#Royal Society of Biology
Text
I keep encountering this category of book that philosophizes broadly about the direction of human life, society, and psychology, calling for a sort of change in our culture or values in some way. In this type of book the writer, implicitly or sometimes very explicitly, declares the ideas of "The Right" and "The Left" to be both fundamentally flawed, and proposes a revolutionary "middle ground" between the two. This middle ground turns out to be right-wing conservatism
The most striking characteristic of these books is that they are very multi-disciplinary in their approach, drawing upon anthropology, biology, sociology, psychology, economics, and history to make their conclusions. This makes the book seem very well-thought-out and provocative on the surface, since it uses such a wide variety of types of evidence and arguments to support its conclusions.
However, instead of having a well-rounded and insightful multidisciplinary analysis, the author is actually simultaneously at the top of a terrifying array of Dunning-Kruger peaks, knowing too little individually about any of the fields he draws upon to realize how little he knows, and is laying it all out like a royal flush of stupid.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Allenypterus montanus was an unusual early coelacanth that lived during the late Carboniferous, around 324 million years ago, in a tropical bay covering what is now central Montana, USA.
Up to about 15cm long (~6"), its tapering tadpole-like body plan somewhat resembled that of modern knifefishes and featherbacks, with the top part of its tail fin highly elongated into a ribbon-like shape and the rest of its tail fins being vestigial. The distinctive humped shape of its back was also much more pronounced in larger, more mature individuals.
It was probably a fairly slow swimmer, and preserved gut contents suggest it mainly ate small soft-bodied prey.
Its closest known relative seems to have been the eel-like Holopterygius – but since around 60 million years and different continents separated them both, this suggests the existence of a whole ghost lineage of other tapering coelacanths yet to be discovered.
———
NixIllustration.com | Tumblr | Patreon
References:
Friedman, Matt, and Michael I. Coates. "A newly recognized fossil coelacanth highlights the early morphological diversification of the clade." Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 273.1583 (2006): 245-250. https://doi.org/10.1098%2Frspb.2005.3316
Lund, Richard, and Wendy Lund. "New genera and species of coelacanths from the Bear Gulch Limestone (Lower Carboniferous) of Montana (USA)." Geobios 17.2 (1984): 237-244. https://www.academia.edu/download/66985268/s0016-6995_2884_2980145-x20210504-8876-dzniic.pdf
Lund, Wendy L., Richard Lund, and G. Klein. "Coelacanth feeding mechanisms and ecology of the Bear Gulch coelacanths." Compte Rendus du Neuvième Congrès International sur la Stratigraphie et la Géologie du Carbonifère 5 (1985): 492-500. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285577607_Coelacanth_Feeding_Mechanisms_and_Ecolqgy_of_the_Bear_Gulch_Coelacanths
Toriño, Pablo, Matías Soto, and Daniel Perea. "A comprehensive phylogenetic analysis of coelacanth fishes (Sarcopterygii, Actinistia) with comments on the composition of the Mawsoniidae and Latimeriidae: Evaluating old and new methodological challenges and constraints." Historical Biology 33.12 (2021): 3423-3443. https://doi.org/10.1080/08912963.2020.1867982
#science illustration#paleontology#paleoart#palaeoblr#allenypterus#actinistia#coelacanthiformes#coelacanth#sarcopterygii#lobe-finned fish#fish#art
298 notes
·
View notes
Text
So I was looking into the Magnus Protocol Episode Hard Reset, and I am losing my shit for so many reasons.
1. The statement giver is Robert Hooke, one of the first people to publish research on microscopy. He was the person who coined the word "cell" in biology, because he thought they looked like the cells where monks lived.
2. The statement takes place in 1694. Hook references using the Protocol on London to stop a plague. Between 1665 and 1666, the Great Plague killed about 20% of the British population. In 1666, the Great Fire of London destroyed 60% of the city.
3. You know who made a ton of money from the fire? Robert Hooke. He made his fortune as a surveyor and architect in the aftermath of the fire, performing over half the property surveys. How fortunate for him.
4. Incidentally, there are no confirmed surviving portraits of Robert Hooke, only ones that may be him. This is rumored to be Isaac Newton's fault, because after Newton took over the Royal Society, they moved to a new location, and Hooke's portrait was "lost." No other portraits went missing.
5. The statement is addressed to Robert Boyle, who you may recognize for Boyle's Law in chemistry. There's a sculpture in Dublin of a young boy who is thought to be Boyle, and it's horrific.

6. This time period is significant for Isaac Newton, because between 1692 and 1693, he suffered "a breakdown of nervous functioning," with insomnia, poor digestion, and "signs of irrationality" in his letters. Incidentally, hair samples from Newton's body later contained high levels of mercury, lead, arsenic, and antimony. Probably because he was literally tasting mercury samples as part of his research.
7. During the statement, I was picturing a scrappy little terrier. It occurred to me that we probably know what kind of dog Isaac Newton had. His favorite dog was a pomeranian. A fucking. Pomeranian. Just picture this little guy developing sentience and sprouting branches.

8. The dog's name was Diamond, and he has his own Wikipedia page. Why? Because (likely apocryphal) stories claim Diamond knocked over a candle and burned over a year's worth of Newton's notes. The fire appears to be real, but blaming Diamond is unfair. Here's an engraving of the alleged incident.

9. After the fire, Newton was said to have exclaimed, "O Diamond, Diamond, thou little knowest the mischief thou hast done." But Diamond would know if he ate from the Tree of Knowledge.
10. Remember Flamsteed from the Maxwell Raynor statement? He and Newton were bitter enemies.
177 notes
·
View notes
Text
African Social Spiders: these spiders live in colonies that can contain up to 2,000 spiders, most of which are female; they hunt, forage, maintain their web, and raise their offspring as a group, without any dominance hierarchy or caste system
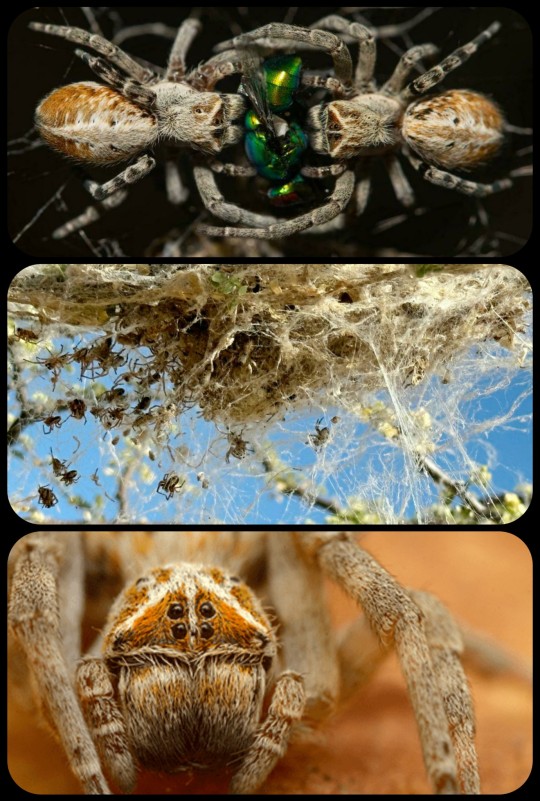

This communal behavior is extremely rare among spiders, which are normally solitary creatures. The African social spider (Stegodyphus dumicola) is one of the few species that has been identified as a true "social spider," forming colonies and living in communal nests where the spiders work together to hunt, forage, build webs, and care for their offspring.

