#SSO ID Information
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Rajasthan SSO ID is a unique digital identity that enables citizens to access various government services and schemes. It is a 10-digit ID that is issued after registering on the official SSO portal. The ID is used to authenticate and authorize citizens' access to various government services, including e-governance, online payments, and more. With an SSO ID, citizens can track their applications, pay bills, and access various services in a secure and convenient manner. The ID is also used to provide personalized services to citizens, making it easier for them to access essential services and benefits.
0 notes
Text
youtube
I have too many thoughts on The Great Gatsby (2013)
Music by Molly Noise (She/Her)
YouTube | Podcast | Patreon
This video sees me delving into the 2013 adaptation of The Great Gatsby directed by Baz Luhrmann; a film that many have regarded as a definitive version of F Scott Fitzgerald's original novel, while others regard it as a dubstep-laden imitation of the literary classic. Which one is it? Settle in and find out, old sport!
Work Cited:
Agur, Colin. "Negotiated Order: The Fourth Amendment, Telephone Surveillance, and Social Interactions, 1878–1968." Information & Culture 48.4 (2013): 419-447. https://conservancy.umn.edu/bitstream/handle/11299/182084/Agur%20-%20I%26C%20-%20Negotiated%20Order.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
“Baz to Make ‘Gatsby’ Choice.” The New York Post, Achived through the Wayback Machine, 10 Feb. 2011, archive.ph/20130111073735/www.nypost.com/p/pagesix/baz_to_make_gatsby_choice_I5ngKh4aqSwiEmZh6H0iKJ#selection-2097.0-2097.27.
Beaton, Kate. “Great Gatsbys.” Hark! A Vagrant, 10 May 2013, www.harkavagrant.com/?id=259-. Accessed 25 July 2023.
“Elvis (2022) and the Utter Mediocrity of Biopics.” Broey Deschanel, Youtube, 27 Sept. 2022, youtu.be/Fu96gDcrEeU. Accessed 25 July 2023.
Ferriss, S. (2018), Refashioning the Modern American Dream: The Great Gatsby, The Wolf of Wall Street, and American Hustle. J Am Cult, 41: 153-175. https://doi.org/10.1111/jacc.12869
Fitzgerald, F. Scott. The Great Gatsby. Charles Scribner’s Sons, 1925.
Kroenert, Tim. “Baz Luhrmann versus the God of Capitalism.” Eureka Street, vol. 23, no. 11, June 2013, pp. 25–26. EBSCOhost, search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=sso&db=a9h&AN=90006908&site=ehost-live&scope=site.
Luhrmann, Baz, et al. The Great Gatsby Screenplay. 2013, stephenfollows.com/resource-docs/scripts/greatgatsby_sp.pdf.
MacLean, Tessa. "Preserving Utopia: Musical Style in Baz Luhrmann's The Great Gatsby." Literature/Film Quarterly 44.2 (2016): 120-131.
McGirr, Lisa. The war on alcohol: Prohibition and the rise of the American state. WW Norton & Company, 2015.
Miller, Alyssa. “Baz Luhrmann Really Is the ‘Stanley Kubrick of Confetti’ and This Is Why.” No Film School, 11 Nov. 2022, nofilmschool.com/baz-luhrmanns-editing-and-visual-style.
Noer, Michael. “No. 14 Gatsby, Jay.” Forbes, 13 Apr. 2010, www.forbes.com/2010/04/13/great-gatsby-bio-opinions-fictional-15-10-fitzgerald.html?sh=672907174535. Accessed 25 July 2023.
Piff, P. K., et al. “Higher Social Class Predicts Increased Unethical Behavior.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 109, no. 11, Feb. 2012, pp. 4086–91, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1118373109.
“Searching for Sugar Man (2012) - Full Cast and Crew.” The Internet Movie Database, Amazon, 2012, www.imdb.com/title/tt2125608/fullcredits/?ref_=tt_cl_sm. Accessed 25 Aug. 2023.
Seitz, Matt Zoller. “Baz Luhrmann Is the Stanley Kubrick of Confetti.” Vulture, 9 Nov. 2022, www.vulture.com/2022/11/baz-luhrmann-knows-hes-the-stanley-kubrick-of-confetti.html.
Stewart, Jack. “The Cars of the Great Gatsby.” The Daily Drive | Consumer Guide®, 16 May 2013, blog.consumerguide.com/the-cars-of-the-great-gatsby/.
#the great gatsby#jay gatsby#nick carraway#daisy buchanan#tom buchanan#f scott fitzgerald#gatsby#nick x gatsby#releasethemckeecut#baz luhrmann#the great gatsby 2013#video essay#Youtube
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Makes The Gem Portal Login Secure and User Friendly?

1. It should be safe to get into GreM.
When you log in, be careful:
Some information about your sales and business may be hidden.
You can't sign in until you buy something. Some people don't like it. To protect people's privacy, it keeps a close eye on them. People are more likely to join if they trust each other.
2. Things you can do to keep your GeM Portal account safe
a) Looking at an item (MFA)
These are the things that GeM users have to show about themselves:
Name and key of someone.
You should still be able to use the phone number or email address you used to make the account.
This card says that you work for the government.
You can feel better about the things you buy if you use a digital signing certificate (DSC) and e-sign.
b) A place to keep coins safe
People who go to the website need to have strong passwords. For them to work, they need numbers, letters (big and small), and other icons. Here's how to keep the keys safe. Roles (RBAC) decide what people in this case can see. When you buy, own, or are in charge, you can do different things. Because of this, there aren't many safety risks.
d) Captcha and other security measures are used to keep hackers out.
Cryptographic key exchange (CAPTCHA) makes sure that only real people can log in. Everything will be safe if you use Security Layer (SSL). Use SSL to protect your information when you pay or sign in to the GeM page. If you keep this a secret, only the right people will be able to see it. This will protect your privacy.
f) Automatic Logout When Not Used
GeM logs people out right away if they don't do anything within a certain amount of time. The person is less likely to let someone else in without getting out first. The word "DSC" in English means "digital signing certificate." We're going to look at this. GeM checks with DSC to make sure the information is right and can't be changed before doing business or signing important papers.
(h) A lot of moving and checking
The GeM page's security is checked often to make sure it follows the most current rules.
3. Parts of the GeM Portal that are simple to use Type in your password.
GeM works hard to make signing in quick and easy, even though safety is very important.
1) Single Sign-On (SSO) is a service People who use SSO only have to log in once to get to a lot of services. They don't need to type their passwords over and over. In this way, the process goes better. Making the sign up process easy.
