#Vietnam Logistics Market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Vietnam Logistics Market Flourishes: CEP and Warehousing Sector Generate over USD 5 Bn in 2022, Fueled by Joint Ventures and Modern Warehousing Systems. What Awaits the Future? :Ken Research
Buy Now
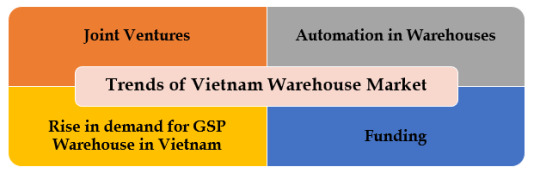
1.Emerging Trends and Developments in Vietnam's Warehousing Market: Joint Ventures, Automation, GSP Warehouse Preference, and Recent Funding Surge.
Interested to Know More about this Report, Request for a sample report
Logos Property and Manulife Investment Management joined forces in 2022 to construct an advanced logistics factory, covering an area of over 116,000 sqm and valued over $80 Mn. Moreover, GLP entered the Vietnamese market through a $1.5 Bn joint venture with SLP.
E-commerce companies are utilizing AI-powered warehouses and sorting centers spanning 0.3 Mn sqm to decrease delivery time during peak periods. Tiki NOW Smart Logistics has integrated robots for task execution, enhancing warehouse efficiency and enabling sellers to save 30% - 40% in costs.
Investment in pharmaceutical storage systems or GSP warehouses is increasing in Vietnam, with foreign firms such as DKSH, Zuellig, and Mega making substantial investments to improve cost-efficiency and optimize manpower in warehouses.
Vietnamese on-demand warehousing platform, Wareflex, secured $785,000 in pre-seed funding from Genesia Ventures and Antler. Additionally, Mirae Asset Daewoo Co. and Naver Corporation, prominent South Korean companies, invested $37 Mn in a warehouse located in Bac Ninh, Vietnam.
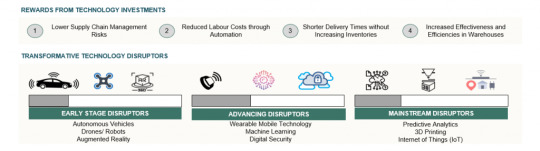
2.Automation Surge: Vietnam's Growing Demand for Modern Warehouses Driven by Increased Investment in New Technologies.
Visit this Link :- Request for custom report
Next generation supply chains in Vietnam are utilizing robotics and automation to perform task such as picking, sorting, inspecting, handling to improve overall efficiency and speed to market. Some warehouses are turning to autonomous vehicles to bring merchandise to sortation while Drones & RFID will be used for Inventory Management. The opportunities seem endless which will result in greater efficiency and productivity.
3.Tech Trends Unleashed: Big Data and Augmented Reality Empower Vietnam's CEP Market in Response to Consumer Demand.

Market Maxomony
Vietnam Logistics Market Segmentation
By Service Mix
Freight Forwarding
Warehousing
CEP
Value Added Services
Vietnam Freight Forwarding Market Segmentation
By Mode of Freight
Road Freight
Sea Freight
Air Freight
By Type of Freight
International Freight
Domestic Freight
By Types of Operators
Small Fleet Operator (SFO)
Medium Fleet Operator (MFO)
Large Fleet Operator (LFO)
By End-User
Retail
Oil and Gas
Textiles
Pharma
Others
Vietnam Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Warehousing Types
General/Industrial/Retail
CFS/ICD
Cold Storage
Agriculture and Others
By Warehouse Locations
Northern
Central
Southern
By End-User
Retail
Oil and Gas
Textiles
Pharma
Others
Request a Call with Expert to know more about Latest Trends
Major Players Mentioned in the Report:
Yusen Logistics
Transimex
Gemadept Corporation
Maersk
Kuehne+Nagel
MP Logistics
ITL
Vietnam Post
Viettel Post
Vietnam Maritime Corporation
Expeditors
Bee Logistics
DB Schenker
Vinafrieght Joint Stock Company
CJ Gemadept
Ceva Logistics
GHN Express
DHL VNPL Express
EMS
Key Target Audience
E-Commerce Companies
Third-Party Logistic Providers
Potential Market Entrants
Freight Forwarding Companies
Warehousing Companies
Cold Storage Companies
Industry Associations
Consulting Agencies
Government Bodies & Regulating Authorities
Time Period Captured in the Report:
Historical Period: 2017-2022
Base Year: 2022
Forecast Period: 2022-2027
For More Insights On Market Intelligence, Refer to the Link Below: –
Vietnam Logistics Market Outlook to 2027
Related Reports by Ken Research: –
Indonesia Logistics Market Outlook to 2027
#Vietnam Supply Chain Industry#Vietnam Logistics Market#Warehousing Industry Vietnam#Delivery Services Sector Vietnam#Vietnam Freight Forwarding Business#Inventory Distribution Industry Vietnam#Vietnam Transportation Market#Logistics Sector Vietnam#Number of Shipping Fleets in Vietnam#Number of Sea Ports in Vietnam#Number of Truck Fleets in Vietnam#Number of Warehouses in Vietnam#Vietnam Freight Forwarding Services Market#Logistics Services Industry Vietnam#Vietnam CEP Services Sector#Value Added Services Division Vietnam#Vietnam Road Freight Market#Sea Freight Industry Vietnam#Vietnam Air Freight Sector#Retail Logistics Division Vietnam#Oil Shipping Market Vietnam#Vietnam Gas Transport Industry#Pharma Warehousing Sector Vietnam#Industrial Delivery Services Sector Vietnam#Vietnam Retail Warehouses Market#CFS Warehouses Industry Vietnam#Vietnam ICD Warehouses Division#Cold Storage Warehouses Sector Vietnam#Vietnam Agriculture Warehouses Market#Vietnam International Logistics Shipments
0 notes
Text
Vietnam Third Party Logistics (3PL) Market Industry Trends, 2023-2030
BlueWeave Consulting, a leading strategic consulting and market research firm, in its recent study, estimated Vietnam Third Party Logistics (3PL) Market size by value at USD 6.09 billion in 2023. During the forecast period between 2024 and 2030, BlueWeave expects Vietnam Third Party Logistics (3PL) Market size to expand at a CAGR of 2.4% reaching a value of USD 7.19 billion by 2030. The Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Market in Vietnam is propelled by Vietnam's supportive government policies, trade agreements, and economic growth are creating a conducive environment for logistics development. The increasing demand for efficient and sustainable logistics solutions, particularly in e-commerce, cold chain, and green logistics, is shaping the industry's future. The country's focus on multi-modal transport and infrastructure development further strengthens its position in the regional logistics landscape.
Sample Request @ https://www.blueweaveconsulting.com/report/vietnam-third-party-logistics-market/report-sample
DTM Service Segment Holds Largest Share of Vietnam 3PL Market
The domestic transportation management (DTM) remains the dominant segment in Vietnam Third Party Logistics (3PL) Market by service, driven by the country's growing manufacturing and e-commerce sectors. Despite challenges, the DTM segment plays a crucial role in supporting logistics infrastructure and trade. Government initiatives and industry collaborations are essential to enhance its competitiveness and foster sustainable growth. The other major service segments in Vietnam Third Party Logistics (3PL) Market include Dedicated Contract Carriage (DCC)/Freight Forwarding, International Transportation Management (ITM), Warehousing &Distribution (W&D), and Value-Added Logistics Services (VALs).
Impact of Escalating Geopolitical Tensions on Vietnam Third Party Logistics (3PL) Market
Intensifying geopolitical tensions could have a multifaceted impact on Vietnam Third Party Logistics (3PL) Market. The increasing geopolitical uncertainties undermine the stability of global supply chains, leading to disruptions that could negatively impact Vietnam's logistics market. Higher costs, delays, and reduced predictability may deter foreign investment and limit growth opportunities for 3PL providers in the country.
Competitive Landscape
Vietnam Third Party Logistics (3PL) Market is highly fragmented, with numerous players serving the market. The key players dominating the market include DHL Vietnam, FedEx Vietnam, Kerry Logistics, Gemadept, Vinafco, Transimex Saigon, Crane Worldwide Logistics, BSS Vietnam, Cargonet LOGISTICS Vietnam, and Mekong Logistics. The key marketing strategies adopted by the players are facility expansion, product diversification, alliances, collaborations, partnerships, and acquisitions to expand their customer reach and gain a competitive edge over their competitors in Vietnam Third Party Logistics (3PL) Market .
Contact Us:
BlueWeave Consulting & Research Pvt Ltd
+1 866 658 6826 | +1 425 320 4776 | +44 1865 60 0662
0 notes
Text
#Vietnam IoT Powered Logistics Market#Market Size#Market Share#Market Trends#Market Analysis#Industry Survey#Market Demand#Top Major Key Player#Market Estimate#Market Segments#Industry Data
0 notes
Text
Lotte Group Pivots: Vietnam Beckons as China Exit Nears: Ken Research
Buy Now
Lotte Group embraces Vietnam's potential while withdrawing from China, capitalizing on the country's promising market opportunities.
Storyline
Lotte Group shifts focus: Vietnam's retail and F&B industries.
Expansion plans: Lotteria restaurants, Lotte Mart hypermarkets, and more.
Vietnam's growth potential: Favorable market conditions and rising consumer income.
As per Ken Research, the company’s retaliation aftermath will lead to strategic realignment.
South Korea based Lotte Group, the country's fifth-largest conglomerate, is accelerating its expansion in Vietnam's retail and F&B sectors as it finalizes its recent withdrawal from the Chinese market. Following his recent release from jail and receiving a presidential pardon, Chairman Shin Dong-bin is poised to visit Vietnam, signaling the group's determination to pursue business in its "third-most important market" after South Korea and Japan. Lotte's focus on Vietnam comes as the company's top executives have been closely monitoring their opportunities in the country, recognizing the growth potential and favorable business environment.
1. Growing Presence in Vietnam

