#Stakeholder Analysis
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
🦩🌳💸Using Decision Trees in Financial Analysis🔍
Decision Trees are a powerful financial analysis tool that clarifies the expected value of capital investment opportunities. It is used in business operations where companies continuously struggle with big decisions on product development, operations management, human resources, and others. Decision Tree analysis method lets us explore the ranging elements influencing a decision.
🦩📉💸Stakeholders and Risk
Let’s say that there is a parent company investing the funds expects some investments across their portfolio of subsidiaries to fail and have hedged against that by diversifying their risk exposures. The sales manager of the company has a lot to gain in regards to increased product quality to offer to potential clients and nothing to lose if the project is not successful. However, for the plant manager that will be in charge of building the new modernized factory, failure may mean losing his job. Such a situation where there is a significant number of different stakeholder points of view introduces an undesirable element of politics in the decision-making process. To mitigate the risk of such politics leading to wrong decisions, we need to ask who bears the risk and what is the risk and look at each decision from the perspective of each stakeholder, when performing our analysis.
🦩📊💸Evaluate Investment Opportunities with Decision Trees
Decision Trees is a great laying out information tool that enables systematic analysis and leads to a more robust and rigorous decision-making process. The technique is excellent for illustrating the structure of investment decisions, and it can be crucial in the evaluation of investment opportunities. Decision Trees in financial analysis are a Net Present Value (NPV) calculation that incorporates different future scenarios based on how likely they are to occur. The cash flows for a given decision are the sum of cash flows for all alternative options, weighted based on their assigned probability.
🦩🌳💸To prepare a Decision Tree analysis, we take the following approach:
Identify the points of decision and the alternative options available at each of them.
Identify aspects of uncertainty and type or range of alternative outcomes.
Estimate the values for the analysis: *Probabilities of events and results from actions *Costs of and possible gains from various events and activities.
Analyze alternative amounts and choose a course (calculate the present value for each state).
🦩🌳💸Decision Tree Analysis is an essential tool in the decision-making process and investment analysis as it determines the value of investment opportunities and clarifies the connection between current and future decisions and uncertain circumstances which enables management to consider the available courses of action with more ease and clarity.
#economy#business#finance#investing#stakeholders#investment#analysis#risk#management#artists on tumblr#digital art#my art#artwork#illustration#drawings#design#creative#creative writing#onlyfans creator
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Are The Major Factors Driving Retinal Biologics Market Growth?
The Retinal Biologics Market is experiencing a surge in demand, fueled by advancements in eye disease treatments and a growing emphasis on vision health. According to a recent analysis by Future Market Insights (FMI), a leading market research firm, the market is currently valued at an impressive US$22.25 billion in 2022. Looking ahead, the market is projected to witness a remarkable Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.1% over the next six years. This translates to a staggering market valuation of US$41.92 billion by 2028, highlighting the significant potential of retinal biologics in revolutionizing eye care.The remarkable expansion of the Global Retinal Biologics sector is fueled by advancements in technology, innovative research, and a growing demand for cutting-edge treatments. As the industry continues to evolve, it presents unprecedented opportunities for stakeholders, investors, and healthcare professionals alike.Key Retinal Biologics Market Insights:
Rising Prevalence of Diabetes-related Eye Disorders and Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) The prevalence of diabetes-related eye disorders and age-related macular degeneration is on the rise, underscoring the growing need for innovative solutions within the Retinal Biologics Industry.Substantial Investment in R&D for Biologics in Retinal Disorders The industry is witnessing a significant influx of research and development resources, aimed at advancing biologics for both infectious and non-infectious retinal disorders. This investment underscores the commitment to addressing unmet medical needs.
Emergence of Specific Biologic Molecules as Therapeutic Targets Specific biologic molecules are gaining prominence as highly promising therapeutic targets, offering new hope for patients with retinal conditions.Gene Therapy as a Solution for Monogenic Retinal Illnesses With a growing number of monogenic retinal illnesses, gene therapy is emerging as a pivotal component of the Retinal Biologics Market, presenting innovative solutions for these challenging conditions.
Request a Sample Copy of This Report Now.https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-8663
#The Retinal Biologics Market is experiencing a surge in demand#fueled by advancements in eye disease treatments and a growing emphasis on vision health. According to a recent analysis by Future Market I#a leading market research firm#the market is currently valued at an impressive US$22.25 billion in 2022. Looking ahead#the market is projected to witness a remarkable Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.1% over the next six years. This translates to a s#highlighting the significant potential of retinal biologics in revolutionizing eye care.The remarkable expansion of the Global Retinal Biol#innovative research#and a growing demand for cutting-edge treatments. As the industry continues to evolve#it presents unprecedented opportunities for stakeholders#investors#and healthcare professionals alike.Key Retinal Biologics Market Insights:Rising Prevalence of Diabetes-related Eye Disorders and Age-relate#underscoring the growing need for innovative solutions within the Retinal Biologics Industry.Substantial Investment in R&D for Biologics in#aimed at advancing biologics for both infectious and non-infectious retinal disorders. This investment underscores the commitment to addres#offering new hope for patients with retinal conditions.Gene Therapy as a Solution for Monogenic Retinal Illnesses With a growing number of#gene therapy is emerging as a pivotal component of the Retinal Biologics Market#presenting innovative solutions for these challenging conditions.Request a Sample Copy of This Report Now.https://www.futuremarketinsights.#institutional sales in the Retinal Biologics Industry#where Retinal Biologics are supplied in speciality clinics and hospitals#will generate higher revenues. In 2018#hospital sales accounted for more than 35% of market revenue.According to the report#retail sales of Retinal Biologics will generate comparable revenues to hospital sales and will expand at an 11.9% annual rate in 2019. Reta#with retail pharmacies generating more money than their counterparts in the future years.Penetration in North America Higher#APEJ’s Attractiveness to IncreaseNorth America continues to be the market leader in Retinal Biologics revenue. According to FMI estimates#North America accounted for more than 46% of global Retinal Biologics Industry revenues in 2018. Revenues in North America are predicted to#continuous growth in the healthcare infrastructure#and a favourable reimbursement scenario.Europe accounted for about one-fourth of the Retinal Biologics market#with Western European countries such as Germany#the United Kingdom#France#Italy
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

#Architectural Models#Design Process#Physical Models#Digital Models#Scale Models#Conceptual Models#Visualization#Communication#Decision-Making#Testing and Analysis#3D Modeling#Architectural Exterior Models#Architectural Interior Models#Model Architecture#Design Quality#Stakeholder Engagement#3D Architectural Visualization#Building Design#Model Making#Architecture
1 note
·
View note
Text
Is design innovation the price of a client-focused construction industry?
Much has been written about customer contribution to innovation however, far less has been given to the potentially hindering innovation. This paper argues that strong client leadership may have negative consequences for innovation, Introduction The view that the customer should play a key role in the innovation process is deeply embedded in management thinking (Reich et al., 1996; Dahlsten,…

View On WordPress
#case study#Client-Centric Approach#construction industry#Cost Analysis#design innovation#Industry Competitiveness#Jamaican Construction Industry#Market Trends#project management#Stakeholder Engagement#Sustainability in Construction#Technology Integration
0 notes
Text
5 Reasons Why I love Being a Business Analyst

I have been a Business Analyst for most of my adult professional career. I fell into the role somewhat by chance (through a merger and acquisition), but it was one of the best things that ever happened to me. There are so many things that I love about being a Business Analyst that it’s hard to narrow it down to just a few, but here we go!
Building Relationships
The business of Business Analysis at its core is all about people. A Business Analyst is a pivotal role that requires being able to navigate all levels of an organization, in all different realms. As a result, the heart of being a BA is building relationships. I can converse with a CEO just as easily as I can talk with someone answering calls at the IT Help Desk. Having this ability has helped me grow my network of connections over the years, and I am grateful for everyone I’ve been able to work with along the way.

Learning New Things
Business Analysis affords the opportunity for continuous learning. The world isn’t static, and everything is constantly changing, from organizational structures, disruptive recent technologies and innovations, government regulations, new ways of working, and the list goes on and on. There is always something new to learn, and as a BA, I always want to be ready for what’s next. This means staying up to speed on what’s happening and learning whatever I need to know to get the job done.

Variety is the Spice of Life
Another thing I especially love about Business Analysis is the variety. No two projects or initiatives are ever the same, nor is every day. In fact, every day in the life of a BA can look vastly different. When I was a consultant, this was even more true. Every new client usually represented a new industry or market for me, and I got to explore many worlds I never would have been exposed to otherwise (PM if you want to hear some amazing stories!).

Delighting Stakeholders
Seeing the joy on a stakeholder’ 'faces when we show them what we built for them is one of the best moments in a Business Analyst’s professional experience. When you see bright smiling eyes appreciating the work you’ve done, there’s nothing more rewarding. No paycheck, no bonus – nothing can compare to making people happy and having a measurable impact on their lives.

