#Plant Based Protein Industry News
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
hi tumblr, your friendly neighborhood culinary student here! the inaugruation luncheon menu is perhaps the single most politically-charged menu i've ever laid eyes on, and i want to deconstruct it. so without further ado:
a culinary student's analysis of the 2025 Inaugural Luncheon Menu
First course: Chesapeake Crab Cake with tomato tartar[e], bay sauce, pickled vegetables, romanesco, dill, and chive oil
right off the bat, we're presented with a single-option menu, which from an event planning (and thus business, which i'm majoring in) standpoint is already a horrible choice. it's also very indicative of Trump's view on choice. my way or the high way, even if its impossible for you. it's immediately alienating people with a shellfish/seafood allergy. this is going to be a common trend here. (also, note the misspelling of "tartare." tartar is a mayo-based sauce. tartare is a finely chopped vegetable dish, which the tomato element is far more likely to be.)
Second course: Greater Omaha Angus Ribeye Steak with Thumbelina carrots, broccoli rabe, carrot top herb sauce, red wine truffle jus, and potato gratin
this course is the most obvious display of values. we start with the omaha steak. statistically, men (however my professor is defining "men") are more likely to prefer steak to other meats, while women (however my professor is defining "women") are more likely to prefer lighter proteins like chicken or fish. it's very in-line with actions taken against women's rights and reproductive health, like the removal of resources.
similarly, this also declares a support of the beef livestock industry, which is the most negatively-impactful sector of the food and beverage industry on the climate. for years, there's been a push to promote alternative meats or make more plant-forward dishes to reduce the impact of beef farming. this is the exact opposite of that. the meat draws the attention in this menu.
this also excludes anyone who cannot eat red meat, or follow diets that exclude it for health, environmental, or political reasons.
then we move to the jus, which is a sauce made primarily using the juice lost in the pan during the cooking process of a meat, normally beef or veal. in this instance, it's combined with red wine and truffles, both viewed as luxurious foodstuffs by most. the dish radiates the vibe of a classic steakhouse dish. very "i'm so high-class, look at me! i'm protein-heavy and full of fancy things!" a very plain meal under a veneer of costly ingredients and percieved value.
Third course: Minnesota Apple Ice Box Terrine with sour cream ice cream and salted caramel
my immediate question, as someone who grew up in NY, is why they went with Minnesota apples as opposed to NY apples when NY is far more known for the fruit. the answer is quite simple. Trump doesn't like NY. NY voted against him, so they chose another state's apples. (this isn't to say that Minnesota apples are lesser than NY ones at all. it's simply a matter of expectation when NYC is the Big Apple and cideries litter the local landscape.)
and again we see the exclusion of those with dietary restrictions with the sour cream ice cream. good luck to anyone in attendance with a dairy allergy or lactose intolerance.
and lastly, a note on the wines. all four were from the USA. not a French or Italian or just generally foreign one in sight. two of the four were California wines, likely as a nod to his Silicon Valley friends. the other two were Virginia and New Mexico.
the menu overall reinforces what we've already seen: a highlight on the rich, the exclusion of anyone who isn't a cishet white man, and even then alienation of anyone who isn't physically flawless. this is fascism in a menu.
#2025 inauguration#menu breakdown#chef shit#sorry my teacher showed us this and its been eating my braincells alive#medic move over i need to yap abt menu psychology#menu psychology#food psychology#us politics#fuck trump
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

Environment & Natural Disasters
As we've all noticed with increasing alarm, natural disasters are occurring with more violence and regularity. The following organizations focus on responding to the climate crisis and protecting the planet as well as groups impacted by climate issues.
For more information on donation methods and accepted currencies, please refer to our list of organizations page.
Clean Air Task Force
As we've seen for a long time now but especially this year with constant natural disasters and alarming news from all over the world, climate change is real and we need to do something about it. Over the past 25 years, CATF, a group of climate and energy experts who think outside the box to solve the climate crisis, has pushed for technology innovations, legal advocacy, research, and policy changes. Their goal is to achieve a zero-emissions, high-energy planet at an affordable cost.
Coalition for Rainforest Nations
Boasting a voluntary membership of over 50 rainforest nations, CORN provides a single voice to countries that didn’t cause the climate emergency but nevertheless feel the brunt of it daily. CORN originated the global conservation mechanism Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (REDD+) to stop deforestation. REDD+ was successfully mandated in the Paris Climate Agreement (2015) and covers 90% of the world’s tropical rainforests.
Good Food Institute
Environmental advocates have long said that the use of animal proteins is one of the least sustainable parts of our food system and mass meat production and consumption put a large burden on the planet. GFI works to create sustainable food sources worldwide, specifically alternative protein sources such as plant-based, cultivated, and fermentation-derived meats. Through their innovation, scientific research, policy advocacy, and public and corporate education, they aim to mitigate the environmental impact of our food system, decrease the risk of zoonotic disease, and ultimately feed more people with fewer resources.
International Rescue Committee
Founded in 1933, the IRC is a long-standing trusted partner in supporting those whose lives have been upended by sudden violence, political or natural. They are no stranger to areas of disaster and conflict throughout the world as they currently work in 40 countries. The IRC provides emergency aid and long-term assistance, including refugee settlement, and focuses on health, education, economic well-being, empowerment, and safety.
Médecins Sans Frontières/Doctors Without Borders (MSF)
Odds are you’ve heard of MSF, the global organization that sends trained medical professionals to the places they’re needed most. MSF has been working globally for over 50 years, providing medical assistance to people affected by conflict, epidemics, disasters, or exclusion from healthcare—no matter what. They’re guided by principles of independence, impartiality, and neutrality to global political policies or movements.
Oceana
Oceana is the largest international advocacy organization for ocean conservation. To protect and restore the world’s oceans, they campaign globally for policies that stop overfishing and plastic pollution, protect habitats and the climate, and increase biodiversity. Oceana conducts its own scientific research and expeditions, is engaged in grassroots activism, and is involved in recommending and supporting policies and litigation.
Waterkeeper Alliance
In 1966, this movement was started by a band of blue-collar fishermen pushing back against industrial polluters, and their tough spirit remains intact through the 300+ local community groups that make up the global Waterkeeper Alliance today. The Alliance works to ensure, preserve, and protect clean and abundant water for all people and creatures. Their programs are diverse, spanning from patrolling waterways against polluters to advocating for environmental laws in courtrooms and town halls and educating in classrooms.
World Central Kitchen
Started by Chef José Andrés, WCK makes sure that people are fed in the wake of humanitarian, climate, and community crises. Their programs advance human and environmental health, offer access to professional culinary training, create jobs, and improve food security. WCK also teaches food safety and cooking classes to native people who live where disasters have occurred, so they may open restaurants and support the local economy more permanently. You can follow where WCK is currently on the ground assisting and feeding people affected by natural and man-made crises here.
13 notes
·
View notes
Note
ok. References: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/23/5115
https://www.pcrm.org/news/health-nutrition/vegan-diet-better-environment-mediterranean-diet
https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2023/jul/20/vegan-diet-cuts-environmental-damage-climate-heating-emissions-study
https://www.ethicalconsumer.org/food-drink/shopping-guide/vegan-meat-alterantive-food-brands
Including books like Sustainable Living and 100 Ways to Live Sustainably.
My response under a read more since it got long
First link:
This study is not necessarily advocating for vegan or vegetarian diets, and it mentions that in the introduction. It mentions instead its evaluation of overconsumption of animal products and underconsumption of various plant sources.
The study also mentions that vegans and vegetarians tend to consume more fruits, vegetables, and legumes and in more variety, as well as fewer refined cereals, added fats and sweets, and non-water beverages. This is known as the healthy user bias. The study even mentions that "the differences in terms of health outcomes ... cannot be directly linked only to the different consumption of protein sources." Even their own analysis of various studies find that most results aren't statistically significant, and those that do have significant statistical correlation include flexitarians, pescetarians, and lacto-ovo vegetarians and exclude vegans.