Above: an African social spider feeding the young spiderlings of her colony by regurgitating food for them, exhibiting a level of maternal/allomaternal care that is relatively uncommon in both spiders and insects
African social spiders can be found in various parts of southwestern Africa, where they will often build a dense silk nest in the branches of a thorn tree and/or shrub. Most of the spiders in the colony are female (more than 85%, according to some studies) and the species itself also has a female-biased primary sex ratio, as researchers have found that female embryos develop in more than 80% of the eggs that the spiders produce.
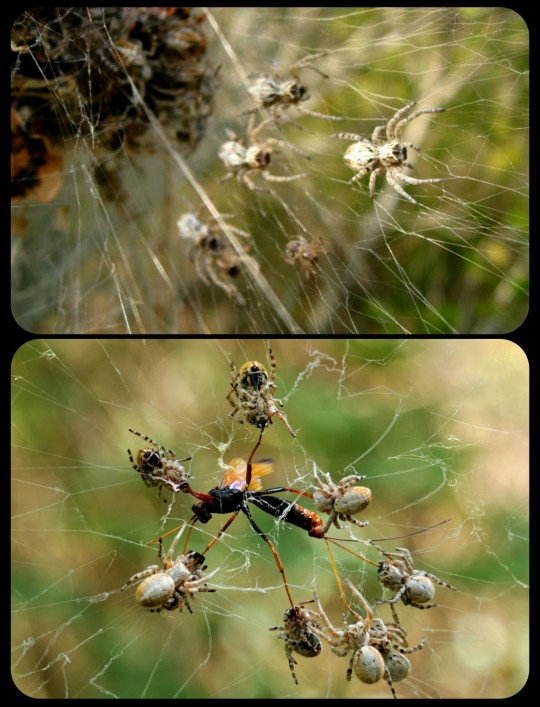

Above: a group of African social spiders working together to subdue their prey, which will be taken back to the nest so that it can be shared with the rest of the colony
There is no evidence that any dominance hierarchy or caste system exists within S. dumicola colonies. The spiders all cooperate to complete a variety of tasks, such as hunting, repairing the web, foraging, defending the colony, caring for the colony's offspring, etc. While none of them are exclusively assigned to a single task, many have a primary role that they fill, often based on their physical size and condition.

Above: close-up photo of S. dumicola
This species also engages in extreme allomaternal care, meaning that many different spiders (including both mothers and "allomothers") all share the responsibility of caring for the colony's offspring; even the unmated females help out with brood care. The mothers/allomothers tend to the eggsacs, regurgitate food for the baby spiderlings, and even engage in matriphagy, which means that they will eventually be cannibalized by the babies.
From The Encyclopedia of Animal Behavior:
... some proportion of females do not reproduce – sometimes as much as 60% – but remain as helpers, contributing to foraging and brood care (allo-mothering). Both breeding females and virgin allo-mothers regurgitate food for colony offspring and eventually let the young consume their bodies. ...
Young that are raised with both mothers and allo-mothers show higher survival and growth than young raised by their mothers alone, suggesting a clear fitness benefit of cooperative breeding.
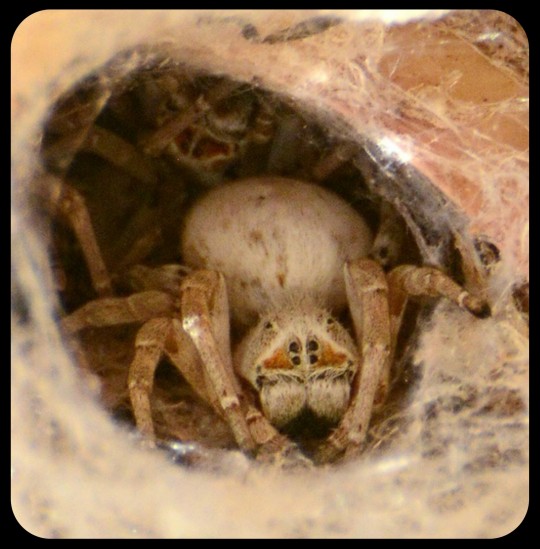

Spiders of this species generally measure about 2.5 - 3.5mm long; they can be found in Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, South Africa, Lesotho, and Eswatini.
Sources & More Info:
Science Direct: Social Spiders
Current Biology: Quick Guide to Social Spiders (PDF)
Phys.org: Untangling the Social Lives of Spiders
Proceedings of the Royal Society B: The Age & Evolution of Sociality in Stegodyphus Spiders
Entomology Today: Social Spiders Divide Labor According to Body Size & Condition
Animal Behaviour: Extreme Allomaternal Care by Unmated Females in a Cooperatively Breeding Spider
National Geographic: Baby Spiders Eat their Mothers
University of Portsmouth: Social Spiders Have Different Ways of Hunting in Groups
Behavioral Ecology: Spider Societies Mitigate Risk by Prioritizing Caution
Behavioral Processes: Warring Arthropod Societies
Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology: Does the African Social Spider Stegodyphus dumicola Control the Sex of Individual Offspring?
#arachnology#spiders#african social spiders#stegodyphus#dumicola#arthropods#arachnids#allomaternal#matriphagy#communal spiders#social spiders#cool bugs#animal facts#tw arachnophobia#cw spiders#anarcho-feminism?#more like arachno-feminism#just a bunch of radfem commie cannibals
219 notes
·
View notes
Text
GCs claim to campaign for the “safety” of women and children. I’ve long suspected this was confined to the “right kind” of women and children. Kathleen Stock, a former trustee of the “LGB Alliance” (public statements of which include “adding the + to LGB gives the green light to paraphilias like bestiality…”) appeared (to me) to suggest that it would be “more honest” for high-profile trans allies to publicly “declare” if they have trans children. Her post made no mention of obtaining the children’s consent. It seems reasonable to interpret this as a call for the public outing of certain trans children. Given “out” trans children have been murdered and 64% are subjected to bullying, it strikes me as, at the very least, callous. Joey Barton, one of the movement’s most high profile (and oft platformed) voices, will shortly stand trial accused of assaulting his wife. Donald Trump, who was found by a jury to have sexually assaulted E. Jean Carroll, has increasingly made attacks on trans people a campaign talking point.
The GC movement has claimed a degree of legitimacy based on previous legal successes, notably the case of Forstater v CGD Europe, in which GC beliefs were declared “worthy of respect in a democratic society”. Some seem to have interpreted this as a licence to persecute trans people. This summer three separate courts gave clear statements to the contrary. The Employment Tribunal upheld the sacking of teacher Kevin Lister after he equated being transgender (as one of his students was) with having a mental illness. The High Court upheld an order banning Joshua Sutcliffe from teaching children after he repeatedly misgendered a child in his care. In Australia, the Federal Court prohibited a dating app from discriminating against trans women. The message from the courts is clear: GC beliefs are worthy of respect, but GCs must also respect trans people.