To learn more about this report Download a Free Sample Report
Lotte boasts an expansive presence in Vietnam, with 270 Lotteria fast-food restaurants and 15 Lotte Mart hypermarkets. Additionally, Lotte's subsidiaries are actively involved in the development of shopping complexes and residential apartments in major cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City. The establishment of Lotte Ventures Vietnam last year further solidifies the group's commitment, making it the very first foreign venture capital firm approved in the country.
2. Vietnam's Favorable Market Conditions

Visit this Link: – Request for custom report
The decision to focus on Vietnam is driven mainly by the country's strong retail sector, experiencing significant growth, and a rising disposable income level. Lotte recognizes Vietnam's potential as a strategic market, benefitting from Korea's positive reputation and strong consumer demand. The group views Vietnam as a key growth driver in the region, offering ample opportunities for expansion and development.
3. Exit from China

Lotte's exit from the Chinese market comes after 14 years of operation, as it faced challenges due to alleged retaliation from China following the deployment of the THAAD missile defense system in 2017. The decision to fully divest from China reflects the company's strategic realignment and its focus on emerging markets with more favorable growth prospects.
Conclusion
Lotte Group's intensified focus on Vietnam's retail and F&B industries signifies its commitment to leveraging the country's growing market potential. As per Ken Research, as the conglomerate completes its withdrawal from China, it aims to capitalize on Vietnam's favorable business environment and consumer-driven growth. Lotte's expansion efforts in Vietnam highlight its strategic vision and determination to establish a strong presence in one of Southeast Asia's most promising markets.
0 notes
Text
Who is the largest exporter of candles?

China holds the position as the largest exporter of candles globally, dominating the market with exports valued at approximately $1.27 billion as of 2022. China's massive manufacturing capabilities, cost-effective production, and efficient logistics network drive this extensive market presence. Chinese manufacturers supply various decorative, scented, and utility candles, catering to diverse global demands.
Poland follows closely as the second-largest exporter, with exports valued at around $987 million. Poland has become a significant player in the candle industry, particularly in the European market. Its products are known for their quality and compliance with European Union standards, making them highly sought after in the region and beyond.
Vietnam ranks third in global candle exports, with a market value of approximately $615 million. Vietnam's candle export industry is characterized by its craftsmanship and innovative designs, appealing to niche markets that prioritize aesthetic and artisanal value.
These countries contribute significantly to meeting the global demand for candles, driven by uses ranging from home decor and aromatherapy to religious and festive celebrations. With the rising popularity of scented candles and environmentally friendly products, many exporters are now focusing on sustainable practices, such as using soy or beeswax and adopting recyclable packaging.
The candle export industry reflects a growing consumer trend toward enhancing home ambiance and wellness. While China remains the largest exporter by sheer volume, countries like Poland and Vietnam have carved niches emphasizing quality and design. Together, they illustrate the diverse factors driving the international candle trade.
For detailed insights and quality candle products, businesses and buyers can explore platforms like DSK Oceani Impex, which connects suppliers with global markets.
#commercial#candles#candle export#chrimas candles#christmas decoration candles#christmas decoration candle#christmas decor#christmas#xmas#happy christmas#happy marry christmas#cats of tumblr#blog#blog post#tumblrpost#new blog#bucktommy#cottagecore#witch#soft grunge#grunge#cincinnati bengals#amy rose#alnst#artists on tumblr#dsk#dskoceanimpex
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Soybean Export from India: Trends, Data, & Market Outlook for 2025

