#Plantation campaign
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
On May 28, 1914, the Institut für Schiffs-und Tropenkrankheiten (Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases, ISTK) in Hamburg began operations in a complex of new brick buildings on the bank of the Elb. The buildings were designed by Fritz Schumacher, who had become the Head of Hamburg’s building department (Leiter des Hochbauamtes) in 1909 after a “flood of architectural projects” accumulated following the industrialization of the harbor in the 1880s and the “new housing and working conditions” that followed. The ISTK was one of these projects, connected to the port by its [...] mission: to research and heal tropical illnesses; [...] to support the Hamburg Port [...]; and to support endeavors of the German Empire overseas.
First established in 1900 by Bernhard Nocht, chief of the Port Medical Service, the ISTK originally operated out of an existing building, but by 1909, when the Hamburg Colonial Institute became its parent organization (and Schumacher was hired by the Hamburg Senate), the operations of the ISTK had outgrown [...]. [I]ts commission by the city was an opportunity for Schumacher to show how he could contribute to guiding the city’s economic and architectural growth in tandem, and for Nocht, an opportunity to establish an unprecedented spatial paradigm for the field of Tropical Medicine that anchored the new frontier of science in the German Empire. [...]
[There was a] shared drive to contribute to the [...] wealth of Hamburg within the context of its expanding global network [...]. [E]ach discipline [...] architecture and medicine were participating in a shared [...] discursive operation. [...]
---
The brick used on the ISTK façades was key to Schumacher’s larger Städtebau plan for Hamburg, which envisioned the city as a vehicle for a “harmonious” synthesis between aesthetics and economy. [...] For Schumacher, brick [was significantly preferable] [...]. Used by [...] Hamburg architects [over the past few decades], who acquired their penchant for neo-gothic brickwork at the Hanover school, brick had both a historical presence and aesthetic pedigree in Hamburg [...]. [T]his material had already been used in Die Speicherstadt, a warehouse district in Hamburg where unequal social conditions had only grown more exacerbated [...]. Die Speicherstadt was constructed in three phases [beginning] in 1883 [...]. By serving the port, the warehouses facilitated the expansion and security of Hamburg’s wealth. [...] Yet the collective profits accrued to the city by these buildings [...] did not increase economic prosperity and social equity for all. [...] [A] residential area for harbor workers was demolished to make way for the warehouses. After the contract for the port expansion was negotiated in 1881, over 20,000 people were pushed out of their homes and into adjacent areas of the city, which soon became overcrowded [...]. In turn, these [...] areas of the city [...] were the worst hit by the Hamburg cholera epidemic of 1892, the most devastating in Europe that year. The 1892 cholera epidemic [...] articulated the growing inability of the Hamburg Senate, comprising the city’s elite, to manage class relationships [...] [in such] a city that was explicitly run by and for the merchant class [...].
In Hamburg, the response to such an ugly disease of the masses was the enforcement of quarantine methods that pushed the working class into the suburbs, isolated immigrants on an island, and separated the sick according to racial identity.
In partnership with the German Empire, Hamburg established new hygiene institutions in the city, including the Port Medical Service (a progenitor of the ISTK). [...] [T]he discourse of [creating the school for tropical medicine] centered around city building and nation building, brick by brick, mark by mark.
---
Just as the exterior condition of the building was, for Schumacher, part of a much larger plan for the city, the program of the building and its interior were part of the German Empire and Tropical Medicine’s much larger interest in controlling the health and wealth of its nation and colonies. [...]
Yet the establishment of the ISTK marked a critical shift in medical thinking [...]. And while the ISTK was not the only institution in Europe to form around the conception and perceived threat of tropical diseases, it was the first to build a facility specifically to support their “exploration and combat” in lockstep, as Nocht described it.
The field of Tropical Medicine had been established in Germany by the very same journal Nocht published his overview of the ISTK. The Archiv für Schiffs- und Tropen-Hygiene unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Pathologie und Therapie was first published in 1897, the same year that the German Empire claimed Kiaochow (northeast China) and about two years after it claimed Southwest Africa (Namibia), Cameroon, Togo, East Africa (Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda), New Guinea (today the northern part of Papua New Guinea), and the Marshall Islands; two years later, it would also claim the Caroline Islands, Palau, Mariana Islands (today Micronesia), and Samoa (today Western Samoa).
---
The inaugural journal [...] marked a paradigm shift [...]. In his opening letter, the editor stated that the aim of Tropical Medicine is to “provide the white race with a home in the tropics.” [...]
As part of the institute’s agenda to support the expansion of the Empire through teaching and development [...], members of the ISTK contributed to the Deutsches Kolonial Lexikon, a three-volume series completed in 1914 (in the same year as the new ISTK buildings) and published in 1920. The three volumes contained maps of the colonies coded to show the areas that were considered “healthy” for Europeans, along with recommended building guidelines for hospitals in the tropics. [...] "Natives" were given separate facilities [...]. The hospital at the ISTK was similarly divided according to identity. An essentializing belief in “intrinsic factors” determined by skin color, constitutive to Tropical Medicine, materialized in the building’s circulation. Potential patients were assessed in the main building to determine their next destination in the hospital. A room labeled “Farbige” (colored) - visible in both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications - shows that the hospital segregated people of color from whites. [...]