The summer of court losses also undermines the movement’s claims to expertise. High profile GC activists often hold themselves out as experts. The courts made clear that many are no such thing. Maya Forstater gave “expert” evidence in the Sutcliffe case. The judge was “not persuaded that she is properly described as an expert”, noting:
“Ms Forstater explained that the use of non-preferred pronouns in this case might be due to cognitive dissonance. Mr Phillips was not, however, able to identify any medical expertise that she might have to opine on that issue.”
Helen Joyce, Director of Advocacy at the GC group “Sex Matters”, purported to give “expert” evidence in the Australian case. The judge said she:
“…does not have any formal education or qualifications even in biology, let alone in gender, sex or law… she is not an expert at all. She has no recognised expertise in any of the areas in which she expresses an opinion.”
In April the Cass Report gave a veneer of scientific legitimacy to the GC movement’s various claims. Both Labour and the Conservatives used the report as justification to prevent trans children from accessing puberty blockers (which, contrary to popular myth, do not prevent puberty but, rather, delay its onset). Cis children are still given access. The report was swiftly rejected by medical bodies around the world. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the Endocrine Society said, in a joint statement, “Medical evidence, not politics, should inform treatment decisions”. The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists followed suit. The British Medical Association called Cass’ claims “unsubstantiated”. I’d argue the report was largely debunked by a Yale School of Medicine review.
15 September 2024
96 notes
·
View notes
Text
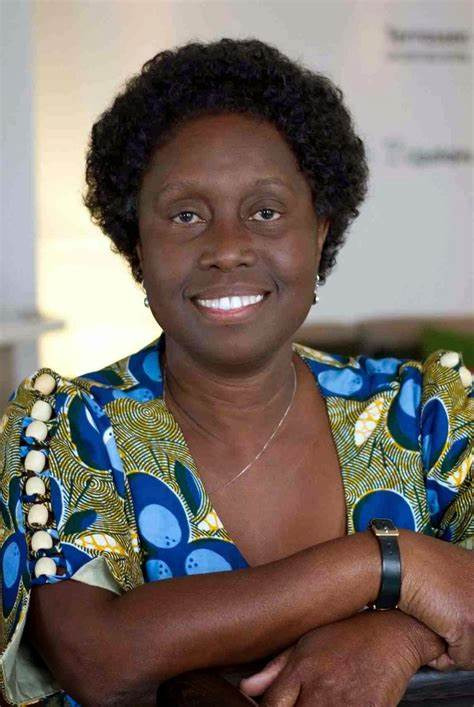


Notable Women In Zoology: Dr. Letitia Eva Takyibea Obeng
Dr. Obeng (1925-2023) was the first Ghanaian woman to obtain a degree in zoology, and the first to be awarded a doctorate. She is described as "the grandmother of female scientists in Ghana".
Her other notable accomplishments include:
A Bachelor of Science in Zoology and Botany (1952), a Master of Science in Parasitology (1962) and a PhD in Tropical Medicine (1964) where she studied the black fly and its relevance to river blindness
Post university, she lectured at the University College of Science and Technology (now known as Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, KNUST) from 1952 to 1959
In 1952, Dr. Obeng became the first female scientist at KNUST
After her husband's death in 19659, she moved to the the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR)
IN 1964, she established the Institute of Aquatic Biology within CSIR to research the huge manmade Volta Lake in Ghana and its inland water system
Dr. Obeng was the first scientist to be employed by the National Research Council of Ghana
In 1965, Dr Obeng became a fellow of the Ghana Academy of Arts and Sciences. In 2006, she became the first female president of the Academy
In 1972, Dr. Obeng delivered the Caroline Haslett Memorial Lecture to the Royal Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce, titled “Nation Building and the African Woman”
In 1972, she was an invited participant in the United Nations Human Environment Conference in Stockholm
In 1974, she began work as the Officer in the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), and in 1989, she became the Director of the UNEP Regional Office for Africa, and the UNEP's Representative to Africa
From 1992 to 1993, Obeng was a Distinguished International Visitor fellow at Radcliff College
In 1997, she received the CSIR Award for Distinguished Career and Service to Science and Technology, the first woman to receive such an award
The CSIR Laboratory (known as The Letitia Obeng Block) was named after her in 1997 as well
She received Ghana's highest national award, Order of the Star of Ghana in 2006
In 2017, she received an honorary Doctor of Science degree from KNUST
She was also the author of numerous publications and works. Two meant for the public were Parasites, the Sly and Sneaky Enemies inside You (1997) and -Anthology of a Lifetime (2019)
165 notes
·
View notes
Text
The first case of a crocodile who made herself pregnant has been identified at a zoo in Costa Rica.
She produced a foetus that was 99.9% genetically identical to herself.
The phenomenon of so-called "virgin birth" has been found in species of birds, fish and other reptiles, but never before in crocodiles.
The scientists say the trait might be inherited from an evolutionary ancestor, so dinosaurs might also have been capable of self-reproduction.
The research has been published in the Royal Society journal, Biology Letters.
The egg was laid by an 18-year-old female American crocodile in Parque Reptilania in January 2018. The foetus inside was fully formed but stillborn and so did not hatch.
Continue Reading
719 notes
·
View notes
Note
do you have any reading recs (books, ~scholarly articles, whatever) in the same vein as this post? (doesn't need to be a super long list, i'm content to branch off with the works cited of whatever you come up with...) as always, love your blog!! :-)
yes :3 split roughly by subtopic, bolded some favs
Evolution in England prior to (Charles) Darwin
Cooter, Roger. The Cultural Meaning of Popular Science: Phrenology and the Organisation of Consent in Nineteenth Century Britain. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press (1985).
Desmond, Adrian. The Politics of Evolution: Morphology, Medicine, and Reform in Radical London. Chicago: University of Chicago Press (1989).
Elliott, Paul. “Erasmus Darwin, Herbert Spencer, and the Origin of the Evolutionary Worldview in British Provincial Scientific Culture, 1770–1850.” Isis 94 (1): 1–29 (2003).
Finchman, Martin. “Biology and Politics: Defining the Boundaries.” In: Lightman, Bernard (Ed.). Victorian Science in Context. Chicago: University of Chicago Press (1997), 94–118.
Fyfe, Aileen. Steam-Powered Knowledge: William Chambers and the Business of Publishing, 1820–1860. Chicago: University of Chicago Press (2012).
Harrison, James. “Erasmus Darwin’s View of Evolution.” Journal of the History of Ideas 32 (2): 247–64 (1971).
McNeil, Maureen. Under the Banner of Science: Erasmus Darwin and his Age. Manchester: Manchester University Press (1987).
Ospovat, Dov. “The Influence of Karl Ernst von Baer’s Embryology 1828–1859: A Reappraisal in Light of Richard Owen’s and William Benjamin Carpenter’s ‘Palaeontological Application of Von Baer’s Law.’” Journal of the History of Biology 9 (1): 1–28 (1976).
Rehbock, Philip F. The Philosophical Naturalists: Themes in Early Nineteenth-Century British Biology. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin Press (1983).
