#Sustainable Technology Practices
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#Sustainable Technology Practices#MacBook Replacement Parts Guide#MacBook Repair Vs. Replacement Cost#MacBook Maintenance Tips#Extending MacBook Lifespan#DIY MacBook Upgrades
0 notes
Text
#Benefits Of Repairable Gadgets#Electronic Waste#Repairability Score#Repairable Electronics#Right To Repair#Sustainable Consumerism#Sustainable Technology Practices
1 note
·
View note
Text
#Silica mining challenges#Silica mining solutions#Health risks of silica mining#Sustainable silica mining practices#Silica dust control measures#Regulations on silica mining#Technological advancements in silica mining
1 note
·
View note
Text
pvc electric red and blue wire #smartratework#tumblr
#flowers#aesthetic#alternative#grunge#1950s#cute#japan#60s#70s#80s#|| Smart Rate Work#Manufacturing encompasses a diverse array of processes and technologies aimed at producing a wide range of products#from everyday essentials to specialized components. Take wires#for instance: these are typically manufactured through drawing processes#where metal rods or strips are pulled through dies to reduce their diameter and achieve the desired thickness. This method ensures uniformi#crucial for applications in electronics#construction#and industrial settings.#On the other hand#the production of bottles involves molding techniques such as blow molding or injection molding. Blow molding heats plastic resin into a mo#used extensively for beverage containers and packaging. Injection molding#meanwhile#injects molten plastic into a mold under high pressure#ideal for producing intricate shapes with precision#like medical vials or automotive parts.#Both wire and bottle manufacturing rely heavily on materials science#engineering precision#and quality control measures to meet stringent specifications. Advances in automation#robotics#and sustainability practices are transforming these industries
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Eco India: Even as technology lends a hand, India's farmers grapple with an uncertain future
Credits:
Supervising Producer: Nooshin Mowla
Field Producer & Script: Juhi Chaudhary
Video Editor: Sujit Lad
Producer: Ipsita Basu
Director of Photography: Harendra Rawat
Voiceover: Soundarya Jayachandran
Executive Producer: Sannuta Raghu
#scroll.in#eco india#solarpunk#india#farmers#farming#technology#sustainability#sustainable agriculture#sustainable practices#Youtube#Asia
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
AIDGC: Pioneering Safety in Handling Dangerous Goods
In a world where hazardous materials play an integral role in various industries, safety must remain a top priority. The Australian Institute of Dangerous Goods Consultants (AIDGC) is at the forefront of revolutionizing how businesses handle dangerous goods. Their unique approach to promoting safety, compliance, and education sets them apart as industry leaders. Let’s explore how AIDGC is making a difference and fostering a culture of responsibility in handling dangerous goods.
Unmatched Expertise: AIDGC’s team of seasoned consultants brings unparalleled expertise to the table. With years of hands-on experience and in-depth knowledge of regulations, they offer reliable guidance to businesses dealing with dangerous goods. From chemicals to flammable substances, AIDGC’s consultants know the intricacies of each industry, ensuring the safe handling and transportation of hazardous materials. Tailored Solutions for Every Business: Recognizing that one size doesn’t fit all, AIDGC provides customized solutions for businesses of all sizes and industries. Their approach is flexible, addressing unique challenges and specific needs. AIDGC works closely with clients to develop comprehensive safety strategies, enhancing their risk management practices and promoting a safety-first culture. Proactive Safety Training: Preventing accidents starts with education. AIDGC conducts cutting-edge training programs that empower employees with the knowledge and skills to handle dangerous goods responsibly. From theoretical understanding to practical simulations, the training equips personnel to react appropriately during emergencies, minimizing potential risks. Embracing Innovation: AIDGC embraces technological advancements to optimize safety measures further. They keep themselves updated on the latest industry trends and incorporate innovative solutions into their consultancy services. By leveraging modern technology, AIDGC ensures businesses stay ahead of the curve in hazardous materials management. Sustainable Practices: Safety and sustainability go hand in hand. AIDGC emphasizes the importance of environmentally responsible practices in handling dangerous goods. Their consultants work with businesses to adopt eco-friendly approaches, reducing their impact on the environment and contributing to a greener future. Conclusion: When it comes to handling dangerous goods, AIDGC stands as a beacon of expertise and innovation. Their unique approach to safety, tailored solutions, proactive training, and commitment to sustainability have earned them a reputation as pioneers in the industry. Collaborating with AIDGC empowers businesses to navigate hazardous materials responsibly, safeguarding their employees, communities, and the planet. By choosing AIDGC, you choose a safer and more sustainable future for your business and the world.