---
Despite belonging to two different disciplines [medicine and architecture], both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications articulate an understanding of health [...] that is linked to concepts of identity separating white upper-class German Europeans from others. [In] Hamburg [...] recent growth of the shipping industry and overt engagement of the German Empire in colonialism brought even more distant global connections to its port. For Schumacher, Hamburg’s presence in a global network meant it needed to strengthen its local identity and economy [by purposefully seeking to showcase "traditional" northern German neo-gothic brickwork while elevating local brick industry] lest it grow too far from its roots. In the case of Tropical Medicine at the ISTK, the “tropics” seemed to act as a foil for the European identity - a constructed category through which the European identity could redescribe itself by exclusion [...].
What it meant to be sick or healthy was taken up by both medicine and architecture - [...] neither in a vacuum.
---
All text above by: Carrie Bly. "Mediums of Medicine: The Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases in Hamburg". Sick Architecture series published by e-flux Architecture. November 2020. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Text within brackets added by me for clarity. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
#abolition#ecology#sorry i know its long ive been looking at this in my drafts for a long long time trying to condense#but its such a rich comparison that i didnt wanna lessen the impact of blys work here#bly in 2022 did dissertation defense in architecture history and theory on political economy of steel in US in 20s and 30#add this to our conversations about brazilian eugenics in 1930s explicitly conflating hygiene modernist architecture and white supremacy#and british tropical medicine establishment in colonial india#and US sanitation and antimosquito campaigns in 1910s panama using jim crow laws and segregation and forcibly testing local women#see chakrabartis work on tropical medicine and empire in south asia and fahim amirs cloudy swords#and greg mitmans work on connections between#US tropical medicine schools and fruit plantations in central america and US military occupation of philippines and rubber in west africa#multispecies#imperial#indigenous#colonial#landscape#temporal#see also us mosquito campaigns in panama and british urban planning in west africa and rohan deb roy work on india bengal entomology#ecologies#bugs#tidalectics#archipelagic thinking#plantations#intimacies of four continents#carceral geography#black methodologies#indigenous pedagogies
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
This morning there was a nation-wide text spam campaign targeting Black Americans (largely students) telling them that they’ve been selected to pick cotton and will be picked up to be sent to a plantation after Trump’s inauguration.
People online are making jokes about it, but it’s genuinely a disturbing sign. Someone was emboldened enough to intentionally run a background on thousands of young Black people and send them racist messages the day after a very exhausting and stressful election.
#please boost this as much as possible#us politics#current events#racism#anti blackness#politics#Trump#us elections
23K notes
·
View notes
Text
Smearing campaigns in these days and ages are so easy. Each month the internet picks a celebrity to hate (most of the time a woman) and one to love (usually an ugly white man). You throw a bone, people take it and run it to the ground because it's a trend then they move on to the next person.

#like obviously plantation Barbie had a campaign against her#but we dont interrogate things#i had dwd flashbacks thinking why the hell cant i escape news about this damn movie and cast#Selena Gomez's fans being use as an exemple to how smear someone was something else#and the leaks about them not wanting to piss off swifties (the latter being proud instead of questioning the toxic environment they are#alimenting daily)#am i rambling ? yeah#we often overshadow the term virality and its negative connotation
1 note
·
View note
Text
DM: And he'll take you, you're staring to head up and then suddenly he will veer into the graveyard and takes you up to, you have definitely seen this woman before Eudora, this very very old Halfling woman, very very pale, she's got like a bonnet that's veiled that's hiding most of her face and she's just sort of sitting on this bench out in the shade. She has a wood cane with a grip that looks like a raven and she's just sort of sitting there quietly and enjoying the breeze and she's doing that thing where she's really still and there's a moment where you're looking at this very old, very still person. Tark (OOC): Oh god, she's dead. DM: Yeah. Tark (OOC): Oh god, she's dead. DM: Yeah until you get a little closer and her head will turn in your direction. Myrna: I hear an approach. That'd be Hector and who you got with you? Tark (OOC): I love her already. Eudora (OOC): I love her so much. DM: I think she had this accent... I hope. Well she does now. Tark (OOC): 'I hope' This is her now. Here you go. Eudora (OOC): You mean you're not giving her a fake Texan accent? DM: I can't. Tark (OOC): *laughs* -DM swearing she can't do a Texan accent and Thaddius agreeing that the attempt wasn't good- DM: So she's not from Illsyronia. Myrna: Who's there with you? Hector: This is Tark and Ms. Wildthorne, who you know. Tark is also a friend of Hunt and says that they are, well potentially both Chosen. DM: She kind of slowly will get up from her bench and you realize her cane isn't just for balance. She kind of taps it ahead of herself and follows it. Tark (OOC): Oh, she's blind. DM: Yeah. She kind of peers up at you through her veil and you see her eyes are completely cataracted. Tark (OOC): Oh. Oh. DM: This is a tiny tiny Halfling woman. Tark (OOC): Yes, my goodness. (IC): And Tark will, like he goes to reach out and shake her hand and then be like, 'Is this the appropriate greeting?' DM: She reaches out and shakes your hand. Tark (OOC): Oh beautiful! Okay. That would've been awkward. Fuckin' alright. (IC): Tark kind of looks back at Eudora like 'Where do I go from here? What do I say?' Myrna: You're a Chosen, you say? Tark: Yes. Myrna: Of the Lunar Lady or someone else? Tark: "No, someone else." He kind of side-eyes like 'should I?' Eudora: Eudora nods encouragingly. Tark: Lady Luck. Myrna: *chuckles* No, seriously. Tark: I am very serious. Myrna: Huh. Alright, well... Tark: If you wish, I could demonstrate? Myrna: Certainly, let's see what you can do. Tark: And then I think *looks through spells* Let's see... I'm trying to decide which... I think he would just, you know what, what else am I gonna do right now? Yeah, I think Tark would just summon the bee. Just like 'alright' 'cause I don't know, 'cause there's no way Tark can heal cataracts so... DM: Yeah. Tark: Let's not, that's not something he can demonstrate and no one else is hurt. DM: Right. Nathaniel (OOC): You can hurt somebody. Eudora: Eudora's fully pulling out a pocket knife or something. Hunt (OOC): Remember you stabbed your own leg. Nathaniel (OOC): There's plenty of people to hurt here. DM: That's true. Tark (OOC): You're not wrong, but no. I'm not. (IC): Tark kind of bats the... 'What are you doing?!' and just summons the bee. DM: She sort of closes her eyes as they are unseeing anyways and sort of listens to it buzzing and I kind of imagine it moves around her and--- Tark: Yeah. DM: She's sort of feeling it flow through the air. Myrna: Alright, another Chosen, interesting. There seem to be a lot of those in these times. Tark: Yes, so that is what we've been finding out also.