Richards, Robert J. Darwin and the Emergence of Evolutionary Theories of Mind and Behaviour. Chicago: University of Chicago Press (1987).
Rupke, Nicolaas. Richard Owen: Biology without Darwin. Chicago: University of Chicago Press (2009 [ 1994]).
Secord, James. Victorian Sensation: The Extraordinary Publication, Reception, and Secret Authorship of Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation. Chicago: University of Chicago Press (2001).
van Wyhe, John. Phrenology and the Origins of Victorian Scientific Naturalism. London: Ashgate (2004).
Winter, Alison. “The Construction of Orthodoxies and Heterodoxies in the Early Life Sciences.” In: Lightman, Bernard (Ed.). Victorian Science in Context. Chicago: University of Chicago Press (1997), 24–50.
Yeo, Richard. “Science and Intellectual Authority in Mid-Nineteenth Century Britain: Robert Chambers and Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation.” Victorian Studies 28 (1): 5–31 (1984).
Edinburgh Lamarckians and Scottish transmutationism
Desmond, Adrian. “Robert E. Grant: The Social Predicament of a Pre-Darwinian Transmutationist.” Journal of the History of Biology 17 (2): 189–223 (1984).
Jenkins, Bill. Evolution Before Darwin. Theories of the Transmutation of Species in Edinburgh, 1804–1834. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press (2019).
Secord, James. “The Edinburgh Lamarckians: Robert Jameson and Robert E. Grant.” Journal of the History of Biology 24 (1): 1–18 (1991).
Corsi, Pietro. ‘Edinburgh Lamarckians? The Authorship of Three Anonymous Papers (1826–1829)’, Journal of the History of Biology 54 (2021), pp. 345–374.
Darwin and Darwinism
Desmond, Adrian and James Moore. Darwin: The Life of a Tormented Evolutionist. New York: W. W. Norton & Company (1994).
van Wyhe, John. “Mind the Gap. Did Darwin Avoid Publishing his Theory for many years?” Notes & Records of the Royal Society 61 (2007), 177–205.
Sloan, Philip R. “Darwin, Vital Matter, and the Transformation of Species.” Journal of the History of Biology 19 (3): 369–445 (1986).
Phillip R. Sloan, “The Making of a Philosophical Naturalist.” In: Hodge, Jonathan and Gregory Radick (Eds.), The Cambridge Companion to Darwin. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press (2009), 17–39.
Sponsel, Alistair. Darwin’s Evolving Identity: Adventure, Ambition, and the Sin of Speculation. Chicago: University of Chicago Press (2018).
Young, Robert M. “Malthus and the Evolutionists: The Common Context of Biological and Social Theory.” Past & Present 43 (1969): 109–45.
Young, Robert M. “Darwin’s Metaphor: Does Nature Select?” The Monist 55 (3): 442–503 (1971).
Bowler, Peter J. The Non-Darwinian Revolution: Reinterpreting a Historical Myth. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press (1988).
Bowler, Peter J. The Eclipse of Darwinism: Anti-Darwinian Evolution Theories in the Decades Around 1900. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press (1983).
Hale, Piers J. “Rejecting the Myth of the Non-Darwinian Revolution.” Victorian Review 41 (2): 13–18 (Fall 2015).
Lightman, Bernard. “Darwin and the popularisation of evolution.” Notes and Records of the Royal Society 64: 5–24 (2010).
Richards, Robert J. The Meaning of Evolution: The Morphological Construction and Ideological Reconstruction of Darwin’s Theory. Chicago: University of Chicago Press (1992).
Ruse, Michael. The Darwinian Revolution: Science Red in Tooth and Claw. Chicago: University of Chicago Press (1979).
Lamarck and Lamarckism
Barthélemy-Madaule, Madeleine. 1982. Lamarck, the Mythical Precursor: A Study of the Relations between Science and Ideology. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Burkhardt, Richard. 1970. Lamarck, Evolution, and the Politics of Science. Journal of the History of Biology 3 (2): 275–298.
Burkhardt, Richard. 1977. The Spirit of System: Lamarck and Evolutionary Biology. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Corsi, Pietro. 1988. The Age of Lamarck: Evolutionary Theories in France, 1790–1830. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Corsi, Pietro. 2005. Before Darwin: Transformist Concepts in European Natural History. Journal of the History of Biology 38 (1): 67-83.
Corsi, Pietro. 2011. The Revolutions of Evolution: Geoffroy and Lamarck, 1825–1840. Bulletin du Musée D’Anthropologie Préhistorique de Monaco 51: 113–134.
Jordanova, Ludmilla. 1984. Lamarck. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Spary, Emma C. 2000. Utopia’s Garden: French Natural History from Old Regime to Revolution. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
listening and learning. the future has always been female
by Michael Roppolo
June 8, 2023 / 1:32 PM / CBS News
Researchers have identified the first known case of a crocodile making herself pregnant — and producing a fetus that was genetically identical to herself. The findings were published Wednesday by a team led by evolutionary biologist Warren Booth from Virginia Tech in Biology Letters, a journal published by the Royal Society.
In 2018, officials with the Parque Reptilandia in Costa Rica found 14 eggs in a female's enclosure. The crocodile had been in isolation since the age of 2, yet she still managed to lay a clutch of eggs at 18.
"Given the period of isolation from mates, these would normally be considered non-viable and discarded," the researchers wrote. But the officials gathered seven eggs that appeared viable and kept them in an incubator.
There were several signs that one of the eggs may be viable, Booth told CBS News.
"Viable eggs are often bright white, whereas infertile may be more yellowish," he said. "When held up to a flashlight, viable crocodile eggs will have a distinct band, whereas non-viable will simply glow yellow."
Costa Rica officials reached out to experts in the U.S. for consultation — ones that specialized in parthenogenesis. The term is derived from the Greek words "parthenos," meaning "virgin," and "genesis," meaning "origin," according to Encyclopedia Britannica.
Booth, and co-author Gordon Schuett of Georgia State University, had published multiple papers on the topic. As such, they were the "go-to people," Booth told CBS News.
Once considered rare, so-called virgin births have been documented among various species — including sawfish, snakes, sharks, and birds. The process, which is more common in the plant and insect worlds, allows a female organism to replicate itself without fertilization from a male.
In 2021, a study found that California condors can have virgin births. Researchers with the San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance said genetic testing confirmed that two male chicks that hatched in 2001 and 2009 from unfertilized eggs were related to their mothers. Neither was related to a male. In 2019, an anaconda housed with two other females gave birth. DNA testing would later confirm that the anaconda babies were reproduced through parthenogenesis.
In the case of the crocodile in Costa Rica, three months after workers found the eggs, none had hatched and only one egg was found to have a fully formed but nonviable fetus. DNA analysis would later determine that the fetus was 99.9% genetically identical to its mother.
Virgin births could be happening in crocodiles without anyone realizing, according to the researchers.
"These findings, therefore, suggest that eggs should be assessed for potential viability when males are absent," they wrote.
The authors suggest that in these cases among reptiles, birds, and now crocodiles, there may be a common evolutionary origin.
