#Recovery Time Objectives (RTO)
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
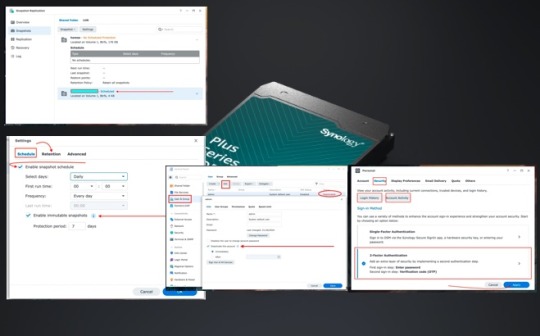
DSM Security: How to Protect Synology DS923+ NAS
We will adhere to industry best practices in configuring and proffering steps for “DSM Security: How to Protect Synology DS923+ NAS”. To ensure the protection of your data and system on the Synology DS923+, it is crucial to implement security controls actively. Active security measures enhance the overall defense posture, guard against potential threats and vulnerabilities, and fortify the…
View On WordPress
#Download Synology’s App#DSM Key Manager#Enable DoS Protection#Protect NAS#Protect Synology NAS#Recovery Point Objectives (RPO)#Recovery Time Objectives (RTO)#Synology#Synology Diskstation#Synology DS923+ NAS#Verification Code (OTP)
1 note
·
View note
Text
How are Amazon backup services used by cloud consulting services?
As more and more businesses move their operations to the cloud, the need for reliable and efficient backup services becomes increasingly critical. AWS Backup is one such service that provides centralized backup and recovery capabilities for Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources. AWS cloud consulting services provider in USA can help organizations leverage AWS Backup to protect their data and applications.
Here are some ways in which AWS cloud consulting services provider in USA can use AWS Backup to benefit their clients:
Centralized Backup Management AWS Backup allows businesses to centrally manage backups for a wide range of AWS resources, including Amazon EBS volumes, Amazon RDS databases, and Amazon DynamoDB tables, among others. By working with an AWS cloud consulting services provider in USA, businesses can ensure that their backup processes are streamlined and managed in a centralized manner.
Consistent Backup Scheduling AWS Backup offers flexible backup scheduling options, allowing businesses to create backup plans that meet their specific needs. With the help of an AWS cloud consulting services provider in USA, businesses can ensure that their backup schedules are consistent and meet their Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs).
Efficient Backup Storage AWS Backup offers efficient backup storage through the use of incremental backups and data deduplication techniques. This helps businesses reduce the amount of storage required for backups, thereby lowering costs. AWS cloud consulting services provider in USA can help businesses optimize their backup storage to minimize costs while still ensuring reliable backups.
Cross-Region Backup Replication AWS Backup also allows businesses to replicate backups across multiple regions for disaster recovery purposes. This means that if a particular region experiences an outage or failure, businesses can quickly recover their data and applications from a backup in another region. AWS cloud consulting services provider in USA can help businesses set up cross-region backup replication to ensure maximum availability and resiliency.
Compliance and Governance AWS Backup also supports compliance and governance requirements through the use of AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies and audit logs. AWS cloud consulting services provider in USA can help businesses ensure that their backup processes are in compliance with relevant regulations and standards, and provide the necessary documentation to auditors.
In conclusion, AWS Backup is a powerful tool for businesses looking to protect their data and applications in the cloud. By working with an AWS cloud consulting services provider in USA, businesses can ensure that their backup processes are streamlined, consistent, efficient, and compliant. If you're looking for a reliable backup solution for your AWS resources, consider working with an AWS cloud consulting services provider in USA to leverage AWS Backup.
#AWS cloud consulting services provider in USA#AWS cloud consulting services provider#AWS cloud consulting services
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you are working in the cloud, you need to treat disaster not as a matter of if, but when. Sooner or later, you are likely to experience some issues regarding the integrity or availability of your data and IT environment. Having a solid Disaster Recovery plan ensures your downtime is kept to a minimum, and that you can restore your operations with minimal damage. This can be the difference between being in or out of business. Amazon Web Services (AWS) users can take advantage of several features in the AWS cloud environment to build a robust recovery plan. Read on to learn how to you can take full advantage of the functions in your AWS environment, to keep your data safe. What Is AWS Disaster Recovery? Disaster recovery is the process of restoring applications, data and hardware to ensure business continuity. An attack or disaster is always close, therefore, it is critical for every organization to have a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) in place. DRP is a documented, structured layout of instructions with the goal to recover disrupted systems and networks in the event of a disaster. While this may sound fairly straightforward, you shouldn’t think of this as a static process in which you can design the plan and rest assured nothing bad will happen. Amazon Web Services defines disaster recovery as “a continual process of analysis and improvement, as business and systems evolve”. Amazon Web Services provides its users with a set of cloud-based disaster recovery services. Organizations migrating to AWS cloud find the ability to cross-region disaster recovery very attractive, increasing the popularity of the platform. How do you start planning a disaster recovery plan for AWS? You should start by conducting a Business Impact Analysis to define two key metrics: Recovery Time Objective(RTO)—the maximum acceptable time your application or system can be offline before the data loss presents a danger for the business continuity. Recovery Point Objective (RPO)—the time it takes to recover your business operations after the disruption started. This metric varies according to the type of data the application uses. For example, modified user data can have an RPO of a few minutes, while infrequently modified data can have an RPO of hours. Timeline of RTO and RPO After defining what RTO and RPO work for your organization, the next step is to choose the disaster recovery method. AWS offers four different methods for backup and disaster recovery, which can be used in combination with each other or with third-party solutions depending on the RPO and RTO metrics. The Cold Method This involves periodically backing up the systems on tape and sending them off-site. Depending on what RPO you determined, you can use services such as S3, Direct Connect, or Import/Export to define backup solutions. Pilot Light Using this method involves scripting the environment as a template and a minimal version of the system is running in a different region. Usually, the database is activated for data replication, such as if needed, there is a core element always ready for recovery. This core, or Pilot Light, can be scaled up in case of a disaster. Although this method reduces the RTO and RPO, it can be costly to implement. This method requires defining retention time and regularly testing the backups. Warm Standby This method ensures a minimal recovery time by running a scaled down version of a fully functional environment. During recovery, this standby infrastructure is scaled up, updating DNS records to re-route the traffic to the new AWS. This approach reduces RTO and RPO. However, since it runs 24/7, it incurs higher costs. Multi-Site This approach duplicates the environment in its totality, meaning there is always another active environment running in a different region. Usually, it involves configuring automated failover to re-route the traffic from the affected site in case of disaster. 5 Tips for Planning Disaster Recovery for AWS
Although AWS doesn’t have a proprietary Disaster Recovery solution, it provides the users with tools they can use to create a customized recovery solution. When implementing an AWS disaster recovery plan, the following tips can come in handy: #1. Backup and Recovery are Not the Same Thing Having recent backups of your organization’s data is essential for a successful recovery. After all, you will only recover what is safely backed up. As important as is to schedule regular backups, it is not enough. Automating the backups, for example by using the snapshots LifeCycle Manager, is a good practice to ensure the data is up to date. Your disaster recovery plan should include processes to access the data quickly in case of an outage or security event. #2. Identify the Critical Data You should conduct an audit of your assets to identify your mission-critical data and applications as part of your DR plan. At this stage, you should choose how your data will be stored, whether using snapshots or Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) for instance. #3. Use Cross-Region Backups One of the most important considerations is to spread your backups geographically to avoid large-scale disasters to affect business continuity. To protect your data, you should take advantage of the AZ (Availability Zones) around the world, to keep your backups in multiple locations. A good practice could be to replicate the EBS volumes to another AZ or, better yet, to another region. This can be done simply by creating a snapshot and recreating the volume in the destination AZ from that snapshot. #4. Test Your Disaster Recovery Plan This ensures you can identify any gaps and potential flaws when there is no disaster around. Therefore, you are better prepared with a well-oiled plan, even if using third-party vendors. #5. Consider a Disaster Recovery as a Service Solution Most companies handle disaster recovery planning in-house. However, more organizations are opting to outsource to third-party services the implementation and maintenance of their DR plans. Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) enables companies to focus on production while their DR plan is being taken care of. The Bottom Line For AWS users, it is very convenient to take advantage of the existing tools provided by AWS to build a customized recovery plan. While AWS doesn’t have a proprietary disaster recovery solution, this is compensated for by the flexibility offered to users to repurpose functions and features to create their own DR solution. In this article, I covered several considerations to keep in mind when planning your DR plan with AWS, which should help your strategy up-to-date and effective.