#D&D mischief#Relni Campaign#Relni Recap#Relni Chapter 52#Just wait till Relni 2#the southern accent I do Swan dubbed it 'plantation owner' even though I'm having that Amara's from Ilsyronia XD#I feel that's gonna get back to Hunt and she's gonna be like 'That fucking elf'#fucking stabbed himself in the leg to make Hunt heal him only to contemplate what to do to prove to Myrna that he's a Chosen of Lady Luck
0 notes
Text
Rotary Club Of Jamshedpur West Launches Tree Plantation Drive
Environmental Initiative Combines Greenery Efforts With Community Outreach The event in Chimti Paharia Village included tree planting and distribution of refreshments to local residents. JAMSHEDPUR ��� The Rotary Club of Jamshedpur West kicked off a tree plantation drive on July 1, 2024, as part of its ongoing environmental sustainability efforts. The initiative, held in Chimti Paharia Village,…

View On WordPress
#आयोजन#biodiversity enhancement#Chimti Paharia Village#Climate Change Initiatives#Community Outreach Jamshedpur#Dr. Amit Mukherjee Rotary#environmental sustainability#Event#Green Jamshedpur Campaign#Jamshedpur Social Responsibility#Rotary Club Jamshedpur West#Tree Plantation Drive
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Photo

Family Room in Portland Family room - large transitional open concept light wood floor family room idea with blue walls and a media wall
#green sectional sofa#blue accents#plantation shutters#sectional sofas#campaign chest#upholstered armchair#green velvet
0 notes
Text
I can dislike Blake Lively for her plantation wedding and tone deaf marketting and believe her when she says she has been harrassed because I'm an adult and my brain is developped enough to hold two truths at once, especially when these two truths have nothing to do with one another.
I'll believe her on her word alone, because when I said "me too" and "believe victims" I didn't mean "but only likeable victims though the annoying ones can stfu". But I don't have to. Because he literally signed a legal document agreeing not to do these behaviors again, emphasis on again.
And while she had the grace to only request that he stop those behaviors so she can keep working and didn't sue his ass right away, he decided to retaliate in a smear campaign that had even the staunchest feminists rallying around him. I'll admit, even I fell for his good guy spiel there, especially because years of his "man enough" podcast have bought him so much good will within the feminist community. And to find out that he was using us to prop up his career and harrass women behind the scenes? That is a betrayal. And the fact that the tactics of his team worked so well is something I have to sit with and unpack.
And yes, it's uncomfortable to realize you've been had. But the solution isn't to double down on a victim. It's to take a step back and admit that we are not immune to propaganda. Only then can we start taking steps to escape, or at least learn to see the signs. If you're 100% convinced propaganda and brainwashing will never work on you, you'll be the first one to fall for it. You have to admit to a fault before you can start fixing it.
And this case is not about the harrassment. She's not suing him for harrassment. She already settled that with a legally binding document. She's suing him for retaliation and exposing something that women in the public eye have been talking about for so long but without any physical proof they couldn't take any legal steps. She's exposing how these pr firms will literally bury women the second they become inconvenient to the industry. Blake Lively is far from the first. But I am hoping this is a step towards making her one of the last.
355 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think it's interesting how there's only frustration for Jacob now, but nothing about Delainey that also got snubbed, for Assad who wasn't even acknowledged by AMC on the (GG) FYC campaigns, people saying they wanted Armand to get raped on screen, the fans that went to plantations plural to make a photoshoot with Brad Pitt's Louis doll, the fans that threw a The Vampire Lestat shirt at a Raleigh Ritchie's concert while he was talking etc... This wasn't the first and probably won't be the last. And most of the time this fandom is crickets. And one sentence isn't enough, just like "Sam will probably call them out during his acceptance speech" isn't enough, just like only praising actors for their chemistry with white co-stars and never for their own individual work isn't enough. You see very little posts today and I doubt there will be any by tomorrow night. People will move on quickly just like they did with the previous events. So, I'm sorry, but this isn't impressive and just feels extremely performative.