2) IDs based on Aadhaar make it easy for people who buy from the government to sign up. People who want to sell can quickly sign up with their PAN. The place where laws start Check what you think you know about a business.
3) A simple look that gadgets can handle GeM login works on phones and computers, so it's easy for people to join.
4) More than one language to talk to each other if you know more than one language, you can use the page.
5) Forgot your email address? Get it with an OTP. People can quickly change their passwords because it's easy to get back in.
6) It's easy for many computers to use. That lets you use GeM from anywhere. It works on Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Microsoft Edge on Windows PCs.
7) Help with bugs and customer service People who can't join can get help from other users or the help line. It takes place every day. A lot of people come in after a long time.
4. Common Login Issues and Troubleshooting
Q1: I have a hard time remembering my GeM pin. How can I get it to work again?
Solution: When you click "Forgot Password," enter your registered email address or phone number. Then, to make a new password, follow the steps for OTP proof.
Q2: I tried to log in several times but failed, so my account is now locked. What should I do?
Solution: Your account could be locked if you kept typing in the wrong password. You have 15 minutes to either try again or use an OTP to change your password.
Q3: The OTP won't go to the number I gave you, right? What should I do?
Solution: Make sure the number on your smart phone is correct. Also, check your trash or junk box if you used an email OTP. To stop it, ask GeM for help.
Q4: Easy to change the email address or phone number I signed up for GeM with.
When you log in, you can change your picture. You might need to use an OTP to confirm the changes for safety reasons.
Q5: When I try to sign in, I see "Session Expired."
You might not have done anything or your plans might have changed. There are two ways to log in again: clear your cookies or start over with the page.
People who work for the Indian government, public sector units (PSUs), and autonomous bodies can buy and sell things and services online through the Government e-Marketplace (GeM).
How to Get into the GeM Portal
People who buy from the government GeM can only be used to buy things for the government. People from the following groups can buy:
Departments of the Centre and the State Government
Government-run businesses
The government and groups that work alone
Schools, colleges, and study groups
Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs)
Municipal Corporations and Government-Linked Organizations
If you work for the government, you have to use either your official email address or an ID that is based on Aadhaar to sign up.
2. Sellers and Service Providers
A lot of different types of businesses can join GeM to sell or provide services.
Producers and traders are the people who make or sell things that the government buys a lot.
MSMEs: These are tiny, small, or medium-sized businesses. Because they follow certain rules, MSMEs can buy things from the government more easily.
New businesses: Through the Start-up India program, well-known new businesses can join GeM.
An OEM is a company that makes something for the first time. They sell things that have their own brand name or patent on them.
The people who work for service providers do a lot of different work, such as IT support, human resources, coaching, transportation, building management, and plenty more.
Groups for men, hobby shops, and self-help groups (SHGs): People who live in the country and run craft shops can also get help from GeM.
3. Not having the chance to sign up
They might not be able to join the program if they don't meet the GeM compliance standards, if they don't have a recent GST registration (except for certain categories that are exempt), or if they fail verification. A company that the government has banned also can't join.
Conclusion:
It's safe and easy for anyone to log in to GeM online. The site has strong protection, digital signatures, automatic proof, and more than one way to prove who you are. This keeps bad people out. SSO, or secure one-sign-on, can be used in more than one language. It's easy to use the new one. Business and the government can use it this way. As long as you follow the rules, GeM is still a safe place to shop or do business. It's getting better. GeM makes it easy, quick, and safe for everyone to do business. GeM changes the way India gets things because it makes it easy for the government and public companies to do business together. No matter if they work for the government, a PSU, an MSME, a maker, or a service provider, GeM makes it easy and safe to buy things. If you meet the requirements and sign up for GeM, you can work for the government in many ways. For more details visit : https://bidhelp.co/
#RWRDC karnataka#northern railway tenders#bihar state electricity board#gujarat revenue department#earthwork tenders#delhi tenders#Secure login on GeM#Easy login on GeM#Effortless bidding on GeM#Consultancy services
0 notes
Text
How To: Configure Qlik Sense Enterprise SaaS to Use Azure AD as an IdP
Introduction
Establishing Qlik Sense Enterprise SaaS to use Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) as an identity provider (IdP) is key for companies aiming to streamline access control and authentication for users. Integration between Azure AD and Qlik Sense Enterprise SaaS allows organizations to take advantage of single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor Authentication (MFA), enhanced security features that improve user experience while increasing security simultaneously.

This detailed guide will take you step-by-step through the steps to configure Qlik Sense Enterprise SaaS so it authenticates users by using Azure A.
Prerequisites
Before starting, be sure to are:
An active Azure AD subscription
An Qlik Sense Enterprise SaaS account with administrative access
Permissions to sign up an application within Azure AD
A brief introduction of OAuth 2.0 as well as OpenID Connect (OIDC).
Step 1: Register Qlik Sense Enterprise SaaS in Azure AD
1.1 Access Azure AD
Log into the Azure portal (https://portal.azure.com).
Go through Azure Active Directory from the left menu.
Click on App registrations, then Click New registration.
1.2 Create a New Application Registration
Choose a name for the application (e.g., "Qlik Sense SaaS").
Under the account types that are supported choose Accounts in this organization directory only.
Under the Redirect URI section, click Web and type in the URL:
https:// .qlikcloud.com/login/callback
Click Register.
1.3 Copy Application Credentials
After registration Copy and store the data science information for future use:
Application (client) ID
Directory (tenant) ID
Step 2: Configure Client Secret
2.1 Generate a Client Secret
Click on Certificates and Secrets within the Azure AD application.
Under Client secret, select for a new client's secret.
Select a description, and then an expiration date.
Copy the secret value.
Step 3: Configure API Permissions
3.1 Assign API Permissions
Visit API permissions in the account of your Azure AD application.
Add permissions by clicking the Add button. Microsoft Graph - Delegated permissions.
Find and select:
openid
Email
Profile
offline_access
Select Add Permissions, and Grant admin permission.
Step 4: Configure Qlik Sense Enterprise SaaS
4.1 Access Identity Provider Settings
Log into Qlik Sense Enterprise SaaS as an administrator.
Navigate to Management Console - Identity Providers.
Click Create New, then select OIDC.
4.2 Enter Azure AD Configuration Details
Complete the fields required:
Issuer (Discovery URL):
https://login.microsoftonline.com//v2.0
(Replace"tenant_id" with Your Azure Directory ID)
Client ID (Paste your Application ID into Azure AD)
The Client Secret (Paste your generated secret client)
Authentication Method: Choose Authorization Code
Redirect URL:
https:// .qlikcloud.com/login/callback
4.3 Map User Claims
In the section titled User Claims Mapping Section, you can configure:
Sub - User ID
email - email
Name - Display name
Click Save to save the settings.