0 notes
Text
ISO 22301 Certification Consultants Handling Actionable Steps and Documentation Needed

Disruptions including cyberattacks, natural disasters, and supply chain failures can devastate organizations in today’s fast-paced business environment. ISO 22301 is the globally recognized standard for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS) to enable organizations to maintain business continuity and the resilience to withstand disruptions. This certification enables organizations to plan, prepare, and recover from unexpected disruptions efficiently.
ISO 22301 standard also requires organizations to have strong continuity management principles, risk assessments, and documentation of critical processes in place. It's a complicated and time-consuming process. This is where ISO 22301 Certification Consultants come into the picture.
These professionals help organizations in the journey of certification, taking charge of the actionable steps and the required documentation to keep up with the standard.
In this page, we will explain the key processes undertaken by ISO consultants in UAE and the documentation needed to ensure that certification is obtained as soon as possible.
ISO 22301 Certification Consultants Handling Actionable Steps
Preliminary Evaluation & Gap Analysis
For conducting an initial assessment and gap analysis, consultants assist organizations in examining their existing business continuity systems and how they measure against ISO 22301 Certification in Dubai.
It helps you define what needs to be improved and what is the requirement of establishing a comprehensive Business Continuity Management System (BCMS).
Reviewing current business continuity measures: This involves consultants taking stock of existing policies, procedures, and response strategies in place and how effective these were.
Identifying the gaps in compliance with the ISO 22301 requirements: Consultants assess the weaknesses in the organization’s continuity planning and offer recommendations for bridging the gaps.
Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
The only way to build a resilient Organization is to understand the potential risks in a business process and how it can disrupt the business. ISO 22301 Consultants in Abu Dhabi help run a risk assessment and business impact analysis (BIA) to determine the threats and vulnerabilities.
Identification of potential threats and vulnerabilities: This includes natural disasters, cyber threats, supply chain disruptions, and operational failures.
Impact analysis of disruptions on business operations: Identifying critical processes and the recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) to help prioritize continuity.
Develop a Business Continuity Plan
Once risks and their potential impacts are identified, external consultants assist clients in creating strong business continuity strategies, customized to their particular needs.
This allows the consultants to: Define recovery and resource allocation strategies
Defining roles and responsibilities: A well-defined structure makes sure that everyone involved understands their duties when a crisis strikes.
Execution of the Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
In order to respond and recover from disruptions effectively, a Business Continuity Plan is a mandatory requirement. BCP solutions are provided in part by consultants who assist organizations in the creation and planning of a structured BCP.
Establishing response and recovery plans: Detailed procedures will identify actions to be taken during an incident to mitigate downtime and losses.
Training must be conducted: Training employees on their responsibilities as part of the BCP and how they should respond to incidents
Testing & Exercising the Plan
NOTE: The Business Continuity Plan shall be tested and exercised regularly to ensure that it remains effective.
Drills, simulation, and testing scenarios: Consultants assist organizations in simulating a range of disruption scenarios, allowing them to evaluate their level of preparedness.
Pinpointing improvements and remedial actions: Evaluations undertaken after tests pinpoint the gaps and what needs updating to ensure better preparedness.
Internal Audit & Audit Readiness
An internal audit will be performed by the organizations prior to obtaining the ISO 22301 in order to verify its conformity to the standard.
Documents review and ensuring compliance: The consultancy team verifies that all necessary documents are present and comply with ISO 22301 requirements.
Audits from the third party: Consultants also prepare the organizations for the certification audit, help in resolving non-conformities, and ensure smooth certification.
Essential Documents Developed by ISO 22301 Consultants
For ISO 22301 Certification in UAE, proper documentation is essential. Such consultants help organizations with preparing critical documentation (among others):
Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) Manual: This document details the organization’s business continuity framework.
Risk Assessment & Business Impact Analysis Reports: In-depth reports outlining potential risk scenarios and their implications on business processes.
Business Continuity Policy & Objectives: State the organization’s commitment and objectives for business continuity
Business Continuity Plan (BCP) & Recovery Procedures: Step-by-step guides for response to and recovery from disruption
Roles, Responsibilities, and Communication Plan: Defines who is responsible for what in case of an incident and how communication is done.
Incident Response Guidelines & Crisis Management: A guide for effective handling of various incident types.
Internal Audit Reports & Corrective Action Plans: Reports on the audit, the issues found, and plans to correct any issues.
Training & Testing Records Provided: Records of employee training, drills, and testing exercises to demonstrate compliance.
Benefits of Working with ISO Consultants
There are many benefits to hiring ISO 22301 Consultants in Dubai to aid organizations in achieving certification in an effective and efficient manner.
Expert Guidance in Compliance and Implementation: Consultants bring in-depth knowledge of ISO 22301 requirements and best practices, ensuring a smooth certification process.
Processes Follow-Through and Documentation: Documentation is an integral part of the certification, and consultants help in ensuring the documents required are prepared accurately.
Lowered Risk of Certification Delays or Failures: By working with an expert, organizations can bypass the most common traps that could become a cause for delay or rejection of certification.
Improved Organizational Resilience: Certification to ISO 22301 strengthens an organization's capacity to manage disruptions, enabling long-term sustainability and business continuity.
The Final Say!!
ISO 22301 standard represents an important commitment for companies working to improve their business continuity and resilience. However, certification is neither easy nor straightforward and will require strong planning, risk management, documentation, and adherence to the standard’s entries.
The ISO 22301 Certification Consultants in UAE play a key role in assisting organizations with this process. Whether it be gap analysis, risk assessments, business continuity strategies, or documentation prep, these professionals help to cover every angle so that organizations are ready for certification. Not only do they streamline the certification process, but their expertise helps an organization respond more effectively to disruptions.
A competent consultant can greatly increase the chances of an organization being granted ISO 22301 certification, as well as ensure long-term resilience and business continuity.
From navigating the certification process to enhancing their current state of preparedness, organizations will get everything they need in this blog through its actionable steps and proper documentation.
0 notes
Text
In today’s digital landscape, technology plays a crucial role in business operations. However, unforeseen disruptions like cyber-attacks, natural disasters, or system failures can occur at any time, risking downtime, data loss, and customer trust. To Overcome these risks, a well-structured Disaster Recovery (DR) plan is essential for maintaining business continuity.
🔑What is Disaster Recovery (DR)? DR is a set of strategies, policies, and technologies designed to help businesses recover from disruptions. It ensures quick restoration of critical IT systems and data, minimizing downtime and financial damage.
💡 Key Steps in Disaster Recovery for Business Continuity:
Risk Assessment & BIA: Identify potential threats and evaluate their impact on business operations.
Define Recovery Objectives: Establish Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) to determine acceptable downtime and data loss.
Backup & Data Replication: Implement effective strategies for data backups and real-time replication.
Develop and Test the DR Plan: Design a detailed DR plan and conduct regular testing to ensure readiness.
Redundancy & Failover Systems: Implement systems that ensure seamless operation even when the primary system fails.
Ongoing Monitoring & Maintenance: Continuously monitor and update the DR plan to adapt to new challenges.
🚀 Clonetab CT-DR: A Powerful Solution for Oracle EBS and ERP Systems
Clonetab CT-DR is an advanced disaster recovery tool that ensures fast, reliable backups and data replication with low RTO & RPO. It’s an intuitive, easy-to-use platform that allows businesses to automate and test recovery procedures efficiently, minimizing downtime and data loss.
