#animal news
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Two pieces of good news for the Rhinos: a baby Javan Rhino (the most endangered) has been born!
Also, a two-year-old white rhino had a successful surgery on her broken foot.
#javan rhino#javan rhino calf#white rhino#endangered animals#endangered species#rhino#rhinoceros#good news#animals#animal news#endangered rhino
442 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wonderful news from the Cyclops Mountains of West Papua today with the rediscovery of Attenborough's long-beaked echidna (Zaglossus attenboroughi)!

(Image credit: Expedition Cyclops)
Previously known a single specimen collected in 1961, Attenborough's long-beaked echidna has long been one of the world's most elusive mammals. Recognised as a distinct species in 1998, an expedition to the Cyclops Mountains in 2007 failed to observe the echidna but found evidence of recent diggings and foraging activity which, alongside local knowledge, implied that the species still survived in those remote mountain forests.
Finally, just a few months ago, a new expedition into its remote mountain home by Expedition Cyclops caught the first ever footage of Attenborough's long-beaked echidna in the wild, which is also the first time it has been seen by scientists in over 60 years. In a remarkable stroke of luck, the echidna was captured on the last of over 80 camera traps on the final day of the trip!
Attenborough's long-beaked echidna is the most distinctive of the three species of long-beaked echidna thanks to its smaller size, shorter, straighter beak and reddish-brown fur. Its habits are virtually unknown, but its differently shaped beak may suggest that it differs in diet and feeding habits from the other two long-beaked echidna species. It appears to be endemic to the highest elevations of the Cyclops Mountains, which are steep, extremely rainy and treacherous to explore, hence why it remained hidden for so long.

(Image credit: Expedition Cyclops)
There are only five species of monotreme alive today, the sole living custodians of a lineage stretching back some 200 million years, and this makes each species extraordinarily valuable. Unfortunately, all three species of long-beaked echidna are threatened with extinction, with Attenborough's long-beaked echidna being classed as critically endangered. Losing any species is a tragedy, but for a group as small and precious as monotremes, any extinction would be especially disastrous.
Alongside the rediscovery of the echidna, Expedition Cyclops also made the first record of Mayr's honeyeater (Ptiloprora mayri) in 16 years and discovered dozens of new species of insects, arachnids, shrimp and frogs. Their work documenting the hidden biodiversity of the Cyclops Mountains is ongoing, so if you'd like to follow and support the expedition make sure to visit their website! https://www.expeditioncyclops.org/
#oceania#papua#west papua#new guinea#wildlife#mammal#mammals#monotreme#monotremes#echidna#echidnas#animal facts#animal news#mammalogy#natural history#my stuff
296 notes
·
View notes
Text
Great news for monotreme lovers!!!

The Sir David Attenborough's Long-Beaked Echidna (Zaglossus attenboroughi) has been sighted for the first time since 1961!
Also known as the Cyclops Long-Beaked Echidna, this nocturnal critter was first described by Western scientists in 1961 during the Dutch colonial era of what was then known as Dutch New Guinea. It was only described from a fragmentary preserved specimen (pictured below) and was of course named after the famous naturalist Sir David Attenborough. However, I do want to point out that, as is the case with many newly discovered species, it was known to the native people of this region way before this and was traditionally hunted for both food and for ceremonial peace offerings. However, according to my research since the species was classified as Critically Endangered, the native villagers were very enthusiastic about its conservation and agreed not to hunt them in order to help preserve the species.

Z. attenboroughi is native to the Cyclops Mountain Chain in northern Indonesian New Guinea and feeds mostly on worms, ants, termites, and other invertebrates by using their long beaks to forage through the soil and creating distinct “nose pokes”. For a long time, these “nose pokes” were the only sign scientists had that this species hadn’t gone extinct. The last unconfirmed sighting by locals was in 2005, though some tracks and burrows that were thought to belong to the species were discovered in 2007.
Now, over 60 years after it was initially described, an expedition of scientists from Oxford University to the Cyclops Mountains has resulted in this elusive monotreme being videotaped by a game trail camera.