Second link
This article references two different studies, "Environmental Impact of Two Plant-Based, Isocaloric and Isoproteic Diets: The Vegan Diet vs. the Mediterranean Diet" and "A Mediterranean Diet and Low-Fat Vegan Diet to Improve Body Weight and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Randomized, Cross-over Trial."
For the first, this goes into one of my main complaints about dietary sustainability analysis in that the calculations are all hypothetical. It does not study if an individual's personal food choices make an impact on foods being produced. I am not arguing that livestock do not have a significant environmental impact or that agriculture does not damage the Earth. They clearly do. But I'm not a libertarian that thinks the free market will solve the ingrained issues with how food is produced.
My other issue with studies like this is that it groups all livestock together and all crops together. Cattle, chickens, fish, shellfish, goats, etc. all have a very different environmental impact. Almonds, wheat, apples, avocados, beans, rice etc. also all have very different environmental impacts. Painting agriculture with broad brushes like this is, in my opinion, not very helpful. I'm also not interested in pointing out the harmful impact of one side of agriculture while completely supporting the other side and acting like we can ignore that. I am more interested in food raised using sustainable techniques vs. industrially grown food rather than pitting animals and plants against each other as a whole. I am anti-capitalist and I do not make my food and animal activism to still be playing into capitalism. I also dislike pretending that crops and livestock are mutually exclusive industries that do not fundamentally play into each other.
As for the second study, I find this one far more interesting but I do have a few things to point out. The study does not mention what the lifestyles of the participants were before the study began, only that they were overweight. It seems to be operating under the assumption that thinner automatically means healthier, which isn't necessarily the case. But are participants normally eating tons of junk food with little fresh fruits and vegetables and then switching to more balanced diets prepared at home? Considering participants are also specifically asked to avoid sweetened drinks, processed meats and snacks, and cream and to limit cured ham and fatty cheeses, there are almost definitely other factors at play than simply meat vs plants. Second, participants attended classes taught by dieticians and physicians. Of course people would be healthier following instructions by people formally educated in health. Third, it is noted that several participants out of 52 change medications during the study, which can impact results.
Third link
See my points from link 2.
Fourth link
I like the recommendations made for vegan companies here. They suggest making some foods at home and avoiding companies that use palm oil or soy from South America as well as brands like Nestle that are famously known for damaging environments all over the world and harming people especially in poor countries. I will add though that this is harder than it looks due to brands having parents companies and Nestle owns lots and lots of companies. Which also plays into my point that personal choice is so insignificant when up against monsters like Nestle that own so much power.
In short, studies like these can provide some helpful data but they do also miss many important pieces because sustainability and nutrition are such complex topics that do not come with easy answers. I also take all studies with a grain of salt because they are all going to still work under the assumption of a capitalist world. My perspective is anti-capitalist and about an uprooting of our relationship to food and agriculture. Under a capitalist system the best we can do is harm reduction and based on trends of the food market I do not see that vegan diets make a material difference. Rather I promote choices that uplift community food, pressure changes to industry norms including legislative pressure, and socialist activism that benefits people and in turn the animals we live next to. Overproduction and overconsumption are real issues.
I'd like to offer my own studies and references but looking through these has used up all my spoons. My recommendations on books though are Braiding Sweetgrass by Robin Wall Kimmerer and Cows Save The Planet by Judith D. Schwartz.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
When you’re told there’s a simple solution to a very complex problem, you’re probably not getting the whole story.
Today’s meat consumption is a good example. Meat and dairy are increasingly under the world’s microscope as livestock—which rely on huge quantities of feed crops and occupy nearly 80 percent of global farmland—accounts for between 14 percent and 30 percent of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. It’s also the source of more frequent antimicrobial-resistant pathogens, and much of the global livestock and seafood industries have been exposed for unsafe and abusive working conditions.
This complex web of problems requires more than one answer. And yet “alternative proteins”—from plant-based to lab-grown “fake” meat and dairy—are being promoted as a simple solution. Products like the Impossible Burger, with its 15-plus ingredients, are now in supermarkets and fast food establishments worldwide. Lab-grown chicken has been on the market in Singapore since late 2020 and will likely soon be approved in the U.S. and elsewhere. These products are being sold as a “win-win-win” for animals, people, and the planet. According to Patrick Brown, the outspoken CEO of Impossible Foods, livestock is “the most destructive technology on earth,” and meat substitutes are “the last chance to save the planet.”
Dramatic claims about plant-based meat, lab-grown meat, and “cellular agriculture” have already succeeded in drawing billions of dollars to the sector, including from big-name investors like Bill Gates and Richard Branson. Governments are now paying attention as well. China is readying major investment in lab-grown meat as part of its latest Five-Year Agricultural Plan, and the U.S. government is ploughing $10 million into a National Institute for Cellular Agriculture. Denmark is also backing alternative proteins through a $98 million plant-based food fund.
But these products and their sustainability credentials rest on shaky ground, as I show in a new report out today, “The Politics of Protein,” from the International Panel of Experts on Sustainable Food Systems (IPES-Food).
[Keep Reading]
88 notes
·
View notes
Text