#interview with the vampire#iwtv#louis de pointe du lac#armand#claudia eparvier#claudia de pointe du lac#claudia de lioncourt#jacob anderson#delainey hayles#assad zaman#Raleigh ritchie#racism
162 notes
·
View notes
Text
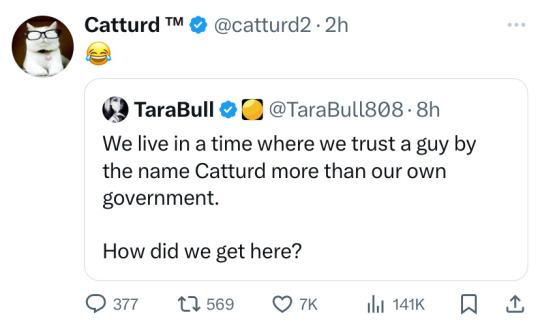
On 12/26, Catturd laid the smack down on a GOP fraud and Globalist named Dan Crenshaw. It was brutal and TaraBull nails the theme. How did we get here? Hillary and Bill picked up the NWO mantle left by GB the 1st and took that for a ride. Bill got caught being blown by interns and revealed he didn’t categorize oral SEX as sex. Hillary got caught stealing the silverware when they finally vacated the White House. Their work improving the government’s image only worsened when she climbed the public service ladders. Oh, she worked for promotions. Unlike Kamala and Bill’s girls, she stayed off her knees. Her work was more hands off and mysterious. In her wake, people were increasingly distrustful of her and government (yet didn’t say much else they go the way of Seth Rich).
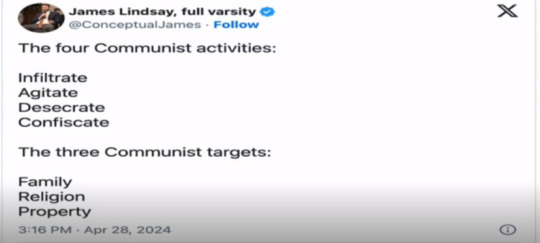
Hillary’s motto was “it takes a village” where the news would replay her waking through a set of an African village was a slow roll intro to communism. Oh, it sounds pretty that your friends and family will help you out, until your friends and family take your kids away because you’re teaching them to read and think and not drink the Koolaid.

The thought plantation doesn’t really care what you say so long as you stay within the guardrails and don’t encourage thoughts beyond the perimeter.
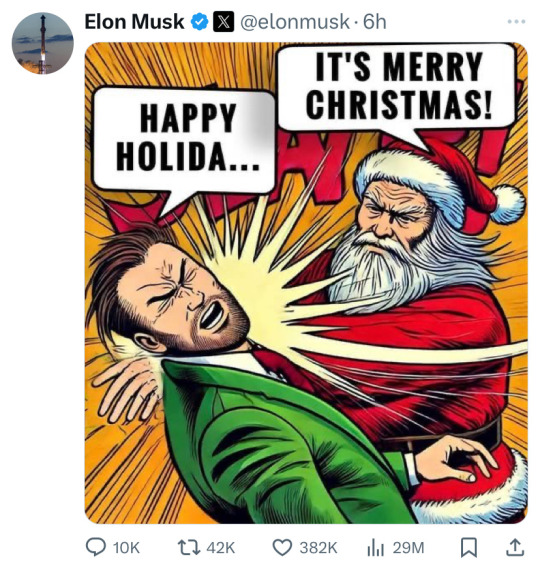
Happy Holidays had been around for years, but switching Christmas to the Holidays coincided with the DNC removing more and more of Christianity from their platform until they eventually swore off God and cemented their government is god complex for the platform. I remember lots of cheering during that DNC televised event (back when the news was the news + my outspoken DNC relatives who denied that the DNC would go so far as to remove God from the platform).
Distrust of the government was always there from those who paid attention. Yet, when the Clintons were in office and were campaigning for each other, that was the sizzling fuse on the dynamite stick that completely blew up with GW2, the 9/11 lies, and The Patriot Act. Had the Clintons not primed the public, 9/11 would not have gone over so well.
Now, when crazy shit happens, most Americans expect some sort of shady background story that’s going to get glossed over.
Meme dump



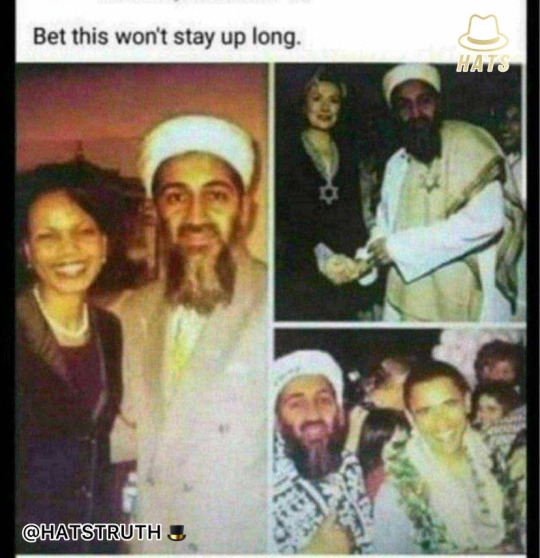
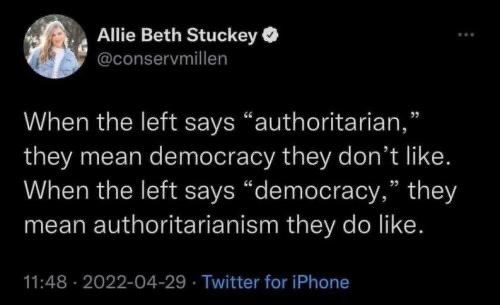

Why is the book on the list? Did you read or see pages from the most recent book in the banned book debate? It was from Bill and Hillary’s daughter. In that book, it talked about men and boys touching each other like it was normal. The media freaked over parents asking libraries to ban the book. I mean, sure, Globalists can ban books but not self-informed parents (breaking from the thought plantation).