Step 5: Test and Verify Integration
5.1 Assign Users in Azure AD
Go to Enterprise Applications in Azure AD.
Choose which Qlik Sense SaaS application.
Click Users and Groups to add users and groups. Assign appropriate users.
5.2 Log into Qlik Sense SaaS with Azure AD
Open Qlik Sense Enterprise SaaS within browser.
Click Sign In with Microsoft.
Log in using in your Azure AD credentials and verify your account.
If the login succeeds, Azure AD is successfully set up to be the IdP to QlikSense Enterprise SaaS.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue 1: Authentication Error
Make sure the redirect URI is identical to the one to the settings in Azure AD and Qlik Sense settings.
Verify that the client's ID and secret are accurate.
Issue 2: User Not Found in Qlik Sense
Confirm that the user has been associated with an account in the Azure AD application.
Make sure you check the claim mappings in Qlik Sense.
Issue 3: Invalid Permissions
Make sure Admin Consent is granted In API Permissions.
Verify that email, openid profile and offline_access permissions are granted.
Conclusion
Follow this step-by-step guide to set up Qlik Sense Enterprise SaaS to utilize Azure AD for its identity Provider (IdP). This integration improves the security of users, their management and access control, while simplifying authentication using SSO. (SSO).
The implementation of Azure Active Directory with Qlik Sense SaaS gives users an improved user experience, improves the compliance of users, and simplifies identity management. If problems arise, examining the claim mappings API access rights, and redirect URIs can help you resolve the issue quickly.
Utilizing Azure AD's authentication capabilities companies can enhance both security and efficiency in the Qlik Sense training enterprise SaaS environment.
FAQs
Q1. Do I have the ability to configure the multi-factor authentication (MFA) in Qlik Sense SaaS users?
Yes MFA can be enabled MFA via Azure AD's Conditional Access Policies.
Q2. Does this integration work with user groups?
Sure, however you must to set up group claim mappings within Azure AD as well as Qlik Sense.
Q3. What is the consequence if the secret client expires?
You must create the new client key in Azure AD and update it to the Qlik Sense settings.
0 notes
Note
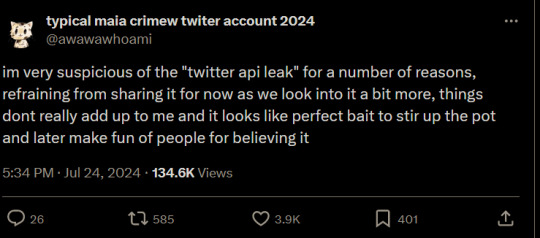
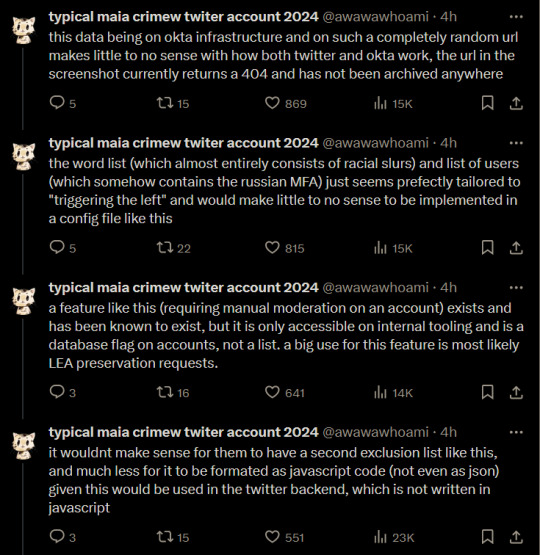
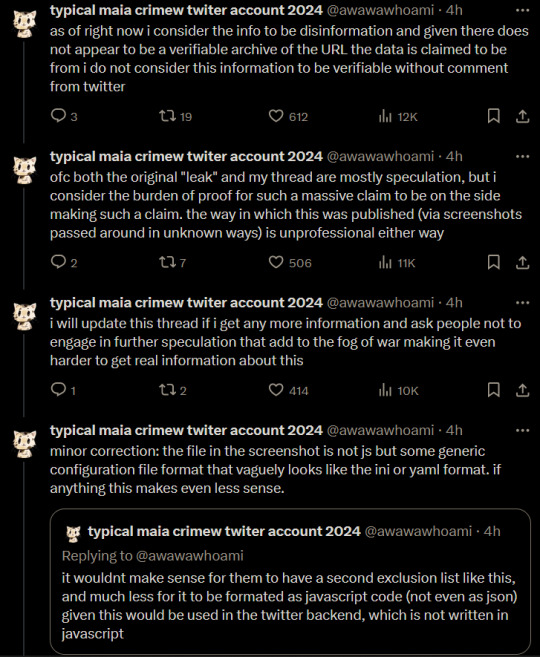
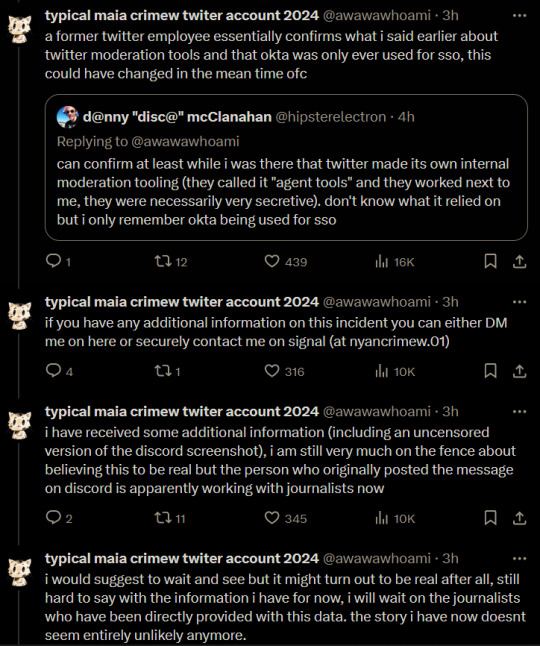
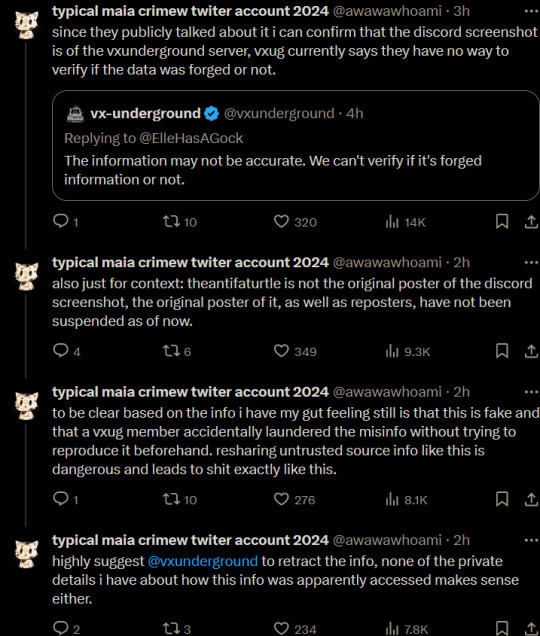
copy pasted behind the read more for screen readers since there is a character limit
ID: series of tweets that read as follows:
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
4h
it wouldnt make sense for them to have a second exclusion list like this, and much less for it to be formated as javascript code (not even as json) given this would be used in the twitter backend, which is not written in javascript
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
4h
as of right now i consider the info to be disinformation and given there does not appear to be a verifiable archive of the URL the data is claimed to be from i do not consider this information to be verifiable without comment from twitter
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
4h
ofc both the original "leak" and my thread are mostly speculation, but i consider the burden of proof for such a massive claim to be on the side making such a claim. the way in which this was published (via screenshots passed around in unknown ways) is unprofessional either way
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
4h
i will update this thread if i get any more information and ask people not to engage in further speculation that add to the fog of war making it even harder to get real information about this
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
4h
minor correction: the file in the screenshot is not js but some generic configuration file format that vaguely looks like the ini or yaml format. if anything this makes even less sense.