#AIDGC#Compliance#Dangerous Goods Consultants#Environmentally Responsible#Expertise#Greener Future#Handling Dangerous Goods#Hazardous Materials Management#Hazardous Materials safety#Innovative Solutions#Proactive Safety Training#Regulations#Risk Management#Safety in Handling Hazardous Materials#Safety Strategies#Safety-first Culture#Sustainable Practices#Tailored Solutions#Technological Advancements
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
From Waste to Wealth: Transforming Trash into Sustainable Success

In a world grappling with environmental concerns and limited resources, the concept of "waste to wealth" holds tremendous promise. Waste, once perceived as a burden, is now recognized as a potential asset that can be transformed into a valuable resource. From recycling and upcycling to innovative technologies, this article explores the various ways in which we can turn waste into wealth, promoting sustainable practices and economic growth.
The Power of Recycling
Recycling has become a household term, but its significance cannot be overstated. By collecting and processing waste materials such as plastic, paper, glass, and metal, we can divert them from landfills and give them a new life. The recycling industry not only reduces the strain on our planet's resources but also creates employment opportunities and contributes to the circular economy. Governments and businesses worldwide are investing in recycling infrastructure and raising awareness to maximize the potential of waste recycling.
Upcycling: Adding Value to Discarded Materials
While recycling focuses on breaking down waste materials, upcycling takes a different approach by transforming them into products of higher value. Instead of downgrading the material, upcycling adds creativity and innovation to turn waste into desirable and unique items. From repurposing old furniture to creating fashion accessories from discarded textiles, upcycling has gained popularity as a sustainable alternative to conventional manufacturing. This practice not only reduces waste but also fosters creativity and entrepreneurial opportunities.
Innovative Technologies for Waste Management
Advancements in technology have revolutionized waste management, offering exciting possibilities for a greener and more sustainable future. One groundbreaking technology that has gained significant attention is waste-to-energy conversion. This process involves transforming organic waste into valuable biogas or biofuels through various techniques such as anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis.
Anaerobic digestion is a biological process that breaks down organic waste in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas as a byproduct. The organic waste, such as food scraps, agricultural residues, and sewage sludge, is placed in an enclosed tank where anaerobic bacteria decompose the waste and generate methane-rich biogas. This biogas can then be used as a renewable energy source for electricity generation, heating, or even as a vehicle fuel. The remaining digestate, which is a nutrient-rich residue, can be utilized as a natural fertilizer for agriculture, closing the loop on waste management.
Pyrolysis is another waste-to-energy conversion process that involves heating organic waste in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the production of biochar, bio-oil, and syngas. Biochar is a stable carbon-rich material that can enhance soil fertility and carbon sequestration, while bio-oil and syngas can be utilized as energy sources. This process can be applied to various types of organic waste, including agricultural residues, forestry waste, and even certain types of plastics.
The waste-to-energy conversion technologies not only offer a sustainable solution for waste management but also contribute to the production of renewable energy. By diverting organic waste from landfills, these processes help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, as landfilling organic waste leads to the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Furthermore, the utilization of biogas and biofuels as energy sources helps decrease reliance on fossil fuels, mitigating the negative impacts of climate change and supporting the transition to a low-carbon economy.
While waste-to-energy conversion primarily focuses on organic waste, technology is also advancing to address the challenges posed by non-recyclable plastics. Traditional recycling methods often face limitations when it comes to certain plastics, such as multilayered packaging and mixed plastics that are difficult to separate and process. To tackle this issue, innovative technologies like plasma gasification and chemical recycling are being explored.
Plasma gasification is a high-temperature process that converts solid waste, including non-recyclable plastics, into a synthetic gas known as syngas. This syngas can be further utilized as a source of energy or as a chemical feedstock for the production of various materials. The process employs extremely high temperatures generated by an electric arc or plasma torch, breaking down the waste into its elemental components.
Chemical recycling, also known as advanced recycling or feedstock recycling, involves breaking down plastics into their molecular building blocks through various chemical processes. These building blocks can then be used as raw materials to produce new plastics, reducing the demand for virgin fossil fuel-based plastics. Chemical recycling has the potential to address the challenges posed by mixed plastics, post-consumer plastics, and plastics that are difficult to recycle through traditional mechanical processes.