"This discovery offers tantalizing insights into the possible reproductive capabilities of the extinct archosaurian relatives of crocodilians and birds, notably members of Pterosauria and Dinosauria," they write, referring to flying reptiles that have been described as "close cousins" of dinosaurs.
Booth told CBS News that crocodiles are at the base of a lineage known as the archosaurs, with the most recent members being birds. All of these creatures use the same complex form of parthenogenesis, or terminal fusion automixis. It is unlikely they all developed independently.
"The cool aspect is that in between crocodiles and birds are the pterosaurs and dinosaurs," he added. "Given that all of these lineages use the same mechanism, it is highly likely that pterosaurs and dinosaurs also had the capacity to produce parthenogenetically."
#crocodilians are so so so so cool anyway one of my forever faves but this is a whole other level of cool#i looooove that there are species that can do this
381 notes
·
View notes
Text
Its honestly very concerning how popular ContraPoints video on "Transtrenders" was. I want to make a post discecting it briefly because I feel the video does a disservice to young trans folk looking to learn, instead leaving them feeling unjustified in their indentitiy under the guise of some radical acceptance
One of the main issues with the video as a whole is how natalie breaks down existing understandings of trans medicine as a tool to try and unseat transmedicalist talking points, and show how being trans is about personal experience and "feelings". While its important to critique transmedicalists, what she does here is undermine what many people see as the best justification for trans existence without replacing it with anything. She does this in my opinion, because she honestly doesn't have anything to replace it with, and doesn't understand the real basis for gender in the world.
Saying this is all well and good, I can critique anyone for not giving good basis for thing but its no help if i don't give anything of substance to back it up either, so heres a brief explanation of why transphobia is a problem, based in actual socio-political analysis.
Patriarchy is an economic structure which has been built up across centuries of accumulated surplus value which was passed down through the eldest son of the ruling class. this is a vast over simplification, but functionally this means there are systems in place in society which privilege men, give them access to more wealth, better positions, and control over non-men. Patriarchy has grown and changed over time and held different shapes depending on the society, we no longer have eldest sons inheriting royal rule (in most places), but we continue to have men as the group with the most economic and social agency in our societies. This privilege that Patriarchs have is constituted not of some magical benefits bestowed upon them from an abstract "system" but are instead taken directly from those who are not men. More specifically, men and Patriarchs take labor and resources from those whom patriarchy considers "non-men". Reproductive labor goes unpaid, women are under privileged in political society, we often don't get choices over our bodies. This isn't merely a coincidence, but serves specifically to give men power and confer more benefits onto them. Because of this, there must be systems in place to manage who is let into the patriarchy, who can be a Patriarch.
The most universal way of doing this is by deciding whether or not someone is a man and conferring onto them certain benefits as long as they uphold this structure, and ostracizing them if they are not. They do this ostracization because if this structure is not upheld artificially through oppression of women and bullying of nonconforming men to keep the categories of man and woman or even man and non-man distinct, the privilege given to the in-group starts to fade. In the same way that "White" is an artificial construct created and upheld to facilitate racism like slavery, imperialism, housing discrimination, and unpaid labor, so too is "manhood" and "womanhood". These constructs appear to be based in existing biology, so they often go without question, but race is also based on such "biology" and that does not mean its a founded construct. The basis for both "race" and "gender" break down once you look at higher level understandings of these concepts. Not all people with xy chromosomes are men, not all people of African decent have black skin, etc etc... I could go on about the "exceptions" for quite some time but you likely know many of them already. These are categories created fundamentally to give one specific category an economic advantage and justify their oppression of those who are outside of said category. The reason we need to respect trans-ness isn't because there is something inherently justified about being transgender, nor because we just have to be really nice to everyone and treat their feelings as absolute truths. Its because the systems which confine us and define gender so rigidly exist purely to oppress and extract value from others. These borders are deeply unjustified and we need to tear them away. We do not need to justify existing outside of the borders, but instead challenge the borders in the first place. Contrapoints fails to meaningfully do this
Natalie focuses almost entirely on the arguments surrounding justifications for transness and gives little thought to the justifications for patriarchy. It is treated as a default, always existing, status quo that is unquestionable. It makes me wonder how aware of it she really is, she seems to get stuck in justifying her own existence. the "Transtrenders" video focuses on a discussion between several characters where the primary issue at hand is how to justify being trans, should it be done through medicial, scientific frameworks? or should it be done from a kind and accepting view of others? She makes arguments against the former for being flawed and the latter for being unfounded, but she never actually replaces it with any critique of society, instead saying:
"Okay, so what am I supposed to tell Jackie Jackson then? What am I supposed to tell the TERFs? That I'm a woman because reasons?"
"No, not even because reasons. Just because you are."
"So it's what, a leap of faith? Oh great. I'm sure that's gonna convince all the rational skeptics. Justine, it makes us sound completely delusional."
"Well Tiffany, delusion is what separates us from the animals."
Which is an extremely unhelpful answer to give after tearing down what is to many, a key aspect in their reasoning for why they are justified in their identities, and while it is partially correct that trying to use one of the specific theories she outlined earlier to justify trans existence is an exercise in futility, she can't seemingly offer any alternative than some kind of "because I said so" when there ARE very good reasons to be in favor of trans acceptance, and historical reasons for our existence. In failing to do so she misleads perhaps an entire generation of trans people into thinking theres no real justification for their existence
The justification comes from understanding that the premise is false, that the forces which try to bind people to a specific societal gender role are themselves the issue.
She tries to point out that we dont need to justify transgender existence because the frameworks which hold us to cisgender existence are the real problem, but without ever talking about these cisgender standards in an actually meaningful way, instead talking abstactly about societies "expectations" or whatnot, where she should could be attacking the real economic forces of patriarchy. She should be tearing down patriarchy first and then using that to liberate trans existence but instead she tears down trans existence without touching patriarchy or any of the coercion or exploitation that arise from it. I consider this a great tragedy, and a prime example of her failures as an educator.
#long#self post#was writing about this to someone in discord and decided to make a version for tumblr#discourse i guess?#contrapoints
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
hi ✩
I'm not new to Tumblr but this is a new account, so here's a get to know me ig;
I go by crowen on here
I'm 17 y/o
I'm already gladly infatuated with someone so please refrain from any flirting
I am deeply in love with music, poetry, books, good films, the universe of cinema in general and black coffee.
I feel very connected to space, stars and the moon especially, hence the space themed username.
I am heavily fixated on solitaire and have been for about 2 years now. It haunts my every thought and I associate everything I do or say to solitaire.
my favourite tv shows are bojack horseman, queens gambit, sherlock holmes BBC, anne with an e, young royals, umbrella academy, heartstopper, gilmore girls, I am not okay with this, the end of the f***ing world, fleabag, everything now and life is strange (not a show but feels like one)
my favourite films are the perks of being a wallflower, girl interrupted, fantastic mister fox, coraline, moonrise kingdom, all the bright places, the edge of seventeen, call me by your name, asteroid city, watership down and dead poets society.
my favourite books are solitaire, loveless, the Harry potter series, the perks of being a wallflower, a good girls guide to murder series, Mathilda, the secret garden, metamorphosis, the bell jar, the narnia series and les misérables.
