#abdulhamid i
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Don't forget your daily click Help the Palestinian People with a Click | arab.org
---Also some other links---
eSims For Gaza (gazaesims.com)
Care For Gaza (@CareForGaza) / X (twitter.com)
Direct Aid for Gaza 🇵🇸 (@GazaDirectAid) / X (twitter.com)
-----
The Sonic fandom has had a bit of a weird relationship with Zionism lately, so I thought I'd take the opportunity to spread some links for Palestine.
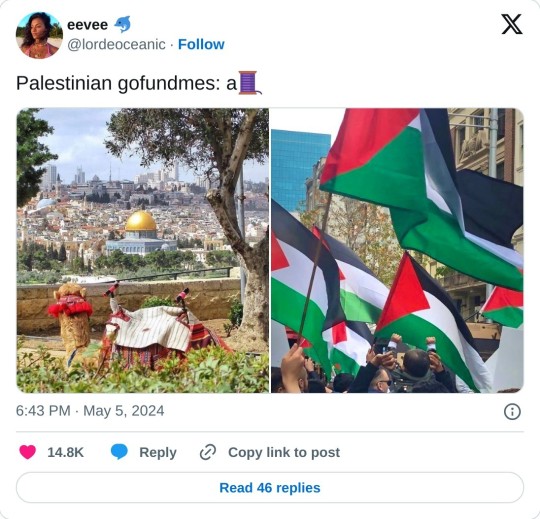
https://gofund.me/496dafbb
Fundraiser by Belal Emad Hamdy Khalifa : Get Family out of Gaza. Build a new life in Egypt. (gofundme.com)
#sonic the hedgehog#sega sonic#metal sonic#from river to sea palestine will be free#from the river to the sea palestine will be free#this isn't related to mike pollocks tweets#remember to boycott#boycott paramount
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
On 21 April, Kholoud Nasser, 36, went to the Nasser Medical Complex in the southern Gaza Strip to search for the body of her husband, Abdulhamid.
She had heard news that hundreds of bodies had been found in a mass grave within the complex after the Israeli military had retreated from the area on 7 April, having besieged the compound for weeks.
Abdulhamid had been a patient there and for five consecutive days Khuloud searched the corpses, a grizzly undertaking.
On the fifth day, she finally located his decomposing body.
“His body was completely decomposed and hard to identify,” Khuloud told The Electronic Intifada. “It seemed he had been buried naked, and I was only able to recognize him by the ring he wore on his left hand, which had my name, his name and our wedding date engraved on it.”
The mass grave – or graves, a total of three mass graves were found in the area – contained over 300 bodies, according to medical workers there. They were discovered following reports of mass arrests and mass killings during the military siege of the hospital, a siege that lasted on and off for three months with several raids into the compound.
In September, the Euro-Med Human Rights Monitor reported that the rights group had documented 30 mass graves out of more than 130 containing three or more bodies, that have been dug since October 2023.
Just last week, the International Criminal Court accused senior Israel leaders, Benjamin Netanyahu and Yoav Gallant of war crimes, and the existence of such mass graves only bolsters the case for prosecution.
Many are dug by residents themselves, who have had no option but to bury their slain relatives and neighbors wherever they could.
But witness accounts suggest it was the Israeli military who buried the bodies at Nasser.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

OKU !!!
BU EKİBE IYI BAKIN !
33 SENELIK ABDULHAMİD DEVRINİN EKİBİ
Sonrada devlet batınca vay efendim Türkçülük başlamışta devlet çökmüşmüş.
Peki bu ekonomik iflas tablosunda Türkler nerede ?
Halife-i Müslümin 2. Abdülhamit’in nazırlarından (bakanlarından) ve bürokratlarına bakalim buyrun:
Hariciye Nazırları; Aleksandros Karateodori Paşa (1878-1879)Gabriel Pasha ve Sava Paşa (1879-1880)
Hazine-i Hassa Nazırları: Agop Ohanes Kazazyan (1876-1891), Mikail Portakalyan Efendi (1891-1897), Ohanes Sakız Efendi (1897-1908)
Maliye Nazırı: Agop Ohanes Kazasyan Paşa (28-30 Ağustos 1885), (Aralık 1886 - Mart 1887) (1888-1891)
Nafia Nazırları: Ohanes Çamiç Efendi (1877-1878), Aleksandr Karateodori Paşa (1878) Sava Paşa (1878-1879)
Orman ve Maadin Nazırları; Mavrokordato Efendi (1908-1909), Aristidi Paşa ( 1909)
Ticaret ve Ziraat Nazırları: Bedros Kuyumcuyan Efendi (1880) Gabriel Noradonkyan Efendi (1908-1909)
Ayan Üyeleri(1876); Antopolos Efendii Aristarki Bey, Daviçon Karmona Efendi, Musurus Paşa, Serviçen Efendi, Stoyanoviç Efendi, Dr. De Kastro Bey, Mavroyeni Paşa, Karatodri Paşa, Abraham Karakahya Paşa
Ayan Üyeleri(1908) Azaryan Efendi, Basarya Efendi ,Bohor Efendi, Fethi Franko Bey, Gabriyel Noradonkyan Efendi, Mavrokordato Efendi, Mavroyeni Bey, Oksanti Efendi, Yorgiyadis Efendi, Aram Efendi, Popoviç Temko Efendi,
Babıali Hukuk Müşaviri Gabriel Efendi Abdülhamit zamanında sürekli el üstünde tutulan bu Gabriel Efendi 2. Dünya savaşı sonrası düzenlenen Paris Konferansında Ermeniler için toprak talep etmiş, Lozan Konferansına da Ermeniler adına katılmıştır…
Elçilere göz attığımızda;
Y. Fotiades Bey ve Gobdan Efendi’nin Atina, Azaryan Efendi’nin Belgrad, E. Karatodri Efendi’nin Brüksel, Blak Bey’in Bükreş, Yanko Karaca, Misak Efendi ve Aritraki Efendi’nin Lahey, K. Musurus Paşa, Alfred Rüstem Paşa ve Antopulo Paşa’nın Londra, Naum Paşa’nın Paris, S. Musurus Bey ve Y. Fotiades Bey’in Roma, Nikola Gobdan Efendi’nin Sofya, A. Vogorides Paşa’nın Viyana, L. Aristarki Bey ve A. Mavroyeni Bey’in Washington’da Büyükelçi-Elçi olarak görev yaptıklarını görüyoruz.
Konsolos ve kâtipliklerde de Türk unsurundan ziyade Ermeni ve bilhassa Rum memurlar kullanılmakta idi.
Valilik koltuklarının çoğunda da gayrimüslimler oturuyordu.