By exploring and implementing these innovative waste management technologies, we can significantly reduce waste generation, minimize environmental pollution, and create valuable resources. Waste-to-energy conversion technologies provide a sustainable alternative to conventional waste disposal methods, generating renewable energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, plasma gasification and chemical recycling offer solutions to the challenges posed by non-recyclable plastics, fostering a more circular economy and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
As technology continues to advance and awareness of environmental issues grows, it is crucial to support and invest in these innovative waste management solutions. Collaboration between governments, businesses, and individuals is vital to drive the adoption of these technologies, promote sustainable practices, and pave the way for a greener and more sustainable future. By harnessing the power of technology, we can transform waste into wealth, mitigate environmental impacts, and build a more resilient planet for generations to come.
The Circular Economy Approach
The circular economy is an economic system that aims to minimize waste generation and maximize resource utilization. It emphasizes the concept of "closing the loop" by designing products that are durable, repairable, and recyclable. Through practices like product life extension, sharing economy models, and responsible consumption, the circular economy reduces the extraction of raw materials and promotes the efficient use of existing resources. By adopting a circular approach, businesses can not only reduce waste and costs but also enhance their brand reputation and contribute to environmental preservation.
Waste Management as a Business Opportunity
The transition from waste to wealth has opened up new avenues for entrepreneurs and innovators. Startups are emerging in various sectors, focusing on waste management and resource recovery. From companies that convert food waste into fertilizer to those that produce eco-friendly packaging materials, these businesses demonstrate the potential for profit while addressing environmental challenges. Governments and investors are supporting these ventures, recognizing their ability to create jobs, drive economic growth, and contribute to a sustainable future.
Community Engagement and Education
Creating a sustainable future requires collective action, and community engagement plays a crucial role. Education and awareness campaigns can help change people's attitudes and behaviors towards waste management. By promoting responsible consumption, waste segregation, and recycling practices, individuals can actively participate in the waste-to-wealth movement. Community initiatives, such as local recycling centers, composting programs, and upcycling workshops, provide platforms for collaboration and knowledge-sharing. Together, we can build a more sustainable and prosperous society.
Conclusion
The waste-to-wealth concept holds immense potential for addressing environmental challenges and creating economic opportunities. By embracing recycling, upcycling, and innovative technologies, we can transform waste into valuable resources, reduce landfill burden, and mitigate the depletion of natural resources. The circular economy approach and the rise of waste management startups further demonstrate the viability of turning waste into a profitable enterprise. However, achieving lasting change requires collective efforts, community engagement, and continuous education. Let us seize the opportunity to turn waste into wealth and build a sustainable future for generations to come.
#Waste to wealth: Transforming trash into valuable resources#Innovative waste management technologies for a sustainable future#Turning waste into renewable energy: Waste-to-energy conversion#From waste to biogas: The power of anaerobic digestion#Waste-to-energy: A greener solution for waste management#Sustainable success: Converting waste into wealth#Waste management revolution: Unlocking the potential of technology#Waste-to-energy technologies: A pathway to a circular economy#Pyrolysis: Transforming organic waste into biofuels#Plasma gasification: Tackling non-recyclable plastics for a greener future#Chemical recycling: Reshaping the plastic waste landscape#Waste-to-energy: A sustainable approach to waste management#Waste transformation: From burden to economic opportunity#Recycling and upcycling: Building wealth from waste#Waste management innovations: Redefining sustainable practices#Waste-to-wealth revolution: Creating value from discarded materials#Turning waste into resources: A roadmap to sustainability#Waste conversion technologies: Bridging the gap between waste and wealth#Waste-to-energy solutions: Powering a greener tomorrow#Sustainable waste management: Embracing the waste-to-wealth concept#Upcycling for a prosperous future: Redefining waste utilization#Waste-to-energy advancements: Paving the way for a circular economy#Waste-to-wealth strategies: Maximizing resource efficiency#Transforming waste into valuable commodities: The future of waste management#Waste conversion technologies: Innovations for a sustainable world#Waste-to-wealth practices: Shaping a more prosperous society#Waste management reimagined: Harnessing technology for a greener planet#Turning waste into renewable resources: The power of waste-to-energy#Circular economy and waste transformation: A pathway to sustainable growth#Waste-to-wealth initiatives: Driving economic and environmental benefits
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Advancements in the PLC Industry: Spotlight on Rabwellplc and Festo PLC
The PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) industry is experiencing remarkable growth, with innovative brands leading the way. Known for their cutting-edge technology and reliable solutions, these companies are key players in enhancing automation processes across various sectors.
