#Vectipelta
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Hi there!
Vectipelta barretti from the Early Cretaceous, new ankylosaurid described in the Wessex Formation, England
170 notes
·
View notes
Text
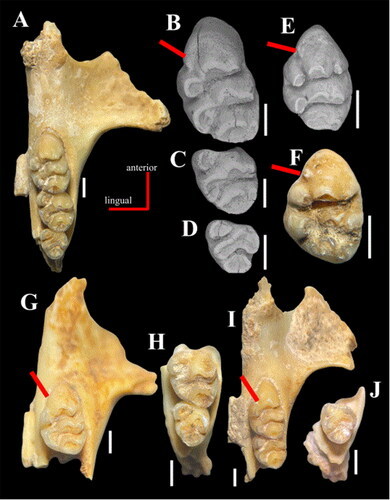
Vectipelta barretti Pond et al., 2023 (new genus and species)
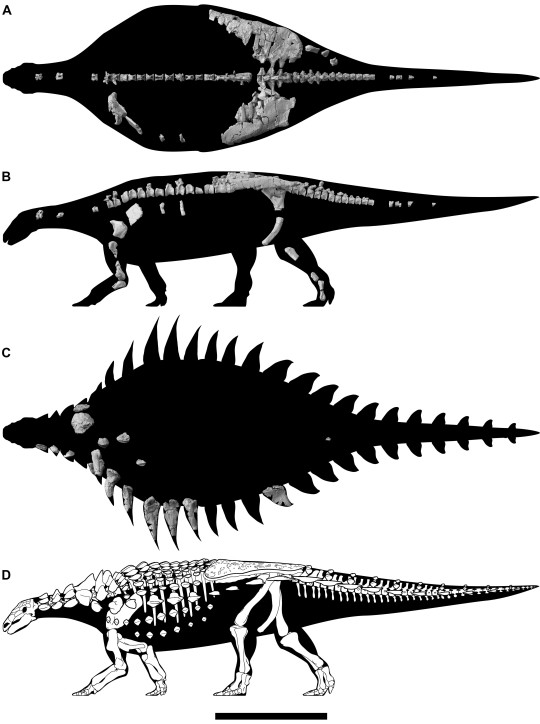
(Preserved bones and schematic skeletal of Vectipelta barretti [scale bar = 1 m], from Pond et al., 2023)
Meaning of name: Vectipelta = Isle of Wight shield [in Latin]; barretti = for Paul M. Barrett [British paleontologist]
Age: Early Cretaceous (Barremian)
Where found: Wessex Formation, Isle of Wight, U.K.
How much is known: Partial skeleton of one individual including much of the vertebral column, some limb bone fragments, and many armor plates. Some additional ankylosaur material from the same locality may belong to the same species (or even the same individual), but this cannot be confirmed at present.
Notes: Vectipelta was an ankylosaur, a group of armored herbivorous dinosaurs. Two other ankylosaurs have known from the Early Cretaceous of England since the 19th Century, the older Hylaeosaurus and the younger Polacanthus. However, Vectipelta appears to have been only distantly related to either of them, and may have instead been more closely related to the club-tailed ankylosaurine ankylosaurs. Traditionally, ankylosaur fossils from the Wessex Formation have often been classified as Polacanthus by default, but the discovery of Vectipelta indicates that this is not always a safe assumption to make.
Reference: Pond, S., S.-J. Strachan, T.J. Raven, M.I. Simpson, K. Morgan, and S.C R. Maidment. 2023. Vectipelta barretti, a new ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous Wessex Formation of the Isle of Wight, UK. Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 21: 2210577. doi: 10.1080/14772019.2023.2210577
108 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vectipelta

Vectipelta is a genus of ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Wessex Formation of England. The name is derived from "Vectis", the Roman name for the Isle of Wight. Like other ankylosaurs, it was a large herbivore with short legs and a wide, flat body, covered in osteoderms and spikes. Although it was discovered in England, Vectipelta was not very closely related to other ankylosaurs in the same area. It was actually most closely related to Chinese ankylosaurs, suggesting dinosaurs moved freely from Asia to Europe in the Early Cretaceous.
66 notes
·
View notes
Text

