#aerospace and operational physiology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Lessons for Leaders: Human Factors and Decision-Making Under Pressure
Introduction Leadership is not always smooth sailing. Picture this: you’re the captain of a ship, navigating a stormy sea, with the crew depending on your every move. Decisions must be made—quickly and accurately. No pressure, right? Yet, this scenario is a perfect metaphor for leadership, especially when the stakes are high. This blog explores how understanding human factors—the science of how…

View On WordPress
#aerospace#aerospace aerospace and operational physiology aviation human factors occupational physiology#aerospace and operational physiology#aerospace physiology#aviation#aviationsafety#blog#blogging#dailyprompt#dailyprompt-2102#dailyprompt-2115#driving#exercise#fasting#fatigue#flight safety#health#healthcare#human#human factors#Human Performance#humanfactors#humanperformance#India#industry#intermittent fasting#military#nutrition#occupational physiology#occupational safety
1 note
·
View note
Text

Latest space station science reveals news for astronaut health and telescope longevity
Recent findings from the International Space Station address wound healing, fine motor control in space, and radiation resistance by the station's Glowbug gamma-ray telescope.
Bioprinted patches could help wounds heal
Researchers have successfully demonstrated the function of a handheld bioprinter that could provide a simple and effective way to treat wounds in space using human skin cells. Crews could use this technology to treat their own injuries and protect crew health and mission success in the future.
Space flight can affect how wounds heal. The Bioprint FirstAid device tested a process for bioprinting a patch to cover a wound and accelerate healing. In the future, a crew member's own cells may be used to create personalized patches for treating an injury. The bioprinting device is easy to use, can be tailored to specific needs, has a low failure rate, and its mechanics are electronics- and maintenance-free. This ESA (European Space Agency) investigation was coordinated by the German Aerospace Center (DLR).
Countering post-flight proficiency challenges
The day they return from space flight, astronauts demonstrate significant impairments in fine motor control and the ability to multitask in simulated flying and driving challenges. This finding could help develop countermeasures so crew members can safely land and conduct early operations on the moon and Mars.
Manual Control used a battery of tests to examine how spaceflight affects cognitive, sensory, and motor function after landing. Researchers concluded that subtle physiological changes that occur during spaceflight degrade post-flight performance. Subsequent tests showed recovery of performance once exposed to the task, suggesting that simulation training immediately before a task could be an effective countermeasure. Researchers also suggest limiting dual or competing tasks during mission-critical phases.
Gamma-ray telescope resilient to space radiation
Researchers have found that the space station's Glowbug gamma-ray telescope could perform in the space radiation environment for multi-year missions. Radiation can affect these types of instruments, but Glowbug regularly detected gamma ray bursts (GRBs) during its one-year operation. Studying GRBs can help scientists better understand the universe and its origins.
Glowbug demonstrated technology to detect and characterize cosmic GRBs, primarily short GRBs, which result from mergers of compact binary star systems containing either two neutron stars or a neutron star and a black hole. Short GRBs produce gravitational waves, ripples in space that travel at the speed of light. Studying these gravitational waves could provide insight into the star systems where they originate and the behavior of matter during the mergers.
IMAGE: A simulator used to test crew members’ ability to fly and drive after spaceflight. Credit: NASA
1 note
·
View note
Text

U.S. Navy grants contract to Collins Elbit for sophisticated display on U.S. F/A-18 pilot helmets
Fernando Valduga By Fernando Valduga 09/11/2023 - 14:00 in Military
Collins Elbit Vision Systems (CEVS) received a contract from the Aircraft Division of the Naval Air Warfare Center for the development, engineering, logistics and test support of the improved helmet-mounted signaling system used in F/A-18E/F Block III and E/A-18G aircraft.
With this contract, CEVS - a joint venture between Collins Aerospace, a Raytheon company, and Elbit Systems of America - formally presents the Zero-G Helmet Mounted Display System+ (HMDS+). The Zero-G HMDS+ will provide an expanded view of the battle space inside the pilot's helmet to allow faster decision making, increasing survival and effectiveness.
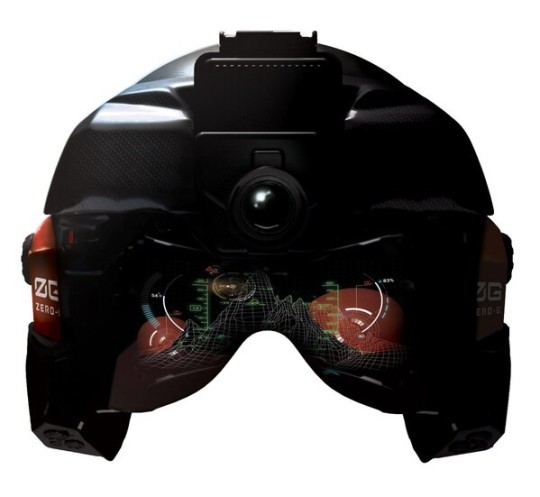