India's agricultural exports continue to gain momentum, with soybean standing as a key contributor. Known for its high nutritional value and diverse industrial applications, soybeans play a pivotal role in the global agri-commodity market. As the world’s demand for plant-based proteins and sustainable oils increases, India's position as a significant player in soybean exports strengthens. This article delves into the current trends in soybean export from India, examines soybean export data, highlights key soybean exporters in India, and explores major soybean-exporting countries for 2024-2025.
The Landscape of Soybean Export from India
India has emerged as a prominent exporter of soybeans, contributing significantly to global trade. Factors such as robust agricultural policies, advancements in farming techniques, and a focus on export-oriented production have bolstered India's soybean export capabilities.
In the 2024-2025 period, soybean exports from India are expected to grow due to increasing international demand. Indian soybeans are sought after for their quality, competitive pricing, and adherence to international standards. The primary export destinations for Indian soybeans include Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and European countries.
Soybean Export Data for 2024-2025
Tracking soybean export data reveals significant insights into India’s performance in the global market.
Volume and Value of Exports: India exported approximately 2.5 million metric tons of soybeans in the fiscal year 2023-2024, generating over $1.2 billion in revenue. The 2024-2025 projections suggest a 10-12% growth, driven by increasing demand from new and existing markets.
Major Importers of Indian Soybeans:
Indonesia and Vietnam: These countries use Indian soybeans primarily for feed and food processing industries.
United Arab Emirates (UAE): A significant importer due to its booming food industry and demand for plant-based products.
European Union (EU): Particularly Germany and the Netherlands, where soybeans are used for biofuels and plant-based protein products.
Export Growth Drivers:
India’s strategic position in Asia ensures shorter shipping times to key markets.
Increased global preference for non-GMO soybeans, a segment where India has an advantage.
Key Soybean Exporters in India
India’s soybean export industry is supported by numerous stakeholders, including farmers, processing companies, and export houses top soybean exporters in India are.
SOPA (Soybean Processors Association of India): SOPA plays a vital role in promoting soybean exports from India. It ensures the quality and branding of Indian soybeans, making them competitive in global markets.
Major Exporting Companies:
ITC Limited: Known for its robust supply chain and adherence to quality standards.
Adani Wilmar: A significant player in agri-exports, including soybeans and soy-derived products.
Ruchi Soya Industries: One of India's largest exporters, supplying non-GMO soybeans globally.
Emerging Players: Smaller exporters and agri-tech startups have also entered the market, leveraging technology to enhance productivity and streamline exports.
India’s Position Among Soybean Exporting Countries
Globally, India ranks among the top 10 soybean exporting countries. However, countries like Brazil, the United States, and Argentina dominate the export landscape.
Global Competitors:
Brazil: The world’s largest soybean exporter, primarily supplying China.
United States: A major exporter with advanced farming technology and extensive trade networks.
Argentina: Known for its high-quality soymeal exports.
India’s Competitive Edge:
Organic and non-GMO soybeans.
Competitive pricing compared to Western exporters.
Proximity to Asian and Middle Eastern markets.
Challenges in Competing Globally: While India has advantages, challenges such as inconsistent yield, fluctuating prices, and logistical issues need addressing to solidify its global standing.
Emerging Trends and Opportunities in Soybean Export
The soybean industry is undergoing transformation due to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements. Key trends for 2024-2025 include:
Shift to Plant-Based Diets: The rise of veganism and plant-based diets globally is driving demand for soy products, including tofu, soy milk, and soy protein isolates.
Sustainability and Traceability: Exporters focusing on sustainable farming and traceability in supply chains will have a competitive edge in international markets.
Government Support: Initiatives such as export incentives, enhanced logistics, and trade agreements are expected to boost soybean exports.
Value-Added Soy Products: Diversifying into soy-derived products like soymeal, soy oil, and soy protein can open new revenue streams for Indian exporters.
Challenges Facing Soybean Export from India
Despite its growth potential, the industry faces several hurdles:
Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns can impact crop yields.
Infrastructure Bottlenecks: Limited storage and transportation facilities hinder efficient exports.
Price Volatility: Global soybean prices are influenced by geopolitical and economic factors, impacting Indian exports.
Addressing these challenges through policy reforms and industry collaboration will be critical for sustained growth.
Future Outlook for Soybean Export from India
The future of soybean exports from India looks promising. With the global demand for soybeans expected to rise by 15-20% in the next decade, India has the opportunity to enhance its market share. Key strategies for growth include:
Investing in sustainable farming practices.
Strengthening trade relations with emerging markets like Africa and Latin America.
Promoting value-added soy products through branding and innovation.
Conclusion
Soybean export from India are poised for remarkable growth in the 2024-2025 period. By leveraging its strengths in quality production and strategic geographic positioning, India can expand its footprint in the global soybean market. However, addressing challenges like climate change, infrastructure, and price volatility will be essential for realizing its full potential. With the concerted efforts of farmers, exporters, and policymakers, India is set to cement its position as a leading player in the global soybean trade.
#soybean export from India#soybean export data#soybean exporters in India#soybean exporting countries#trade data#global trade data#international trade
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Top 10 Furniture Exporters in 2024 – Who is Leading the Global Market
The global furniture market is experiencing significant growth, driven by factors such as increased disposable income, urbanization, and a rising demand for aesthetically appealing and functional furniture. As the demand for high-quality furniture rises worldwide, several key players are leading the charge in furniture exports, setting benchmarks for design, quality, and sustainability. In this blog, we will look at the Top 10 exporters of furniture in 2024, exploring who dominates the market and why.

Additionally, if you are searching for the Top 10 Furniture exporters in Gujarat, this article will highlight some key players who are making waves, particularly in the Indian market.
1. China: A Global Giant in Furniture Exports
China continues to dominate the global furniture export market in 2024, maintaining its position as the world’s largest furniture manufacturer and exporter. China’s competitive edge lies in its vast production capacity, low labor costs, and efficient supply chain logistics. Chinese companies produce a wide variety of furniture, ranging from affordable to luxury segments, catering to global markets with high demand.
Key Strengths: Cost-effective production, diverse product range, and strong supply chain.
Major Export Destinations: United States, Europe, Southeast Asia.
2. Vietnam: Emerging Powerhouse in Furniture Exports
Vietnam has rapidly climbed the ranks to become the second-largest furniture exporter globally. The country's growth is driven by its favorable business environment, access to high-quality raw materials, and skilled labor. Vietnamese furniture, particularly wooden furniture, is gaining popularity due to its craftsmanship, competitive pricing, and eco-friendly practices. Vietnam’s strong focus on sustainability and responsible sourcing has enhanced its reputation as a trusted exporter.
Key Strengths: Skilled craftsmanship, eco-friendly furniture, and competitive pricing.
Major Export Destinations: United States, Japan, Europe.
3. Italy: A Legacy of Design Excellence
Italy has long been recognized as a leader in high-end, luxury furniture design. Italian furniture is synonymous with elegance, quality, and innovation. The country’s furniture industry boasts a rich tradition of artisanal craftsmanship, combined with cutting-edge technology. Italian furniture exports primarily target the luxury market, making Italy one of the most sought-after destinations for premium furniture buyers.
Key Strengths: High-end luxury designs, artisanal craftsmanship, and innovation.
Major Export Destinations: United States, Middle East, Europe.
4. Poland: Rising Star in European Furniture Exports
Poland has steadily established itself as one of the Top 10 furniture exporters in the world, thanks to its highly efficient production processes, access to European markets, and emphasis on quality. The Polish furniture industry is known for producing modern, functional designs at competitive prices, making it a go-to supplier for furniture retailers across Europe and beyond.
Key Strengths: Competitive pricing, modern designs, and proximity to European markets.
Major Export Destinations: Germany, France, United Kingdom.
5. Germany: Engineering Precision Meets Furniture Design
Germany’s furniture industry is known for its emphasis on engineering precision, quality materials, and sustainable production. As one of the largest furniture exporters in Europe, Germany’s furniture sector caters to both residential and commercial markets. German furniture manufacturers are renowned for their focus on sustainability, with eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient production methods.
Key Strengths: High-quality engineering, sustainable production, and innovative designs.
Major Export Destinations: United States, European Union, Asia.
6. United States: Strong Domestic Production and Export Growth
While the United States is primarily a furniture importer, it also plays a significant role as a furniture exporter, particularly in high-end segments. U.S. furniture manufacturers are known for their innovation, customization, and premium materials. American furniture companies focus on producing contemporary designs, often tailored to meet specific customer needs. This has helped U.S. companies carve a niche in international markets.
Key Strengths: Customization, premium materials, and contemporary designs.
Major Export Destinations: Canada, Mexico, European Union.
7. Malaysia: A Key Player in Southeast Asia’s Furniture Market
Malaysia is another rising star in the global furniture export market, particularly known for its wooden furniture. With a strong focus on sustainable forestry practices and high-quality craftsmanship, Malaysia’s furniture industry continues to expand its global footprint. The country’s strategic location and access to abundant raw materials have made it a key exporter to markets in Europe, the United States, and the Middle East.
Key Strengths: Sustainable sourcing, quality craftsmanship, and competitive pricing.
Major Export Destinations: United States, Europe, Middle East.
8. India: A Growing Force in Global Furniture Exports
India has been steadily growing its presence in the global furniture market, particularly as one of the Top 10 Furniture exporters in Gujarat. Indian furniture manufacturers offer a blend of traditional craftsmanship with modern designs, making their products appealing to both domestic and international markets. Gujarat, in particular, has become a hub for furniture production, with companies focusing on high-quality, sustainable, and handcrafted furniture.
India’s growing furniture industry benefits from its vast pool of skilled artisans, access to raw materials, and an expanding global customer base. Indian exporters are increasingly recognized for offering customized, handmade furniture, which is in high demand in markets such as the U.S. and Europe.
Key Strengths: Handcrafted designs, sustainable materials, and customization.
Major Export Destinations: United States, Europe, Middle East.
9. Turkey: Blending Tradition with Modern Innovation
Turkey’s furniture industry is characterized by its blend of traditional craftsmanship with contemporary designs. The country’s strategic location, connecting Europe and Asia, gives it a unique advantage in global trade. Turkish furniture manufacturers are known for their innovative designs, attention to detail, and competitive pricing, making them one of the Top 10 furniture exporters globally.
Key Strengths: Strategic location, blend of tradition and modernity, and competitive pricing.
Major Export Destinations: Europe, Middle East, Africa.
10. Indonesia: Traditional Craftsmanship Meets Global Demand
Indonesia’s furniture industry is deeply rooted in its rich heritage of craftsmanship, particularly in wooden furniture. The country is a significant exporter of teak and other hardwood furniture, valued for its durability and aesthetic appeal. Indonesian furniture is known for its intricate designs and use of natural materials, which resonate well with eco-conscious consumers. With a growing focus on sustainability and responsible sourcing, Indonesia is cementing its position as a leading furniture exporter.
Key Strengths: Sustainable hardwood furniture, traditional craftsmanship, and eco-friendly designs.
Major Export Destinations: United States, Europe, Asia.
Best Exporter of Furniture – Who Tops the List?
When it comes to identifying the Best exporter of Furniture globally, it is essential to consider factors such as product quality, innovation, sustainability practices, and market reach. While China continues to lead in terms of volume, countries like Italy, Vietnam, and Poland are gaining ground due to their focus on design, craftsmanship, and eco-friendly practices.
For those looking for the Top 10 Furniture exporter in Gujarat, India is making significant strides in the furniture industry. Gujarat has emerged as a key player in furniture exports, with companies that focus on high-quality, handcrafted furniture. The state’s strong manufacturing capabilities, coupled with skilled artisans and sustainable production practices, have positioned it as a rising force in global furniture exports.
Conclusion
As the global furniture market continues to evolve, several countries have distinguished themselves as the Top 10 exporters of furniture in 2024. From China’s dominance in mass production to Italy’s luxury craftsmanship and Vietnam’s focus on eco-friendly practices, these exporters are shaping the future of the global furniture industry.
For businesses and consumers alike, understanding the strengths of each exporting country can help in making informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are in the market for high-end luxury furniture or cost-effective, sustainable options, the global furniture export market offers a diverse range of choices to meet every need.
#Furniture exporters in Gujarat#Top 10 exporter of Furniture#Top 10 Furniture exporter in Gujarat#Best exporter of Furniture#India#Export and Import#FMCG exporter#Pharmaceutical exporter#agrochemical exporter#textile exporter#automotive industry product exporter#plastic product exporter
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
How High-Performance Stretch Film Transforms Shipping in Vietnam