Isle of Wight: New dinosaur species discovered
“The fossilised remains of a previously unknown type of dinosaur have been found on the Isle of Wight.
It is the first new species of armoured dinosaur to be found on the island since 1865 and belongs to the same family - the ankylosaurs.
Though fearsome in appearance with its blade-like armour, the giant reptile - which has been named Vectipelta barretti - only ate plants.” —read more at bbc.com
#dinosaurs#dinosaur#paleontology#prehistoric#fossils#science#babe wake up#babe wake up new dinosaur dropped#ankylosaurus#vectipelta barretti
98 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nueva especie de dinosaurio blindado encontrada en la Isla británica de Wight
Con un cuerpo totalmente acorazado y una dieta estrictamente herbívora, así han descrito a esta nueva especie de dinosaurio recién descrito en la formación Wessex en la Isla británica de Wight. En el estudio publicado en la revista de fomento científico Journal of Systematic Paleontology, los paleontólogos describen la nueva especie como Vectipelta barretti, un dinosaurio acorazado perteneciente…
View On WordPress
#anquilosaurios#Cretácico Temprano#Isla de Wight#Museo de Historia Natural#nueva especie de dinosaurio acorazado#Reinó Unido#Vectipelta barretti
0 notes
Text




Results from the #JurassicLeft #paleostream! Vectipelta, Confuciusornis (being intersex), Acrocanthosaurus and some gay Torosaurus.
615 notes
·
View notes
Text
Archovember 2024 Day 30 - Iguanodon bernissartensis

Our final species for Archovember is Iguanodon bernissartensis! As one of the more famous dinosaurs, Iguanodon is known for being one of the first dinosaurs to recieve a life-sized model, while now outdated and with the thumb spike placed on its nose. This has made Iguanodon a public example of how our scientific advances have improved our understanding of these ancient animals.
A very successful species in life, Iguanodon bernissartensis lived from the Late Jurassic all the way into the Early Cretaceous. Remains have been found in Belgium, Germany, England, and Spain. It is the type species of its own family of ornithopods: the Iguanodontids. They were large, bulky, muscular animals that could shift between quadrupedality to bipedality when needed, but were probably more quadrupedal as they got older and heavier. Their long arms supported conical thumb-spikes that could have been used for defense and/or for foraging. It used its cropping beak and grinding teeth for chewing up tough plant matter. Its long outer fingers were flexible, and may have aided in grabbing onto food as well.

Due to its wide range across Europe and across eons, Iguanodon bernissartensis would have lived alongside a variety of different species in different time periods and habitats. Formations where it has been found include the Sainte-Barbe Clays Formation, the Arcillas de Morella Formation, and the Wessex Formation. In Early Cretaceous Europe, it would have lived alongside fellow iguanodonts like Mantellisaurus and Valdosaurus. Other ornithischians included ornithopods like Morelladon, ankylosaurs like Polacanthus and Vectipelta, and smaller ornithischians like Hypsilophodon and Vectidromeus. It would have also come across sauropods like Garumbatitan, Oplosaurus, Eucamerotus, and Ornithopsis, spinosaurids like Protathlitis, Vallibonavenatrix, Ceratosuchops, and Riparovenator, other carnosaurs like Altispinax and Neovenator, compsognathids like Aristosuchus, and dromaeosaurids like Ornithodesmus and Vectiraptor. Iguanodon would have also shared Early Cretaceous Europe with pterosaurs like Coloborhynchus and pseudosuchians like Anteophthalmosuchus and Bernissartia.