Helping Others Grow
Another thing I have been able to do as a Business Analyst is to help train, mentor, and grow a newer generation of Business Analysts. While it’s a rewarding profession, being a BA is not an easy job. There is so much to know, and much of it you can only learn through experience. As a seasoned professional, it’s been my pleasure to support other young analysts as they develop into qualified, competent practitioners.

Final Thoughts
In this blog, I covered a few of the things I love about being a Business Analyst. Every analyst has their own journey and experiences, and I am eager to hear what other people enjoy about the profession. If you care to share, please do so in the comments section below! Read the full article
#analysis#ba#bas#business#career#growth#journey#learning#love#mentoring#profession#professionals#stakeholders
0 notes
Text
People in project management - what the professional qualifications fail to do!
I wanted to explore a subject which has been close to my heart for more years than I can say. How did we get to a situation where the presumption is that human capital productivity stays constant in periods of intense change? I have spent almost 10 years writing and podcasting in an attempt to provide some insightful commentary based on my personal consulting experience. The temptation is often…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
"California has approved a bill to help address the dark side effects of the externally glitzy fast-fashion sector, putting the onus on manufacturers to implement repair and recycling programs.
According to CalMatters' Digital Democracy project, California Gov. Gavin Newsom signed the Responsible Textile Recovery Act of 2024 on Sept. 28, more than a year after the bill began making its way through the state legislature.
The act seeks to address the growing problem of waste from the fashion industry. CalMatters notes in its analysis that the Golden State tossed more than 1.3 million tons of textiles in 2018.
As it stands, the state ships 45% of the items that are donated overseas, which contributes to environmental pollution, and once there, much of it still ends up in landfills, where it produces potent heat-trapping gases such as methane.
In Ghana, for example, which has seen its beaches polluted by fast-fashion waste, 40% of the 15 million garments received each week are discarded. All in all, despite the fact that 95% of California's materials are recyclable, only 15% of clothing and textiles are reused.
Democratic state senator Josh Newman, the bill's sponsor, told the Guardian that these concerning figures inspired him to take action.
"We worked really hard to consult with and eventually to align all of the stakeholders in the life cycle of textiles so that at the end there was no opposition," he explained. "That's an immensely hard thing to do when you consider the magnitude of the problem and all of the very different interests."
According to the Guardian, the program is expected to go into effect in 2028, with its numerous backers anticipating it could create as many as 1,000 jobs in the Golden State.
Details are still being hammered out. However, garment manufacturers who aren't already participating in eco-friendly programs will have incentives to adopt greener practices, with recycling collection sites and mail-back programs among the possibilities.
And while some have worried that small businesses and mid-sized brands could be disproportionately impacted by the legislation and end up passing on the prices to consumers, Newman estimates that the cost should be less than 10 cents per garment or textile."
-via The Cool Down, October 3, 2024
#california#united states#us politics#north america#fashion#fast fashion#waste#sustainability#sustainable fashion#hope this ends up actually having some teeth
996 notes
·
View notes
Text
Raw Data to Actionable Insights
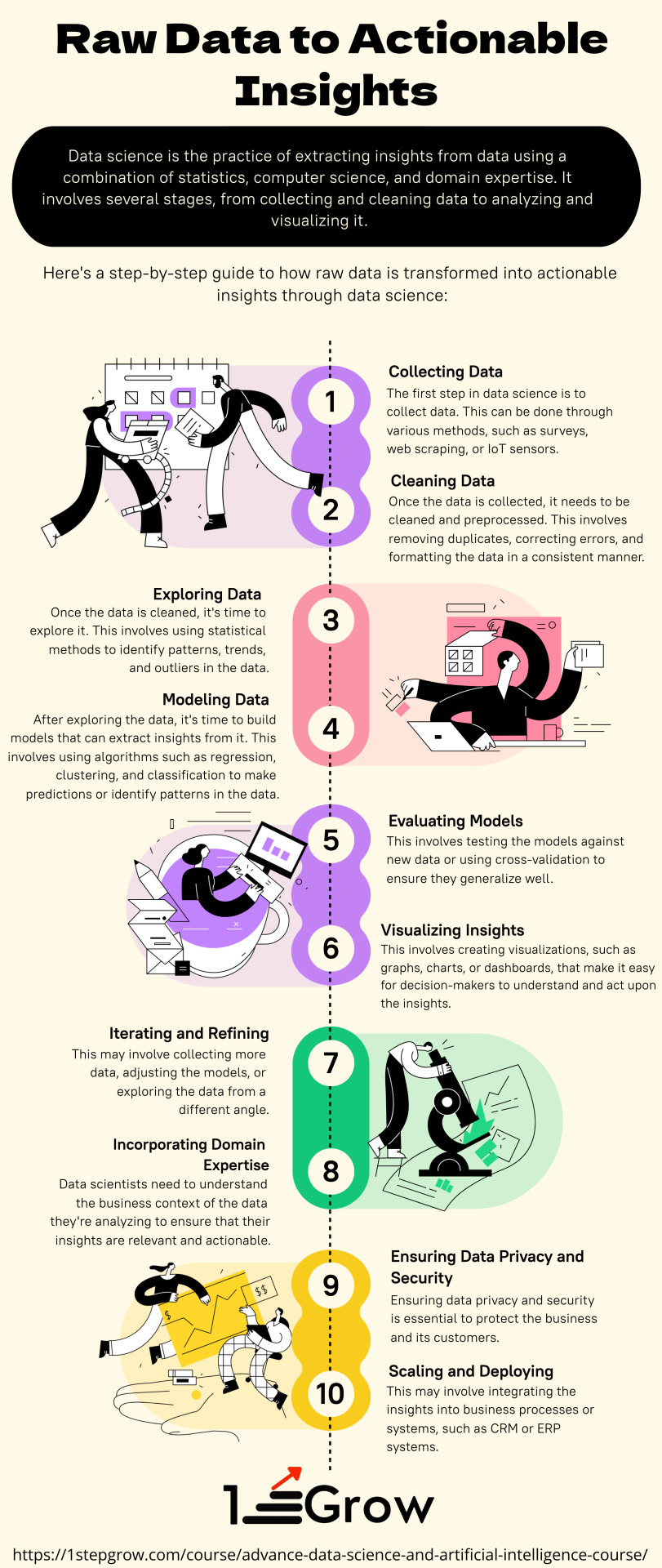
This infographic illustrates the process of turning raw data into actionable insights. It starts with the collection and analysis of data, followed by the identification of patterns and trends. The insights gained from this analysis can then be used to inform decision-making and drive action. The infographic emphasizes the importance of data visualization and communication in order to effectively convey insights to stakeholders. Ultimately, the goal is to turn raw data into valuable information that can drive positive outcomes for individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. For more information, visit: 1stepGrow
#data analysis#data visualization#actionable insights#decision-making#patterns#trends#communication#stakeholders#raw data#information#outcomes.#artificial intelligence and data science course#data science course#data science course bangalore#top data science course#data science course python#online data science course#data science and ai course
0 notes
Text
Here, have a spark of hope.
The reality is that no single person can fix the entirety of the current ecological imbalance that has been literally centuries in the making at this point. Yet there are so, so many of us who care, and who are doing what we can to make a difference in whatever every day to day ways we're able. I often think of conservation efforts like the Loren Eiseley story "The Star Thrower" (aka, "the starfish story"). Amid a beach full of stranded starfish, one person cannot possibly save them all, but they can spend what time they have saving those they're able.
And this study shows that these efforts do, in fact, make a difference, not just for starfish but a myriad of species. This meta-analysis of almost 200 studies definitively proves that conservation preserves and restores biodiversity, keeping more species from going extinct. It's all too easy to get entangled in the losses, but we even more need to allow ourselves to celebrate the wins.
That success is crucial to convincing governmental entities and other stakeholders that putting funds toward conservation efforts makes a significant difference and is not only worth the investment, but worth increasing. And, on a personal level, it's necessary for those of us who care so deeply for this world to know when our efforts are having an impact, to buoy us up when the anxiety and grief over ecological destruction wears us down.
There is hope. Keep it up, folks; it's helping <3
#conservation#environment#environmentalism#extinction#endangered species#animals#wildlife#biodiversity#nature#science#scicomm#hope#solarpunk#hopepunk#hopecore#hopeposting#optimism#ecology#habitat restoration#restoration ecology
614 notes
·
View notes
Text
I once had a conversation with someone on here where I (history major at the time) was attempting to describe how I thought business majors spent their time, and I think I said something like “I think its just a bunch of people in suits shaking each others hands, smiling disingenuously, and saying ‘business’ back and forth at each other.”
And now I have a job where I am occasionally required to do things like “listen to a lecture series on Business Analysis: Working with Stakeholders Using Elicitation and Collaboration” and my main (only) take away is that I was absolutely correct on all counts except that I did not include enough buzz words
#this is not the kind of information my brain is designed to retain#the ghost ship babbles to herself in the night
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this story from EcoWatch:
A new report has found that climate lawsuits being filed against companies are on the rise all over the world, and most of them have been successful.