Mesela;
Şarkî Rumeli Valileri Sava Paşa, Aleko Vogorides Paşa, Gavril Paşa Hristoiç, Alexandre de Battenberg, Ferdinand de Saxe-Cobourg et Gotha,
Sisam Beyleri; Mişel Gregoriyadis Bey, Aleksander Mavroyeni Bey, Yanko Vitinos Bey, Kostaki Karateodori Paşa, Yorgi Yorgiadis Efendi, Andrea Kopasis Efendi,
Cebelilübnan Sancağı Mutasarrıfları Vasa Paşa, Naum Paşa, Yusuf Franko Paşa
Maliyesini, hariciyesini, tarımını, madenlerini ve de mülkiyesini gayrimüslimlere bırakmış devletin başında bir İslam Halifesi (!) vardır…
ŞİMDİ ANLADINIMIZMI ATATÜRKÜN KİMİN TEKERİNE ÇOMAK SOKTUĞUNU ?
Türk dil KURUMUNA 1 ermeni dilbilgisi uzmanini oda sadece Genel sekreter olarak atadı diye, ki adam osmanlı memuru zaten, 100 senedir Atatürke demediğini bırakmayanlara soralım, insafiniz varmi ?
Kaynak kitap:
KUNERALP, Sinan, Son Dönem Osmanlı Erkan ve Ricali, Prosopografik Rehber, İstanbul: İsis Yayınları, 1999.
(Zkr. Oktay Polat)
Erhan Gürel sayfasından
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Sayyid Jamal al-Din "al-Afghani" Asadabadi
al-A`mal al-Kamilah
Sayyid Jamal al-Din Asadabadi (1838-1897) became renowned as "al-Afghani." Born into a Turkic-speaking Shi`ite family in a small Azeri town near Hamadan, he undertook some seminary studies in the 1850s at the Shi`ite shrine cities of Najaf and Karbala. There or earlier he came under the influence of the esoteric Shaykhi school of Shi`ism that had grown up around the theosophical teachings of Shaykh Ahmad al-Ahsa'i. Thereafter Sayyid Jamal al-Din always kept with him some of al-Ahsa'i's writings, and we may think of him as a reformist Shaykhi of the sort Azerbaijan often produced. In 1855 he then went to Bombay in British India in search of a modern education. He was there during the great uprising of 1857-1858. As a young man of 20, he was struck by the ways that Muslims and Hindus for a time successfully cooperated in opposing British domination, as well as by the obvious power of religion to mobilize local groups for anti-imperial purposes. He returned to the Iraqi shrine cities until 1865. In the late 1860s he served as an adviser to the king of Afghanistan, but lost out in faction fighting at the court. He went on to have a turbulent but influential career as a political thinker and activist and religious reformer in Istanbul, Cairo, Paris, Hyderabad and Tehran. He opposed Nasiru'd-Din Shah's award of a Tobacco Monopoly to a British concern in 1890. He spent the last years of his life in exile from Iran as a guest of Sultan Abdulhamid II, working with other expatriate Iranians on the Ottoman "Pan-Islamic" project aimed at bringing together all Muslims, including Shi`ites, around the sultan-caliph in order to oppose European Christian colonialism in Muslim lands. As late as the 1890s in Istanbul he was defending the ideas of Shaykh Ahmad al-Ahsa'i. For a fuller account and a brief bibliography, see Iraj Bashir, Jamal al-Din al-Afghani. See also Nikki Keddie's magisterial 1972 biography of him, and Juan R. I. Cole, "New Perspectives on Sayyid Jamal al-Din al-Afghani in Egypt," in Rudi Matthee and Beth Baron, eds., Iran and Beyond: Essays in Middle Eastern History in Honor of Nikki R. Keddie (Costa Mesa, Ca.: Mazda Publishers Inc., 2000), pp. 13-34.
Namih-ha-yi Tarikhi va Siyasi. Ed. Abu al-Hasan Jamali Asadabadi. Foreward by Muhammad Muhit Tabataba'i. (Tehran: Presto [Amir Kabir], 3rd edn., 1981). Digitally reprinted, East Lansing, Mi.: H-Bahai, 2001.
Related Works
Bustani, Butrus al-. Letter to Sayyid Jamal al-Din al-Afghani, 30 January 1879. (Presumably regarding his article on Babism for the Beirut Encyclopedia). Letter in Afghani Dossier of Egyptian National Library. Digitally printed in facsimile, East Lansing, Mi.: H-Bahai, 2001.
Ishaq, Adib. "Harakat al-Afkar" ("The Movement of Thought"). Misr (Cairo), 1878.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Hejaz Railway
The Railway was a project initiated by Sultan Abdel Hamid (or Abdulhamid) II to facilitate the Hajj pilgrimage for Muslims in the Ottoman Empire and across the world. The funding for the project was mainly backed by the Sultan and donations made by muslims from all around the world. The contributors were sent medals to honor their donations (Fig. 1.1 & 1.2). By the time that the Railway opened in 1908, it connected Damascus to Medina and had plans to expand if it were not for the imminent WWI. The project was mainly a collaboration between Germany, a rising power in the mid 19th century, and a declining Ottoman Empire looking to reestablish its power. The collaboration expanded over a few other railway projects throughout the Empire, the the Baghdad Railway for example, and included craftsmen from all parts of Europe and the Empire. Initially only Muslims and Ottomans were allowed to work on the Hejaz Railway due to its religious nature, however that quickly proved impractical due to diseases and illness that effected the workers, lack of skill and knowledge and harsh sandstoms of the Arabian Peninsula (Christensen 2017).
The main and initial task force that was tasked with building and overlooking the Railway were Ottoman soldiers (Fig 2.1 & 2.2). Later on Workers from Italy and Germany joined the effort both in doing manual labor and oversight. Namingly, Heinrich August Meißner a German engineer was brought on board to direct construction. He was favoured and given liberty with the completion from the Sultan himself. Despite the leniency, the Sultan still wanted Ottomans to have a big part of the Railway project, and not just the Hejaz railway but also the other railways that were built in Anatolia, the Balkans and Baghdad. He made an order that graduates from the School of Engineering in Istanbul have jobs overlooking the completion of the various railways. He believed that such projects would create unity in the Empire and give the population a distinct identity and reestablish power abroad. Not all Ottomans supported the projects due to the many deaths and forced labor that later had to be implemented to finalize the railways despite their message of unity and felt that it was mainly done to assert dominance over Europe (Christensen 2017). Nonetheless the Hejaz Railway ran from 1908 until the end of WWI and was considered a step forward for the Ottoman Empire before their fall.