🔒 Why Disaster Recovery Matters: With a robust disaster recovery plan and the right tools, businesses can quickly bounce back from unexpected disruptions, ensuring continuous service and long-term success.
#BusinessContinuity#DisasterRecovery#DataProtection#ITInfrastructure#Clonetab#RiskManagement#CyberResilience#TechSolutions#OracleEBS#ERPSystems#Oracle#EBS#ERP#database#DBA#OracleDBA#Business#USA#UK
0 notes
Text
"How Do AWS Solution Architects Balance Flexibility and Complexity in Cloud Designs?"

When designing applications that span multiple AWS regions, there are several architectural considerations to ensure the deployment is highly available, performant, secure, and cost-efficient. Multi-region deployments are crucial for global applications that require low latency, disaster recovery, regulatory compliance, or redundancy. As an AWS Solution Architect, understanding these considerations can significantly impact the design and success of multi-region AWS architectures.
Here are the key architectural considerations for multi-region AWS deployments:
1. High Availability and Fault Tolerance
Overview:
A primary reason for multi-region deployments is to ensure high availability and fault tolerance. By distributing workloads across multiple regions, you can safeguard your application against regional failures such as natural disasters, power outages, or network disruptions.
Key Strategies:
Cross-Region Replication: Use services like Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, and DynamoDB with cross-region replication to ensure that data is available in multiple regions.
Amazon Route 53: Implement Route 53, AWS’s DNS service, to route traffic to healthy endpoints based on the health of applications in different regions.
Multi-Region Load Balancing: Leverage AWS Global Accelerator or use Application Load Balancers to distribute traffic across multiple regions based on geographic location or latency.
Considerations:
Latency: While multi-region architectures improve availability, there may be increased latency due to data replication and cross-region data transfer.
Data Synchronization: Managing real-time data synchronization and consistency across regions can be complex, especially for stateful applications.
2. Latency Optimization
Overview:
For applications that require low-latency access to end-users, it’s essential to distribute resources across regions that are geographically closer to the users.
Key Strategies:
Amazon CloudFront: Use CloudFront, AWS’s Content Delivery Network (CDN), to cache static content in edge locations worldwide, reducing latency for global users.
Regional Replication: Place resources such as EC2 instances and databases in regions close to users to minimize the round-trip time for data retrieval.
Route Traffic Based on Latency: Using Route 53 latency-based routing, AWS can direct user traffic to the region with the lowest response time, improving performance.
Considerations:
Geo-Location Specific Requirements: Ensure your regions comply with data residency laws and regional regulations, which may affect where you store and process data.
Network Design: A multi-region setup can introduce additional complexity in managing networking across different regions, especially in terms of routing traffic and securing communications.
3. Disaster Recovery and Backup
Overview:
A multi-region architecture helps achieve disaster recovery by ensuring that workloads can be quickly shifted to another region in case of failure. Disaster recovery (DR) strategies can vary from simple data backup to fully automated, multi-region failover.
Key Strategies:
Backup Across Regions: Implement cross-region backups using services like Amazon S3, RDS, and EBS Snapshots to ensure that data can be restored in the event of a regional failure.
Active-Active vs. Active-Passive Deployment: Choose between active-active (both regions serving traffic) or active-passive (one region is a standby) failover strategies based on business requirements for recovery time and data consistency.
Automated Failover: Use AWS CloudFormation or AWS Elastic Beanstalk for automated infrastructure deployment and failover when regions go down.
Considerations:
Cost: Multi-region deployments can increase costs due to data transfer between regions and maintaining resources in standby mode.
Recovery Time Objectives (RTO): The speed of recovery is critical. The architect must determine whether the application can tolerate some downtime or requires near-instant failover.
4. Data Sovereignty and Compliance
Overview:
Many organizations must comply with laws and regulations regarding where data can be stored and processed, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union or data residency laws in other countries.
Key Strategies:
Region-Specific Storage: Place sensitive data in specific regions that comply with local data residency laws, using services like S3, DynamoDB, or RDS.
Encryption: Ensure that data is encrypted at rest and in transit to meet security and compliance standards. Utilize AWS Key Management Service (KMS) to manage encryption keys across regions.
Audit and Monitoring: Leverage AWS CloudTrail and AWS Config to monitor resources across regions for compliance and security requirements.
Considerations:
Regional Regulations: Carefully assess regulatory requirements for each region and implement controls that prevent cross-border data transfer when prohibited by local laws.
Data Residency: Choose specific AWS regions that are compliant with the local laws where the business operates, especially when dealing with customer data.
5. Cost Optimization
Overview:
Multi-region architectures can increase costs due to the need to replicate data, transfer traffic, and maintain redundant infrastructure. However, there are strategies to optimize costs while maintaining performance and availability.
Key Strategies:
Right-Sizing Resources: Continuously monitor and right-size EC2 instances, databases, and storage across regions based on actual usage to avoid over-provisioning.
Spot Instances and Reserved Instances: Take advantage of EC2 Spot Instances for non-critical workloads in multiple regions or use Reserved Instances to lock in lower pricing for long-term, predictable workloads.
Data Transfer Costs: Be mindful of the costs associated with cross-region data transfer. Design the architecture to minimize data movement, such as by using CloudFront for caching static content and reducing the need for data replication across regions.
Considerations:
Data Transfer Fees: Data transferred across AWS regions is subject to charges, which can accumulate quickly if not carefully managed.
Balancing Cost and Performance: Achieving cost efficiency in a multi-region deployment requires balancing the need for high availability with the cost of maintaining redundant resources in different regions.
6. Network Design and Connectivity
Overview:
A robust network design is essential for connecting resources across multiple regions while maintaining security and performance.
Key Strategies:
AWS Transit Gateway: Use AWS Transit Gateway to simplify and centralize the network architecture by connecting multiple VPCs across regions. This helps manage inter-region traffic efficiently.
VPC Peering and Direct Connect: Set up VPC Peering or AWS Direct Connect to establish private, low-latency connectivity between regions.
PrivateLink and VPN: Use AWS PrivateLink and VPN connections for secure and private communication between services across regions.
Considerations:
Latency Impact: Inter-region connectivity can introduce latency, so careful planning is required to ensure that the architecture remains performant, especially for applications that rely on low-latency access.
Security Risks: Managing multiple connections across regions increases the attack surface. It’s essential to implement strong security controls, such as using AWS Shield for DDoS protection and AWS IAM for fine-grained access management.
7. Automation and Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Overview:
Managing infrastructure across multiple regions can quickly become complex, so automation is key to ensuring consistency and reducing human error.
Key Strategies:
AWS CloudFormation: Use AWS CloudFormation or Terraform to automate the deployment of resources across multiple regions. This ensures that infrastructure is consistent and repeatable.
CI/CD Pipelines: Implement CI/CD pipelines (using services like AWS CodePipeline) to automatically deploy code and updates to applications across regions.
Considerations:
Complexity of Automation: Automation can become complicated in multi-region environments, particularly when dependencies span multiple regions or require region-specific configurations.
Versioning and Rollbacks: Careful version control and rollback strategies are necessary to ensure that changes are deployed safely and reliably across regions.
Conclusion
Designing a multi-region AWS architecture requires careful planning and consideration of factors like availability, latency, disaster recovery, security, and cost. An effective multi-region deployment enhances the resilience and global reach of applications, providing a seamless experience for users around the world. However, it also introduces challenges that require expertise in network design, data replication, regulatory compliance, and cost management. By carefully addressing these architectural considerations, businesses can build a robust, scalable, and secure multi-region infrastructure on AWS.
#awstraining#cloudservices#softwaredeveloper#training#iot#data#azurecloud#artificialintelligence#softwareengineer#cloudsecurity#cloudtechnology#business#jenkins#softwaretesting#onlinetraining#ansible#microsoftazure#digitaltransformation#ai#reactjs#awscertification#google#cloudstorage#git#devopstools#coder#innovation#cloudsolutions#informationtechnology#startup
0 notes
Text
The Role of Data Recovery Houston Experts in Disaster Recovery Planning
Disaster recovery planning is crucial for safeguarding an organization’s critical data against unexpected disruptions. In Houston, where businesses rely heavily on data integrity, expert services play a vital role. This article delves into how data recovery Houston experts contribute to effective disaster recovery strategies.
