#Tech Data
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
0 notes
Text
for anyone too young to know this: watching The Truman Show is a vastly different experience now, compared to how it was before youtube and social media influencers became normal
before it was like, "what a horrifying thing to do to a human being! to take away their autonomy and privacy, all for the sake of profits! to create fake scenarios for them to react to, just to retain viewership! to ruin their happiness just so some corporate entity could harvest money from their very humanity! how could anyone do something so evil?"
and now it's like, "ah, yeah. this is still deeply fucked up, but it's pretty much what every influencer has been doing to their kids for a decade now. probably bad that we've normalized this experience"
#the truman show#sbs rambles#I keep thinking about how children on popular youtube channels should probably have laws to protect them#social workers assigned to them maybe#I dunno#they did not sign up to have their lives sold for profit#but here we are#tho#I guess none of us signed up for it#and our data is harvested more than ever#god#high-tech capitalism sucks turns out#OH WAIT because tumblr is bad at getting context sometimes#let me specify:#I am not saying that the movie The Truman Show is bad or that it normalizes this#like all good sci-fi (because it is kind of sci-fi) it's there to warn us of what the future could hold#and it did that in a very good way - it's a beautiful movie#I could see someone with a bad faith take assuming I meant that it was part of the problem#it absolutely wasn't. it didn't normalize this; we did#youtube did and social media#it's us that's the problem#or more specifically: big corporations and a lack of regulation#that's the origin of most modern problems
89K notes
·
View notes
Text

8K notes
·
View notes
Text

#glitch#glitch gif#gif#glitchart#glitch art#art#vaporwave#synthwave#retrowave#retrofuture#retroart#retro#vhs#monitor#corrupted data#80s aesthetic#1980s#1980s aesthetic#80s#aes#aesthetic#neon#purple#purple aesthetic#computer#old tech#noir#neonnoir#mood#aesthetics
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
As cameras becomes more normalized (Sarah Bernhardt encouraging it, grifters on the rise, young artists using it), I wanna express how I will never turn to it because it fundamentally bores me to my core. There is no reason for me to want to use cameras because I will never want to give up my autonomy in creating art. I never want to become reliant on an inhuman object for expression, least of all if that object is created and controlled by manufacturing companies. I paint not because I want a painting but because I love the process of painting. So even in a future where everyone’s accepted it, I’m never gonna sway on this.
if i have to explain to you that using a camera to take a picture is not the same as using generative ai to generate an image then you are a fucking moron.
#ask me#anon#no more patience for this#i've heard this for the past 2 years#“an object created and controlled by companies” anon the company cannot barge into your home and take your camera away#or randomly change how it works on a whim. you OWN the camera that's the whole POINT#the entire point of a camera is that i can control it and my body to produce art. photography is one of the most PHYSICAL forms of artmakin#you have to communicate with your space and subjects and be conscious of your position in a physical world.#that's what makes a camera a tool. generative ai (if used wholesale) is not a tool because it's not an implement that helps you#do a task. it just does the task for you. you wouldn't call a microwave a “tool”#but most importantly a camera captures a REPRESENTATION of reality. it captures a specific irreproducible moment and all its data#read Roland Barthes: Studium & Punctum#generative ai creates an algorithmic IMITATION of reality. it isn't truth. it's the average of truths.#while conceptually that's interesting (if we wanna get into media theory) but that alone should tell you why a camera and ai aren't the sam#ai is incomparable to all previous mediums of art because no medium has ever solely relied on generative automation for its creation#no medium of art has also been so thoroughly constructed to be merged into online digital surveillance capitalism#so reliant on the collection and commodification of personal information for production#if you think using a camera is “automation” you have worms in your brain and you need to see a doctor#if you continue to deny that ai is an apparatus of tech capitalism and is being weaponized against you the consumer you're delusional#the fact that SO many tumblr lefists are ready to defend ai while talking about smashing the surveillance state is baffling to me#and their defense is always “well i don't engage in systems that would make me vulnerable to ai so if you own an apple phone that's on you”#you aren't a communist you're just self-centered
594 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hot New Planetary System Just Dropped.
We hope you like your planetary systems extra spicy. 🔥
A new system of seven sizzling planets has been discovered using data from our retired Kepler space telescope.
Named Kepler-385, it’s part of a new catalog of planet candidates and multi-planet systems discovered using Kepler.
The discovery helps illustrate that multi-planetary systems have more circular orbits around the host star than systems with only one or two planets.
Our Kepler mission is responsible for the discovery of the most known exoplanets to date. The space telescope’s observations ended in 2018, but its data continues to paint a more detailed picture of our galaxy today.
Here are a few more things to know about Kepler-385:

All seven planets are between the size of Earth and Neptune.

