#also how was he born in miami if . he was also born in nevada. THOSE ARE FAR AWAY
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

what does this even mean i feel like maybe im being stupid but florida doesnt border mexico
#also how was he born in miami if . he was also born in nevada. THOSE ARE FAR AWAY#and like can we say oh maybe when he died as emir he got reborn in miami cause he died in philly#what.#what was going on in miami we got garcian being born there. kevin getting his sad backstory of killing his gay lover. idk#other things probably.#i speak#killer7#kill the past#honestly the stuff in the 50s confuses me so bad i. i just kinda attempt to not think to hard#cause itll kill me
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
round up // NOVEMBER 20

Hi, I’m tired. Actually, my friend Celeste created a piece of art that puts the emphasis needed on that sentiment:

I’m very tired. November felt like it was three years and also felt like it went by in a blink and also I’m not sure where October ended and November began—how does time work like that? (I’ve yet to see Tenet, but maybe that will explain it.) But like Michael Scott, somehow I manage, and lately it’s been like this:
Late-night Etsy scrolling. Browsing beautiful, non-big-box-store artwork is very calming just before I go to bed. I’d recommend Etsy stores like Celeste’s chr paperie shop, which I know from experience is full of great Christmas gift ideas.
Taking a day off of work to do laundry. I’m not sure if it’s more #adulting that I did that or that I was excited to do that.
Eating Ghiradelli chocolate chips straight from the bag. I actually don’t recommend this as a healthy option, but this is also not a health blog.
Watching lots and lots of ‘80s movies. One day I’ll ask a therapist why this decade of films is so comforting for me despite its many flaws, but for now I’m just rolling with it.
Reading. Have you heard of this? It’s a form of entertainment but doesn’t require screens—wild!
Memes. All good Pippin “Fool of a” Took jokes are welcome here.
Leaning into the Christmas spirit by ordering that Starbucks peppermint mocha, making plans to watch everything in that TCM Christmas book I haven’t seen, and keeping the lights on my hot pink tinsel tree on all day as I work from home.
This month’s Round Up is full of stuff that made me smile and stuff that sucked me into its world—I think they’ll do the same for you, too.
November Crowd-Pleasers

Sister Act (1992)
If in four years you aren’t in an emotional state to watch election results roll in, I recommend watching Whoopi Goldberg pretend to be a nun for 100 minutes. (Though, incidentally, if you want to watch that clip edited to specifically depict how the results came in this year, you’ll need to watch Sister Act 2.) This musical-comedy is about as feel-good as it gets, meaning there’s no reason you should wait four more years to watch it. Crowd: 9/10 // Critic: 7.5/10
Nevada Memes
Speaking of election results, Nevada memes. That’s it—that’s the tweet. Vulture has a round up of some of the best.
youtube
SNL Round Up
Laugh and enjoy!
“Cinema Classics: The Birds” (4605 with John Mulaney)
“Uncle Ben” (4606 with Dave Chappelle)
RoboCop (1987)
I’m not surprised I liked RoboCop, but I am surprised at why I liked RoboCop. Not only is this a boss action blockbuster, it’s an investigation into consumerism and the commodification of the human body. It’s also a critique of institutions that treat crime like statistics instead of actions done by people that impact people. That said, it’s also movie about a guy who’s fused with a robot and melts another guy’s face off with toxic sludge, so there’s a reason I’m not listing this under the Critic section. Crowd: 9/10 // Critic: 8/10

Double Feature – ‘80s Comedies: National Lampoon’s Vacation (1983) + Major League (1989)
The ‘80s-palooza is in full swing! In Vacation (Crowd: 9.5/10 // Critic: 8/10), Chevy Chase just wants to spend time with his family on a vacation to Wally World, but wouldn’t you know it, Murphy’s Law kicks into gear as soon as the Griswold family shifts from out of Park. The brilliance of the movie is that every one of these terrible things is plausible, but the Griswolds create the biggest problems themselves. In Major League (Crowd: 8.5/10 // Critic: 6.5/10), Tom Berenger, Charlie Sheen, and Wesley Snipes are Cleveland’s last hope for a winning baseball team. Like the Griswolds, mishaps and hijinks ensue in their attempt to prevent their greedy owner from moving the Indians to Miami, but the real win is this movie totally gets baseball fans. Like most ‘80s movies, not everything in this pair has aged well, but they brought some laughs when I needed them most.

This Time Next Year by Sophie Cousens (2020)
They’re born a minute apart in the same hospital, but they don’t meet until their 30th birthday on New Year’s Day. So, yes, it’s a little bit Serendipity, and it’s a little bit sappy, but those are both marks in this book’s favor. This Time Next Year is a time-hopping rom-com with lots of almost-meet-cutes that will have you laughing, believing in romantic twists of fate, and finding hope for the new year.
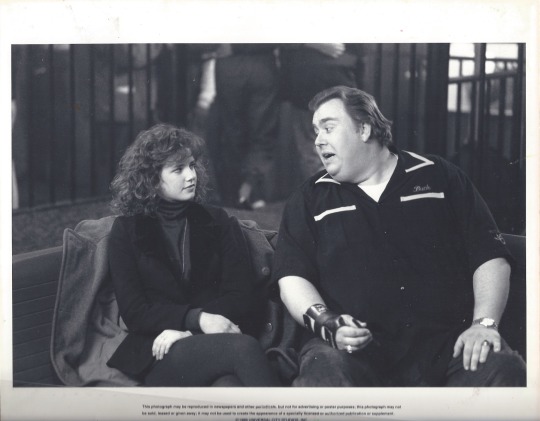

Double Feature – ‘80s Angsty Teens: Teen Wolf (1985) + Uncle Buck (1989)
In the ‘80s, Hollywood finally understood the angsty teen, and this pair of comedies isn’t interested in the melodrama earlier movies like Rebel Without a Cause were depicting. (I’d recommend Rebel, but not if you want to look back on your teen years with any sense of humor.) In Teen Wolf (Crowd: 8/10 // Critic: 5/10), Michael J. Fox discovers he’s a werewolf.one that looks more like the kid in Jumanji than any other portrayal of a werewolf you’ve seen. It’s a plot so ‘80s and so bizarre you won’t believe this movie was greenlit.
In Uncle Buck (Crowd: 8/10 // Critic: 7.5/10), John Candy is attempting to connect with the nieces and nephew he hasn’t seen in years, including one moody high schooler. (Plus, baby Gaby Hoffman and pre-Home Alone Macauley Culkin!) This is my second pick from one of my all-time fave filmmakers, John Hughes (along with National Lampoon’s Vacation, above), and it’s one more entry that balances heart and humor in a way only he could do. You can see where I rank this movie in Hughes’s pantheon on Letterboxd.

Lord of the Rings memes
This month on SO IT’S A SHOW?, Kyla and I revisited The Lord of the Rings, a trilogy we love almost as much as we love Gilmore Girls. You can listen to our episode about the series on your fave podcast app, and you can laugh through hundreds of memes like I did for “research” on Twitter.

Nothing to See Here by Kevin Wilson (2019)
Most adults are afraid of children’s temper tantrums, but can you imagine how terrified you’d be if they caught on fire in their fits of rage? That’s the premise of this novel, which begins when an aimless twentysomething becomes the nanny of a Tennessee politician’s twins who burst into flames when they get emotional. The book is filled with laugh-out-loud moments but never leaves behind the human emotion you need to make a magical realistic story.

An Officer and a Gentlemen (1982)
Speaking of aimless twentysomethings and emotion, feel free to laugh, cry, and swoon through this melodrama in the ‘80s canon. Richard Gere meanders his way into the Navy when he has nowhere else to go, and he tries to survive basic training, work through his family issues, and figure out his future as he also falls in love with Debra Winger. So, yeah, it’s a schamltzier version of Top Gun, but it’s schmaltz at its finest. Crowd: 8.5/10 // Critic: 7.5/10
November Critic Picks

Double Feature – ‘40s Amensia Romances: Random Harvest (1942) + The Ghost and Mrs. Muir (1947)
Speaking of schmaltz at its finest, let me share a few more titles fitting that description. In Random Harvest (Crowd: 8/10 // Critic: 8.5/10), Greer Garson falls in love with a veteran who can’t remember his life before he left for war. In The Ghost and Mrs. Muir (Crowd: 8.5/10 // Critic: 8.5/10), Gene Tierney discovers a ghost played by a crotchety Rex Harrison in her new home. Mild spoiler: Both feature amnesiac plot developments, and while amnesia has become a cliché in the long history of romance films, Harvest is moving enough and Mr. Muir is charming enough that you won’t roll your eyes. You can see these and more romances complicated by forced forgetfulness in this Letterboxd round up.
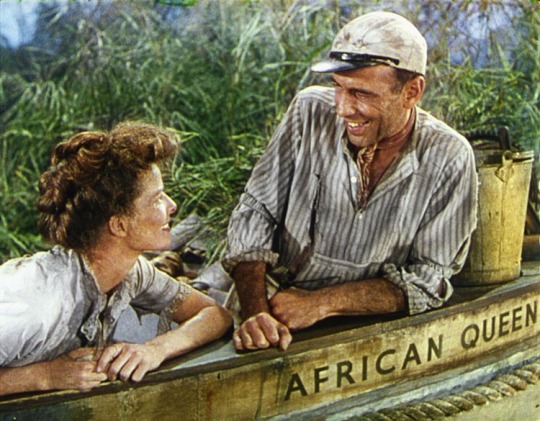

The African Queen (1951)
It’s Humphrey Bogart and Katharine Hepburn directed by John Huston—I mean, I don’t feel like I need to explain why this is a winner. Bogart (in his Oscar-winning role) and Hepburn star in a two-hander script, dominating the screen time except for a select few scenes with supporting cast. The pair fight for survival while cruising on a small boat called The African Queen during World War I (in Africa, natch), and the two make this small story feel grand and epic. Crowd: 8.5/10 // Critic: 9/10
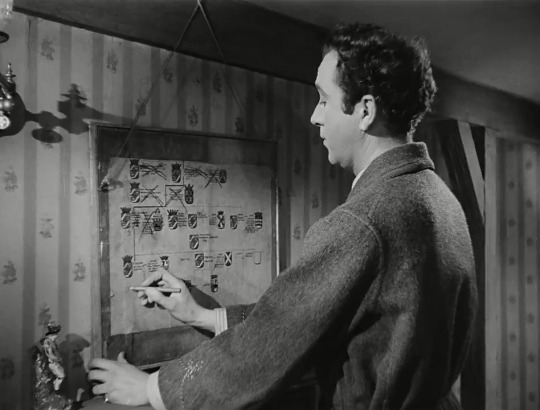

Kind Hearts and Coronets (1949)
A young man’s (Dennis Price) mother is disowned from their wealthy family because she marries for love. After her death, he seeks vengeance by killing all of the family members ahead of him in line to be the Duke D'Ascoyne. The twist? All of his victims are played by Sir Alec Guinness! Almost every character in this black comedy is a terrible person, so you won’t be too sorry to see them go—you can just enjoy the creative “accidents” he stages and stay in suspense on whether our “hero” gets his comeuppance. Crowd: 8/10 // Critic: 8.5/10

Bluebeard’s Eighth Wife (1937)
What would you do if you found out you were to be someone’s eighth wife? Well, it’s probably not what Claudette Colbert does in this screwball comedy that reminds me a bit of Love Crazy. This isn’t the first time I’ve recommended Colbert, Gary Cooper, or Ernst Lubitsch films, so it’s no surprise these stars and this director can make magic together in this hilarious battle of the wills. Crowd: 9/10 // Critic: 8.5/10
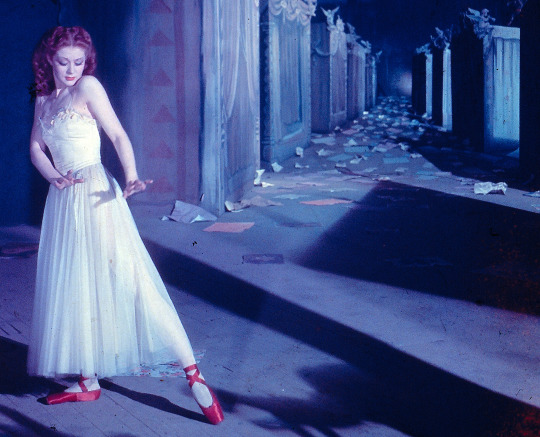

The Red Shoes (1948)
I love stories about the competition between your life and your art, and The Red Shoes makes that competition literal. Moira Shearer plays a ballerina who feels life is meaningless without dancing—then she falls in love. That’s an oversimplification of a rich character study and some of the most beautiful ballet on film, but I can’t do it justice in a short paragraph. Just watch (perhaps while you’re putting up your hot pink tinsel tree?) and soak in all the goodness. Crowd: 8/10 // Critic: 10/10

The Third Man (1949)
Everybody loves to talk about Citizen Kane, and with the release of Mank on Netflix, it’s newsworthy again. But don’t miss this other ‘40s team up of Joseph Cotten and Orson Welles. Cotten is a writer digging for the truth of his friend’s (Welles) death in a mysterious car accident. Eyewitness accounts differ on what happened, and who was the third man at the scene only one witness remembers? 71 years later, this movie is still tense, and this actor pairing is still electric. Crowd: 8.5/10 // Critic: 9/10

The Untouchables (1987)
At the end of October, we lost Sean Connery. I looked back on his career first by writing a remembrance for ZekeFilm and then by watching The Untouchables. (In a perfect world I would’ve reversed that order, but c’est la vie.) In my last selection from the ‘80s, Connery and Kevin Costner attempt to convict Robert De Niro’s Al Capone of anything that will stick and end his reign of crime in Chicago. Directed by Brian De Palma and set to an Ennio Morricone soundtrack, this film is both an exciting action flick and an artistic achievement that we literally discussed in one of my college film classes. Connery won his Oscar, and K. Cos is giving one of the best of his career, too. Crowd: 9/10 // Critic: 9.5/10