The report by the Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment at the London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE) — Global trends in climate change litigation: 2024 snapshot — said that roughly 230 climate cases have been brought against trade associations and corporations since 2015, more than two-thirds of which have been filed since 2020.
“Climate litigation… has become an undeniably significant trend in how stakeholders are seeking to advance climate action and accountability,” said Andy Raine, the United Nations Environment Programme’s deputy director of law division, as The Guardian reported.
One of the fastest growing types of litigation concerns “climate washing.” According to the report, 47 of these lawsuits were filed against governments and companies last year.
The report stated that there had been “more than 140 such cases filed to date on climate washing, making this one of the most rapidly expanding areas of litigation,” a press release from LSE said.
Of the almost 140 climate-washing cases between 2016 and 2023, 77 had reached official decisions, with 54 being found in favor of the claimant.
Most climate cases that have been filed in the past have been against governments. In the United States, 15 percent of climate cases filed in 2023 were against companies, while 40 percent of cases in the rest of the world involved companies.
In 2023, more than 30 “polluter pays” lawsuits filed worldwide sought to hold corporations accountable for climate harms allegedly stemming from their production of greenhouse gas emissions.
Six “turning off the taps” lawsuits challenging the funding of activities and projects not in line with climate action were identified in the report.
The report’s analysis was based on more than 2,600 climate cases compiled by Columbia Law School’s Sabin Center for Climate Change. Approximately 70 percent of these lawsuits have been filed since the adoption of the Paris Agreement in 2015, with 233 having been filed in 2023.
Climate lawsuits have been brought in 55 total countries, with cases having been filed in Portugal and Panama for the first time.
The authors of the study confirmed that climate litigation has been increasing in the Global South, noting that “over 200 climate cases from these countries are recorded in the Global database, comprising around 8% of all cases.”
The U.S. had the most climate litigation cases filed last year with 129. The United Kingdom had the second highest number with 24, followed by Brazil with 10, Germany with seven and Australia with six.
The U.S. also had the most documented climate cases with a total of 1,745. Australia has had 132 overall, with just six filed in 2023.
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding the Southern Perimeter’s Republican Lean: A Multi-Factor Analysis

The political landscape of the United States is often discussed in terms of blue and red states, with certain regions consistently leaning Republican or Democrat. However, the southern perimeter of the continental U.S.—stretching from California to Florida—presents a unique case study. Despite cultural diversity, varying industries, and demographic shifts, this region generally leans Republican. This alignment, which includes border states with Mexico and those along the Gulf Coast, emerges from a complex interplay of geography, economics, historical values, and cultural attitudes.
1. Geographical and Climatic Influences
The southern perimeter is defined by its warmer climates, which attract specific demographics, most notably retirees. States like Florida have become retirement havens, drawing older populations from traditionally Democratic northern regions. This migration brings a demographic that often prioritizes conservative values such as lower taxes, property rights, and fiscal conservatism, aligning well with Republican ideologies. The subtropical to desert-like climate also shapes industries in these states, favoring agriculture, tourism, and energy sectors that lean conservative due to their reliance on limited government intervention and favorable regulatory policies.
Additionally, the shape and layout of these states play a role. California’s extensive north-south reach and diverse climate foster a mix of political ideologies, making it more complex, though its highly populated coastal cities tend toward Democratic dominance. By contrast, Arizona and Texas, with expansive rural and desert regions along the border, amplify conservative values centered on self-reliance and individualism, often associated with frontier mentality.
2. Historical and Cultural Factors
Southern states, including those on the southern perimeter, have a strong cultural legacy of conservatism rooted in a combination of frontier independence, skepticism of federal oversight, and a tradition of states’ rights. This tradition resonates with Republican ideology, which emphasizes limited government, individual liberties, and a cautious approach to social change. While California may stand as an exception due to its urban liberal hubs, the states from Texas through Florida reflect this traditional conservatism that has persisted over decades, reinforced by political institutions and local values.
Texas, in particular, embodies this “frontier spirit.” The state’s long history as a republic, combined with its emphasis on rugged individualism and suspicion of centralized power, aligns with Republican principles. Arizona, with its substantial rural population and similar desert environment, mirrors this mindset. The “frontier mentality” persists in these areas, where local culture values autonomy and self-reliance—traits that naturally dovetail with conservative ideologies.
3. Economics and Industry Patterns
Economic structures in these states contribute heavily to their conservative leanings. Texas, for example, is a major oil producer, while Florida’s economy is driven by tourism and agriculture. These industries often thrive under conservative economic policies, which typically favor deregulation, low taxes, and minimal government interference. Republican economic policies are seen as beneficial by stakeholders in these sectors, making the party an appealing choice for many business owners and workers.
Moreover, certain industries in these states feel the impact of immigration more directly, leading to support for stricter border policies and a more conservative stance on national security. Agriculture and construction in Arizona, Texas, and Florida rely heavily on immigrant labor but also face challenges from undocumented immigration, shaping local attitudes toward Republican policies that prioritize border enforcement and immigration control.
4. Proximity to the Mexican Border and the “Diversity Paradox”
For border states like Texas and Arizona, proximity to Mexico brings border security and immigration issues to the forefront of local politics. This isn’t just about geographical closeness; it’s about the daily reality of cross-border dynamics that influence attitudes toward national security, cultural integration, and economic impacts. The southern perimeter’s conservative alignment is often reinforced by a sense of “us vs. them,” a cultural boundary that shapes perceptions of national identity and sovereignty.
Counterintuitively, the high diversity in these border states does not automatically translate to liberal leanings. Instead, the influx of new populations can sometimes trigger a conservative backlash, as local communities respond to perceived cultural and economic shifts. This “diversity paradox” suggests that in some cases, increasing diversity can actually entrench conservative ideologies as groups seek to preserve traditional values in the face of demographic changes. California and New Mexico differ here, as both have deeply rooted Hispanic and Native American populations that pre-date current immigration concerns, leading to a multicultural identity that integrates rather than reacts to diversity.
5. Rural-Urban Divide and Population Distribution
The rural-urban divide is a significant factor in understanding Republican dominance in the southern perimeter states. Urban centers in Texas (Austin, Houston, and Dallas), Arizona (Phoenix), and Florida (Miami) tend to lean Democratic, but the vast rural areas and smaller towns remain conservative strongholds. Given that these rural and suburban regions often have disproportionate legislative influence due to gerrymandering and districting practices, Republican preferences are amplified politically.
In these rural areas, the appeal of Republican ideology is tied to a distrust of federal intervention and a commitment to traditional social values. The conservative emphasis on “law and order” and the right to bear arms resonates with rural populations who prioritize self-sufficiency and often feel culturally alienated from urban liberalism. This dynamic creates a political landscape where urban and rural values clash, but the rural-dominated districts sustain Republican influence at state and federal levels.
6. Geopolitical Significance and National Policy
Border security, immigration, and national security are not merely abstract political issues in the southern perimeter states; they are local realities. The Republican party’s stance on border control and immigration resonates with communities directly impacted by these policies. For residents in states like Texas and Arizona, issues of border security are personal and immediate, influencing their political alignment. The southern perimeter’s exposure to these cross-border dynamics fuels support for policies that emphasize strict immigration enforcement, contributing to the region’s Republican leanings.
Furthermore, the high visibility of national debates on immigration and security in these states places them in a unique geopolitical position. Residents of the southern perimeter often view federal immigration policies through the lens of local impact, which can heighten conservative stances on enforcement and sovereignty, particularly during times of political polarization on these issues.
The southern perimeter’s Republican alignment, spanning from California to Florida, is a product of interwoven geographical, economic, cultural, and historical factors. From the lure of warm climates drawing conservative-leaning demographics to the economic structures that benefit from conservative policies, each element reinforces the region’s political leanings. The combination of rural influence, frontier mentality, and proximity to the Mexican border creates a unique political identity that sustains Republican dominance.
While California and New Mexico serve as exceptions due to their own unique geographic and cultural compositions, the southern perimeter as a whole demonstrates the impact of physical geography and local demographics on political identity. This analysis underscores how politics in border states cannot be reduced to simple assumptions about diversity or proximity to Mexico; instead, it is the product of complex, localized dynamics that shape conservative values and Republican support across the region.
#south#southern border#souther states#border#southern perimeter#border states#border patrol#republican#conservatives#geography#history#analysis#political science#mexico#california#arizona#texas#new mexico#louisiana#mississippi#alabama#florida#georgia#south carolina#politics#united states#america#north america
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
September was a busy month for Russian influence operations—and for those tasked with disrupting them. News coverage of a series of U.S. government actions revealed Russia was using fake domains and personas, front media outlets, real media outlets acting as covert agents, and social media influencers to distort public conversation around the globe.