Quote

typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
4h
Replying to @awawawhoami
it wouldnt make sense for them to have a second exclusion list like this, and much less for it to be formated as javascript code (not even as json) given this would be used in the twitter backend, which is not written in javascript
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
3h
a former twitter employee essentially confirms what i said earlier about twitter moderation tools and that okta was only ever used for sso, this could have changed in the mean time ofc
Quote

d@nny "disc@" mcClanahan
@hipsterelectron
·
4h
Replying to @awawawhoami
can confirm at least while i was there that twitter made its own internal moderation tooling (they called it "agent tools" and they worked next to me, they were necessarily very secretive). don't know what it relied on but i only remember okta being used for sso
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
3h
if you have any additional information on this incident you can either DM me on here or securely contact me on signal (at nyancrimew.01)
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
3h
i have received some additional information (including an uncensored version of the discord screenshot), i am still very much on the fence about believing this to be real but the person who originally posted the message on discord is apparently working with journalists now
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
3h
i would suggest to wait and see but it might turn out to be real after all, still hard to say with the information i have for now, i will wait on the journalists who have been directly provided with this data. the story i have now doesnt seem entirely unlikely anymore.
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
3h
since they publicly talked about it i can confirm that the discord screenshot is of the vxunderground server, vxug currently says they have no way to verify if the data was forged or not.
Quote

vx-underground
@vxunderground
·
4h
Replying to @ElleHasAGock
The information may not be accurate. We can't verify if it's forged information or not.
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
2h
also just for context: theantifaturtle is not the original poster of the discord screenshot, the original poster of it, as well as reposters, have not been suspended as of now.
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
2h
to be clear based on the info i have my gut feeling still is that this is fake and that a vxug member accidentally laundered the misinfo without trying to reproduce it beforehand. resharing untrusted source info like this is dangerous and leads to shit exactly like this.
typical maia crimew twiter account 2024
@awawawhoami
·
2h
highly suggest
@vxunderground
to retract the info, none of the private details i have about how this info was apparently accessed makes sense either.
End ID
Did you see the Twitter API leak that revealed "protected users" who get the green flag to break ToS and a list of "allowed" slurs?
you can read my twitter thread objectively analyzing info surrounding the alleged leak where i conclude (up to now) that this leak is most likely forged here
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Holistic cybersecurity services and solutions
Holistic cybersecurity services and solutions focus on a comprehensive, end-to-end approach to protect an organization’s digital ecosystem. This type of cybersecurity strategy aims not only to defend against individual threats but also to build a resilient infrastructure that can adapt to evolving cyber risks.
Key Components of Holistic Cybersecurity
1. Risk Assessment & Management
• Identifying and evaluating risks to understand vulnerabilities, threat vectors, and the potential impact on the business.
• Using a combination of internal audits, penetration testing, and threat modeling.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Enforcing strict policies to manage who has access to systems and data, including user authentication, authorization, and monitoring.
• Utilizing technologies like multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), and privileged access management (PAM).
3. Network Security
• Protecting the organization’s network infrastructure through firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and zero-trust network access (ZTNA).
• Regular network monitoring and segmentation to minimize the risk of lateral movement during an attack.
4. Endpoint Protection
• Securing individual devices (e.g., laptops, mobile devices) with endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
• Implementing software and hardware policies that prevent unauthorized access or malware infiltration.
5. Data Protection and Encryption
• Encrypting sensitive data both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access or breaches.
• Implementing data loss prevention (DLP) tools to monitor and control data movement.
6. Cloud Security
• Ensuring that cloud services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) meet security requirements and best practices, such as encryption, access control, and configuration management.
• Monitoring cloud environments continuously for suspicious activity.
7. Security Awareness Training
• Educating employees on the latest security practices, phishing prevention, and proper data handling.
• Regularly updating training to adapt to new threats and vulnerabilities.
8. Incident Response & Disaster Recovery
• Establishing and testing an incident response (IR) plan that includes detection, containment, and mitigation procedures.
• Having a disaster recovery (DR) plan that covers data backup, restoration, and business continuity to minimize downtime.
9. Threat Intelligence and Continuous Monitoring
• Collecting threat intelligence to stay updated on emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and attacker techniques.
• Leveraging Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to analyze and monitor events in real time.
10. Compliance and Governance
• Ensuring the cybersecurity strategy aligns with regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and industry standards (e.g., NIST, ISO/IEC 27001).
• Establishing governance policies to manage cybersecurity risks and accountability across the organization.
Holistic Cybersecurity Solutions in Practice
Implementing a holistic cybersecurity framework means adopting an integrated solution that pulls together technologies, people, and processes into one streamlined, proactive defense. Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) and Security Operations Centers (SOCs) play a critical role here by offering continuous monitoring, incident response, and expert support to manage and mitigate risks. By viewing cybersecurity as a collective and interconnected ecosystem, organizations can adapt better to changing threat landscapes and secure their most valuable assets across all fronts.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Types Of Cyber Security:
Here are the main types of cybersecurity, each focusing on different aspects of protecting systems, networks, and data:
1. Network Security
Focus: Protecting the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of computer networks.