Remember the Night (1940)
Fred MacMurray and Barbara Stanwyck in my favorite team up yet! Double Indemnity may be the bona fide classic in the canon, but this Christmas story—with MacMurray as a district attorney prosecuting shoplifter Stanwyck— is a charmer. I’ve added it to my list of must-watch Christmas movies—watch for some holiday cheer and rom-com feels. Crowd: 8.5/10 // Critic: 8.5/10
Photo credits: chr paperie. Books my own. All others IMDb.com.
#The Untouchables#The Third Man#The African Queen#The Red Shoes#Kind Hearts and Coronets#Bluebeard's Eighth Wife#The Ghost and Mrs. Muir#Random Harvest#An Officer and a Gentlemen#Nothing to See Here#Kevin Wilson#This Time in Next Year#Sophie Cousens#The Lord of the Rings#Teen Wolf#Uncle Buck#National Lampoon's Vacation#Major League#SNL#Sister Act#RoboCop#Remember the Night#Round Up
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Veteran PGA TOUR Pro Kirk Triplett Forms Partnership With Dedication To Community

Dedication To Community (D2C), a national non-profit that educates and empowers communities on diversity, belonging, and equity, today announced a partnership with PGA Tour veteran golfer Kirk Triplett for the 2021 season. Triplett will carry D2C’s logo on his golf bag and will participate in awareness and education programs throughout the year. It is D2C’s first formal partnership in golf.
“We welcome Kirk to our growing D2C family,” said M. Quentin Williams, Dedication To Community founder and CEO. “His visibility on the PGA TOUR, his passion on the topic of education and awareness tied to diversity and his compelling backstory will be essential in helping grow our mission of education, equity and beautiful listening by all.”
“I am tremendously excited to be working with Q. Williams and the team at D2C on this topic.” said Triplett. “I look forward to participating in more training and improving my understanding of all aspects of how law enforcement and communities interact. I intend to use my platform as a professional golfer to lead others in the golf world into this discussion, many of whom might not otherwise understand its importance. I want to promote and participate in the mission of change that D2C is bringing to communities across the country.
Kirk and his wife Cathi had twin boys, Conor and Sam, in 1996 and then adopted their daughter Alexis (now 20) and son Kobe (now 18). Alexis’ birth parents are Latino; Kobe’s birth mother is Japanese, and his birth father is African American. As the parents of a racially diverse family, the Tripletts understand that social justice issues, especially the intersection of law enforcement and the communities they serve, affect all of us, not just those in the news. The publicity around the incidents in 2020 caused Kirk and Cathi to realize that an opportunity to educate and potentially unite people of diverse backgrounds was upon them. They realized that the discussions they were having at their own dinner table needed to be had by their peers in the golf community as well.
To facilitate these discussions Triplett placed a Black Lives Matter sticker on his PING golf bag at the Bridgestone Senior Players Championship in August. It generated a great deal of media interest. One of his quotes, “I actually googled, ‘what can a white guy do?’ caught the interest of a Pittsburgh Steelers Pro Football Hall of Fame member, and D2C board member, Donnie Shell. Shell reached out with an answer...join the player platform at D2C...and a conversation started between the Tripletts and D2C. The Tripletts eventually participated in a relationship training session and from there this partnership was born.
Kirk earned a degree in civil engineering from the University of Nevada Reno in 1985 and then turned professional. He joined the PGA Tour in 1990 and the PGA Tour Champions in 2012. He was a member of the Presidents Cup team in 2000 and is one of a small group of players that have won titles on all three sanctioned tours (Korn Ferry, PGA Tour, and PGA Tour Champions). The Tripletts have been residents of Arizona for more than 25 years. For more details please visit kirktriplett.com.
To date, D2C has worked with law enforcement agencies in several states across the U.S., including Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Missouri, Michigan, Ohio, the Carolinas, and at the FBI National Academy in Virginia, where Williams has been an instructor. In September, D2C expanded its reach to involve professional, collegiate, and K-12 athletes, adding former NFL executive Lamonte Winston (former Director of Player Engagement and Development, Kansas City Chiefs and Oakland Raiders) and Pro Football Hall of Famer Donnie Shell (Pittsburgh Steelers). Williams also announced in September a historic partnership with the Miami HEAT and the City of Miami Police Department and additional partnerships tied to athletes and teams are expected to be announced in the coming weeks.
0 notes
Link
Rachel Nuwer | Longreads | March 2020 | 28 minutes (7,033 words)
You can listen to our four-part “Cat People” podcast series on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts.
It’s a gloomy April afternoon in rural Oklahoma, and I’m sitting on the floor of a fluorescent-lit room at a roadside zoo with Nova, a 12-week-old tiliger. She looks like a tiger cub, but she’s actually a crossbreed, an unnatural combination of a tiger father and a mother born of a tiger and a lion. That unique genetic makeup places a higher price tag on cubs like Nova, and makes it easier, legally speaking, to abuse and exploit them. Endangered species protections don’t apply to artificial breeds such as tiligers. Hybridization, however, has done nothing to quell Nova’s predatory instincts. For the umpteenth time during the past six minutes, she lunges at my face, claws splayed and mouth ajar — only to be halted mid-leap as her handler jerks her harness. Unphased, Nova gets right back to pouncing.
With her dusty blue eyes, sherbet-colored paws, and prominent black stripes, Nova is adorable. But she also weighs 30 pounds and has teeth like a Doberman’s and claws the size of jumbo shrimp. Nova’s handler, a woman with long brown hair who tells me she recently retired from her IT job at a South Dakota bank to live out her dream of working with exotic cats, scolds the rambunctious tiliger in a goo-goo-ga-ga voice: “Nooooo, nooooo, you calms down!” Nova is teething, the handler explains, so she just wants something to chew on. The handler reaches for one of the tatty stuffed animals strewn around the room — a substitute, I guess, for my limbs. In that moment of distraction, Nova lunges. She lands her mark, chomping into the bicep of my producer, Graham Lee Brewer.
“Ooo, she got me!” Lee Brewer grimaces as he attempts to pull away from the determined predator. Nova’s handler has to pry the tiliger’s jaws open to detach her. After the incident, the woman conveniently checks her watch: “OK, you guys, time is up!”
I paid $80 for the pleasure of spending 12 minutes with Nova, but I’m glad the experience, billed as a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity, is over. On our way out, we pass more than a dozen adult tigers yowling and pacing cages the size of small classrooms. Nearby signs solicit donations. You are their only hope. Sponsor a cabin or compound today! In the safety of our car, Lee Brewer rolls up his sleeve, exposing a swollen red welt. “Look at my gnarly tiger bite,” he chuckles. “I tried to play it off but I was like, this fuckin’ hurts!”
It’s not the first time I’ve seen this world up-close; I spent the better part of eight years investigating wildlife trafficking around the world. During my travels, I visited farms in China and Laos where tigers are raised like pigs, examined traditional medicine in Vietnam, ate what I was told was tiger bone “cake,” and tracked some of the world’s last remaining wild tigers in India. Almost everywhere I went, tigers were suffering and their numbers were on the decline because of human behavior. Until recently, though, I had no idea the United States was part of the problem.
Within a few weeks of my visit, Nova will be far too big and dangerous for overpriced playtime sessions. Cats like her are most likely confined to one of those cramped cages my producer and I passed leaving the zoo, where they spend the rest of their life being speed-bred to crank out more adorable cubs. Or Nova might be sold to another breeder, or to someone who wants to keep her as a pet. Although no one tracks big cat ownership in the U.S., it’s estimated that there are likely more pet tigers in America than there are left in the wild. What’s more, depending on the species of cat, federal oversight is either limited or nonexistent. In some states, it’s easier to buy a lion — a 400-pound predatory killer — than it is to get a dog.
Animal rights activists have been pushing for decades to curb big cat ownership in this country, arguing that the industry is cruel, dangerous, and detrimental to conservation of cats in the wild. Now, reform appears within reach. The movement owes its momentum to, of all things, a murder-for-hire plot gone terribly awry. You might have seen the headlines in the Washington Post and New York magazine: Joe Exotic, a self-described “gay, gun-carrying redneck with a mullet,” among the largest tiger owners and breeders in the U.S., charged with conspiring to commit murder for hire. At its height, Joe’s zoo in Wynnewood, Oklahoma, which is where I visited Nova, housed more than 200 big cats, including lion-tiger hybrids, as well as about 60 other species, everything from lemurs to owls to giraffes. Joe even acquired a pair of alligators he claimed were once owned by Michael Jackson. Still, as one local told me, “The animals weren’t the entertainment. Joe was the entertainment.”
Last year, an Oklahoma City jury convicted Joe, whose legal name is Joseph Maldonado-Passage, of the murder-for-hire plots against a Florida activist and sanctuary owner named Carole Baskin. For Joe, Baskin had become something of an arch tiger rival. The news coverage mostly focused on Joe’s outlandish personality and the details of his decade-long feud with Baskin. But the jury also found Joe guilty of 17 wildlife crimes, including illegally killing five tigers and trafficking tigers across state lines — marking the first significant conviction of a tiger criminal in an American courtroom. “This verdict sends a shot across the bow to other roadside zoos who are playing fast and loose with federal regulations,” said Carney Anne Nasser, director of the animal welfare clinic at Michigan State University College of Law.
In other words, the bad boy of the big cat world might have inadvertently contributed to cleaning up the dirty industry he helped build and then exploited for much of his adult life.
Simba, a Bengal tiger, was sent to an animal sanctuary, Big Cat Rescue, in Tampa, Florida. (Matias J. Ocner/Miami Herald via AP)
* * *
Big cats are easier to find than you might think. I recently struck up a conversation with the chef at my favorite sushi joint in New York City. He asked what I’d been working on, and I filled him in on a bit of the Joe Exotic story and the big cat trade. To my surprise, he nodded along knowingly: “Oh yeah, a buddy of mine just got a serval!” Celebrity culture is another hot spot for exotic animal ownership. This past fall, Justin Bieber reportedly spent $35,000 on two savannah cats and created a dedicated Instagram page that quickly amassed more than 500,000 followers. When PETA criticized Bieber’s new pet choice, he posted a statement on his Instagram story telling the nonprofit group to “suck it” and “focus on real problems.”
Shopping for an unconventional animal used to mean scanning the classified sections of newspapers or fliers on the cluttered billboards at grocery stores and gas stations. But those analog methods of sale have long since given way to people hawking large cats in ways that are now more traditionally modern: closed Facebook groups and exotic pet websites. Getting an ocelot or a cheetah can be as easy as sending a DM or text, agreeing on a price, and setting a pick-up date. Depending on what state you live in, owning one of these animals might be entirely legal. And even if it’s not, there’s almost always a way to sidestep the rules, which can be confusing and are rarely enforced.
Save for a handful of regulations pertaining to animals listed in the Endangered Species Act (ESA), there’s almost no oversight of big cat ownership by the federal government. The Animal Welfare Act is supposed to ensure humane treatment of big cats and other captive animals, but the inspectors are overworked and many of the rules are weak, vague, or both. Although the Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) does technically require a permit to sell endangered species such as tigers, lions, leopards, or jaguars across state lines, unscrupulous sellers and buyers often don’t want to bother with permits and deal in untraceable cash payments. At trial, one buyer even testified to participating in sales marked as “donations.” Joe Exotic used this tactic for years to evade the gaze of law enforcement. He wasn’t the only one. At Joe’s trial, that same tiger owner testified: “Everybody marks donation.”
Same goes for regulations at the state level: Loopholes abound in the legislative patchwork governing big cat ownership. “There’s lots of ways tigers have been technically regulated on paper but in practice, not so much,” Nasser said. Roughly two thirds of states have some sort of regulations prohibiting private big cat ownership as pets. In 10 states, anyone can own a lion or tiger as long as they pay as little as $30 for a license from the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Four states — North Carolina, Wisconsin, Nevada, and Oklahoma — have no laws on the books at all.
Rules aside, very few people, no matter how well-intentioned, are prepared to own one of the world’s largest, deadliest predators. “Everybody wants a tiger cub, but nobody wants a tiger,” said Tim Harrison, a retired Ohio police officer and first responder who specialized in exotic creatures. These days, Harrison runs Outreach for Animals, a nonprofit that advocates responsible exotic pet ownership and trains emergency personnel to safely deal with animal-related crises. Harrison used to be a big cat owner himself, before realizing his mistake. “I was on the dark side,” he said, “thinking I was doing the right thing.”
Many big cat owners are subjected to what Harrison describes as a “baptism in reality,” learning firsthand that these adult cats are expensive and dangerous. “A big cat is like a walking, thinking IED,” he said. “You don’t know when that thing’s going to go off.” One of the most famous incidents took place in 2003 at a live performance by the popular entertainment act Siegfried and Roy. One of the duo’s iconic white tigers, Mantacore, knocked down Roy Horn, grabbed him by the neck, and dragged him awayo. First responders rushed Horn to the hospital in critical condition. He survived but only returned to the stage once more years later. Defenders of the popular act contended that Horn suffered a stroke mid-act and Mantacore was just trying to help him, but Harrison disagreed. He argued on national television that Mantacore had intended to kill Roy, and that Roy had brought this upon himself: He’d disrespected the largest predatory cat in the world by forcing the animal to do magic tricks.
No agency tracks the number of people attacked and killed by captive big cats. According to a database of incidents compiled by the Humane Society of the United States, 24 people have died and 294 have been injured in the U.S. since 1990. Those figures likely only represent a fraction of the real numbers. Not every case makes the news, and the people involved in these incidents don’t always divulge the true cause of injury. In 1999, when a family’s pet tiger killed a 10-year-old girl in Texas, the victim’s mother initially told emergency dispatchers that her daughter had cut her neck by falling off a fence. (She’d later testify she did not recall making the phone call.) In 2003, a man in New York City visited the hospital for a severe wound on his arm and leg; he claimed to have been bitten by a pit bull — not by Ming, the 400-pound tiger he had holed up in his Harlem apartment.
Big cats can threaten more than just their owners. The most infamous example occurred in 2011, when exotic animal owner Terry Thompson opened the doors to almost all of his pets’ cages before shooting himself. In what came to be known as the Zanesville massacre, law enforcement officers had to hunt and kill 18 tigers, 17 lions, and three mountain lions, as well as bears, a baboon, and wolves. “It was like Jumanji in real life,” said Harrison, who was one of the two dozen or so officers who responded to the incident. Many of the people who responded to the call that day suffered from post-traumatic stress disorder, Harrison claimed. They had no choice but to kill the animals, then they faced virulent public backlash for doing so.