The spate of announcements by the U.S. Justice Department and U.S. State Department, as well as a public hearing featuring Big Tech leadership held by the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence, underlines the extent to which Russia remains focused on interfering in U.S. political discourse and undermining confidence in U.S. elections. This is not particularly surprising on its own, as covert influence operations are as old as politics. What the unsealed indictments from the Justice Department, the report by the State Department, and the committee hearing emphasize is that bots and trolls on social media are only part of the picture—and that no single platform or government agency can successfully tackle foreign influence on its own.
As researchers of adversarial abuse of the internet, we have tracked social media influence operations for years. One of us, Renée, was tapped by the Senate Select Committee in 2017 to examine data sets detailing the activity of the Internet Research Agency—the infamous troll farm in St. Petersburg—on Facebook, Google, and Twitter, now known as X. The trolls, who masqueraded as Americans ranging from Black Lives Matter activists to Texas secessionists, had taken the United States by surprise. But that campaign, which featured fake personas slinking into the online communities of ordinary Americans, was only part of Russia’s effort to manipulate U.S. political discourse. The committee subsequently requested an analysis of the social media activities of the GRU—Russian military intelligence—which had concurrently run a decidedly different set of tactics, including hack and leak operations that shifted media coverage in the run-up to the 2016 U.S. presidential election. Russian operatives also reportedly hacked into U.S. voter databases and voting machine vendors but did not go so far as to change actual votes.
Social media is an attractive tool for covert propagandists, who can quickly create fake accounts, tailor content for target audiences, and insert virtual interlopers into real online communities. There is little repercussion for getting caught. However, two presidential election cycles after the Russian Internet Agency first masqueraded as Americans on social media platforms, it is important to emphasize that running inauthentic covert networks on social media has always been only one part of a broader strategy—and sometimes, it has actually been the least effective part. Adversaries also use a range of other tools, from spear phishing campaigns to cyberattacks to other media channels for propaganda. In response to these full-spectrum campaigns, vigilance and response by U.S. tech platforms are necessary. But alone, that will not be enough. Multi-stakeholder action is required.
The first set of announcements by the Justice Department on Sept. 4 featured two distinct strategies. The first announcement, a seizure of 32 internet domains used by a Russia-linked operation known in the research community as “Doppelganger,” reiterates the interconnected nature of social media influence operations, which often create fake social media accounts and external websites whose content they share. Doppelganger got its name from its modus operandi: spoofs of existing media outlets. The actors behind it, Russian companies Social Design Agency and Structura, created fake news outlets that mirror real media properties (such as a website that looked like the Washington Post) and purported offshoots of real entities (such as the nonexistent CNN California). The websites host the content and steal logos, branding, and sometimes even the names of journalists from real outlets. The operation shares fake content from these domains on social media, often using redirect links so that when unwitting users click on a link, it redirects to a spoofed website. Users might not realize they are on a fake media property, and social media companies have to expend resources to continually search for redirect links that take little effort to generate. Indeed, Meta’s 2024 Q1 Adversarial Threat Report noted that the company’s teams are engaged in daily efforts to thwart Doppelganger activities. Some other social media companies and researchers use these signals, which Meta shares publicly, as leads for their own investigations.
The domains seized by the Justice Department are just a portion of the overall number of pages that Doppelganger has run. Most are garbage sites that get little traction, and most of the accounts linking to them have few followers. These efforts nonetheless require vigilance to ensure that they don’t manage to eventually grow an audience. And so, the platforms play whack-a-mole. Meta publishes lists of domains in threat-sharing reports, though not all social media companies act in response; some, like Telegram, take an avowedly hands-off approach to dealing with state propagandists, purportedly to avoid limiting political speech. X, which used to be among the most proactive and transparent in its dealings with state trolls, has not only significantly backed off curtailing inauthentic accounts, but also removed transparency labels denoting overt Russian propaganda accounts. In turn, recent leaks from Doppelganger show the Social Design Agency claiming that X is the “the only mass platform that could currently be utilized in the U.S.” At the U.S. Senate Select Committee on Intelligence hearing on Sept. 18, Sen. Mark Warner called out several platforms (including X, TikTok, Telegram, and Discord) that “pride themselves of giving the proverbial middle finger to governments all around the world.” These differences in moderation policies and enforcement mean that propagandists can prioritize those platforms that do not have the desire or resources to disrupt their activities.
However, dealing with a committed adversary necessitates more than playing whack-a-mole with fake accounts and redirect links on social media. The Justice Department’s domain seizure was able to target the core of the operation: the fake websites themselves. This is not a question of true versus false content, but demonstrable fraud against existing media companies, and partisans across the aisle support disrupting these operations. Multi-stakeholder action can create far more impactful setbacks for Doppelganger, such as Google blocking Doppelganger domains from appearing on Google News, and government and hosting infrastructure forcing Doppelganger operatives to begin website development from scratch. Press coverage should also be careful not to exaggerate the impact of Russia’s efforts, since, as Thomas Rid recently described, the “biggest boost the Doppelganger campaigners got was from the West’s own anxious coverage of the project.”
A second set of announcements in September by the Justice Department and State Department highlighted a distinct strategy: the use of illicit finance to fund media properties and popular influencers spreading content deemed useful to Russia. An indictment unsealed by the Justice Department alleged that two employees from RT—an overt Russian state-affiliated media entity with foreign-facing outlets around the world—secretly funneled nearly $10 million into a Tennessee-based content company. The company acted as a front to recruit prominent right-wing American influencers to make videos and post them on social media. Two of the RT employees allegedly edited, posted, and “directed the posting” of hundreds of these videos.
Much of the content from the Tennessee company focused on divisive issues, like Russia’s war in Ukraine, and evergreen topics like illegal immigration and free speech. The influencers restated common right-wing opinions; the operators were not trying to make their procured talent introduce entirely new ideas, it seemed, but rather keep Russia’s preferred topics of conversation visibly present within social media discourse while nudging them just a bit further toward sensational extremes. In one example from the indictment, one of the RT employees asked an influencer to make a video speculating about whether an Islamic State-claimed massacre in Moscow might really have been perpetrated by Ukraine. The right-wing influencers themselves, who received sizeable sums of money and accrued millions of views on YouTube and other platforms, appear to have been unwitting and have not been charged with any wrongdoing.
This strategy of surreptitiously funding useful voices, which hearkens back to Soviet techniques to manipulate Western debates during the Cold War, leverages social media’s power players: authentic influencers with established audiences and a knack for engagement. Influence operations that create fake personas face two challenges: plausibility and resonance. Fake accounts pretending to be Americans periodically reveal themselves by botching slang or talking about irrelevant topics. They have a hard time growing a following. The influencers, by contrast, know what works, and they frequently get boosted by even more popular influencers aligned with their ideas. Musk, who has more than 190 million followers on X, reportedly engaged with content from the front media company at least 60 times.
Social media companies are not well suited to identify these more obscured forms of manipulation. The beneficiaries of Russian funding were real influencers, and their social media accounts do not violate platform authenticity policies. They are expressing opinions held by real Americans, even if they are Russia-aligned. Assuming the coordination of funding and topics did not take place on social media, the platforms likely lack insight into offline information that intelligence agencies or other entities collect. The violations are primarily external, as well—mainly the alleged conspiracy to commit money laundering and the alleged violation of the Foreign Agents Registration Act. Here, too, a multi-stakeholder response is necessary: Open-source investigators, journalists, and the U.S. intelligence community can contribute by uncovering this illicit behavior, and the U.S. government can work with international partners to expose, and, where appropriate, impose sanctions and other legal remedies to deter future operations.
The degree to which these activities happen beyond social media—and beyond the awareness of the platform companies—was driven home in a Sept. 13 speech by U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken. He highlighted other front media entities allegedly operated by RT, including some with a more global focus, such as African Stream and Berlin-based Red. According to the State Department, RT also operates online fundraising efforts for the Russian military and coordinates directly with the Russian government to interfere in elections, including the Moldovan presidential election later this month. These activities go far beyond the typical remit of overt state media, and likely explain why Meta and YouTube—neither of which had previously banned RT after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine—responded to the news by banning the outlet and all of its subsidiary channels.