Efficient shipping is becoming increasingly vital in Vietnam's booming economy. From bustling markets to high-tech industrial zones, the need for effective transportation and secure packaging has never been greater. Enter high-performance stretch film—a game-changer that's transforming the way Vietnamese businesses handle shipping. This guide will show you how high-performance stretch film can enhance your shipping processes, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
The Basics of Stretch Film
What is Stretch Film?
Stretch film is a highly stretchable plastic film used to wrap products on pallets, ensuring they remain secure during transit. Its primary purpose is to hold loads tightly together, preventing them from shifting, tipping, or getting damaged. This makes it an essential tool in the shipping and logistics industry.
Types of Stretch Film
There are two main types of stretch film—cast and blown. Cast stretch film is produced using a continuous process called casting, which results in a clear, glossy film. It offers excellent clarity, making it easier to identify wrapped products. On the other hand, blown stretch film is manufactured using a blown extrusion process, resulting in a more robust and tear-resistant film with a matte finish. Each type has its own strengths and is suitable for different applications.
Key Attributes of High-Performance Stretch Film
High-performance stretch film boasts several key attributes that set it apart from standard films. These include superior stretchability, puncture resistance, and load retention capabilities. These features ensure that high-performance stretch film provides better protection and stability for your shipments, making it an invaluable asset in the shipping process.
Selecting the Right Stretch Film for Your Needs
Factors to Consider
Choosing the right stretch film involves considering several factors, including the size and weight of your load, as well as the shipping conditions. Heavier loads may require a thicker, more robust film, while lighter loads can be secured with a thinner film. Additionally, consider the shipping environment—will your products be exposed to extreme temperatures or rough handling? These factors will help determine the most suitable stretch film for your needs.
Environmental Considerations
In today's environmentally conscious world, opting for sustainable and eco-friendly stretch films can make a significant difference. Look for films made from recyclable materials or those that use less plastic without compromising on strength and durability. This not only helps reduce your carbon footprint but also aligns your business with global sustainability initiatives.
Cost-Effectiveness
Balancing quality with budget constraints is crucial when selecting stretch film. While high-performance stretch film may come at a higher initial cost, its enhanced durability and efficiency can lead to long-term savings. Invest in quality stretch film to minimize material usage and reduce the risk of product damage during transit, ultimately lowering your overall shipping costs.
Benefits of Using High-Performance Stretch Film
Enhanced Load Stability and Protection
One of the primary benefits of high-performance stretch film is its ability to provide enhanced load stability and protection. The superior stretchability and load retention capabilities ensure that your products remain securely wrapped throughout the shipping process, reducing the risk of damage or loss.
Reduction in Material Usage and Cost Savings
High-performance stretch film is designed to maximize efficiency, requiring less material to achieve the same level of protection as standard films. This reduction in material usage translates to cost savings, making it a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes.
Increased Efficiency in Packing and Handling
Using high-performance stretch film can significantly improve the efficiency of your packing and handling processes. Its superior stretchability and puncture resistance mean fewer breaks and interruptions, allowing for smoother and faster wrapping. This increased efficiency can lead to faster turnaround times and improved overall productivity.
Compliance with Vietnamese Regulatory Standards
Adhering to regulatory standards is essential for businesses operating in Vietnam. High-performance stretch film complies with Vietnamese regulatory standards and best practices, ensuring that your shipments meet all necessary requirements. This compliance helps build trust with customers and partners, reinforcing your commitment to quality and reliability.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