Its star is 10% larger and 5% hotter than our Sun.

This system is one of over 700 that Kepler’s data has revealed.
youtube
The planets’ orbits have been represented in sound.
Now that you’ve heard a little about this planetary system, get acquainted with more exoplanets and why we want to explore them.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#NASA#exoplanets#Kepler#space telescope#space#universe#data sonification#sounds of space#space sounds#tech#technology#telescope#Youtube
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

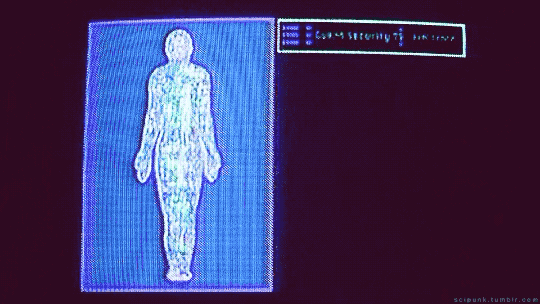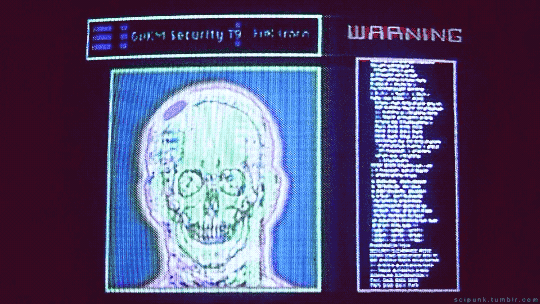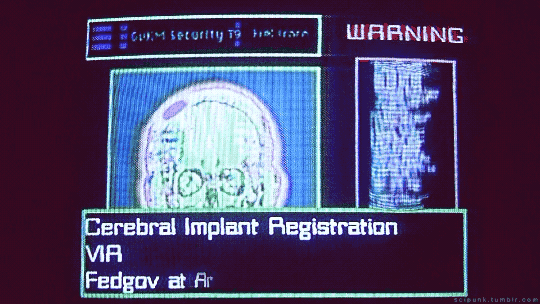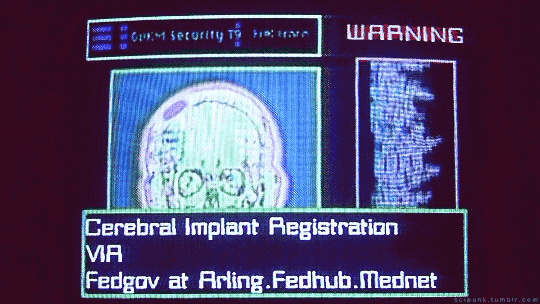
Johnny Mnemonic (1995)
#johnny mnemonic#cyberpunk aesthetic#brain implant#cybernetics#cyberpunk#data#gifs#gifset#computers#hackers#tech gadgets#90s movies#90s aesthetic#retro futuristic#90s#brain scan#keanu reeves#scifi#scifi aesthetic
525 notes
·
View notes
Text

The internal components of a wireless router
447 notes
·
View notes
Text

Control Data Corporation 607 tape drive
200 notes
·
View notes
Text
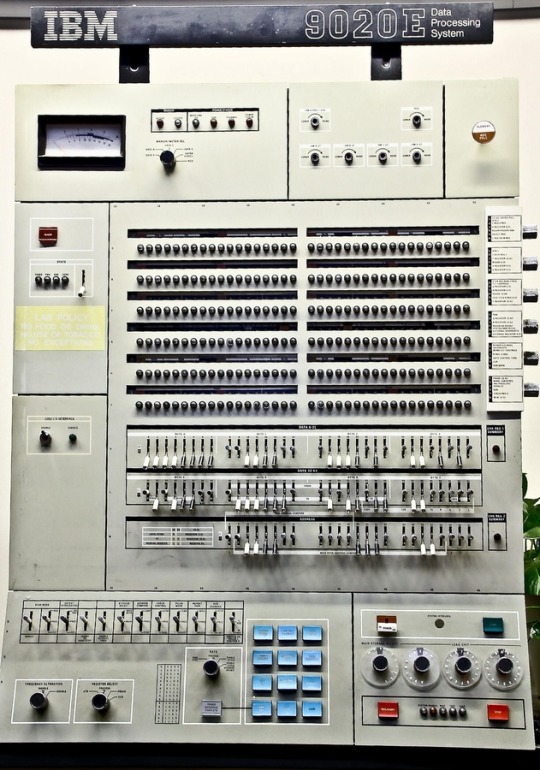