Our argument is not that the steps taken by social media companies to combat influence operations are unimportant or that the platforms cannot do better. When social media companies fail to combat influence operations, manipulators can grow their followings. Social media companies can and should continue to build integrity teams to tackle these abuses. But fake social media accounts are only one tool in a modern propagandist’s toolbox. Ensuring that U.S. public discourse is authentic—whether or not people like the specifics of what’s being said—is a challenge that requires many hands to fix.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reference Book
Rioux, M. H., Buettgen, A., Zubrow, E., & Viera, J. (Eds.). (2024). Handbook of Disability: Critical Thought and Social Change in a Globalizing World (1st ed. 2024). Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6056-7

[ID in alt text]
This is the Handbook of Disability, edited by Marcia H. Rioux, Alexis Buettgen, Ezra Zubrow, and José Viera. The editors are a collection of various rigorous and highly-experienced professors in Health, Economics, and Anthropology, and a disabled advocate with almost 20 years of experience in human rights advocacy. This handbook was first published in 2021 and republished as the current first edition in 2024. I can’t describe it better than the editors did: “This important reference work maps the terrain of disability across the world by providing an overview of issues, concerns and developments in the domains of society, culture, medicine, law, policy, justice, education, economics, and science and technology. It is a truly inclusive volume bringing together perspectives from researchers, activists, professionals, service providers, international development experts and policymakers based in the global North and South, and it particularly focuses on the voices of the principal stakeholders---disabled persons themselves” (Rioux et al., 2024). This reference work first surveys past historical events related to disability, then examines current disability conventions, before highlighting as-of-yet addressed areas that the editors predict will shift the discourse in the future. The writing may seem dense, but this is a really great collection of research, trend detection, and intersectional analysis of just about everything disability related. While it may seem intimidating at 80 chapters, it is well organized with an easy to follow table of contents, and an index at the back. References are included so you can also use this handbook as a treasure trove of new sources. Even just reading the chapters that seem interesting to you will help provide a better understanding of the past, current, and future direction of disability justice. This book is perfect for anyone interested in gaining a deeper understanding of the current state of disability studies and serves as a good primer in disability justice.
#disability studies#disability justice#reference book#handbook of disability#critical thought and social change in a globalizing world#Marcia H. Roux#Alexis Buettgen#Ezra Zubrow#José Viera
5 notes
·
View notes
Text


By: SEGM
Published: Apr 15, 2024
The Cass Review of England’s gender services for children and young people, initiated four years ago, culminated earlier this week in the publication of the final 388-page report. The report was accompanied by 9 systematic reviews of evidence supporting the recommendations. Within hours, NHS England responded, thanking Dr. Hilary Cass and her team for “stepping up to lead such a complex review.” NHS England committed to following through on Dr. Cass’ recommendations, and acknowledged the national and international significance of this seminal work: “Your final report will not just shape the future of healthcare in this country for children and young people experiencing gender distress but will be of major international importance and significance.”
A wide range of stakeholders–from patients and clinicians to bioethicists, legal scholars and healthcare historians–will undoubtedly be studying the hundreds of pages of the Cass report and the accompanying studies for weeks and probably years to come. However, there is also considerable urgency to understand its key take-aways and the likely implications.
Balancing two conflicting priorities–the need for an unrushed, thorough and accurate analysis, as well as our commitment to the members of the healthcare community to inform them of key developments in the field–SEGM has decided to release our preliminary analysis. We chose to focus only on the most salient aspects of the Cass Report that will likely lead to a change in clinical practice.
What we present below is SEGM’s interpretation of the key messages in the report. We do not doubt that every person who reads the report will find a new “angle” and perhaps have a different interpretation. As always, we welcome disagreement and debate. The “many eyes of science” are needed now more than ever.
Summary
The Cass Review marks the end in England of the era of a highly medicalized approach to the treatment of young people with gender-related distress, which has come to be known as “gender-affirming care.” While the treatment protocol for youth comprising of puberty blockers, cross-sex hormones, and surgery, known as the “Dutch Protocol,” was invented in the Netherlands in the 1990’s, the report points out the concept of “gender-affirming care”–the notion that the doctors must accept children’s declarations of identity at face value and must assist them in gender change as early as possible–actually originated in the United States, and only then spread internationally.
The Cass Review provides a scathing assessment of the gender-affirming approach in general, and the gender-clinic model of care, which operationalized this approach of on-demand provision of gender-reassignment interventions, in particular. Going forward, England will treat gender dysphoric youth <18 using standard psychological and psychotherapeutic approaches, with very few young people receiving endocrine gender reassignment interventions (gender-transition surgeries for <18s have never been allowed in England). Further, the review noted that the group of young adults 18-25 is subject to many of the same concerns as the <18s, and recommended that the new regional “hubs” being set up to help gender dysphoric youth be expanded to include patients up to 25 years old.
NHS England (NHSE) welcomed the Cass Review’s recommendations and expressed a firm commitment to implement the recommended changes. However, NHSE went one major step further, announcing that they will be initiating a Cass-style review into the adult gender dysphoria clinics (GDCs) in England. NHSE had already decided to bring forward to 2024 its periodic review of the adult “service specifications,” which set out what clinical services adult clinics provide; as a consequence of Cass’ recommendations, they are additionally launching a much broader review of the entire adult gender clinic system. This was in part due to the concerns raised by the Cass Review that a vulnerable group of 17-25-year-olds represents fundamentally the same group of youth as the <18s, and needs similar protections from non-evidence-based practices. Further, whistleblower complaints from adult clinics corroborated concerns that vulnerable adults were not receiving proper evidence-based care. The refusal by all but one adult gender clinic to cooperate in the outcome analysis for the 9000 patients as part of the Cass Review likely contributed to NHSE’s determination to investigate the adult service. Adult gender dysphoria clinics see patients aged 17 and upwards, and NHSE has written to require them to halt appointments with 17-year-olds.
In summary, the care for <18s in England will no longer be based on the “gender-affirming” model of care but instead will treat youth with gender distress similarly to how it treats youth with other developmental struggles. Further, with the announcement of the adult gender clinic review, England starts a new chapter in the history of gender medicine, with a new focus on vulnerable gender-dysphoric young adults.
Many more developments are expected from England in the coming months. To what extent the UK changes will impact the West’s approach to helping young gender-dysphoric individuals remains to be seen. In SEGM’s view, the impact will likely be significant, even if delayed, as other countries contend with England’s findings and their implications for evidence-based clinical practice.
Detail Regarding Social Transition, Puberty Blockers, Cross-Sex Hormones, Surgery, and Overall Care Delivery Model
Social Gender Transition
The Cass Review positions social transition as an active healthcare intervention “because it may have significant effects on the child or young person in terms of their psychological functioning and longer-term outcomes.” (UK and other countries’ clinicians increasingly use “social prescribing” interventions in order to impact health outcomes).
For young children, the review strongly discourages social transition, noting that “sex of rearing” may profoundly alter a child’s developmental trajectory, with long-ranging consequences. Should parents insist on it, the review recommended that a healthcare professional be involved in helping parents understand the risk-benefit ratio of such a profound and likely life-altering decision.
For older teens, the review recognizes the autonomy of young people’s self-expression but strongly recommends that parents be involved in the decision, noting that secret transitions cause a rift between teens and their families, destabilizing the very support networks that are essential for young people’s long-term well-being.
More generally, should social transitions be undertaken, the review recommended only a partial, rather than complete, social transition, especially for younger children, noting how many children currently live in fear of being “found out.” The discontinuation of the use of puberty blockers (discussed next) will make that fear a certainty. Thus, it would be highly unwise for a parent to create a situation where a young child is living in “stealth.”
These recommendations were supported by interviews with patients and families, and by a systematic review of evidence of social transition published in a peer-reviewed BMJ journal. The review found a dearth of evidence and concluded, “professionals working in the area of gender identity and those seeking support should be aware of the absence of robust evidence of the benefits or harms of social transition for children and adolescents.”
The recognition of not only the potential benefits, but also the potential harms, and the unknown benefit-harm ratio of social gender transition is noteworthy.
Puberty Blockers
The use of puberty blockers to stop normally-timed puberty will no longer be offered as part of England’s publicly funded healthcare system. This is not a “new development” as the problems with using puberty blockers for gender dysphoria were already part of the Cass Review’s interim report, and NHSE had updated its puberty blocker policy a month before the issuing of the final Cass Review.
The rationale for withdrawing puberty blockers from medical practice is manifold. It ranges from unclear treatment aims (besides altering a child’s body), a lack of credible evidence that stopping normally-timed puberty leads to improvements in mental health, safety concerns (e.g., bone health), and profound unknowns across a range of health domains, especially brain development. The fact that nearly 100 percent of puberty-blocked youth proceeded with cross-sex hormones was treated as a negative signal that puberty blockers may be setting children on an irreversible path of gender transition.
As we noted in our earlier analysis, the NHS guidance regarding discontinuing the use of puberty blockers for stopping normally-timed puberty affects only the NHS clinics. Private clinics (including the single non-NHS youth clinic operating in the UK, as well as online clinics based abroad but serving UK citizens) are not subject to the NHS policies. This created a loophole that could be exploited to circumvent NHS actions to safeguard England’s youth from harmful medical interventions. In response to these concerns, Health Minister Victoria Atkins made clear the government’s intention to limit private gender care for under 18s and to eradicate the online trade in hormones, following Cass’ recommendations.