Zanesville is an extreme example, but it’s not the only case of exotics turned loose. One problem is there’s a lack of places equipped to take in these animals — even zoos don’t want them. Since starring in a 2011 documentary The Elephant in the Living Room, about exotic cat ownership, Harrison gets about 30 calls a year from people desperate to find a new home for their lions or tigers. With few options, some people donate their cats to shady facilities that use them for breeding. Others abandon them. The New York Times recently reported that a woman looking for a place to smoke a joint stumbled upon a caged tiger in a vacant home in Houston. Unsurprisingly, the owner did not immediately come forward to claim the tiger, but she was later arrested and charged with one misdemeanor count of cruelty to a nonlivestock animal.
A sign warning motorists that exotic animals are on the loose rests on I-70 Wednesday, Oct. 19, 2011, near Zanesville, Ohio. (AP Photo/Tony Dejak)
* * *
As a boy, Joe Exotic raised pigeons and captured porcupines, racoons, and baby antelope at his childhood homes in Kansas and rural Wyoming. But it was the death of his older brother, Garold Wayne, in a car accident in 1997, that precipitated Joe’s entrance into the tiger business: Joe convinced his parents to use the roughly $140,000 settlement they received to open a wildlife rescue center.
Before Joe and his parents had completed the first cages at the GW Exotic Animal Memorial Foundation in 1999, someone dropped off an unwanted mountain lion and black bear. Soon after, they received a call about two tigers, a black leopard, and a mountain lion found in a backyard. Joe set out with a horse trailer and tranquilizers to collect the animals, which were skinny and malnourished. When Joe spoke to me this spring on the phone from a county jail in Oklahoma, he told me there was an excitement about the uncertainty and possibility of those early days. “I had no intention of being Joe Exotic or the Tiger King or anything like that,” said Joe, who came up with the “Tiger King” moniker because people struggled to pronounce his original surname, Schreibvogel. “But I never said no to a rescue.”
Pretty soon, Joe started breeding his own tigers. He bred some 400 big cats over the years. He sold the animals to buyers on both coasts for as much as $5,000 each. By the mid-2000s, Joe had become one of the largest exotic animal operators in the country. He owned dozens of species and put together a traveling magic show. Although Joe had been “about the animals” in the beginning, as time passed, according to Joe’s ex-boyfriend John Finlay, fame and profit monopolized his thinking. Joe’s niece, Chealsi Putman, who helped out at the zoo for years, noticed the same evolution. “It’s like he’s seen dollar signs,” Putman told me. “He figured out a way to make money and ran with it.”
Not all big cat owners are similarly motivated. For some, it’s a grossly misplaced desire to help an endangered species — not realizing that big cats bred in the U.S. are hybridized mutts that have no genetic worth for wild tiger conservation. For others, like 54-year-old Deborah Pierce, the motivation is something more akin to love, or infatuation. Pierce started small, rehabbing injured wildlife at her house and volunteering and working at a local veterinary clinic and zoo after she graduated from high school. But helping lion keepers wasn’t enough to satisfy Pierce. “I wanted one of my own to just spend time with,” she said.
Pierce was encouraged when she learned that at the time her home state of South Carolina had no laws preventing her from owning a big cat. She talked her husband into helping her construct a double-fenced pen on their secluded, wooded property. She easily found a dealer on the internet selling lion cubs for $1,500 — like Nova, “picture babies” that were too large for cub petting by the time of sale — and arranged to purchase a female cub. “I could afford her easier than I could afford a new bulldog,” Pierce said. She named the lion Elsa, and a few months later, she got Charlie, a baby cougar, to keep Elsa company.
That was 12 years ago. Pierce’s perspective has since changed. She’s emptied her savings account on her cats. They eat $5,000 worth of meat a year and the veterinary bills run around $10,000 annually. Last year, the county hit her with an $1,100 fine for not having the proper paperwork. (South Carolina started regulating big cats in 2018.) Pierce no longer has time to ride horses, her other great love, and her husband left her in 2016, breaking not only her heart, she said, but also Charlie and Elsa’s. She’s put a dream of moving out to Arizona on hold as well. State laws there strictly regulate private ownership of big cats, and finding a sanctuary where Elsa and Charlie could stay has proven too difficult. “They’re my best friends,” Pierce said, “but if I had it all to go over again, I wouldn’t have gotten them.”
At this point, Pierce has resigned herself to the long haul, perhaps as many as another eight years given the lifespan of captive big cats. “I just want to be able to give Elsa and Charlie a happy life,” she said. “Their happiness is more important than mine, in my eyes.”
A month after I visited Pierce, she emailed with bad news. Charlie had died in surgery. “His heart was still beating, but he wouldn’t breathe when the oxygen came off,” she wrote. “So, we let him slip away.” Elsa, she says, has been inconsolable, and Deb blames herself for not bringing Charlie to the vet earlier. The bill for Charlie’s last visit, which totaled $4,800, even after the vet gave Pierce a significant discount, has only added to her stress. “I just hope nothing happens to Elsa before money is available again,” she says. “That’s my number one worry right now.”
* * *
The modern exotic animal craze traces back to the ’70s and ’80s and a phenomenon called zoo babies. Each spring, interstate signs and TV commercials featured photos of blue-eyed, squealing balls of fuzz debuting at major zoos around the country, an irresistible marketing lure for families that turned out to snap photos and cuddle the newest arrivals. Zoo babies were among the industry’s number one moneymaking programs, and tigers were always the biggest draw. As an added bonus, zoos advertised these activities under the guise of conservation. “You’d get your T-shirt, get your picture taken, and you’d walk away feeling like you’ve saved the world — you’ve saved tigers,” Harrison said.
But there was a problem, and Harrison, who worked as an exotic animal veterinary assistant as a teenager in Ohio, noticed it. There were lots of zoo babies but no zoo adolescents. When Harrison eventually began asking the staff about what had happened to last year’s tiger cubs, he’d get vague answers about the animals being traded off to different zoos. To Harrison, that math didn’t add up: Even the largest zoos around the country had only two or three adult tigers. But zoos annually paraded hundreds of babies out for pictures and play sessions.
Jack Hanna holds two Bengal Tiger cubs that were born and bred in captivity during a groundbreaking ceremony at the Dallas Zoo in 1998. (AP Photo/Tim Sharp)
Harrison eventually learned the dark truth: After the cubs reached a certain age they became “zoo surplus” and were sold at exotic animal auctions to private buyers. These auctions were raucous events, attended mostly by veteran wildlife keepers and professional breeders that zoos relied on to supply their collections. Harrison attended a few and noticed the same employees who weeks earlier had been talking up the conservation value of the zoo’s tiger babies, holding cub after cub up by their armpits to sell to the highest buyer. The whole scene was commonplace at the time. “No one thought anything of it,” Harrison said.
The zoo baby phenomenon led to a surge in private big cat ownership. In the 1990s, according to Harrison, wildlife-related television spread the idea of owning a pet tiger to a much wider audience. Jack Hanna types bottle-fed cubs and paraded tigers on leashes on talk shows. The predators appeared no more dangerous than a golden retriever. “It was like somebody flipped a switch on,” Harrison said. At the time, Harrison was the lone police officer in Ohio who could handle big cat emergencies; he suddenly went from getting a couple calls a year to getting more than 100. After removing an unruly pet from someone’s property, he’d ask people why they thought it was a good idea to own a lion or tiger. Many responded it was because they’d seen it on TV. Harrison started calling it the Steve Irwin syndrome.
That turns out to be an apt diagnosis. According to research conducted by scientists at Duke University, seeing a wild animal in an unnatural, human setting — a chimpanzee drinking out of a baby bottle or sitting through a talk show interview — makes people less likely to donate to a conservation organization that aids that species and more likely to think the creature in question would make a great pet. According to Kara Walker, now a behavioral ecologist at North Carolina State University and lead author of the research, published in 2011 in the journal PLOS One, this also extends to people’s thought process after an encounter with a cub, which might go something like: Look at this cuddly tiger! I got to pet it for 20 minutes and it licked my hand and now I can have a tiger, too!
Enterprising private exotic animal owners capitalized on the moment. They realized they could make a killing holding their own cub petting events at malls, fairs, and roadside zoos, which compounded an already vicious breeding pattern. “I call it the breed and dump cycle,” said Nasser, the Michigan State law professor. That cycle is largely responsible for the proliferation of tigers throughout the U.S., and by the middle of the last decade, the most notorious of all the breed-and-dump outfits belonged to Joe Exotic.
But cub-petting events weren’t enough for Joe. Concerned with fame and fortune, he plotted ways to grow his online following and commercialize the business. He started selling Tiger King–branded candy, apparel, and condoms. He also kept zoo costs down by euthanizing sterile or defective tigers and turned donated animals that weren’t moneymakers — especially emus — into cat food. During regular inspections of Joe’s zoo, the USDA cited hundreds of American Welfare Act violations. The agency conducted four investigations, including one that looked into the deaths of 23 tiger cubs from 2009 to 2010. (As an endangered species, tigers cannot be killed unless there is a legitimate reason, such as ending the life of a sick tiger.) Animal rights groups such as PETA conducted their own covert investigations, revealing what they claimed was gross abuse — dead and dying animals, extremely crowded cages lacking basic necessities such as water, and untrained staff who routinely abused animals. In retaliation, Joe launched social media attacks and filed dozens of contrived police reports claiming his accusers were the ones who were breaking the law.
For years, Joe’s strategy worked: Profit off cubs. Evade his enemies. Skirt the law. It probably would’ve continued to work had Joe’s path not collided, as he once put it, with “some bitch down there in Florida.”
* * *
Carole Baskin in 2017 walking the property at Big Cat Rescue, a nonprofit sanctuary committed to humane treatment of rescued animals, often coming from exploitive for-profit operations. (Loren Elliott/Tampa Bay Times via AP)
Vultures circle overhead as Carole Baskin and I make our way along a secluded stretch of the Upper Tampa Bay Trail, about 15 miles outside of downtown Tampa. A spring breeze flutters her waist-length blond hair and blows through the thick surrounding brush of oaks and palmettos. Despite the blue sky and sunshine, the trail is empty. The only sound is the rustle of leaves and crunch of Baskin’s leopard-print boots on the pavement. It was this trail, Baskin explained to me, on which she regularly bikes to work, that a hitman had identified as a place to take her out.
Baskin is arguably the most well-known activist in the country campaigning against big cat ownership. She also takes in unwanted exotic cats at Big Cat Rescue, her sanctuary in Tampa, which currently houses 66 cats belonging to 11 different species. It’s one of the few places in the U.S. capable of providing these animals with a safe, reasonably good life in captivity.
Like Harrison, Baskin used to be part of the problem. A pivot from big cat owner to big cat conservationist is a common story among advocates in the field. Baskin stumbled into owning an exotic cat in the early 1990s at the age of 31. She and her ex-husband, Don, worked together in the real estate business. They used llamas to mitigate the brush on the Florida properties they sold, and the easiest place to get a llama was at an exotic animal auction. At one memorable event, a man seated next to Baskin bid on a baby bobcat. Baskin couldn’t help but lean over and whisper: “When that cat grows up, she is going to tear your face off.”
“I’m a taxidermist,” the man replied. “I’m just gonna club her in the head in the parking lot and make her into a den ornament.”
Baskin was horrified. Don outbid the man and they brought home the 6-month-old kitten, which Baskin named Windsong. As Windsong grew, the bobcat terrorized Baskin’s daughter and the family’s German shepherd. The solution, Baskin decided, was to get Windsong a playmate. Don found a guy in Minnesota who agreed to sell them a bobcat kitten. Turned out, the man was a fur farmer; Baskin and Don came back from that trip with 56 bobcat and lynx kittens — everything the farmer had for sale. The following year, they returned to rescue the 28 adult cats, too.
With their home overrun by exotic cats, Baskin and Don transformed a nearby 40-acre property they owned into a sanctuary, albeit with misguided tourism and breeding components. They called it Wildlife on Easy Street. They amassed a collection of at least 150 exotic cats of 17 species. For $75 a night, visitors could share a small cabin with a bobcat, cougar, or serval. Baskin started breeding half a dozen big cat species, including ocelots and leopards. Pre-internet, all Baskin’s information came from breeders and dealers, who had their own motivations. “They were saying, ‘Oh, you should breed these animals because they’re endangered and the zoos don’t know what they’re doing and they’re going to disappear from the wild,’” Baskin said. “So, we thought, well, that’s something we could definitely do to help save the cats.”
But people who bought kittens from Baskin often returned the cats after they grew up. Once, a Siberian lynx — an animal Baskin swore she recognized from when it was young — showed up at auctions. People started donating cats to Baskin’s sanctuary by the dozens. Some years, she turned away hundreds of animals due to a lack of space. Around the same time, Baskin started attending conferences held by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums, where she learned a few hard truths. None of these cats had any conservation value for their species. In fact, Baskin realized big cats had no business being bred and kept as pets at all.
In 1997, Baskin pulled a 180. She stopped breeding and began spaying and neutering all of her animals. She started enforcing a new rule in 2003: Big Cat Rescue, her rebranded sanctuary, would take any unwanted tiger, lion, savannah, or whatever else, but in return the owner had to sign a contract forfeiting their right to own a big cat. “We’re the only place that absolutely insists that if you’re going to dump an animal here, you are never going to own another exotic cat,” Baskin said.
The contracts were a good start, but Carole had an even bigger goal in mind: ending all big cat ownership. Critical to realizing that vision is Howard Baskin, a businessman from Poughkeepsie, New York, who Carole met at an event at the Florida aquarium in 2002. (Baskin’s previous husband walked out the door one day and was never seen or heard from again — though she was questioned, no evidence was ever found linking Baskin to his disappearance.) A lifelong bachelor with a Harvard MBA and a law degree from the University of Miami, Howard appears in many ways Carole’s opposite. Carole dresses like a Woodstock attendee and carries herself with the breezy grace of a dancer. Howard trundles along, turtle-like, in dad-style khakis with a cell phone holster. But they make a good team. Howard handles the administrative and legal duties and Carole focuses on advocacy. “On our honeymoon, we wrote a 25-year plan to stop the big cat abuses that bad guys hold dear,” Carole said.