#i want to go back#retro#hardware#retro tech#desktop#vintage computing#ibm#ibm 9020E data processing system
695 notes
·
View notes
Text
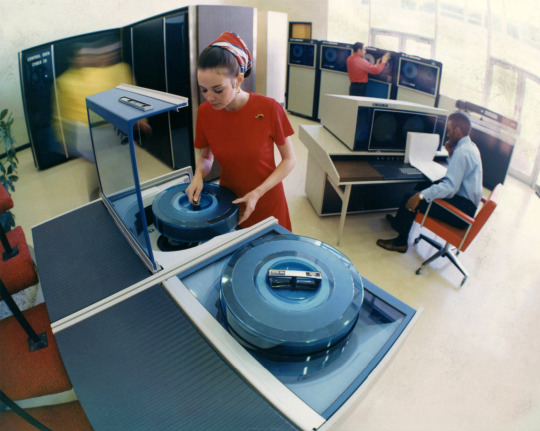

Cyber 70 mainframe computer system by Control Data Corporation, circa 1974.
507 notes
·
View notes
Photo

(via Vending machine error reveals secret face image database of college students | Ars Technica)
Canada-based University of Waterloo is racing to remove M&M-branded smart vending machines from campus after outraged students discovered the machines were covertly collecting facial-recognition data without their consent.
The scandal started when a student using the alias SquidKid47 posted an image on Reddit showing a campus vending machine error message, "Invenda.Vending.FacialRecognitionApp.exe," displayed after the machine failed to launch a facial recognition application that nobody expected to be part of the process of using a vending machine.
"Hey, so why do the stupid M&M machines have facial recognition?" SquidKid47 pondered.
The Reddit post sparked an investigation from a fourth-year student named River Stanley, who was writing for a university publication called MathNEWS.
Stanley sounded alarm after consulting Invenda sales brochures that promised "the machines are capable of sending estimated ages and genders" of every person who used the machines without ever requesting consent.
This frustrated Stanley, who discovered that Canada's privacy commissioner had years ago investigated a shopping mall operator called Cadillac Fairview after discovering some of the malls' informational kiosks were secretly "using facial recognition software on unsuspecting patrons."
Only because of that official investigation did Canadians learn that "over 5 million nonconsenting Canadians" were scanned into Cadillac Fairview's database, Stanley reported. Where Cadillac Fairview was ultimately forced to delete the entire database, Stanley wrote that consequences for collecting similarly sensitive facial recognition data without consent for Invenda clients like Mars remain unclear.
Stanley's report ended with a call for students to demand that the university "bar facial recognition vending machines from campus."
what the motherfuck
#m&m vending machine#secret face image database#college students#massive invasion of privacy#tech#collecting facial-recognition data without consent
474 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tech monopolists use their market power to invade your privacy
On SEPTEMBER 24th, I'll be speaking IN PERSON at the BOSTON PUBLIC LIBRARY!