50 notes
·
View notes
Note
Imagine support someone who have a history supporting Hollywood Biggest Abusers like Harvey Weinstein and Wood Allen, a racist who admited did blackface and got married in a plantation and more a LIAR meanwhile the guy the falsely accused of SA have all the proofs that she's lying and playing the victim and doesn't take no for an answer and wanted to take full control of a movie with her stupid husband and she promoted this movie as if she were Margot Robbie with Barbie
So you are just spouting all the shit that Justin Baldoni's PR team wants you to believe. Blake Lively has not been proven a liar that is just your opinion. So sorry Blake got married at a popular wedding venue and made a bad joke about putting on too much bronzer to play a trick on some boys in the 10th grade when America's Next Top Model was on national TV still doing actual black face. It is nothing but a narrative, a rumor that Justin Baldoni's team is pushing, that Blake just wanted the movie rights all to herself. Nothing right now has been proven.
You see not only have I read the lawsuits, I've been looking into smear campaigns for a year. Specifically smear campaigns by the PR team that Justin Baldoni hired before he ever hired them. They are a PR team whose specialty is rehabilitating the image of men facing abuse allegations by starting smear campaigns against their victims using the DARVO strategy.
They are paying for bots and a handful of influencers to spread a bunch of rumors(that is all they are) about her and to find a bunch of little clips of Blake Lively being a little problematic. You believe Justin because that is what he is paying for you to believe. We have no idea what evidence Blake Lively has to refute any of what he is saying because she's actually trying to have a fair fight in a court room while Justin Baldoni is playing dirty and releasing all of this "evidence" that is not being fact checked by the court. He is doing this both as an intimidation tactic against Blake so she'll settle her lawsuit and to sway a potential jury in his favor before the trial ever starts.
So be honest. You're just believing rumors and adding to the dog pile of a woman that was horribly harassed. Which if you've read her lawsuit, the allegations against him are much more horrible than you can imagine. Much more horrible than someone having gray morals.
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Blake Lovely always gave me bad vibes. I never liked her". Except that's not true. Social media at large liked Blake!!! They loved her whenever she shows up for the Met Gala. They loved her and Ryan's relationship. Always praising them for their relationship and commitment for each other. Loved her for her witty Instagram posts. It's just not true that the internet has always "had bad vibes" about Blake!! Even if you claim to be that one person out of millions who never liked Blake, it's still not true to say the internet never liked Blake.
"She destroyed her own reputation" is simply false too!! Because she was doing just fine prior to this!! Even if she had a questionable history or made some bad choices in the past, those things that everyone kept bringing up like her plantation wedding and whatever, those things were never a problem before and people still loved her so clearly her reputation was fine.
Y'all just want to say she ruined her own reputation because y'all want to absolve yourself of any guilt for playing a part of this smear campaign. Y'all don't want to admit that you were the stupid one and you fell for a man's propaganda. Like don't just go online and go "oh my bad" for show, actually look at yourself and figure out what is wrong with you!!
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The sacrosanctity of slave property in this war has operated most injuriously to the Confederacy," the assistant secretary of war said bluntly in July 1863. And so it had. "The planter is more ready to contribute his sons than his slaves to the war," the Mobile Register declared in outrage during one impressment campaign. It was a damning accusation, and one that at this distance seems palpably true. Slaveholders offered more opposition to slave impressment than to conscription. F. S. Blount, chief impressment agent in the Department of Alabama, Mississippi, and East Louisiana, talked of his failures to get enough slaves "to complete a road so vitally important to the protection of the very individuals, whose highest patriotic impulses never ascend above their own Petty ... schemes for the accumulation of wealth." "You cheerfully yield your children to your country, how you refuse your servants?" one broadside blasted. Slavery, as it turned out, was a form of property that dangerously attenuated citizens' allegiance to the state and submission to its authority. Planters colluded with their slaves in thwarting impressment agents, giving them passes or running them into the woods at the first approach of government agents. They took oaths of allegiance in occupied territory to hold onto their slaves and guided Yankee detachments back to their plantations to repossess their worldly wealth in cotton and slaves. They attacked military commanders who did not make it a priority to protect their property or prevent its escape, and they demanded that politicians represent their interests against the demands of the War Department and the Davis administration. For some, any state would do--Union, Confederate, Brazilian--if it adequately protected their property in slaves.
Slaveholders, it seems, were more concerned with property than nation. Do historians' robust assertions of the strength and endurance of Confederate nationalism take that into account? How else are we to explain the actions of a group insane enough to take a region and all its people into a perilous war, but not patriotic enough to do what it took to fight it? Everywhere in the C.S.A. the policy on slave impressment was resisted. In some places that resistance reached a scale that could only be called massive civil disobedience. In Georgia and North Carolina, legislatures battled the tyranny of the federal government on behalf of slaveholders' inalienable rights of property in slaves. In South Carolina, that struggle went to extremes as planters who had long been "ready with excuses for not furnishing labor to defend Charleston" stacked the legislature with their own and then wrote legislation designed, as Brigadier General John S. Preston charged, "as an explicit declaration that this State does not intend to contribute another slave or soldier to the public defense." As chief of the Bureau of Conscription, Preston, himself a Carolinian, had been out trying to procure "men and labor for the public defense." But there was no military situation so dire as to prevent quibbling. In 1863 Preston had managed to get only 450 of the 2,500 slaves requisitioned by the Engineer's Department, while the governor and legislature ignored the War Department's urging to pass relevant legislation. And again in 1864, even as General Sherman advanced toward Charleston, he could not get the 2,500 men called for. Then in late 1864, with Sherman's legions virtually at the gates, the legislature of South Carolina passed two acts--one asserting ultimate state authority over conscription and another over impressment--so in conflict with the instructions of the War Department that Preston denounced them as "treason to the Confederate States." "May you be endowed with strength and wisdom to overcome enemies stronger than yankee armies--the folly and wickedness of our own people," Preston wrote his president. Planters would not sacrifice the very property they had created the government to protect.