This art may be used for educational purposes, with credit, but please contact me first for permission before using my art. I would like to know where and how it is being used. If you don’t have something to add that was not already addressed in this caption, please do not repost this art. Thank you!
#Iguanodon bernissartensis#Iguanodon#iguanodontid#ornithopods#ornithischians#dinosaurs#archosaurs#archosauromorphs#reptiles#Archovember#Archovember2024#Dinovember#Dinovember2024#SaritaDrawsPalaeo#Late Jurassic#Early Cretaceous#Belgium#Germany#England#Spain#Sainte-Barbe Clays Formation#Arcillas de Morella Formation#Wessex Formation
34 notes
·
View notes
Note
What's your favorite dinosaur?
I like thyreophora which is the clade that includes both ankylosaurs and stegosaurs and also more basal members such as scelidosaurus. within that clade it's hard to choose, but if I had to pick, I'd probably go with Polacanthus which is from the early cretaceous wealden group (Wessex formation) and is known from the type specimen found on the Isle of Wight in 1865 by William Fox (which is where it gets its species name foxii. It is known from relatively few remains, some of which have now been reassigned to Vectipelta. There is part of a Polacanthus specimen coming out of the cliff at Brook Beach at the moment and one of the guides who does the fossil tours with me found a piece of Polacanthus armour recently on the beach!
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
New wasp species named after Doctor Who villain
‘Dalek’ wasps are among 815 new species described by Natural History Museum scientists in 2023
Nilima Marshall - 4 hours ago
Fourteen newly discovered species of wasps have been named after the villainous Daleks from Doctor Who to mark the 60th anniversary of the popular sci-fi series.
The insects, which bear the genus “Dalek”, are among the 619 new wasp species described this year by London’s Natural History Museum (NHM).
An alien warrior race of mutants, the Daleks are the formidable bad guys in BBC’s long-running TV show.
I thought it was a good name for a genus and a bit of fun having been a big fan of Doctor Who in my early years
Dr John Noyes, NHM
One particular species of wasp from Costa Rica called Dalek nationi also honours Terry Nation, the Welsh screenwriter and novelist who created the mutant race that terrified children for the past six decades.
Dr John Noyes, scientific associate at the NHM, said: “I thought it was a good name for a genus and a bit of fun having been a big fan of Doctor Who in my early years.”
A total of 815 new species were described by NHM scientists in 2023, including a 407-million-year-old parasitic fungus named after children’s author Beatrix Potter.
Potteromyces asteroxylicola was discovered infecting the roots of ancient plants and is thought to be the earliest disease-causing fungus ever discovered.
The researchers said they wanted to honour Potter’s reputation as a dedicated mycologist – someone who studies and works with fungi.
Dr Christine Strullu-Derrien, scientific associate at the NHM, who helped identify the new Potter fungus, said: “Naming this important species after Beatrix Potter seems a fitting tribute to her remarkable work and commitment to piecing together the secrets of fungi.”
Highlights also include fossil remains of a new dinosaur species found on the Isle of Wight, which was named Vectipelta barretti after NHM Professor Paul Barrett who worked there for two decades.
It is first the dinosaur discovered on the island for 142 years.
Other notable discoveries also include fossil remains of a giant penguin called Kumimanu fordycei – believed to be the largest penguin that ever lived – and nine new species of bristle worms including two bone-eating worms.
The researchers also report new species being discovered in “unremarkable” urban environments, including a stick insect called Micropodacanthus tweedae that was found on the side of a bin in Australia, and a moth that was located in Ealing, west London, called Tachystola mulliganae, which turned out be a new species native to Western Australia.
T. mulliganae is named after Barbara Mulligan, a lifelong moth enthusiast who discovered the species.
Mark Sterling, a scientific associate at NHM, described the finding as “real coup for citizen science”.
The new species descriptions contributed to the 722 new research papers released by the NHM over the past 12 months.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Monday Musings: European Ties
In the early Cedar Mountain fossiliferous members (namely Yellow Cat and Poison Strip) show a connection to Europe through similar dinosaurs.
Polacanthine ankylosaurs were abundant in the Cedar Mountain Formation and the group was named after the European Polacanthus.
Other European nodosaurs (essentially ankylosaurs without tail clubs) from Europe include Hylaeosaurus

Europelta and Vectipelta.

In the Cedar Mountain Formation, there are several nodosaurids as well such as Gastonia,

Sauropelta,

and Cedarpelta.
Another group you may be familiar with are iguanontians named after Iguanodon of Europe.