Understanding the Importance of Data Recovery Houston Services
Even a brief data loss incident can disrupt operations in today's data-driven landscape. Data recovery Houston services are indispensable in mitigating risks, restoring functionality, and maintaining customer trust. These experts provide a foundational layer of security by ensuring businesses are equipped to handle unforeseen challenges.
How Data Recovery Houston Experts Assess Risks and Vulnerabilities
Every disaster recovery plan starts with an assessment of potential threats. Data recovery Houston specialists conduct in-depth risk analyses, identifying weak points in data storage systems. These insights enable businesses to implement preventive measures, safeguarding sensitive information from cyber threats, hardware failures, or natural disasters.
Crafting Customized Recovery Plans with Data Recovery Houston Professionals
A one-size-fits-all approach rarely suffices in disaster recovery. Data recovery Houston experts tailor recovery plans to address each organization’s unique needs. From prioritizing mission-critical systems to setting realistic recovery time objectives (RTOs), these professionals ensure businesses are ready to bounce back swiftly.
Leveraging Advanced Tools and Techniques by Data Recovery Houston Teams
The technical expertise of data recovery Houston professionals is unparalleled. They employ cutting-edge tools and techniques, such as RAID reconstruction and encrypted file recovery, to retrieve lost data efficiently. This technological edge minimizes downtime and enhances data security during recovery efforts.
Data Recovery Houston Experts and the Integration of Cloud Solutions
Cloud technology is a game-changer in disaster recovery. Data recovery Houston specialists help businesses integrate cloud solutions into their strategies, enabling real-time backups and remote data accessibility. This synergy between local expertise and cloud infrastructure ensures seamless recovery during large-scale disruptions.
Training and Preparing Teams with Data Recovery Houston Support
A robust disaster recovery plan extends beyond technical solutions. Data recovery Houston services often include training programs to prepare teams for emergencies. From conducting mock drills to educating staff on identifying threats, these initiatives foster a culture of preparedness.
Long-Term Benefits of Collaborating with Data Recovery Houston Experts
Partnering with data recovery Houston specialists yields long-term advantages. Businesses safeguard their data and enhance their operational resilience. The ability to recover quickly from disasters boosts competitiveness and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
Conclusion
The role of data recovery Houston experts in disaster recovery planning cannot be overstated. From risk assessment to seamless data restoration, these professionals provide the expertise to protect vital assets. In a world where data is a cornerstone of success, investing in specialized recovery services ensures businesses remain resilient against any challenge.
0 notes
Text
Amazon Web Service S3: How It Works And Its Advantages

Object storage from Amazon web service S3 is designed to allow you to access any quantity of data from any location.
What is Amazon S3?
An object storage solution with industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance is Amazon Simple Storage solution (Amazon S3). For almost any use case, including data lakes, cloud-native apps, and mobile apps, millions of users across all sizes and sectors store, manage, analyze, and safeguard any quantity of data. You may optimize expenses, arrange and analyze data, and set up precise access restrictions to satisfy certain business and regulatory requirements with affordable storage classes and user-friendly administration tools.
How it works
Data is stored by Amazon S3 as objects in buckets S3. A file and its metadata are objects. A bucket is an object’s container. You must first establish a bucket and choose an AWS Region and bucket name before you can store your data in Amazon web service S3. After that, you upload your data as objects in S3 to that bucket. Every object in the bucket has a key, also known as a key name, which serves as its unique identification.
You can customize the functionality offered by S3 to suit your unique use case. For instance, you can restore mistakenly erased or overwritten objects by using Amazon S3 Versioning to store multiple copies of an object in the same bucket. Only those with specifically allowed access permissions can access buckets and the items within them since they are private. S3 Access Points, bucket policies, AWS IAM policies, and ACLs can manage access.Image credit to Amazon
Advantages of Amazon S3
Amazon S3 has unparalleled performance and can store almost any size of data, up to exabytes. Because Amazon web service S3 is completely elastic, it will automatically expand and contract as you add and delete data. You simply pay for what you use, and there’s no need to supply storage.
Sturdiness and accessibility
Amazon S3 offers industry-leading availability and the cloud’s most robust storage. Supported by the strongest SLAs in the cloud, S3’s distinctive architecture is built to deliver 99.99% availability and 99.999999999% (11 nines) data durability by default.
Data protection and security
Protect your data with unmatched security, compliance, and access control. Besides being private, safe, and encrypted by default, Amazon S3 has many auditing options to monitor requests for access to your resources.
Best performance at the lowest cost
Large volumes of data that are accessed frequently, seldom, or infrequently can be cost-effectively stored with Amazon web service S3 automated data lifecycle management and numerous storage classes with the greatest pricing performance for any application. Amazon S3 provides the throughput, latency, flexibility, and resilience to guarantee that storage never restricts performance.
S3 amazon price
A 12-month free trial of S3’s free tier includes 100 GB of data transfer out per month, 20,000 GET requests, 2,000 PUT, COPY, POST, or LIST requests, and 5GB of Amazon S3 storage in the S3 Standard storage class.
Only pay for what you actually use. There isn’t a minimum fee. The Amazon S3 Pricing of requests and data retrieval, data transport and acceleration, data management and insights, replication, and transform and query features are the cost components of S3.
Use cases
Construct a data lake
A data lake can hold any size structured or unstructured data. High-performance computers, AI, machine learning, and data analytics maximize data value.
A secure Amazon S3 data lake lets Salesforce users search, retrieve, and analyze all their data.
Make a backup and restore important data
With S3’s powerful replication capabilities, data security with AWS Backup, and a range of AWS Partner Network solutions, you can meet your recovery time goal (RTO), recovery point objective (RPO), and compliance needs.
Terabytes of photos may be restored in a matter of hours rather than days with Ancestry’s usage of Amazon web service S3 Glacier storage classes.
Data archiving at the most affordable price
To cut expenses, remove operational hassles, and obtain fresh insights, move your archives to the Amazon S3 Glacier storage classes.
Using Amazon S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval, the UK public service broadcaster BBC safely moved their 100-year-old flagship archive.
Make use of your data
Amazon S3 might be the beginning of your generative AI journey because it averages over 100 million requests per second and stores over 350 trillion objects exabytes of data for almost every use case.
