#Sony E mount
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


Sighhh. Just a dumb sunset I saw today… *kicks rocks
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#Sigma#24-70mm#F2.8#DG DN Art#Sony E mount#lens#optical performance#build quality#zoom range#maximum aperture#versatile#autofocus#dust-resistant#splash-resistant#photography#videography#portraits#landscapes#low-light#nature#bokeh#colors#sharp#detailed#sturdy#metal construction#fast-moving subjects.#photo editor#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Understanding the difference between T-stop and F-stop when working with cine lens for sony e mount
Understanding the difference between T-stop and F-stop is crucial when working with cine lens for sony e mount, as it directly impacts the amount of light that reaches the camera sensor. Here’s a detailed explanation:
T-Stop (Transmission Stop)
Definition: T-stop is a measure of the actual light transmission through the lens, taking into account the light losses due to reflection and absorption within the lens elements.
Measurement: T-stop is determined by measuring the amount of light that actually passes through the lens and reaches the sensor. It is a more accurate representation of the effective light transmission.
Advantages:
Consistency: T-stops are consistent across different lenses, making it easier to match exposure levels when switching lenses.
Accuracy: T-stops provide a more accurate measure of the light reaching the sensor, which is crucial for precise exposure control in filmmaking.
Repeatability: T-stops ensure that the same T-stop setting on different lenses will result in the same amount of light reaching the sensor, which is important for maintaining consistent exposure during a shoot.
F-Stop (Focal Ratio)
Definition: F-stop is a theoretical measure of the lens aperture size relative to the focal length. It is calculated as the ratio of the lens’s focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil (aperture).
Measurement: F-stop is a theoretical value and does not account for light losses within the lens. It is based on the physical dimensions of the lens and the aperture.
Advantages:
Simplicity: F-stops are easier to calculate and understand, as they are based on simple geometric principles.
Standardization: F-stops are widely used in photography and are familiar to most photographers and filmmakers.
Key Differences
Light Transmission:
T-stop: Measures the actual light transmission, accounting for losses.
F-stop: Measures the theoretical light transmission, without accounting for losses.
Consistency:
T-stop: Provides consistent light transmission across different lenses.
F-stop: Can vary between lenses due to differences in lens design and materials.
Application:
T-stop: More commonly used in professional filmmaking where precise exposure control is critical.
F-stop: More commonly used in still photography and consumer-level videography.
Practical Example Imagine you have two cine lens for sony e mount with the same F-stop value, say f/2.8. One lens might be a simple prime lens, while the other is a complex zoom lens with multiple elements. Due to the differences in design and materials, the actual amount of light reaching the sensor might differ between the two lenses. If you measure the T-stop, you might find that the prime lens has a T-stop of T2.8, while the zoom lens has a T-stop of T3.2. This means that the zoom lens is actually transmitting less light than the prime lens, even though both have the same F-stop value.
Conclusion In summary, T-stop is a more accurate and consistent measure of light transmission compared to F-stop. While F-stop is a theoretical value based on lens dimensions, T-stop accounts for real-world light losses within the lens. For professional filmmakers who require precise exposure control, T-stop is the preferred measurement.
0 notes
Text
For over seven decades, Tamron has been a name synonymous with innovation and quality in the world of photographic lenses. They've consistently pushed the boundaries of optical technology, creating lenses that empower photographers to capture their vision with clarity and precision. While Tamron caters to various camera systems, their commitment to the E mount ecosystem, especially for Sony cameras, deserves a closer look. This blog post will delve into the world of Tamron E mount lenses, exploring their features, benefits, and how they can enhance your photographic journey.
A Legacy of Innovation and Quality
Tamron's history is rooted in a passion for optical excellence. From their early innovations in zoom lens technology to their current offerings, they've maintained a focus on delivering high-quality optics at competitive prices. This dedication to value and performance has made Tamron a favorite among photographers of all levels, from casual shooters to seasoned professionals.
The Power of the E Mount: A Gateway to Creative Freedom
The E mount has become a dominant force in the mirrorless camera world, particularly with Sony's popular lineup. Tamron has recognized the potential of this system and has invested heavily in developing a comprehensive range of E mount lenses. This means photographers using Sony (and other compatible) cameras have access to a wealth of Tamron's optical expertise.
Exploring the Tamron E Mount Lens Lineup
Tamron's E mount lens offerings cover a wide range of photographic needs:
Zoom Lenses: Versatility at Your Fingertips: Tamron's zoom lenses for E mount are designed for versatility and convenience. Whether you're traveling, shooting landscapes, or capturing everyday moments, these lenses offer a range of focal lengths in a single, compact package. This eliminates the need to constantly switch lenses, allowing you to stay focused on your composition and capture fleeting moments.
Prime Lenses: The Pursuit of Optical Perfection: For photographers who prioritize image quality and low-light performance, Tamron's E mount prime lenses are an excellent choice. Their fixed focal length allows for larger apertures, resulting in beautiful bokeh and exceptional sharpness. These lenses are ideal for portraiture, street photography, and any situation where image quality is paramount.
Specialty Lenses: Expanding Your Creative Horizons: Tamron also offers specialized lenses for E mount, such as macro lenses for close-up photography. These lenses open up new creative avenues, allowing you to explore the intricate details of the world around you.
Key Features and Technologies in Tamron E Mount Lenses
Tamron incorporates several key technologies into their E mount lenses to enhance performance and usability:
Vibration Compensation (VC): Tamron's VC technology minimizes the effects of camera shake, resulting in sharper images, especially when shooting at slower shutter speeds or with telephoto lenses. This is a crucial feature for handheld photography and ensures crisp, clear results even in challenging conditions.
Fast and Quiet Autofocus: Tamron's autofocus systems are designed for speed and accuracy. Whether you're capturing still images or shooting video, you can rely on Tamron lenses to deliver smooth and reliable autofocus performance.
High-Quality Optics: Tamron utilizes advanced optical designs and high-quality glass elements to ensure exceptional image quality across the entire focal range. Their lenses are designed to minimize distortion, chromatic aberration, and other optical imperfections, resulting in stunningly clear and detailed images.
Durable Construction: Tamron lenses are built to withstand the rigors of professional use. Their robust construction ensures that your lens will perform reliably, even in challenging environments.
Why Choose Tamron E Mount Lenses?
There are several compelling reasons to consider Tamron E mount lenses for your Sony (or other compatible) camera:
Excellent Value: Tamron lenses often offer comparable performance to first-party lenses at a more competitive price point. This makes them an attractive option for photographers who are looking for high-quality optics without breaking the bank.
Wide Selection: Tamron offers a diverse range of E mount lenses, ensuring that you can find the perfect lens for your specific needs and shooting style.
Continuous Innovation: Tamron is constantly innovating, developing new technologies and features to improve their lenses. This commitment to innovation ensures that you're getting the latest and greatest in optical technology.
Trusted Brand: Tamron has a long history of producing high-quality lenses, and their reputation for excellence is well-deserved.
Choosing the Right Tamron E Mount Lens for You
Selecting the right lens depends on several factors, including your budget, shooting style, and specific needs. Consider the following:
Focal Length: Choose a focal length that suits the type of photography you enjoy. Wide-angle lenses are great for landscapes and architecture, while telephoto lenses are ideal for wildlife and sports.
Aperture: A wider aperture (smaller f-number) is better for low-light shooting and creating a shallow depth of field.
Zoom vs. Prime: Zoom lenses offer versatility, while prime lenses typically offer better image quality and low-light performance.
Tamron E Mount Lenses: A Perfect Partner for Your Creative Vision
Whether you're a Sony shooter looking for a versatile zoom, a high-performance prime, or a specialized lens for macro photography, Tamron has an E mount option worth considering. Their commitment to quality, innovation, and value makes them a compelling choice for photographers of all levels. So, explore the Tamron E mount lineup, find the perfect lens to complement your camera, and unleash your creative potential. Whether you're searching for an E mount Lens, a Sony E mount Lens, a Canon E mount Lens, a Nikon E mount Lens, an E mount Lens for Nikon, an E mount Lens for Canon, or an E mount Lens for Sony, Tamron offers a range of options that could be the perfect fit for your photographic needs.
Read Full Blog - Expanding Your Creative Vision with Exceptional Optics
#E mount Lens#Sony E mount Lens#Canon E mount Lens#Nikon E mount Lens#E mount Lens for Nikon#E mount Lens for Canon#E mount Lens for Sony
0 notes
Text
No, OM System Isn't the Only Brand That Can Stand Up to Wet Weather
Late last year, we announced new changes to our reviews system. This is on top of all the other testing that we’ve done for years and called on the industry for. As it is, we’re constantly revamping our system of camera reviews. Today, we’re beginning the start of calling out what we believe to be falsehoods in the photography world. And this one has to do with a false statement about wet…
#Canon EF to Sony E mount Metabones adapter#digital camera world#insurance#ip durability#ip52#ip53#ip54#leica#lenses#LensRentals#nikon#OM SYSTEM#panasonic#sigma#sony#tamron#weather resistance
0 notes
Text
#Aerial Photography#BIONZ XR Image Processing Engine#Drone Photography#High-Resolution Sensor#Interchangeable E-Mount Lens System#Lightweight Design#Mountain Photography#Nature Photography#Remote Operation#Sony Camera Remote SDK#Sony ILX-LR1
0 notes
Text
THIS MURAL OF MASA KHADER IS ON A WALL AT CASTLEWOOD PLACE
Masa Khader, along with her family, tragically lost her life in an Israeli airstrike on their home in Rafah, Gaza Strip on 21st October. The airstrike claimed the lives of Masa, her 4-year-old sister Lina, and their parents, Loay Khader and Samar al-Atras
BY EMMALENE BLAKE Finding information about this mural online proved challenging. Masa Khader, along with her family, tragically lost her life in an Israeli airstrike on their home in Rafah, Gaza Strip on 21st October. The airstrike claimed the lives of Masa, her 4-year-old sister Lina, and their parents, Loay Khader and Samar al-Atrash. Samia al-Atrash, Masa’s aunt and the woman seen cradling…