Solutions?
In a video interview with Critical Theory in Berlin[8] he proposes to set up a planned economy to reduce emissions yearly and instate sanctions forcing corporations to pursue technocratic solutions (e.g. drawing down Co2 from the atmosphere) in a bid to recuperate the power of the state for planetary salvation.
In a co-authored editorial Seize the Means of Carbon Removal: The Political Economy of Direct Air Capture,[9] he plays through different scenarios of carbon removal from the air and demands that the “the left” confront it. Natural carbon sinks cannot possibly do all the work, so what remains apparent is the inherent need for new technological advancements and centralized planning to make capture solutions viable.
Malm, however, believes if the “means of removal” were socialised, capital accumulation could be off the table and the process would help repair climate damage, never mind the ecological and energetic costs of those technologies.
To be clear, large-scale carbon capture and storage technology is merely a hype, not a viable technology at our disposal. It remains unproven at scale, with current test facilities shutting down due to repeated mechanical failures[10] and exorbitant operating costs.[11]
It requires vast industrial complexes and a further scarring of the environment, all the while releasing more Co2 to the atmosphere than sequestered (as seen in Norway’s Sleipner Facility,[12] currently the best facility on Earth).
From geoengineering [R.F. – see Return Fire vol.3 pg8] utopia, Malm continues during his interview, and I am paraphrasing: If we can lock up people inside their houses for a period of time, surely we can say you can’t eat beef from Brazil any longer. Even if a State is able to stop industrial beef production in the tropics for all groups and people, is this really the way to create lasting social change? Swedish authoritarianism, and the state naiveté fabricated by social democracy, shines through his political theory.
Malm’s authoritarian desires continue in Corona, Climate, Chronic Emergency. Here he plays with ideas such as “mandatory global veganism”[13] and invokes the “duty” of the “richest countries” to “lead and assist a global turn to plant-based protein” to oppose the consumption of “bushmeat”[14] in other parts of the world. “Bushmeat” here, refers to how Indigenous people, farmers and low-income households hunt and subsist on local animals (e.g. rabbits, snakes, iguanas, deer, gazelle, etc.), as they have for centuries. Malm exhibits colonial hubris, meanwhile demonstrating an uncritical belief in industrial food systems and the relationships they engender.
The careless, and ultimately Eurocentric and racist, assertions by Malm are even more dumbfounding considering his credentials as a human geographer, situated at one of among Sweden’s most prestigious universities. Human geography research is famous for revealing the ecological harms of colonial land management schemes and, later, “fortress” and “community” conservation programs.[15] These programs have been largely ineffective, failing to curtail “commercial poaching” and intensifying attacks on Indigenous people, militarizing forests and regimenting ecologically destructive practices.[16] Enforcing authoritarian relationships over land, especially against so-called “subsistence poachers” – or acquiring “bushmeat” in Malm’s words – has been a resolute disaster extending colonial practices of land control, degradation and warfare into nature.[17]
This insanity extends to silence regarding the Indigenous people under constant attack by mines and wind turbines in Sweden. As Kuhn points out, Malm “does not mention the Sámi with a single word”, although they see themselves as “radical environmentalists by the very nature of their traditional livelihood”. Kuhn explains this might be because “all Swedish leftists do” this, or because it is “easier to point to struggles far away”, or even that he has “political reasons” for ignoring them (e.g. them not talking about “fossil capital”?). At the same time, he goes into great length telling of his own involvement in an action group horribly named “Indians of the Concrete Jungle”. In essence, he likes Indigenous peoples when they resist in attention-grabbing news headlines, but demonstrates radical disinterest, if not contempt, for their lifeways, culture and autonomy with his political philosophy and proposals.
#academia#Andreas Malm#authoritarian#climate crisis#Climate Justice#colonialism#communism#crisis#eco-Leninism#eco-modernism#geo-engineering#green-washing#How to Blow Up a Pipeline#industrialism#insurrection#leftism#Return Fire#sabotage#Sweden#technology#autonomous zones#autonomy#anarchism#revolution#ecology#climate change#resistance#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The process of Going Vegan
Going vegan is a lifestyle that can improve your health, the environment, and the welfare of many living beings. Here are some tips to help you understand the process and make it easier.
What is veganism?
Veganism is more than a diet; it is a lifestyle that excludes all animal products, such as meat, dairy products, eggs, and others. Stopping the use of products that come from animals, such as leather, is also part of the process. The reason for choosing this lifestyle varies from person to person, but most agree on ethical concerns, the treatment of animals and the environment. The vegan diet is often confused with vegetarianism. Vegetarians do not consume any meat, but their diet may include animal products. Some consume dairy products, while others may include eggs in their diet. Veganism may seem stricter because it goes beyond food.