"The team followed a new development process that incorporated initial and continuous information from the pilot to put the best solution in the field. The result is an innovative and adaptable HMDS that will follow a long and successful line of HMDS in the CEVS field," said CEVS co-general manager Jeff Hoberg.
In addition to providing greater capacity, the balanced and ultralight design of the Zero-G HMDS+™ will significantly decrease the physiological tension that pilots experience.
For the last 30 years, CEVS has been at the forefront of developing and providing solutions that keep pilots safe and ready for battle.
Tags: Military AviationCollins AerospaceElbit SystemsF/A-18E/F Super HornetHMDS - Helmet Mounted Display System
Sharing
tweet
Fernando Valduga
Fernando Valduga
Aviation photographer and pilot since 1992, he has participated in several events and air operations, such as Cruzex, AirVenture, Daytona Airshow and FIDAE. He has work published in specialized aviation magazines in Brazil and abroad. Uses Canon equipment during his photographic work throughout the world of aviation.
Related news
MILITARY
VIDEO: Remotely piloted aircraft makes history by landing on British aircraft carriers at sea
11/09/2023 - 12:00
MILITARY
Rolls-Royce will complete initial tests of the F130 engine for the B-52J by the end of the year
11/09/2023 - 10:00
MILITARY
Delivery of Danish F-35 fighters delays again
11/09/2023 - 08:33
SAAB
Saab acquires U.S. Artificial Intelligence solution provider CrowdAI
11/09/2023 - 08:12
Rafale fighters of the Air Force of the Emirate of Qatar.
MILITARY
Rafales on the rise? French hunting seeks additional sales in the Middle East
10/09/2023 - 13:00
MILITARY
More photos of car tires protecting Russian military aircraft
09/09/2023 - 21:42
homeMain PageEditorialsINFORMATIONeventsCooperateSpecialitiesadvertiseabout
Cavok Brazil - Digital Tchê Web Creation
Commercial
Executive
Helicopters
HISTORY
Military
Brazilian Air Force
Space
Specialities
Cavok Brazil - Digital Tchê Web Creation
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Digestive Enzyme Market to Witness High Growth Owing to Rising Consumer Awareness About Digestive Health
Digestive enzymes are proteins that help break down food into smaller components that can be absorbed and utilized by the body. They play a crucial role in digestion by breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Growing preference for low-fat, high-fiber diets; rising cases of digestive disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS); and increasing consumer awareness about digestive health are some of the key factors promoting digestive enzymes market.
The Global Digestive Enzyme Market is estimated to be valued at US$ 857.43 Mn in 2024 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 9.5% over the forecast period 2024 To 2031. Key Takeaways Key players operating in the digestive enzyme market are National Enzyme Company, Garden of Life LLC, Country Life LLC, Rainbow Light Nutritional System Inc., Food State Inc., Matsun Nutrition, Metagenics, Inc., TwinLab Corporation, Abbott Nutrition, Amway Corporation, Klaire Labs, Zenwise Health LLC, Integrative Therapeutics, LLC, Douglas Labs, Enzymedica Inc., Thorne Research Inc., Pure Encapsulations, LLC, Ortho Molecular Products Inc., Allergy Research Group, and Biotics Research Corp. The increasing occurrence of gut-related health issues and growing consumer awareness regarding digestive health provide key opportunities for market players. Technological advancements in enzyme engineering help develop enzymes that can withstand heat and acidity of the digestive tract and effectively break down macronutrients. Market Drivers The rising geriatric population is one of the major drivers of the Digestive Enzyme Market Share. Older adults are more susceptible to digestive disorders due to age-related physiological changes and declining enzyme production. Therefore, digestive enzymes supplements help enhance their digestive health. Another important driver is the increasing prevalence of lifestyle diseases like obesity and diabetes. Digestive enzymes play a role in weight management and help metabolize food more efficiently in patients with diabetes. The market is also driven by changing consumer preferences for enzymatically pre-digested and hypoallergenic foods
Fastest growing region: Asia Pacific region is poised to grow at the fastest pace during the forecast period, estimated to expand at a CAGR of over 11%. Factors such as rising health consciousness, growing disposable incomes, increasing digestive ailments and preference for herbal/natural remedies will drive higher adoption of enzyme supplements. China and India offer massive untapped market opportunities owing to their large population bases and improving economic conditions.
Get more insights on Digestive Enzyme Market
About Author:
Money Singh is a seasoned content writer with over four years of experience in the market research sector. Her expertise spans various industries, including food and beverages, biotechnology, chemical and materials, defense and aerospace, consumer goods, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/money-singh-590844163)
0 notes
Text

Retired Air Force Colonel Merryl Tengesdal (born May 30, 1971) is the first African American female U-2 pilot in history and the first African American woman to fly the Air Force’s U-2 Dragon Lady Spy Plane. She is the only African American woman alongside five white women and two African American men to fly spy planes.
She was born in the Bronx. She graduated from the University of New Haven in Connecticut with a BS in Electrical Engineering. She completed the Navy’s Officer Candidate School.
She flew the SH-60B Seahawk helicopter, a derivative of the Army’s UH-60 Black Hawk. The SH-60B Seahawk is used for anti-submarine warfare, search and rescue, anti-ship warfare, drug interdiction, cargo lift, and special operations.
She participated in combat operations for the Navy (1997-2000) in the Caribbean, South America, and the Middle East. She became an instructor pilot on the T-6 Texan II for the Joint Student Undergraduate Pilot Training program at Moody Air Force Base. She cross-commissioned in the Air Force and after undergoing the rigorous U-2 pilot training program for nine months and conducting training missions aboard the TU-2S, she emerged as one of few to qualify to fly the Lockheed U-2S Dragon Lady at Beale Air Force Base.
She was the 9th Reconnaissance Wing Chief of Flight Safety and 9th Physiological Support Squadron Director of Operations. She served as Commander of Detachment 2 WR/ALC where she was in charge of flight test and Program Depot Maintenance for the U-2S aircraft. She worked at the North American Aerospace Defense Command and Northern Command J8 staff. She became the Deputy Operations Group Commander and then Inspector General of the 9th Reconnaissance Wing. She was the Director of Inspections for the Inspector General of the Air Force at the Pentagon before retiring from the Air Force in 2017 as a Colonel.
She broke racial and gender barriers as a U-2 pilot in a field that is still dominated by white males. As such she is an inspiration to young women and particularly young Black women. #africanhistory365 #africanexcellence
0 notes
Text
Digital Twins: Analyzing Growth and Emerging Trends
In the realm of digital transformation, the concept of a "digital twin" has emerged as a powerful tool, reshaping the way we design, simulate, and manage physical assets and systems. A digital twin is a virtual replica or representation of a physical object, process, or system, augmented with real-time data and analytics. By mirroring the physical world in a digital environment, digital twins enable organizations to gain valuable insights, optimize performance, and drive innovation across various industries and sectors.
Understanding Digital Twins
At its core, a digital twin is more than just a 3D model or simulation. It is a dynamic, data-driven replica of a physical entity, continuously updated with real-time information from sensors, IoT devices, and other sources. This virtual representation enables organizations to monitor, analyze, and simulate the behavior of physical assets or systems, facilitating informed decision-making and proactive management.
Applications Across Industries
Digital twins find applications across diverse industries and sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, automotive, aerospace, energy, and infrastructure. Some common applications include:
Manufacturing: Digital twins enable manufacturers to simulate production processes, optimize equipment performance, and predict maintenance needs, leading to improved efficiency and quality.
Healthcare: In healthcare, digital twins can replicate patient physiology, enabling personalized treatment planning, surgical simulations, and medical device optimization.
Automotive: Automotive companies utilize digital twins to design and test vehicle prototypes, simulate driving conditions, and optimize vehicle performance and safety features.
Aerospace: Digital twins facilitate the design, testing, and maintenance of aircraft and spacecraft, enhancing safety, reliability, and operational efficiency.
Energy: In the energy sector, digital twins are used to monitor and optimize power plants, predict equipment failures, and optimize energy production and distribution.
Infrastructure: Digital twins of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure assets enable predictive maintenance, lifecycle management, and urban planning, ensuring resilience and sustainability.