View On WordPress
#29 March 2024#climate change#COVID-19 pandemic#EMMALENE BLAKE#Fotonique#FX30#Gaza Strip#George Floyd#healthcare workers#iconic figures#Infomatique#Israeli airstrike#Kellie Harrington#LGBTQ+ rights#Masa Khader#Mural#Palestinian flag#Rafah#representation#Sigma 24-105mm lens EF Mount adapted for E-Mount body#Sinéad O’Connor#social justice#Sony#William Murphy
1 note
·
View note
Note
Hi Froggy,
I hope you've been well! I wanted to reach out and first say that you inspired me many years ago to rescue a corgi! She was a grump, I think she may have taken her name (Elphaba) too literally. She recently crossed the rainbow bridge, but she was such fun and a joy. I hope our pups are playing together, somewhere peaceful.
I have a question unrelated to stumpy Corgis. I'm a veteran birth doula and an aspiring birth photographer! I've been trying to research cameras, lenses, and all sorts of technical stuff. I'm leaving towards purchasing the new Nikon ZF, because of the purported low-light capabilities.
Lenses are throwing me completely.
Do you have any guidance or resources to help a newbie like myself? Not really looking for an in-depth answer (I know how complicated things can get), but maybe a general push in the right direction?
If you don't want or can't answer, no hard feelings! I enjoy just seeing your posts on my dash and I hope the rest of your year is amazing and calm!-Steph
(continued...)
My budget is pretty flexible, since I am an independent contractor the expense would be tallied towards my taxes. But that being said, maybe $1-3k? I know it's important to invest more into lenses!
Usually, I am in a hospital, and lighting is extremely variable. I would be shooting mostly in low-light before baby is born. During delivery and after there is usually a spotlight or fluorescent lighting. The low lighting is exactly why I was looking at the new ZF, but if you have suggestions on that too I'm happy to hear them!
It's very cramped when the baby is born, most medical and support staff are clustered around the laboring person.
Warning! A lot of birth photos will have baby crowning or blood. It's a messy business, so I don't want to trigger you if you're sensitive to those sorts of images.
I will not be able to be directly next to the laboring parent, more than likely I'll be a few feet away, possibly behind the parents or standing on a stool.
After the baby is born, I'll be able to get closer to both parents and baby!
Here's a portfolio that is close to what I would like to provide (once again TW for blood and crowning):
https://www.sarahginderphotography.com/birth-photography-north-new-jersey
I cannot thank you enough for any help or advice, this whole endeavor is like learning a new language!
----------------------------
Note from Future Froggie...
I went way overboard on this response, as usual. I have decided I'm going to break it up into 3 parts.
First, an encyclopedia of lens terminology.
Second, a camera and lens buying guide.
Third, practical advice for shooting in cramped rooms with tricky lighting conditions.
While this will be geared towards the original ask, I think this could be helpful to a lot of people. So, let's learn about lenses!
--------------------------
Lenses throw everybody, just because there are so many options. It can be overwhelming to look at a picture like this and wonder what will suit you best.