Another notable name in the industry is recognized for its high-quality components and systems that optimize production efficiency. Together, these brands are revolutionizing the way industries operate, making automation more accessible and effective.
The future of the PLC industry looks bright, with continuous advancements in technology and an increasing demand for automation. Embracing these innovations not only boosts productivity but also contributes to sustainable practices in manufacturing.
Let’s celebrate the progress in the PLC industry and look forward to exciting developments ahead!
#Rabwellplc#innovation#production efficiency#manufacturing#sustainable practices#PLC industry#technology advancements#automation
0 notes
Text
The future of logistics is now: AI & Automation trends to watch in 2025
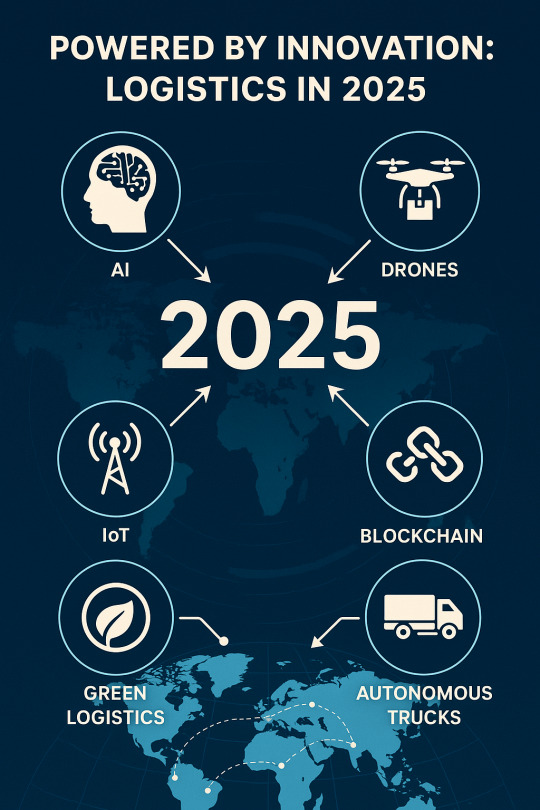
Problem: Traditional Logistics Can’t Keep Up Anymore
The logistics industry has always been the backbone of global trade. But in 2025, old systems are simply not fast, smart, or flexible enough to keep up. Rising fuel costs, unpredictable demand, labor shortages, and supply chain disruptions have pushed logistics companies to rethink operations.
Manual tracking, slow warehouse operations, and disconnected systems lead to delivery delays, increased costs, and unhappy customers. To stay competitive, logistics providers need more than just manpower, they need intelligence and automation.
Promise: Ai and automation are transforming the game in 2025
The good news? AI-powered logistics and smart automation are no longer futuristic concepts , they’re reality in 2025. From autonomous delivery vehicles to predictive inventory and smart route optimization, AI in logistics is unlocking new levels of efficiency, speed, and visibility.
Companies adopting logistics automation in 2025 are seeing:
Up to 30% faster deliveries
Real-time tracking with 99% accuracy
Reduced fuel and labor costs
Smarter demand forecasting and fewer stockouts
📊 Proof: real-world applications of Ai in logistics (2025)
Let’s break down how AI and automation are actively reshaping logistics today:
1. Smart warehousing and robotics
Modern warehouses in 2025 use AI-powered robots to pick, pack, and sort packages. These systems reduce human error and boost throughput.
Example: Amazon’s AI-driven robotic warehouses process thousands of orders per minute with near-perfect accuracy.
2. Predictive Analytics and Inventory Management
AI tools now predict demand trends based on historical data, weather patterns, and customer behavior helping companies avoid overstocking or stockouts.
Stat: Companies using predictive logistics AI report up to 40% reduction in excess inventory.
3. Autonomous Delivery Vehicles & Drones
Self-driving trucks and drones are no longer pilot projects; they're actively delivering goods in urban and rural areas.
Example: FedEx and UPS are deploying AI-guided autonomous trucks for regional deliveries in the U.S.
4. AI Route Optimization
AI platforms like ClearMetal and Locus use real-time data to optimize delivery routes in minimizing fuel consumption and delivery time.
Result: Businesses save thousands monthly by avoiding traffic, delays, and inefficient planning.