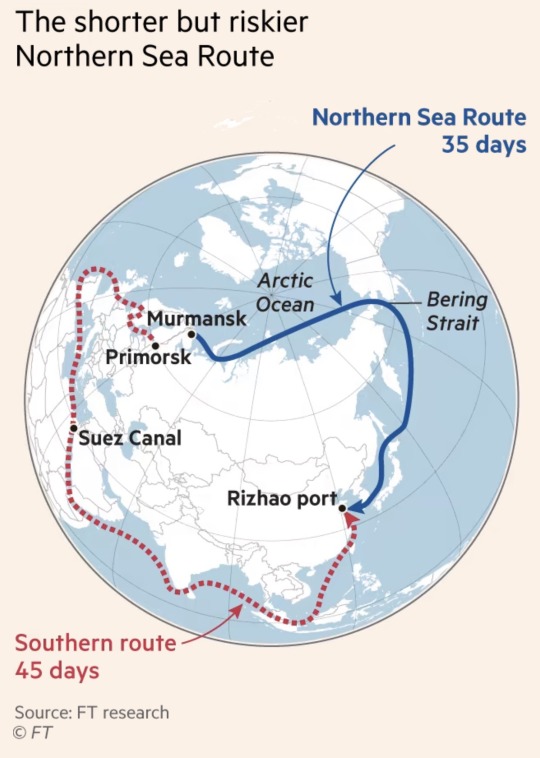
The new route Russia is using to export its oil to China. Unfortunately global warming and the melting of the icecaps only benefits Russia geopolitically. What’s the big deal? you might wonder. A 10-day reduction in transport time is huge when it comes to the velocity of capital. Power accrues to the nations that control key maritime trade routes.
*
Between climate change and the new Cold War, the future doesn’t look pretty. China’s economy is imploding thanks to their reliance on a debt-fueled real estate bonanza, their misguided zero COVID policy, and Xi Jinping’s head-scratchingly bad policies (and of course, his consolidation of power). Siding with Russia was a huge mistake… Now China’s biggest export markets are trying to decouple or at least diversify away from them. Youth unemployment is so bad in China (21%, but possibly significantly higher) that the government has decided to stop publishing such data. The Philippines and Vietnam are pivoting toward the US. South Korea and Japan are putting their long, historical feud aside to join forces against China. Japanese military neutrality is over. Meanwhile a tiny island called Taiwan makes over 92% of the world’s advanced semiconductors and will likely be invaded in our lifetime. Will an (economically) weakened China make it more or less likely that Xi will invade Taiwan? (Strongmen facing a domestic crisis and loss of popular support do often start wars as a kind of “gamble for resurrection,” but Xi might have become more risk adverse as he observes Russia’s debacle in Ukraine. Plus, an amphibious invasion is logistically extremely difficult to pull off.)
Defense spending worldwide is skyrocketing, climbing back toward Cold War levels. The lines on the map are hardening, particularly in the Asian/Pacific theater and the European theater. A nuclear trifecta of Russia-China-North Korea is emerging. Yes, it is a marriage of convenience, but quite a dangerous one given that Russia will likely transfer technology (specifically, platforms to deliver nuclear warheads) to North Korea in exchange for Soviet-compatible ammunition/arms to use in Ukraine. I hate feeling like the world is a frog getting boiled but as I finish this 26-part BBC documentary on World War I, I can’t help but feel that the geopolitical situation is very unstable.
Oh, the madness of nation states! Wake me up when it’s over.
#geopolitics#political economy#trade#war#military industrial complex#cold war#new cold war#russia#China#capitalism
10 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you know how a show can get performed in a new country? Is it just a matter of a local company obtaining the rights/license or is there some global head honcho team that decides which countries they want to perform in? And do you think POTO will ever come to Vietnam?
In very oversimplified terms, it's a collaboration between the local producer (who see an interest in the market and have the big bucks to mount a such a grand-scale production) and RUG (who will then decide if it's feasible to embark on such venture and will be responsible for organizing a tour along with casting and all the logistics behind). If it's going to be a translated production (like in China and Korea), I imagine it's much more complicated.
For the local producer they have to make sure there's an audience that could fill their seats enough to make a profit and a theatre that can meet the demands of the production and the approval of the head office. The planning takes years with theatres sometimes having to be built from scratch (with Phantom in mind). Often these producers are seasoned companies who have a track record of producing shows in the past but there had been newcomers to the field as well (who happen to be very rich). Phantom is a very expensive production.
I'm not familiar at all with the Vietnamese theatre scene but musical exposure and readiness is another factor to consider. People must be familiar with this performing arts genre and are known to willingly shell out money for it (proven if a similar show had successfully been staged in the past).
I'm sure I'm missing something but that's the gist of it based on my limited knowledge. Hope that helps!
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
The “study” part of study abroad
I was flung hard back into student life this past week when classes resumed with my first class being at 6:45am on Monday. I quite literally had to wake up with the roosters (Vietnam definitely has different standards for where animals can be kept. During my travels around I literally saw cows grazing in urban residential areas).
Classes at FTU meet twice a week for periods of two hours and fifteen minutes. So far my classes have usually began late and/or ended early, but they still end up being longer than what I am used to. One nice thing is that all of my classes are conveniently located in one building. The downside to many classes being in one building, however, is that the elevators get very hectic during class change times. There ends up being a mass of students in line to get on them and then the max amount of people possible squeeze into each elevator. I personally opt to take the stairs over dealing with this. My lowest class is on the sixth floor so I should have killer legs by the time the semester finishes.
Class grades are mostly dependent on a group midterm project and a final exam. There’s not really smaller assessments or assignments. I also have not had to purchase any textbooks or access codes, a typical semester expense that I am glad to not have. All of my classes have Facebook groups where lecture notes and important announcements are posted, and every class has a student monitor who keeps attendance and is available for questions. Although all of my classes are in English, sometimes things are in Vietnamese, but fortunately my peers have been helpful in translating and explaining things.
After all this discussion about my classes I realized I neglected to put which courses I am actually taking, so here they are: International Trade Policy, Basic Marketing, Logistics and International Freight Forwarding, and Supply Chain Management. I am aware that none of these are particularly unique, but one interesting thing I have found about them is they cover content in the context of Vietnam. I just had a meeting for a group project that analyzes the supply chain models of global brands and comparable Vietnamese brands. As a supply chain major I look forward to learning about Vietnam in this context and seeing how this project progresses.
Outside of class I had a fairly relaxed week where the focus was just trying to settle into regular life in Hanoi after traveling around. I tried out a recommended laundry shop. I have found that in Vietnamese cities there’s not usually self-service laundromats, you have to use laundry services where they wash and dry everything for you. They generally charge around $1USD/kg and so far all of the services I have used have done a good job, so I can’t complain.
I also tried more food options within walking distance of where I live. The people who run this one restaurant always try to persuade me to come in whenever I walk past so I finally gave them a chance and realized that I have been sleeping on them. They served very delicious bún chả, a Hanoi specialty consisting of pork served with vermicelli noodles and vegetables. It is also custom to eat seafood spring rolls as a side pairing. It makes for a very filling meal on a rainy Hanoi evening. This may sound silly, but I also found that the Circle K is a great spot. There are Circle K’s everywhere and they usually have seating areas. Their banh mi and coffee combo for 21k dong (roughly $0.89) makes a great afternoon pick-me-up between classes. I also like to stop by for late night snacks.
I have also been spending more time with the other exchange students. Sometimes we’ll have meals together and the other night a group of us went to a jazz club just to try something new. I also hope to do more with local students as well, but it has so far been easier to socialize with the exchange students.
I did not think to take many photos this week since I was no longer in tourist mode, but here’s a few, featuring bún chả and jazz as mentioned.