It's a lot of pressure too, because lenses are more important than the camera in a lot of ways. Interchangeable lenses are probably the biggest advantage big cameras have over smartphones these days.
But I think I can help get you up to speed.
The following terms are photospeak you might hear in camera and lens reviews and if you aren't familiar with them, it can make it difficult to figure out what camera and lens to purchase.
I tried to put these in an order that makes sense, but some terms relate to other terms and you may have to read the list twice to make sure you understand how everything mushes together.
Froggie's Encyclopedia of Lens Terms
Lens Mount
Every camera has a specific lens mount. Sony calls theirs the E Mount. Nikon has the F Mount (older) and the Z Mount (mirrorless). So you need to make sure the lens you are looking at is compatible with the mount on your camera.
Mirrorless cameras all upgraded to a mount with a "short flange distance." Going without a mirror allows the lenses to be closer to the sensor.
Long story short... Short flange distance = easier lens design = sharper/lighter lenses.
However, if you want to use older DSLR lenses, there are adapters for Nikon and Canon that allow you to do that.
Aperture
"Aperture" is an opening at the front of the lens. It gets bigger to let in more light or smaller to restrict light.

Wider apertures have a shallower depth of field, causing blurry foregrounds and backgrounds outside the plane of focus. Smaller apertures expand the focus area to keep more stuff from being blurry, but they let in much less light and are difficult to use in dark environments.
Aperture can be a creative decision or it can be a technical decision or it can be a mix of both. If you need a blurry background, use a wider aperture. If you need everything in focus, use a smaller aperture. If you need more light in a dark scene, open it up.
F-stop
"F-stop" is a number representing how big the aperture is. A lower number is a bigger hole. Higher number is a smaller hole. It is helpful to memorize f-stops as they are not easily divisible. Cameras generally allow third stops, half stops, and full stops.
These are all a "full stop" apart.

Stop Down/Open Up
When someone says to "stop down" a lens, they are telling you to make the aperture smaller or use a higher f-stop number.
If they say to "open up" they are saying to make the hole bigger or lower the f-stop number.
Depth of Field (DoF)
Depth of field refers to how much of the photo is in focus. Things in front of the plane of focus will get blurrier and blurrier and things behind the plane of focus will get blurrier and blurrier. A shallow depth of field means only a tiny sliver of your image will be in focus. A deep depth of field means almost everything will be in focus.
The wider the aperture, the shallower the depth of field.
The smaller the aperture, the deeper the depth of field.

Focal Plane or Plane of Focus
The focal plane is the sharpest point within the depth of field. You can imagine an imaginary section of 3D space where things within the depth of field are sharp and things outside are blurry. The farther away from the focal plane, the blurrier they will get. But the focal plane is not always dead center of the depth of field.
Typically, at close distances, things will be sharp half in front of where you focused and half behind where you focused. As things get farther away, that changes to more 1/3 in front and 2/3 behind. The ratio changes even more at greater distances, but the 50-50 and 1/3-2/3 ratios are typically what photographers try to remember.
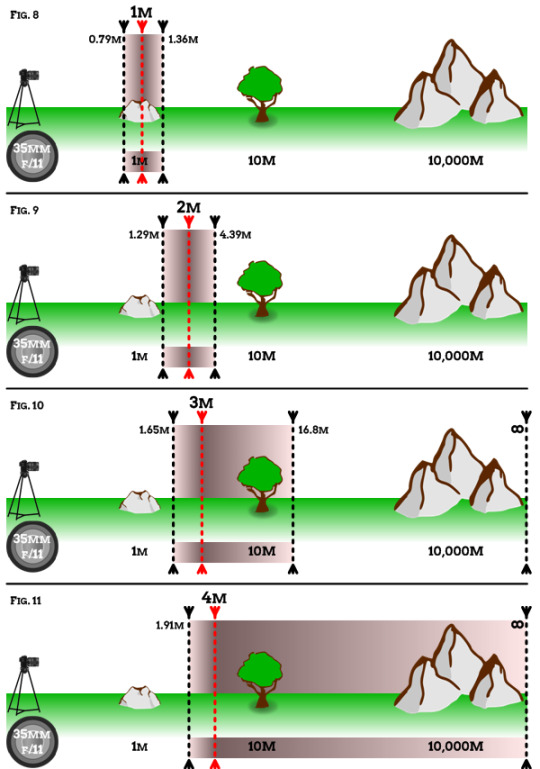
Shallow Depth of Field
The focal plane is something you need to be very aware of at close distances with a wide aperture—as the depth of field can end up as a tiny sliver.
Let's say you are only a few feet away from a baby and you have the aperture set at f/1.2. You focus on the nearest baby eye, and then you notice its ears and nose are out of focus.
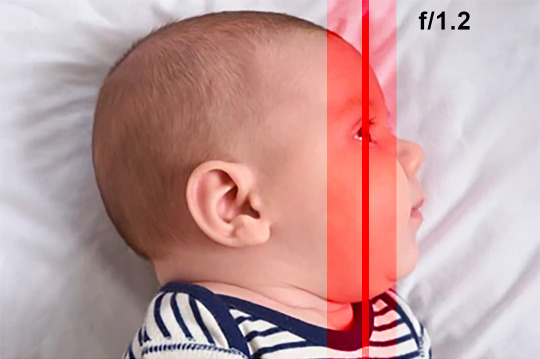
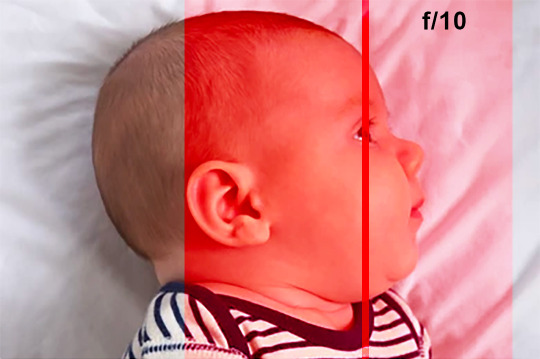
The plane of focus and shallow depth of field are causing this issue. This might be a worthy compromise if you are in a dark room and your ISO is very high and you are worried about too much noise.
However, if you can use a flash or some kind of lighting, you can stop down your lens and increase that depth of field around the focal plane.
Bokeh
Bokeh is the quality of the blurriness. Some people are more obsessed with how good the blurry parts of the photo are more so than the in focus parts. Bokeh is typically judged by "bokeh balls" which are just out-of-focus lights in the background. While I like attractive bokeh balls as much as the next photographer, I will admit this is one of the sillier aspects of photography.