Key Benefits and Challenges
The adoption of digital twins offers several key benefits, including:
Improved Efficiency: Digital twins enable organizations to identify inefficiencies, optimize processes, and reduce downtime, leading to cost savings and increased productivity.
Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing real-time data, digital twins can predict equipment failures, schedule maintenance proactively, and extend asset lifespan.
Informed Decision-Making: Digital twins provide stakeholders with valuable insights and predictive analytics, enabling informed decision-making and risk management.
However, the implementation of digital twins also poses challenges, such as data integration, cybersecurity, scalability, and interoperability. Addressing these challenges requires robust data governance, cybersecurity measures, and collaboration across organizational silos.
The Future of Digital Twins
As technology continues to evolve, the potential of digital twins is poised to expand further. Advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT connectivity will enable more sophisticated and autonomous digital twins, capable of self-optimization and adaptive control.
In conclusion, digital twins represent a paradigm shift in how we conceptualize, design, and manage physical assets and systems. By harnessing the power of digital twins, organizations can unlock new opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and sustainability, paving the way for a smarter, more connected future.
0 notes
Link
The 2023 Annual Highlights of Results from the International Space Station is now available. This new edition contains bibliometric analyses, a list of all the publications documented in fiscal year 2023, and synopses of the most recent and recognized scientific findings from investigations conducted on the space station. These investigations are sponsored by NASA and all international partners – CSA (Canadian Space Agency), ESA (European Space Agency), JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), and the State Space Corporation Roscosmos (Roscosmos) – for the advancement of science, technology, and education. These new peer-reviewed publications include insights that advance the commercialization of space and benefit humankind. Over 4,000 scientific publications have been collected from more than 5,000 investigators during the life of the space station. Between Oct. 1, 2022, and Sept. 30, 2023, more than 300 publications were reported, most of them undergoing rigorous scientific review before release and dissemination. An in-depth bibliometric analysis of station science shows that the citation impact of these publications has been above national and global standards since 2010. This impact demonstrates that space station science continues to produce groundbreaking results for investigators around the world to further explore. Some of the findings presented in this edition include: Improved measurement of cosmic particles (Italian Space Agency) New ultrasound technologies for detection of physiological changes (CSA) Enhanced understanding of coordinated function in brain activity (ESA) Development of better semiconductor materials (NASA) Impacts of spaceflight on connective tissue for improved tissue remodeling (ROSCOSMOS) Understanding the behavior of granular materials for better spacecraft design (JAXA) The content in the Annual Highlights of Results from the International Space Station has been reviewed and approved by the Program Science Forum, a team of scientists and administrators from the international partnership of space agencies dedicated to planning, improving, and communicating the research operated on the space station. See the list of Station Research Results publications here and read more about the space station’s annual highlights of results and accomplishments here. Keep Exploring Discover More Topics Space Station Research Results Space Station Research and Technology ISS National Laboratory Opportunities and Information for Researchers
0 notes
Text
What is shot peening ?
Ever Wondered What is shot peening ? Shot peening is a specialized surface treatment technique used to enhance the durability, strength, and performance of various materials, particularly metals and alloys. By subjecting a component's surface to high-velocity, small, spherical particles, shot peening introduces controlled compressive stresses that counteract tensile stresses and improve the material's resistance to fatigue, cracking, and corrosion. This article delves into the principles, process, and applications of shot peening as an essential method in modern engineering.
The Principles of Shot Peening
The fundamental principle behind shot peening lies in its ability to induce beneficial residual stresses into the material's surface. The process involves directing a stream of tiny, round media (such as steel, glass, or ceramic beads) at the target component using specialized equipment. As these particles collide with the surface, they create localized plastic deformation, leading to the development of compressive stresses on the outer layer. These compressive stresses act as a barrier against potential cracks and enhance the material's fatigue life, making it more reliable under cyclic loading conditions.
The Shot Peening Process
The shot peening process is carried out with precision, as the intensity and coverage of the peening effect are critical to its success. Several key factors are considered during the process:
Media Selection: The choice of media depends on the material being treated and the desired outcome. Harder media imparts deeper compressive layers, while softer media is suited for delicate materials.
Particle Velocity: The kinetic energy of the particles is crucial in determining the depth and intensity of the compressive layer. The velocity is carefully controlled to ensure effective results without causing surface damage.
Coverage and Overlapping: Ensuring complete coverage of the component's surface while avoiding over-peening is essential. Overlapping patterns are employed to maintain uniform stress distribution.
Applications of Shot Peening
Aerospace Industry: Shot peening is extensively used in aircraft and spacecraft components like turbine blades, landing gears, and engine components. The treatment helps improve fatigue resistance and extends the service life of critical parts.
Automotive Sector: In the automotive industry, shot peening enhances the durability of various engine and transmission components, improving their performance and reducing the risk of premature failure.
Medical Implants: Medical implants like orthopedic implants benefit from shot peening, as it increases their resistance to wear and fatigue in the demanding physiological environment.
Industrial Machinery: Shot peening finds applications in various industrial machinery components, such as gears, springs, and shafts, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing downtime.
Conclusion
Shot peening is a highly effective surface treatment process that enhances material performance by inducing controlled compressive stresses. Its ability to improve fatigue resistance and prevent crack propagation makes it a valuable technique in multiple industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and manufacturing. As technology continues to advance, shot peening will likely remain a critical tool in engineering, ensuring the longevity and reliability of vital components. By embracing this unique method, engineers can optimize material performance and contribute to the advancement of modern technologies.
0 notes
Text
Lessons from Aerospace Physiology for Everyday Fitness and Wellbeing
Ever wonder what fighter pilots and astronauts can teach you about your morning jog or your latest attempt at a 10-minute plank? Surprisingly, a lot. Aerospace physiology, the science of how the human body adapts to the extreme conditions of flight and space, offers some incredible insights into how we can live healthier, fitter, and more resilient lives here on Earth. Spoiler alert: you don’t…