6 notes
·
View notes
Text





Exporting Fresh Fruits from Developing Countries: Opportunities, Challenges, and Solutions
Global markets offer substantial prospects for developing nations to export a diverse range of fresh fruits—including mangoes, pineapples, papayas, and various exotic tropical produce. Consumer demand in key regions such as the European Union, North America, China, Japan, and South Korea is driven by an increasing appetite for nutritious, year‐round, and distinctive fruits. However, successfully tapping these markets requires navigating strict regulatory environments, intricate logistics, and other market-specific hurdles. This article examines these prospects and obstacles while proposing practical solutions.
Opportunities in Exporting Fresh Fruits
Developing countries are well positioned to satisfy the global craving for tropical and subtropical fruits. Regions in Southeast Asia, South Asia, and Africa are known for producing a broad spectrum of high-quality produce.
From Southeast Asia:
Mangoes: Varieties from Thailand, Vietnam, and the Philippines are highly sought after.
Pineapples: Well recognized from Thailand, the Philippines, and Indonesia.
Papayas: Widely produced and exported.
Exotic Fruits:
Durian: Increasing in popularity in East Asian markets.
Mangosteen: Appreciated for its unique flavor and nutritional benefits.
Dragon Fruit (Pitaya): Valued for its striking appearance and subtle taste.
Rambutan, Lychee, and Longan: Cater to niche markets in East Asia and parts of Europe.
From South Asia:
Mangoes: For instance, India is one of the largest producers and exporters.
Bananas: Although Latin America dominates, South Asia also contributes.
Papayas and Guavas: These fruits offer distinct tropical flavors.
Citrus Fruits: Depending on the variety and season, some citrus products are exported internationally.
From Africa:
Bananas: Countries such as Cameroon, Ghana, and Ivory Coast are key suppliers, particularly to the European Union.
Pineapples and Citrus: Certain nations also export these fruits.
Other Produce: In some cases, smaller-scale exports include mangoes and avocados.
Market Specifics:
European Union: A major importer of African bananas and pineapples as well as tropical produce from Asia, the EU’s high quality and safety standards shape the range of available products.
North America: Although largely reliant on Latin American imports, there is growing interest in Asian produce such as mangoes, papayas, and exotic varieties like dragon fruit and durian.
East Asia (China, Japan, South Korea): These markets favor both conventional tropical fruits and more unusual offerings. Shifts in consumer preferences and premium market segments have boosted imports from Southeast Asia, and to a lesser extent, South Asia and Africa.
These varied offerings not only deliver unique flavors but also enable consumers to enjoy a consistent supply of fruits that are otherwise unavailable locally. Coupled with a rising interest in healthy, exotic, and sustainably sourced produce, these factors create a conducive environment for exporters from developing regions.
Key Challenges and Strategies to Overcome Them
Exporters must address challenges ranging from regulatory requirements to logistical complexities. Tailoring strategies to meet these obstacles is essential for sustained success.
1. Regulatory and Technical Challenges
Issues:
Food Safety and Quality: International markets demand strict compliance with pesticide residue limits, contamination controls, and rigorous quality benchmarks.
Phytosanitary Measures: Certification and quarantine protocols are critical to prevent pest and disease outbreaks.
Certifications: Standards such as GlobalGAP, HACCP, and ISO add layers of complexity, especially for smaller producers.
Labeling and Packaging: Varied requirements regarding nutritional information, country-of-origin labels, and packaging materials can lead to delays.
Strategies:
Capacity Building: Provide technical training for growers and exporters to master international standards and certification procedures.
Adopt Global Standards: Foster public–private partnerships to integrate widely recognized safety and quality benchmarks.
Streamline Certification: Work closely with local and international certification bodies to simplify compliance.
Government Support: Secure subsidized certification costs, technical assistance, and pursue mutual recognition agreements with importing regions.
2. Logistical Challenges
Exporting fresh produce involves two primary transport modes—air cargo and sea shipping—each presenting unique issues.
Air Cargo:
High Costs: Elevated operational and fuel expenses can reduce profit margins, especially for low-value shipments.
Capacity Constraints: Aircraft limitations require efficient load management.
Regulatory and Security Protocols: Stringent security measures and customs documentation can lead to delays.
Time Sensitivity: Minor disruptions can be critical for perishable goods.
Specialized Handling: Perishables and hazardous materials necessitate specific care.
Air Cargo Strategies:
Route and Capacity Optimization: Utilize advanced planning and cargo consolidation tools.
Technology Investment: Implement real-time tracking systems to address potential disruptions proactively.
Enhanced Training: Regularly update staff on international regulations.
Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with reliable logistics providers and freight forwarders.
Flexible Contracting: Negotiate adaptable agreements to match capacity fluctuations.
Sea Shipping:
Port Congestion: High traffic can result in delays during loading and unloading.
Container Imbalances: Uneven availability of containers may disrupt schedules.
Cargo Damage: Rough handling, adverse weather, and mechanical issues can compromise produce quality.
Complex Documentation: Varying customs procedures add administrative burdens.
Environmental Factors: Weather-related disruptions can force rerouting and delays.
Sea Shipping Strategies:
Optimized Supply Chain Planning: Leverage predictive analytics and advanced management software.
Infrastructure Investment: Collaborate with port authorities to adopt digital tracking and automated handling systems.
Flexible Routing: Develop alternative routes and contingency plans.
Strengthened Communication: Enhance coordination with shipping lines, port operators, and customs brokers.
Quality Control: Enforce strict packaging standards and conduct regular audits to reduce damage risks.
3. Market Access and Economic Challenges
Issues:
Trade Barriers: Tariffs, quotas, and non-tariff barriers (e.g., sanitary measures) can restrict market entry.
Customs Complexities: Bureaucratic procedures may lead to shipment delays and increased costs.
Financial Constraints: Limited access to capital can hinder investments in technology and infrastructure.
Market Risks: Fluctuations in currency and unforeseen disruptions pose economic challenges.
Strategies:
Trade Agreements: Advocate for inclusion in regional and bilateral trade deals to reduce tariffs and streamline customs.
Market Diversification: Explore niche or premium markets that are less impacted by trade barriers.
Financial Support: Access microfinance, subsidies, and export insurance to mitigate risks.
Collective Action: Form cooperatives or export consortia to pool resources and strengthen bargaining power.
Digital Facilitation: Utilize electronic documentation and integrated logistics platforms to improve customs clearance.
Recommendations for Agribusinesses and Farmers’ Cooperatives
To leverage the opportunities and address the challenges outlined, the following recommendations are proposed for agribusinesses and cooperatives in developing countries:
1. Prioritize Quality and Compliance
Implement Good Agricultural Practices (GAP): Embrace GAP from cultivation to packaging to ensure safety, traceability, and overall quality. Certifications like GlobalGAP can serve as a key milestone.
Enhance Post-Harvest Handling: Invest in or partner with facilities that offer cleaning, sorting, grading, cooling, and packaging to minimize losses and preserve quality.
Focus on Food Safety: Establish robust management systems, such as HACCP, to address hazards and comply with international safety standards.
Stay Informed: Continuously monitor regulatory changes and engage with export promotion agencies and industry publications.
2. Optimize Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Forge Strong Partnerships: Collaborate with experienced freight forwarders, shipping lines, and customs brokers specializing in perishables.
Invest in Cold Chain Logistics: Ensure access to refrigerated transport and storage solutions to maintain freshness during long-distance shipments.
Improve Packaging and Handling: Utilize appropriate materials and train staff in proper handling techniques.
Adopt Technological Solutions: Implement real-time tracking and supply chain management systems to monitor shipments and manage inventory effectively.
3. Enhance Market Access and Diversification
Conduct Comprehensive Market Research: Understand consumer preferences, pricing, and trends in target markets to tailor product offerings.
Diversify Markets: Reduce dependency on a single region by exploring multiple export destinations.
Engage in Trade Fairs and Missions: Network with buyers and gain insights by participating in international trade events.
Develop Branding Strategies: Create compelling brand narratives that highlight unique qualities, and consider certifications like Fair Trade or organic to appeal to niche markets.
4. Strengthen Collaboration and Capacity Building
Form Cooperatives and Consortia: Small-scale farmers can increase their bargaining power and reduce costs through collective action.