Proposal: Why you should embrace logistics automation in 2025
If you’re in the logistics business or rely heavily on shipping and supply chains, now is the time to act.
Here’s what you can do:
Audit Your Current Tech Stack
Identify where manual systems are costing you time and money. Focus on warehouse operations, delivery tracking, and customer service.
Invest in Scalable AI Solutions
Start with tools that offer immediate ROI such as AI route planners or automated inventory systems.
Partner with a Logistics Tech Expert
Don’t go it alone. Collaborate with a logistics software development company that understands AI in logistics 2025 and can build custom automation solutions for your business.
Train your team for the Ai shift
Technology is only powerful if your people can use it. Upskill your staff in AI-powered systems and digital tools.
Conclusion :
The logistics industry in 2025 is smarter, faster, and more data-driven than ever thanks to AI and automation. Businesses that invest today in intelligent logistics solutions will gain a competitive edge, reduce operational costs, and exceed customer expectations.
Don’t let outdated systems slow you down. Embrace the AI revolution in logistics now.
#“latest logistics innovations 2025”#“AI and automation in supply chain”#“future of logistics industry”#“transportation tech innovations”#logistics mobile app development trends”#Logistics innovations 2025#Supply chain trends 2025#Future of logistics industry#Smart logistics solutions#Emerging logistics technologies#Top logistics tech trends for 2025#Logistics automation and smart warehouses#Sustainable logistics practices in 2025
1 note
·
View note
Text
How Sustainability Business Practices Powering Green Technology
When we talk about sustainability, it is no longer just a buzzword—it's a driving force behind innovation and growth. As our businesses strive to reduce their environmental footprint, green technology is emerging as a powerful ally. We can invest in renewable energy sources like solar and wind and transform how we power our data centers, significantly offsetting energy consumption. But sustainability goes beyond clean energy; it's about optimizing operations and creating a brighter, more efficient future for our businesses and the planet.
From adopting cloud computing to managing e-waste responsibly and training employees on eco-friendly practices, businesses are integrating sustainable strategies that benefit the planet and enhance efficiency and competitiveness. The future of green technology, particularly in optimizing energy consumption, lies in harnessing AI and IoT. These technologies can identify inefficiencies and automate energy management, offering eco-friendly services and solutions that are both innovative and sustainable.
As companies embrace sustainability, the shift towards green technology reshapes the entire business ecosystem. Optimizing data centers—traditionally one of the largest energy consumers—is now a top priority. By leveraging cloud computing, businesses can drastically reduce their carbon footprint, improving energy efficiency while cutting costs. We can manage e-waste and ensure that equipment is recycled.
Training employees in sustainable practices and fostering a culture of environmental responsibility throughout the organization is not just a task; it's a mission. This holistic approach to sustainability meets growing consumer demands for eco-consciousness and positions businesses toward a greener and more resilient future. Each of us has a crucial role in this transition, and together, we can make a significant impact.
Sustainable Business Practices Helping Technology Go Green

1-Energy-Efficient Facilities
Implementing energy-efficient facilities involves upgrading buildings with advanced insulation, smart lighting management, and smart energy management systems. This approach reduces energy consumption, lowers operational costs, and minimizes the overall carbon footprint, supporting long-term sustainability.
2-Adopt the Cloud
Cloud computing allows businesses to reduce energy usage by consolidating IT infrastructure. Cloud providers often use energy-efficient, renewable-powered data centers, enabling companies to streamline operations, enhance scalability, and contribute to global energy conservation.
3-Embrace Green Computing Practices
Green computing involves using energy-efficient hardware, optimizing software, and implementing power management strategies. By adopting these practices, businesses can lower energy consumption, reduce electronic waste, and maintain productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
4-Establish Internal Equipment Recycling
Internal equipment recycling programs ensure outdated technology is repurposed, donated, or recycled responsibly. Partnering with certified recyclers helps businesses reduce e-waste, safely dispose of hazardous materials, and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
5-AI and IoT To Optimize Energy Consumption
AI and IoT technologies are the future. They monitor and optimize energy usage in real-time. By identifying inefficiencies and automating energy management, businesses can reduce waste, enhance operational efficiency, and significantly lower their carbon footprint. The potential of these technologies is truly exciting and promising for a greener future.
Why Web Synergies?
As business environments move forward, the challenges of a rapidly changing world, embracing sustainable practices is not just an option—it's a necessity. Integrating green technology into every aspect of your operations can reduce environmental impact while enhancing efficiency and innovation.