View On WordPress
#aerospace#aerospace aerospace and operational physiology aviation human factors occupational physiology#aerospace and operational physiology#aerospace physiology#aviation#aviationsafety#blog#blogging#dailyprompt#dailyprompt-2102#dailyprompt-2115#driving#exercise#fasting#fatigue#flight safety#health#healthcare#human#human factors#Human Performance#humanfactors#humanperformance#India#industry#intermittent fasting#military#nutrition#occupational physiology#occupational safety
1 note
·
View note
Text
Careers in Space Science
Space is a field of science that includes all scientific disciplines including space exploration and the study of natural phenomena and physical bodies that occur in outer space, such as space medicine and astrobiology. It is also considered as a science which covers a broad range of disciplines, from meteorology and geology to lunar, solar, and planetary science, to astronomy and astrophysics, to the life sciences and many more kinds of sciences. Space science courses online is a relatively young field and has good strategic assets. Space science covers every small question related to space from then till now every small question about space and happenings in it has been answered by space science.
Space science courses online is a field that shapes the future of young scientists from basic to advanced levels by giving them in-depth knowledge about the Earth and an understanding of the universe. Thus, the field of space science helps in building up a future where people are enthusiastic enough to learn about science and technology more and more thus having a good rate of literacy in science and technology can be a great deal for the future. If we’re among the ones who dream of making their mark in the field of science, then we are the lucky ones as we get to know about our universe.
According to recent trends, we get to know that Space Exploration and related careers are an ever-expanding area with a great potential for numerous future career specialists. This field requires a highly competitive skill set of space technologies, management, media skills, knowledge of physical and biological sciences, and many more. And by all this, we get to know that space has become a huge arena for specialists in every field to operate.
We see ‘n’ number of career options in the field of space science if our broader interest topic is
Space; some of which are mentioned in this article:
Astronomy Courses: A field of science that deals with the study of outer space like galaxies, solar systems, stars, black holes, planets, and so many different celestial bodies.
Astronauts: The people who actually go to outer space and explore it with all the pinpoints carried in their minds.
Space Technology: It includes all spacecraft, satellites, space stations, support infrastructure equipment, various other procedures related to space and space warfare.
Engineering: The astronauts and space stations may fetch a large part of people’s attention but it is the engineers who are the backbone of Space exploration. From the designing of spacecraft, launch vehicles, space stations, satellites, and many more to an immense scope in fields like aerospace, robotics, computer engineering, material sciences, as well as mechanical and telecom engineering we see that engineers are a supporting hand in the development of space technology.
Space Research: It involves people from different fields like astrophysicists (astronomers who study celestial objects and how they interact with other space bodies), biologists (research how spaceflight affects those living in a spacecraft or the space station), biochemists, and biophysicists (look into the chemical and physical aspects of all things and their biological actions), geoscientists (study & analyze the physical nature of the Earth), astrobiologists (research life as it exists on Earth to learn about life that may exist on other planets) are all examples of space scientists who do the research part and let the space stations know about the situations and major happenings in space. Beyond research, there is a field of teaching also in space stations where you could work as an associate professor of space physics and also be involved in the analysis of data obtained from spacecraft.
Space Law: It is the body of law governing space-related activities which comprises a wide range of agreements, conventions, treaties, and the regulations of international organizations that the space stations have to follow, and if any laws are violated then strict actions are imposed on them.
Space Tourism: A growing number of businesses are aiming to step into the space tourism industry. Some big players engaged and hiring in this field are Virgin Galactic, SpaceX, Blue Origin, Orion, Orion Span (Space Hotel), and Boeing as they know that currently space tourism is in trend and many people want to explore more about space these days.
Space Architecture: This involves the study and practice of designing and constructing inhabitable environments in outer space because it is found that outer space also has a living and people can live in it. There are plans to have space hotels but not in the too-distant future!
Space Medicine/Psychology: It is the practice of medicine for astronauts in outer space. A large part of it involves mitigating the physiological changes caused by weightlessness as well as psychological issues because it is not an easy life in outer space as it is somewhat easy on the earth.
Exploring these careers is worthwhile and entering the field of space is in trend these days.
pioneer organization working towards development of science and astronomy in India. It aims to create a scientifically aware society and contribute to technological and social development. You can also enroll with them in various courses and Discover Universe and also get experts help in guiding you to build your career in the field of Space Science.
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo

November 14 of every year is marked as World Diabetes Day as it’s the birthday of University of Toronto physician Sir Frederick Banting who was the first to use insulin clinically to treat diabetes in 1922. He shared the 1923 Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine with three other scientists for the work on insulin. As a practicing physician for 20+ years who has prescribed insulin and its many forms for years to my own patients, Banting’s legacy is huge in my work. What is not as well known about Banting is that he is also considered one of the fathers of aviation medicine. The photo here is of Sir Frederick Banting on the left and one of his closest friends and fellow physician researchers, Wilbur Franks. In the late 1930s with the clouds of war approaching, Banting assembled a team of physicians and scientists in Toronto to address the physiologic challenges of high performance flight. With Banting’s help, Wilbur Franks developed the first practical G-suit to help pilots handle the stresses of high-G maneuvers in combat. The G-suits were first used operationally in 1942 in North Africa by the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy. Initially fluid filled, they refined the design to a more comfortable and practical gas-filled version which set the pattern for G-suits used by fighter pilots today. For years the only high-G human centrifuge outside of Germany was at the University of Toronto at Banting’s research institute. When Banting died in 1941 in a plane crash on his way to Britain to assist Franks with the operational testing of the G-suit, Franks carried on the work. To this day, Canadian contributions to aerospace medicine are huge and a disproportionate number of Canadian astronauts come from medical or medical research backgrounds. #avgeek #aviation #instagramaviation #instaaviation #aviationlovers #flight #FrederickBanting #WilburFranks #insulin #diabetes #aviationmedicine #aerospacemedicine #Gsuit #UniversityofToronto #Toronto #Canada #AvGeeksAero #AvGeekSchoolofKnowledge #AvGeekNation https://www.instagram.com/p/CWWDh49v_dD/?utm_medium=tumblr
#avgeek#aviation#instagramaviation#instaaviation#aviationlovers#flight#frederickbanting#wilburfranks#insulin#diabetes#aviationmedicine#aerospacemedicine#gsuit#universityoftoronto#toronto#canada#avgeeksaero#avgeekschoolofknowledge#avgeeknation
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Small Businesses with Big Plans for the Moon and Mars
Today is Small Business Saturday, which the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) recognizes as a day to celebrate and support small businesses and all they do for their communities.

Source: Techshot
We are proud to partner with small businesses across the country through NASA’s Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) and Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) programs, which have funded the research, development and demonstration of innovative space technologies since 1982. This year, we’ve awarded 571 SBIR/STTR contracts totaling nearly $180 million to companies who will support our future exploration:
Techshot, Inc. was selected to bioprint micro-organs in a zero-gravity environment for research and testing of organs-on-chip devices, which simulate the physiological functions of body organs at a miniature scale for health research without the need for expensive tests or live subjects.
CertainTech, Inc., with the George Washington University, will demonstrate an improved water recovery system for restoring nontoxic water from wastewater using nanotechnology.
Electrochem, Inc. was contracted to create a compact and lightweight regenerative fuel cell system that can store energy from an electrolyzer during the lunar day to be used for operations during the lunar night.

Source: Electrochem
Small businesses are also developing technologies for the Artemis missions to the Moon and for human and robotic exploration of Mars. As we prepare to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024, these are just a few of the small businesses working with us to make it happen.
Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Services
Masten Space Systems, Astrobotic and Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems are three NASA SBIR/STTR alumni now eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts. Other small businesses selected as CLPS providers include Ceres Robotics, Deep Space Systems, Intuitive Machines, Moon Express, and Orbit Beyond. Under the Artemis program, these companies could land robotic missions on the Moon to perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help the human exploration that will follow. The first delivery could be as early as July 2021.

A Pathfinder CubeSat
One cornerstone of our return to the Moon is a small spaceship called Gateway that will orbit our nearest neighbor to provide more access to the lunar surface. SBIR/STTR alum Advanced Space Systems will develop a CubeSat that will test out the lunar orbit planned for Gateway, demonstrating how to enter into and operate in the unique orbit. The Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) could launch as early as December 2020.
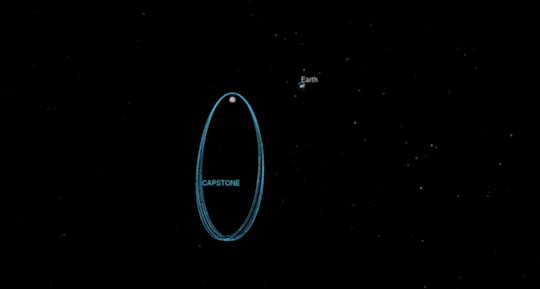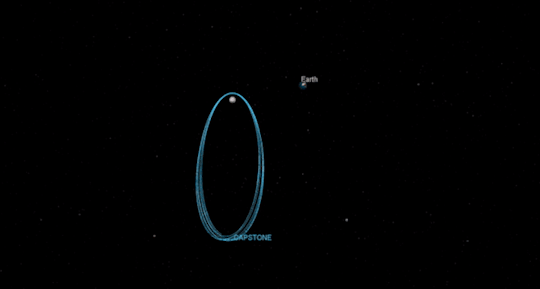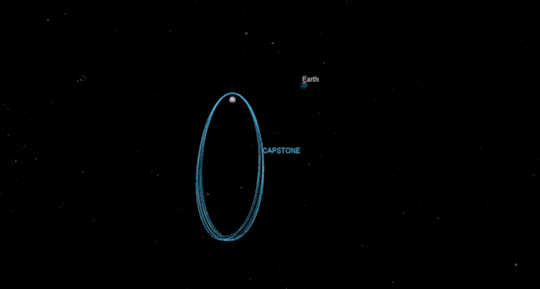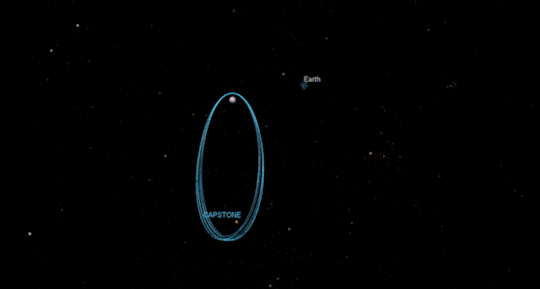
Tipping Point for Moon to Mars
We selected 14 companies as part of our Tipping Point solicitation, which fosters the development of critical, industry-led space capabilities for our future missions. These small businesses all proposed unique technologies that could benefit the Artemis program.
Many of these small businesses are also NASA SBIR/STTR alumni whose Tipping Point awards are related to their SBIR or STTR awards. For example, Infinity Fuel Cell and Hydrogen, Inc. (Infinity Fuel) will develop a power and energy product that could be used for lunar rovers, surface equipment, and habitats. This technology stems from a new type of fuel cell that Infinity Fuel developed with the help of NASA SBIR/STTR awards.
CU Aerospace and Astrobotic are also small businesses whose Tipping Point award can be traced back to technology developed through the NASA SBIR/STTR program. CU Aerospace will build a CubeSat with two different propulsion systems, which will offer high performance at a low cost, and Astrobotic will develop small rover “scouts” that can host payloads and interface with landers on the lunar surface.