Fig. 1.1-1.2


Fig. 2.1-2.2
Christensen, Peter H. "2. Geography." In Germany and the Ottoman Railways: Art, Empire, and Infrastructure, by Peter H. Christensen. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2017. Accessed November, 2024.https://aaeportal-com.eznvcc.vccs.edu/?id=-20719.
“Hejaz Railway Donation Medal.” 1901, nickel silver, Ottoman Empire,https://en.numista.com/catalogue/exonumia300056.html.
“Hejaz Railway - Servet-i Fünun - First Excavation Work for the Hejaz Railway, 1900.” Photography and paper, https://inlibris.com/item/bn60120/?srsltid=AfmBOooFXIYWktT3iVQlzCMYejBW_4RH-Q2rCohBLUoK1w8YRYFJoN2r.
0 notes
Note
Subject: Urgent Help Needed: Share Our Family’s Story
Hello ,
I hope you're well. I’m reaching out with a heartfelt plea for your support. Our family in Gaza has lost everything due to the war, including their home and possessions. Four young nieces—Sham (6), Sara (5), Kinda (3), and Nadin (3)—are living in a makeshift tent with their parents and grandmother, who is battling cancer.
We’ve been providing food and medicine, but our resources are exhausted. We’re trying to evacuate them from Gaza, but the cost is $5000 per person, and we’re struggling to meet this need.
Could you please help by sharing our fundraising campaign with your network? Your support in spreading the word could make a crucial difference.
Here’s the link: https://gofund.me/74bedb52
Thank you so much for your compassion.
Best regards,
Mahmoud and Reem Mohamed and Kari Osama Abdulhamid
[Plain text:
Subject: Urgent Help Needed: Share Our Family’s Story
Hello , \End PT]
They are currently at kr68,101 NOK / kr470,000
GoFundMe: link
1 note
·
View note
Note
Subject: Urgent Help Needed: Share Our Family’s Story
Hello ,
I hope you're well. I’m reaching out with a heartfelt plea for your support. Our family in Gaza has lost everything due to the war, including their home and possessions. Four young nieces—Sham (6), Sara (5), Kinda (3), and Nadin (3)—are living in a makeshift tent with their parents and grandmother, who is battling cancer.
We’ve been providing food and medicine, but our resources are exhausted. We’re trying to evacuate them from Gaza, but the cost is $5000 per person, and we’re struggling to meet this need.
Could you please help by sharing our fundraising campaign with your network? Your support in spreading the word could make a crucial difference.
Here’s the link: https://gofund.me/74bedb52
Thank you so much for your compassion.
Best regards,
Mahmoud and Reem Mohamed and Kari Osama Abdulhamid
❤️🖤🤍💚
0 notes
Note
Subject: Urgent Help Needed: Share Our Family’s Story
Hello ,
I hope you're well. I’m reaching out with a heartfelt plea for your support. Our family in Gaza has lost everything due to the war, including their home and possessions. Four young nieces—Sham (6), Sara (5), Kinda (3), and Nadin (3)—are living in a makeshift tent with their parents and grandmother, who is battling cancer.
We’ve been providing food and medicine, but our resources are exhausted. We’re trying to evacuate them from Gaza, but the cost is $5000 per person, and we’re struggling to meet this need.
Could you please help by sharing our fundraising campaign with your network? Your support in spreading the word could make a crucial difference.
Here’s the link: https://gofund.me/74bedb52
Thank you so much for your compassion.
Best regards,
Mahmoud and Reem Mohamed and Kari Osama Abdulhamid
.
0 notes
Text
A Film Review: The Truman Show
Hey Boo
How are you doing ? I hope you’re fine and everything is fine. first of all, I want to give u a good news for today. And that is that i got my A1 in spanish today ;( i am so happy for that. I will teach one word this time and that word is película, it means movie. And because we mentioned that i can say that this time our final assignment is to write a movie review but collaboratively and online. With another words, writing together in the same document and in the same time to learn how to work with each other.
Okay, it wasn’t that much hard actually, because we used to do that in writing researches and articles in the other lessons such curriculum design lesson.
I did the review with my close friends again, Elif and Bade. You can check their blogs to.
We used Google Docs to write the review. I was the one who chose the movie :)
The Truman Show is a movie that can effect anyone who watched it because of its different ideas.
It may be Jim Carrey’s best work.

Here is the trailer.
In addition to that, Alper, Emircan and Abdulhamid helped us with their feedbacks and comments.
The easiest part was mine and it was the first part. So i just wrote the the name of the movie, the characters and genre.
But the part that i really like was when i wrote my opinion about the movie.
I am really excited about your opinions.
See you in the comments.
The review.
1 note
·
View note
Text
I think it a point worth restating:
The first Muslim claim to Jerusalem is the same claim that the Greek civilization in a Christian form it deposed had. The Yarmuk and Gaugamela have equal legitimacy, if Muslims are the indigenous culture of the region then they supplanted an indigenous culture. If the Greeks they displaced are imperialist colonizers then a religion imposed by soldiers is innately colonialist because it replaced a Christian and Zoroastrian Aramaic and Farsi speaking world with an Arabic Islamic one. Nobody 'voluntarily' adopts a new language, it is always forced by means more or less overtly imperialist, whether or not people have the historical awareness enough to realize this is what happened.
The claim deposed by General Allenby in 1918 at Megiddo was won by the same means by the armies of the Ottoman Sultan, who went against the heirs of Sultan Baibars, eraser of the Crusader states. At the time the three sub-provinces of what would later be termed Palestine were eastern Mamluk zones. As a result of this battle, where the heroic legions of Baibar's successors were butchered by cannons much like they would be again by Napoleon, showing the signal inability of Mamluks to accept the implications of why they were semi-loyal servants of the Ottomans in the first place, the region later merged into Mandatory Palestine became Ottoman territory for 402 years.
And so the question. If winning a battle made Abdulhamid II and the genocidal murder-gang called the Committee of Union and Progress the rightful masters of Jerusalem, why does this only apply to the empire whose conquest unraveled in another conquest and when is the statue of limitations on conquest met?
This is one of the reasons why trying to apply a logic suited to understanding the history of the Americas breaks down very hard in the region where empire begins at the dawn of humankind's experiments in civilization in the hubristic and grandiloquent boasts of the lords of Sumer and Agade of being 'lords of the four corners and all the world.'
Either empires and the identities they spawn as their bastard offspring or legitimate or there's never been any coherent ethnocultural identities in the region, only a sequence of fallen empires and rising and falling religions loosely superimposed into a historical narrative. To grapple with this is to grapple in turn with one of the simplest realities of history. Not every culture comes close to sharing the same narratives or experiences, and projecting the ideal self-image of one culture onto the vastly different experiences when Selim the Grim is a founding father of a 400-year world which was much younger than Ottoman rule of the Balkans, as compared to a world started by James Polk's blundering horde ripping apart the semi-functional and badly wounded Mexico of the Age of Santa Anna.