At Web Synergies, we understand the power of sustainability in driving long-term success. Our commitment to helping businesses adopt eco-friendly solutions, from optimizing data centers to leveraging AI and IoT, positions us as a trusted partner in your journey toward a greener future. We can create a more sustainable world where technology drives progress and protects the planet for future generations.
#sustainable business practices#green technology solutions#eco-friendly business strategies#sustainability in technology#sustainable IT solutions#energy-efficient data centres#cloud computing for sustainability#green computing practices#AI for energy optimisation#IoT in sustainable business#internal equipment recycling#managing e-waste in tech
0 notes
Text
Adapting to Change | How a Construction Cost Estimating Service Reflects Post-Pandemic Architecture Trends
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically reshaped the world in many ways, and architecture and construction were no exception. As businesses, governments, and individuals adjusted to a new reality, architectural trends shifted to reflect the changing needs and priorities. The rise of remote work, health and wellness concerns, and sustainability considerations all influence post-pandemic architecture. For construction professionals, accurately predicting the costs associated with these evolving trends requires expertise and an adaptive approach. A construction cost estimating service plays a crucial role in translating these new architectural trends into budget forecasts that ensure projects align with both contemporary demands and financial realities.
Health and Wellness in Architecture
The post-pandemic world has heightened awareness around health, safety, and wellness, influencing design priorities in both residential and commercial buildings. Features such as improved ventilation, touchless systems, enhanced cleaning protocols, and biophilic design are now at the forefront of architectural planning. Incorporating these features requires more thoughtful material selection, specialized systems, and layout adjustments—all of which affect the overall cost.
A construction cost estimating service helps by:
Calculating costs for enhanced HVAC systems: Modern ventilation systems that improve air quality are now considered a necessity in many buildings. Estimators evaluate the costs of high-performance HVAC systems, including filtration and UV systems to sanitize the air.
Incorporating biophilic design features: The integration of natural elements like indoor plants, green walls, or natural lighting can increase construction costs. Estimators forecast the costs of implementing these sustainable design features, which enhance the occupant's health and well-being.
Factoring in touchless and smart systems: The demand for touchless technologies in elevators, faucets, doors, and lighting has surged. These systems can significantly impact the budget, and estimators need to evaluate both installation and long-term maintenance costs.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Building Design
The pandemic has shown that flexibility in design is more critical than ever. The future of work is likely to involve a hybrid model, with employees spending time both in the office and at home. As a result, buildings must be adaptable, with spaces that can be easily reconfigured to accommodate changing needs. This adaptability requires careful consideration of layout, movable walls, and multipurpose rooms.
A construction cost estimating service assists by:
Assessing costs for modular and flexible construction systems: The use of modular systems that allow for easy reconfiguration of interior spaces can be more expensive upfront, but they offer long-term flexibility. Estimators calculate the initial and potential long-term costs of these systems.
Evaluating the expense of adaptable spaces: Offices that can easily transform into collaborative spaces or quiet zones for remote work require specialized designs and finishes. Cost estimators provide insights into how these flexible spaces impact the overall budget.
Factoring in future-proofing elements: Buildings that are designed to adapt to new technology, office layouts, or residential trends require investments in infrastructure such as extra power outlets, robust Wi-Fi networks, and data cabling. Estimators calculate these future-proofing costs into the initial budget.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
The pandemic has increased focus on sustainability, with more individuals and businesses prioritizing environmental impact and energy efficiency. In the post-pandemic era, green building practices are no longer a luxury but an expectation. From net-zero energy buildings to the use of sustainable materials, the integration of sustainability into architecture affects the overall cost structure.
A construction cost estimating service can support these efforts by:
Estimating costs for energy-efficient technologies: Solar panels, energy-efficient windows, green roofs, and sustainable insulation are in high demand as part of eco-conscious building practices. Estimators ensure that the integration of these technologies is adequately budgeted.
Accounting for green certification processes: Many buildings aim to achieve certifications such as LEED or BREEAM. The requirements for these certifications may increase both direct costs and timeframes. Estimators factor these additional requirements into the budget.
Evaluating lifecycle cost benefits: While sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs may increase upfront costs, they often provide long-term savings through lower operational expenses. Estimators incorporate these lifecycle savings into the cost estimate, demonstrating both the immediate investment and the long-term financial benefits.