As we noted earlier, the NHS intends to conduct research into puberty blockers, and there has been much speculation about research design in general, and the eligibility for research in particular. The quote below from the final Cass Review suggests that eligibility may be limited only to natal males with early-onset and long-lasting gender dysphoria. It appears to suggest that natal females may not be eligible, as they can successfully undergo convincing masculinization with the help of testosterone at virtually any age:
14.56 Transgender males masculinise well on testosterone, so there is no obvious benefit of puberty blockers in helping them to “pass” in later life, particularly if the use of puberty blockers does not lead to an increase in adult Height. 14.57 For transgender females, there is benefit in stopping irreversible changes such as lower voice and facial hair. This has to be balanced against adequacy of penile growth for vaginoplasty, leaving a small window of time tо achieve both these aims. 14.58 In summary, there seems to be а very narrow indication for the use of puberty blockers in birth-registered males as the start of a medical transition pathway in order to stop irreversible pubertal changes. Other indications remain unproven at this time.
As we noted earlier, the NSHE made it clear in its puberty blocker update policy that there are no guarantees that such research will obtain the necessary ethical approval.
Like other recommendations in the Cass Review, the puberty blockers recommendation was based on extensive stakeholder consultation, and supported by a systematic review of evidence, which showed no credible psychological benefits of puberty suppression in the treatment of gender dysphoric youth. As we explained earlier, the original 2020 NICE systematic evidence review was updated in 2023, but newly-identified studies did not change its conclusions.
Cross-Sex Hormones
Shortly before the publication of the final Cass Review, NHSE issued an updated policy about the cross-sex hormones. As we noted at the time in our earlier analysis, the policy was only a minor update, necessitated by the launch of the new gender services, and it represented only minor changes. Cross-sex hormones for those around their 16th birthday were still allowed, although a new centralized team not directly involved in care of the young person would need to approve the medical necessity. At the time, SEGM posited that following the final Cass Review, the NHS will commit to a more thorough review of the cross-sex hormones policy, and further updates. This indeed has occurred.
According to NHS England’s response to the final Cass Report:
NHS England will review the use of gender affirming hormones through a process of updated evidence review and public consultation, similar to the rigorous process that was followed to review the use of puberty suppressing hormones.
NHS England has made clear that there will be a single cross-sex hormones policy “which will cover all people over the age of 16,” with further details to follow.
NHSE acknowledged Dr. Cass’s recommendation that “the new providers should be ‘extremely cautious’ when considering whether to refer young people under 18 years for consideration of hormone intervention.” To support this recommendation while the new cross-sex hormones policy is being developed, NHSE has “established a national multi-disciplinary team (MDT) that will review and need to agree all recommendations for hormone intervention.” Further, NHSE noted that the “first meeting of this new national MDT will take place later this month” chaired initially by Professor Judith Ellis, former CEO of the Royal College of Paediatric and Child Health.
The original NICE systematic review of evidence for the effects of cross-sex hormones was conducted in 2020, and it found similar problems in the evidence base as the puberty blockers review (unreliable evidence base), but with a signal that there may be some small short-term improvements in mental health following cross-sex hormones administration. The new systematic review of cross-sex hormones confirmed these findings.
The final Cass Review expressed concern over how small these changes were, considering the fact that the introduction of the long-awaited cross-sex hormones and desired physical changes is expected to lead to short-term improvements in mood. This suggests that the Cass Review is concerned not only with the low certainty of the reported benefits due to poor study designs, but also with the possibility that the small improvements may be short-lived and due to the potential placebo effect:
15.27 When a young person has been on puberty blockers, a short-term boost in mental wellbeing is to be expected when sex hormones are introduced. Testosterone is faster to produce physical changes than oestrogen, and birth-registered girls can expect to start seeing body changes in line with their identified gender within a few months. The start of long anticipated physical changes would be expected to improve mood, at least in the short term, and it is perhaps surprising that there is not a greater effect size. However, much longer term follow-up is needed to understand the full psychological impact of medical transition.
The NHSE’s announcement made it clear that the final cross-sex hormones policy will be based on the updated systematic review of evidence.
Surgery
Surgeries have never been available to under 18’s in England, so no systematic reviews of surgeries has been conducted, and no additional changes to the policy for youth under 18 are needed. However, NHSE’s announcement of the Cass-style review into the adult gender clinics raises questions about whether surgical interventions for young adults will now come under scrutiny as well.
Change in the Delivery Care Model Overall
In addition to making specific recommendations overall about social transition and endocrine interventions, the review challenged the concept that gender dysphoria/gender incongruence in youth as an exceptional condition that needs exceptional treatments delivered via exceptional models of care exemplified by gender clinics.
The healthcare delivery system for gender dysphoric youth will be restructured to provide a fundamentally different model of care, and realign it with the way care is typically organized in England. Every gender-dysphoric child or young person will have a dedicated primary care provider (a pediatrician or a GP) overseeing their care and well-being. Children and young people with mental health conditions, or those whose gender incongruence is causing distress, will receive psychotherapeutic and psychological services from the second level of care at the Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS).
Very few young people will be referred to super-specialized tertiary services, which will carefully examine the medical necessity of cross-sex hormones. The referring clinicians will need to demonstrate why cross-sex hormones delivered to under-18’s are medically indicated and preferred over allowing the young person to reach maturity, and a centralized team not directly involved in the care of the young person will need to agree with this assessment. It is expected that in the end, very few young people will be treated with interventions to alter their bodies.
Other notable aspects of the final report
The final Cass Review made a number of other highly consequential statements and observations. It is impossible to do a thorough overview of all of them given the short time since the report’s release, but we will highlight several that stood out to SEGM as particularly noteworthy.
Although chiefly forward-looking, the review described the alarming inadequacies of clinical practice at GIDS.
While the focus is on service improvement, the legal ramifications of the unsafe practice at GIDS in the longer term must be apparent to NHSE. GIDS refused to participate in the review’s research study, to compare clinical practice at a range of European pediatric gender clinics, therefore the report (at Appendix 9) of the Multi-Professional Review Group (MPRG) which oversaw GIDS’s referrals for puberty blockers is the major source of information about what went on there. The MPRG painted an extraordinary picture. It was not clear how thoroughly different treatment options had been discussed, and most children and parents were asking to obtain puberty blockers from their first appointment with GIDS, having “turned for information to the media and online resources, with many accessing LGBTQ+ and GD support groups which appear to be mainly affirmative in nature.”
Concerns of over treatment of neurodiverse and same-sex attracted youth.
Neurodiversity was suspected or diagnosed in a majority of children referred for puberty blockers and where sexuality was discussed “most cases are of same sex, opposite-gender attracted children.” The MPRG were “concerned about the lack of evidence of professional curiosity” about these children’s lives shown by GIDS clinicians. A recurrent concern was “the inadequacy and on occasion inaccuracy of answers given to children and their families by GIDS and their failure to correct child and parental misconceptions about puberty, puberty blockers and hormones.” Unsurprsingly, then, they note that the Care Quality Commission’s (CQC) observation that consent taking was judged to be “not in line with NHS and GMC requirements.” Records varied “from succinct to disorganised.”
A scathing assessment of poor quality and lack of independence for the guidelines by WPATH, The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and the Endocrine Society (ES).
As part of the Cass Review, an independent team of research methodologists assessed all the current treatment guidelines and recommendations for quality in a systematic review, using the internationally recognized AGREE II methodology for evaluating guideline quality. The AAP 2018 treatment recommendations guidelines scored amongst those at the bottom of the 23 reviewed guidelines. The WPATH and the ES treatment recommendations did not fare much better. The review noted a marked lack of independence in guideline authorship, noting circular referencing: one non-evidence-based guideline was used to justify another non-evidence-based guideline’s recommendation. The significant overlap in authorship between the guidelines (especially between WPATH and ES) was noted as a significant cause for concern, as was WPATH’s refusal to acknowledge the results of their own systematic review in its adolescent section. The report points out that only the Swedish and Finnish treatment recommendations appear credible, but even they lack the specificity needed for the NHS to operationalize the treatment recommendations in the UK context. The concern over the proliferation of non-evidence-based guidelines, which at times do acknowledge the poor quality evidence but then issue strong recommendations to medically transition youth anyway, has been seconded in the BMJ article dedicated to this specific aspect of the Cass review findings.
Condemnation of the “toxic” nature of debate within which standard psychological therapies were rebranded "conversion practices."
The Cass Review drew attention to the difficulty of undertaking the review amid an “increasingly toxic, ideological and polarized public debate” that ill-served children. The report noted that it is essential to explore children’s complex needs and stated that it is “harmful to equate this approach to conversion therapy as it may prevent young people from getting the emotional support they deserve.” Furthermore, potential accusations of conversion practice “when following an approach that would be considered normal clinical practice” in other scenarios made clinicians wary of offering support to young people, leaving them without the help they deserve. The report highlighted the potential for legislation on conversion practices to complicate the situation and emphasized that “strong safeguards must be built into any potential legislation” to guard against the risk that clinical staff feel that discharging their duty of care would expose them to legal challenge.