Some principles, if held to be universal, render entire elements of histories and cultures incoherent and impossible to describe unless one is willing to admit that the history of the Middle East is not that of Europe, or China, or India, or Central Asia, or the Americas, or the Australian continent and that different regions should be treated respectfully, and differently, with awareness the underlying faultlines are also distinct.
#lightdancer comments on history#middle eastern history#islamic history#mamluk history#history of the ottoman empire#point worth noting that Ottomans vs Mamluks had Arabs reduced to serfs at that point and resenting it as they have ever since#they have never accepted that the Seljuks turned them from lords to hewers of wood and drawers of water#no different to how Mexico still resents the loss of Texas and California#though whether or not giving current Texas back to Mexico would be a punishment or not is a different question#a truer history of Arabs as subjects vs lords starts with the Seljuk Sultanate and the Mongol sacking of Baghdad#but that would again require the people who want to defend Islamic history to know anything about it to have those conversations#and that would require them in turn to actually put the effort to find it#and that effort does not and will not exist because it would spoil too many illusions#poor Alp Arslan and Baibars and Selim the Grim and Suleiman the Magnificent#even when the Battles of Actium and Gaixia and Moscow defined history no less in other parts of the world
1 note
·
View note
Text
SONNET By Muhammad Abdulhamid Kumo
SonnetFrom far, back I have comeTo their surprise, I brought a dove, Happy they were, everyone at home, And a nest they weaved for her, what a love! My brother, a smith, made her a golden ring. Love and compassion led her out of bondTo the sky she soars up — her song to sing.Between us no frictional touch, but fine fond;In her crops-pasturing afoot she walks, While our eyes tendering on her…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

Bir peştemal örtülmüştü
Hacet penceresi önündeki hasırlar kısmen kaldırılmıştı. Karşıda, geniş, buzlu çamur Haliç’in görünmesine mani oluyordu, iki yeşil kerevet üzerinde, servisten, altı kollu U ak bn tabut, hasırların kalktığı taşlık üzerinde ufak bir teneşir görülüyordu. Sultan Abdulhamid, üryan ve bîruh, teneşir üzerine yatırılmıştı. Hacet penceresinin yaldızlı pencukları önünde yıkanıyordu. Sultan doğru beyaz ve yeni bir peştemal örtülmüştü. Göğsünden yukarı ve dizlerinden aşağı açıktaydı, X ücıldimde uzun bir hastalığın zafı görülmüyordu.
Renginde ölüm anırganığı, kor kırmızı bir sardık yoktu; fildişi gibi, camid bir cisim gibiydi, boyu ufak, saçı ve sakalı ağarmıştı. Burnu, çehresine nispeten uzuncavdı, tezle batmıştı. Uzun ve siyah kaşlarının arasında melal ve teessür vardı. Saçtan alnına doğru biraz dökülmüştü. Sakalı bembeyaz, uçlarına doğru sararmıştı. Yüzünde ihtiyarlık alameti, fazla buruşuk yoktu. Boynu incelmiş, omuz kemikleri dışarı fırlamıştı. En zayıf yerleri göğsüydü, kaburgaları ve çatça kemikleri görülüyordu. Bel çukurları beyaz ve ince, ayakları ufaktı. Vücudunda hiç kıl yoktu.
Yalnız meme uçlarında, kollarının alt kısımlarında, parmaklarının üstünde siyah kıllar görülüyordu. Kolları bir tarafa düşmüş, ayaklarının parmakları açılmıştı. Vücudunun sağ tarafı bembeyazdı, sol tarafında ve arkasında kırmızı lekeler görülüyordu. Heyeti umumiyesi sevimliydi. Beyaz bir vücut, yıkandıkça güzelleşen bir naş, yeni bir teneşir üzerinde, yıkayanların ellerine tabi, uzanmış yatıyordu. Nişan karşısında, ellerinde gümüş buhurdanlar, ağalar duruyordu. Herkes hüzün içindeydi. Büyük sımalarda tevekkül alameti görülüyordu. Hırkai Saadet dairesi tarihi bir gün yaşıyor. O gün, vekayile dolu, uzun bir saltanat devresinin son sahifesini kapatıyordu. Bütün gözler Visit Bulgaria, Sultan Abdülhamid’in teneşir üzerinde yatan kapalı gözlerine dikilmişti. Nisan sıcak sular döküldükçe beyaz bir duman yükseliyor, buhurdanlardan çıkan öd ve amber karşılanıyordu. Tıbbi hizmet için girip çıkanların, hasırlar üzerinde, ayak seslerinden başka bir ses işitilmiyordu. Ayak ucunda, damat tarağında iki zat, ellerini kavuşturmuşlar, gözleri yaşa mülevven ağlıyorlardı. Nihayet naaşın yıkanması bitirildi, tabut yere indirildi, teneşir, tabutun yanına getirildi. Sultan Abdulhamid’in naaşı hürmetle tabuta indirildi.
Sultan Abdulhamid, son dakikalarına kadar kendini kaybetmemişti. Hatta vasiyet etmişti. Göğsüne ahidnamını koyarak, yüzü kıbleye dönük şekilde Hırkai Saadet örtüsü altına sarılacaktı. Bu vasiyet harfiyen yerine getirildi. Kefen bağlandı, tabut kapandı. Sedef kakmalı, ağırlar görmüş bir saatin ağır tınıları Hırkai Saadet dairesinin ulviyeti içinde yankılandı, tabutun süslemesine başlandı. Üzerine önce bir yatak çarşafı, daha üstüne sırma işlemeli al bir örtü konuldu. Ayak ucuna lacivert yakın çiçekli bir kumaş sarıldı. En üste Kabe örtüleri, kıymetli taşlarla süslenmiş kemerler konuldu. Başına ve kollarına şallar sarıldı. Baş tarafına yeşil atlas üzerine kırmızı bir fes konuldu. Naaş yıkanırken, çıplak bir tabut, tahta bir teneşir, Hırkai Saadet dairesinin göz kamaştıran renkleri ve yaldızlarına tezat teşkil ediyordu. Şimdi Sultan Abdulhamid’in ipekler, şallar, sırmalar, kıymetli taşlarla süslü tabutu, dairenin ihtişam ve ulviyetine uygun bir şekilde hazırlanmıştı.