Regain your health
One of the biggest motivations for many people is to regain their health and feel good. A well-planned vegan diet can reduce the risk of disease and give you the vitamins and minerals you may need. These diseases include diabetes and even cancer. A recent study compared the effects of a low-fat vegan diet to a conventional portion-controlled diet in individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D). Participants on the vegan diet experienced improvements in glycemic control and had lower levels of cholesterol. Additionally, body weight decreased in the vegan group. (Talwadekar, 2024)
Think of the environment
Not eating meat also benefits the environment in an impactful way. Animal agriculture is one of the biggest causes of greenhouse gas emissions and water pollution. An article by Gale Environmental Studies Online Collection states that livestock require many more resources to raise than plants do, many people believe that a diet consisting of plants is the best solution for a world with a rapidly growing human population. Compared to growing potatoes or rice, producing beef requires 160 times more land per calorie, and produces 11 times more greenhouse gases. (Blackwell, 2021)

4 Tips for transitioning to a vegan diet: You must begin this change little by little. The changes do not have to be drastic at first. Start adding more plant-based products and at the same time reduce your meat consumption.
1. Seek information: Before making changes to the way you eat you should educate yourself about this diet. It is important to know what foods can provide you with certain nutrients. Reading labels when shopping is very crucial in the transition to a vegan diet. There are products that contain ingredients of animal origin that at first glance are not obvious. Also, reading labels helps us learn about the nutritional value in each product we eat. In addition, we get ideas about calorie content, fiber content and can monitor sugar and sodium levels.
2. Look for substitutes: There are many plant-based alternatives available today. The vegan industry has grown a lot in the last few years making the transition easier for those looking for vegan alternatives for their diet. Eating outside the home can make the process a bit more difficult. Before going out, look for restaurants that offer a menu that includes vegan alternatives.
3. Create a plan: Making a weekly plan may make the process easier and can ensure that you get the nutrients you need. You can use recipe books, and you can get many good recipes on the internet. Do not be afraid to be creative and try new combinations you have never eaten before. To make sure you get the nutrients you need, try to eat a variety of foods, and take supplements. Protein, iron, and b12 deficiencies are some of the concerns of people making this change.
4. Be patient: It is normal to make mistakes or be tempted in the process. It may take time to make the adjustment. It is normal to have cravings, especially at the beginning stage. Look for substitutes for your favorite foods. Use a variety of seasoning to enhance you cooking and take it to the next level.
Deciding to enter this change is a very personal decision that requires preparation and education. You must learn about the benefits it could bring to you and the environment. Health benefits and satisfaction are a step towards bringing change to the world.
Works cited:
Talwadekar, Manasi. “Low-Fat Vegan Diet May Improve Cardiometabolic Health in T1D.” Internal Medicine News, Apr. 2024, p. N.PAG. EBSCOhost, research.ebsco.com/linkprocessor/plink?id=e6b8ab96-9ea3-3f2b-8623-90a64371220a.
Blackwell, Amy Hackney. "Veganism." Gale Environmental Studies Online Collection, Gale, 2021. Gale In Context: Environmental Studies, link.gale.com/apps/doc/NFVPGH435019656/GRNR?u=lincclin_pcc&sid=bookmark-GRNR&xid=67c44948. Accessed 15 Jan. 2025.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Soybean Export from India: Trends, Data, & Market Outlook for 2025

India's agricultural exports continue to gain momentum, with soybean standing as a key contributor. Known for its high nutritional value and diverse industrial applications, soybeans play a pivotal role in the global agri-commodity market. As the world’s demand for plant-based proteins and sustainable oils increases, India's position as a significant player in soybean exports strengthens. This article delves into the current trends in soybean export from India, examines soybean export data, highlights key soybean exporters in India, and explores major soybean-exporting countries for 2024-2025.
The Landscape of Soybean Export from India
India has emerged as a prominent exporter of soybeans, contributing significantly to global trade. Factors such as robust agricultural policies, advancements in farming techniques, and a focus on export-oriented production have bolstered India's soybean export capabilities.
In the 2024-2025 period, soybean exports from India are expected to grow due to increasing international demand. Indian soybeans are sought after for their quality, competitive pricing, and adherence to international standards. The primary export destinations for Indian soybeans include Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and European countries.
Soybean Export Data for 2024-2025
Tracking soybean export data reveals significant insights into India’s performance in the global market.
Volume and Value of Exports: India exported approximately 2.5 million metric tons of soybeans in the fiscal year 2023-2024, generating over $1.2 billion in revenue. The 2024-2025 projections suggest a 10-12% growth, driven by increasing demand from new and existing markets.
Major Importers of Indian Soybeans:
Indonesia and Vietnam: These countries use Indian soybeans primarily for feed and food processing industries.
United Arab Emirates (UAE): A significant importer due to its booming food industry and demand for plant-based products.
European Union (EU): Particularly Germany and the Netherlands, where soybeans are used for biofuels and plant-based protein products.
Export Growth Drivers:
India’s strategic position in Asia ensures shorter shipping times to key markets.
Increased global preference for non-GMO soybeans, a segment where India has an advantage.
Key Soybean Exporters in India
India’s soybean export industry is supported by numerous stakeholders, including farmers, processing companies, and export houses top soybean exporters in India are.
SOPA (Soybean Processors Association of India): SOPA plays a vital role in promoting soybean exports from India. It ensures the quality and branding of Indian soybeans, making them competitive in global markets.
Major Exporting Companies:
ITC Limited: Known for its robust supply chain and adherence to quality standards.
Adani Wilmar: A significant player in agri-exports, including soybeans and soy-derived products.
Ruchi Soya Industries: One of India's largest exporters, supplying non-GMO soybeans globally.
Emerging Players: Smaller exporters and agri-tech startups have also entered the market, leveraging technology to enhance productivity and streamline exports.
India’s Position Among Soybean Exporting Countries
Globally, India ranks among the top 10 soybean exporting countries. However, countries like Brazil, the United States, and Argentina dominate the export landscape.
Global Competitors:
Brazil: The world’s largest soybean exporter, primarily supplying China.
United States: A major exporter with advanced farming technology and extensive trade networks.
Argentina: Known for its high-quality soymeal exports.
India’s Competitive Edge:
Organic and non-GMO soybeans.
Competitive pricing compared to Western exporters.
Proximity to Asian and Middle Eastern markets.
Challenges in Competing Globally: While India has advantages, challenges such as inconsistent yield, fluctuating prices, and logistical issues need addressing to solidify its global standing.
Emerging Trends and Opportunities in Soybean Export
The soybean industry is undergoing transformation due to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements. Key trends for 2024-2025 include:
Shift to Plant-Based Diets: The rise of veganism and plant-based diets globally is driving demand for soy products, including tofu, soy milk, and soy protein isolates.
Sustainability and Traceability: Exporters focusing on sustainable farming and traceability in supply chains will have a competitive edge in international markets.
Government Support: Initiatives such as export incentives, enhanced logistics, and trade agreements are expected to boost soybean exports.
Value-Added Soy Products: Diversifying into soy-derived products like soymeal, soy oil, and soy protein can open new revenue streams for Indian exporters.
Challenges Facing Soybean Export from India
Despite its growth potential, the industry faces several hurdles:
Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns can impact crop yields.
Infrastructure Bottlenecks: Limited storage and transportation facilities hinder efficient exports.
Price Volatility: Global soybean prices are influenced by geopolitical and economic factors, impacting Indian exports.
Addressing these challenges through policy reforms and industry collaboration will be critical for sustained growth.
Future Outlook for Soybean Export from India
The future of soybean exports from India looks promising. With the global demand for soybeans expected to rise by 15-20% in the next decade, India has the opportunity to enhance its market share. Key strategies for growth include:
Investing in sustainable farming practices.
Strengthening trade relations with emerging markets like Africa and Latin America.
Promoting value-added soy products through branding and innovation.
Conclusion
Soybean export from India are poised for remarkable growth in the 2024-2025 period. By leveraging its strengths in quality production and strategic geographic positioning, India can expand its footprint in the global soybean market. However, addressing challenges like climate change, infrastructure, and price volatility will be essential for realizing its full potential. With the concerted efforts of farmers, exporters, and policymakers, India is set to cement its position as a leading player in the global soybean trade.
#soybean export from India#soybean export data#soybean exporters in India#soybean exporting countries#trade data#global trade data#international trade
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Innovation Is Reshaping the Food Industry