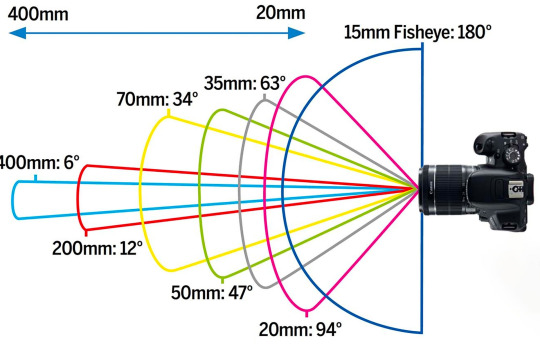
Field of View (FoV)/Angle of View
This is how much stuff you can fit in frame at a given distance. Wide angle lenses can fit more stuff in at a shorter distance and telephoto lenses can fill the frame with stuff that is farther away. The focal length of the lens determines the field of view. The focal length is designated by millimeters and the field of view by degrees.
Focal Length
Technically, this is "the distance between the lens's optical center and the camera's sensor."
In simpler terms, this is how you determine the field of view of a given lens.
A short focal length, like 10mm, will have a wider field of view. You have to be very close to your subject to fill the frame with them.
And a longer focal length, like 500mm, will allow you to fill the frame with your subject from farther distances.
Typically all lenses are designated by their focal length. If someone says, "Hand me the 50" they mean a 50mm lens.
35mm Equivalent
Not every camera has the same sized sensor. So when we talk about lenses, we need a reference to help us understand how a given lens will behave. A 50mm f/2.8 lens does not have the same field of view or depth of field when placed on different sensors. So, we need a standard for comparison.
The standard that is used is the "full frame" sensor which is roughly the same size as a 35mm piece of film.
Anything smaller is considered a "cropped sensor."
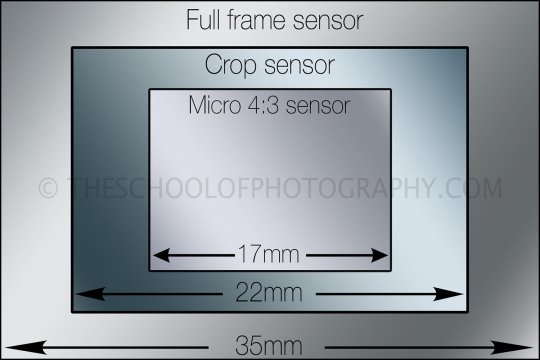

Those cropped sensor cameras have a "crop factor"—a simple multiplier that helps you understand how lenses compare. And when you use this multiplier it tells you the "35mm equivalent."
Confused yet? Yeah, sorry, it would be easier if camera manufacturers chose metrics that didn't change depending on the sensor, but this allows them to make their cameras and lenses seem more impressive in the marketing.
There are two main cropped sensors for ILCs. (Interchangeable lens cameras.) APS-C and Micro Four Thirds. They have a "crop factor" of 1.5x and 2x respectively. The Micro 4/3 sensor is half the size of Full Frame, therefore it has a 2x crop factor. And when you apply this crop factor to the aperture and focal length you can determine how a lens will behave.
For example, a 50mm f/2.8 lens on a micro 4/3 sensor would behave the same as a 100mm f/5.6 lens on a full frame—as 100mm is 2x 50mm and f/5.6 is 2 stops above f/2.8.
As you can see, the Micro 4/3 lens is not going to do as well in low light. The iPhone boasts an aperture of f/1.8 on its main lens, but when you figure out the 35mm equivalent, it's more like an f/8 lens.
I went to all the effort to explain this because it demonstrates that larger sensors allow you to work in cramped spaces with less light. If you want to use a 50mm in a hospital room, you probably can on a full frame. But on a Micro 4/3 you might need to be out in the hall because your lens is acting like it is 100mm. So the Zf would be a good choice in this regard.
Camera Shake
This is the bad kind of blurry. Humans are not tripods, so when you are handholding a lens, you need to make sure your shutter speed is fast enough to freeze the action of your image. Camera shake is very easy to control on wide angle lenses and very difficult to manage with telephoto lenses.
Reciprocal Rule
The reciprocal rule states that in order to get sharp photos without blurry camera shake, you must set your shutter speed to 1 over twice the focal length of your lens. So if you have a 100mm lens, you need to set your shutter speed at 1/200 to be safe.
This rule breaks down at a shutter speed of 1/50 if there is anything moving in your image. So if a dog is running or a car is driving by, it will have a motion trail, but at least it won't be due to your shaky hands.
Image Stabilization
This is a feature some lenses have that helps reduce camera shake. Image stabilization can counteract shaky hands and let you get sharp photos with a much slower shutter speed. Newer cameras have sensor stabilization which does the same thing. And if you pair up a stabilized sensor with a stabilized lens, it is almost as effective as using a tripod.
Stabilization is measured in stops. You might hear a lens has 4 stops of stabilization. That means you can handhold the lens and not get camera shake with a shutter speed 4 stops below the reciprocal rule. So for that 100mm lens, that 1/200 becomes roughly 1/12. And if your sensor has 4 stops, you could handhold a shot for nearly a second without any shake.
However, at shutter speeds that slow, if anything in the frame is moving, they will probably have motion blur. But for still life scenes, or maybe a sleeping baby, this can be very handy if you don't have a tripod with you.
If being able to handhold at lower shutter speeds seems important, then you might want to seek out a lens with stabilization and pair it to a camera with sensor stabilization for maximum stable-osity.
Lens Compression
Lens compression is kind of a myth, but I think we still call it compression because it is easier to explain to beginners than optical physics. The lens doesn't really compress anything, it's actually a matter of distance and the aforementioned physics. But I'm going to go with the easy explanation for now.
Lens compression is a phenomenon seen with different focal lengths. If you take a photo with a 500mm lens, the background will seem to compress with the foreground. Thus objects in the background will seem much larger in size.