Small Businesses, Big Impact
This is just a handful of the small businesses supporting our journey back to the Moon and on to Mars, and just a taste of how they impact the economy and American innovation. We are grateful for the contributions that small businesses make—though they be but “small,” they are fierce.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
794 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dr. Anne Pearce’s Timeline

May 12, 2149 - Anne Elizabeth Pearce is born to single-mother, Systems Alliance Captain Louise Pearce in London, Earth. Raised in the city for the better part of her childhood, Anne grew up on Earth but soon became familiar with space as her mother’s military career advanced, especially heading into the First Contact War of 2157.
2160 - Anne is 11 years old and moves to her first space station due to her mother’s deployment. She becomes quite familiar with many other Alliance families, and is often set to stay with other parents whose spouses are sent off on active duty. (If Shepard is from the Spacer background, Louise Pearce and Hannah Shepard are of the same cohort).
2167 - Anne is 18 years old and decides to boldly apply to one of the many universities on the Citadel, despite lingering tensions after First Contact. She is accepted into the Engineering program, with an eventual specialization into Aerospace Engineering. During these years, Anne full invests her social life amid aliens, despite some tensions. She is one of a few humans attending her program, but it does not dissuade her in the slightest.
2171 - Anne graduates with her Bachelors of Engineering, and begins working part-time for a small firm designing passenger vehicles for civilian use. In the meantime, she pursues her Masters degree. It is at age 22 that she becomes involved with Lucilla, a turian barista who works at a local cafe, sweet on Anne ever since she began ordering coffee there. Their relationship lasts for a year, mostly as something ‘hush hush’ to avoid scrutiny from their friends. They spend a good part of their time together navigating the various difficulties and incompatibilities between human and turian physiology and biology. Despite ending their relationship, they remain friends to this day.
2173 - Anne is 24 years old and graduates with her Masters in Engineering, and continues her work with the firm while living in an apartment on the Citadel. She becomes quite busy with her work, earning two promotions over the course of two years. However, she also becomes quite enthralled with the nightlife of the Wards and has a number of personal relationships in this time. Most are short-lived.
2177 - Anne completes her Doctorate of Engineering (PhD) by the age of 28 after a grueling four years in competitive academia. She becomes a research assistant for a renowned Asari professor, Dr. Talia T’Suzsa (elder sister to professional Kepesh-Yakshi player, Polgara T’Suzsa) and begins a co-operative research project as part of her studies. This connection allows Anne to build a competitive portfolio of design, comfortable with both human and asari ship designs, looking to link them to bring out the best of both worlds.
2178 - After graduation, Anne is offered a position working for the Systems Alliance. While she takes quite a lot of time to deliberate the offer, she decides to take her career to new heights - and in a way, follow her mother’s footsteps, albeit in her own way. She begins working for the Alliance as an Engineering Director within a small team that seeks to perform retrofits and redesigns for the Alliance fleet at large.
** (It is in this time that she meets Lieutenant-Commander Magnus Shepard by chance, bumping into him and taking his coffee from the local café by mistake. Realizing she had been quite rude in her hurry, she meets up with him later at his quarters, and the two spend the night talking together. This is the first date. While Anne is polyamorous, Shepard becomes her primary partner. They are married by 2180.)
2183 - The events of Eden Prime unfurl. Anne is currently working a busy career within the Alliance, working to create more ships that combine other species’ constructions with their own. Similar to the SSV-Normandy SR-1, there are a number of ships in progress that the Alliance is intent to bring to the fleet. However, the Battle of the Citadel brings about destruction and danger to the station. Anne is evacuated in time, but experienced some of her worst fears that day.
** With Shepard’s death, Anne finds herself at an utter loss. She always knew it was a possibility, but with no recovery of his body and an empty casket at the service, she never felt like she got proper closure. For six months, Anne takes a bereavement leave from the Alliance. Slowly, but surely, she gets back to work.
2185 - After the Battle of the Citadel, Anne is relocated to London to work for the Alliance out of their headquarters there. Rumours of Shepard’s reappearance circulate but are never confirmed until nearly seven months later.
** Anne is in utter shock but relieved that Shepard is alive. They are a great distance apart but keep in communication with one another as best they can. Shepard also begins a relationship with Miranda Lawson, which Anne is aware and encouraging of the relationship.
2186 - The Reaper invasion begins. London is hit first, devastatingly so. Anne is one of a lucky few who are escorted on an immediate escape vessel to the Citadel. However, her mother, Major Louise Peace, was killed in action during the initial attack on Earth. Anne rarely gets time to process her grief before the Alliance summons herself and her colleagues to work on a Top Secret project - the Crucible. From there, Anne spends most of her time organizing and completing parts of the blue prints to put together the ultimate tool to help them win the reaper war.
2187+ - After the war, Anne returns to Earth once again to help with the rebuilding efforts.
** After Shepard’s disappearance, assumed to be KIA, Anne processes her grief in the company of Miranda, who she had previously established a relationship with during Shepard’s last send-off party in Anderson’s apartment. From there, they had a discussion regarding their futures, and Anne already offered to be a gestational surrogate for Miranda and Magnus’ child. After the war, she takes up that offer, and the two raise a daughter together - Hannah Louise Pearce-Shepard.
#ANNE PEARCE: HEADCANON#[ anyway this is my mass effect oc and i finally sorted out her timeline ]#[ Me1 inspired me a bit ]#[ but also i wanted to include her canon with my mshep just in case yall wanna play in or around that ]#[ but otherwise if a shepard wants to write with her there's canon where she's on her own ]
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo

What is the function of LED plant growth light? What are the characteristics?
Light has two effects on plant growth, one is indirect, and the other is direct. LED plant light manufacturers are more environmentally friendly and energy-saving. LED plant lights provide photosynthesis to plants, promote plant growth, shorten the time it takes for plants to bloom and bear fruit, and increase production! In modernization, it is an indispensable product of crops.
The law of plant growth must require sunlight, and the LED plant growth lamp is a kind of lamp that uses the principle of sunlight to replace sunlight to provide the environment for plant growth and development. Therefore, it can better promote the growth of plants at night or under dark conditions.
What is the function of LED plant growth light? What are the characteristics?
1. According to the degree of plant light, control the irradiation time of the LED plant light.
It is generally believed that almost all living organisms need to rest. Therefore, it is not feasible to use LED plant lights to supplement the light of plants 24 hours a day. After a lot of research and experimentation, it has been proved that it is appropriate to control the plants to add light for 16 hours and 18 hours, and leave enough time for the plants to rest for 4-6 hours. For bright plants, when the sun can meet their growth needs under sunny conditions, the sun can meet their growth needs. It takes about 11 hours to supplement the plants with a plant growth lamp. Similarly, if the requirements for light are not very high, if there is sunlight, it can already meet its growth needs. The time for supplementing light with LED plant lights only needs to be set according to the local sunrise and sunset time, and the supplementary light time can try to avoid effective rest time for plants.
Plant growth lamp supplement light time 1. As supplementary light, it can enhance the light at any time of the day, which can extend the effective lighting time. 2. Whether it is at dusk or at night, it can effectively extend and scientifically control the light required by plants. 3. In a greenhouse or plant laboratory, it can completely replace natural light and promote plant growth. 4. Thoroughly solve the situation that the seedlings need to be eaten according to the day, and arrange the time according to the delivery date of the seedlings. The choice of plant growth lamp Scientific choice of light source can better grasp the speed and quality of plant growth. When using artificial light sources, we must choose the natural light closest to satisfying the conditions of plant photosynthesis. Measure the photosynthetic luminous flux density produced by the light source to the plant, grasp the photosynthesis rate of the plant and the efficiency of the light source, the light quantity of photosynthetically effective photons in the chloroplast initiates the photosynthesis of the plant: including the light response and the subsequent dark response.
2. Set the irradiation time of LED plant lights according to the planting environment.
The plant growing environment mentioned here includes the regional differences between north and south, spring, summer, autumn and winter, as well as the difference in the intensity of indoor and outdoor sunlight. According to the law of light, the stronger the equator, the stronger in summer and winter. According to local conditions, the irradiation time of LED plant growth lights can be set according to local conditions. The acceptable light for indoor and outdoor planting is very different. It takes 16 hours and 18 hours to charge with LED plant lights. It can adjust the light intensity of LED plant lights according to the degree of indoor natural light reception, while outdoor plant growth lights can refer to the first point to supplement light. 1. Convert electrical energy into radiant energy with high efficiency. 2. Achieve high radiation intensity within the effective range of photosynthesis, especially low infrared radiation (heat radiation) 3. The emission spectrum of the bulb meets the physiological requirements of plants, especially in the effective spectrum of photosynthesis.
The LED plant growth lamp used in the field of plant cultivation also embodies the following characteristics: the wavelength type is abundant, which coincides with the spectrum scale of plant photosynthesis and light morphology; the half width of the spectrum wave width is narrow, which can be combined to obtain pure monochromatic light and composite spectrum according to the needs. LED plant lights can focus on specific wavelengths of light to irradiate crops in a balanced manner; plant lights can not only adjust the flowering and firming of crops, but also control plant height and plant nutrients; the system generates less heat and occupies a small space, which can be used for multi-layered cultivation planes The combined system realizes low heat load and miniaturization of production space; in addition, the strong durability of LED plant lights also reduces operating costs.
LED plant light manufacturers do not use fertilizers at all for organic planting, but they can use organic fertilizers: farmhouse fertilizers, mineral fertilizers, biological bacteria fertilizers, etc. after high-temperature fermentation and harmless treatment. Due to the limitation of this kind of fertilization, the growth cycle of plants is bound to be affected, and the current large demand in the market appears to be in short supply. Therefore, shortening the production cycle is one of the methods.
This kind of LED plant lamp has strong roots, promotes, regulates the flowering period and flower color, promotes fruit maturity, coloring, and enhances the taste and quality of the fruit! Because of these obvious characteristics, LED plant lights are very suitable for plant cultivation in a controllable equipment environment, such as plant tissue culture, equipment gardening and factory seedlings, and aerospace ecological life support systems. The effects of different spectral components of LED plant lights on plants.
www.86yr.com
1 note
·
View note
Text

Dr. Gloria Twine Chisum (born May 17, 1930) experimental psychologist is known for developing protective eyewear for pilots in extreme conditions.
She was born in Muskogee, Oklahoma. She grew up in Muskogee. She graduated from Howard University with a BA in Psychology and completed an MS in Psychology. She pledged Alpha Kappa Alpha Sorority and was involved with the Howard University Players.
She entered the University of Pennsylvania, earning a Ph.D. Her dissertation was titled “Transposition as a Function of the Number of Test Trials.” She parlayed her graduate research into her professional career mainly in military research. One of her first positions was as the manager of the Life Sciences Research Group for the Navy. She was head of the Environmental Physiology Research Team at the Naval Air Development Center.
She served as a consultant to all branches of the Department of Defense, as well as many other organizations throughout the world. In the 1970s she represented the US government in several conferences held by the North Atlantic Treaty Organization Advisory Group for Aerospace Research and Development. She developed specialized, protective goggles for pilots who operate high-performing aircraft, significantly decreasing their exposure to bright light and loss of consciousness.
She received the Aerospace Medical Association’s Raymond F. Longacre Award, the University of Pennsylvania Alumni Award of Merit, and the Scientific Achievement Award. She authored two books, the AN/PVS-5 Night Vision Laboratory Assessment, and a book on laser eye protection for flight personnel. She is the first African American woman to serve as a member of the Board of Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania.
She married physician Melvin “Jack” Chisum (1955-2014). He died on October 22, 2014. #africanhistory365 #africanexcellence #alphakappaalpha
0 notes
Text
First space tourists will face big risks, as private companies gear up for paid suborbital flights
by Sara M. Langston