Food innovation refers to introducing novel ideas, products, and technologies that change how society produces, processes, packages, distributes, and consumes food. It goes beyond merely creating new recipes or flavors - food innovation encompasses advances in agriculture, food science, sustainability, and packaging. The goal is to enhance efficiency, safety, nutrition, and the overall consumer experience.
The need for food innovation arises from the ever-changing demands of consumers and the pressing challenges faced by the industry. As the global population continues to grow, so does the demand for food. Additionally, sustainability concerns, climate change, and limited resources prompt exploring alternative food growing and production methods. Innovations in food aim to enhance food security, minimize environmental impact, and offer consumers healthier, more diverse options.
Food innovation occurs through a combination of research, collaboration, and creativity. Scientists, entrepreneurs, farmers, and food industry professionals work together to develop new technologies and processes. Research institutions and startups play a crucial role in conducting experiments, testing new concepts, and bringing innovative products to the market.
In recent years, the food industry has witnessed groundbreaking innovations reshaping how people interact with food. The plant-based movement has gained immense traction, with plant-based alternatives for meat, dairy, and seafood becoming mainstream. Companies have developed plant-based burgers, vegan cheeses, and sustainable seafood alternatives using cutting-edge technologies. Beyond plant-based options, innovations have also focused on alternative protein sources, such as insect-based proteins and lab-grown meats, offering sustainable and protein-rich alternatives.
Swedish startup Mycorena is boosting microbial protein production through its fungi-based mycoprotein called Promyc. This ingredient can be used to create meat and tuna alternatives, beverage additives, and dessert ingredients, offering plant-based and sustainable options for consumers.
Finnish startup Onego Bio has developed a product genetically identical to egg whites using fermentation, and without using actual chickens. It uses precision fermentation of a microflora called Trichoderma reesei to produce ovalbumin, the protein found in chicken egg whites. This technology offers a sustainable and animal-friendly alternative for various food applications, including baked goods, desserts, sauces, and dressings.
Companies like New Culture are incorporating animal-free casein into their cheeses through precision fermentation. This breakthrough allows them to produce animal-free mozzarella cheese, offering a delicious and cruelty-free alternative to traditional dairy products.
In addition, consumers increasingly seek transparency in food choices, leading to the clean label movement. Brands are responding by using simple natural ingredients and avoiding artificial additives and preservatives.
Breakthrough innovations in the food industry are revolutionizing how society grows, produces, and consumes food, focusing on sustainability, nutrition, and convenience. One such innovation is plastic-free and smart packaging. Food companies are exploring biodegradable and even edible packaging solutions in response to environmental concerns. Smart packaging using nanotechnology is also gaining popularity, allowing consumers to assess food safety and quality easily.
The Internet of Things (IoT) in agriculture employs sensors and data analytics for optimizing crop conditions, irrigation, and pest control, reducing resource usage. Food waste reduction solutions, such as surplus food redistribution platforms, are being developed to combat the global food waste crisis. Moreover, biotechnology and data science advances enable personalized nutrition, tailoring dietary recommendations to individuals based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health goals. These innovations promise a more sustainable, healthier, and efficient food future.
Food innovation is driving a remarkable transformation in the food industry, responding to the challenges and opportunities of today. From new plant-based products to sustainable agriculture and cutting-edge technologies, the future of food promises to be more diverse, nutritious, and sustainable. As consumers, entrepreneurs, and stakeholders continue to embrace innovation, the food industry's journey toward a more resilient and conscious future is set to continue.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why You Should Buy Vegan Food: A Look at Vezlay Foods
Introduction
Have you ever thought about going vegan? Maybe you've heard about the health benefits or the positive impact on the environment. But how do you start, and where do you find the right products? In this article, we're diving into the world of vegan food, focusing on a key player in the industry, Vezlay Foods. Whether you're a seasoned vegan or just curious, you'll find valuable insights here. And if you're looking to Buy Vegan Food, Vezlay Foods is a great place to start.
The Rise of Vegan Food
Veganism isn't just a trend; it's a movement. It has its roots in ancient cultures, but it's grown massively in recent years. From a niche lifestyle to mainstream adoption, veganism is now endorsed by celebrities, influencers, and athletes alike. With increasing awareness of health and environmental issues, more people are choosing to buy vegan food and embrace this lifestyle.
Health Benefits of Buy Vegan Food
Switching to a vegan diet can do wonders for your health. It's packed with nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. Studies have shown that a plant-based diet can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Additionally, vegan food can boost your mood and mental health, thanks to its rich nutrient profile.
Environmental Impact of Veganism
Choosing vegan food isn't just good for you; it's good for the planet. The production of plant-based foods generates a lower carbon footprint compared to animal products. It also conserves water and land resources. Plus, by opting to buy vegan food, you're supporting animal welfare and reducing the demand for factory farming.
Challenges of Maintaining a Vegan Diet
While the benefits are clear, maintaining a vegan diet can come with challenges. There are misconceptions that vegan diets lack essential nutrients like protein and B12. However, with proper planning and a variety of foods, these concerns can be easily managed. Social and cultural factors can also pose challenges, but the growing availability of vegan options is making it easier.
Introduction to Vezlay Foods
Enter Vezlay Foods, a company dedicated to making veganism accessible and delicious. Founded with a mission to provide healthy and sustainable food options, Vezlay offers a wide range of vegan products. Their innovative approach and commitment to quality have made them a favorite among vegans and non-vegans alike.