Changes in Residential Design
The pandemic has also affected the way residential spaces are designed. As more people worked and studied from home, the demand for dedicated home offices, larger living spaces, and outdoor areas increased. Homeowners are seeking spaces that enhance their quality of life and provide greater comfort, privacy, and connection to the outdoors.
A construction cost estimating service helps by:
Estimating the costs for home office and study spaces: Dedicated home offices or study spaces require additional design considerations such as soundproofing, technology integration, and proper lighting. Estimators calculate the costs associated with creating these spaces.
Factoring in outdoor living spaces: Outdoor areas such as patios, gardens, and outdoor kitchens have become essential. Estimators evaluate the costs of landscaping, outdoor furniture, and specialized features like fire pits, ensuring that the outdoor living space is fully integrated into the budget.
Evaluating the impact of larger floorplans: As more people seek larger homes to accommodate home offices and extended family, the costs of materials and labor can increase. Estimators adjust the budget based on changes in square footage and layout.
Conclusion
The post-pandemic era has brought about a new wave of architectural trends focused on health, flexibility, sustainability, and comfort. As architects and builders embrace these trends, construction cost estimating services play a crucial role in ensuring that projects meet both the design requirements and the budget constraints. From advanced HVAC systems to sustainable building materials and adaptable layouts, accurate cost estimations are key to successfully implementing these changes. As the world continues to adapt, construction professionals must remain agile and responsive to the evolving needs of the built environment, ensuring that both current and future construction projects reflect the demands of a post-pandemic society.
#post-pandemic architecture#flexible design#health-conscious buildings#construction estimating service#biophilic design#HVAC system costs#sustainable materials#energy-efficient buildings#hybrid workspaces#modular construction#smart buildings#net-zero buildings#green certifications#home office designs#outdoor living spaces#adaptable buildings#post-COVID office spaces#pandemic architecture trends#touchless technologies#remote work design#smart home features#circular building practices#building flexibility costs#construction cost forecasting#building sustainability#energy-saving construction#design for adaptability#building future-proofing#wellness-oriented construction#workplace design changes
0 notes
Text
#Sustainable Technology Practices#MacBook Replacement Parts Guide#MacBook Repair Vs. Replacement Cost#MacBook Maintenance Tips#Extending MacBook Lifespan#DIY MacBook Upgrades
0 notes
Text
Global Automatic Industrial Plate Pasteurizers Powerhouses: Top 5 Countries Driving Growth
The global Automatic Industrial Plate Pasteurizers market is expected to grow significantly, with industry revenue projected to rise from $442.3 million in 2024 to $1,224.6 million by 2035. The market is anticipated to expand at an annual growth rate ranging from 7.1% to 10.2% between 2025 and 2035. The U.S., Germany, China, Japan, and the UK are the top five markets, collectively holding a substantial demand share.
Check detailed insights here - https://datastringconsulting.com/industry-analysis/automatic-industrial-plate-pasteurizers-market-research-report
The market is experiencing a major transition, fueled by technological advancements and sustainability practices that are reshaping the landscape of Automatic Industrial Plate Pasteurizers. These innovations have made significant strides in various industries, particularly in food and beverage, improving the speed, efficiency, and customization of pasteurization processes. Notably, the dairy industry has been revolutionized by these pasteurizers, as they provide uniform heat treatment, minimizing bacterial contamination and enhancing product safety. The integration of digital control systems offers greater accuracy and reporting, ensuring compliance with stringent food safety regulations globally.
Potential Application Areas
Juice Manufacturing: Automatic Industrial Plate Pasteurizers are essential in the juice manufacturing industry to ensure the safety, freshness, and longevity of beverages. These systems rapidly heat and cool juices, killing pathogens without compromising taste or nutritional value. Major players such as Krones AG and HRS Heat Exchangers offer efficient solutions that guarantee high energy performance and consistency across juice production lines.
Brewing Industry: The brewing industry heavily relies on Automatic Industrial Plate Pasteurizers to ensure the quality and longevity of beer. These pasteurizers effectively kill yeast and other microorganisms, preventing spoilage and stabilizing the beer’s flavor. Renowned companies like Alfa Laval and SPX FLOW offer customized pasteurization solutions that optimize brewing processes while maintaining product quality and flavor consistency.
Industry Leadership and Strategies
The Automatic Industrial Plate Pasteurizers market is highly competitive, with leading companies like Alfa Laval, Tetra Pak, GEA Group, SPX FLOW, Krones AG, MicroThermics Inc., ABL Technologies Ltd, Shanghai Joylong Industry Co. Ltd, Tetra Laval International SA, Stephan Machinery GmbH, REDA S.P.A., and FASA AB at the forefront. These companies are driving innovation by adopting new technologies and forming strategic partnerships to expand their market reach.