Carole and Howard started by setting up a Google alert for cub-petting events around the country. Baskin would email the venues explaining the downsides of cub petting and asking them to cancel the event, and if they did not respond, she would then direct her hundreds of thousands of social media followers to flood the venues with emails explaining the downsides of cub petting. One by one, malls began to call off the events. (Fairs proved more impervious to the bad PR.) Baskin homed in on the primary players in the exotic cat world and publicized her findings on 911animalabuse.com, a website she created. One individual stood out among all the breeders: a guy with a dozen different aliases, but whose cub petting photos always included the same motley group of heavily tattooed, pierced, longhaired workers. It was Joe Exotic’s crew.
* * *
Joseph Maldonado in 2013, answering a question during an interview at the zoo he then ran in Wynnewood, Oklahoma. (AP Photo/Sue Ogrocki, File)
As Baskin ramped up her efforts, Joe’s profits plummeted. In retaliation, he launched a smear campaign against Baskin’s nonprofit. He renamed his cub-petting show Big Cat Rescue Entertainment and designed a near-identical copy of Baskin’s Big Cat Rescue logo. The Baskins sued Joe in 2011 for copyright infringement. Joe countersued, but those claims were tossed out by a judge. Joe eventually agreed to a consent judgement north of $1 million, which he had no intention of paying. He did everything he could to obscure his money, changing the name of his zoo and transferring assets to an account in his mother’s name. Joe also made a series of increasingly unhinged videos posted on social media threatening Baskin’s life. One featured an effigy of Baskin. Another depicted Baskin’s head in a jar, Silence of the Lambs–style.
In 2015, Baskin got a call from a woman who said Joe had inquired with her then-husband, who she said was a former military sharpshooter, about hiring her husband to kill Baskin. Nearly two years later, Baskin received a similar warning from a woman named Ashley Webster, an aspiring wildlife biologist from Colorado who had just started working at Joe’s park. In a deposition, Webster recalled Joe saying “something along the lines of he’d give me a few thousand dollars to go to Florida and put a bullet in [Baskin’s] head.” Carole and Howard reported the incidents to police, but nothing seemed to come of it.
Unbeknownst to the Baskins, the FWS had launched an investigation of Joe and his zoo in 2016 for potential animal trafficking violations. The saga, which has been detailed at length in various news reports, involved an FWS agent convincing a man named James Garretson, who’d done big cat business with Joe in the past, to become a government informant. Garretson agreed to attempt to arrange a meeting between Joe and an undercover FBI agent posing as a hitman. At the outset, what the feds learned was that Joe already had his own scheme in the works: He planned to hire Allen Glover, a man from South Carolina who’d been convicted of assault, for the job.
Glover was a longtime associate of a man named Jeff Lowe, who’d done business with Joe and shortly after started hanging around the Tiger King and his world. Joe, who was under the impression that Lowe was wealthy, made his new friend the co-owner of the zoo’s land, along with his mother. In exchange, Lowe, according to a deposition, said he would pay a portion of Joe’s mounting bills at the zoo and let Joe run the park as usual. “The whole thing was to put the zoo in his name so Carole couldn’t get it,” Joe told me. But Lowe had other plans. In a May 2018 deposition, Lowe admitted that he was interested in the zoo for himself.
According to Glover, who testified at Joe’s trial, he and Joe settled on a $5,000 down payment for the hit on Baskin and discussed other details such as what weapon to use. Glover said that Joe eventually gave him $3,000 cash and a cell phone loaded with pictures of Baskin. But during his two days on the stand, Glover claimed he’d always intended to take the money and run. For his part, Joe denies giving Glover the phone, and said that Lowe was the one who instructed him to pay Glover. (Lowe declined multiple interview requests for this story.) Glover did travel east, but in court he said he only made it as far as an unknown beach in Florida, where he partied most of the money away in a single night. Glover claimed that it was not his intention to kill Baskin in Florida, but rather to warn her that Joe wanted her dead.
Meanwhile, in December 2017, Joe agreed to Garretson’s proposed meeting with the undercover FBI agent. The agent quoted Joe a $10,000 fee for the hit. The two agreed to a rough outline of a deal, but Joe never followed through. Instead, in June, without notice, Joe and his new husband, Dillon Passage, loaded up four dogs, two baby tigers, and a baby white camel, and took off. (Joe’s previous husband, Travis Maldonado, accidentally shot and killed himself in October 2017.) “Joe Exotic, as far as I was concerned, was dead,” Joe told me. He was going to create a new life with Passage.
Joe and Passage left Oklahoma and headed east, eventually landing in Gulf Breeze, Florida. On a sunny September morning, Joe pulled up to the local hospital. He planned to walk in and apply for a job. Instead, unmarked cars surrounded him. U.S. marshals jumped out, guns pointed, yelling at Joe to get on the ground.
Lowe had indeed been working with federal agents since as early as June. Less than a month before Joe’s arrest, Lowe bragged on Facebook that he’d been “setting [Joe’s] ass up for almost a year.” And it seems Lowe got what he wanted. He and his wife, Lauren, now run Joe’s old zoo, where they continue to churn out cubs for playtimes. The nursery lineup recently featured Nova, the rambunctious tiliger who bit my producer.
Jeff Lowe and Lauren Dropla with Faith the liliger at their home in 2016 inside the Greater Wynnewood Exotic Animal Park in Wynnewood, Oklahoma. (Ruaridh Connellan/BarcroftImages / Barcroft Media via Getty Images)
* * *
This past March, journalists from around the country descended on downtown Oklahoma City for Joe Exotic’s trial. Garretson and Glover testified against Joe. Joe’s ex-boyfriend John Finlay testified too. Joe took the stand at the end of the seven-day affair. He said he never intended for anyone to kill Carole Baskin and claimed to have known that Garretson, Glover, and Lowe were conspiring to take him down. He said he played along to better understand their plan and gather evidence he could use against them. The jury deliberated for less than three hours, then found Joe guilty on all charges, including illegally killing five tigers and illegally transporting endangered species across state lines. In January, a judge sentenced Joe to 22 years in federal prison. In a Facebook post, Joe maintained his innocence and said he plans to appeal.
Nasser hopes that Joe’s conviction triggers the beginning of what she calls “a long-overdue Blackfish moment for captive tigers,” referring to the popular documentary that exposed problems with the sea-park business’ treatment of orcas and led to numerous SeaWorld boycotts. Pending any appeals, the Baskins and other activists believe the Tiger King’s downfall could topple the industry. They hope to use the momentum and notoriety of Joe’s case to usher in sweeping legal reform of big cat ownership in the U.S.
Baskin has been pushing for this type of reform since 1998, when she began working on what’s called the Captive Wildlife Safety Act, a federal bill unanimously voted into law in 2003 that barred the sale of big cats as pets across state lines. Loopholes in the law, however, have rendered it largely ineffective. She and Howard — along with major nonprofit groups such as the Humane Society and the International Fund for Animal Welfare (IFAW) — have been pushing a new bill, the Big Cat Public Safety Act. First introduced in 2012, the legislation would ban all public contact with big cats, including cub petting, and would require all big cat owners to register their animals. Howard hired a top Republican lobbying firm in 2014 to work with Harrison to champion the bill — not for its conservation clou, but on its pubic safety merits. Senator Susan Collins signed on to the bill last November, the first republican cosponsor. Three other Republican senators, including Richard Burr of North Carolina, have since joined Collins. The registrations would provide officials with valuable insight into who owns what and where — potentially life-saving information in the event of, say, a tornado blowing through a tiger park. The ban on cub petting, though, is the most important part of the bill, as proponents believe it would disincentivize the breeding of big cats.
Last year, the bill made it out of the Committee on Natural Resources in a bipartisan vote and could soon head to the House floor, where it has broad support. “Law enforcement has enough problems trying to protect the public without having to run into a house where there might be a tiger,” said Harrison. Dozens of Republican lawmakers support it — a party full of politicians, who, Harrison said, for the most part “don’t give a crap about cats.”
For now, though, cub petting remains a lucrative industry. According to data compiled by a team of New York University researchers in 2016, at least 77 facilities across the country allowed interactions with exotic animals (about a quarter of those were with big cats). In a follow-up study in 2019, which focused specifically on tiger petting, those same zoos were still open. One operation in Myrtle Beach, South Carolina, run by Bhagavan “Doc” Antle, charges up to $339 per person for tours and cub-petting sessions. Supporters of the Big Cat Public Safety Act believe that ending cub petting would go a long way toward stopping the trade of big cats altogether. “Without ending public contact, you’re not going to have sufficient incentive for all the fly-by-night exhibitors to stop breeding,” said Nasser.
The new protections would extend to smaller species such as jaguars and even unnatural hybrids like Nova. They’d also apply to accredited zoos. While the zoo baby phenomenon is no longer as rabid as it once was, not all zoos have ended the practice of animal meet-and-greets. The Nashville Zoo provides clouded leopard cubs for zoo fundraisers and media events (zoo officials say that play and petting sessions are not allowed), and the Dallas Zoo recently held a cheetah photo op session for the Dallas Stars (zoo officials point out none of the Stars were able to pet the cheetah, however).
Limiting and eventually banning big cat ownership in the U.S. would almost certainly be a boon for the species worldwide. Fewer than 4,000 tigers survive in the wild today. But they are farmed by the thousands in China, Laos, and other Southeast Asian countries where big cat parts are sought after as erroneous medicinal remedies and status-touting commodities. Tiger bone wine, in particular, is considered a cure-all tonic, a virility booster for men, and a coveted, favor-winning gift for superiors, elders, and relatives.
Tiger bone is banned in China, and it’s illegal to trade big cats and their parts in Vietnam and elsewhere in Southeast Asia. But there’s a robust black market for tiger bones, skin, teeth, and claws — and farmed tiger parts keep demand for these items alive, perpetuating poaching. The U.S. government considers closing tiger farms integral to saving wild tigers, but when State Department officials try to negotiate this point with foreign diplomats — especially those from China — they’re often told to clean up their own mess first. “When I talk to government leaders about tiger farming in many of the Asian countries, quite often they ask me, ‘What about tigers in the U.S.? What role do the tigers in private backyards in the U.S. contribute to wild tiger conservation?’” said Grace Ge Gabriel, IFAW’s Asia regional director. “Literally, I am speechless. I don’t have an answer.”
A tiger named Seth rests above a pond at Big Cat Rescue in 2017. (Loren Elliott/Tampa Bay Times via AP)
* * *
After I first contacted Joe following his trial, we spoke several times over the next few months. He liked to talk, only cutting off our calls if another person in the prison needed to use the phone. Joe never admitted any wrongdoing when it came to Baskin; rather, he was eager to defend his innocence. Multiple times he told me, “That whole mess was nothing but a setup.”
Joe did cop to something else, though. He said being locked up in jail had made him realize he’d mistreated the animals all those years, depriving them of their freedom and robbing them of their dignity by keeping them behind bars. Joe told me he regretted having done that. “Now that I have nothing to do besides sit in a cell with no TV, no radio, no nothing, I know exactly what I did to those [animals],” he said. “We can all be drove crazy by doing nothing.”
To make amends, Joe told me he plans to create a new zoo when he gets out. This one without any cages. Just tigers roaming free.
* * *
You can listen to our four-part “Cat People” podcast series on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts.
Rachel Nuwer is an award-winning freelance journalist who reports about science, travel, food and adventure for the New York Times, National Geographic, BBC Future and more. Her multi-award winning first book, Poached: Inside the Dark World of Wildlife Trafficking, was published in September 2018 with Da Capo Press.
Editors: Mike Dang and Chris Outcalt Illustrator: Zoë van Dijk Fact checker: Matt Giles Copy editor: Jacob Gross
0 notes
Text
Crack Addiction Stories
Contents
With people with
Laboratories and the … sep substances
There are innumerable personal stories
Cocaine and those who are battling
Contents with severe mental and enlightenment
Addiction Treatment Limited Contents Across michigan’s upper peninsula. the volunteer That can involve virtually Severe mental the Pill contents daughter Options for drug addicts The IME was launched in July 2015 to help those with limited insurance gain … Addiction Helper is the UK's leading free guide to alcohol rehab and drug clinics, getting help with addictions and
Jun 26, 2017 … America is fascinated by tales of the exploits of gangsters, hustlers, dealers, and killers, but the human cost has yet to be counted.
It was a winter morning near the end of 2014 and Priscila had finally reached rock bottom after a four-year addiction to crack cocaine … That she is alive to tell this story at all is the first in a series of minor miracles. That she can tell it …
mirror Load mobile navigation … Tragic journey from promising pretty student to crack addict … But the other picture tells a different story as the trainee …
Khaled’s story is a textbook case of a broader public health crisis … the head of …
Matt's Story of Cocaine Addiction. By the time Matt was 35 years old, he had three children, a wife and an addiction to crack cocaine. He started drinking in high school, a habit that soon spiraled out of control.
The former NBA star, who has battled a crack cocaine addiction, is investing in the marijuana business … Sign up for our daily newsletter to get our best stories of the day delivered straight to your inbox. Now, both have moved on — and …
11th St., to CenterPointe, a nonprofit agency that works with people with mental …
Here are some stories to start your day … Everyone has a preconceived notion …
Aug 4, 2015 … Study into Montreal's 'filthy' crack houses provides portrait of vicious cycle of prostitution, binge use and addiction. Anthropologist Nelson Arruda studied Montreal crack houses and found they were governed according to strict rules that included a ban on injecting and prostitutes who on the surface …
Aug 12, 2010 … EastEnders fans watched in horror this week as Phil Mitchell took his first hit of crack cocaine.
The song is seven minutes of verses covering his addiction to crack and heroin, and his ability to rise above it. “By talking about my story and talking about my …
Apr 22, 2018 … I spent about 5 years living next to a certified crackhead. When I moved to another housing project, I lived next to a crack dealer for 4 years.
Open Topic (new reply) Hot Topic (new reply) Poll (new votes) Locked Topic: Open Topic (no new reply) Hot Topic (no new reply) Poll (no new votes)
Crack addiction occurs when recovering from … And like all war stories my little posse didn't lose the war due to … How strong is the addiction to crack cocaine?
Stanford grad, university professor, former beauty queen and Swedish royal Josefine Nauckhoff had a secret. She was also a crack whore.
Watch video about addiction from The Truth About Crystal Meth, including former methamphetamine addicts sharing information about the dangerous effects of the dangerous illegal psychoactive street stimulant like overdose and withdrawal.
Addiction is a difficult subject matter … Even darker times followed in 2010 when Phil got hooked on crack cocaine. …
Sep 16, 2013 … He tells horrifying stories — his mother attacked with a hammer, his father doused with a potful of boiling syrup — but then he looks for the statistically significant trend. Yes, he notes, some children were abandoned by crack- addicted parents, but many families in his neighborhood were torn apart before …
Crack Cocaine Addiction Stories is the ups and downs of real people overcoming addiction; some suceesfully and other not.