Grendene is employing a data lake built on Amazon web service S3 to develop a generative AI-based virtual assistant for its sales force.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#AmazonWebServiceS3#AmazonS3#AI#AWSBackup#S3storage#dataavailability#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
If you are working in the cloud, you need to treat disaster not as a matter of if, but when. Sooner or later, you are likely to experience some issues regarding the integrity or availability of your data and IT environment. Having a solid Disaster Recovery plan ensures your downtime is kept to a minimum, and that you can restore your operations with minimal damage. This can be the difference between being in or out of business. Amazon Web Services (AWS) users can take advantage of several features in the AWS cloud environment to build a robust recovery plan. Read on to learn how to you can take full advantage of the functions in your AWS environment, to keep your data safe. What Is AWS Disaster Recovery? Disaster recovery is the process of restoring applications, data and hardware to ensure business continuity. An attack or disaster is always close, therefore, it is critical for every organization to have a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) in place. DRP is a documented, structured layout of instructions with the goal to recover disrupted systems and networks in the event of a disaster. While this may sound fairly straightforward, you shouldn’t think of this as a static process in which you can design the plan and rest assured nothing bad will happen. Amazon Web Services defines disaster recovery as “a continual process of analysis and improvement, as business and systems evolve”. Amazon Web Services provides its users with a set of cloud-based disaster recovery services. Organizations migrating to AWS cloud find the ability to cross-region disaster recovery very attractive, increasing the popularity of the platform. How do you start planning a disaster recovery plan for AWS? You should start by conducting a Business Impact Analysis to define two key metrics: Recovery Time Objective(RTO)—the maximum acceptable time your application or system can be offline before the data loss presents a danger for the business continuity. Recovery Point Objective (RPO)—the time it takes to recover your business operations after the disruption started. This metric varies according to the type of data the application uses. For example, modified user data can have an RPO of a few minutes, while infrequently modified data can have an RPO of hours. Timeline of RTO and RPO After defining what RTO and RPO work for your organization, the next step is to choose the disaster recovery method. AWS offers four different methods for backup and disaster recovery, which can be used in combination with each other or with third-party solutions depending on the RPO and RTO metrics. The Cold Method This involves periodically backing up the systems on tape and sending them off-site. Depending on what RPO you determined, you can use services such as S3, Direct Connect, or Import/Export to define backup solutions. Pilot Light Using this method involves scripting the environment as a template and a minimal version of the system is running in a different region. Usually, the database is activated for data replication, such as if needed, there is a core element always ready for recovery. This core, or Pilot Light, can be scaled up in case of a disaster. Although this method reduces the RTO and RPO, it can be costly to implement. This method requires defining retention time and regularly testing the backups. Warm Standby This method ensures a minimal recovery time by running a scaled down version of a fully functional environment. During recovery, this standby infrastructure is scaled up, updating DNS records to re-route the traffic to the new AWS. This approach reduces RTO and RPO. However, since it runs 24/7, it incurs higher costs. Multi-Site This approach duplicates the environment in its totality, meaning there is always another active environment running in a different region. Usually, it involves configuring automated failover to re-route the traffic from the affected site in case of disaster. 5 Tips for Planning Disaster Recovery for AWS
Although AWS doesn’t have a proprietary Disaster Recovery solution, it provides the users with tools they can use to create a customized recovery solution. When implementing an AWS disaster recovery plan, the following tips can come in handy: #1. Backup and Recovery are Not the Same Thing Having recent backups of your organization’s data is essential for a successful recovery. After all, you will only recover what is safely backed up. As important as is to schedule regular backups, it is not enough. Automating the backups, for example by using the snapshots LifeCycle Manager, is a good practice to ensure the data is up to date. Your disaster recovery plan should include processes to access the data quickly in case of an outage or security event. #2. Identify the Critical Data You should conduct an audit of your assets to identify your mission-critical data and applications as part of your DR plan. At this stage, you should choose how your data will be stored, whether using snapshots or Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) for instance. #3. Use Cross-Region Backups One of the most important considerations is to spread your backups geographically to avoid large-scale disasters to affect business continuity. To protect your data, you should take advantage of the AZ (Availability Zones) around the world, to keep your backups in multiple locations. A good practice could be to replicate the EBS volumes to another AZ or, better yet, to another region. This can be done simply by creating a snapshot and recreating the volume in the destination AZ from that snapshot. #4. Test Your Disaster Recovery Plan This ensures you can identify any gaps and potential flaws when there is no disaster around. Therefore, you are better prepared with a well-oiled plan, even if using third-party vendors. #5. Consider a Disaster Recovery as a Service Solution Most companies handle disaster recovery planning in-house. However, more organizations are opting to outsource to third-party services the implementation and maintenance of their DR plans. Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) enables companies to focus on production while their DR plan is being taken care of. The Bottom Line For AWS users, it is very convenient to take advantage of the existing tools provided by AWS to build a customized recovery plan. While AWS doesn’t have a proprietary disaster recovery solution, this is compensated for by the flexibility offered to users to repurpose functions and features to create their own DR solution. In this article, I covered several considerations to keep in mind when planning your DR plan with AWS, which should help your strategy up-to-date and effective.
0 notes
Text
If you are working in the cloud, you need to treat disaster not as a matter of if, but when. Sooner or later, you are likely to experience some issues regarding the integrity or availability of your data and IT environment. Having a solid Disaster Recovery plan ensures your downtime is kept to a minimum, and that you can restore your operations with minimal damage. This can be the difference between being in or out of business. Amazon Web Services (AWS) users can take advantage of several features in the AWS cloud environment to build a robust recovery plan. Read on to learn how to you can take full advantage of the functions in your AWS environment, to keep your data safe. What Is AWS Disaster Recovery? Disaster recovery is the process of restoring applications, data and hardware to ensure business continuity. An attack or disaster is always close, therefore, it is critical for every organization to have a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) in place. DRP is a documented, structured layout of instructions with the goal to recover disrupted systems and networks in the event of a disaster. While this may sound fairly straightforward, you shouldn’t think of this as a static process in which you can design the plan and rest assured nothing bad will happen. Amazon Web Services defines disaster recovery as “a continual process of analysis and improvement, as business and systems evolve”. Amazon Web Services provides its users with a set of cloud-based disaster recovery services. Organizations migrating to AWS cloud find the ability to cross-region disaster recovery very attractive, increasing the popularity of the platform. How do you start planning a disaster recovery plan for AWS? You should start by conducting a Business Impact Analysis to define two key metrics: Recovery Time Objective(RTO)—the maximum acceptable time your application or system can be offline before the data loss presents a danger for the business continuity. Recovery Point Objective (RPO)—the time it takes to recover your business operations after the disruption started. This metric varies according to the type of data the application uses. For example, modified user data can have an RPO of a few minutes, while infrequently modified data can have an RPO of hours. Timeline of RTO and RPO After defining what RTO and RPO work for your organization, the next step is to choose the disaster recovery method. AWS offers four different methods for backup and disaster recovery, which can be used in combination with each other or with third-party solutions depending on the RPO and RTO metrics. The Cold Method This involves periodically backing up the systems on tape and sending them off-site. Depending on what RPO you determined, you can use services such as S3, Direct Connect, or Import/Export to define backup solutions. Pilot Light Using this method involves scripting the environment as a template and a minimal version of the system is running in a different region. Usually, the database is activated for data replication, such as if needed, there is a core element always ready for recovery. This core, or Pilot Light, can be scaled up in case of a disaster. Although this method reduces the RTO and RPO, it can be costly to implement. This method requires defining retention time and regularly testing the backups. Warm Standby This method ensures a minimal recovery time by running a scaled down version of a fully functional environment. During recovery, this standby infrastructure is scaled up, updating DNS records to re-route the traffic to the new AWS. This approach reduces RTO and RPO. However, since it runs 24/7, it incurs higher costs. Multi-Site This approach duplicates the environment in its totality, meaning there is always another active environment running in a different region. Usually, it involves configuring automated failover to re-route the traffic from the affected site in case of disaster. 5 Tips for Planning Disaster Recovery for AWS
Although AWS doesn’t have a proprietary Disaster Recovery solution, it provides the users with tools they can use to create a customized recovery solution. When implementing an AWS disaster recovery plan, the following tips can come in handy: #1. Backup and Recovery are Not the Same Thing Having recent backups of your organization’s data is essential for a successful recovery. After all, you will only recover what is safely backed up. As important as is to schedule regular backups, it is not enough. Automating the backups, for example by using the snapshots LifeCycle Manager, is a good practice to ensure the data is up to date. Your disaster recovery plan should include processes to access the data quickly in case of an outage or security event. #2. Identify the Critical Data You should conduct an audit of your assets to identify your mission-critical data and applications as part of your DR plan. At this stage, you should choose how your data will be stored, whether using snapshots or Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) for instance. #3. Use Cross-Region Backups One of the most important considerations is to spread your backups geographically to avoid large-scale disasters to affect business continuity. To protect your data, you should take advantage of the AZ (Availability Zones) around the world, to keep your backups in multiple locations. A good practice could be to replicate the EBS volumes to another AZ or, better yet, to another region. This can be done simply by creating a snapshot and recreating the volume in the destination AZ from that snapshot. #4. Test Your Disaster Recovery Plan This ensures you can identify any gaps and potential flaws when there is no disaster around. Therefore, you are better prepared with a well-oiled plan, even if using third-party vendors. #5. Consider a Disaster Recovery as a Service Solution Most companies handle disaster recovery planning in-house. However, more organizations are opting to outsource to third-party services the implementation and maintenance of their DR plans. Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) enables companies to focus on production while their DR plan is being taken care of. The Bottom Line For AWS users, it is very convenient to take advantage of the existing tools provided by AWS to build a customized recovery plan. While AWS doesn’t have a proprietary disaster recovery solution, this is compensated for by the flexibility offered to users to repurpose functions and features to create their own DR solution. In this article, I covered several considerations to keep in mind when planning your DR plan with AWS, which should help your strategy up-to-date and effective.