This also happens with faces.

Wider lenses exaggerate distance. At 10mm, the lens would only be a few inches away from someone's face.

From the lens's point of view, the ears are several times farther away from the lens than the tip of the nose. So the lens is like, "Your ears are really far away! And far away things are really small, right?" So the lens gives us a big nose and small ears and makes us look a bit alien.
But at 100mm, the lens will be several yards away.

From this perspective, the lens feels like your ears and your nose are nearly the same distance away. And the lens is now like, "Things that are the same distance away do not get bigger or smaller." The lens seems to compress or flatten the face, causing a more flattering appearance in the image.
Minimum focus distance
This is sometimes called the working distance. This is how close you can get to your subject while maintaining focus. If you get too close, your camera will just hunt and freak out perpetually until you back up and it can lock on again. This isn't always advertised prominently for lenses, so you need to make sure the lens will be able to focus in the space you plan to use it.
Extension Tubes
Sometimes called "macro extension tubes." These are spacers you put between your camera and lens to decrease the minimum focus distance. In some cases you can even turn a normal lens into a macro lens. These tubes are able to stack and the more you put on, the more into the macro realm you can go. They come in smart and dumb versions. The dumb ones require you to manual focus whereas the smart ones can still use the autofocus system. I highly recommend the smart ones, as they are not too much more expensive.
Lens Imperfections
There are a few imperfections that can plague all lenses and their quality is sometimes judged by how well they mitigate those imperfections. Here are some of those attributes.
Lens Distortion
As lenses get wider, they allow a larger field of view by accepting light rays that are coming from the side of your lens. Let's look at this image again.
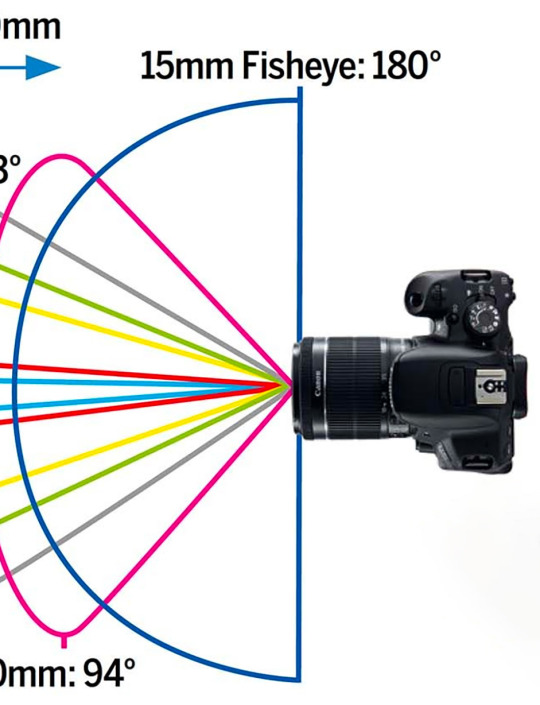
Your lens then has to correct those rays and send them to a square, flat sensor. If you look at the 180 degree fisheye, that entire arc has to be flattened and made square. And as good as optical engineering has become, the wider the lens, the harder it is to keep the image from distorting.
This is typically called "barrel distortion." Minor distortion can actually be corrected in editing software. Every lens has correction algorithms. Though sometimes it is best to embrace the distortion, like on a fisheye lens. Make the distortion a feature and not a bug.

Chromatic Aberration
This is the fancy name for color fringing. This is a defect in the lens that cause false colors to contaminate certain objects in a photo. Typically this happens around dark skinny things against a bright background, such as tree branches.
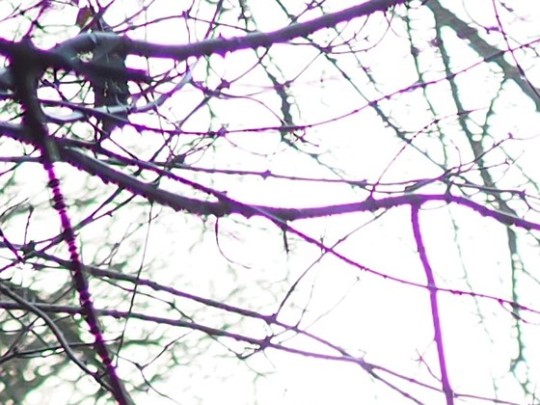