Photo credit: Cyclops Expedition
Attenborough’s Long-Beaked Echidna might somewhat resemble hedgehogs in appearance and behavior, however, they are one of only five species of egg-laying mammals known as monotremes! The other four species are the Short-Beaked Echidna, Western Long-Beaked Echidna, Eastern Long-Beaked Echidna, and the Platypus. The Attenborough’s Long-Beaked Echidna is the smallest species of Echidna and is apparently more closely related to the Short-Beaked Echidna than it is to the other two species of Long-Beakeds. It also possesses a more reddish coloration. All species of monotremes are known for, as I mentioned before, laying eggs instead of giving live birth like placental mammals and marsupials do. Monotremes also lack nipples and instead produce milk for their young out of modified sweat glands like how the early ancestors of all mammals did. Male Platypi/Platypuses (both terms are correct) and Echidnas also have ankle spurs which are highly venomous in the case of the Platypus, but Echidnas seem to have lost their venom and instead use them to help dig. Apparently, they also seasonally secrete a creamy substance their spurs but this, while kinda gross, is harmless.
While the rediscovery of this species is super exciting, we mustn’t forget that Attenborough’s Long-Beaked Echidna is considered Critically Endangered and is still at risk of extinction. Habitat loss and poaching seem to be the biggest threats to this species and many other unique creatures endemic to Oceania.
#monotreme#echidna#new discoveries#critically endangered#science#infodump#animals#endangered species#new guinea#animal news
185 notes
·
View notes
Text
18+ account MDNI

#funny animals#wild animals#cute animals#animals#animal adventures#animal aesthetic#animal antics#animal behavior#animal bite#animal biology#animal babies#animal encounters#animal eyes#animal emote#animal friends#animal humor#animal instincts#animal imagery#animal jokes#animal kingdom#animal lover#animal life#animal memes#animal mother#animal nature#animal news#animal of the day#animal photography#animal photoshoot#animal portrait
16 notes
·
View notes
Text

16 notes
·
View notes
Text
LOST ECHIDNA FOUND!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Long-lost echidna species seen for first time in over 60 years
#animals#animal news#echidna#HES SO CUTE i love he#luna.txt#i put two separate articles so people can see both!
68 notes
·
View notes
Text
Y'ALL! The squirrels in California have started actively hunting voles as part of their regular diet. This is wild.


11 notes
·
View notes
Text
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
#fave#animals#endangered species#white nose#white nose syndrome#bats#animal news#i think im gonna start a new tag for that lol
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
They found the stolen baby donkey!! She’s home safe!!

Look at her!!
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
74!? 74!? REALLY!? amazing

WISDOM UPDATE
53K notes
·
View notes
Text

The passing process once again!
✨🌟✨Happy new year!!✨🌟✨
Best wishes and all the success possible for all of you for 2025!!
You got this!
(and yes 5 look at them so .... backward style haha)
29K notes
·
View notes
Text
BIG NEWS echidnas sound like wheezy pigeons
#there’s a recording in the article they sound as weird as you’d expect them to#australian wildlife#monotremes#echidnas#animal news#my stuff
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
This year has gone by fast! There are only 44 more days left of 2023 so to celebrate I’m gonna make a post about five extinct animals that were described this year!
1. Bos primigenius thrinacius n. ssp.

(Bos primigenius thrinacius n. ssp. Size estimate of a bull, cow, and calf compared to a human and an adult Palaeoloxodon falconeri. Art by Joschua Knüppe)
This new sub species of Aurochs lived on the Greek island of Kythera during the Late Pleistocene. The sub species was probably present on Kythera while it was still part of the mainland, but became trapped when it was separated sometime during the Middle to Late Pleistocene and their small size was a result of insular dwarfism. Insular dwarfism is a common phenomenon in evolution where a population of large animals becomes trapped on an island and slowly evolve to become smaller over time to better adapt to the reduced space and resources. The opposite, insular gigantism, where an island-bound population of small animals grows larger than their mainland counterparts also occurs regularly. During the Pleistocene, the various islands of Greece were full of giant swans and miniature elephants but now we know they had tiny cattle roaming about as well.
2. Garumbatitan morellensis
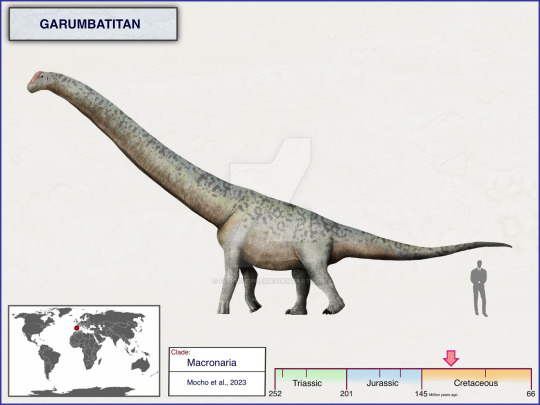
(Size comparison between Garumbatitan morellensis and a human. Art by cisiopurple on Deviantart)
Meaning “Garumba Giant”, Garumbatitan morellensis was a species of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Cretaceous period in what is now Spain. Its remains were first discovered in 1998 at the Arcillas de Morella Formation near the city of Morella, however, they would not be excavated until an expedition in 2005. More material would later be discovered in a 2008 expedition and a paper would be published on the findings in 2016, but it wasn’t until this year that the species was officially named and described. Its genus named is a mix of the name for the tallest mountain in the region it was discovered in, Mola de la Garumba, and the Greek word “Titan”.
3. Nihohae matakoi