Key Components: Firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and virtual private networks (VPNs).
2. Application Security
Focus: Ensuring software applications are secure throughout their lifecycle.
Key Components: Secure coding practices, application testing, and patch management.
3. Endpoint Security
Focus: Securing individual devices (endpoints) like computers, smartphones, and servers.
Key Components: Antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR), and device management.
4. Data Security
Focus: Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches.
Key Components: Encryption, data masking, and access controls.
5. Cloud Security
Focus: Protecting data, applications, and services hosted in cloud environments.
Key Components: Identity and access management (IAM), secure configurations, and compliance controls.
6. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Focus: Ensuring that only authorized users have access to specific resources.
Key Components: Multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), and role-based access control (RBAC).
7. Operational Security (OpSec)
Focus: Protecting sensitive information and processes within an organization.
Key Components: Risk assessment, incident response planning, and policy development.
8. Incident Response and Management
Focus: Preparing for and responding to cybersecurity incidents.
Key Components: Incident response plans, forensic analysis, and post-incident reviews.
9. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Focus: Ensuring organizational resilience during and after a cybersecurity incident.
Key Components: Disaster recovery plans, business impact analysis, and data backup solutions.
10. Physical Security
Focus: Protecting physical assets such as data centers and hardware from physical threats.
Key Components: Surveillance systems, access controls, and environmental controls.
11. Compliance and Governance
Focus: Ensuring adherence to regulatory and industry standards.
Key Components: Policies, audits, and risk management frameworks (like NIST, ISO 27001).
These types of cybersecurity collectively contribute to a comprehensive security strategy, helping organizations mitigate risks and protect against a variety of cyber threats. If you have questions about any specific type or need further details, feel free to ask!
0 notes
Text
AdNovum Singapore - 7 Must-Have Cybersecurity Services for Every Business
Technological innovations are becoming more sophisticated, but so are the threats that can jeopardise data, interrupt business activities, and harm a brand's image. As companies navigate this challenging digital terrain, allocating resources towards robust cybersecurity services becomes necessary.
Explore the fundamental cybersecurity services every business needs, focusing on their importance to securing your brand's assets.

7 Cybersecurity Services Every Business Needs
1. Risk Assessment and Management
A comprehensive risk assessment is the foundation of any effective cybersecurity strategy. This service involves identifying, evaluating, and prioritising risks to an organisation's information assets. Cybersecurity consulting services are necessary for thorough risk assessments by leveraging their expertise to identify vulnerabilities internal teams might overlook. Through detailed analysis and usage of advanced tools, consultants can provide actionable insights and recommendations to mitigate identified risks. This proactive approach ensures that businesses are aware of potential threats and can implement appropriate measures to address them, reducing the likelihood of a security breach.
2. Network Security
Securing the corporate network is a top priority for any business. Network security services encompass a range of solutions designed to protect data's integrity, confidentiality, and availability as it travels across networks. This process includes the implementation of firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS). Cybersecurity consulting services assist businesses in selecting and configuring these tools to ensure maximum effectiveness. Companies can prevent unauthorised access and potential data breaches by continuously monitoring network traffic and identifying suspicious activities. Additionally, consultants can help develop and enforce network security policies that govern how data is accessed and transmitted within the organisation, further enhancing the overall security posture.
3. Endpoint Protection
Endpoints, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, are often targeted by cybercriminals as entry points into an organisation's network. Endpoint protection services aim to secure these devices by deploying antivirus software, encryption, and advanced threat protection. Cybersecurity consulting services can help businesses implement comprehensive endpoint protection strategies that cover all devices used by employees, whether they are on-premises or working remotely. Businesses can significantly reduce the risk of malware infections, data breaches, and other cyber threats by ensuring that all endpoints are properly secured. Consultants also provide ongoing support and updates to keep endpoint protection measures current with evolving threats.
4. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Managing who has access to what data and systems within an organisation is essential for maintaining security. Identity and Access Management (IAM) services provide a structured approach to managing user identities and controlling access to critical resources. This process includes the implementation of single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access control (RBAC). Cybersecurity consulting services assist businesses in designing and deploying IAM solutions that align with their specific needs and security requirements. By implementing robust IAM practices, companies can ensure that only authorised users access sensitive information, thereby reducing the risk of insider threats and unauthorised access.
ALSO READ: Building a Resilient Organization with Cyber Risk Management

5. Data Encryption
Data encryption is a vital service that protects sensitive information by converting it into an unreadable format that can only be decrypted by authorised parties. This process ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorised individuals, it remains protected. Cybersecurity consulting services can guide businesses in selecting and implementing encryption technologies best suited to their data protection needs. This approach includes encryption for data at rest, data in transit, and data in use. By securing data through encryption, businesses can enhance compliance with data protection regulations and protect their intellectual property and customer information from cyber threats.
6. Security Awareness Training
Human error is one of the leading causes of cybersecurity incidents. Security awareness training is then essential to mitigate this risk. This service involves educating employees about the latest cyber threats, safe online practices, and the importance of following security protocols. Cybersecurity consulting services can develop customised training programs that address the organisation's specific needs and challenges. By raising awareness and fostering a security culture, businesses can empower their employees to recognise and respond to potential threats, reducing the likelihood of successful cyber attacks.
7. Incident Response and Recovery
Despite the best preventive measures, cyber incidents can still occur. Having a robust incident response and recovery plan is critical for minimising the impact of a breach. Cybersecurity services in this area include developing incident response plans, regular drills and simulations, and post-incident analysis. Cybersecurity consulting services provide expertise in crafting and refining these plans to ensure a swift and effective response to any security incident. By being prepared to respond to and recover from cyber incidents, businesses can minimise downtime, reduce financial losses, and maintain customer trust.
Conclusion
Investing in cybersecurity services is of utmost importance in safeguarding a company's digital assets. By using the knowledge and skills of cybersecurity consulting services, businesses can establish comprehensive and efficient security protocols that cater to their specific challenges and vulnerabilities. These services encompass risk evaluation, network security, endpoint protection, and incident response, offering the essential layers of protection needed to combat the constantly evolving cyber threats. Visit Adnovum to take the first step towards a more secure future for your business.