It's easy to greet the FTC's new report on social media privacy, which concludes that tech giants have terrible privacy practices with a resounding "duh," but that would be a grave mistake.
Much to the disappointment of autocrats and would-be autocrats, administrative agencies like the FTC can't just make rules up. In order to enact policies, regulators have to do their homework: for example, they can do "market studies," which go beyond anything you'd get out of an MBA or Master of Public Policy program, thanks to the agency's legal authority to force companies to reveal their confidential business information.
Market studies are fabulous in their own right. The UK Competition and Markets Authority has a fantastic research group called the Digital Markets Unit that has published some of the most fascinating deep dives into how parts of the tech industry actually function, 400+ page bangers that pierce the Shield of Boringness that tech firms use to hide their operations. I recommend their ad-tech study:
https://www.gov.uk/cma-cases/online-platforms-and-digital-advertising-market-study
In and of themselves, good market studies are powerful things. They expose workings. They inform debate. When they're undertaken by wealthy, powerful countries, they provide enforcement roadmaps for smaller, poorer nations who are being tormented in the same way, by the same companies, that the regulator studied.
But market studies are really just curtain-raisers. After a regulator establishes the facts about a market, they can intervene. They can propose new regulations, and they can impose "conduct remedies" (punishments that restrict corporate behavior) on companies that are cheating.
Now, the stolen, corrupt, illegitimate, extremist, bullshit Supreme Court just made regulation a lot harder. In a case called Loper Bright, SCOTUS killed the longstanding principle of "Chevron deference," which basically meant that when an agency said it had built a factual case to support a regulation, courts should assume they're not lying:
https://jacobin.com/2024/07/scotus-decisions-chevron-immunity-loper
The death of Chevron Deference means that many important regulations – past, present and future – are going to get dragged in front of a judge, most likely one of those Texas MAGA mouth-breathers in the Fifth Circuit, to be neutered or killed. But even so, regulators still have options – they can still impose conduct remedies, which are unaffected by the sabotage of Chevron Deference.
Pre-Loper, post-Loper, and today, the careful, thorough investigation of the facts of how markets operate is the prelude to doing things about how those markets operate. Facts matter. They matter even if there's a change in government, because once the facts are in the public domain, other governments can use them as the basis for action.
Which is why, when the FTC uses its powers to compel disclosures from the largest tech companies in the world, and then assesses those disclosures and concludes that these companies engage in "vast surveillance," in ways that the users don't realize and that these companies "fail to adequately protect users, that matters.
What's more, the Commission concludes that "data abuses can fuel market dominance, and market dominance can, in turn, further enable data abuses and practices that harm consumers." In other words: tech monopolists spy on us in order to achieve and maintain their monopolies, and then they spy on us some more, and that hurts us.
So if you're wondering what kind of action this report is teeing up, I think we can safely say that the FTC believes that there's evidence that the unregulated, rampant practices of the commercial surveillance industry are illegal. First, because commercial surveillance harms us as "consumers." "Consumer welfare" is the one rubric for enforcement that the right-wing economists who hijacked antitrust law in the Reagan era left intact, and here we have the Commission giving us evidence that surveillance hurts us, and that it comes about as a result of monopoly, and that the more companies spy, the stronger their monopolies become.
But the Commission also tees up another kind of enforcement: Section 5, the long (long!) neglected power of the agency to punish companies for "unfair and deceptive methods of competition," a very broad power indeed:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/10/the-courage-to-govern/#whos-in-charge
In the study, the Commission shows – pretty convincingly! – that the commercial surveillance sector routinely tricks people who have no idea how their data is being used. Most people don't understand, for example, that the platforms use all kinds of inducements to get web publishers to embed tracking pixels, fonts, analytics beacons, etc that send user-data back to the Big Tech databases, where it's merged with data from your direct interactions with the company. Likewise, most people don't understand the shadowy data-broker industry, which sells Big Tech gigantic amounts of data harvested by your credit card company, by Bluetooth and wifi monitoring devices on streets and in stores, and by your car. Data-brokers buy this data from anyone who claims to have it, including people who are probably lying, like Nissan, who claims that it has records of the smells inside drivers' cars, as well as those drivers' sex-lives:
https://nypost.com/2023/09/06/nissan-kia-collect-data-about-drivers-sexual-activity/
Or Cox Communications, which claims that it is secretly recording and transcribing the conversations we have in range of the mics on our speakers, phones, and other IoT devices:
https://www.404media.co/heres-the-pitch-deck-for-active-listening-ad-targeting/
(If there's a kernel of truth to Cox's bullshit, my guess it's that they've convinced some of the sleazier "smart TV" companies to secretly turn on their mics, then inflated this into a marketdroid's wet-dream of "we have logged every word uttered by Americans and can use it to target ads.)
Notwithstanding the rampant fraud inside the data brokerage industry, there's no question that some of the data they offer for sale is real, that it's intimate and sensitive, and that the people it's harvested from never consented to its collection. How do you opt out of public facial recognition cameras? "Just don't have a face" isn't a realistic opt-out policy.
And if the public is being deceived about the collection of this data, they're even more in the dark about the way it's used – merged with on-platform usage data and data from apps and the web, then analyzed for the purposes of drawing "inferences" about you and your traits.
What's more, the companies have chaotic, bullshit internal processes for handling your data, which also rise to the level of "deceptive and unfair" conduct. For example, if you send these companies a deletion request for your data, they'll tell you they deleted the data, but actually, they keep it, after "de-identifying" it.
De-identification is a highly theoretical way of sanitizing data by removing the "personally identifiers" from it. In practice, most de-identified data can be quickly re-identified, and nearly all de-identified data can eventually be re-identified:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/08/the-fire-of-orodruin/#are-we-the-baddies
Breaches, re-identification, and weaponization are extraordinarily hard to prevent. In general, we should operate on the assumption that any data that's collected will probably leak, and any data that's retained will almost certainly leak someday. To have even a hope of preventing this, companies have to treat data with enormous care, maintaining detailed logs and conducting regular audits. But the Commission found that the biggest tech companies are extraordinarily sloppy, to the point where "they often could not even identify all the data points they collected or all of the third parties they shared that data with."