Modern lenses have nearly eliminated this, except for the super cheap models, but if you do end up with fringing, this can be easily corrected in Lightroom or Photoshop. And many lenses even have that correction built in and all you have to do is check a box.
Sharpness
You might not think of sharpness as an optical flaw, but no lens is perfectly sharp. And the quest to make a perfectly sharp lens involves engineering those optical flaws to a minimum.
A "sharp lens" is one with incredible fidelity. Even zoomed in beyond 100%, sharp lenses will show great detail. If you can't get close to the subject and need to crop your photo later, having a sharp lens can make up for the loss in resolution—as you can upscale without much loss in quality. If you plan to make large high quality prints, a sharp lens will help more than tons of megapixels.
That said, if you truly want to get the most out of a high megapixel camera, a sharp lens comes in handy here too. A smartphone may boast in the marketing as having 200 megapixels, but it has a tiny plastic lens. So even though it technically has 200 megapixels on the sensor, the lens will give it the equivalent of maybe 8-10 megapixels worth of detail. People forget, the lens has a resolution as well, and if the lens cannot resolve 200 megapixels, you aren't going to get a 200 megapixel image.
A sharp lens will allow for more detail than higher megapixels. In some cases you need to double or triple the number of pixels to see an increase in detail. Whereas you can put a super sharp lens on a 12 megapixel camera and blow any smartphone out of the water.
And if you put a sharp lens on a 50 megapixel camera, you can almost see into skin pores.
So... sharp = more detail. And more detail gives you greater cropping power for when you can't get close to babies.
Now, I am obligated to say that some photo nerds chase sharpness as if it is some holy grail. They need the sharpest lens so all of their pixels are perfect at 100% zoom even though no one ever looks at an image that close. There are amazing photos that have been blurry. There are amazing photos taken with 50 year old vintage glass. Sharpness is just another tool. If you need to crop. If you need to upscale. If you need to print large... it is a great help. But nearly every lens made for a modern mirrorless camera is "sharp" to some degree.
So, if you need extra sharpness for certain situations, do your research and find a lens that is sharp as can be. But sharpness should be like 8th on the list of priorities.
Soft Lens
A "soft" lens is how a non-sharp lens is referred to. Most modern optics for mirrorless cameras have some degree of sharposity.
Sharpitude.
Sharp...ness.
So you don't need to worry too much about getting a detrimentally soft lens unless you go super duper budget. This is why I usually recommend people skip the "kit lens" unless they absolutely can't afford anything better.
Though sometimes people purposely get vintage lenses because they don't like sharpness and prefer the "character" of older lenses. The imperfections can achieve a different artistic goal. Though this can also be achieved through lens filters... or Vaseline.
I'm looking at you, Barbara Walters.

Sharpness at the Corners
When I read that in my head just now I said it the same way I do "Panic! at the Disco."
Engineers will prioritize sharpness at the center of the lens since that is where most of the interesting stuff tends to be. But also, the light rays at the center tend to be the most parallel as they head to the sensor, so they don't need as much correction. The rays coming from the sides have to be bent and manipulated to correct for distortion, so keeping things sharp at the corners can be a challenge.
Now, knowing that, and knowing how the aperture works, you can infer that when you stop down your lens and make the hole smaller, all of the light rays are constricted to a smaller area. This makes them easier for your lens to deal with, so if a lens has problems with corner sharpness, you can usually stop down to improve this. So if a lens is soft at the corners at f/1.8, you might be able to go to f/2 or f/4 to get better results.
Vignetting
Vignetting is a circular area of darkness at the perimeter of your photo. This is another side effect caused by the same things as soft corners. When correcting those non-parallel light rays, it causes them to travel an ever so slightly farther distance getting to your sensor. And the inverse square law tells us that light becomes dimmer as it travels longer distances.
This is very easy to correct. Usually your camera has a setting to correct vignetting if you are outputting JPEG files. And if you are shooting RAW photos, your editing software should have a check box to fix the vignetting—usually the same one that fixes chromatic aberration. This is usually called "lens correction" in most menus.
Also, same as with corner sharpness, stopping down your lens will usually fix this optically rather than with software algorithms.
Contrast
Contrast is probably the most important attribute to determine lens quality. Good contrast can make a soft lens look good. But lens contrast is not always consistent. It can get better or worse depending on the lighting in your scene.
The best way to test the contrast of a lens is to take a picture of something that is backlit. A person with the sun behind them is a great indicator. If they have no light on them, the person should fall into inky darkness. But if a lens has poor contrast, they will seem like a faded gray.
Focus Breathing
Focus breathing is a phenomenon where your focal length changes depending on how far away your subject is. It's usually not a big deal and most people don't even notice it, but if you ever do video, it can cause a few headaches. Some people can get annoyed because they feel they aren't getting the advertised focal length on the lens they bought. Like, if you get a 300mm lens and it only goes to 250mm for things super far away, that can be annoying.
This video explains it in detail.
youtube
Lens Types
Prime Lens
A "prime lens" has a fixed focal length and cannot be zoomed. Typically prime lenses are "faster" (wider max aperture) and sharper. Weirdly they can be very inexpensive or the most expensive. They can be extremely lightweight or weigh a ton. And if you want the sharpest lens possible or the fastest lens possible or both, it will be expensive and heavy.
Having at least one fast prime is usually recommended for any professional photographer.
Zoom Lens
A "zoom lens" allows you to zoom. Obviously. But there are few that go below an aperture of f/2.8, so less light gathering and you sacrifice a bit of sharpness. However, if you don't know how much space you will have to work with, the flexibility of a zoom can be invaluable.
Be warned, while a cheap prime lens can still take fairly good photos, cheap zooms are usually pretty terrible. There are plenty of reasonably priced zoom lenses to choose from, but if the price seems too good to be true, I would trust that intinct.
Wide Angle Lens
A "wide angle lens" is any focal length below 35mm. Wider focal lengths allow you to get more stuff in the photo at shorter distances. A theme you might notice with photography is that every benefit has a compromise or consequence to go with it. Wide angle lenses are wonderful if you are in a cramped space. They also make it easy to keep everything in focus. But as you go wider, distances become exaggerated and barrel distortion becomes more pronounced and harder to correct.
Things that are close to the lens seem huge and things farther away seem tiny. One trick to remember is things in the center of the frame will be less affected by distortion. Something to take into account when taking those smartphone selfies.
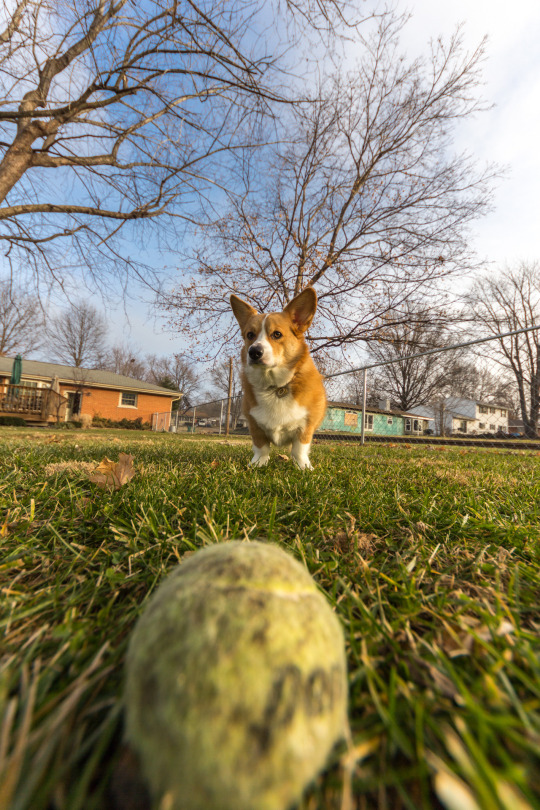