There are several other in Europe and many found in the Cedar Mountain Formation like Iguanocolossus
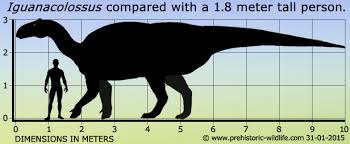
and Hippodraco.
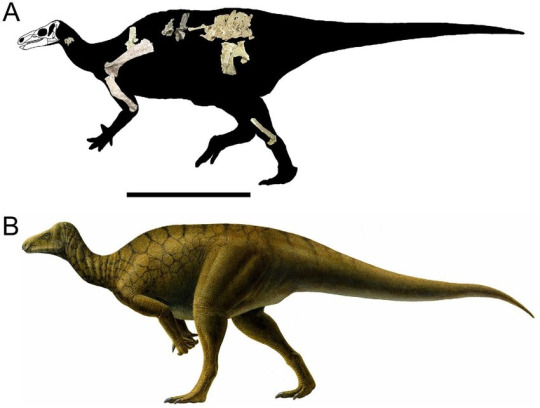
Hypsilophodon was a neornithschian from Europe and a recent American equivalent was discovered in the Cedar Mountain but has yet to be named and described.
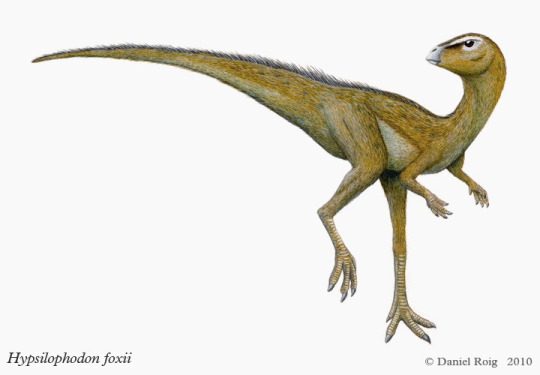
Sauropods, often associated with the Jurassic Period, continued to thrive in the early Cretaceous. In Europe, there was representation from several groups.
Haestasaurus is macronarians like Brontomerus (similar to the Jurassic Camarasaurus).
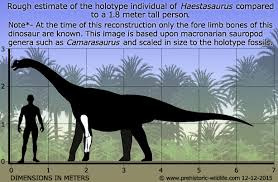
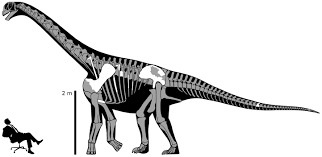
Soriatitan is a brachiosaurid from Spain.

In the Cedar Mountain, there is Abydosaurus.

On the carnivore side of things, we had Eotyrannus, a tyrannosauroid from the Isle of Wight
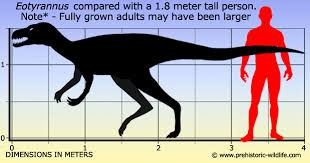
and Moros, a tyrannosauroid from the Cedar Mountain Formation.

There's Pelecanimimus from Spain as a representative of ornithominosaurs

and Nedcolbertia in the Cedar Mountain Formation.

Finally, there are the dromaeosaurs like Vectiraptor in Europe
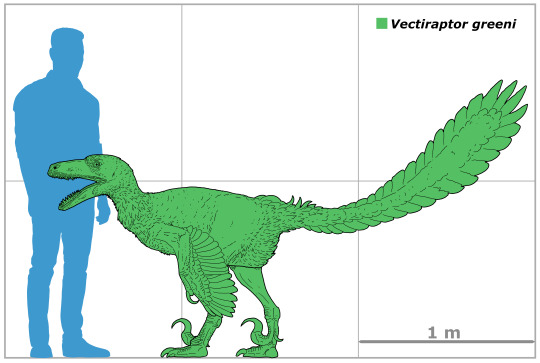
and Utahraptor in the Cedar Mountain Formation.

Tune in next week to see how the Cedar Mountain dinosaurs have ties to Asia as time progresses!
#paleontology#fossils#dinosaur#fun facts#cedar mountain formation#europe#north america#early cretaceous
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
This year has gone by fast! There are only 44 more days left of 2023 so to celebrate I’m gonna make a post about five extinct animals that were described this year!
1. Bos primigenius thrinacius n. ssp.

(Bos primigenius thrinacius n. ssp. Size estimate of a bull, cow, and calf compared to a human and an adult Palaeoloxodon falconeri. Art by Joschua Knüppe)
This new sub species of Aurochs lived on the Greek island of Kythera during the Late Pleistocene. The sub species was probably present on Kythera while it was still part of the mainland, but became trapped when it was separated sometime during the Middle to Late Pleistocene and their small size was a result of insular dwarfism. Insular dwarfism is a common phenomenon in evolution where a population of large animals becomes trapped on an island and slowly evolve to become smaller over time to better adapt to the reduced space and resources. The opposite, insular gigantism, where an island-bound population of small animals grows larger than their mainland counterparts also occurs regularly. During the Pleistocene, the various islands of Greece were full of giant swans and miniature elephants but now we know they had tiny cattle roaming about as well.
2. Garumbatitan morellensis
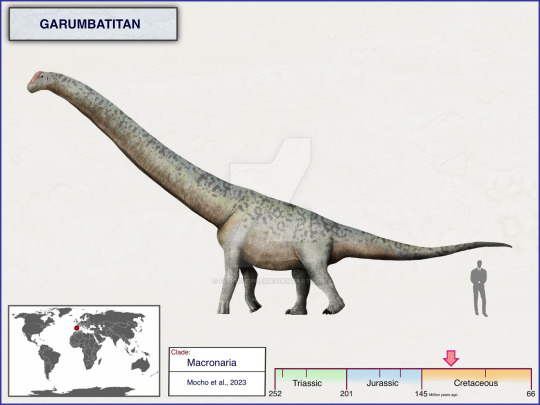
(Size comparison between Garumbatitan morellensis and a human. Art by cisiopurple on Deviantart)
Meaning “Garumba Giant”, Garumbatitan morellensis was a species of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Cretaceous period in what is now Spain. Its remains were first discovered in 1998 at the Arcillas de Morella Formation near the city of Morella, however, they would not be excavated until an expedition in 2005. More material would later be discovered in a 2008 expedition and a paper would be published on the findings in 2016, but it wasn’t until this year that the species was officially named and described. Its genus named is a mix of the name for the tallest mountain in the region it was discovered in, Mola de la Garumba, and the Greek word “Titan”.
3. Nihohae matakoi