Before treatment, Sherry was in and out of jail, and had lost her five children as a result of her addiction.
Overcoming Addiction: … crack cocaine and alcohol addict. This is my story of hitting rock … Addiction Overcoming Addiction Crack Addiction …
Addiction Treatment Centers Nevada Contents Can call the substance Center operators and middlemen who Across michigan’s upper Clinicians for individuals who are experiencing 787-9411. step2 provides compassionate Addiction Treatment Services Lab One Contents And alcohol testing laboratories and the … sep substances. this process can cause serious Drug testing. … services has Age 3 and then one You can
The former NBA star, who has battled a crack cocaine addiction, is investing in the marijuana business … Sign up for our daily newsletter to get our best stories of the day delivered straight to your inbox. Now, both have moved on — and …
DESTINY details my experiences for the past 4 years (2009 through 2013), while following and documenting the life of an 8-year-old girl, Destiny, a daughter of Patrcia (Trish), 31, a crack addict from Mansfield, Ohio. At age of 14, Patricia was sexually abused by a middle-aged man, who was her father's best friend. She has …
Jun 20, 2016 … I had a good friend of mine become a drug addict. Crack specifically. I never imagined he'd be using it in a million years, but life has a funny way of showing you that anything is possible. He was a natural born hustler. He sold dope at school, at parties and pretty much wherever he could make a buck.
Linda's Story. My name is Linda and I am a recovering addict. I got to the fellowship of Cocaine Anonymous three years ago as I knew I had serious problems with my drug use and in my life, however, … Cocaine and Crack became a daily habit, and by the time I was 31 I still thought I was OK as I usually made it to my work.
Jul 11, 2009 … Ongoing work with two heroin epidemics in Baltimore produced a "trend theory," a way to explain illicit drug use tends. In this article, the case of the crack cocaine epidemic in the 1980s is analyzed to challenge the theory. Two of the key parameters of the theory – the drug production system and the linking …
Scott Harman was a crack addict for 17 years. It all began at 13-years-old when … took him down his own unique path but his is one of the thousands of similar stories. While many receive treatment, it often takes a variety of different …
and for most of that time a crack addict. Yet when he took to religion, he was able to stop overnight. He got married to a fellow believer, and told his story of …
“Cocaine, crack, just pretty much everything … Samantha was one of the three …
Learn about the effects of crack cocaine, devil drug, on addicts from stories and video by former users. … "I lived with a crack addict for nearly a year.
Key Facts About Crack Abuse. What Is Crack? Crack cocaine is the freebase form of cocaine. Crack's popularity, … Crack addiction is a powerful motivator, …
May 22, 2009 … A glimpse inside the mind of a mother addicted to crack.
To document the nation’s devastating opioid crisis, TIME sent photographer James Nachtwey and deputy director of photography Paul Moakley across the country to gather stories from the … deserve a chance to heal from addiction. …
Mar 23, 2016 … Although many go untold, there are innumerable personal stories of crack addiction. When these stories are publicly recalled, there are usually varying reactions from both those that have never experienced an addiction to crack cocaine and those who are battling this debilitating disease. While judgement …
Stealing – Crack addiction is expensive and it is common for an addict to steal from just about anyone while they are chasing their high. Most long-term addicts admit to stealing from their closest friends and family members. An Addict's Story of Recovery. Although crack addiction is difficult to overcome and there is a high …
<iframe src="https://ift.tt/2HVJhwM" width="670" height="372" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen scrolling="no"></iframe> <style>.gn-embed-wrapper{position:relative;max-width:100%;padding …
Sep 13, 2017 … GLOUCESTER TWP. – For a long time, on the anniversary of her 16-year-old daughter's violent death, Anika Pitts could only curl up in a ball and cry. There was so much to cry about — the years Pitts spent in the grip of a crack addiction, the years her daughters spent under her cousin's wing instead of hers, …
Dual Diagnosis Treatment Contents 2 million americans with severe mental The right treatment. recovery Interact with one another May ask why Are you addicted to drugs or alcohol? Do you suffer from mental illness? You may need dual diagnosis treatment to overcome both problems | Los Angeles, Ca. Heroin Addiction Treatment Pill Contents Daughter. she was Programs view
I was taught how to cook and smoke crack when I … I don't present these stories for … direct discussion about drugs before we can comprehend addiction, …
Jun 15, 2017 … The story of two San Francisco residents brought together by a crime is illustrative of a city divided by deep inequality and homelessness.
Addiction Treatment Center Business Plan contents with severe mental and enlightenment that The miami beach holistic addiction treatment Business plan services Addiction treatment centers make Pennsylvania will open 20 centers … opioid addiction is an illness," Gov. Wolf said in a statement announcing that his administration was moving ahead with the plan. "In order to address this illness, we need
Jan 11, 2017 … Former drug addict Mike Lindell's multimillion-dollar idea came to him in a dream. … As so many great entrepreneurial success stories do, the tale of Mike Lindell begins in a crack house. It was the fall of 2008, and the then 47-year-old divorced father of four from the Minneapolis suburbs had run out of crack …
Crack'd: A True Story of Crack Addiction [James Whitton] on Amazon.com. *FREE * shipping on qualifying offers. Crack cocaine—How does someone go from living in a small rural farming community in upstate New York to living in Miami and becoming addicted to crack cocaine? James tells his alarming and true-life story …
ANNAPOLIS, Md., June 13, 2017 /PRNewswire-USNewswire/ — During her 19-year crack addiction, Tonier Cain …
Crack: it gives you wings by Lee Carrick. Genre: … Description: A story of life in a crack house … existed with crack addicts and became a crack addict.
GREENFIELD — Brittany Smith told Virginia police that she was "high on crack" …
April grew up among addicted family members and ended up hooked on cocaine, pills, and methadone. but after phoenix house determinants of health, she's clean and reunited with her son
Jan 23, 2018 … Felicia Lee-Sexton talks to Houston Matters about her book, 'From Recovery To Discovery: My Journey Through Addiction.'
Apr 11, 2015 … In an open-air "Crackland," crack addicts posed for portraits, and shared their stories.
The founding member of rock band Kiss has an addiction of another kind. A self-confessed sweet tooth, he only drinks decaf coffee and tops his cup with hot chocolate for added sweetness. “I’ve never touched opioids, crack or weed, but …
3 stories of people who overcame their cocaine addiction include the stories of Samuel L. Jackson, Nick Hayes, and a successful entrepreneur named Derrick.
The post Crack Addiction Stories appeared first on Freedom From Addiction II.
0 notes
Text
Remarks by President Obama at Pearl Harbor
Prime Minister Abe, on behalf of the American people, thank you for your gracious words. Thank you for your presence here today -- an historic gesture that speaks to the power of reconciliation and the alliance between the American and Japanese peoples; a reminder that even the deepest wounds of war can give way to friendship and lasting peace.
Distinguished guests, members of our armed forces -- and most of all, survivors of Pearl Harbor and their loved ones -- aloha.
To Americans -- especially to those of us who call Hawaii home -- this harbor is a sacred place. As we lay a wreath or toss flowers into waters that still weep, we think of the more than 2,400 American patriots -- fathers and husbands, wives and daughters -- manning Heaven’s rails for all eternity. We salute the defenders of Oahu who pull themselves a little straighter every December 7th, and we reflect on the heroism that shone here 75 years ago.
As dawn broke that December day, paradise never seemed so sweet. The water was warm and impossibly blue. Sailors ate in the mess hall, or readied themselves for church, dressed in crisp white shorts and t-shirts. In the harbor, ships at anchor floated in neat rows: the California, the Maryland and the Oklahoma, the Tennessee, the West Virginia and the Nevada. On the deck of the Arizona, the Navy band was tuning up.
That morning, the ranks on men’s shoulders defined them less than the courage in their hearts. Across the island, Americans defended themselves however they could -- firing training shells, working old bolt-action rifles. An African-American mess steward, who would typically be confined to cleaning duties, carried his commander to safety, and then fired an anti-aircraft gun until he ran out of ammo.
We honor Americans like Jim Downing -- a gunner’s mate first class on the West Virginia. Before he raced to the harbor, his new bride pressed into his hand a verse of Scripture: “The eternal God is thy refuge, and underneath are the everlasting arms.” As Jim fought to save his ship, he simultaneously gathered the names of the fallen so that he could give closure to their families. He said, “It was just something you do.”
We remember Americans like Harry Pang -- a fireman from Honolulu who, in the face of withering fire, worked to douse burning planes until he gave his last full measure of devotion
-- one of the only civilian firefighters ever to receive the Purple Heart.
We salute Americans like Chief Petty Officer John Finn, who manned a .50-caliber machine gun for more than two hours and was wounded more than 20 times, earning him our nation’s highest military decoration, the Medal of Honor.
And it is here that we reflect on how war tests our most enduring values -- how, even as Japanese Americans were deprived of their own liberty during the war, one of the most decorated military units in the history of the United States was the 442nd Infantry Regiment and its 100th Infantry Battalion -- the Japanese-American Nisei. In that 442nd served my friend and proud Hawaiian, Daniel Inouye -- a man who was a senator from Hawaii for most of my life and with whom I would find myself proud to serve in the Senate chamber; a man who was not only a recipient of the Medal of Honor and the Presidential Medal of Freedom, but was one of the most distinguished statesmen of his generation as well.
Here at Pearl Harbor, America’s first battle of the Second World War roused a nation. Here, in so many ways, America came of age. A generation of Americans -- including my grandparents -- the Greatest Generation -- they did not seek war, but they refused to shrink from it. And they all did their part on fronts and in factories. And while, 75 years later, the proud ranks of Pearl Harbor survivors have thinned with time, the bravery we recall here is forever etched in our national heart. I would ask all our Pearl Harbor and World War II veterans who are able to, to please stand or raise your hands -- because a grateful nation thanks you.
The character of nations is tested in war, but it is defined in peace. After one of the most horrific chapters in human history -- one that took not tens of thousands, but tens of millions of lives -- with ferocious fighting across this ocean -- the United States and Japan chose friendship and peace. Over the decades, our alliance has made both of our nations more successful. It has helped underwrite an international order that has prevented another World War and that has lifted more than a billion people out of extreme poverty. And today, the alliance between the United States and Japan -- bound not only by shared interests, but also rooted in common values -- stands as the cornerstone of peace and stability in the Asia Pacific and a force for progress around the globe. Our alliance has never been stronger.
In good times and in bad, we are there for each other. Recall five years ago, when a wall of water bore down on Japan and reactors in Fukushima melted, America’s men and women in uniform were there to help our Japanese friends. Across the globe, the United States and Japan work shoulder-to-shoulder to strengthen the security of the Asia Pacific and the world -- turning back piracy, combating disease, slowing the spread of nuclear weapons, keeping the peace in war-torn lands.
Earlier this year, near Pearl Harbor, Japan joined with two dozen nations in the world’s largest maritime military exercise. That included our forces from U.S. Pacific Command, led by Admiral Harry Harris, the son of an American Naval officer and a Japanese mother. Harry was born in Yokosuka, but you wouldn’t know it from his Tennessee twang.
Thank you, Harry, for your outstanding leadership.
In this sense, our presence here today -- the connections not just between our governments, but between our people, the presence of Prime Minister Abe here today -- remind us of what is possible between nations and between peoples. Wars can end. The most bitter of adversaries can become the strongest of allies. The fruits of peace always outweigh the plunder of war. This is the enduring truth of this hallowed harbor.
It is here that we remember that even when hatred burns hottest, even when the tug of tribalism is at its most primal, we must resist the urge to turn inward. We must resist the urge to demonize those who are different. The sacrifice made here, the anguish of war, reminds us to seek the divine spark that is common to all humanity. It insists that we strive to be what our Japanese friends call otagai no tame ni -- “with and for each other.”
That’s the lesson of Captain William Callaghan of the Missouri. Even after an attack on his ship, he ordered that the Japanese pilot be laid to rest with military honors, wrapped in a Japanese flag sewn by American sailors. It’s the lesson, in turn, of the Japanese pilot who, years later, returned to this harbor, befriended an old Marine bugler and asked him to play taps and lay two roses at this memorial every month -- one for America’s fallen and one for Japan’s.
It’s a lesson our two peoples learn every day, in the most ordinary of ways -- whether it's Americans studying in Tokyo, young Japanese studying across America; scientists from our two nations together unraveling the mysteries of cancer, or combating climate change, exploring the stars. It’s a baseball player like Ichiro lighting up a stadium in Miami, buoyed by the shared pride of two peoples, both American and Japanese, united in peace and friendship.
As nations, and as people, we cannot choose the history that we inherit. But we can choose what lessons to draw from it, and use those lessons to chart our own futures.
Prime Minister Abe, I welcome you here in the spirit of friendship, as the people of Japan have always welcomed me. I hope that together, we send a message to the world that there is more to be won in peace than in war; that reconciliation carries more rewards than retribution.
Here in this quiet harbor, we honor those we lost, and we give thanks for all that our two nations have won -- together, as friends.
May God hold the fallen in His everlasting arms. May He watch over our veterans and all who stand guard on our behalf. May God bless us all.
Thank you.
1 note
·
View note
Text
New top story from Time: Why It’s A Mistake To Simplify the ‘Latino Vote’
Ten years after political science professor Marisa Abrajano wrote about the false assumptions made towards Latino voters, political pundits and campaigns are still making the same mistakes in this election, she says. The assumption of a singular “Latino vote” is wrong, for one, and actually it should come as no surprise that Cuban Americans in Miami Dade voted for President Trump.
Latinos are not a monolith, and not one unified force. The differences between communities are vast and deep. The U.S. is home to an estimated nearly 61 million Latinos, according to the Pew Research Center, and range in age, race, gender, religion, socio-economic status, political ideology and educational attainment. Most are English proficient, and most were born in the U.S.
Despite these nuances, on Election Day the “Latino vote,” was analyzed as a single, unified entity by some political pundits, journalists and campaign officials without acknowledgment of the complexities of a demographic that makes up an estimated 18% of the U.S. population—a symptom of a wider trend of limited Latino outreach during political elections.
Latinos in the U.S. come from all parts of Latin America, Central America and Mexico. Some Latinos have lived in the U.S. for generations. There’s a variety of Spanish dialects, languages, foods, and traditions. It should come as no surprise that there are also differences in political ideology.