This has serious implications for consumer privacy, obviously, but there's also a big national security dimension. Given the recent panic at the prospect that the Chinese government is using Tiktok to spy on Americans, it's pretty amazing that American commercial surveillance has escaped serious Congressional scrutiny.
After all, it would be a simple matter to use the tech platforms targeting systems to identify and push ads (including ads linking to malicious sites) to Congressional staffers ("under-40s with Political Science college degrees within one mile of Congress") or, say, NORAD personnel ("Air Force enlistees within one mile of Cheyenne Mountain").
Those targeting parameters should be enough to worry Congress, but there's a whole universe of potential characteristics that can be selected, hence the Commission's conclusion that "profound threats to users can occur when targeting occurs based on sensitive categories."
The FTC's findings about the dangers of all this data are timely, given the current wrangle over another antitrust case. In August, a federal court found that Google is a monopolist in search, and that the company used its data lakes to secure and maintain its monopoly.
This kicked off widespread demands for the court to order Google to share its data with competitors in order to erase that competitive advantage. Holy moly is this a bad idea – as the FTC study shows, the data that Google stole from us all is incredibly toxic. Arguing that we can fix the Google problem by sharing that data far and wide is like proposing that we can "solve" the fact that only some countries have nuclear warheads by "democratizing" access to planet-busting bombs:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/08/07/revealed-preferences/#extinguish-v-improve
To address the competitive advantage Google achieved by engaging in the reckless, harmful conduct detailed in this FTC report, we should delete all that data. Sure, that may seem inconceivable, but come on, surely the right amount of toxic, nonconsensually harvested data on the public that should be retained by corporations is zero:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/09/19/just-stop-putting-that-up-your-ass/#harm-reduction
Some people argue that we don't need to share out the data that Google never should have been allowed to collect – it's enough to share out the "inferences" that Google drew from that data, and from other data its other tentacles (Youtube, Android, etc) shoved into its gaping maw, as well as the oceans of data-broker slurry it stirred into the mix.
But as the report finds, the most unethical, least consensual data was "personal information that these systems infer, that was purchased from third parties, or that was derived from users’ and non-users’ activities off of the platform." We gotta delete that, too. Especially that.
A major focus of the report is the way that the platforms handled children's data. Platforms have special obligations when it comes to kids' data, because while Congress has failed to act on consumer privacy, they did bestir themselves to enact a children's privacy law. In 2000, Congress passed the Children's Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA), which puts strict limits on the collection, retention and processing of data on kids under 13.
Now, there are two ways to think about COPPA. One view is, "if you're not certain that everyone in your data-set is over 13, you shouldn't be collecting or processing their data at all." Another is, "In order to ensure that everyone whose data you're collecting and processing is over 13, you should collect a gigantic amount of data on all of them, including the under-13s, in order to be sure that not collecting under-13s' data." That second approach would be ironically self-defeating, obviously, though it's one that's gaining traction around the world and in state legislatures, as "age verification" laws find legislative support.
The platforms, meanwhile, found a third, even stupider approach: rather than collecting nothing because they can't verify ages, or collecting everything to verify ages, they collect everything, but make you click a box that says, "I'm over 13":
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/09/how-to-make-a-child-safe-tiktok/
It will not surprise you to learn that many children under 13 have figured out that they can click the "I'm over 13" box and go on their merry way. It won't surprise you, but apparently, it will surprise the hell out of the platforms, who claimed that they had zero underage users on the basis that everyone has to click the "I'm over 13" box to get an account on the service.
By failing to pass comprehensive privacy legislation for 36 years (and counting), Congress delegated privacy protection to self-regulation by the companies themselves. They've been marking their own homework, and now, thanks to the FTC's power to compel disclosures, we can say for certain that the platforms cheat.
No surprise that the FTC's top recommendation is for Congress to pass a new privacy law. But they've got other, eminently sensible recommendations, like requiring the companies to do a better job of protecting their users' data: collect less, store less, delete it after use, stop combining data from their various lines of business, and stop sharing data with third parties.
Remember, the FTC has broad powers to order "conduct remedies" like this, and these are largely unaffected by the Supreme Court's "Chevron deference" decision in Loper-Bright.
The FTC says that privacy policies should be "clear, simple, and easily understood," and says that ad-targeting should be severely restricted. They want clearer consent for data inferences (including AI), and that companies should monitor their own processes with regular, stringent audits.
They also have recommendations for competition regulators – remember, the Biden administration has a "whole of government" antitrust approach that asks every agency to use its power to break up corporate concentration:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2021/08/party-its-1979-og-antitrust-back-baby
They say that competition enforcers factor in the privacy implications of proposed mergers, and think about how promoting privacy could also promote competition (in other words, if Google's stolen data helped it secure a monopoly, then making them delete that data will weaken their market power).
I understand the reflex to greet a report like this with cheap cynicism, but that's a mistake. There's a difference between "everybody knows" that tech is screwing us on privacy, and "a federal agency has concluded" that this is true. These market studies make a difference – if you doubt it, consider for a moment that Cigna is suing the FTC for releasing a landmark market study showing how its Express Scripts division has used its monopoly power to jack up the price of prescription drugs:
https://www.fiercehealthcare.com/payers/express-scripts-files-suit-against-ftc-demands-retraction-report-pbm-industry
Big business is shit-scared of this kind of research by federal agencies – if they think this threatens their power, why shouldn't we take them at their word?
This report is a milestone, and – as with the UK Competition and Markets Authority reports – it's a banger. Even after Loper-Bright, this report can form the factual foundation for muscular conduct remedies that will limit what the largest tech companies can do.
But without privacy law, the data brokerages that feed the tech giants will be largely unaffected. True, the Consumer Finance Protection Bureau is doing some good work at the margins here:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/16/the-second-best-time-is-now/#the-point-of-a-system-is-what-it-does
But we need to do more than curb the worst excesses of the largest data-brokers. We need to kill this sector, and to do that, Congress has to act:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/12/06/privacy-first/#but-not-just-privacy