(A pair of Nihohae matakoi hunting some squid. Art by Daniel Verhelst)
Nihohae matakoi was a species of dolphin that belonged to the now extinct Waipatiid family and lived during the Oligocene in the waters surrounding what is now New Zealand. It possessed a bizarre set of tusk-like teeth that protruded from its beak. It is thought that this dolphin used it’s strange teeth much like a sawfish to stun their prey before consuming them. The holotype specimen was discovered all the way back in 1998 in Awamoko Valley on New Zealand’s South Island. The specimen consisted of a nearly complete skull, a single atlas and axis, eight vertebrae, and seven ribs. However, Nihohae matakoi would not be officially described until 2023. Its genus name combines the Māori words “Niho”, meaning “teeth”, and “Hae”, meaning “slashing”. The species name is also derived from Māori and comes from the words “Mata”, meaning “face” or “point”, and “Koi”, meaning “sharp”.
4. Perucetus colossus

(A pair of Perucetus swim together in the shallows. Art by Gabuded on Deviantart)
Another cetacean, Perucetus colossus was a species of early whale that lived during the Bartonian age of the Middle Eocene and was found in Peru (obviously). The remains we have or Perucetus are pretty fragmentary, but it has an estimated length of around 55.8-65.9 ft and was probably just as, if not heavier, than the modern Blue Whale. Due to the density of its bones and its absolute chonkiness, Perucetus likely was not a fast swimmer and likely lived in shallow waters and fed on crustaceans and mollusks. However, this is just speculation as very little about its ecology is known.
5. Vectipelta barretti

(A pair of Vectipelta barretti graze near a stream. Art by Stuart Pond)
Vectipelta barretti was an ankylosaurian dinosaur that lived during the Early Cretaceous in what is now England. It was discovered in the Wessex Formation and it’s genus name means “Isle of Wight shield”. The holotype specimen of Vectipelta was originally discovered in November of 1993, however, at the time it was believed that the specimen belonged to the genus Polacanthus. In May of 2021 it was discovered that the specimen was in fact a new genus and in June of 2023 it was officially named and described. Funnily enough, fossil evidence suggests that Vectipelta might be millions of years older than Polacanthus, the genus it was originally thought to be a member of.
I hope you all enjoyed reading about these recently described prehistoric species! I LOVE dinosaurs and other extinct animals and can’t wait to see what new discoveries 2024 has to offer!
#dinosaur love#animals#new discoveries#infodump#science#dinosaur#peru#new zealand#isle of wight#Kythera#new species#animal news#animal facts#dinosaur facts#paleontology#spain#2023#ankylosauria#sauropod#aurochs#cetacean#perucetus
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
New UK Dinosaur Found

Artist’s depiction:

From the article:
It is the first new species of armoured dinosaur to be found on the island since 1865 and belongs to the same family - the ankylosaurs.
Though fearsome in appearance with its blade-like armour, the giant reptile - which has been named Vectipelta barretti - only ate plants.
It was discovered in rocks dating back between 66 and 145 million years.
The name Vectipelta barretti is a tip of the hat to Professor Paul Barrett, who has worked at the Natural History Museum in London for 20 years.
He said he was "flattered and absolutely delighted to have been recognised in this way", and insisted "that any physical resemblance is purely accidental".