Read More:
0 notes
Text
Next - Gen cyber security

Introduction
Welcome and Orientation
Overview of the Next-Gen Cyber Security Skills course in Bangalore
Introduction to instructors and fellow participants
Setting goals and expectations for the course
Module 1: Foundations of Cyber Security
Understanding Cyber Security
Definition and importance of cyber security in today’s world
Current landscape and emerging threats
Cyber Security Terminology
Key terms and concepts crucial for the Bangalore cyber security course
Overview of common attack vectors and defenses
Cyber Security Frameworks and Standards
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
ISO/IEC 27001
CIS Controls and their relevance to Bangalore’s cyber security environment
Module 2: Network Security
Network Security Fundamentals
Basic networking concepts vital for Bangalore cyber security professionals
Understanding firewalls, VPNs, and IDS/IPS
Securing Network Infrastructure
Techniques for network segmentation and isolation
Secure network design and architecture
Wireless Network Security
Wireless security protocols (WPA3, WPA2)
Securing wireless access points in a Bangalore context
Module 3: Application Security
Introduction to Application Security
Common vulnerabilities (OWASP Top Ten)
Secure coding practices essential for Bangalore developers
Web Application Security
Addressing Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and SQL Injection
Integrating secure development lifecycle (SDLC) practices
Mobile Application Security
Addressing mobile-specific threats and vulnerabilities
Best practices for securing mobile apps in the Bangalore market
Module 4: Endpoint Security
Endpoint Protection
Anti-virus and anti-malware solutions
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools
Securing Operating Systems
Hardening Windows and Linux systems
Effective patch management and software updates
BYOD and IoT Security
Managing Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies in Bangalore
Securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices
Module 5: Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Fundamentals of IAM
Authentication vs. Authorization
Identity lifecycle management and its application in Bangalore businesses
Access Control Mechanisms
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Identity Management Solutions
Single Sign-On (SSO) and Federation
Identity as a Service (IDaaS) platforms and their relevance
Module 6: Cloud Security
Cloud Security Basics
Understanding cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
Shared responsibility model for cloud security
Securing Cloud Environments
Best practices for AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud in Bangalore
Cloud security posture management
Cloud Compliance and Governance
Regulatory requirements and compliance standards applicable in Bangalore
Data protection and privacy in the cloud
Module 7: Threat Intelligence and Incident Response
Cyber Threat Intelligence
Gathering and analyzing threat data
Using threat intelligence platforms effectively
Incident Response Planning
Developing an incident response plan
Incident detection and analysis
Handling Security Incidents
Containment, eradication, and recovery strategies
Post-incident activities and lessons learned
Module 8: Security Operations and Monitoring
Security Operations Center (SOC)
Roles and responsibilities of SOC teams
Setting up and managing a SOC in Bangalore
Monitoring and Logging
Importance of logging and monitoring
Using SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools
Threat Hunting
Proactive threat hunting techniques
Leveraging advanced analytics and AI for threat detection
Module 9: Compliance and Legal Aspects
Understanding Cyber Security Regulations
Key regulations (GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, etc.)
Compliance requirements for organizations in Bangalore
Legal Considerations in Cyber Security
Data breach laws and notification requirements
Intellectual property and cyber crime laws
Auditing and Assessment
Conducting security audits and assessments
Preparing for compliance audits
Module 10: Capstone Project and Certification
Capstone Project
Real-world scenario-based project
Applying learned skills to solve complex problems
Exam Preparation
Review of key concepts and practice exams
Tips and strategies for passing the certification exam
Certification and Next Steps
Receiving course completion certificate
Exploring advanced certifications and career paths
Conclusion and Course Wrap-Up
Final Q&A Session
Addressing any remaining questions
Sharing additional resources and tools
Networking and Alumni Community
Joining the course alumni network
Continued learning and professional development opportunities in Bangalore
This Next-Gen Cyber Security course in Bangalore will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in the evolving field of cyber security
0 notes
Text
The Evolution of Identity and Access Management: SCIM, SAML vs. OpenID Connect, and Integration Challenges
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, Identity and Access Management (IAM) has become crucial for organizations to ensure security, compliance, and efficiency. The increasing reliance on technology has necessitated the development of sophisticated IAM protocols and standards. This blog will explore a SCIM example, compare SAML vs. OpenID Connect, and discuss the challenges and solutions associated with IAM integration.

Understanding SCIM: An Example
System for Cross-domain Identity Management (SCIM) is a standard protocol designed to simplify the management of user identities in cloud-based applications and services. SCIM automates the exchange of user identity information between identity providers and service providers, ensuring seamless integration and synchronization.
SCIM Example
Consider an organization using multiple cloud services, such as Office 365, Google Workspace, and Salesforce. Managing user identities manually across these platforms can be cumbersome and error-prone. By implementing SCIM, the organization can automate the provisioning and deprovisioning of user accounts.
For instance, when a new employee joins the company, the IAM system can automatically create their user account in all relevant cloud services using SCIM. Similarly, when an employee leaves, their access can be revoked across all platforms in a streamlined manner. This automation enhances security, reduces administrative workload, and ensures consistent identity data across all systems.

Comparing SAML vs. OpenID Connect
When it comes to authentication protocols, SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) and OpenID Connect are two of the most widely used standards. Both serve the purpose of providing secure authentication, but they do so in different ways and are suited to different use cases.
SAML
SAML is an XML-based framework primarily used for Single Sign-On (SSO) in enterprise environments. It allows users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications without re-entering credentials. SAML is commonly used in scenarios where secure, federated access to web applications is required, such as accessing corporate intranets or SaaS applications.
OpenID Connect
OpenID Connect is a modern identity layer built on top of the OAuth 2.0 protocol. It uses JSON-based tokens and is designed for mobile and web applications. OpenID Connect provides a more flexible and user-friendly approach to authentication, making it ideal for consumer-facing applications where user experience is paramount.
SAML vs. OpenID Connect: Key Differences
Protocol Structure: SAML uses XML, whereas OpenID Connect uses JSON.
Use Cases: SAML is suited for enterprise SSO, while OpenID Connect is better for modern web and mobile applications.
Token Types: SAML uses assertions, whereas OpenID Connect uses ID tokens.
User Experience: OpenID Connect generally offers a more seamless and user-friendly experience compared to SAML.
The Challenges of IAM Integration
With the growing reliance on technology, integrating various IAM components and protocols has become increasingly complex. Effective IAM integration is essential for ensuring that different systems work together harmoniously, providing a seamless and secure user experience. However, several challenges can arise during the integration process.
Compatibility Issues
Organizations often use a mix of legacy systems and modern applications, leading to compatibility issues. Ensuring that different IAM solutions can communicate and share identity data effectively is a significant challenge.