Invest in Training: Provide education on GAP, post-harvest handling, quality control, and export processes in partnership with agricultural extension services and research institutions.
Access Financial Support: Explore government programs, export promotion initiatives, and microfinance options to secure necessary funding.
Build Relationships: Cultivate trust and open communication with buyers, importers, distributors, and other stakeholders.
5. Embrace Sustainability
Adopt Sustainable Farming Practices: Use environmentally friendly methods and pursue certifications like organic or Rainforest Alliance.
Minimize Waste: Implement strategies to reduce post-harvest losses and optimize resource use.
Promote Fair Labor Practices: Ensure equitable wages and working conditions throughout the value chain to enhance social sustainability and brand reputation.
By adopting these recommendations, agribusinesses and farmers’ cooperatives can enhance their competitiveness, navigate market challenges effectively, and capitalize on the growing global demand for fresh fruits—ultimately driving sustainable growth and contributing to economic development.
I hope you enjoyed reading this post and learned something new and useful from it. If you did, please share it with your friends and colleagues who might be interested in Agriculture and Agribusiness.
Mr. Kosona Chriv
Group Chief Sales and Marketing Officer
Solina / Sahel Agri-Sol Group (Ivory Coast, Senegal, Mali, Nigeria, Tanzania)
https://sahelagrisol.com
Chief Operating Officer (COO)
Deko Group (Nigeria, Cambodia)
Senior Advisor
Adalidda (India, Cambodia)
Follow me on
BlueSky https://bsky.app/profile/kosona.bsky.social
LinkedIn https://www.linkedin.com/in/kosona
Photo: Fresh mangosteens (AI-generated image)
#FreshFruitExport#DevelopingCountries#TropicalFruit#MangoExport#PineappleExport#PapayaExport#ExoticFruit#DurianExport#MangosteenExport#DragonFruitExport#RambutanExport#LycheeExport#LonganExport#BananaExport#CitrusExport
1 note
·
View note
Text
Air Cushion Packaging Market Analysis: Expected Growth Over 5% CAGR (2021-2027)
Astute Analytica, a prominent market research firm, has recently published a comprehensive report that offers an extensive analysis of the global Air Cushion Packaging market. This report goes beyond mere statistics, providing deep insights into various critical aspects such as market segmentation, key players, market valuation, and regional overviews. It serves as a valuable resource for businesses and stakeholders seeking to navigate this evolving industry landscape.
The Global Air Cushion Packaging Market forecasts a CAGR of more than 5% during the forecast period 2021-2027
Market Valuation
The report includes a thorough evaluation of the market valuation, drawing from historical data, current trends, and future projections. By employing rigorous analytical methods, it effectively captures the growth trajectory of the market. This detailed assessment allows businesses to understand the factors driving growth and make informed decisions regarding investments and strategic initiatives.
A Request of this Sample PDF File@- https://www.astuteanalytica.com/request-sample/air-cushion-packaging-market
Comprehensive Market Overview
Astute Analytica's report provides a holistic overview of the global Air Cushion Packaging market. It encapsulates a wide array of information related to market dynamics, including growth drivers, challenges, and opportunities. Stakeholders can leverage these insights to formulate effective strategies and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Key Players in the Market
The report identifies and profiles the major players who are influencing the global Air Cushion Packaging market. Through meticulous research, it presents a clear view of the competitive landscape, detailing the strategies, market presence, and significant developments of leading companies. This section is vital for stakeholders who wish to understand the positioning and actions of their competitors.
Key Companies:
Several key industry participants of the air cushion packaging market include Sealed Air Corp, Abriso N.V., Shandong Xinniu, Pregis, 3G Packaging Corp., and Atlantic Packaging.
For Purchase Enquiry: https://www.astuteanalytica.com/industry-report/air-cushion-packaging-market
Segmentation Analysis
A crucial component of the report is the segmentation analysis, which delves into various market segments based on industry verticals, applications, and geographic regions. This detailed examination provides stakeholders with a nuanced understanding of market dynamics, enabling them to identify opportunities for growth and areas for investment.
Market Segmentation:
By Form
Air Tubes
Air Bubble
Air Pillows
Air Bags
By Function
Void Fill
Blocking & Bracing
Wrapping
Edge Protection
Cushioning
Others
By Color
Green
White
Blue
By End-User
Consumer Electronics
E-commerce
FMCG Manufacturing
Home Furnishing
Logistics (Transport, Shipping, and Warehousing)
Personal Care & Cosmetics
Pharmaceuticals
Retail
Others
By Region
North America
The U.S.
Canada
Mexico
Europe
Eastern Europe
Russia
Poland
Rest of Eastern Europe
Western Europe
The UK
Germany
France
Italy
Spain
Rest of Western Europe
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
ASEAN
Malaysia
Indonesia
Thailand
Philippines
Vietnam
Rest of ASEAN
Australia & New Zealand
Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East & Africa (MEA)
UAE
Saudi Arabia
Qatar
South Africa
Egypt
Rest of MEA
South America
Brazil
Argentina
Rest of South America
Research Methodology
Astute Analytica is recognized for its rigorous research methodology and dedication to delivering actionable insights. The firm has rapidly established a solid reputation by providing tangible outcomes to clients. The report is built on a foundation of both primary and secondary research, offering a granular perspective on market demand and business environments across various segments.
Beneficiaries of the Report
The insights presented in this report are invaluable for a range of stakeholders, including:
Industry Value Chain Participants: Those directly or indirectly involved in the Air Cushion Packaging market need to stay informed about leading competitors and current market trends.
Analysts and Suppliers: Individuals seeking up-to-date insights into this dynamic market will find the report particularly beneficial.
Competitors: Companies looking to benchmark their performance and assess their market positions can leverage the data and analysis provided in this research.
Astute Analytica's report on the global Air Cushion Packaging market is an essential resource that empowers stakeholders with the knowledge needed to navigate and thrive in this competitive landscape.
Download Sample PDF Report@- https://www.astuteanalytica.com/request-sample/air-cushion-packaging-market
About Astute Analytica:
Astute Analytica is a global analytics and advisory company that has built a solid reputation in a short period, thanks to the tangible outcomes we have delivered to our clients. We pride ourselves in generating unparalleled, in-depth, and uncannily accurate estimates and projections for our very demanding clients spread across different verticals. We have a long list of satisfied and repeat clients from a wide spectrum including technology, healthcare, chemicals, semiconductors, FMCG, and many more. These happy customers come to us from all across the globe.
They are able to make well-calibrated decisions and leverage highly lucrative opportunities while surmounting the fierce challenges all because we analyse for them the complex business environment, segment-wise existing and emerging possibilities, technology formations, growth estimates, and even the strategic choices available. In short, a complete package. All this is possible because we have a highly qualified, competent, and experienced team of professionals comprising business analysts, economists, consultants, and technology experts. In our list of priorities, you-our patron-come at the top. You can be sure of the best cost-effective, value-added package from us, should you decide to engage with us.
Get in touch with us
Phone number: +18884296757
Email: [email protected]
Visit our website: https://www.astuteanalytica.com/
LinkedIn | Twitter | YouTube | Facebook | Pinterest
0 notes
Text
Custom Activewear Tank Tops Manufacturing Solutions
At Thygesen Textile Vietnam, we simplify the process of manufacturing high-quality custom tank tops. With years of expertise, we efficiently manage every step—from material sourcing and design development to sampling and bulk production—ensuring precision, consistency, and cost-effectiveness. Our dedicated team works closely with clients to provide tailored solutions that align with their brand identity and market needs.
Our full-package service includes fabric sourcing, pattern making, and a fully integrated production line that guarantees superior craftsmanship. We offer extensive customization options, such as fabric selection (organic cotton, performance blends), custom dyeing, size adjustments, and branding elements like labels, tags, and packaging. Additional design features, including prints and embroidery, help brands stand out in the competitive market.
We maintain strict quality control with in-line inspections at all production stages, adhering to AQL standards. Sustainability is also a priority—we incorporate eco-friendly materials and LEAN manufacturing principles to reduce waste and minimize environmental impact.
For global brands, our streamlined ordering process ensures smooth communication and hassle-free logistics, regardless of location. Let’s bring your tank top designs to life with quality, innovation, and care.
Read the full article here: https://thygesenapparel.com/custom-activewear-manufacturing/custom-activewear-tank-tops-manufacturing