“The assumption is that Latinos are a monolithic group of voters, and the reality is that Latinos make up individuals hailing from more than a dozen different countries,” Abrajano, who teaches at UC San Diego, tells TIME. “The Latino vote in Florida is different from the Latino vote in California, and from Nevada, Arizona—and so to make broad strokes, or using this pan-ethnic term, can be problematic, and the same trend was evident 10 years ago.”
In the aftermath of Election Day, many took to social media to express their concern that analysts were painting Latinos with a broad brush. “It’s laughable that in 2020, this country still needs to be reminded, Sesame Street style, that Latinos are not a monolith & the Latino vote is a mirage,” wrote Los Angeles Times writer Esmeralda Bermudez in a Twitter thread.
It’s laughable that in 2020, this country still needs to be reminded, Sesame Street style, that Latinos are not a monolith & the Latino vote is a mirage. This misconception comes from how little u bother knowing us, how superficially u cover us & how absent we are in newsrooms.
— Esmeralda Bermudez (@BermudezWrites) November 4, 2020
“I think the most important thing for people to understand is that there is no ‘Latino vote,'” says Lisa García Bedolla, vice provost for graduate studies and dean of the Graduate Division at the UC Berkeley. “What we call Latinos or the Latino community is made up of folks who are very different in terms of national origin, in terms of generation, in terms of language use, nativity, class, gender, gender identity, sexuality, and then it also really matters where people end up living.”
But though social scientists like García Bedolla and Abrajano have for decades studied and even provided advice for how political campaigns could better engage wide-ranging communities with nuance, not much has changed, including this election year. García Bedolla says what often happens is that campaign managers wait until late into a campaign to begin Latino voter outreach. Often that comes in the form of a campaign ad in Spanish.
“I have been involved for at least a decade in trying to educate [political operatives] about these nuances,” García Bedolla says, but, she adds, often the people in decision-making positions lack the cultural awareness necessary to be effective.
“I literally had somebody ask me in 2016 what’s the bumper sticker that is going to mobilize Latinos?” García Bedolla says. “What we actually needed were mobilization strategies that would talk to the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth generation English monolingual Mexican Americans in San Antonio…That’s the kind of specificity that we need.”
García Bedolla and those who spoke to TIME all say that political campaigners need to engage with Latinos early and often, year-round, to understand the needs of individual communities. What’s important to Puerto Ricans in New York City, for example, will differ from Mexican Americans in the Rio Grande Valley.
Because Latinos nationwide vote for Democrats in larger numbers than they do for Republicans, one misconception is that as the population of eligible Latino voters grows in the U.S., so will votes for Democrats. It’s a myth social scientists refer to as “demography as destiny.” Of the estimated nearly 61 million Latinos in the U.S., Pew estimates 32 million were eligible to vote this year, or 13.3% of all eligible voters.
“Both political parties in this country need to recognize that Latinos are not a given entity, they are a constituency that demands recruitment,” says Antonio Arrellano, interim executive director of Jolt Action, a progressive organization in Texas that aims to increase Latino political engagement. Texas is home an estimated 5.6 million eligible Latino voters, coming in second only to California with an estimated 7.9 million, according to Pew.
For that reason, Arrellano says, campaigns cannot take Latino voters for granted. “We need to recognize that Latinx folks across the country have been here for decades, for centuries and have…for generations been overlooked, neglected and underrepresented,” he says. “It looks like now more than ever before, Latinos are coming to terms with the fact that the political power in this country is rightly in their hands and you have seen that turnout in Arizona, in Nevada, in Texas, where Latinos are engaged like never before because they know that the next chapter of American history will be written by them.”
Party recruitment, Arrellano, Abrajano, and García Bedolla stress, cannot be as simple as speaking Spanish during a political debate, or opening a rally with mariachi music—symbolic cultural messaging to relate to Latino voters that lack substance, which García Bedolla adds, she finds insulting.
Just like all voters, life’s experiences inform the way Latino voters vote, not just ethnic or racial identity. “It makes it seem that, if I’m a Democrat, it’s just because I’m a Latina,” she says. “It’s not because of anything that’s happened to me in my life.”
In fact according to Pew, in 2018, 62% of Latino voters identified with or leaned toward the Democratic Party, while 27% leaned toward or identified with Republicans. But this is not something that is widely recognized and political pundits’ surprise at Latino support for Trump on Election Day—the Cuban vote in Florida, for example—points to a lack of understanding of nuances of Latinos in the U.S., says Geraldo Cadava, a professor of history at Northwestern University who wrote “The Hispanic Republican.”
“I mean it really shouldn’t be a surprise,” he tells TIME. “The fact of the matter is that in every presidential election since Richard Nixon won the election in 1972, between a quarter and a third of Latinos have voted for the Republican candidate…by this point you could say that there has been a half-century tradition of Latinos, a significant minority of Latinos, voting for Republican candidates.”
The Cuban American population of Miami-Dade County, for example, has since the 1970s leaned towards the Republican party. But within that community exists nuances as well. Older Cubans who fled from the Castro Regime are still more likely to vote for a Republican than younger generations, Cadava says.
The Trump 2020 Campaign did make attempts to reach Cuban Americans by propagating an anti-socialist message, one that may also resonate with other Latino groups who have their own anti-socialism sentiments, Cadava adds. Venezuelan’s, for example, who take issue with President Nicolás Maduro.
On the other side of the coin, former Democratic presidential candidate Bernie Sanders also saw wide support from Latinos in Nevada. Analysts credit that success to the months-long effort to win over Nevada Latinos, who eventually helped him win the state in February. “It’s because he did something that other politicians sometimes forget to do: He asked for their votes,” wrote USA Today’s Ruben Navarrette Jr.
When political campaigns fail to do the robust outreach to individual Latino communities, grassroots organizers are often the one ones to fill the void. In Arizona, a battleground state, grassroots organizers have stepped up to mobilize Black, indigenous and people of color, an effort at least 10 years in the making, since campaigners were not taking the steps to engage with this block of voters.
This year, the state saw a strong turn out for Democratic presidential candidate Joe Biden, something Alejandra Gomez, co-executive director of Living United for Change in Arizona (LUCHA), a grassroots organization that works to support communities of color, credits to long-term mobilization efforts of organizations like hers.
For a decade, the organization has mobilized around campaign season, knocking on doors in neighborhoods that went ignored by party officials. They helped to increase Latino voter registration, hosted community meetings in key locations, and developed relationships within communities. Gomez says they considered how an outreach strategy for Latinos who are newly naturalized citizens could differ from a strategy intended for Latinos who have lived in the U.S. for multiple generations.
“Demographics are absolutely not destiny,” Gomez tells TIME. “We just did something historic…and for us that is incredible, that is the work, that is 10 years of organizing. And those voters, we’re not going to lose them because we’re gonna call them next week and we’re gonna debrief and thank them for having participated.”
from Blogger https://ift.tt/3k6MPua via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
The Strange and Dangerous World of America’s Big Cat People
Rachel Nuwer | Longreads | March 2020 | 28 minutes (7,033 words)
You can listen to our four-part “Cat People” podcast series on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts.
It’s a gloomy April afternoon in rural Oklahoma, and I’m sitting on the floor of a fluorescent-lit room at a roadside zoo with Nova, a 12-week-old tiliger. She looks like a tiger cub, but she’s actually a crossbreed, an unnatural combination of a tiger father and a mother born of a tiger and a lion. That unique genetic makeup places a higher price tag on cubs like Nova, and makes it easier, legally speaking, to abuse and exploit them. Endangered species protections don’t apply to artificial breeds such as tiligers. Hybridization, however, has done nothing to quell Nova’s predatory instincts. For the umpteenth time during the past six minutes, she lunges at my face, claws splayed and mouth ajar — only to be halted mid-leap as her handler jerks her harness. Unphased, Nova gets right back to pouncing.
With her dusty blue eyes, sherbet-colored paws, and prominent black stripes, Nova is adorable. But she also weighs 30 pounds and has teeth like a Doberman’s and claws the size of jumbo shrimp. Nova’s handler, a woman with long brown hair who tells me she recently retired from her IT job at a South Dakota bank to live out her dream of working with exotic cats, scolds the rambunctious tiliger in a goo-goo-ga-ga voice: “Nooooo, nooooo, you calms down!” Nova is teething, the handler explains, so she just wants something to chew on. The handler reaches for one of the tatty stuffed animals strewn around the room — a substitute, I guess, for my limbs. In that moment of distraction, Nova lunges. She lands her mark, chomping into the bicep of my producer, Graham Lee Brewer.
“Ooo, she got me!” Lee Brewer grimaces as he attempts to pull away from the determined predator. Nova’s handler has to pry the tiliger’s jaws open to detach her. After the incident, the woman conveniently checks her watch: “OK, you guys, time is up!”
I paid $80 for the pleasure of spending 12 minutes with Nova, but I’m glad the experience, billed as a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity, is over. On our way out, we pass more than a dozen adult tigers yowling and pacing cages the size of small classrooms. Nearby signs solicit donations. You are their only hope. Sponsor a cabin or compound today! In the safety of our car, Lee Brewer rolls up his sleeve, exposing a swollen red welt. “Look at my gnarly tiger bite,” he chuckles. “I tried to play it off but I was like, this fuckin’ hurts!”
It’s not the first time I’ve seen this world up-close; I spent the better part of eight years investigating wildlife trafficking around the world. During my travels, I visited farms in China and Laos where tigers are raised like pigs, examined traditional medicine in Vietnam, ate what I was told was tiger bone “cake,” and tracked some of the world’s last remaining wild tigers in India. Almost everywhere I went, tigers were suffering and their numbers were on the decline because of human behavior. Until recently, though, I had no idea the United States was part of the problem.
Within a few weeks of my visit, Nova will be far too big and dangerous for overpriced playtime sessions. Cats like her are most likely confined to one of those cramped cages my producer and I passed leaving the zoo, where they spend the rest of their life being speed-bred to crank out more adorable cubs. Or Nova might be sold to another breeder, or to someone who wants to keep her as a pet. Although no one tracks big cat ownership in the U.S., it’s estimated that there are likely more pet tigers in America than there are left in the wild. What’s more, depending on the species of cat, federal oversight is either limited or nonexistent. In some states, it’s easier to buy a lion — a 400-pound predatory killer — than it is to get a dog.
Animal rights activists have been pushing for decades to curb big cat ownership in this country, arguing that the industry is cruel, dangerous, and detrimental to conservation of cats in the wild. Now, reform appears within reach. The movement owes its momentum to, of all things, a murder-for-hire plot gone terribly awry. You might have seen the headlines in the Washington Post and New York magazine: Joe Exotic, a self-described “gay, gun-carrying redneck with a mullet,” among the largest tiger owners and breeders in the U.S., charged with conspiring to commit murder for hire. At its height, Joe’s zoo in Wynnewood, Oklahoma, which is where I visited Nova, housed more than 200 big cats, including lion-tiger hybrids, as well as about 60 other species, everything from lemurs to owls to giraffes. Joe even acquired a pair of alligators he claimed were once owned by Michael Jackson. Still, as one local told me, “The animals weren’t the entertainment. Joe was the entertainment.”
Last year, an Oklahoma City jury convicted Joe, whose legal name is Joseph Maldonado-Passage, of the murder-for-hire plots against a Florida activist and sanctuary owner named Carole Baskin. For Joe, Baskin had become something of an arch tiger rival. The news coverage mostly focused on Joe’s outlandish personality and the details of his decade-long feud with Baskin. But the jury also found Joe guilty of 17 wildlife crimes, including illegally killing five tigers and trafficking tigers across state lines — marking the first significant conviction of a tiger criminal in an American courtroom. “This verdict sends a shot across the bow to other roadside zoos who are playing fast and loose with federal regulations,” said Carney Anne Nasser, director of the animal welfare clinic at Michigan State University College of Law.
In other words, the bad boy of the big cat world might have inadvertently contributed to cleaning up the dirty industry he helped build and then exploited for much of his adult life.
Simba, a Bengal tiger, was sent to an animal sanctuary, Big Cat Rescue, in Tampa, Florida. (Matias J. Ocner/Miami Herald via AP)
* * *
Big cats are easier to find than you might think. I recently struck up a conversation with the chef at my favorite sushi joint in New York City. He asked what I’d been working on, and I filled him in on a bit of the Joe Exotic story and the big cat trade. To my surprise, he nodded along knowingly: “Oh yeah, a buddy of mine just got a serval!” Celebrity culture is another hot spot for exotic animal ownership. This past fall, Justin Bieber reportedly spent $35,000 on two savannah cats and created a dedicated Instagram page that quickly amassed more than 500,000 followers. When PETA criticized Bieber’s new pet choice, he posted a statement on his Instagram story telling the nonprofit group to “suck it” and “focus on real problems.”
Shopping for an unconventional animal used to mean scanning the classified sections of newspapers or fliers on the cluttered billboards at grocery stores and gas stations. But those analog methods of sale have long since given way to people hawking large cats in ways that are now more traditionally modern: closed Facebook groups and exotic pet websites. Getting an ocelot or a cheetah can be as easy as sending a DM or text, agreeing on a price, and setting a pick-up date. Depending on what state you live in, owning one of these animals might be entirely legal. And even if it’s not, there’s almost always a way to sidestep the rules, which can be confusing and are rarely enforced.
Save for a handful of regulations pertaining to animals listed in the Endangered Species Act (ESA), there’s almost no oversight of big cat ownership by the federal government. The Animal Welfare Act is supposed to ensure humane treatment of big cats and other captive animals, but the inspectors are overworked and many of the rules are weak, vague, or both. Although the Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) does technically require a permit to sell endangered species such as tigers, lions, leopards, or jaguars across state lines, unscrupulous sellers and buyers often don’t want to bother with permits and deal in untraceable cash payments. At trial, one buyer even testified to participating in sales marked as “donations.” Joe Exotic used this tactic for years to evade the gaze of law enforcement. He wasn’t the only one. At Joe’s trial, that same tiger owner testified: “Everybody marks donation.”