(A pair of Nihohae matakoi hunting some squid. Art by Daniel Verhelst)
Nihohae matakoi was a species of dolphin that belonged to the now extinct Waipatiid family and lived during the Oligocene in the waters surrounding what is now New Zealand. It possessed a bizarre set of tusk-like teeth that protruded from its beak. It is thought that this dolphin used it’s strange teeth much like a sawfish to stun their prey before consuming them. The holotype specimen was discovered all the way back in 1998 in Awamoko Valley on New Zealand’s South Island. The specimen consisted of a nearly complete skull, a single atlas and axis, eight vertebrae, and seven ribs. However, Nihohae matakoi would not be officially described until 2023. Its genus name combines the Māori words “Niho”, meaning “teeth”, and “Hae”, meaning “slashing”. The species name is also derived from Māori and comes from the words “Mata”, meaning “face” or “point”, and “Koi”, meaning “sharp”.
4. Perucetus colossus

(A pair of Perucetus swim together in the shallows. Art by Gabuded on Deviantart)
Another cetacean, Perucetus colossus was a species of early whale that lived during the Bartonian age of the Middle Eocene and was found in Peru (obviously). The remains we have or Perucetus are pretty fragmentary, but it has an estimated length of around 55.8-65.9 ft and was probably just as, if not heavier, than the modern Blue Whale. Due to the density of its bones and its absolute chonkiness, Perucetus likely was not a fast swimmer and likely lived in shallow waters and fed on crustaceans and mollusks. However, this is just speculation as very little about its ecology is known.
5. Vectipelta barretti

(A pair of Vectipelta barretti graze near a stream. Art by Stuart Pond)
Vectipelta barretti was an ankylosaurian dinosaur that lived during the Early Cretaceous in what is now England. It was discovered in the Wessex Formation and it’s genus name means “Isle of Wight shield”. The holotype specimen of Vectipelta was originally discovered in November of 1993, however, at the time it was believed that the specimen belonged to the genus Polacanthus. In May of 2021 it was discovered that the specimen was in fact a new genus and in June of 2023 it was officially named and described. Funnily enough, fossil evidence suggests that Vectipelta might be millions of years older than Polacanthus, the genus it was originally thought to be a member of.
I hope you all enjoyed reading about these recently described prehistoric species! I LOVE dinosaurs and other extinct animals and can’t wait to see what new discoveries 2024 has to offer!
#dinosaur love#animals#new discoveries#infodump#science#dinosaur#peru#new zealand#isle of wight#Kythera#new species#animal news#animal facts#dinosaur facts#paleontology#spain#2023#ankylosauria#sauropod#aurochs#cetacean#perucetus
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://english.radio.cz/beavers-build-planned-dams-protected-landscape-area-while-local-officials-still-8841536

A beaver colony in the Brdy region has gained overnight fame by building several dams in the Brdy protected landscape area, creating a natural wetland exactly where it was needed. It saved the local authorities 30 million crowns, and has the public cracking jokes about public administration and red tape.
The administration of the Brdy protected landscape area, which had gained approval for the 30 million crown project, was dealing with red tape and seeking the respective building permits from the Vltava River Basin authorities when the dam project was completed almost overnight by a local colony of beavers.
They could not have chosen their location better –erecting the dams on a bypass gully that was built by soldiers in the former military base years ago, so as to drain the area. The revitalization project drafted by environmentalists was supposed to remedy this. Bohumil Fišer, head of the Brdy Protected Landscape Area Administration says Nature took its course and the beavers created the necessary biotope conditions practically overnight.
#good news#beavers#brdy#beaver#ecosystem engineers#environmentalism#science#environment#nature#animals#Czech Republic
24K notes
·
View notes