Herkes çekildi. Yalnız, süslü sütunlar, mülevven duvarlar, parlak levhalar arasında, başı harem dairesine yöneltilmiş tabut, solda Daire-i Hümâyûn’ın penceresinden altınlar ve sırmalarla süslü yeşil perdeler, ağır sırma püsküller, altın şebekeler, kıymetli ve tarihî levhalar, kadim kelâmı hatırlatanlar görülüyordu. Arzhane önünden bir ağıt sesi işitildi. Damad Paşalardan muhterem bir zat, etkilenmiş adımlarıyla ilerledi. Hırkai Saadet duvarının k��şesinde melûl ve mahzun durdu. Ellerini açtı, gözleri tabuta yönelik kısa bir dua etti, ansızın bir hıçkırık, müzeyyen kubbelerde yankı bıraktı.
Saat dokuz. Hırkai Saadet kapısının önünde sırmalı üniformalar, kalpaklar ve şapkalardan oluşan birbirinden farklı heyetler bekliyordu. Yabancılar bu muazzam daireyi merak ve hayretle izliyordu. Ulema, arkalarında geniş kollu, püsküllü yeşil ve mor ilmihallerle, saygıyla karşılanıyordu. Kalabalık giderek artıyordu. Veliaht, şehzadeler, büyük uniformalarıyla katılıyorlardı. Şubat güneşi altında, nişan, sırma ve özellikle uniformaların parıltısından başka bir şey göze çarpmıyordu.
Hırkai Saadet dairesinin kapısı bir anda açıldı. Bütün gözler o tarafa çevrildi, kalabalık o yöne doğru sıkıştı. Kapının iki tarafı dolup taştı. Herkes, kalpleri derin bir hüzünle, cenazeyi görmek istiyordu. Nihayet, elmaslı kemerler, sırmalı Kabe örtüleri, al atlaslarla süslü tabut, kırmızı fesi ile, parmak uçlarında, görkemli ve muazzam bir şekilde dışarı çıktı. Devlet erkânı, zabitler, Sultan Abdulhamid’in cenazesi için alayda yerlerini aldılar. Bütün gözler tabuta dikilmişti. Tabut, Hırkai Saadet kapısı önüne yüksek bir mevkiye konuldu. Hamidiye Camii’nin Kürsü Şeyhi, sırmalı yeşil esvabı, göğsünde nişanı ile taşın üzerine çıktı. Etrafına bakınarak sordu:
— Merhumu nasıl bilirsiniz?
Velilerin hazin, müteessir birçok sesi, serviler arasında yankılandı:
— İyi biliriz.
Kısa bir fatiha ile merasime son verildi. Tabut kaldırıldı. Sultan Ahmedi Silis Kütüphanesi’nin, Arz Odası’nın sağından ağır ağır geçti. Babüssaade önüne geldi, cenaze namazı alelhusul burada kılındı. Alay burada düzenlendi. Şehzadegan, ayan, mebusan, devlet erkânı, sefirler ve ümera, hep burada toplandılar. Arada sırada, teşrifat memurlarının sırmalı elbiseleri içinde ellerinde beyaz bir kağıtla:
Ayan, mebusan, ricali ilmiye, ümera…, diye çağırdıkları işitildi. Nihayet alay düzenlendi. Servilerin önünde saray hizmetlileri ve zabıtan tebaası dizilmişlerdi. Piyade askerleri, silahlarını omuzlarına asmışlar, sakin adımlarla yürüyorlardı. Tabutun önünde dede torunları, Şazeli dergahı dervişleri ilerliyordu. Tabutu taşıyanlar, Enderun hümayun ağaları ve saray erkânıydı.
0 notes
Text
Cho’lpon and Abdulla Qodiriy
If you didn’t listen to our podcast episode on Abdurauf Fitrat, you may be wondering why a podcast about asymmetrical warfare is talking about two writers. There’s the personal reason and the “academic” reason.
On the personal side: Abdurauf Fitrat, Cho’lpon, and Abdulla Qodiriy are why I became interested in Central Asian history, particular during the Russian Civil War and the Sovietization of the Central Asian States. So, this episode is a chance for me to highlight fascinating people who inspired this podcast.
Academically, Cho’lpon, Qodiriy, and Fitrat were key members of the Jadid movement who shaped the cultural landscape of Turkestan during the civil war. They are representative of the people the Soviets found threatening as they tried to solidify their hold on the region. So, even if they weren’t physically fighting, they were building a cultural and social framework that fundamentally threatened the Soviet dream projects for the region.
Cho’lpon
Cho’lpon, also known as Abdulhamid Sulaymon ogli Yunusov is considered to be one of the great Uzbek poets of the 20th century. He fundamentally reshaped poetry while also working as a playwright, novelist, translator, and political activist. He was born in Andijan to a wealthy merchant in the 1890s and started his education in a Russian school. His father wanted him to attend a madrasa and he ran away to Tashkent, where he tried to make it as a writer. While in Tashkent, he became involved in editing and writing for Jadid journals and in their intellectual and literary circles. He was close to both Mahmud Xo’ja Behbudiy (who was murdered by the Bukharan Emir during the Russian/Central Asian Civil Wars) and Abdurauf Fitrat, who became his mentor, pushed him to focus on poetry, and gave him his penname: Cho’lpon which translates to morning star.
Russian Civil War
When the Russian Revolution occurred, there were mixed reactions within the Jadids. Fitrat would write that this was just one more calamity to afflict the Russians, but Chol’pon wrote a poem called the Red Banner, celebrating the Revolution. This excerpt translated by Christopher Fort gives you a sense of how that poem went:
“Red banner! There, look how it waves in the wind, As if the qibla wind is greeting it! It is not glad to see the poor in this state, For the poor man has the right because it is his. Has the red blood of the poor not flown like rivers To take the banner from the darkness into the light? Are there no workers left in Siberian exile To take the banner to the oppressed and weak people? You, bourgeoisie, conceited upper classes, don’t approach the red banner! Were you not its bloodsucking enemy? Now the black will not approach those white rays of light, Now those black forces’ time has pass!” - Cho’lpon, Night, pg. 8-9
Cho’lpon was involved in the creation of the Kokand Autonomy and even wrote a poem to celebrate its creation and mourned its destruction by the Tashkent Soviet. When the Bolsheviks entered the region, the Jadids welcomed them because they had no one else to support their work. The Jadids had always been a minority in the region and remained powerless and isolated as Turkestan succumbed to civil war. Working with the Bolsheviks, the Jadids helped overthrow the emirs, the Russian settlers, and the Basmachi.