0 notes
Text
Unlock Resilience with D.A. Lamont Consulting Services: Your Trusted Partner in Disaster Recovery Consulting
In today's unpredictable world, organizations face an array of challenges that can disrupt their operations, from natural disasters to cyber threats. At D.A. Lamont Consulting Services, we understand the importance of being prepared for the unexpected. Our mission is to empower businesses with effective disaster recovery consulting strategies that ensure resilience and continuity.
Who We Are
D.A. Lamont Consulting Services is a dedicated team of experts passionate about helping businesses navigate the complexities of disaster recovery. With years of experience in the field, we specialize in tailoring solutions to meet the unique needs of each client. Our comprehensive approach combines best practices with innovative techniques, ensuring that you are well-equipped to handle any disruption that may arise.
Why Disaster Recovery Consulting Matters
Disaster recovery consulting is crucial for any organization aiming to protect its assets and maintain operational stability. Without a solid recovery plan in place, businesses risk losing valuable data, resources, and ultimately, customer trust. Our consulting services focus on identifying potential vulnerabilities within your organization and developing a robust disaster recovery plan that aligns with your specific goals.
Our Approach
Assessment: We start with a thorough assessment of your current operations and existing disaster recovery plans. This helps us identify weaknesses and areas for improvement.
Strategy Development: Based on our assessment, we collaborate with your team to develop a customized disaster recovery strategy that suits your organization’s needs. This includes defining critical business functions and establishing recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO).
Implementation: Our consultants will guide you through the implementation process, ensuring that all components of your disaster recovery plan are effectively integrated into your business operations.
Testing and Maintenance: A plan is only as good as its execution. We offer ongoing support, including regular testing of your disaster recovery procedures to ensure they remain effective and up-to-date in the face of changing circumstances.
The Benefits of Partnering with D.A. Lamont Consulting Services
Expertise: Our team is equipped with extensive knowledge of industry best practices, enabling us to provide insights that can significantly enhance your disaster recovery plans.
Tailored Solutions: We recognize that no two businesses are alike. Our personalized approach ensures that your disaster recovery strategy is uniquely suited to your organization’s size, industry, and specific needs.
Peace of Mind: With a solid disaster recovery plan in place, you can focus on your core business activities, knowing that you are prepared for any unforeseen events.
Conclusion
In a world where disruptions can happen at any moment, having a reliable disaster recovery plan is essential for business continuity. At D.A. Lamont Consulting Services, we are committed to providing the highest level of disaster recovery consulting to help you safeguard your organization’s future. Don’t leave your business’s resilience to chance—partner with us today and ensure that you are prepared for whatever challenges lie ahead.
For more information about our disaster recovery consulting services, visit D.A. Lamont Consulting Services. Let us help you build a more resilient organization, capable of thriving in the face of adversity.
0 notes
Text
Choosing the right cloud disaster recovery solution requires careful consideration of factors like Recovery Point Objectives (RPO), Recovery Time Objectives (RTO), data security, scalability, cost, and vendor reliability. Implementing best practices can minimize downtime and data loss, ensuring that businesses remain resilient during disasters.
#cloud disaster recovery#cloud DR solution#business continuity#disaster recovery plan#RPO#RTO#data security#scalable recovery#cloud DR vendors#disaster recovery testing#geographic redundancy
0 notes
Text
Drei Viertel der Opfer von Ransomware zahlen Lösegeld

Eine internationale Umfrage unter 900 IT- und Security-Verantwortlichen zeigt, dass 83 Prozent der Unternehmen im vergangenen Jahr Ziel von Ransomware-Angriffen waren, was alarmierende Trends in Bezug auf Häufigkeit, Schwere und Folgen von Angriffen aufzeigt. Ein Anbieter im Bereich identitätsbasierter Cyber-Resilienz, ist mit einer internationalen Studie der Prävalenz, Häufigkeit und den durch Lösegeldzahlungen und Kollateralschäden verursachten Kosten von Ransomware-Angriffen auf den Grund gegangen. Für die Studie wurden 900 IT- und Sicherheitsexperten in Unternehmen aus verschiedenen Branchen in Deutschland, Frankreich, Großbritannien und den USA befragt. Die Studie wurde von Semperis in der ersten Jahreshälfte 2024 durchgeführt. Zentrale Ergebnisse - Ransomware-Angriffe bleiben kein einmaliges Ereignis: 74 Prozent der Befragten, die in den letzten 12 Monaten gegen Lösegeld angegriffen wurden, wurden mehrfach angegriffen – viele innerhalb einer Woche. - Unternehmen können es nicht mit Ransomware aufnehmen: In Deutschland waren 82 Prozent der befragten Unternehmen in den vergangenen zwölf Monaten von Ransomware betroffen, davon 78 Prozent sogar öfter als einmal. 66 Prozent bezahlten mehrfach Lösegeld, 49 Prozent – und mit diesem Wert ist Deutschland unter allen Regionen in dieser Studie Spitzenreiter – sogar öfter als vier Mal. Im Gesamtdurchschnitt aller befragten Länder zahlten 78 Prozent der betroffenen Unternehmen Lösegeld – davon 72 Prozent mehrmals und 33 Prozent viermal oder häufiger. - Nur wenige Unternehmen sehen eine Alternative zur Lösegeldzahlung: 87 Prozent der Angriffe führten zu Betriebsunterbrechungen – selbst bei denen, die Lösegeld zahlten – einschließlich Datenverlust und der Notwendigkeit, Systeme offline zu nehmen. Für 16 Prozent der Befragten stellte der Angriff ein Dilemma um Alles oder Nichts dar – bei den Befragten aus Deutschland lag dieser Wert bei 19 Prozent. - Die Zahlung von Lösegeld garantiert keine Rückkehr zum normalen Geschäftsbetrieb: 35 Prozent der Opfer, die Lösegeld gezahlt haben, erhielten entweder keine oder fehlerhafte Decodierungsschlüssel. - Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) werden nicht erreicht: 49 Prozent der Befragten benötigten 1-7 Tage, um den Geschäftsbetrieb nach einem Ransomware-Angriff auf ein Minimum an IT-Funktionalität wiederherzustellen, und 12 Prozent benötigten 7 Tage oder länger. Die Ergebnisse unterstreichen einen alarmierenden Trend zu mehreren, manchmal gleichzeitigen Angriffen, was Führungskräfte dazu zwingt, ihre Cyber-Resilienz-Strategien neu zu bewerten, um häufige Fehlerquellen, wie beispielsweise unzureichende Backup- und Wiederherstellungspraktiken für Identitätssysteme, zu beheben. Fehlender Identitätsschutz Obwohl 70 Prozent der Befragten angaben, dass sie über einen Plan zur Wiederherstellung von Identitäten verfügen, was einen starken Fortschritt in Richtung IAM-zentrierter Sicherheit signalisiert, gaben nur 27 Prozent (36 Prozent in Deutschland) an, über dedizierte, Active Directory-spezifische Backup-Systeme zu verfügen. Ohne AD-spezifische, Malware-freie Backups und einen getesteten Wiederherstellungsplan wird die Wiederherstellung länger dauern, was die Wahrscheinlichkeit erhöht, dass sich das Unternehmen entscheidet, Lösegeld zu zahlen, um den Geschäftsbetrieb wiederherzustellen. „Im Mittelpunkt dieser ganzen Diskussion steht die Rentabilität von Unternehmen. Angreifer versuchen, diese zu gefährden, um sie überzeugen können, sich freizukaufen. Wenn ihnen ein erfolgreicher Angriff auf die Identität gelingt, besitzen sie Privilegien, die sie dann zu ihrem Vorteil nutzen können,“ erläutert Chris Inglis, Semperis Strategic Advisor und erster U.S. National Cybersecurity Director. „Wenn man bedenkt, dass es eine 24/7-Bedrohung für die heutigen Unternehmen gibt, kann man nie sagen ‚Ich bin in Sicherheit‘ oder sich einen Moment frei nehmen. Das Beste, was sie tun können, ist, ihre Umgebung verteidigungsfähig zu machen und sie dann zu verteidigen.“ Von den anhaltenden Herausforderungen im Bereich der Cybersicherheit, die Unternehmen nannten, stand die mangelnde Unterstützung durch den Vorstand ganz oben auf der Liste. Weitere Bedenken betrafen Budgetbeschränkungen, Personalmangel, veraltete Systeme sowie Vorschriften und Richtlinien zur Cybersicherheit. Lösegeld verweigern „Damit die Geschäftsleitung und der Vorstand eine fundierte Entscheidung gegen die Zahlung von Lösegeld treffen können, müssen sie wissen, wie lange die Wiederherstellung dauern wird und sich darauf verlassen können,“ erklärt Oliver Keizers, Area Vice President EMEA bei Semperis. „Dafür müssen Unternehmen ihren Wiederherstellungsplan in einem möglichst realitätsnahen Szenario testen und ihn dem Vorstand vorstellen, bevor ein Angriff erfolgt. Auf diese Weise sind die Entscheidungsträger im Ernstfall in der Lage, den Angreifern eine Zahlung zu verweigern.“ Über Semperis Für Sicherheitsteams, die mit der Verteidigung von hybriden und Multi-Cloud-Umgebungen betraut sind, stellt Semperis die Integrität und Verfügbarkeit von kritischen Enterprise-Directory-Diensten bei jedem Schritt in der Cyber-Kill-Chain sicher und verkürzt die Wiederherstellungszeit um 90 Prozent. Semperis hat seinen Hauptsitz in Hoboken, New Jersey, und ist international tätig, wobei das Forschungs- und Entwicklungsteam über die USA, Kanada und Israel verteilt ist. Passende Artikel zum Thema Lesen Sie den ganzen Artikel