Questioning the assumption of the gender identity theory.
While some have criticized the Cass Review for relying on constructs coming from the gender identity theory (e.g., referring to “gender identity” without critically assessing the origin and validity of this concept), the report did briefly address the outdated nature of the assumptions on which the “gender-affirming” care model is based. The report noted that the theory of gender identity development was set forth in 1966 by Kohlberg, who described a typical progression whereby by the age of 5-6, children develop gender identity constancy.
The report noted the obvious fact that the current patterns of both identifying as transgender for the first time at much older ages and also the growing phenomenon of detransition and re-identification with natal sex demonstrably contradict this theory.
The review considered a range of factors that may have contributed to the current phenomenon of a sharp rise of trans identification in youth. It noted that while biology likely plays a role, “since biological factors have not changed in the last 10 years it is necessary to look at other possible reasons for the increase in referrals and the disproportionate representation of birth-registered females.”
8.23 For children and young people with gender incongruence, ‘innate’ or biological factors may play a part in some individuals, in ways that are not yet understood, and in others psychosocial factors, including life experiences, societal and cultural influences, may be more important. Since biological factors have not changed in the last 10 years it is necessary to look at other possible reasons for the increase in referrals and the disproportionate representationof birth-registered females.
Recognition that the challenges in the mental health of Generation Z are likely at the root of the current phenomenon of trans identification in youth.
The report acknowledged the likely multi-factorial basis for the current explosion of gender-dysphoric youth, with a focus on “Gen Z” and the significant mental health crisis affecting this population more generally, as well as the role of social media.
7.21 The striking increase in young people presenting with gender incongruence/dysphoria needs to be considered within the context of poor mental health and emotional distress amongst the broader adolescent population, particularly given their high rates of co-existing mental health problems and neurodiversity. 7.22 Internationally, there have been increasing concerns about the mental health of Generation Z. The reasons for this are highly speculative, although there is ongoing debate about the contribution of excessive smartphone use and social media as discussed above.
Suggestion that the invention and the availability of the Dutch protocol likely contributed to the rapid rise in gender dysphoria in youth.
The report noted that the sharp rise in the numbers of gender dysphoric youth in the West also coincided with the introduction of puberty blockers into general medical practice. Of note, the Netherlands experienced a similar spike several years before the rest of the West–and incidentally, the Netherlands introduced the Dutch protocol/blockers into clinical use several years before the rest of the West. This lends further credibility to the theory that the very availability of the Dutch protocol treatment may have contributed to the growing numbers of youth seeing their developmental struggles through the “gender identity” lens and pursing medical interventions.
8.50 The dramatic increase in presentations to NHS gender clinics from 2014, as well as in several other countries, coincided with puberty blockers being made available off protocol and to a wider group of young people. The only country with an earlier acceleration in referrals is the Netherlands, where the Dutch protocol was developed.
Clear attribution of the “gender-affirming” model of care to the United States.
While it was the Dutch clinicians who came up with the “innovative clinical practice” to use puberty blockers in an off-label way to stop normally-timed puberty of gender-dysphoric youth, the report suggests that it was the Americans who propagated the approach of allowing the child to direct what medical interventions they need based on their self-declared identity.
Specifically, the review credits an American psychologist Diane Ehrensaft, who pioneered and promulgated this theory, which has become the core of the “gender-affirming” model of care. The report describes the model as a belief that “a child of any age may be cognizant of their authentic identity and will benefit from a social transition at any stage of development.”
2.13 In 2007 Norman Spack established a clinic in Boston, USA modelled on the Dutch protocol and began prescribing puberty blockers from early puberty (Tanner stage 2). 2.14 Practice in the USA began to diverge from the models of care in Canada and the Netherlands, following instead a gender affirmative model advocated by Diane Ehrensaft (Eherensaft, 2017). She described the three approaches as follows (Ehrensaft, 2017): “The first model, represented in the work of Drs Susan Bradley and Ken Zucker [Canada], assumes that young children have malleable gender brains, so to speak, and that treatment goals can include helping a young child accept the gender that matches the sex assigned to them at birth. The second model, represented in the work of practitioners in the Netherlands, allows that a child may have knowledge of their gender identity at a young age, but should wait until the advent of adolescence before engaging in any full transition from one gender to another. The third model, represented in the work of an international consortium of gender affirmative theoreticians and practitioners, allows that a child of any age may be cognizant of their authentic identity and will benefit from a social transition at any stage of development.” 2.15 The third model - the ‘affirmative model’ - has subsequently become dominant in many countries. As a result, some gender services have moved away from a more exploratory approach, and this is seen by some advocacy and support groups as a move to ‘gatekeeping’ model.
Incidentally, (a fact the the report does not mention), Ehrensaft was also a notable figure in promoting the now-defunct theory of repressed memory of satanic abuse, and published on the subject. This subject is outside the scope of this analysis, but notably, the epidemic stopped only after successful lawsuits demonstrating that some psychologists facilitated the patients’ “recovering” non-existing memories of abuse as an explanation of the patient's distress.
Clear acknowledgment of detransition as a growing phenomenon that can no longer be ignored.
There was a chapter dedicated to detransitioners, and the term “detransition” was mentioned in the report over 80 times, citing a number of studies from the UK and internationally. The report recognized that the rate of detransition and regret among the novel population of youth is unknown, but suggested it is no longer negligible, citing a UK study of double-digit detransition in a relatively short follow-up period. Of note, a recent US study found that among participants who were medically transitioning, almost 30 percent ceased medical transition based on a 4-year average followup, but the reasons for the cessation were not explored.
Suggestion of lack of data integrity in gender clinics.
The Cass Review revealed that in a truly unexpected turn of events, all but one adult gender clinic refused to cooperate in a data analysis project that would have allowed tracking of longer-term outcomes of 9,000 gender dysphoric young people, which included both those who underwent gender transitions as well as those who chose less invasive options. The responsibility for the research, which has obtained ethics permission, has now been handed over to NHSE, which will conduct the review without the gender clinics’s cooperation. The objection of the gender clinics and the responses to those objections (both contained in the appendices to the report) suggest that the reasons for the lack of cooperation may be ideological.
Further, there are indications through the report that there may be a lack of integrity in the gender clinic approach to data collection and reporting more generally. For example, the Cass team was advised by GIDS/Tavistock (the youth gender clinic) that only 27 percent of the referred cases were referred for endocrine interventions (puberty blockers and/or cross-sex hormones), creating the impression that only a minority of gender dysphoric youth are intervened with medically.
However, the context of the report signaled that this figure is open to misinterpretation (without directly calling it misleading). The report noted that the 27 percent only applies to the young people who were referred directly to the two adolescent endocrine centers. Among the 73 percent “non-referred” for endocrine interventions, 69 percent actually went on to adult gender clinics, where most likely received hormonal interventions.
The question of what percentage of youth referred to gender clinics end up transitioning is an open one. In the Netherlands, which claims a cautious approach, this number appears to be around 70-80 percent. It is reasonable to expect similar or even higher numbers among gender clinic staff who subscribe to the “gender-affirming” model of care.
Problems with applying the Dutch protocol to the “wrong” population.
The report clarifies that GIDS/Tavistock’s approach to validating the Dutch protocol failed on at least 3 accounts. As previously discussed, the clinic started scaling the treatment before they analyzed and published the results and they also changed the protocol where the minimum age of 12 for puberty blocked was dropped and replaced by pubertal tanner stage 2 stage–which can be as young as ages 8-9 in girls. However, the report highlights another important deviation, which may be responsible for the sheer scale of the current problem.
While the research study (aka “Early Intervention Study”) was only approved to include youth with the classic early childhood, the pre-pubertal onset of gender dysphoria that intensified in adolescence with no other significant mental health problems (to replicate the Dutch research), when the clinic chose to scale it widely, it expanded eligibility to all youth including those whose gender dysphoria emerged post-puberty and in the context of complex mental health problems (p. 73). The latter group currently represents the single biggest affected demographic.
The fact that the Dutch research is currently being applied to the very demographic which was originally contra-indicated for gender transition and that this problem is not confined to the UK but is a worldwide problem, has been highlighted in a number of recent publications and emphasized in the Cass report.
The current “suicide and suicidality narrative” surrounding gender-dysphoric youth is misleading.
The Cass Review noted that “balanced information, which is realistic and practical, and does not over-exaggerate or underestimate the risks, is essential to support everyone involved and identify young people in most urgent need of help.” The review commented on the thankfully low rates of completed suicides in the population of trans-identified youth, pointing out the latest evidence from Finland. However, the review appropriately recognized every suicide is a tragic event and the causes in each individual case must be clearly understood. The report noted a recent UK analysis of suicides using the National Child Mortality Database (NCMD). The analysis of 91 cases of youth suicides between April 2019 and March 2020 (1-year span) identified 108 total deaths across the entire population of the UK that were likely due to suicide. In examining the factors contributing to suicides, the Child Death Overview Panel concluded that Household functioning was found to be the most common contributing factor (69%), followed by mental health problems (55%), bullying (23%), and neurodevelopmental conditions (16%). Sexual orientation, sexual identity, and gender identity were assessed as a factor in 9 percent of total suicides. The Cass report did not provide an additional breakdown for sexual orientation vs gender identity. However, the report did note that systematic reviews failed to provide evidence that endocrine interventions reduce suicides.