For his part, Cho’lpon lived a wandering life after the fall of the Kokand Autonomy, apparently working at a theater briefly, but he still mourned the devastation the wars imparted on Turkestan, publishing a poem “To the Despoiled Land.” The excerpt I read is from Adeeb Khalid’s Book Making Uzbekistan
“O mighty land whose mountains salute the sky, Why are there dark clouds over your head? “Your beautiful green pastures have been trampled, They have no cattle, no horses. Which gallows have the shepherds been hanged from? Why, instead of neighing and bleating, There are only mournful cries? Why is this? Where are the beautiful girls, the youthful brides? Is there no answer from heaven or earth? Or from the despoiled land?! Why is the poisoned arrow Of the plundered, heavy crown still in your breast? Why don’t you have the iron revenge That once destroyed your enemies? O, free land that has never put up with slavery, Why does a shadow lie throttling you?” - Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 217
As we can tell from this poem, Cho’lpon was deeply affected by the destruction that was unleashed to the region. I don’t think anyone can blame him for, as we have mentioned many times in this podcast, the destruction was devastating and afflicted the indigenous populations the hardest. However, the Soviets would use these poems and this “anti-Bolshevik” sentiment against Cho’lpon in the 30s when Stalin’s Purge sought to break the Central Asian intelligentsia.
Crafting a Literary and Cultural Legacy
Cho’lpon returned to Bukhara in 1920 after Fitrat offered him a job to work at Axbori Buxoro the main newspaper of the People’s Soviet Republic of Bukhara
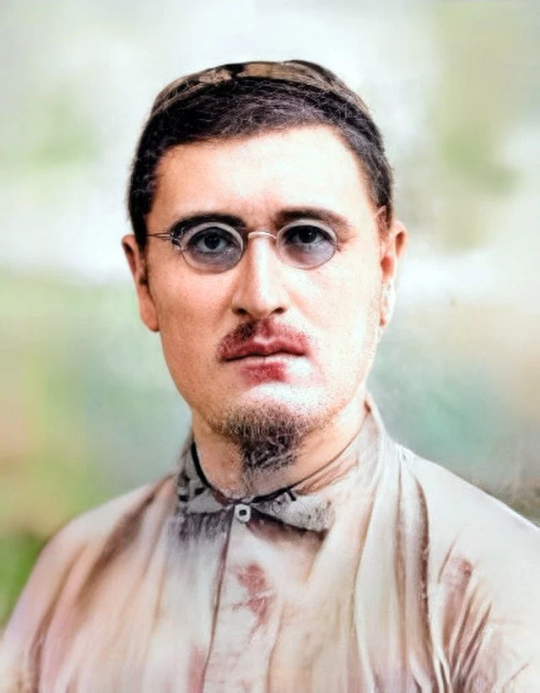

Cho'lpon
[Image Description: A color photo of a man wearing a skull cap, round wire frame glasses, and a tan shirt. He has short brown hair and a short, closely clipped mustache, and goatee. Behind him are out of focus trees]
Cho’lpon, like Fitrat, was heavily involved in crafting a Turkic specific identity for Turkestan, no longer writing in Persian, but in a Turkic language crafted by Fitrat, Cho’lpon introduced the Turkic meter to local poetry. He was a main contributor to the anthology Young Uzbek Poets and produced three collections of poems. He also translated several works in Persian and Russian, and introduced many Uzbeks to Shakespeare, Chekhov, and Gogol. He was a big supporter of rejuvenating the theater scene in Tashkent and wrote many plays. As the horrors of the war passed and the region entered a new decade, Cho’lpon and many Jadids saw the 1920s as a chance to rebuild. Cho’lpon believed that the revolution and civil war had created the conditions needed for the Uzbek state to take its place in the world. He would write in 1922:
“The famous Pobedonostsev, champion of the Christianizing policies of Il’minskii – who (himself) was a Rustam in the matter of Christianizing the Muslims of inner Russia and the teacher of our own Ostroumov to’ra – once wrote, “Among the natives, the people most useful, or at any rate the most harmless, for us are those who can speak Russian with some embarrassment and write it with many mistakes, and who are therefore afraid not just of our governors but of any functionary sitting behind a desk” Now we are earning the right to answer back not just in Russian, but in the languages of the civilized nations of Europe…I the free young men of the Uzbek [nation] and even its unfree young girls begin a revolt against the legacy of Il’minskii,…then we too can win our right to join the community of peoples without being beaten and humiliated” - Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 179
Cho’lpon was also involved in the “liberation” of women – although the Jadid’s definition of women’s liberation was different from the Bolshevik’s definition. The Bolsheviks pushed the unveiling of women and wanted to “Europeanify” Muslim women. This was partially a result of their own efforts to end gender standards, but it was also a direct assault on Islam. The Jadids support women’s rights and many unveiled their own wives. Cho’lpon wrote a play about the veil and his book Night is about the cruel fate of a girl forced to marry an official who already has three other wives and how the justice system fails its people, especially women. He was also against the practice to seclude women, believing it contributed to their lack of education and “backwardness.” Like other Jadids, Cho’lpon found it hard to align liberation in the theoretical realm and how it was implemented in the real world, especially when there was this undercurrent of “attacking” Islam. Many people in the rural areas and women did unveil were murdered by angry mobs. Cho’lpon would have several wives and it seems he struggled with maintaining relationships with women. I think it’s also fair to say that he had considerable trauma from the civil wars and the destruction he witnessed, and it most likely affected his relationship with those closest to him.
The Fall
The Jadids exercised considerable local power free in the early 1920s and were in the process of creating their own nationalistic Islamic, modern government. The Bolsheviks distrusted this government because it didn’t match Communist principles. In 1923, they struck fast and hard, forcing the Xojaev’ government to oust four of its own members, including Abdurauf Fitrat who was discussed last episode. Fitrat went into exile in Moscow in 1923. In 1924, Cho’lpon traveled to Moscow to study at the Uzbek Drama studio. At this point, he was still tolerated in Central Asia and the Soviets weren’t yet attacking him outright.
By 1927, several Russian writers and Central Asia leaders who wanted to establish their pro-Communist credentials were attacking Fitrat, Cho’lpon, Qodiriy, among others. One indigenous Communist would complain in 1927 that
“the Uzbek literary language of today is doubtless Cho’lpon’s language. Who is Cho’lpon? Whose poet is he? Cho’lpon…is a poet of the nationalist, patriotic, pessimist, intelligentsia. His ideology is the ideology of this group” - Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 334
He was also
“an idealist and an individualist, and therefore sees every political and social event not from the side of the masses but of his own personal point of view” - Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 334
In 1927, people were still brave enough to defend Cho’lpon. An indigenous writer, Oybek, wrote that Cho’lpon was like “Pushkin” who the young generation loved because of “his simple language, his delicious style, his technique” he was like Pushkin who “remained Pushkin even after the revolution because his works created the immortal richness of Russian literature” (Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 335). As the decade came to a close, Fitrat and Cho’lpon were used as a litmus test for whether someone was truly communist or not. If you defended Cho’lpon, you were lacking in your communist understanding and credentials. If you attacked him, you were safe from Stalin’s purge…for a time.