Same goes for regulations at the state level: Loopholes abound in the legislative patchwork governing big cat ownership. “There’s lots of ways tigers have been technically regulated on paper but in practice, not so much,” Nasser said. Roughly two thirds of states have some sort of regulations prohibiting private big cat ownership as pets. In 10 states, anyone can own a lion or tiger as long as they pay as little as $30 for a license from the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Four states — North Carolina, Wisconsin, Nevada, and Oklahoma — have no laws on the books at all.
Rules aside, very few people, no matter how well-intentioned, are prepared to own one of the world’s largest, deadliest predators. “Everybody wants a tiger cub, but nobody wants a tiger,” said Tim Harrison, a retired Ohio police officer and first responder who specialized in exotic creatures. These days, Harrison runs Outreach for Animals, a nonprofit that advocates responsible exotic pet ownership and trains emergency personnel to safely deal with animal-related crises. Harrison used to be a big cat owner himself, before realizing his mistake. “I was on the dark side,” he said, “thinking I was doing the right thing.”
Many big cat owners are subjected to what Harrison describes as a “baptism in reality,” learning firsthand that these adult cats are expensive and dangerous. “A big cat is like a walking, thinking IED,” he said. “You don’t know when that thing’s going to go off.” One of the most famous incidents took place in 2003 at a live performance by the popular entertainment act Siegfried and Roy. One of the duo’s iconic white tigers, Mantacore, knocked down Roy Horn, grabbed him by the neck, and dragged him awayo. First responders rushed Horn to the hospital in critical condition. He survived but only returned to the stage once more years later. Defenders of the popular act contended that Horn suffered a stroke mid-act and Mantacore was just trying to help him, but Harrison disagreed. He argued on national television that Mantacore had intended to kill Roy, and that Roy had brought this upon himself: He’d disrespected the largest predatory cat in the world by forcing the animal to do magic tricks.
No agency tracks the number of people attacked and killed by captive big cats. According to a database of incidents compiled by the Humane Society of the United States, 24 people have died and 294 have been injured in the U.S. since 1990. Those figures likely only represent a fraction of the real numbers. Not every case makes the news, and the people involved in these incidents don’t always divulge the true cause of injury. In 1999, when a family’s pet tiger killed a 10-year-old girl in Texas, the victim’s mother initially told emergency dispatchers that her daughter had cut her neck by falling off a fence. (She’d later testify she did not recall making the phone call.) In 2003, a man in New York City visited the hospital for a severe wound on his arm and leg; he claimed to have been bitten by a pit bull — not by Ming, the 400-pound tiger he had holed up in his Harlem apartment.
Big cats can threaten more than just their owners. The most infamous example occurred in 2011, when exotic animal owner Terry Thompson opened the doors to almost all of his pets’ cages before shooting himself. In what came to be known as the Zanesville massacre, law enforcement officers had to hunt and kill 18 tigers, 17 lions, and three mountain lions, as well as bears, a baboon, and wolves. “It was like Jumanji in real life,” said Harrison, who was one of the two dozen or so officers who responded to the incident. Many of the people who responded to the call that day suffered from post-traumatic stress disorder, Harrison claimed. They had no choice but to kill the animals, then they faced virulent public backlash for doing so.
Zanesville is an extreme example, but it’s not the only case of exotics turned loose. One problem is there’s a lack of places equipped to take in these animals — even zoos don’t want them. Since starring in a 2011 documentary The Elephant in the Living Room, about exotic cat ownership, Harrison gets about 30 calls a year from people desperate to find a new home for their lions or tigers. With few options, some people donate their cats to shady facilities that use them for breeding. Others abandon them. The New York Times recently reported that a woman looking for a place to smoke a joint stumbled upon a caged tiger in a vacant home in Houston. Unsurprisingly, the owner did not immediately come forward to claim the tiger, but she was later arrested and charged with one misdemeanor count of cruelty to a nonlivestock animal.
A sign warning motorists that exotic animals are on the loose rests on I-70 Wednesday, Oct. 19, 2011, near Zanesville, Ohio. (AP Photo/Tony Dejak)
* * *
As a boy, Joe Exotic raised pigeons and captured porcupines, racoons, and baby antelope at his childhood homes in Kansas and rural Wyoming. But it was the death of his older brother, Garold Wayne, in a car accident in 1997, that precipitated Joe’s entrance into the tiger business: Joe convinced his parents to use the roughly $140,000 settlement they received to open a wildlife rescue center.
Before Joe and his parents had completed the first cages at the GW Exotic Animal Memorial Foundation in 1999, someone dropped off an unwanted mountain lion and black bear. Soon after, they received a call about two tigers, a black leopard, and a mountain lion found in a backyard. Joe set out with a horse trailer and tranquilizers to collect the animals, which were skinny and malnourished. When Joe spoke to me this spring on the phone from a county jail in Oklahoma, he told me there was an excitement about the uncertainty and possibility of those early days. “I had no intention of being Joe Exotic or the Tiger King or anything like that,” said Joe, who came up with the “Tiger King” moniker because people struggled to pronounce his original surname, Schreibvogel. “But I never said no to a rescue.”
Pretty soon, Joe started breeding his own tigers. He bred some 400 big cats over the years. He sold the animals to buyers on both coasts for as much as $5,000 each. By the mid-2000s, Joe had become one of the largest exotic animal operators in the country. He owned dozens of species and put together a traveling magic show. Although Joe had been “about the animals” in the beginning, as time passed, according to Joe’s ex-boyfriend John Finlay, fame and profit monopolized his thinking. Joe’s niece, Chealsi Putman, who helped out at the zoo for years, noticed the same evolution. “It’s like he’s seen dollar signs,” Putman told me. “He figured out a way to make money and ran with it.”
Not all big cat owners are similarly motivated. For some, it’s a grossly misplaced desire to help an endangered species — not realizing that big cats bred in the U.S. are hybridized mutts that have no genetic worth for wild tiger conservation. For others, like 54-year-old Deborah Pierce, the motivation is something more akin to love, or infatuation. Pierce started small, rehabbing injured wildlife at her house and volunteering and working at a local veterinary clinic and zoo after she graduated from high school. But helping lion keepers wasn’t enough to satisfy Pierce. “I wanted one of my own to just spend time with,” she said.
Pierce was encouraged when she learned that at the time her home state of South Carolina had no laws preventing her from owning a big cat. She talked her husband into helping her construct a double-fenced pen on their secluded, wooded property. She easily found a dealer on the internet selling lion cubs for $1,500 — like Nova, “picture babies” that were too large for cub petting by the time of sale — and arranged to purchase a female cub. “I could afford her easier than I could afford a new bulldog,” Pierce said. She named the lion Elsa, and a few months later, she got Charlie, a baby cougar, to keep Elsa company.
That was 12 years ago. Pierce’s perspective has since changed. She’s emptied her savings account on her cats. They eat $5,000 worth of meat a year and the veterinary bills run around $10,000 annually. Last year, the county hit her with an $1,100 fine for not having the proper paperwork. (South Carolina started regulating big cats in 2018.) Pierce no longer has time to ride horses, her other great love, and her husband left her in 2016, breaking not only her heart, she said, but also Charlie and Elsa’s. She’s put a dream of moving out to Arizona on hold as well. State laws there strictly regulate private ownership of big cats, and finding a sanctuary where Elsa and Charlie could stay has proven too difficult. “They’re my best friends,” Pierce said, “but if I had it all to go over again, I wouldn’t have gotten them.”
At this point, Pierce has resigned herself to the long haul, perhaps as many as another eight years given the lifespan of captive big cats. “I just want to be able to give Elsa and Charlie a happy life,” she said. “Their happiness is more important than mine, in my eyes.”
A month after I visited Pierce, she emailed with bad news. Charlie had died in surgery. “His heart was still beating, but he wouldn’t breathe when the oxygen came off,” she wrote. “So, we let him slip away.” Elsa, she says, has been inconsolable, and Deb blames herself for not bringing Charlie to the vet earlier. The bill for Charlie’s last visit, which totaled $4,800, even after the vet gave Pierce a significant discount, has only added to her stress. “I just hope nothing happens to Elsa before money is available again,” she says. “That’s my number one worry right now.”
* * *
The modern exotic animal craze traces back to the ’70s and ’80s and a phenomenon called zoo babies. Each spring, interstate signs and TV commercials featured photos of blue-eyed, squealing balls of fuzz debuting at major zoos around the country, an irresistible marketing lure for families that turned out to snap photos and cuddle the newest arrivals. Zoo babies were among the industry’s number one moneymaking programs, and tigers were always the biggest draw. As an added bonus, zoos advertised these activities under the guise of conservation. “You’d get your T-shirt, get your picture taken, and you’d walk away feeling like you’ve saved the world — you’ve saved tigers,” Harrison said.
But there was a problem, and Harrison, who worked as an exotic animal veterinary assistant as a teenager in Ohio, noticed it. There were lots of zoo babies but no zoo adolescents. When Harrison eventually began asking the staff about what had happened to last year’s tiger cubs, he’d get vague answers about the animals being traded off to different zoos. To Harrison, that math didn’t add up: Even the largest zoos around the country had only two or three adult tigers. But zoos annually paraded hundreds of babies out for pictures and play sessions.
Jack Hanna holds two Bengal Tiger cubs that were born and bred in captivity during a groundbreaking ceremony at the Dallas Zoo in 1998. (AP Photo/Tim Sharp)
Harrison eventually learned the dark truth: After the cubs reached a certain age they became “zoo surplus” and were sold at exotic animal auctions to private buyers. These auctions were raucous events, attended mostly by veteran wildlife keepers and professional breeders that zoos relied on to supply their collections. Harrison attended a few and noticed the same employees who weeks earlier had been talking up the conservation value of the zoo’s tiger babies, holding cub after cub up by their armpits to sell to the highest buyer. The whole scene was commonplace at the time. “No one thought anything of it,” Harrison said.
The zoo baby phenomenon led to a surge in private big cat ownership. In the 1990s, according to Harrison, wildlife-related television spread the idea of owning a pet tiger to a much wider audience. Jack Hanna types bottle-fed cubs and paraded tigers on leashes on talk shows. The predators appeared no more dangerous than a golden retriever. “It was like somebody flipped a switch on,” Harrison said. At the time, Harrison was the lone police officer in Ohio who could handle big cat emergencies; he suddenly went from getting a couple calls a year to getting more than 100. After removing an unruly pet from someone’s property, he’d ask people why they thought it was a good idea to own a lion or tiger. Many responded it was because they’d seen it on TV. Harrison started calling it the Steve Irwin syndrome.
That turns out to be an apt diagnosis. According to research conducted by scientists at Duke University, seeing a wild animal in an unnatural, human setting — a chimpanzee drinking out of a baby bottle or sitting through a talk show interview — makes people less likely to donate to a conservation organization that aids that species and more likely to think the creature in question would make a great pet. According to Kara Walker, now a behavioral ecologist at North Carolina State University and lead author of the research, published in 2011 in the journal PLOS One, this also extends to people’s thought process after an encounter with a cub, which might go something like: Look at this cuddly tiger! I got to pet it for 20 minutes and it licked my hand and now I can have a tiger, too!
Enterprising private exotic animal owners capitalized on the moment. They realized they could make a killing holding their own cub petting events at malls, fairs, and roadside zoos, which compounded an already vicious breeding pattern. “I call it the breed and dump cycle,” said Nasser, the Michigan State law professor. That cycle is largely responsible for the proliferation of tigers throughout the U.S., and by the middle of the last decade, the most notorious of all the breed-and-dump outfits belonged to Joe Exotic.
But cub-petting events weren’t enough for Joe. Concerned with fame and fortune, he plotted ways to grow his online following and commercialize the business. He started selling Tiger King–branded candy, apparel, and condoms. He also kept zoo costs down by euthanizing sterile or defective tigers and turned donated animals that weren’t moneymakers — especially emus — into cat food. During regular inspections of Joe’s zoo, the USDA cited hundreds of American Welfare Act violations. The agency conducted four investigations, including one that looked into the deaths of 23 tiger cubs from 2009 to 2010. (As an endangered species, tigers cannot be killed unless there is a legitimate reason, such as ending the life of a sick tiger.) Animal rights groups such as PETA conducted their own covert investigations, revealing what they claimed was gross abuse — dead and dying animals, extremely crowded cages lacking basic necessities such as water, and untrained staff who routinely abused animals. In retaliation, Joe launched social media attacks and filed dozens of contrived police reports claiming his accusers were the ones who were breaking the law.
For years, Joe’s strategy worked: Profit off cubs. Evade his enemies. Skirt the law. It probably would’ve continued to work had Joe’s path not collided, as he once put it, with “some bitch down there in Florida.”
* * *
Carole Baskin in 2017 walking the property at Big Cat Rescue, a nonprofit sanctuary committed to humane treatment of rescued animals, often coming from exploitive for-profit operations. (Loren Elliott/Tampa Bay Times via AP)
Vultures circle overhead as Carole Baskin and I make our way along a secluded stretch of the Upper Tampa Bay Trail, about 15 miles outside of downtown Tampa. A spring breeze flutters her waist-length blond hair and blows through the thick surrounding brush of oaks and palmettos. Despite the blue sky and sunshine, the trail is empty. The only sound is the rustle of leaves and crunch of Baskin’s leopard-print boots on the pavement. It was this trail, Baskin explained to me, on which she regularly bikes to work, that a hitman had identified as a place to take her out.
Baskin is arguably the most well-known activist in the country campaigning against big cat ownership. She also takes in unwanted exotic cats at Big Cat Rescue, her sanctuary in Tampa, which currently houses 66 cats belonging to 11 different species. It’s one of the few places in the U.S. capable of providing these animals with a safe, reasonably good life in captivity.
Like Harrison, Baskin used to be part of the problem. A pivot from big cat owner to big cat conservationist is a common story among advocates in the field. Baskin stumbled into owning an exotic cat in the early 1990s at the age of 31. She and her ex-husband, Don, worked together in the real estate business. They used llamas to mitigate the brush on the Florida properties they sold, and the easiest place to get a llama was at an exotic animal auction. At one memorable event, a man seated next to Baskin bid on a baby bobcat. Baskin couldn’t help but lean over and whisper: “When that cat grows up, she is going to tear your face off.”
“I’m a taxidermist,” the man replied. “I’m just gonna club her in the head in the parking lot and make her into a den ornament.”