Data Consistency
Maintaining consistent identity data across multiple platforms is crucial for security and compliance. Any discrepancies in user data can lead to unauthorized access or account lockouts.
Scalability
As organizations grow, their IAM systems must be able to scale accordingly. Integrating IAM solutions that can handle an increasing number of users and applications without compromising performance is vital.
Security Concerns
Integrating multiple IAM solutions can introduce security vulnerabilities if not done correctly. Ensuring that data is securely transmitted and that all systems adhere to robust security protocols is paramount.
Solutions for Effective IAM Integration
To overcome these challenges, organizations should adopt a strategic approach to IAM integration:
Standardization
Adopting standard protocols such as SCIM, SAML, and OpenID Connect can simplify integration by ensuring compatibility and consistency across different systems.
Centralized Identity Management
Implementing a centralized IAM platform can help streamline identity management processes and ensure consistent data across all applications and services.
Regular Audits
Conducting regular audits of IAM systems and processes can help identify and address potential vulnerabilities and inconsistencies, ensuring that the integration remains secure and effective.
Vendor Support
Working with reputable IAM vendors who offer comprehensive support and integration services can significantly ease the integration process and ensure a successful deployment.
Conclusion
As organizations continue to increase their reliance on technology, the need for robust and effective IAM integration becomes more critical. By understanding the differences between SAML vs. OpenID Connect, leveraging standards like SCIM, and adopting strategic integration practices, organizations can enhance security, streamline operations, and provide a seamless user experience. The right IAM solutions not only protect against cyber threats but also empower businesses to thrive in the digital age.
0 notes
Text
Authorization vs Authentication: Key Differences Explained

What’s Authorization vs Authentication?
An organisation’s identity and access management (IAM) solution separates authentication and authorization. Users are authenticated. Users are authorised to access system resources.
Authentication requires users to give credentials like passwords or fingerprint scans.Access to a resource or network is determined by user permissions. For instance, file system permissions determine whether a user can create, read, update, or delete files. In addition to humans, gadgets, automated workloads, and web apps require authentication and authorization. IAM systems can handle authentication and authorization separately or together.
Verification is frequently required for authorization. Users must be identified before a system may provide them access.
Hacked user accounts and access rights are rising due to identity-based assaults. These attacks make up 30% of cyberattacks, according to the IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence Index.
Identity and permission restrict access and prevent data breaches. Strong authentication prevents hackers from taking over user accounts. These accounts are less vulnerable to hackers with strong authorization.
Realising authentication
Authentication method
User credentials authentication factors are exchanged during authentication, abbreviated “authn.” A user’s identity is verified by authentication factors.
New system users create authentication factors. When logging in, these factors appear. Present factors are compared to file factors. A match means the system trusts the user. Regular authentication factors include:
A password, PIN, or security question that only the user knows.
Possession factors: A SMS-sent one-time PIN (OTP) or a physical security token that only the user holds.
Factors: Facial and fingerprint recognition.
Individual apps and resources can authenticate themselves. Users can authenticate once to access numerous resources in a secure domain in many organisations’ integrated systems, such as SSO.
SAML and OIDC are prevalent authentication protocols. SAMl employs XML messages to communicate authentication information, while OIDC uses “ID tokens” JSON Web Tokens (JWTs).
Verification methods
SFA verifies a user’s identification with one factor. Logging into social media with a username and password is SFA.
Multifactor authentication (MFA) uses a password and fingerprint scan.
2FA is a sort of MFA that requires two elements. Most internet users have used 2FA, such as a banking app requiring a password and a phone-sent PIN.
A passwordless authentication mechanism uses no passwords or knowledge factors. Passwordless systems are popular at preventing credential thieves from stealing knowledge factors, which are easy to steal.
User riskiness determines authentication requirements in adaptive authentication systems using artificial intelligence and machine learning. User wanting to access secret data may need to provide numerous authentication factors before system verification.
Exemplary authentication
Mobile phone unlocking with a fingerprint and PIN.
New bank account opening requires ID.
Browsers scan digital certificates to verify website legitimacy.
Each API call includes an app’s private API key to verify itself.
Know permission
Authorisation workings
Permissions determine authorization, or “authz.” System permissions govern user access and behaviour.
The authorization system enforces user permissions set by administrators and security leaders. Accessing a resource or taking an action requires the authorization system to validate a user’s permissions.
Examine a sensitive client database. This database is only visible to authorised users. Database access depends on authorization if they can. Reading, creating, deleting, and updating entries?
Authorization protocols like OAuth 2.0 employ access tokens to grant user permissions. Data is shared between apps using OAuth. If a user consents, OAuth lets a social networking site examine their email contacts for friends.
Authority types
Role-based access control (RBAC) determines user access permissions. Firewall configurations can be viewed but not changed by a junior security analyst, while the head of network security can.
Attribute-based access control (ABAC) uses user, object, and action attributes including name, resource type, and time of day to allocate access. ABAC analyses all relevant attributes and only gives access if a user meets established requirements. User access to sensitive data may be restricted to work hours and seniority in an ABAC system.
ALL users must follow centrally specified access control (MAC) policies. RBAC and ABAC are more granular than MAC systems, which use clearance or trust ratings to establish access. Programme access to sensitive system resources is controlled by MAC in several operating systems.
DAC systems let resource owners specify their own access policies. DAC is more flexible than MAC’s blankets.
Authorization instances
Email logins only display emails. Non-authorized users cannot view messages.
Healthcare records systems only allow doctors with specific approval to examine patient data.
A user creates a shared file document. Other users can view but not edit the document since they set access settings to “read only”.
An unknown programme can’t change laptop settings.
Authentication and authorization secure networks.
Authentication and authorization protect sensitive data and network resources from insiders and outsiders. Authentication protects user accounts, whereas authorization protects access systems.
Basis for identification and access management
IDAM systems detect user activity, prohibit unauthorised access to network assets, and enforce granular permissions so only authorised users can access resources. To establish meaningful access controls, organisations must answer two key questions: authentication and authorization.
You who? What can you accomplish with this system? (Authentication) Organisations must identify users to grant appropriate access levels (Authorization). The correct authentication factors are needed for a network administrator to log in. When that happens, the IAM system will let the user add and remove users.
Resisting advanced cyberattacks
Thieves are hijacking user accounts and misusing their privileges to cause havoc as organisational security procedures improve. IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence Index: Identity-based assaults rose 71% between 2022 and 2023.
Cybercriminals can easily launch these efforts. Breach-force attacks, infostealer software, and buying credentials from other hackers can crack passwords. X-Force Threat Intelligence Index discovered that 90% of dark web cloud assets are cloud account credentials. Using generative AI techniques, hackers can create more powerful phishing attacks in less time.
