ways to use it for good. He starts charities and fundraisers- he shocks the wealthy world by going rogue- and gives away most of what he earns instead of hoarding it. And it’s no secret it’s thanks to Lisa.
Now Hector: I know everyone headcanons Hector as being a veterinarian, but for me, I think it makes more sense for him to be a mortuary or a medical examiner. He’s lovely with his pets, but at the same time, I don’t think he has the stomach to do what vets have to do. Vets have to talk to owners and their families and be personable and bright. He sees his pets as possessions, not family members. So a job where it’s just him and no one else- no crying kid or elderly companion to reassure would be better suited for him.
Hector is naturally inquisitive- a trait we saw even when he was imprisoned, so I think being a medical examiner would be very rewarding to him. He’d find it invigorating, to get down the truth of a mysterious death or shocking murder. And because he’s not squeamish, he’d be very clear and articulate presenting information on the stand.
Issac’s big thing throughout the series is loyalty and personal growth. S2 Isacc and S4 Issac are very different people. So I’m basing this more on S4 Isaac. I think he’d benefit in a position of some power, but also of some charity. Maybe as a politician or a professional lobbyist. He advocates for causes he believes are just and does not shy away from verbal confrontation when it comes to hashing out right vs. wrong.
I could see this being the way he meets Vlad and Hector. If some sort of tragedy or panic happened, and a large emergency medical response was involved, I could see Isacc propositioning Dracula for donations, in exchange for dinner and a chance to sway his mind about a certain political vote. Hector would be on the other end of that tragedy, dealing with those who lost their lives. Perhaps Issac seeks out Hector as a form of outreach, to prove he is committed to what he says he stands for. He connects Hector with Dracula, and the three of them find they’re all rather pleasant company compared to the majority of the unremarkable humans out there. They can all look death in the face and feel no fear. They don’t do bullshit, and they get along well because of it.
#castlevania headcanons#castlevania imagine#modern!au#castlevania modern!au#castlevania fanfiction#castlevania#alucard castlevania#trevor belmont#alucard tepes#sypha belnades#castlevania hector#hector castlevania#isaac laforeze#isaac castlevania#vlad dracula tepes#dracula castlevania#lisa tepes#lisa tepes castlevania#hc
150 notes
·
View notes
Text
Read The Books of Earthsea (the collected volumes of books in the Earthsea setting, with some commentary) by Ursula K. LeGuin. They're good. I wish I had read them as a child, but I'm glad I read them now, because they're good.
I really like the way there is a clear authorial vision for the world and what it is animated by. All the magic is kept delightfully vague. Perhaps the most consistent pattern in magic is that it places us into a world in which symbols can prescribe the world as well as describe it, in which they have the same power of reality that they do over society. Symbols are territory shared between science and art, and it is clear that whatever her respect for the scientific approach, in Earthsea LeGuin has decided to favor the artistic interpretation, which I am also generally fonder of. Much harder for people to do powerscaling to, though certainly they do try.
The highly dubious social science (think anarchist anthropology, but a bit of an older flavor) that LeGuin functionally endorses as part of the worldbuilding and narrative comes out charming and hopeful. In the hands of a less able writer, I imagine it could seem trite and silly, but it is not in the hands of a less able writer so instead it is fun.
The books have an overarching theme a lot of people on here wouldn't like, which is something along the lines of "death is very sad but is a part of life and everyone who tells you otherwise is a bastard", which around these parts gets you tarred as pro-death by people who appear to sincerely believe they will achieve immortality, probably because of AI or something. But as you can probably tell I think those people are very silly. "Death is a part of life" may be cope but at least it's not delusional.
Since Earthsea is so very good I don't have that much to say about it. Who should read it? Well, who shouldn't read it, more like. Don't read Earthsea if you can't stand books with dragons in them, or insist on a coherent account of magical theory in your fantasy, probably. Or maybe do and expand your horizons. Otherwise, go ahead, they're good books. If you read them, don't skip number four. Especially if you want to.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
What I am proposing, essentially, is that we engage in a kind of thought experiment. What if, as a recent title put it, “we have never been modern”? What if there never was any fundamental break, and therefore, we are not living in a fundamentally different moral, social, or political universe than the Piaroa or Tiv or rural Malagasy? There are a million different ways to define “modernity.” According to some it mainly has to do with science and technology, for others it’s a matter of individualism; others, capitalism, or bureaucratic rationality, or alienation, or an ideal of freedom of one sort or another. However they define it, almost everyone agrees that at somewhere in the sixteenth, or seventeenth, or eighteenth centuries, a Great Transformation occurred, that it occurred in Western Europe and its settler colonies, and that because of it, we became “modern.” And that once we did, we became a fundamentally different sort of creature than anything that had come before. But what if we kicked this whole apparatus away? What if we blew up the wall? What if we accepted that the people who Columbus or Vasco da Gama “discovered” on their expeditions were just us? Or certainly, just as much “us” as Columbus and Vasco da Gama ever were? I’m not arguing that nothing important has changed over the last five hundred years, any more than I’m arguing that cultural differences are unimportant. In one sense everyone, every community, every individual for that matter, lives in their own unique universe. By “blowing up walls,” I mean most of all, blowing up the arrogant, unreflecting assumptions which tell us we have nothing in common with 98% of people who ever lived, so we don’t really have to think about them. Since, after all, if you assume the fundamental break, the only theoretical question you can ask is some variation on “what makes us so special?” Once we get rid of those assumptions, decide to at least entertain the notion we aren’t quite so special as we might like to think, we can also begin to think about what really has changed and what hasn’t.
Fragments of an Anarchist Anthropology, by David Graeber
#david graeber#anarchism#social science#anthropology#history#world history#politics#quote#quotes#books#book quotes#colonialism#capitalism#modernity
77 notes
·
View notes