Ready to take your suborbital selfie? EvgeniyShkolenko
On May 30, 2020, millions of Americans watched the inaugural SpaceX Crew Dragon launch NASA astronauts to the International Space Station. This mission marked two significant events: First, the return of launch to orbit capability for human spaceflight from the United States. Secondly, it successfully demonstrated private sector capability to build and operate a launch vehicle for human spaceflight.
While SpaceX may be the first private space company to accomplish this, it is not alone. Boeing’s Starliner and Lockheed’s Orion capsule are also being developed for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, and training has begun for safety operations on the spacecraft.
As an aerospace lawyer working and teaching on human spaceflight law and policy for over a decade, I have a professional and personal appreciation for current spaceflight technologies and astronaut developments.
For many, the Crew Dragon launch marked the start to a new era of commercial access to space and private human spaceflight. However, given logistical and destination requirements for Earth orbit or beyond, the onset of larger-scale private human spaceflight is more likely to emerge within the suborbital space market.
Commercial suborbital flights coming next
A suborbital flight, in contrast to SpaceX’s recent orbital flight, is a brief spaceflight that fails to complete one full orbit of the Earth. That is, you launch your space vehicle to the edge of space and come right back down. Virgin Galactic has been inching closer to commercial suborbital launch operator status with successful crewed test flights in February 2019. In fact, Virgin Galactic’s SpaceShipTwo, an air-launched suborbital rocket, and Blue Origin’s New Shepard, a rocket-launched space capsule, are projected to commence suborbital flights catering to both space tourists and scientific research this year. Each suborbital flight presents a unique spaceflight experience, trajectory and set of regulatory requirements.
While industry continues to test and refine tech and operations, the Federal Aviation Administration – which regulates launch, reentry and spaceports for U.S. commercial spaceflight – is also morphing to address the needs of the emerging private space industry.
What you need to know before you fly to space

In a suborbital flight, the crew and passengers enjoy a brief parabolic flight that takes them to the cusp of space and then back to Earth. The Conversation, CC BY-SA
Spaceflight is regarded as an inherently dangerous activity. While some hazards of spaceflight and the space environment – like G-forces, radiation, vibration and microgravity – are well documented, many risks remain unknown. The scope of physiological risks spans pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight operations and activities.
FAA regulations also focus on the safety and protection of the public on the ground, not the civilian passengers who are called spaceflight participants. This includes anyone who is not crew or a government astronaut on a spacecraft.
As a result, regulations stipulate minimum requirements with regard to medical fitness and training for space tourists, as well as informed consent, and waivers of liability to protect the launch operator.
So prospective space participants are taking a big risk.
Medical criteria
No standardized medical criteria exists for screening or selecting spaceflight participants. Unlike flight crew which require a Class II airman’s medical certificate, there is no similar requirement for fitness to fly for space tourists. Where the law is silent or lacking, the FAA’s Recommended Practices for Human Space Flight Occupant Safety can provide general guidance.
Here the FAA recommends a spaceflight participant receive a medical consultation within 12 months of flight from a physician trained or familiar with aerospace medicine. Since this is a not a legal requirement, ultimately it will be up to the launch operator to determine fitness-to-fly and “no-go” criteria for preexisting conditions.
Virgin Galactic, for example, has few restrictions: no upper age limit, and weight limit only as it relates to practical space vehicle requirements.
When it comes to the risks from radiation, the FAA tries to reduce the exposure for crew members. But it considers the radiation risks of a space tourist taking a single suborbital joy ride as insignificant.
Training
Similar to how airlines provide safety information before a flight, the launch operators are required to instruct space tourists on how to respond to emergency situations including smoke, fire, loss of cabin pressure and emergency exit.
This is a minimal requirement, and each launch operator determines its training protocol. Virgin Galactic, for instance, offers a three-day training with a focus on participant’s gear, communications and function, and spacecraft cabin.
Flight crew, in contrast, must be trained and qualified to perform their critical functions, and withstand the pressures of spaceflight. Orbital or long-duration spaceflights, however, will likely require more stringent commercial industry training protocols than for suborbital flights.
Informed consent
The FAA set the age requirement for civilian participants at 18 years.
This is necessary to ensure the participant can provide informed consent. In addition, the regulations dictate that the launch operator inform crews and participants that the U.S. government does not certify the spaceflight and space vehicle as safe for humans.
The launch operator must also inform the participants in writing of the risks of launch and reentry, the safety record of the vehicle, and that both known and unknown space hazards and risks could result in serious injury, either partial or total physical or mental disability.
Waivers of liability
The spaceflight participant is also required to sign a reciprocal waiver of liability with the commercial launch operator and an indemnification agreement with the Federal Government.
However, participants don’t sign a waiver with other participants. Meaning, if an accident occurs, spaceflight participants can sue each other but generally not the launch operator or the government.
To protect oneself, it would be advisable to take out insurance. A few companies, including AXA XL and Allianz, are beginning to offer third-party liability insurance for civilians to engage in spaceflight.
The space industry expects that many people may want to go to space in the near future, and private spaceflight is being marketed as the next experience in luxury escapism and scientific research.
But the hazardous nature of spaceflight also requires critical understanding of the risks and uncertainties in human spaceflight. The industry is still in its infancy, and the best practices and regulations for human spaceflight are still evolving.

About The Author:
Sara M. Langston is an Assistant Professor of Spaceflight Operations at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license.
9 notes
·
View notes