stephanie mccurry, confederate reckoning: power and politics in the civil war south; bolding mine bc ijbol 😂😂😂😂😂
#oh no did you accidentally enshrine into your constitution#a government primarily concerned with convincing a bunch of rich guys they are god-kings of their own domain#with no allegiance whatsoever to the body politic#and subsequently discover this is a little inconvenient when you're trying to stage a traitorous rebellion?#too bad... so sad....#(i mean the really sad part is we are still living with the consequences of this culture a century and a half later)#(but let me have this... let me have my schadenfreude at this one specific historical moment...)#(let me point and laugh at the war-losing traitor losers who lost.....)#confederage reckoning#bookblogging
22 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi I'm the Anon that mentioned Blake's link to Allen and Weinstein
https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/news/general-news/blake-lively-woody-allen-cafe-society-working-907665/
https://betches.com/blake-lively-controversies-plantation-wedding-harvey-weinstein/
https://www.mercurynews.com/2024/12/27/how-blake-lively-once-complicated-her-advocacy-against-hollywood-predators/
The issue is people are not willing to see that she did not simply have empathy for the victims excusing her behavior saying "there is no perfect victim" not realizing how dangerous that isAnd saying her career could ruin don't you think the multiple actors and actresses supported the victims were also risking their career by speaking up?
https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/entertainment-arts-41580010.amp
And now even though there are rumors it is interesting to note that even "reportedly" Taylor is also distancing herself from Blake.
Hi Anon. It is so not pleasant to see you again.
First of all the hollywood report link you sent me is the wrong link. This is the right link.
Second the quote is about Harvey Weinstein not Woody Allen.
Third I knew. I knew, I knew I KNEW that, that quote you sent me, that Blake said 'that was not my experience with him" was taken out of context and guess what? It was.
Blake did technically say those words but she also said that
"I think that if people hear these stories... I do believe in humanity enough to think that this wouldn't have just continued"
And
"I never heard any stories like this - I never heard anything specific - but it's devastating to hear"
And
"As important as it is to remain furious about this, it's important to also say that this exists everywhere so remember to look everywhere. This isn't a single incident. This cannot happen, this should not happen, and it happens in every single industry."
She also talks about how sexual assault is normalised and she has had plenty of things happen to her, like say if a director grabbed her butt she wouldn't think it was sexual assault even though it was. She talks about how important it is that we are furious about sexual assault and that we stay furious and that we don't just focus on these few stories but on humanity as a whole.
Honestly reading this article makes me sympathize with Blake even more.
I am not surprised that the ant* Blake camp is taking that one singular line out of context and are just running with it. Because that line implies that Blake doesn't actually believe Harvey Weinstein's victims when it's absolutely not true.
The reason I believed from the start that, that specific quote was taken out of context is because it's normal for reporter to ask 'this person has done these awful things, have they done something like this to you?' and it's normal for person responding to say 'no that wasn't my experience but I believe the allegations against that person.'
I haven't actually looked that much into Blake so when people said that she likes Weinstein I didn't go fact checking if it was true or not, because even if she does I was still very much going to Believe her. But from what I've read it doesn't seem like she's all that fond of him.
Anon I'm going to take a guess as to what happened here. You got sucked into tiktok/youtube wormhole of drama bait anti Blake content where no one does their due diligence and everyone is just looking for anything and everything they can find to use against Blake. So when I asked for source about the Woody Allen quote you went looking for a credible source and found the betches article which was published in January 2025 after this "drama" started which tries to take the quote out of context from a 2017 article when the allegations against Weinstein were first made. The betches article also regurgitates all of the smear campaign talking points because they even come to the actual point. I think you don't like Blake Lively and you went looking for "valid" reasons to justify how you feel.
The 2017 article is titled - Balke Lively on Harvey Weinstein claims : "it's devastating to hear". Gee I wonder why. Also the terrible Flaa interview where they talk about liking Weinstein's work was from 2016, the allegation against him became well known in 2017. And even though she does not say in these exact words it's very clear to me that Blake Lively wishes that allegations against him would have come out/became well known sooner.
And finally about Taylor Swift. I've been a Swiftie long enough to know better than to believe 'Taylor hates her friends!!!' headlines. I'm going to talk about that in detail later but Baldoni's team does not want Swifties on Blake's side hence these rumors. But let's pretend for a second that it's actually true and Taylor is keeping her distance from Blake. What does that prove? Amber Heard has talked about how the smear campaign against her affected her friendships and how her close friends who stood by her started keeping their distance from her because of how the media portrayed her. And then you see something similar happening to Blake Lively and think hmm Blake is clearly the problem here? Are you serious?
I'm not going to respond to asks like these anymore because they are just a massive waste of time. Anon I hope you have a terrible day for wasting my time.