The paperback edition of The Lost Cause, my nationally bestselling, hopeful solarpunk novel is out this month!

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/09/20/water-also-wet/#marking-their-own-homework

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#coppa#privacy first#ftc#section 5 of the ftc act#privacy#consumer privacy#big tech#antitrust#monopolies#data brokers#radium suppositories#commercial surveillance#surveillance#google#a look behind the screens
231 notes
·
View notes
Text

492 notes
·
View notes
Text

#matrix#the matrix#vhs#retrofuture#retro tech#cyberpunk#cyberpunk city#vaporwave#synthwave#retrowave#retro#art#80s aesthetic#80s#1980s aesthetic#1980s#aes#aesthetic#neon#aesthetics#gif#noir#neonnoir#green#glitch#glitch gif#glitchart#corrupted data#corrupted#monitor
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

"In their statement on Friday, NPD warned that the “the information that was suspected of being breached contained name, email address, phone number, social security number, and mailing address(es).” It recommended the public to take a number of steps to safeguard their identities, including freezing their credit and putting fraud alerts on their files at big credit bureaus.
The breach came to public awareness after a class-action lawsuit was filed August 1 in U.S. District Court in Florida, which was first reported by Bloomberg Law.
National Public Data did not share how many people were at risk, but hackers, who have been identified as part of the hacking group USDoD, have been offering, for sale, what they claimed were billions of NPD records since April, though the Washington Post reported that “security researchers who looked at the trove said some of the claims were exaggerated.”"
source 1
source 2
source 3
free database created by Pentester to see if your information has been leaked
#destiel meme news#destiel meme#news#united states#us news#cybersecurity#data breach#hacking#tech industry#cyber security#identity theft#social security#national public data
227 notes
·
View notes