Baskin was horrified. Don outbid the man and they brought home the 6-month-old kitten, which Baskin named Windsong. As Windsong grew, the bobcat terrorized Baskin’s daughter and the family’s German shepherd. The solution, Baskin decided, was to get Windsong a playmate. Don found a guy in Minnesota who agreed to sell them a bobcat kitten. Turned out, the man was a fur farmer; Baskin and Don came back from that trip with 56 bobcat and lynx kittens — everything the farmer had for sale. The following year, they returned to rescue the 28 adult cats, too.
With their home overrun by exotic cats, Baskin and Don transformed a nearby 40-acre property they owned into a sanctuary, albeit with misguided tourism and breeding components. They called it Wildlife on Easy Street. They amassed a collection of at least 150 exotic cats of 17 species. For $75 a night, visitors could share a small cabin with a bobcat, cougar, or serval. Baskin started breeding half a dozen big cat species, including ocelots and leopards. Pre-internet, all Baskin’s information came from breeders and dealers, who had their own motivations. “They were saying, ‘Oh, you should breed these animals because they’re endangered and the zoos don’t know what they’re doing and they’re going to disappear from the wild,’” Baskin said. “So, we thought, well, that’s something we could definitely do to help save the cats.”
But people who bought kittens from Baskin often returned the cats after they grew up. Once, a Siberian lynx — an animal Baskin swore she recognized from when it was young — showed up at auctions. People started donating cats to Baskin’s sanctuary by the dozens. Some years, she turned away hundreds of animals due to a lack of space. Around the same time, Baskin started attending conferences held by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums, where she learned a few hard truths. None of these cats had any conservation value for their species. In fact, Baskin realized big cats had no business being bred and kept as pets at all.
In 1997, Baskin pulled a 180. She stopped breeding and began spaying and neutering all of her animals. She started enforcing a new rule in 2003: Big Cat Rescue, her rebranded sanctuary, would take any unwanted tiger, lion, savannah, or whatever else, but in return the owner had to sign a contract forfeiting their right to own a big cat. “We’re the only place that absolutely insists that if you’re going to dump an animal here, you are never going to own another exotic cat,” Baskin said.
The contracts were a good start, but Carole had an even bigger goal in mind: ending all big cat ownership. Critical to realizing that vision is Howard Baskin, a businessman from Poughkeepsie, New York, who Carole met at an event at the Florida aquarium in 2002. (Baskin’s previous husband walked out the door one day and was never seen or heard from again — though she was questioned, no evidence was ever found linking Baskin to his disappearance.) A lifelong bachelor with a Harvard MBA and a law degree from the University of Miami, Howard appears in many ways Carole’s opposite. Carole dresses like a Woodstock attendee and carries herself with the breezy grace of a dancer. Howard trundles along, turtle-like, in dad-style khakis with a cell phone holster. But they make a good team. Howard handles the administrative and legal duties and Carole focuses on advocacy. “On our honeymoon, we wrote a 25-year plan to stop the big cat abuses that bad guys hold dear,” Carole said.
Carole and Howard started by setting up a Google alert for cub-petting events around the country. Baskin would email the venues explaining the downsides of cub petting and asking them to cancel the event, and if they did not respond, she would then direct her hundreds of thousands of social media followers to flood the venues with emails explaining the downsides of cub petting. One by one, malls began to call off the events. (Fairs proved more impervious to the bad PR.) Baskin homed in on the primary players in the exotic cat world and publicized her findings on 911animalabuse.com, a website she created. One individual stood out among all the breeders: a guy with a dozen different aliases, but whose cub petting photos always included the same motley group of heavily tattooed, pierced, longhaired workers. It was Joe Exotic’s crew.
* * *
Joseph Maldonado in 2013, answering a question during an interview at the zoo he then ran in Wynnewood, Oklahoma. (AP Photo/Sue Ogrocki, File)
As Baskin ramped up her efforts, Joe’s profits plummeted. In retaliation, he launched a smear campaign against Baskin’s nonprofit. He renamed his cub-petting show Big Cat Rescue Entertainment and designed a near-identical copy of Baskin’s Big Cat Rescue logo. The Baskins sued Joe in 2011 for copyright infringement. Joe countersued, but those claims were tossed out by a judge. Joe eventually agreed to a consent judgement north of $1 million, which he had no intention of paying. He did everything he could to obscure his money, changing the name of his zoo and transferring assets to an account in his mother’s name. Joe also made a series of increasingly unhinged videos posted on social media threatening Baskin’s life. One featured an effigy of Baskin. Another depicted Baskin’s head in a jar, Silence of the Lambs–style.
In 2015, Baskin got a call from a woman who said Joe had inquired with her then-husband, who she said was a former military sharpshooter, about hiring her husband to kill Baskin. Nearly two years later, Baskin received a similar warning from a woman named Ashley Webster, an aspiring wildlife biologist from Colorado who had just started working at Joe’s park. In a deposition, Webster recalled Joe saying “something along the lines of he’d give me a few thousand dollars to go to Florida and put a bullet in [Baskin’s] head.” Carole and Howard reported the incidents to police, but nothing seemed to come of it.
Unbeknownst to the Baskins, the FWS had launched an investigation of Joe and his zoo in 2016 for potential animal trafficking violations. The saga, which has been detailed at length in various news reports, involved an FWS agent convincing a man named James Garretson, who’d done big cat business with Joe in the past, to become a government informant. Garretson agreed to attempt to arrange a meeting between Joe and an undercover FBI agent posing as a hitman. At the outset, what the feds learned was that Joe already had his own scheme in the works: He planned to hire Allen Glover, a man from South Carolina who’d been convicted of assault, for the job.
Glover was a longtime associate of a man named Jeff Lowe, who’d done business with Joe and shortly after started hanging around the Tiger King and his world. Joe, who was under the impression that Lowe was wealthy, made his new friend the co-owner of the zoo’s land, along with his mother. In exchange, Lowe, according to a deposition, said he would pay a portion of Joe’s mounting bills at the zoo and let Joe run the park as usual. “The whole thing was to put the zoo in his name so Carole couldn’t get it,” Joe told me. But Lowe had other plans. In a May 2018 deposition, Lowe admitted that he was interested in the zoo for himself.
According to Glover, who testified at Joe’s trial, he and Joe settled on a $5,000 down payment for the hit on Baskin and discussed other details such as what weapon to use. Glover said that Joe eventually gave him $3,000 cash and a cell phone loaded with pictures of Baskin. But during his two days on the stand, Glover claimed he’d always intended to take the money and run. For his part, Joe denies giving Glover the phone, and said that Lowe was the one who instructed him to pay Glover. (Lowe declined multiple interview requests for this story.) Glover did travel east, but in court he said he only made it as far as an unknown beach in Florida, where he partied most of the money away in a single night. Glover claimed that it was not his intention to kill Baskin in Florida, but rather to warn her that Joe wanted her dead.
Meanwhile, in December 2017, Joe agreed to Garretson’s proposed meeting with the undercover FBI agent. The agent quoted Joe a $10,000 fee for the hit. The two agreed to a rough outline of a deal, but Joe never followed through. Instead, in June, without notice, Joe and his new husband, Dillon Passage, loaded up four dogs, two baby tigers, and a baby white camel, and took off. (Joe’s previous husband, Travis Maldonado, accidentally shot and killed himself in October 2017.) “Joe Exotic, as far as I was concerned, was dead,” Joe told me. He was going to create a new life with Passage.
Joe and Passage left Oklahoma and headed east, eventually landing in Gulf Breeze, Florida. On a sunny September morning, Joe pulled up to the local hospital. He planned to walk in and apply for a job. Instead, unmarked cars surrounded him. U.S. marshals jumped out, guns pointed, yelling at Joe to get on the ground.
Lowe had indeed been working with federal agents since as early as June. Less than a month before Joe’s arrest, Lowe bragged on Facebook that he’d been “setting [Joe’s] ass up for almost a year.” And it seems Lowe got what he wanted. He and his wife, Lauren, now run Joe’s old zoo, where they continue to churn out cubs for playtimes. The nursery lineup recently featured Nova, the rambunctious tiliger who bit my producer.
Jeff Lowe and Lauren Dropla with Faith the liliger at their home in 2016 inside the Greater Wynnewood Exotic Animal Park in Wynnewood, Oklahoma. (Ruaridh Connellan/BarcroftImages / Barcroft Media via Getty Images)
* * *
This past March, journalists from around the country descended on downtown Oklahoma City for Joe Exotic’s trial. Garretson and Glover testified against Joe. Joe’s ex-boyfriend John Finlay testified too. Joe took the stand at the end of the seven-day affair. He said he never intended for anyone to kill Carole Baskin and claimed to have known that Garretson, Glover, and Lowe were conspiring to take him down. He said he played along to better understand their plan and gather evidence he could use against them. The jury deliberated for less than three hours, then found Joe guilty on all charges, including illegally killing five tigers and illegally transporting endangered species across state lines. In January, a judge sentenced Joe to 22 years in federal prison. In a Facebook post, Joe maintained his innocence and said he plans to appeal.
Nasser hopes that Joe’s conviction triggers the beginning of what she calls “a long-overdue Blackfish moment for captive tigers,” referring to the popular documentary that exposed problems with the sea-park business’ treatment of orcas and led to numerous SeaWorld boycotts. Pending any appeals, the Baskins and other activists believe the Tiger King’s downfall could topple the industry. They hope to use the momentum and notoriety of Joe’s case to usher in sweeping legal reform of big cat ownership in the U.S.
Baskin has been pushing for this type of reform since 1998, when she began working on what’s called the Captive Wildlife Safety Act, a federal bill unanimously voted into law in 2003 that barred the sale of big cats as pets across state lines. Loopholes in the law, however, have rendered it largely ineffective. She and Howard — along with major nonprofit groups such as the Humane Society and the International Fund for Animal Welfare (IFAW) — have been pushing a new bill, the Big Cat Public Safety Act. First introduced in 2012, the legislation would ban all public contact with big cats, including cub petting, and would require all big cat owners to register their animals. Howard hired a top Republican lobbying firm in 2014 to work with Harrison to champion the bill — not for its conservation clou, but on its pubic safety merits. Senator Susan Collins signed on to the bill last November, the first republican cosponsor. Three other Republican senators, including Richard Burr of North Carolina, have since joined Collins. The registrations would provide officials with valuable insight into who owns what and where — potentially life-saving information in the event of, say, a tornado blowing through a tiger park. The ban on cub petting, though, is the most important part of the bill, as proponents believe it would disincentivize the breeding of big cats.
Last year, the bill made it out of the Committee on Natural Resources in a bipartisan vote and could soon head to the House floor, where it has broad support. “Law enforcement has enough problems trying to protect the public without having to run into a house where there might be a tiger,” said Harrison. Dozens of Republican lawmakers support it — a party full of politicians, who, Harrison said, for the most part “don’t give a crap about cats.”
For now, though, cub petting remains a lucrative industry. According to data compiled by a team of New York University researchers in 2016, at least 77 facilities across the country allowed interactions with exotic animals (about a quarter of those were with big cats). In a follow-up study in 2019, which focused specifically on tiger petting, those same zoos were still open. One operation in Myrtle Beach, South Carolina, run by Bhagavan “Doc” Antle, charges up to $339 per person for tours and cub-petting sessions. Supporters of the Big Cat Public Safety Act believe that ending cub petting would go a long way toward stopping the trade of big cats altogether. “Without ending public contact, you’re not going to have sufficient incentive for all the fly-by-night exhibitors to stop breeding,” said Nasser.
The new protections would extend to smaller species such as jaguars and even unnatural hybrids like Nova. They’d also apply to accredited zoos. While the zoo baby phenomenon is no longer as rabid as it once was, not all zoos have ended the practice of animal meet-and-greets. The Nashville Zoo provides clouded leopard cubs for zoo fundraisers and media events (zoo officials say that play and petting sessions are not allowed), and the Dallas Zoo recently held a cheetah photo op session for the Dallas Stars (zoo officials point out none of the Stars were able to pet the cheetah, however).
Limiting and eventually banning big cat ownership in the U.S. would almost certainly be a boon for the species worldwide. Fewer than 4,000 tigers survive in the wild today. But they are farmed by the thousands in China, Laos, and other Southeast Asian countries where big cat parts are sought after as erroneous medicinal remedies and status-touting commodities. Tiger bone wine, in particular, is considered a cure-all tonic, a virility booster for men, and a coveted, favor-winning gift for superiors, elders, and relatives.
Tiger bone is banned in China, and it’s illegal to trade big cats and their parts in Vietnam and elsewhere in Southeast Asia. But there’s a robust black market for tiger bones, skin, teeth, and claws — and farmed tiger parts keep demand for these items alive, perpetuating poaching. The U.S. government considers closing tiger farms integral to saving wild tigers, but when State Department officials try to negotiate this point with foreign diplomats — especially those from China — they’re often told to clean up their own mess first. “When I talk to government leaders about tiger farming in many of the Asian countries, quite often they ask me, ‘What about tigers in the U.S.? What role do the tigers in private backyards in the U.S. contribute to wild tiger conservation?’” said Grace Ge Gabriel, IFAW’s Asia regional director. “Literally, I am speechless. I don’t have an answer.”
A tiger named Seth rests above a pond at Big Cat Rescue in 2017. (Loren Elliott/Tampa Bay Times via AP)
* * *
After I first contacted Joe following his trial, we spoke several times over the next few months. He liked to talk, only cutting off our calls if another person in the prison needed to use the phone. Joe never admitted any wrongdoing when it came to Baskin; rather, he was eager to defend his innocence. Multiple times he told me, “That whole mess was nothing but a setup.”
Joe did cop to something else, though. He said being locked up in jail had made him realize he’d mistreated the animals all those years, depriving them of their freedom and robbing them of their dignity by keeping them behind bars. Joe told me he regretted having done that. “Now that I have nothing to do besides sit in a cell with no TV, no radio, no nothing, I know exactly what I did to those [animals],” he said. “We can all be drove crazy by doing nothing.”
To make amends, Joe told me he plans to create a new zoo when he gets out. This one without any cages. Just tigers roaming free.
* * *
You can listen to our four-part “Cat People” podcast series on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts.
Rachel Nuwer is an award-winning freelance journalist who reports about science, travel, food and adventure for the New York Times, National Geographic, BBC Future and more. Her multi-award winning first book, Poached: Inside the Dark World of Wildlife Trafficking, was published in September 2018 with Da Capo Press.
Editors: Mike Dang and Chris Outcalt Illustrator: Zoë van Dijk Fact checker: Matt Giles Copy editor: Jacob Gross
from Blogger https://ift.tt/2IRh34g via IFTTT
0 notes