#blake lively#anti justin baldoni#pro blake lively#i stand with blake lively#taylor swift#again im censoring certain phrases so that they don't show up in certain tags#my english is terrible so i normally write something and leave it alone for a couple hours#then go check if ive made any grammar or spelling mistakes and i try to correct as much of them as i could#i haven't done this for this post because its sunday morning and i have plans#and ive already wasted more time on this than i would've liked to#so just bare with my terrible english
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
AN ARTICLE ON THE BRITISH LOOTING FROM AFRICA
AND SUFFERING OF AFRICANS
The British should return every loot of all kinds back to Africa
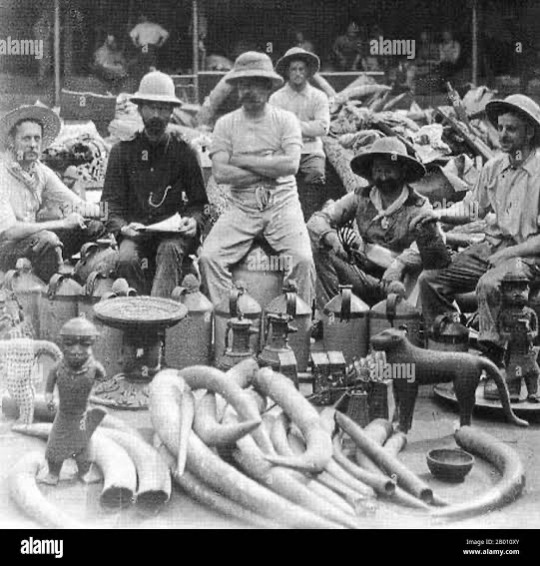


IF THEY CONDEMN SLAVE TRADE THEY SHOULD START BY RETURNING THE LOOTS COLLECTED FROM AFRICA ALL IN THE NAME OF TRADE AND RELIGION ,IF OUR CULTURE WAS BAD WHY DID THEY TAKE AWAY OUR HERITAGE AND STORE THEM IN A MUSEUM ?
The looting of Africa during the colonial era occurred through a combination of methods and strategies employed by European colonial powers, including Britain. Here are some of the ways in which Africa was looted during this period:
Military Conquest: European colonial powers, including the British, often used military force to conquer and control African territories. This involved armed conflicts, wars of conquest, and the suppression of local resistance movements. Through these military campaigns, colonial powers gained control over land and resources.
Resource Extraction: One of the primary motivations for colonialism in Africa was the exploitation of its abundant natural resources. European colonial powers, including Britain, extracted valuable resources such as minerals, rubber, timber, and agricultural products from African colonies. These resources were often taken for the economic benefit of the colonial powers.
Forced Labor: Colonial powers imposed forced labor systems on Africans to work in mines, plantations, and other labor-intensive industries. These labor practices were exploitative and often involved harsh working conditions and little compensation.
Taxation and Economic Exploitation: Africans were subjected to unfair taxation systems that drained wealth from their communities. Colonial administrations imposed taxes on land, crops, and other economic activities, forcing Africans to generate revenue for the colonial authorities.
Land Dispossession: Africans frequently lost access to their ancestral lands as colonial governments allocated land to European settlers and corporations. This land dispossession disrupted traditional agricultural practices and led to social and economic dislocation.
Confiscation of Cultural Artifacts: Colonial powers often confiscated cultural artifacts, sculptures, art, and religious items from Africa. These items were frequently transported to Europe and ended up in museums, private collections, or auction houses.
Unequal Trade Agreements: Colonial powers imposed trade agreements that favored their own economies. Africans often received minimal compensation for their raw materials and agricultural products, while European countries reaped significant profits from these trade relationships.
Suppression of Indigenous Cultures: The suppression of indigenous African cultures and languages was another aspect of colonialism. European powers sought to impose their own cultural norms and values, often devaluing or erasing African traditions.
Missionaries played a complex role in the context of colonialism and the looting of Africa. While their primary mission was to spread Christianity and convert indigenous populations to Christianity, their activities and interactions with colonial authorities had various effects on the looting of Africa:
1. Cultural Influence: Missionaries often sought to replace indigenous African religions with Christianity. In doing so, they promoted European cultural norms, values, and practices, which contributed to cultural change and, in some cases, the erosion of traditional African cultures.
2. Collaboration with Colonial Powers: In some instances, missionaries worked closely with colonial authorities. They provided moral and religious justification for colonialism and sometimes acted as intermediaries between the colonial administration and local communities. This collaboration could indirectly support the colonial exploitation of resources.
3. Access to Resources: Missionary activities occasionally granted them access to valuable resources and artifacts. They may have collected religious objects, manuscripts, and other items from indigenous communities, which were sometimes sent back to Europe as part of ethnographic or religious collections.
4. Education and Healthcare: Missionaries established schools, hospitals, and other institutions in African communities. While these services were aimed at spreading Christianity, they also provided education and healthcare to local populations, which could have positive impacts on individuals and communities.
5. Advocacy for Indigenous Rights: Some missionaries, particularly in later years, became advocates for the rights of indigenous populations. They witnessed the injustices of colonialism and spoke out against the mistreatment of Africans, including forced labor and land dispossession.
6. Conversion and Social Change: The conversion of Africans to Christianity brought about significant social changes in some communities. It could lead to shifts in social hierarchies, family structures, and gender roles, sometimes contributing to social upheaval.