Popular Products by Vezlay Foods
Vezlay Foods has an impressive lineup of products. From vegan meats like soy-based chicken and mutton to ready-to-eat meals and snacks, they've got something for everyone. Their products are designed to mimic the taste and texture of traditional meat, making the transition to veganism seamless.
Nutritional Value of Vezlay Products
What sets Vezlay Foods apart is their focus on nutrition. Their products are made with high-quality ingredients that offer substantial health benefits. For instance, their vegan meats are rich in protein and low in fat. Compared to traditional meat products, Vezlay Foods' offerings are a healthier and more ethical choice.
Cooking with Vezlay Foods
If you're new to vegan cooking, Vezlay Foods makes it easy. Their products come with simple recipes and cooking tips. Whether you're making a quick stir-fry or planning a gourmet meal, Vezlay's vegan options can be a game-changer. Try incorporating their products into your weekly meal plan for delicious and nutritious meals.
Buy Vegan Food
Wondering where to buy vegan food? Vezlay Foods' products are available in many health food stores and online. Shopping online can be particularly convenient, offering a broader range of products and often at competitive prices. Look for budget-friendly options and stock up on your favorites.
Customer Reviews and Testimonials
Don't just take our word for it; check out what customers are saying. Many users have shared their positive experiences with Vezlay Foods, praising the taste, convenience, and health benefits. Success stories highlight how Vezlay products have helped people transition to a vegan diet and improve their overall well-being.
Veganism in Different Cultures
Veganism isn't limited to one region; it's a global phenomenon. Different cultures have their own traditional vegan dishes, from Indian curries to Mediterranean salads. Vezlay Foods takes inspiration from these diverse culinary traditions, offering products that cater to various tastes and preferences.
Vegan Food and Fitness
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are increasingly turning to vegan diets for optimal performance. Vegan food provides ample protein and other nutrients essential for muscle recovery and energy. Vezlay Foods offers products perfect for pre and post-workout meals, ensuring you get the nutrition you need to stay active.
Future of Vegan Food
The future of vegan food looks promising, with continuous innovations and growing popularity. Vezlay Foods is at the forefront, constantly developing new products to meet the demands of health-conscious consumers. Keep an eye on upcoming trends and new releases from Vezlay as they continue to lead the way in vegan food innovation.
Conclusion
Vegan food is more than just a diet; it's a lifestyle that benefits your health, the environment, and animal welfare. Vezlay Foods plays a significant role in promoting veganism by providing delicious, nutritious, and sustainable products. So why not give Vezlay a try and start your journey towards a healthier and more compassionate lifestyle? Remember, when you buy vegan food from Vezlay, you're making a positive choice for yourself and the planet.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ready for another example of the UN being a political organization and not a scientific one? Here's a rundown from Environmental Studies professor Matthew Hayek:
Part 2 of the blitz on “healthy meat”. Did you hear the UN now says meat is “crucial” and offers better nutrition than plant foods? Again, they come from a report with industry meddling, self-citing, deceptive and contradictory press releases and takeaways
The report is in four parts the first of which is a review of evidence of nutritional value of animal foods, based on more than 500 peer-reviewed sources. Sounds pretty fair. But this was a “narrative review”. Not a systemic one. Which means that they’re not reviewing all of the evidence, and aren’t using any external guidelines. The cards can fall in any direction because they’re not wedded to a particular protocol.

From the jump, they key messages starts with a baseless talking point that meat’s protein is “high quality”. This isn’t true.

It’s derived from DIAAS, which is a metric that assumes meat proteins are higher than plant proteins. We know plant proteins like beans need to be cooked (to break down anti-nutrients) and combined (e.g. rice & beans). But DIAAS ranks raw, uncombined ingredients. The “high quality protein” myth talking point flies in the face of peer-reviewed research & reviews like @GardnerPhD that show plant proteins are absorbable, complete, and sustainable.
This is the danger of using a “narrative review”. It’s the lowest, most subjective form you can do, because it’s not reproducible, transparent, or complete. It can reproduce any biases that the authors harbor. They even say it!