0 notes
Text
Challenges in exploring chili and turmeric

Introduction
India is one of the largest producers and exporters of chilies and turmeric, renowned for their quality and strong demand worldwide. However, despite this dominance, the country faces several challenges in expanding its exports and maintaining a competitive edge in global markets. These challenges range from stringent international regulations to increasing competition and logistical inefficiencies. Addressing these issues is crucial for Indian exporters, including Prabhu Group, to sustain and grow their market share.
Key Challenges
Compliance with International Standards Major importing markets, such as the European Union and the United States, have strict regulations regarding pesticide residues, contamination, and food safety. Meeting these evolving standards requires constant monitoring, investment in better agricultural practices, and adherence to international quality certifications.
Rising Competition Countries like China and Vietnam are emerging as strong competitors, offering cheaper alternatives to Indian chilies and turmeric. These countries benefit from lower production costs, government support, and efficient supply chains, making it harder for Indian exporters to compete solely on price.
Logistics and Supply Chain Issues High shipping costs, port congestion, and delays in transportation pose significant hurdles for Indian spice exporters. Inconsistent supply chain management can lead to longer delivery times, increased costs, and reduced competitiveness in the global market.

Solutions for Prabhu Group
To overcome these challenges and strengthen its export capabilities, Prabhu Group can implement the following strategies:
Invest in Quality Certifications Obtaining certifications such as Global GAP, ISO, and organic labels will help build trust with international buyers and ensure compliance with stringent food safety standards.
Focus on Niche, High-Value Markets Rather than competing on price, Prabhu Group can target premium segments such as organic, non-GMO, and sustainably sourced chilies and turmeric. These markets often have higher profit margins and demand superior quality products.
Collaborate with Reliable Logistics Providers Partnering with experienced logistics companies can help streamline shipping, reduce delays, and optimize costs. Developing strong relationships with shipping firms and investing in better packaging solutions will also ensure product integrity during transit.

0 notes
Text
1509 Basmati Rice Manufacturer From India
India has always been a leader in rice production because of its perfect climate conditions, fertile soil, and a long history of cultivation methodology. Authentic rice grains are produced by Indian farmers using traditional farming methods and organic manuring. Proper quality checks are conducted from the fields to the packaging stage. Foodsy Export is a top-rated 1509 basmati rice manufacturer and a trusted 1509 basmati rice exporter in the international market.
With extraordinary characteristics, 1509 basmati rice takes pride in providing the best texture and taste to each food delicacy with its alluring aroma and nutty flavor. The premium-quality rice grains are directly sourced from the fertile fields of northern India. Quality commitment and sustainability practices make Foodsy Export a reliable 1509 Basmati rice manufacturer and the best 1509 Basmati rice supplier.
Why Foodsy Export is a Trusted 1509 Basmati Rice Manufacturer and Exporter in India
Foodsy Export is the market leader that produces 1509 Basmati Rice. Being a household name, the trusted 1509 basmati rice supplier has always kept a promise about quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction. A modern processing complex with strict standards of quality control was devised to make sure the exports met the very high standards abroad.
India is a world producer and exporter of 1509 basmati rice. The premium quality of basmati grains has earned Foodsy Export a worldwide reputation. Foodsy Export uses the most advanced milling and grading facilities that retain the natural taste, fragrance, and characteristic character of 1509 Basmati Rice. The plant focuses on excellent cleaning and packaging performance that helps in achieving maximum recovery with minimum waste.
What is 1509 Basmati Rice?
1509 basmati rice is a premium type of basmati that has become widespread with a set of attributes:
Long-length grains
Rich aroma and nutty flavor
Soft in texture and non-sticky after cooking
High elongation ratio, up to double the size after cooking.
Low cooking time compared to other basmati rice varieties.
More nutritional content; a good source of carbohydrates and minerals.
Owing to such wonderful characteristics, 1509 basmati rice is heavily recommended for preparing conventional rice recipes such as biryanis, pilaf, pulao, and fried rice.
What Sets Foodsy Export Apart?
Foodsy Export is an international 1509 basmati rice exporter that exports its products to a broad international market that has spread over different regions like the Middle East, Europe, North America, and Asia. The timely shipment ensures that all export regulations are followed.
Follow ambitious policies for promoting sustainable agricultural practices, technical support, or even farm assistance to decrease the environmental footprint together with the efficiency of the yield. Despite the premium quality, Foodsy Export offers competitive pricing, and their 1509 Basmati Rice is a product of choice among bulk buyers, retailers, and food service providers.
1509 Basmati Rice is in stiff competition with various types of rice, such as 1121 Basmati, Pusa Basmati, and even more non-Basmati rice varieties available in Pakistan, Thailand, or Vietnam. However, Foodsy Export has its strength in a competitive range in terms of the following:
Our rice gets quality checked multiple times up to the global standard.
Private labeling and packaging they done according to what the customers actually want.
Good interaction with logistics vendors helps Foodsy Export complete the process promptly with fewer transit complications.
Customer centricity with a committed, dedicated customer service wing for smooth conveyance and proper satisfaction of each customer's individual needs.
Leading 1509 Basmati Rice Exporter Exporting Authenticity to Global Market
Foodsy Export has a streamlined process to ensure high-quality rice is delivered to clients all over the world with efficiency. Their export process includes:
Sourcing: direct procurement from farmers who follow sustainable practices.
Processing: milling, polishing, and grading in state-of-the-art facilities.
Quality Assurance: Stringent quality standards before dispatch.
Packaging: hygienic, durable, and customizable packaging solutions.
Shipping: Reliable logistics partnerships for smooth international shipping.
Why Choose Foodsy Export as Your 1509 Basmati Rice Supplier and Exporter?
Whether you are a retailer, distributor, or food service provider, association with Foodsy Export ensures:
The rice we supply is of international quality.
Available in raw, parboiled, and steam forms.
Best value for premium quality.
Efficient supply chain management for on-time shipments.
1509 Basmati Rice continues to win hearts across the globe. Low prices but high production and fine cooking make this a top choice in global kitchens. Foodsy Export stands amongst the brightest 1509 Basmati rice manufacturers and carries the best-quality 1509 Basmati rice for consumers throughout the world with a promise of quality, sustainably practiced, and customer satisfaction amidst one of the most competitive marketplaces for rice.
Anyone who would want to source this superior quality 1509 Basmati Rice would need a good trading partner who combines the best of quality with the best competitive price to add on top personal service, which makes it easy to sell for their clients across the world.
0 notes