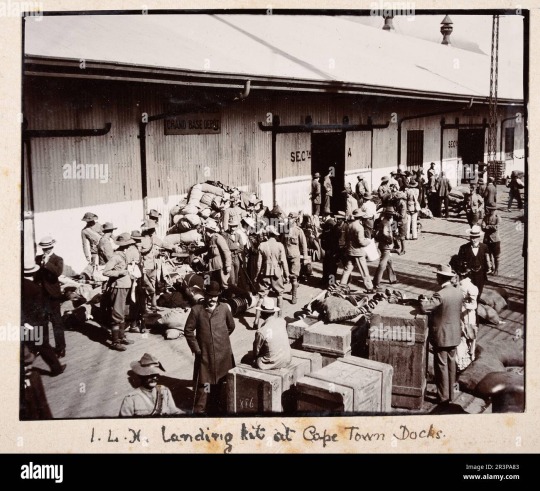


1. Cultural Bias: The British, like many Europeans of their time, often viewed their own culture, including Christianity, as superior to the indigenous cultures and religions they encountered in Africa. This cultural bias led to the condemnation of indigenous African religions and gods as "pagan" or "heathen."
2. Religious Conversion: Part of the colonial mission was to spread Christianity among the indigenous populations. Missionaries were sent to Africa with the aim of converting people to Christianity, which often involved suppressing or condemning traditional African religions and deities seen as incompatible with Christianity.
3. Economic Interests: The British Empire, like other colonial powers, was driven by economic interests. They often saw the resources and wealth of African societies as valuable commodities to be exploited. This economic agenda could involve looting or confiscating sacred artifacts, including religious objects, for financial gain.
4. Ethnographic Research: Some British colonial officials and scholars engaged in ethnographic research to study African cultures, including their religious practices. While this research aimed to document indigenous cultures, it could sometimes involve the collection of religious artifacts and objects, which were then sent to museums or private collections in Europe.
5. Cultural Imperialism: Colonialism was not just about economic and political domination; it also involved cultural imperialism. This included an attempt to impose European cultural norms, values, and religious beliefs on African societies, often at the expense of indigenous traditions.

The issue of repatriating cultural artifacts looted from Africa during the colonial era has gained significant attention in recent years. Countries and communities in Africa have long called for the return of these treasures, which hold deep cultural and historical significance. Among the former colonial powers, Britain stands at the forefront of this debate. This article explores the ongoing discussion surrounding Britain's role in returning looted artifacts to Africa.
A Legacy of Colonialism:
Britain's colonial history left a profound impact on many African nations, including the removal of countless cultural treasures. During the height of the British Empire, valuable artifacts, sculptures, manuscripts, and sacred items were taken from their places of origin. These items found their way into the collections of museums, private collectors, and institutions in Britain.
The Case for Repatriation:
Advocates for repatriation argue that these artifacts rightfully belong to the countries and communities from which they were taken. They emphasize the importance of returning stolen cultural heritage as a step towards justice and reconciliation. Many African nations view these artifacts as integral to their cultural identity and heritage.
International Momentum:
In recent years, there has been a growing international momentum to address this issue. Museums and institutions worldwide are engaging in discussions about repatriation. Some institutions have initiated efforts to return specific items to their countries of origin, acknowledging their historical and moral responsibility.
Britain's Response:
Britain, home to several renowned museums housing African artifacts, has faced increasing pressure to address this issue. The British Museum, for instance, has faced calls to repatriate numerous artifacts, including the Benin Bronzes and the Elgin Marbles, which have origins in Africa and Greece, respectively.
In response to these demands, some British institutions have started to collaborate with African countries to explore the possibility of returning certain artifacts. These discussions aim to find mutually agreeable solutions that respect both the historical context and the cultural significance of these items.
Challenges and Complexities:
Repatriation is a complex process involving legal, ethical, and logistical challenges. Determining rightful ownership and ensuring proper care and preservation upon return are critical considerations. Additionally, questions arise about how to address the legacy of colonialism and rectify historical injustices.
The Way Forward:
The debate over repatriation is ongoing and highlights the need for respectful dialogue and cooperation between nations. While the return of looted artifacts is an essential step, it should also be part of broader efforts to promote cultural understanding, collaboration, and acknowledgment of historical wrongs.
The issue of Britain returning looted artifacts to Africa is part of a global conversation about justice, cultural heritage, and historical responsibility. While there are complexities to navigate, the growing recognition of the importance of repatriation signifies a potential path forward towards reconciliation and healing between nations and their shared history. The ongoing discussions reflect a commitment to addressing past injustices and fostering a more inclusive and culturally rich future.
They condemn slave trades yet they’re still with our treasures and cultural artifacts and heritage
#life#animals#culture#aesthetic#black history#blm blacklivesmatter#anime and manga#architecture#black community#history#blacklivesmatter#black heritage#heritage
217 notes
·
View notes
Text
BJP Leader Geeta Murmu Launches 'A Tree for Mother' Campaign
Tree plantation drive inaugurated in Galudih by BJP’s Geeta Murmu to promote environmental conservation. A tree plantation campaign titled ‘A Tree for Mother’ was launched by BJP leader Geeta Murmu in Galudih. JAMSHEDPUR – Under the leadership of BJP leader and Galudih Mandal in-charge Geeta Murmu, the ‘A Tree for Mother’ campaign was launched on Saturday in Ullda and Barakhurshi villages of…

View On WordPress
#A Tree for Mother campaign#जनजीवन#Barakhurshi village news#BJP environmental initiatives#environmental conservation Jharkhand#Galudih Mandal in-charge#Galudih tree plantation#Geeta Murmu BJP#Jamshedpur latest updates#JHARKHAND NEWS#Life#Ullda Panchayat event
0 notes