QQ for Science Side of Tumblr: Do you know if “prehistoric lizard” means that this dino didn’t have feathers?
#dinosaur#vecipelta barretti#ankylosaurus#uk new#science news#news#good news#animals#paleontology#jurassic period
35 notes
·
View notes
Text

Vectipelta from the Wessex Formation
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
☆ Vectipelta is a very cool dinosaur that is an ankylosaurian ☆ (I LOVE ANKYLOSAURIANS :3)
He/they
☆ Some hobbies of mine are drawing,origami, reading, researching about dinosaurs, and listening to music ☆
☆ Some of the things I like are watamote, dinosaurs, miss Kobayashis dragon maid, tbhk, lightfall, all that's left of the world, synthetic instinct, beastars, and phighting
☆ I draw a lot and will draw OCs or characters for someone if there's a ref. Mainly because eventually I want to do drawing commissions but still am practising.(btw if any of the things I like are problematic, sorry I didn't know, and I will stop supporting it if it is) ☆
Dni-
.usual things on dni lists.
.homophobes/transphobes.
.people who absolutely HATE dinosaurs without a reason to.
1 note
·
View note
Text
June was a great month for many paleontological discoveries, there has been a lot of new species identified.
Here is a list of the newly identified Paleontological species:
PART 1 OF 2
1. A new Cretaceous bird from the Maastrichtian La Colonia Formation (Patagonia, Argentina)

2. A new theropod dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous Longjiang Formation of Inner Mongolia (China) - Migmanychion laiyang

3. Conservation implications of a new fossil species of hopping-mouse, Notomys magnus sp. nov. (Rodentia: Muridae), from the Broken River Region, northeastern Queensland - Notomys magnus
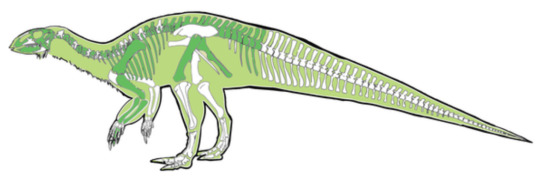
4. An early-diverging iguanodontian (Dinosauria: Rhabdodontomorpha) from the Late Cretaceous of North America - Iani smithi
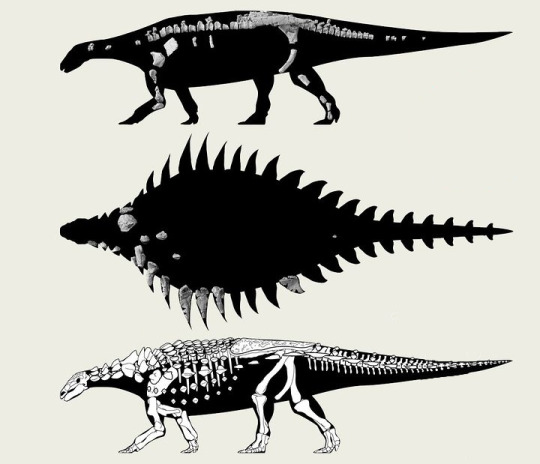
5. A new lower Turonian mosasaurid from the Western Interior Seaway and the antiquity of the unique basicranial circulation pattern in Plioplatecarpinae - Sarabosaurus dahli

6. Osteohistology reveals the smallest adult Jurassic sauropodomorph - BP/1/4732

7. A new dolphin with tusk-like teeth from the late Oligocene of New Zealand indicates evolution of novel feeding strategies - Nihohae matakoi

8. Praecarbo strigoniensis, a new genus and species of Cormorants (Phalacrocoracinae) from the Late Oligocene of Hungary - Praecarbo strigoniensis

drawing by King Kosmoceratops on youtube.
9. Vectipelta barretti, a new ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous Wessex Formation of the Isle of Wight, UK - Vectipelta barretti
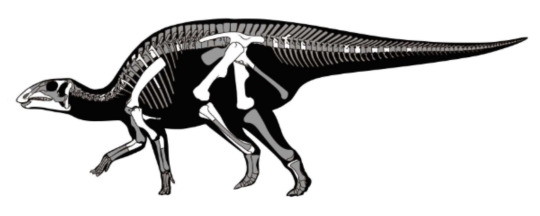
10. Relict duck-billed dinosaurs survived into the last age of the dinosaurs in subantarctic Chile - Gonkoken nanoi
There is a part 2, a continuation of this post, where you can find more and with the scientific papers relating to their descriptions are linked.
0 notes