Despite the subjective methods, and the pro-animal slant of the reviewers and funders, many of the findings and key messages are quite tame and even at odds with the headlines. Oh look, their own *subjective* review of others’ *rigorous systemic* reviews found mixed results of animal food benefits to kids. Hardly the same as the headlines! They imply that everyone needs to eat animals, especially pregnant women and kids, or risk deficiencies and disorders.

A bulk of the *new* analysis here, which we could consider systemic, just looked at gaps in countries diet guidelines. They found that they’re not particularly specific, and they leave out sustainability recommendations.

And yet the final conclusion was that all countries should provide guidance on animal foods. Why? We’ve already established that their benefits are context-specific, some confer risks, and many have huge environmental impacts that guidelines don’t account for.

Gee, I wonder why the authors could be motivated to pressure countries to include animal foods in their guidelines…

These groups have major meat and dairy, feed, and animal pharma conglomerates as their contributors. They are not advocacy NGOs, they are mouthpiece trade groups for the most powerful donors in the global animal agriculture trade.
Even more worrying, the document implies that representatives of industry groups served as funders and *reviewers*. That level of industry meddling is a huge and unprecedented conflict. And would be reprehensible for other industries with high-emitting products. There should also be little wonder why the press and key messages don’t distinguish between low-income countries, whose diets are lacking in *many* food groups, with high income, where most people (from most groups and life stages) consume more than enough protein. Industry would benefit from meat consumption being higher, regardless of the risks and contexts. Those biases made their way all through the key messages and headlines of this report.
The @UNFAO needs to deeply reconsider its criteria for commissioning reports and media. This level of financial conflicts, the authoritative and deeply misleading headlines, subjective methods, and the lack of skeptical and independent review are all serious concerns.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unleashing the Power of Plant-Based Whey Protein: A Game-Changer in Nutrition

When it comes to fitness and wellness, protein holds a significant place in the spotlight. Whey protein, derived from milk, has long been the go-to choice for athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike due to its impressive amino acid profile and easy absorption. However, with the rise of plant-based diets and the growing demand for sustainable alternatives, a new star has emerged on the nutrition scene: plant-based whey protein. In this article, we will explore the benefits and potential of Plant-Based whey protein as a game-changer in nutrition.
Understanding Plant-Based Whey protein:
Plant-Based whey protein, often referred to as "plant protein" or "vegan protein," is a groundbreaking innovation in the nutrition industry. Unlike traditional whey protein sourced from animal milk, this alternative is derived entirely from plants, making it suitable for vegans, vegetarians, and those with lactose intolerance.

Sources of Plant-Based Whey protein:
Pea Protein: Derived from yellow peas, pea protein is a top contender among Plant-Based proteins. It contains an impressive amino acid profile, particularly rich in branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), which play a crucial role in muscle recovery and growth.
Brown Rice Protein: Brown rice protein is a hypoallergenic option that offers a complete amino acid profile. It is gentle on the digestive system and ideal for individuals with food sensitivities.
Hemp Protein: Hemp protein is extracted from hemp seeds and is renowned for its high fiber content and omega-3 fatty acids, making it an excellent choice for overall health and wellness.
Soy Protein: Soy protein is one of the oldest plant-based protein sources. While it is a complete protein, there have been concerns about its impact on hormone balance, leading some to prefer other options.
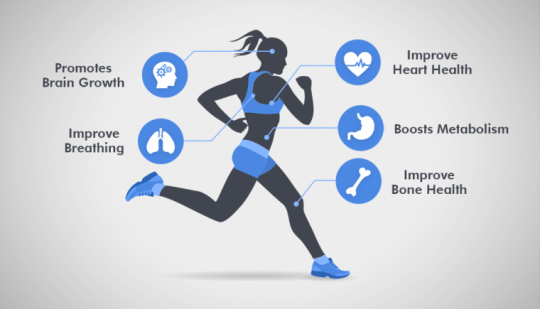
Benefits of Plant-Based Whey protein:
Suitable for All Dietary Needs: Plant-based whey protein is an inclusive option, accommodating various dietary restrictions, including veganism, lactose intolerance, and vegetarianism.
Sustainable and Environmentally Friendly: Animal agriculture is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation. By opting for plant-based whey protein, consumers actively contribute to a more sustainable future and reduce their environmental footprint.
Supports Muscle Building and Recovery: Contrary to common misconceptions, Plant-Based Whey protein can be just as effective as animal-based protein in supporting muscle growth and post-workout recovery. Its amino acid profiles are often carefully blended to ensure a complete range of essential amino acids.
Low in Cholesterol and Saturated Fat: Unlike animal-derived whey protein, plant-based options are naturally cholesterol-free and low in saturated fat. This makes them heart-healthy choices for individuals concerned about cardiovascular health.
Promotes Weight Management: Plant-Based Whey protein can be an ally in weight management due to its satiating effect, helping to curb hunger and support a balanced diet.

Incorporating Plant-Based Whey proteininto Your Diet:
There are numerous ways to incorporate plant-based whey protein into your daily diet. Popular options include:
Smoothies and Shakes: Blend your favorite plant-based whey protein powder with fruits, vegetables, and almond milk for a delicious and nutrient-packed smoothie.
Baking: Upgrade your baked goods by adding plant-based whey protein to recipes for pancakes, muffins, and energy bars.
Breakfast Bowls: Sprinkle plant-based whey protein over oatmeal, yogurt, or chia pudding to boost protein content.
Protein-Packed Snacks: Look for plant-based protein snacks like protein bars and bites to fuel your day on the go.