0 notes
Text
AWS Storage Services
AWS Storage Services offers a range of safe and scalable cloud storage solutions to meet a variety of business requirements. These services, which are all intended to guarantee data durability, availability, and security, include object storage with Amazon S3, block storage via Amazon EBS, and archive solutions like Amazon Glacier. By putting into practice efficient backup, disaster recovery, and data management plans that are customized to meet their unique needs, businesses may use these services to enhance operational effectiveness and control expenses.
Aligning storage solutions with business goals like RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) is crucial to maximizing the potential of AWS Storage Services. By assisting in the determination of acceptable levels of data loss and downtime, these metrics help pick suitable storage configurations and replication algorithms. To guarantee that the storage solutions continue to satisfy changing business objectives, regular testing and cost analysis are also essential. This methodical approach to using AWS Storage Services can greatly improve disaster recovery and data management capabilities. For in-depth analysis, check out the Operisoft blog.
0 notes
Text
"What Are the Key Architectural Considerations for Multi-Region AWS Deployments?"

When designing applications that span multiple AWS regions, there are several architectural considerations to ensure the deployment is highly available, performant, secure, and cost-efficient. Multi-region deployments are crucial for global applications that require low latency, disaster recovery, regulatory compliance, or redundancy. As an AWS Solution Architect, understanding these considerations can significantly impact the design and success of multi-region AWS architectures.
Here are the key architectural considerations for multi-region AWS deployments:
1. High Availability and Fault Tolerance
Overview:
A primary reason for multi-region deployments is to ensure high availability and fault tolerance. By distributing workloads across multiple regions, you can safeguard your application against regional failures such as natural disasters, power outages, or network disruptions.
Key Strategies:
Cross-Region Replication: Use services like Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, and DynamoDB with cross-region replication to ensure that data is available in multiple regions.
Amazon Route 53: Implement Route 53, AWS’s DNS service, to route traffic to healthy endpoints based on the health of applications in different regions.
Multi-Region Load Balancing: Leverage AWS Global Accelerator or use Application Load Balancers to distribute traffic across multiple regions based on geographic location or latency.
Considerations:
Latency: While multi-region architectures improve availability, there may be increased latency due to data replication and cross-region data transfer.
Data Synchronization: Managing real-time data synchronization and consistency across regions can be complex, especially for stateful applications.
2. Latency Optimization
Overview:
For applications that require low-latency access to end-users, it’s essential to distribute resources across regions that are geographically closer to the users.
Key Strategies:
Amazon CloudFront: Use CloudFront, AWS’s Content Delivery Network (CDN), to cache static content in edge locations worldwide, reducing latency for global users.
Regional Replication: Place resources such as EC2 instances and databases in regions close to users to minimize the round-trip time for data retrieval.
Route Traffic Based on Latency: Using Route 53 latency-based routing, AWS can direct user traffic to the region with the lowest response time, improving performance.
Considerations:
Geo-Location Specific Requirements: Ensure your regions comply with data residency laws and regional regulations, which may affect where you store and process data.
Network Design: A multi-region setup can introduce additional complexity in managing networking across different regions, especially in terms of routing traffic and securing communications.
3. Disaster Recovery and Backup
Overview:
A multi-region architecture helps achieve disaster recovery by ensuring that workloads can be quickly shifted to another region in case of failure. Disaster recovery (DR) strategies can vary from simple data backup to fully automated, multi-region failover.
Key Strategies:
Backup Across Regions: Implement cross-region backups using services like Amazon S3, RDS, and EBS Snapshots to ensure that data can be restored in the event of a regional failure.
Active-Active vs. Active-Passive Deployment: Choose between active-active (both regions serving traffic) or active-passive (one region is a standby) failover strategies based on business requirements for recovery time and data consistency.
Automated Failover: Use AWS CloudFormation or AWS Elastic Beanstalk for automated infrastructure deployment and failover when regions go down.
Considerations:
Cost: Multi-region deployments can increase costs due to data transfer between regions and maintaining resources in standby mode.
Recovery Time Objectives (RTO): The speed of recovery is critical. The architect must determine whether the application can tolerate some downtime or requires near-instant failover.
4. Data Sovereignty and Compliance
Overview:
Many organizations must comply with laws and regulations regarding where data can be stored and processed, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union or data residency laws in other countries.
Key Strategies:
Region-Specific Storage: Place sensitive data in specific regions that comply with local data residency laws, using services like S3, DynamoDB, or RDS.
Encryption: Ensure that data is encrypted at rest and in transit to meet security and compliance standards. Utilize AWS Key Management Service (KMS) to manage encryption keys across regions.
Audit and Monitoring: Leverage AWS CloudTrail and AWS Config to monitor resources across regions for compliance and security requirements.
Considerations:
Regional Regulations: Carefully assess regulatory requirements for each region and implement controls that prevent cross-border data transfer when prohibited by local laws.
Data Residency: Choose specific AWS regions that are compliant with the local laws where the business operates, especially when dealing with customer data.
5. Cost Optimization
Overview:
Multi-region architectures can increase costs due to the need to replicate data, transfer traffic, and maintain redundant infrastructure. However, there are strategies to optimize costs while maintaining performance and availability.
Key Strategies:
Right-Sizing Resources: Continuously monitor and right-size EC2 instances, databases, and storage across regions based on actual usage to avoid over-provisioning.
Spot Instances and Reserved Instances: Take advantage of EC2 Spot Instances for non-critical workloads in multiple regions or use Reserved Instances to lock in lower pricing for long-term, predictable workloads.
Data Transfer Costs: Be mindful of the costs associated with cross-region data transfer. Design the architecture to minimize data movement, such as by using CloudFront for caching static content and reducing the need for data replication across regions.