Pravda Vostoka, the Russian-language paper of the Central Committee of Communist Party of Uzbekistan published a news article titled “The Bark of the Chained Dogs of the Khan of Kokand.” It was one of the vilest attacks against Cho’lpon and other members of the Uzbek intelligentsia. The attack was written by El’ Registan, the future author of the Soviet national anthem of 1943. He claimed that Cho’lpon was a “prostitute of the pen…a stoker of chauvinism” whose anti-Soviet works were recited “in chorus by Basmachis taken prisoner and could now be heard all across Uzbekistan in any teahouse” (Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 372). The article went on to attack other writers, including Qodiriy and Fitrat, and was the first nail in Cho’lpon’s coffin.
For his part, Cho’lpon wrote that El’ Registan’s criticism was “an old matter, for which I was abused plenty then. Now it’s necessary to abuse me for new misdeeds, if there are any” (Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 372)
Why attack Cho’lpon? He was only a poet and playwright. What made him so threatening to the Soviet project? The answer may lie in his poem, Autumn in which he wrote:
“O you who come from cold places, clothed in ice May that grating voice of yours be lost in the snow. O you who pick the fruits of my garden, May your dark heads be buried in the earth.” - Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 217
Cho’lpon’s poems, while simple, were gut-wrenching and easy to understand and read. He was able to capture complex thoughts and translate them into the simplest of imagery and feelings for people to latch onto. Cho’lpon had a visceral reaction to the destruction of the civil war and channeled it into his writing and the Bolsheviks knew he wasn’t the only one upset about what had happened to the region. While the Basmachis contributed to the death and violence, it was also easy to blame the Russians for bringing the horrors with them, as they had done in the 1800s, with their colonial projects. Additionally, Cho’lpon was a Jadid, many of whom made up the current government of the Soviet republics. The reforms he and other Jadids fought for not only conflicted with Communist reforms, it was another option. Historically, the Communists have never tolerated dissent or other governmental options and so the Jadids had to go.
Cho’lpon’s greatest power though, may have been his own sarcasm. I mean this with all the love in the word but Cho’lpon was a sarcastic little bitch. In 1937, he was called before the Writer’s Union to answer charges of nationalism leveled against him and he replied,
“I have many mistakes, but I will correct them with your help. But what training have you given me in these years?”
and when they published his book without an explanatory preface he pointed it out, saying
“Abuse was required here, for the youth should not be allowed to read Cho’lpon’s work without an intermediary…Why did the work of this nationalist appear without a preface?” - Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 382
He seemingly didn’t take the criticism seriously and so had the potential to undermine the power of the various organizations put in place to keep writers and intellectuals in control.
Finally, and most damningly, Cho’lpon was a member of the old guard. He was part of a world that could not exist comfortably alongside Communism. He thought about government and the world with the bias and frameworks of a world that no longer existed. The Bolsheviks didn’t care if he could change his way of thinking or if he even wanted to. All that mattered was that he represented an old world and a potential new world that didn’t rely on Communist principles. That, in itself, was enough to murder him.
Arrest and Execution
Cho’lpon returned from Moscow in 1927 to stage plays around Uzbekistan, but returned to Moscow in 1932 when he could no longer tolerate being the Bolshevik’s favorite punching bag. While in Moscow he focused on translating European writers in Uzbek. He returned to Central Asia in 1934 and wrote his first and only novel Night. Whether he wrote it to earn the Bolshevik’s good graces, to write a final, scathing indictment of Communism, or just to play with the novel structure, is still up for debate. It is a challenging, but beautifully written and engaging book (I like it better than O’tkan Kunlar, but don’t tell anyone). It is supposedly the first book in a duology (Christopher Fort writes a great paragraph in his introduction to Night that this missing second book may have never even existed in any written format, but more of a thought in Cho’lpon’s head). It is about the horrors of a young woman faces when forced to marry an older man in the 1910s Central Asia. In the novel, he attacked the powerlessness of women in Turkestani society and the old practices of polygamy and forced marriages, but also corruption local rulers, the ulama, and even the Jadids themselves. You can buy Night translated by Christopher Fort from any bookstore. The book wasn’t hated by the Bolsheviks and Cho’lpon was arrested on July 13th, 1937.
He was charged as a nationalist and for being part of a secret society known as Milliy Ittihod (National Union) which we’ll cover in our next episode. Instead of denying the fake charges, Cho’lpon “confessed,” most likely because he was smart enough to understand there was no salvation possible. He was a dead man the moment he was arrested. The NKVD murdered him, alongside Fitrat and Qodiriy on October 4, 1938.
After he was murdered during the Stalinist purges, Cho’lpon’s works were never published or discussed until a brave editor attempted to include his poems in an anthology of Uzbek poetry in 1968 and was severely reprehended by the Soviet government. His work was passed around secretly, but he remained persona non grata until the fall of the Soviet Union. He has now been rehabilitated as a hero of Uzbekistan.
Abdulla Qodiriy
Abdulla Qodiriy was born in Tashkent in 1894 to a family of modest means. He attended a Russian-native class and worked several odd jobs before publishing his first piece in 1915. He did not reach critical fame until the 1920s, when he became an editor for the satirical magazine: Mushtum (the Fist). His work with Mushtum was groundbreaking. He took the living language he heard on the street and immortalized it in writing while perfecting satire in Uzbek literature.
Attacking the ulama
While he was a brilliant satirist, he could also be quite cruel and his favorite targets were the ulama, eshons, and bureaucrats. He often depicted the ulama as traditionalists and conservative who were narrow-minded and unable to understand the world and Islam. Despite this, he was well versed in Islam. He studied at the Beglarbegi Madara in Tashkent, he spoke Arabic, Persian, and Turkic. He even took part in discussions with ulama while he wrote Mushtum.

Abdulla Qodiriy
[Image Description: A green staamp with a black adn white photo of a man with short dark hair and a short mustache. He is wearing a black shirt and a grey suit coat. The stamp says 2004 125-00 on top, Abdulla Qodiriy (1894-1938) along the side, and O'zbekiston on the bottom]
An example of his wit can be found in his piece called Shayxontahur mausoleum. These mausoleums or shrines were an integral part of Central Asian life. The leaders of the Bukharan Soviet tour down shrines or mausoleums because they thought the ulama and eschons who cared for the shrine took advantage of the faith of the people and that the act of paying respects to the dead was “backwards.” So, they tore down the shrines and replaced them with schools. Qodiriy’s piece memorialized the demolition of the Shayxontahur mausoleum. It was a drawing of two devils: Iblis and Azazel, bemoaning the fact that “our house is being destroyed, the customs of our ancestors are being trampled” (Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 225). An accompanying article compared the two demons to certain ulama who had opposed the destruction. It is almost as scathing as some of Fitrat’s works deconstructing Islamic beliefs and traditions.