Verification and permission, however rudimentary, protect against identity theft and account misuse, including AI-powered attacks.
Biometrics can replace passwords, making account theft tougher.
Limiting user privileges to necessary resources and actions in granular authorization systems reduces lateral mobility. This reduces malware and insider threat harm from access privileges abuse.
IBM Security Verify adds more than authentication and authorization. Verify lets you safeguard accounts with passwordless and multifactor authentication and regulate apps with contextual access controls.
Read more on govindhtech.com
#authorization#authentication#key#differences#explained#cyberattacks#ibm#xforce#Intelligence#index#verificationmethods#exemplary#authoritytypes#access#management#generativeai#ai#technology#technews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Key Components of the Salesforce Security Model
Salesforce, as a leading cloud-based Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platform, serves countless organizations across various industries. Its vast array of features makes it a powerhouse for managing sales, customer service, marketing automation, and business analytics. However, the extensive capabilities of Salesforce also mean that ensuring robust security is paramount. Understanding the Salesforce Security Model is crucial for organizations to protect their data and maintain trust with their customers.
Key Components of the Salesforce Security Model
1. User Authentication: Salesforce employs a comprehensive authentication process to ensure that only authorized users can access the platform. This includes standard username and password combinations, as well as more secure methods such as two-factor authentication (2FA) and Single Sign-On (SSO) from external trusted systems.
2. Profiles and Permission Sets: These are the core elements of Salesforce’s security model. Profiles define how users access objects and data, including which fields they can see and the records they are allowed to interact with. Permission sets, on the other hand, are add-ons to profiles that provide additional access without altering the original profile structure. They are extremely useful for granting specific permissions to users on a temporary basis or for more granular control.
3. Record-Level Security: To manage data visibility at the record level, Salesforce uses Organization-Wide Defaults (OWDs), Role Hierarchies, Sharing Rules, and Manual Sharing. OWDs set the baseline access level for records. Role hierarchies allow higher-level roles in the hierarchy to access data accessible to roles beneath them. Sharing rules enable administrators to define exceptions to OWDs for particular groups of users, while manual sharing allows users to share individual records with others.
4. Field-Level Security: This allows administrators to control access to specific fields, even if a user has access to the object. Field-level security settings can be adjusted to ensure that sensitive information, like personal customer details or financial data, is only visible to users who require it to perform their job.
5. Audit Trails: Salesforce provides a detailed audit trail that records the date, time, user ID, and type of action taken on any record within the system. This feature helps in monitoring usage patterns and detecting potential unauthorized or malicious activity.
Best Practices for Maximizing Salesforce Security
Regularly review and update access permissions: As roles within an organization change, so should access permissions in Salesforce. Regular audits can help prevent privilege creep and ensure that users only have access to the data necessary for their roles.
Use data encryption: Salesforce offers several options for encrypting data at rest and in transit, which protects sensitive information from interception or unauthorized access.
Train users on security practices: Regular training sessions on security best practices can significantly reduce risks associated with phishing, social engineering, and accidental data exposure.
Implement comprehensive monitoring: Utilizing Salesforce’s event monitoring and field history tracking can help administrators spot unusual access patterns and potential security breaches.
By effectively leveraging the Salesforce Security Model, organizations can protect their vital data while making the most of Salesforce’s powerful CRM capabilities. Security in Salesforce is not just about technology; it’s about creating a culture of security mindfulness throughout the organization.
0 notes
Text
Week 6: Digital Citizenship
Digital citizenship is the ethical and responsible use of technology in digital spaces. In our increasingly digital world, digital citizenship concepts and practices are essential for safe and effective online navigation. Digital literacy, online etiquette, and digital rights and duties are all part of this notion. Digital citizenship adapts traditional citizenship to the digital world. Traditional citizenship requires being alert, well-informed, and involved in a community or nation. Digital citizenship is a concept that includes a range of theoretical conceptions, from those that emphasize the technological aspect, while others investigate the affordances of digital media to suggest new forms of citizenship (Gleason & von Gillern 2018). Conversely, digital citizenship expands online rights and duties. The link between digital and traditional citizenship emphasizes ethical behavior, involvement, and community participation in both. Digital citizenship includes a wide range of behaviors, habits, and abilities needed to responsibly use the internet. To navigate the online world in a time when the internet and digital technologies are critical, digital citizenship must be understood. This notion includes ethical behavior, digital technology skills, online safety, and digital community participation. Digital citizenship emphasises responsible, ethical, and safe digital behaviour. Digital literacy, critical thinking, courteous online behavior, and digital safety and well-being are vital. Digital citizenship will help people navigate the internet safely and ethically as technology advances. Platform studies is an interdisciplinary field that analyzes digital platforms' technological and cultural foundations. Software, social media, online markets, and other digital platforms allow users to engage, generate, and share information. Platform studies examine the technological, social, cultural, economic, and political effects of various platforms. "Platformization" involves adapting industries, services, and activities to digital platforms. Digital technology, networked infrastructures, and online ecosystems are integrated into corporate models and operations. Platformization affects retail, transportation, media, banking, healthcare, and education. Digital citizenship affects political involvement, civic engagement, and democratic government in the digital age, making it crucial to the election process. Digital citizenship is essential for informed engagement, proactive involvement, and the promotion of democratic values in the digital age to influence elections. Digital people improve the voting system by learning how to use technology, encouraging online ethics, and ensuring election fairness and security. This improves inclusion, transparency, and resilience. Digital citizenship and political involvement are closely linked in the modern era because digital technologies affect political participation. Digital citizenship conveys a different set of practices from simply casting a vote at a polling booth or participating in civil society to participating in online discussion (Luci & Julian 2021). Digital citizenship helps people to actively and intelligently participate in politics, creating a more educated, involved, and participatory democracy. Digital literacy and effective use of technology allow people to participate in political debates, advocate for social change, and hold government institutions responsible.
Refrences Gleason, B & von Gillern, S 2018, “Digital Citizenship with Social Media,” Gale Academic OneFile, accessed May 20, 2024, <https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?p=AONE&u=swinburne1&id=GALE%7CA524180840&v=2.1&it=r&aty=sso%3A+shibboleth>.
Luci, P & Julian, S-G 2021, “Digital Rights, Digital Citizenship and Digital Literacy,” ProQuest, accessed May 20, 2024, <https://www.proquest.com/docview/2553580375/abstract/D6F85F5BC934457FPQ/1?accountid=14205&sourcetype=Scholarly%20Journals>.
0 notes