If you look, the ball looks huge in frame because it was only a few inches from the lens. Otis was literally smaller in frame than the ball despite only being about 2 feet away. However, he doesn't look all stretchy like the ball because he is centered.
Standard Lens
A "standard" or "normal lens" represents about the same field of view as the human eye. Generally around 40mm to 55mm on a full frame camera (there is some debate on this, but close enough). This is right about where you can take pictures of faces without the unflattering side effects of wide angle.
Telephoto Lens
A "telephoto lens" allows you to stand farther away and still fill the frame with your subject. Usually lenses 200mm and above are considered telephoto. These are often heavy and expensive.
Specialty Lenses
Ultrawide
This is just an extremely wide angle lens. At this point, you just except the massive amounts of distortion and embrace it. These lenses are extremely fun.
Medium Telephoto
These are sometimes called "portrait" lenses as well. They are a little more tele than standard and not quite tele enough for long distance photography. Usually in the 70-200mm range. This is the focal range that allows you to still be close to your subject but you are far enough away to get extra flattering lens compression on faces.
Superzoom Lens
A "superzoom" has an extremely large focal range. It can go from very wide to very telephoto. These are usually not wonderful lenses, although they have improved on mirrorless cameras in recent years. There are a few that could even be used professionally now. But most are just a huge mediocre compromise for vacation pix.
The cheap ones aren't fast, they aren't sharp, and every time you zoom people think your camera is having an erection.

If you are traveling and you have no idea what you might be photographing and carrying around a bunch of lenses is impractical, these have utility. But the larger the focal range, the more mediocre they get. Typically if the zoom range exceeds ~150mm you will start noticing that mediocrity. So a 70-200mm can be fantastic. But an 18-300mm will be very mid.
Macro
A macro lens is any lens that has 1x or more magnification. 1x magnification is a designation that relates the sensor size to how much of the subject fills the frame of your image. For 1x, that ratio should be 1:1.
So if you imagine a quarter lying on top of an image sensor, that's how big the quarter should be in your photo. 2x magnification would be like if a quarter doubled in size and you laid it on top of the image sensor. And so on.
Beware of lenses claiming to be macro and really only having a short working distance. 0.5x is not macro, but is sometimes advertised as so.
Tilt Shift Lens
This is a very niche lens. Most people know of it from the photos that make everyone look like they are in a miniature land.
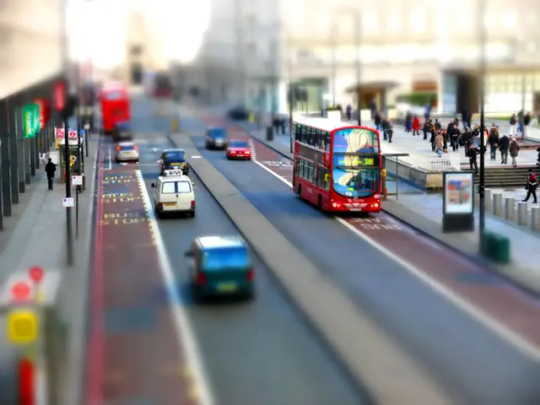

For every other lens, the focal plane is perpendicular. If you move the camera at an angle, the focal plane will match that movement. So what the tilt shift lens allows you to do is angle the focal plane so your depth of field goes in bonkers directions.
Product photographers love this because you can take a photo of an array of products from a 45 degree angle and keep everything in focus.

This image would be impossible to maintain complete focus of all the objects without a tilt shift lens.

In this example, without tilting the lens, the tip of the multitool is out of focus.

And now you can see the camera hasn't moved, but the lens is at a steeper angle. And you'll also notice the entire tool is in focus.
But wait, there's more! Did you forget about the shifting? Architectual photographers can use the shift function of the lens to correct perspective distortion and keep buildings looking straight.

Will this lens help in the photographing of infants?
Probably not.
But I bet you thought it was cool and are glad I included it.
Recommended Essential Lenses
I didn't know what to call this section. These are just the collection of lenses most photographers will try to acquire as they build out their kit.
Nifty Fifty
This is probably the first lens everyone should buy. Almost every brand has their own version. It is an inexpensive 50mm lens with a sub f/2 aperture. Canon's Nifty Fifty or "Plastic Fantastic" is probably the most famous example. It is only $125 and has an f/1.8 aperture.
This lens may not be the sharpest and it might have a lot of plastic-y, cheap feeling parts, but it is a wonderful way to get started with photography. You can use the wide aperture to experiment with bokeh and shallow depth of field. And the 50mm focal length is probably one of the most versatile. Not too wide, so people look normal, and not too tele, so you aren't a mile away from your subjects.
The Holy Trinity
The "Holy Trinity" is meant to describe the 3 lenses that can handle nearly every photographic task while maintaining professional quality results. Typically these lenses are all f/2.8 and are high quality zoom lenses. The 16-35mm, the 24-70mm, and the 70-200mm.
Most photographers can accomplish just about any task with these lenses in their bag.
Froggie's Holy Hexagon
That said, if I had an unlimited budget I would actually have 6 lenses to cover everything. Beyond the Holy Trinity, I would get a fast prime, an ultrawide, and a macro lens.
A fast prime can see in the dark and has more background blur. The nifty fifty would work great for this.
An ultrawide is one of the most fun lenses you will ever use, even if it distorts everything to a crazy degree and isn't useful very often. It is great for breaking you out of photographic ruts and can really get the creative juices flowing.

And a macro lens is not just useful for making tiny things big. It also allows you to focus at any distance. Sometimes you just need to get a tad bit closer than your other lenses will allow. Macro lenses are also pretty great portrait lenses and can serve multiple functions.