Qodiriy was a faithful Muslim who saw no contradiction between being a practicing Muslim and criticizing the ulama. During one of his interrogations with the NKVD, he said
“I am a reformist, a proponent of renewal. In Islam, I only recognize faith in God the munificent as the highest reality. As for the other innovations, most of them I consider to be the work of Muslim clerics - Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 225
Success as a Novelist
In 1925, he published O’tgun Kunlar, his first novel and the first prose novel written in the Uzbek language. It is about Atabek and the love of his life Kumush. They marry, but Atabek’s mother hates Kumush and forces Atabek to take a second wife, Zainab. Things go terribly and people die. It sold 10,000 copies and his second novel, also a historical fiction, Mehrobdan Choyon (Scorpion in the Altar) which was published in 1928, sold 7000 copies.
In 1932, Qodiriy was admitted to the Uzbekistan Writer’s Union and two years later was actually elected as one of its delegates to the First Congress of the All-Union organization (where he and Sadriddin Ayni met Maxim Gorky and a picture was taken of the trio).
Despite finding success in the literary world, Qodiriy’s satire got him in trouble with the Bolshevik authorities and he was arrested in 1926 for making fun of Akmal Ikromov, a Communist Uzbek vying with Fazulla Xojaev for leadership over the Bukharan Soviet Republic. The Soviets had grown weary of Mushtum and used this as an excuse to get rid of its editor. He was thrown in jail for six months before being released – this time – but was banned from writing for the press. Instead, he a living writing original work and translating. He also found odd jobs such as writing the letter P in the first major Russian-Uzbek dictionary in 1934, translated a collection of antireligious essays, and worked on a film script based on Chekhov’s Cherry Orchard.
Arrest and Execution
Fayzulla Xojaev commissioned Qodiriy to write about the Uzbek peasantry which would be published as a serialized piece called Obid Ketmon. This worked was vilified for being anti-Soviet and Qodiriy was accused of being antisocial and apolitical. He, like Cho’lpon and Fitrat, became the favorite punching bag of anyone trying to prove their Communist credentials. He watched as Fitrat was arrested in July 1937, Cho’lpon was arrested on July 13th, 1937, and Qodiriy was finally arrested on the last day of 1937. Qodiriy was accused of being a member of a counter revolutionary organization that collaborated with Trotskyites, of carrying out anti-Soviet work in the press, and have direct relations with Xojaev and Ikromov (who were dead at the time of Qodiriy’s arrest). Qodiriy admitted to being a nationalist until 1932, but then mended his ways. According to his son, when Qodiriy was given his “confession” to sign (and would serve as his death warrant) he wrote:
“This resolution was announced me to (I read it); I do not agree to the charges contained in it and do not accept them” - Adeeb Khalid, Making Uzbekistan, pg. 386
He, along with Fitrat and Cho’lpon, were murdered on October 4th, 1938.
References
Making Uzbekistan: Nation, Empire, and Revolution in the Early USSR by Adeeb Khalid
Night by Cho’lpon, translated by Christopher Fort
Days Gone By by Abdull Qodiriy, translated by Carol Ermakova
#queer historian#history blog#central asia#central asian history#queer podcaster#spotify#cho'lpon#abdulla qodiriy#central asian literature#Spotify
1 note
·
View note
Note
Shouq bint Hamid AlGhaleb fiancée of AbdulHamid AlSaleh is from the Hashimate family but from a different side she’s as what they call”sharifa”similar status to what sharif Hassan bin Zeid or sharifa Farah Alluhaymaq family have they aren’t royals since they’re not descends of sharif Hussein or king Abdullah 1 but close to the royal family some say that’s the arranged marriage in the family but princess Alia don’t seem to believe in arranged marriages I mean her parents divorce is a proof.
Thanks for the info. Very interesting to know this!
1 note
·
View note
Text
İtalya Libya sivil havacılığına uyguladığı ambargoyu kaldırdı
İtalya, Libya sivil havacılığına uyguladığı ambargoyu kaldırdı
İtalya’nın, yaklaşık 10 yıldır Libya sivil havacılığına uyguladığı ambargoyu kaldırdığı duyuruldu. Libya Ulusal Birlik Hükümeti Başbakanı Abdulhamid Dibeybe, resmi Facebook sayfasında yaptığı açıklamada, İtalya hükümetinin bu ambargoyu kaldırma ve eylül ayından itibaren uçuşların yeniden başlamasına izin verme kararı aldığını belirtti. Dibeybe, İtalya Başbakanı Giorgia Meloni’ye ve ambargonun kaldırılmasında katkısı olan herkese teşekkür etti.
İtalyan hükümeti henüz konuyla ilgili resmi bir açıklama yapmadı. Ancak Libya Başbakanı Dibeybe, 7 Haziran’da gerçekleştirdiği resmi ziyaret sırasında İtalya Başbakanı Meloni ile enerji, güvenlik ve altyapı alanlarında anlaşmalar imzalamıştı. İkili ayrıca, Libya sivil havacılığına yönelik hava ambargosunun kaldırılması için çalışmalar yapan ikili komitelerin ilerlemesini ele almıştı.
Avrupa Komisyonu, 2014 yılında güvenlik kontrolleriyle ilgili gerekçelerle Libya Hava Yolları’na ait uçakların Avrupa Birliği üyesi ülkelerin hava sahasından geçişini yasaklamıştı. Ancak İtalya’nın bu ambargoyu kaldırma kararı, Libya sivil havacılığının uluslararası arenada daha fazla faaliyet gösterebilmesine olanak sağlayabilir.
The post İtalya, Libya sivil havacılığına uyguladığı ambargoyu kaldırdı first appeared on 0 554 1730000 I [email protected] / Güncel Havacılık Haberleri.
source https://www.aeroportist.com/italya-libya-sivil-havaciligina-uyguladigi-ambargoyu-kaldirdi/
#İtalya#Libya sivil havacılığına uyguladığı ambargoyu kaldırdı https://www.aeroportist.com/italya-li
0 notes
Text
شېخ دي مونځ روژه کړې زه به ډکې پيالۍ اخلم
هر سړے پېدا دے خپل خپل کار لره کنه...
The priest may fast and pray, that has never been my way, for me another rule... The cup of life is full
For me another way is there not? I will take a good long pull, may I not?
Khushal khan khattak
#literature #pashtoliterature #pashtoode #pashtopoetry #khushalkhan #ghanikhan #hamzashinwari #rehmanbaba #abdulhamid #alikhan #kazimkhan #ashrafkhan #orientallanguages #Usafxai
0 notes