I major in biology, physics, chemistry and math but I suck at most of it, I'm not really good at studying generally, but biology and chemistry is pretty interesting otherwise.
I really like cats, crystals and insects, I particularly like to collect dead insects and pin them into frames for my room. I also collect animal bones for similar reasons.
I'm pretty sure I have depression among other issues but it's rather complicated to get a diagnosis and medical help because of some personal issues, so yeah that's fun lols.
I kin tori spring, bojack horseman(not a flex.) , chloe price, charlie kelmeckis, mia polanco, sydney novak, remus lupin AND sirius black(the marauders fandom versions), anne shirley, susana kaysen, theodore finch, fleabag, nadine byrd, ladybird, matilda wormwood and alyssa foley.
i also own another blog solely dedicated to poetry and maybe eventual writing (I really love literature a lot), the blog is called @aionios-monaxia
that's all for now lmao good luck to anyone with the patience to read it all, bye ★*・゚⋆ ༄
btw, please send me anons I find them very entertaining!
#solitaire#young royals#heartstopper#moonrise kingdom#wes anderson#fantastic mr fox#harry potter#narnia#bugs#animal bones#the end of the fucking world#i am not okay with this#the umbrella academy#queens gambit#bojack horseman#the marauders#coraline#asteroid city#astrology#cinema#coffee#tori spring#micheal holden#bbc sherlock#anne with an e#girl interrupted#the perks of being a wallflower#the edge of seventeen#all the bright places#everything now
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
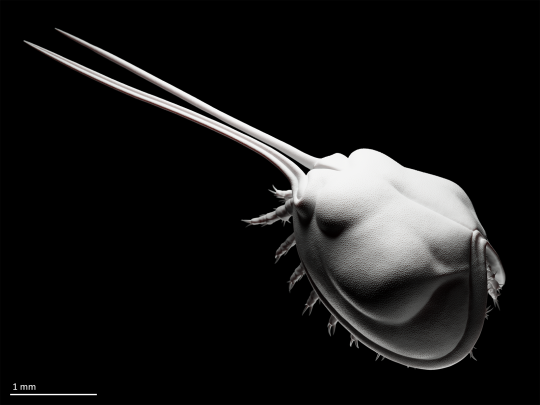
Sculpt of the small bivalved arthropod Gladioscutum lauriei from the middle Cambrian of Australia (after Hinz-Schallreuter & Jones 1994).
Gladioscutum had a body only 2-3 mm long, but, being undoubtedly aware of its disappointingly small size compared to its cooler Cambrian cousins like radiodonts and trilobites, tried to make up for it with a pair of (presumably) front-facing spines that were at least as long as the rest of the head shield.
Other than improving its self-esteem, the function of Gladioscutum's extremely elongated spines is unknown. The enlarged spines of other small Cambrian bivalved arthropods have been suggested to fulfill a sensory role, but this remains speculative (Zhang et al. 2014).
References and notes:
Gladioscutum was originally described as an "archaeocopid", an order that is now known to be an artificial grouping of various small bivalved arthropod fossils superficially resembling modern ostracod crustaceans. To my knowledge, the affinities of Gladioscutum have not been reinvestigated since its initial description, but its appearance (marginal rims, valve lobation, ornamented surface, simple hinge line) and age seem bradoriid-y enough (Hou et al. 2001) for me to more or less confidently reconstruct it as one (top scientific rigour as always on this blog).
Appendage morphology is unknown in Gladioscutum - what little soft anatomy I have not modestly hidden under the head hield is based on the bradoriid Indiana sp. from the Chengjiang Biota (Zhai et al. 2019). In that species, only the antennae are differentiated from the rest of the appendages, which has the double advantage of (1) not making crazy hypotheses about limb specialization in Gladioscutum and (2) giving me fewer different types of limbs to sculpt.
Like Gladioscutum, most bradoriids are only known from their decay-resistant valves, which are often squashed flat in a so-called "butterfly" position. This arrangement has been traditionally interpreted as the life position of the animals, which were implied to crawl over the seafloor like tiny crabs (e.g., Hou et al. 1996). Yet, undistorted fossils of head shields preserved in 3D are almost always closely drawn together, which is similar to the way modern bivalved arthropods like ostracods are articulated (protecting the soft limbs and body) and probably more reflective of the actual life position of bradoriids (Betts et al. 2016), as depicted here.
References:
Betts, M. J., Brock, G. A., & Paterson, J. R. (2016). Butterflies of the Cambrian benthos? Shield position in bradoriid arthropods. Lethaia, 49(4), 478–491. https://doi.org/10.1111/let.12160
Hinz-Schallreuter, I., & Jones, P. J. (1994). Gladioscutum lauriei n.gen. N.sp. (Archaeocopida) from the Middle Cambrian of the Georgina Basin, central Australia. Paläontologische Zeitschrift, 68(3), 361–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02991349
Hou, X., Siveter, D. J., Williams, M., Walossek, D., & Bergström, J. (1997). Appendages of the arthropod Kunmingella from the early Cambrian of China: Its bearing on the systematic position of the Bradoriida and the fossil record of the Ostracoda. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 351(1344), 1131–1145. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.1996.0098
Hou, X., Siveter, D. J., Williams, M., & Xiang-hong, F. (2001). A monograph of the Bradoriid arthropods from the Lower Cambrian of SW China. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of The Royal Society of Edinburgh, 92(3), 347–409. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0263593300000286
Zhai, D., Williams, M., Siveter, D. J., Harvey, T. H. P., Sansom, R. S., Gabbott, S. E., Siveter, D. J., Ma, X., Zhou, R., Liu, Y., & Hou, X. (2019). Variation in appendages in early Cambrian bradoriids reveals a wide range of body plans in stem-euarthropods. Communications Biology, 2(1), Article 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-019-0573-5
Zhang, H., Dong, X., & Xiao, S. (2014). New Bivalved Arthropods from the Cambrian (Series 3, Drumian Stage) of Western Hunan, South China. Acta Geologica Sinica - English Edition, 88(5), 1388–1396. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.12306
#i'll probably make more art of cambrian bivalved arthropods with fucked up spines#because there is no shortage of them#and they still manage to all look rather distinct#gladioscutum#bradoriid#(?)#arthropod#cambrian#paleozoic#australia#paleontology#palaeoblr#paleoart#my art
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
Examining Miscalculations and Intersex Definitions Regarding Sax's .018% Claim
The debate surrounding the definition of intersex and their characteristics has been a topic of debate within various professional fields, advocacy organizations, and studies for decades. Amidst this discourse includes a response from Dr. Leonard Sax, who claims to provide a "clinician's standpoint" despite lacking specialized expertise in these conditions, having only served as a primary care physician.
However, his arguments stand in stark contrast to those of Fausto-Sterling, a world-renowned professor of biology and gender studies. Furthermore, they diverge significantly from the consensus among major health associations, medical organizations, intersex rights groups, and human rights organizations.