And if anyone is interested in sports or wildlife photos, a nice telephoto lens might be a seventh lens to consider.
I think that is the end of part 1.
I hope this was helpful. And I look forward to posting part 2 soon.
89 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey pukicho you still got that $1900 lens?
I'm not interested in buying it due to lack of money and reason too just seeing how its doing.
I haven’t sold it! It’s the trickiest sell doctor pukicho has ever had to do, because it’s both niche, and expensive!! But I WILL do it, and once I do, I will tell all of you. Also I’m bringing it down to $1800 so if u have a Sony E mount, LETS DO THIS!!
5K notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
7 Artisans 85mm f/1.8 AF Full Frame Lens For Sony E Mount My New Favorite Prime
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi again! i am going to buy the nikon z7 tomorrow and before i commit I just want to ask if its definitely a match with the mount on 7artisans, the 50mm 0.95 from sony? ^^
Good question! I'm not 100% sure as I already had Nikon lenses amd bought the Nikon adaptor, but a quick Google search says that if your Sony lens is an E mount you can get an adaptor for them to work on the Z mount Nikon xx
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’ve been asked to explain my kit and my workflow by @savage-daughter-of-nikitie.
I use either a Canon 80D, Canon 5D Mk IV or a Sony A7Riv with a sigma MC-11 mount converter. I also have a Canon 300D and a Canon 70D from both of which I have removed the internal infrared filter, so that I can shoot in the Infrared.
I have a number of tripods and LED light panels which I sometimes use, but for most general things I prefer to use natural light with perhaps a small reflector.
Lens-wise, my aviation photography is done using either a Sigma 60-600mm f/4.5-6.3 OS DG Sports or a Canon 100-400mm f/4.5-5.6L MkI.
For other general photography such as landscapes and when I do portraits, (which I don’t post here). I have a range of lenses but my favourites are:
* Canon EF 24-70mm f/2.8l USM
* Canon 50mm f/1.8
* Lensbaby Velvet 56mm f/1.6
* Canon EF-S 10-22mm f/3.5-4.5 (this won’t fit on the Sony / MC-11 combo)
For macro photography I generally use either a Sigma 105mm f/2.8 EX DG OS HSM macro or, very occasionally, a Canon MP-E 65mm 1-5x Macro with a lot of light and a macro rail.
I occasionally use a Newer variable ND e.g to slow flowing water and I have various intervalometers, and all of the Pluto Trigger and Dripper kit for water droplets or complex triggering.
I also use my phone camera more and more and then achieve effects in Lightroom, Photoshop or Topaz AI
My workflow varies depending upon the type of photography. By way of an example, for the flower studies my workflow is:
1. Photos were taken on a variety of kit, mainly my phone.
2. Import into Lightroom
3. Square crop the flower and rotate to get the best light/symmetry/arrangement.
4. Use Lightroom’s Subject Mask to initially mask the flower and refine using brush addition/subtraction
5. Duplicate and invert the mask to effectively mask the background
6. Set exposure, contrast, highlights, shadows, whites, blacks and saturation to zero. This removes the background allowing the flower to stand alone but gives me the option to recover the background should I wish to later.
7. At this point any issues with masking become very noticeable so I will often refine both flower and background masks once more.
8. Return to the flower mask and set the exposure, contrast, white balance, response curves, saturation and sharpness as required, to make the flower pop.
9. I often apply radial masks to even the exposure or highlight the inner or outer sections at this point.
10. Use the heal tools to remove pollen specs, imperfections or other issues. Lightroom’s content aware AI healing is extremely good these days.
11. I then catalogue, add metadata, and export to a number of private and public storage and distribution services.
I have two projects I want to start as we move into winter, life permitting.
Firstly, I want to try to do some star trails. Near where I live there is a park on an escarpment running east west, with a couple of stone crosses that can be photographed from the south with the Polaris (the North Star, which is the centre or rotation in the night sky) just above the top of one of them.
I also want to play more with my 70D and do some more IR photography. This makes warmer parts of the scene brighter and cooler darker and can lead to some eerie effects. I have a long standing desire to visit a certain chateau in France and photograph it in IR.
This is probably way more than you were asking for and I’m not sure is this is what you wanted to know, but I hope it helps.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

Art doesn’t require the best equipment, I know… and many wonderful artists start with nothing. I was lucky to find a beautiful, video-capable camera to expand on and play with my pre-existing understanding of photo and video arts.
I love Nikii. She’s a beautiful camera with such potential I could only ever dream of fully harnessing.
I always imagined a Sony for me… and Sony’s E mount system does fill me with envy at times. This Z6ii is a full-frame goddess equipped with everything I could ever hope for to taste the mirrorless world from my prior film and consumer digital camera experience.
Besides, the Z system has lenses hailed as the most crisp and beautiful glass on the market.
��also, yes… I will be buying a cropped sensor Sony for everyday experimentation with much cheaper lenses. The Sony a1 line and FX line are my dream cams after all… full-frame anyway.
We won’t talk about medium format today.
This return to form required letting go of other people’s expectations, imposed values and even getting rid of some unwanted things I let people convince me to invest in; a drum kit for one. My only comfortable instruments were always my voice, my heart, a pencil, qwerty keyboard and a camera… so I now have mics and cameras with pencils and qwerty keyboards as support.
It sucks to lose your heart in self-sacrifice believing it’s for a common community goal.
Now, with therapy and introspection I find again my roots of self-expression. Nikii sets that beautiful road before me and I’m forever grateful for her presence in my life. Promise I’ll focus on a Z8 line upgrade before I cheat with Sony.
Okay… well maybe I’m polycamera-ous.
#art therapy#photography therapy#photography lovers#self expression#self care#photography#healing#nikon z6ii#nikon mirrorless camera#z6ii#love
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Beautiful Gray Wolves West Yellowstone Montana Winter Snow Wolfpack Sony A1 ILCE-1 Fine Art Wolf Apex Predator Photography! Canis Lupus Sony Alpha 1 & Sony FE Telephoto Zoom 70-200mm f/2.8 GM OSS E-Mount Lens SEL70200G West Yellowstone Elliot McGucken
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sony embraces the e-mount competition because it assumes that alpha is best
Since Soni launched her first full-frame Alpha Mirrorless camera, Original Sony A7 and A7RIn 2013, the mirrorless camera space has changed dramatically. There has been no increase in competition with Canon, Nikon, Panasonic and others in 2018 and 2019. “We are very happy that the market is expanding.” Petpixel At the CP+ Show in Yokohama, Japan in February. “Creators’ behavior is diverse,” Oshima…
0 notes