The problem with the notion of the “diagnostic assessment.”
The report zooms in on a central argument leveled by gender-affirming clinicians that “gender-affirming” treatments are only provided following a diagnostic assessment, and therefore are medically necessary. The review aptly points out that neither the DSM-5 diagnosis of “gender dysphoria,” nor the “de-pathologized” ICD-11 diagnosis of “gender incongruence,” have a known predictive validity. In other words, a young person can meet the diagnostic criteria today, but nothing is known about how likely the young person is to continue to experience gender-incongruent feelings in the future.
16.8 A formal diagnosis of gender dysphoria is frequently cited as a prerequisite for accessing hormone treatment. However, it is not reliably predictive of whether that young person will have longstanding gender incongruence in the future, or whether medical intervention will be the best option for them. Depending on what has caused their distress or dysphoria, it may be resolved by medical treatment, but it may also be resolved in other ways.
The Cass Report notes, “The Review was unable to obtain clear criteria from the GIDS team on their criteria for referral for endocrine intervention.” The report also points out that if the causes for gender-related stress are “psychosocial,” “sociocultural” and/or “dynamic,” providing invasive and irreversible interventions to such young people presents a challenging ethical dilemma.
16.9 As discussed in Chapter 8, the nature and causes of gender dysphoria/incongruence are complex and poorly understood, and there is very limited understanding of the currently presenting population of predominantly birth registered adolescent females. Each individual will have a different mix of biopsychosocial factors, but if potentially dynamic psychosocial or sociocultural factors predominate in a significant proportion of people, one of the most challenging ethical questions is whether and/ or when medical intervention is the correct response.
Further, the report takes on the notion of the “diagnostic assessment” itself, noting that there is no formalized assessment process whereby one can determine how to conduct such an assessment, and how to arrive at predictable outcomes as to which young person is referred to the endocrine interventions and which one is not. The report notes:
10.17 There was also a general lack of understanding among service users participating in the lived experience focus groups about what the assessment was for and confusion about what was assessment and what was diagnosis. Thoughts on the purpose of the assessment included: • To support young people to explore their options and access the care that’s right for them. • To get validation of their trans identity and access to the medication pathway. • To make the person comfortable and focus on what they’re looking for from the service. • To ensure patients have an understanding of the healthcare options available.
The report concluded that, following a review of international clinical practice, “there was no approach to assessment that could be directly adopted for use in the NHS.” One needs to be developed to meet key goals (support identification of individual needs, allow outcomes to be measured more consistently and ensure children and young people have a similar experience of the service.)
The fundamentally new model will focus on assessment with the goal of “case formulation” followed by psychotherapy as the first line of treatment.
The new treatment framework will be comprised of the assessment, case formulation, diagnosis, care plan. Due to the problems described above (lack of specificity of what the goal of the “assessment” are), the report sets out a new and clear expectation of the role of the assessment. Rather than attempting to identify which young person should be referred to endocrine interventions, the goal is to “derive a multi-level formulation for a child or young person who presents to the NHS seeking help around their gender or experience of gender-related distress.”
The starting point of the assessment is to assess immediate risk and assess complex care needs. Assuming any immediate risks (if any) are addressed using standard psychotherapeutic approaches, the next goal is to come up with a “case formulation.” A case formulation is a standard psychotherapeutic process whereby clinicians synthesize the complexity of the young person’s situation to develop an individualized treatment plan.

The report makes it clear that if any interventions are indicated, standard psychotherapeutic interventions for mental health conditions, as well as more specific exploration of gender-related distress (if indicated), will be the primary treatment. Referrals to endocrine interventions will only be accepted from the Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS) with onus on the clinician making the referral to demonstrate to a centralized team that includes members not directly involved in the care the medical necessity of cross-sex hormones. As mentioned elsewhere, Cass recommended extreme caution in prescribing cross-ses hormones to youth, and the NHS has committed to updating its current cross-sex hormones policy to align it with the final report recommendations.
Recognition of the need to update the diagnostic categories to meet the changing clinical presentations of gender-related distress, and the phenomenon of detransition.
The Cass Review subtly but powerfully signals that the DSM-5 “gender dysphoria” diagnosis appears to be preferred by most clinicians, while the attempt to “de-pathologize” the condition in ICD-11 is less clinically useful.
At the same time, the report recognizes that neither of these diagnostic categories are adequate for the current complexity of the presentations. The diagnosis itself was criticized for relying on outdated notions of preferences for sexed stereotypes from “previous decades,” and the “DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for gender dysphoria has a low threshold based on overlapping criteria” leading to the risk of overdiagnosis and overtreatment. Further, the report indicated that the diagnosis is unhelpful in the care for the growing number of detransitioners as it does not have any specific categories for this growing patient population.
New focus on young adults.
The report recognized the new understanding of adolescent development and that adolescence does not stop at 18 but extends into mid-20s. Noting the disproportionate number of non-neurotypical individuals struggling with gender identity, the report noted that neurodiverse young people are particularly vulnerable “into their early 20s or longer because of their tendency to want black-and-white answers, and their difficulty in tolerating uncertainty.”
Consistent with that, the report recommends that the restructured approach to gender-dysphoric youth does not stop at 18, but subsumes the category of young adults. In addition, the report notes that while the provision of adult gender services fell outside of the review’s remit, several staff in adult gender clinics “contacted the Review in confidence with concerns about their experiences working in adult gender services.” Adult clinic “whistleblowers” shared that adult services experienced a similar influx of young adults, primarily females with complex mental health problems, presenting to adult gender clinics with an expectation of rapid provision of “gender-affirming” medical interventions, as well as growing numbers of detransitioners. The whistleblowers expressed deep concerns about the harm to the vulnerable population of young adults which seemed to represent the same demographic that began to be seen at the Tavistock a few years ago.
As a result, the review recommended a heightened focus on the adult services, and the NHS has responded by announcing an investigation into the adult NHS gender clinics.
Call for the development of new treatments and clear clinical targets.
The review recognizes the the evidence base for psychotherapeutic approaches to the management of gender dysphoria in youth is very low quality. At the same time, the report pointed out that standard therapeutic interventions for distress are the standard of care in medicine, and that no studies of the application of this approach to gender dysphoria have shown harm.
The review stated unambiguously that the “ultimate goal of any intervention is to help the child or young person to function and thrive, they need to be provided with tools and strategies to give them the best opportunity to do so.” The review called for the development of an “explicit clinical pathway for non-medical interventions, as well as a research strategy for evaluating their effectiveness.”
With this recommendation, the Cass report has redirected the clinical community towards the development and study of non-invasive clinical interventions with a focus on long-term outcomes, with the goal of helping young people achieve the best quality of life.
SEGM Take-Aways
The single most salient take-away is that the so-called “gender-affirming” model of care, which treats young people’s declarations of transgender identity as an indication that any physical body modification desired by the young person is medically necessary, is over in England. So is the era of the “gender-clinic model of care,” which exists to operationalize the highly medicalized “gender-affirming” care model.
We end our take-away by pointing the readers to a powerful editorial by the BMJ Editor in Chief. The entirety of this short editorial is worth reading, but we will highlight the more salient quotes below:
“Offering treatments without an adequate understanding of benefits and harms is unethical. All of this matters even more when the treatments are not trivial; puberty blockers and hormone therapies are major, life altering interventions.”
“Without doubt, the advocacy and clinical practice for medical treatment of gender dysphoria had moved ahead of the evidence—a recipe for harm.”
“...Families, carers, advocates, and clinicians—acting in the best interests of children and adolescents—face a clear choice whether to allow the Cass review to deepen division or use it as a driver of better care.”
This analysis, published by the Editor-in-Chief of one of the most prestigious medical journals in the world, signals that the implications of the Cass Review will likely reverberate worldwide. It now appears inevitable that the arc of history has bent in the direction of reversal of gender-affirming care worldwide, although in some countries it will take considerably longer to change medical practice.
The Cass Review is a historic document the significance of which cannot be overstated. It is also multi-faceted, and no single analysis can do it justice. We have done our best to synthesize the most salient aspects of the review after a single reading. We have no doubt that we missed other important aspects and we trust that others will point them out.
#SEGM#Society for Evidence Based Gender Medicine#Cass report#Cass review#Dr. Hilary Cass#Hilary Cass#NHS England#National Health Service#gender affirming care#gender affirming healthcare#gender affirmation#medical scandal#medical malpractice#medical corruption#religion is a mental illness
12 notes
·
View notes