Leading/Major Health Associations
The definition of intersex is resoundingly clear among leading health associations. The World Health Organization recognizes that intersex individuals are those "born with natural variations in biological or physiological characteristics, including sexual anatomy, reproductive organs, and/or chromosomal patterns that do not fit traditional definitions of male or female." Similarly, the National Institute of Health acknowledges individuals who are "born with, or who develop naturally in puberty, biological sex characteristics that are not typically male or female." The National Health Services emphasizes that intersex "involves genes, hormones, and reproductive organs, including genitals, and a person's physical sex development can differ internally, externally, or both."
Major/Leading Medical Associations
Major medical associations provide crucial insights into the understanding of intersex variations. The The American Medical Association adopts a broader definition, recognizing those with "a congenital condition with inconsistent chromosomal, gonadal, or anatomic sex development." Likewise, the Royal Australasian College of Physicians (PDF - which trains and accredits physicians in Australia and New Zealand) recognizes the significance of "congenital variations in a person's physical, hormonal, or genetic characteristics that do not match strict medical definitions of female or male sex." Additionally, the Center for Disease Control highlights the concept of "variations in physical sex characteristics, including anatomy, hormones, chromosomes, or other traits, that differ from expectations generally associated with male and female bodies." The International Symposium on Disorders of Sex Development notes there to be over 40 conditions
Leading Intersex Rights organizations
Intersex rights organizations, including Intersex Human Rights of Australia and Brújula Intersexual in Mexico, explicitly disagree with Dr. Leonard Sax's narrow definition of intersex individuals. They align themselves with more inclusive perspectives. For instance, Intersex Society of North America (working with) InterACT still use Fausto-Sterling's estimates over a decade later. Intersex Campaign for Equality in the United States also uses Sterling's estimates, believing the figures may even be higher than 2%. Intersex Asia and Intersex Russia both use estimates ranging from 0.5%-1.7%, Russia even including PCOS by name (which would be higher than 1.7%). InterAction from Germany's Intersex Rights suggests a range of 1-2 individuals per 100 births, highlighting how the medical community tries to "keep the frequency as extremely low as possible". Stop Intersex Mutilations from France posits there are over 40 variations and also suggests the prevalence might surpass 1.7%. Additionally, OII Europe presents prevalence estimates of 1:200 and 1.7% in their materials.
These organizations stress that intersex variations encompass a wide spectrum of biological and physiological characteristics beyond chromosomal ambiguity, challenging Sax's limited viewpoint.
Major human rights organizations
unequivocally support intersex individuals. The Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights emphasizes that intersex individuals are "born with a wide range of natural variations in their sex characteristics that don't fit the typical definition of male or female." Amnesty International notes that intersex encompasses "a wide umbrella of natural variations" (1.7%) and human rights abuses faced by intersex individuals. Human Rights Watch and the Human Rights Campaign underline the broader definition of intersex, acknowledging variations in genitalia, chromosomes, gonads, internal sex organs, hormone production, hormone response, and secondary sex traits, noting 1.7% as a prevalence rate. These human rights organizations underscore the importance of acknowledging intersex variations to ensure the protection of human rights.
Other Medical Orgs
Additional medical organizations like the Société Internationale d'Urologie (PDF) (an international professional organization dedicated to the field of urology), and the National Society of Genetic Counselors (uses 1.7%, says sex is not based on chromosones) adopt definitions that align with broader medical perspectives, they recognize the complexities of intersex conditions and advocate for understanding beyond binary definitions. Furthermore, the Endocrine Society acknowledges CAH to be part of a continuum of disorders, acknowledging the variations in severity.
Examining oversights: Discrepancies in Calculations
What's interesting is that even within Sax's own criteria, defining intersex as when 'the chromosomal sex is inconsistent with phenotypic sex, in which the phenotype is not classifiable as either male or female,' there's an evident inclusion of conditions like 'sex reversals' and ambiguous genitalia. However, Sax overlooks contributors such as mixed gonadal dysgenesis (MGD), as well as Swyer Syndrome and de la Chapelle syndrome, despite the former being the second leading cause of ambiguous genitalia.
Let's do the math
CAH (.0077) + CAIS (.0076) = .0153
+ ovotestes (.0012) + Idiopathic (.0009) = .0174
+ PAIS (.00076) = .01816
Fausto-Sterling includes de la Chapelle syndrome and MGD, although not as separate statistics. MGD is amalgamated with Turner's statistics, and de la Chapelle syndrome is grouped with other sex chromosome variations. However, Sax completely disregards these conditions when he discards several categories from his estimates, effectively throwing out qualifying numbers and ignoring their potential impact on the overall prevalence of intersex conditions.
While newer studies suggest a prevalence of .004 for de la Chappelle, we also have to consider that neither study includes Swyer Syndrome (+.00125), and PAIS is now recognized as at least as common as CAIS, with the latter being less likely to cause ambiguous genitalia at birth, and more likely to be identified in childhood.
The leading causes of ambiguous genitalia are CAH (.0077), PAIS (.00076), MGD (.005) and ovotestes (.0012), which places us just below (.01466) the ambiguous genitalia observed at birth from Mothers And Babies Reports from Australia, if we account for 15% (0.0006) of de la Chapelle births having ambiguous genitalia, it brings ambiguous genitalia at birth to a total of .015% found before.
If he includes CAH, PAIS (since CAIS is often not identified until childhood), ovotestes and idiopathic causes under his definition of intersex, it leaves us with .005% of births with ambiguous genitalia without a possible causing condition. This gap can easily be explained by his exclusion of MGD and de la Chapelle syndrome.
If we count only CAIS (.0076) and CAH (.0077), and the newer study estimate of de la Chapelle (.004), it already surpasses Sax's estimate at .0193.
With the addition of ovotestes (.0012), idiopathic (.0009), MGD (.005) and Sawyer syndrome (.00125) it brings us to .022%. With older estimates of PAIS (.00076), .0234%; with newer ones (.0076), just a bit above .03%, which is over two thirds an increase of Sax's original estimate.
There is overwhelming support for a more comprehensive understanding of intersex variations that emphasizes the importance of respecting a wide range of biological and physiological characteristics beyond mere genital and chromosomal definitions. This approach is essential in safeguarding human rights and ensuring equitable treatment for all individuals
TLDR;;
The collective stance of experts and organizations, spanning from health associations to human rights advocates, sharply contrasts with the limited definition created by Sax. He claims to know other clinicians' thoughts, without any evidence to back it up. As stated previously, he also lacks education and clinical experience on intersex individuals, he is a family doctor.
#intersex studies#actually intersex#intersex activism#intersex awareness#intersex discussion#intersex issues#intersex erasure#intersex theory#intersex things#intersex#purrspectives#intersex advocacy#queer activism#queer stuff#queer tag#intersex tag
24 notes
·
View notes
Note
hey lychee heeyyy if you ever wanna yk talk about the beeduo kids I will. I will Very gladly listen (<- avid listener)
my french hw is looking at me very badly.