Key strategies employed by market leaders include:
APEX Engineered Products focuses on adopting innovations that enhance pasteurization effectiveness and reduce energy consumption.
Alfa Laval emphasizes the design of hygienic, customizable equipment suitable for diverse beverage types.
GEA Group integrates advanced data analytics for process optimization while maintaining high standards of biosecurity and sterility.
Krones AG offers versatile and flexible solutions to adapt to rapidly evolving market trends, particularly in the beverage sector.
Report Scope
The report explores various segments of the Automatic Industrial Plate Pasteurizers market, including:
Technology Type: Flash Pasteurization, HTST Pasteurization, UHT Pasteurization
Application Type: Dairy Processing, Beverage Processing, Industrial Waste Water Management, Others
Product Type: Batch, Continuous
End-User: Industrial Factories, Commercial Bakeries, Brewery Facilities, and Others
About DataString Consulting
DataString Consulting assists companies in formulating strategies, creating roadmaps for TAM (Total Addressable Market) expansion, revenue diversification, and entering new markets. The firm provides in-depth insights into emerging trends, competitor landscapes, and customer demographics. Their tailored strategies filter industry noise into new opportunities, reducing the time between products and their market niches.
As a leading market research firm, DataString Consulting offers a comprehensive range of B2B and B2C market research and business intelligence solutions under one roof. With more than 30 years of combined experience, their leadership team provides expert consulting in strategy, opportunity assessment, and solution-oriented business approaches to address industry challenges.
#Automatic Industrial Plate Pasteurizers#Food and Beverage Processing#Juice Manufacturing#Brewing Industry#Technological Advancements in Pasteurization#Dairy Industry#Market Research#Global Market Trends#Sustainability Practices in Food Processing#Food Safety and Regulation#DataString Consulting#Strategic Market Insights#Business Intelligence Solutions#Revenue Growth Forecasts#Industry Innovation#Market Expansion Strategies
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Luxury of Lab Grown Diamond Rings with Lucenjuri
The jewelry industry is witnessing a remarkable transformation, particularly with the rise of lab grown diamond rings. One brand that stands out in this innovative space is Lucenjuri.
Lucenjuri is dedicated to providing exquisite, ethically sourced lab grown diamonds that sparkle just as brilliantly as their mined counterparts. These diamonds are created using advanced technology that replicates the natural processes, resulting in stunning gems that are environmentally friendly and conflict-free.
Choosing a lab grown diamond ring from Lucenjuri not only allows you to embrace elegance and luxury but also supports sustainable practices in the jewelry industry. With a variety of styles and designs, Lucenjuri offers something for everyone, making it easier to find the perfect ring for any occasion.
Investing in a lab grown diamond ring means you can enjoy the beauty of diamonds while contributing to a more sustainable future. Discover the enchanting world of Lucenjuri and elevate your jewelry collection with their remarkable lab grown diamond rings!
#diamond rings#styles and designs#luxury#ethically sourced#advanced technology#sustainable practices#lab grown diamonds
0 notes
Text
Rivers at Risk: The Global Water Crisis
Every cloud has a silver lining—or so they say. The truth is, when it comes to water, we’re mainly looking at a storm on the horizon. As highlighted in the powerful DW Documentary, the global water crisis isn’t just a headline; it’s a lurking threat weaving through the fabric of our societies, particularly driven by agriculture. With nearly 70% of freshwater resources allocated to farming, the…
#Agricultural Practices#agriculture#Environmental Issues#farming#Global Water Crisis#sustainability#Sustainable Agriculture#sustainable-agriculture#Technology#Water Management#Water Scarcity
0 notes
Text
#Full-Service Restaurants Market#Restaurant Industry Trends#Market Research Report#Dining Out Market#Fine Dining Restaurants#Casual Dining Restaurants#Food and Beverage Industry#Consumer Dining Preferences#Restaurant Market Growth#Hospitality Industry Trends#Market Size and Forecast#Restaurant Chains and Franchises#Food Service Industry#Emerging Dining Trends#Competitive Landscape#Customer Experience in Restaurants#Global Restaurant Market#Sustainable Dining Practices#Technology in Restaurants#Post-Pandemic Dining Trends
0 notes