Considerations:
Data Transfer Fees: Data transferred across AWS regions is subject to charges, which can accumulate quickly if not carefully managed.
Balancing Cost and Performance: Achieving cost efficiency in a multi-region deployment requires balancing the need for high availability with the cost of maintaining redundant resources in different regions.
6. Network Design and Connectivity
Overview:
A robust network design is essential for connecting resources across multiple regions while maintaining security and performance.
Key Strategies:
AWS Transit Gateway: Use AWS Transit Gateway to simplify and centralize the network architecture by connecting multiple VPCs across regions. This helps manage inter-region traffic efficiently.
VPC Peering and Direct Connect: Set up VPC Peering or AWS Direct Connect to establish private, low-latency connectivity between regions.
PrivateLink and VPN: Use AWS PrivateLink and VPN connections for secure and private communication between services across regions.
Considerations:
Latency Impact: Inter-region connectivity can introduce latency, so careful planning is required to ensure that the architecture remains performant, especially for applications that rely on low-latency access.
Security Risks: Managing multiple connections across regions increases the attack surface. It’s essential to implement strong security controls, such as using AWS Shield for DDoS protection and AWS IAM for fine-grained access management.
7. Automation and Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Overview:
Managing infrastructure across multiple regions can quickly become complex, so automation is key to ensuring consistency and reducing human error.
Key Strategies:
AWS CloudFormation: Use AWS CloudFormation or Terraform to automate the deployment of resources across multiple regions. This ensures that infrastructure is consistent and repeatable.
CI/CD Pipelines: Implement CI/CD pipelines (using services like AWS CodePipeline) to automatically deploy code and updates to applications across regions.
Considerations:
Complexity of Automation: Automation can become complicated in multi-region environments, particularly when dependencies span multiple regions or require region-specific configurations.
Versioning and Rollbacks: Careful version control and rollback strategies are necessary to ensure that changes are deployed safely and reliably across regions.
Conclusion
Designing a multi-region AWS architecture requires careful planning and consideration of factors like availability, latency, disaster recovery, security, and cost. An effective multi-region deployment enhances the resilience and global reach of applications, providing a seamless experience for users around the world. However, it also introduces challenges that require expertise in network design, data replication, regulatory compliance, and cost management. By carefully addressing these architectural considerations, businesses can build a robust, scalable, and secure multi-region infrastructure on AWS.
#awstraining#cloudservices#softwaredeveloper#training#iot#data#azurecloud#artificialintelligence#softwareengineer#cloudsecurity#cloudtechnology#business#jenkins#softwaretesting#onlinetraining#ansible#microsoftazure#digitaltransformation#ai#reactjs#awscertification#google#cloudstorage#git#devopstools#coder#innovation#cloudsolutions#informationtechnology#startup
0 notes
Text
Global Cyber Resilience Report 2024: Overconfidence and Gaps in Cybersecurity Revealed
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/global-cyber-resilience-report-2024-overconfidence-and-gaps-in-cybersecurity-revealed/
Global Cyber Resilience Report 2024: Overconfidence and Gaps in Cybersecurity Revealed
The Global Cyber Resilience Report 2024 presents an in-depth analysis of the current state of cyber resilience across various industries worldwide. Based on a survey conducted by Cohesity and Censuswide, involving 3,139 IT and Security Operations (SecOps) decision-makers from eight countries, this report sheds light on the significant gaps between perceived and actual cyber resilience capabilities.
Survey Demographics and Scope
The survey, conducted in June 2024, covered both public and private organizations across several countries:
United States: ~500 respondents
United Kingdom: ~500 respondents
Australia: ~500 respondents
France: ~400 respondents
Germany: ~400 respondents
Japan: ~300 respondents
Singapore: ~300 respondents
Malaysia: ~200 respondents
Participants were evenly split between IT and SecOps professionals, providing a comprehensive overview of the current cyber resilience landscape.
Key Findings
1. Overestimation of Cyber Resilience
A striking revelation from the survey is the overestimation of cyber resilience capabilities among organizations. Only 2% of respondents indicated that they could recover their data and restore business processes within 24 hours of a cyberattack. This starkly contrasts with the confidence expressed by nearly 4 in 5 (78%) respondents in their organization’s cyber resilience strategy.
2. Ransom Payments: A Growing Concern
The willingness to pay ransoms has become alarmingly common. Approximately 75% of respondents indicated their organization would pay over $1 million to recover data and restore business operations, with 22% willing to pay over $3 million. In the past year, 69% of respondents admitted to paying a ransom, despite 77% having policies against such payments.
Slow Recovery Times
Recovery times reported by organizations reveal significant vulnerabilities:
Only 2% could recover within 24 hours.
18% could recover within 1-3 days.
32% required 4-6 days.
31% needed 1-2 weeks.
16% would need 3+ weeks.
These recovery times fall short of the targeted optimum recovery time objectives (RTO), with 98% aiming for recovery within one day and 45% targeting within two hours.
4. Insufficient Data Privacy Compliance
Just over 2 in 5 (42%) respondents claimed their organization could identify sensitive data and comply with applicable data privacy laws. This indicates a significant gap in necessary IT and security capabilities.
5. Zero Trust Security Deficiencies
Despite the availability of effective security measures, many organizations have not adopted them:
48% have not deployed multifactor authentication (MFA).
Only 52% have implemented MFA.
Quorum controls or administrative rules requiring multiple approvals are used by 49%.
Role-based access controls (RBAC) are deployed by 46%.
These deficiencies leave organizations vulnerable to both external and internal threats.
The Escalating Threat Landscape
The survey underscores the increasing threat of cyberattacks:
In 2022, 74% of respondents felt the threat of ransomware was rising. By 2023, this figure rose to 93%, and in 2024, it reached 96%.
Two-thirds (67%) of respondents reported being victims of ransomware in the past six months.
Industries Most Affected
The report identifies seven industries that have been hardest hit by cyberattacks:
IT & Technology (40%)
Banking & Wealth Management (27%)
Financial Services (27%)
Telecommunications & Media (24%)
Government & Public Services (23%)
Utilities (21%)
Manufacturing (21%)
Areas of Critical Concern
1. Confidence-Capability Paradox
The disparity between confidence in cyber resilience strategies and the actual capability to execute these strategies effectively is evident. While many organizations have a cyber resilience plan, their ability to recover quickly from attacks lags significantly behind their goals.
2. Rampant Ransom Payments
The prevalence of ransom payments, often in contradiction to organizational policies, highlights a reactive rather than proactive approach to cyber resilience. The financial impact of paying ransoms extends beyond the immediate cost, affecting downtime, lost opportunities, and reputational damage.
3. Zero Trust Security Deficiencies
The failure to implement robust data access controls like MFA and RBAC poses a significant risk to organizations. Effective security measures are essential for protecting critical data and ensuring business continuity.
Recommendations for Improvement
To address these critical issues, the report suggests several actionable strategies:
Engage in rigorous testing, drills, and simulations to ensure the effectiveness of backup and recovery processes.
Sign up for ransomware resilience workshops to enhance cyber incident response capabilities.
Automate testing of backup data to verify integrity and recoverability without manual intervention.
Maintain detailed documentation and recovery playbooks to ensure all stakeholders understand their roles during an incident.
Conclusion
The Global Cyber Resilience Report 2024 that was commissioned by Cohesity highlights the urgent need for organizations to bridge the gap between their perceived and actual cyber resilience capabilities. By identifying and addressing these vulnerabilities, organizations can enhance their ability to recover from cyberattacks and protect critical data, ensuring a more secure and resilient future.
The comprehensive data and insights from this report serve as a crucial resource for IT and SecOp professionals aiming to strengthen their cyber resilience strategies and safeguard their organizations against the evolving threat landscape.
#2022#2023#2024#amp#Analysis#approach#authentication#backup#backup and recovery#banking#bridge#Business#business continuity#comprehensive#Critical Issues#cyber#cyber security#cyberattack#Cyberattacks#cybersecurity#data#data privacy#decision-makers#documentation#financial#financial services#Future#gap#Global#Government
0 notes