ANYWAY i have been having very heavy brainrto about a second beeduo kid her name is Maple and she is absolutely perfect in every single way.
i have.l extensive enderman headcanons about pretty much all of their society and biology - because im sick and dumb in the head mostly, but also because i have a pretty detailed space au with endermen as a race where most of the wordbuilding came from. Then again, in my canon continuation au (wich started with the idea of making a better ending to the dsmp and then spiraled into like two more seasons and twenty to forty more years of story) ranboo is, in fact, a full blooded enderman and also a prince from the end so i kinda needed to get mysself some lore for that too.
Strictly maple specific biology fact include
endermen do not have any gender, but they also do not have any sexes. Unlike humans and other human based hybrids, endermen reproduce entirely asexually.
enderman reproduction is strictly based on the End, because endermen are technically made of End Dirt. There's a small, slightly related specie of enderman that is instead made of Nether Dirt. Ranboo is a little bit of an experiment, because they're made of both. (it was not an experiment on purpose. His older sister accidentally spilled the wrong dirt while he was being made)
This works basically like these: two or more people (more often more, as children are raised communally in hauntings. The only "single parent" household that really exists in the end is the royal family, and that's a whole other can of worms) decide they want a child. They gather around one of the Sacred Birth Places, which is any space that has a decently high density of dragon magic, and then they perform a ritual that i have yet to properly think about to make that baby. The baby is then made from the magic dirt and it'll proceed to grow pretty much like a human child.
The Dirt Baby is made 40% of dragon magic, 10% of Dirt, and 50% of their parent's shared souls.
(in my minecraft wordbuilding, a "soul" is the code a player runs on. For endermen player specifically, their sould is physically made into the enderpearl)
(the endermen that get farmed for the pearls aren't players, mostly. Kinda like the difference between and ape and a human irl)
Now enderian children. They are such fucked up little creatures and i love them very much.
First fact! They Do Not Have Mouths
just like. they don't. just skin down there.
It is mostly a defense mechanism: most predators in the end do not have the same kind of night vision enderman have, and hunt mostly by sound. Which means endermen children are uniquely silent and still most of the time.
The mouth does open with time - it fully opens around the time an enderman is fully matured. My ranboo, for example, still has his mouth kind of attatched by new lmanburg, and gets it fully open by the end of canon
children, not having mouths, cannot actually speak. They communicate mostly by vibrating (a purring kind of sound they produce with a secondary set of vocal cords that sits in their chest, just below their pearl. It can make a purring sound, a static kinda sound, and many many others), gesturing, and flapping of their secondary ears
their two sets of secondary ears are much smaller than the main set and will gradually disappear by the time they're like, 12 (which is also when the mouth is generally open Enough to start making sounds). Think of it like losing baby teeth.
And now, the star of the show (and the end of this post bc it is getting kind of long and i do actually need to study lmao)
BABY MAPLE!!!!
maple happens when Micheal is around thirteen (so think, 9 to 10 years after the end of the serie), and after a lot of things have happened in my regular canon
(For context, in that time period: The main villains (the egg and dream and dream xd) have all, separately, been defeated. Ranboo has been brought back to like, michael has lost his first two lives, the nukes have been launched, the apocalypse has happened for a few years, the dsmp as a political entity has been disbanded and every association to that has been made a bannable offense, our Main Cast beeduo family included has moved to a new, much normaler city, ranboo has discovered he's the long lost prince to the enderian empire and he has got a mother and a sister and he's actually even fucking richer than he was before, benchtrio has gotten a decent new life, michael has started elementary school and made a few friends, wilbur has gotten so much fucking therapy and is gradually trying to mend his relationship with his family. Not necessarily in that order).
At one point they just. decide to have a baby, just because, and michael is SUPER fucking on board with the idea. he loves the thought of a baby sibling, he adores the idea of having a partner iin crime, he's already decided the ways he will corrupt them to his side and use them to get more ice cream after dinner. he's happier about it than his parents tbh and they're really proud of that.
So they go to the end, and poof out baby maple with the usual enderian dark magic. Maple is a biological beeduo mix, and since my tubbo is a dragon hybrid, she's half enderman half dragon.
Given that she's made of end Dirt she's mostly enderman looking and deveopment wise, but she will grow wings at one point and her horns look a lot more like tubbo's than ranboo's.
Her name was given by tommy, because she has a cute little tail that looks like a maple leaf. He absolutely cried when they told him they're calling her maple, and he will deny this to his death.
They raised her pretty gender neutral because of the whole "endermen do not have gender thing" (and also bc in my minecraft world. people do not have gender at all mostly? Like sexes exist for human and human hybrids but there's a much much less strict gender spectrum) - but the second she was aware what gender identity was she fell in love with being a girl, and that was it. She was like, 6, but her opinion never changed much.
She becomes taller than michael by the time she's seven. He is adeguately horrified by that fact. She is still shorter than ranboo tho and it makes him gloat quite a bit.
She's very fem presenting, but she keeps her hair short by endermen tradition. (for enderman, the act of cutting one's hair is considered basic hygene. Not cutting it indicates grief, mourning, or a general tragedy big enough that you can't even take care of yourself. Ranboo, who still didn't remember this but did it by instincts, stopped cutting his hair after doomsday. Even decades post canon he keeps it super fucking long, out of the respect for the Goddess of Death that allowed his revival) (and also he thinks he looks relly fucking pretty with long hair) (he is right)
i have more thoughts but it Is 6 (six) pm so i am stopping. Good lick and very much thank you if you actually read my whole rambling lmao
#nova answers#nova aus#future just wait#plague speaks#i mean#could count as a write too but it isnt polished enough lmao#beeduo kids#maple tag!
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

The full finished Archaeopteryx picture.
I actually entered this into the Royal Society of Biology's BioArtAttack competition last September. It didn't say anything about drawing prehistoric creatures so I decided to draw what I wanted and hope for the best. I have absolutely no idea what place I came in, but they accepted it, so there's that.
#paleoart#archaeopteryx#bird#dinosaur#prehistoric#solnhofen#traditional art#maniraptora#fact file#BioArtAttack
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
♡ M.D.| ROYALTY | ANGST
Royalty. Royals. Pureblood. Truly a fickle thing.
Something that Malleus wants to ignore. Forget. His love for you goes beyond that, beyond the rules. The norms set up by society, and you know it. You do... Yet infinity is a long time... And you don’t live long. 100 years is nothing to him, yet it’s all you have. All you have to spend...
Royalty. Royals. Pureblood. Fae.
His voice cracks upon every word. A man that seems always so put together, kneeling before you, pleading—begging. He shall cut the tongue of every man or woman that spoke unwell of you. He swears it. He does. You can't leave him. His hands shake, pressed against your waist, tears close to falling. His heart aches, as if being ripped from his chest. He can make it better. He can. He has not the strength you possess. Neither the grace as you cry, pleading—begging for him to let you go. To let you go.
Royalty. Royals. Pureblood. Human. Mortal.
Something that Malleus wants to ignore. Forget. His love for you goes beyond that, beyond the rules. Beyond basic biology. Beyond the differences that are so large, far too large to ignore, and you know it. You do. 100 years is nothing... Merely a second... an hour that drags along...
Humans never belong with Fae.

#diasomnia x reader#diasomnia#diasomnia angst#malleus draconia#malleus x reader#malleus angst#T.MANOR.DRABBLES
200 notes
·
View notes