Conclusion:
Plant-Based Whey protein is a revolutionary addition to the world of nutrition, offering a sustainable, ethical, and health-conscious alternative to traditional whey protein. Packed with essential amino acids and boasting numerous health benefits, this plant-based option is suitable for individuals of all dietary preferences and fitness goals. Embracing plant-based whey protein not only supports personal well-being but also contributes to a greener, more eco-friendly planet – a win-win for both you and the environment. So, why not embark on this exciting journey of nourishing your body and the world with the power of Plant-Based Whey protein?
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Illustration Photo: Sugarcane is one of the most efficient producers of biomass of all plant species and can be used as a renewable fuel. The new variety Ho 06-9002 has a high fiber content, excellent regrowth ability over 4 to 5 years, is cold-tolerant, has a high stalk population, and produces excellent biomass yields. (credits: USDA Media by Lance Cheung / Public domain)
Repsol Entrepreneurs Fund for Startups in the Energy Transition
At the Repsol Foundation, we have been supporting entrepreneurship and entrepreneurs for more than 10 years through Fondo de Emprendedores, our accelerator for start-ups that provide technological solutions to meet the challenges of the Energy Transition. This is a perfect program for start-ups in the testing phase with real customers, or that will reach this phase in 1–2 years.
This program aims to accelerate startups working in any of the following:
SCOPE 1: LOW-CARBON ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES AND CIRCULAR ECONOMY 1. Recycling and treatment technologies: conversion of biomass, new processes for converting waste into chemical products 2. Biogas production, upgrading, transport and end use technologies 3. Low environmental impact H2 renewable solutions for production, blending, transport and storage 4. Advanced biofuel production and conversion technologies (liquefaction or de novo, gasification) and synthetic fuels for road, maritime and aviation transport 5. Processing of chemicals and other organic materials for circular economy 6. Low-carbon lubricants for industrial and automotive applications 7. CO2 Capture, Use and/or Storage Technologies. CO2 Direct Air Capture: new absorbent materials and efficient process design 8. COX, H2 conversion processes to Hydrocarbons 9. Low carbon technologies for Oil & Gas operations, including energy efficiency, GHG direct emissions (scopes 1 and 2), Methane emissions, CCS or Geothermal. 10. Other technologies related to this scope’s heading
SCOPE 2: BIOTECHNOLOGY AND NANOTECHNOLOGY FOR SUSTAINABLE SOLUTIONS 1. Bio conversion of organic material to chemicals. Biorefinery, biofactory 2. Protein engineering, development of biocatalysts and enzymes 3. Gene editing technologies and applications in energy and materials 4. Plastic biodegradation technologies 5. Biosensors design, production and end use. 6. Anti-corrosive, anti-bacterial, thermal nanocoating for pipelines and infrastructures 7. Organic and inorganic membrane technologies, including new materials 8. Improvement of the properties of fuels, lubricants and chemicals 9. Other technologies related to this scope’s heading
SCOPE 3: PRODUCTS AND SERVICES BASED ON ENERGY MANAGEMENT AND RENEWABLES 1. Intelligent energy management systems 2. New batteries and fuel cells technologies 3. Distributed energy solutions 4. Energy conversion and storage systems 5. Advanced mobility solutions 6. Renewable energy generation, maintenance and control and commercialization. 7. Other technologies related to this scope’s heading
SCOPE 4: DIGITAL TECHNOLOGIES FOR THE ENERGY SECTOR 1. Artificial intelligence applied to process optimization and energy efficiency. 2. Digital twins and intelligent interfaces for process control 3. Digital technologies for predictive and prescriptive maintenance 4. Smart trading for the energy marketplace 5. Computational chemistry tools for energy applications 6. Remote sensing, IoT and robotic solutions for industrial assets and environment 7. Quantum computing applications in energy sector 8. Other technologies related to this scope’s heading SCOPE 5: NATURAL SOLUTIONS FOR CARBON FOOTPRINT REDUCTION 1. Reforestation and afforestation technologies for resilient CO2 absorption sinks 2. Advanced monitoring, reporting and verification technologies in CO2 absorption 3. Digital technologies applied to carbon markets value chain 4. Technologies for ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) project certification 5. Other technologies related to this scope’s heading
Startups admitted to the Program will receive during the acceleration period a contribution of FIVE THOUSAND EUROS (€ 5,000) per month as ordinary funds. Additionally, admitted Startups may request up to a maximum of FORTY THOUSAND EUROS (€ 40,000) per year as extraordinary funds for strategic expenses to achieve the milestones of the Work Plan (as defined in section 4.4), mainly to complete the pilot test. The disbursement of this additional contribution will be subject to the exclusive decision of Fundación Repsol.
Application Deadline: March 10, 2023
Check more https://adalidda.com/posts/c4qmPwNwToZAAbf2L/repsol-entrepreneurs-fund-for-startups-in-the-energy/call
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I used to see posts like this and kinda cringe and scroll past but I've gotten tired of the misinformation and general anti-vegan sentiment on Tumblr. So here's why I disagree with a lot of the points on this post:
1. The use of agave. Personally, I live in Europe, and have not encountered people using agave in place of honey. I HAVE encountered people online who are "plant-based" and tout using different kinds of sugar sources as if they will be healthier for you. They won't, sugar is sugar, no matter where it comes from. Conflating veganism as a diet with veganism as an activism stance is understandable, but being vegan is more than a diet choice.
2. Honey and bees. I could talk all day on this subject but ultimately, no, buying honey is absolutely not good for the bees. For one, honey bees do not search for a new home because of an excess of honey, they do it because the colony has become so large the queen's pheromones can no longer control the entire workforce. This causes some bees to leave and swarm. It's a natural process we assume they've been doing to reproduce for longer than we've been farming them.
In terms of not harvesting the honey and the bees using the cells they use for their young to store more honey, yes this does happen. But only in hives managed by humans. The solution is not to harvest honey, but to stop keeping bees in artificial hives entirely. Honey bees are bred and shipped around the world (lookup Californian almonds and honey bees) specifically to pollinate crops in places that they have no business being in. By keeping bees, you are creating more competition for your country's natural pollinators, who are the insects who REALLY need our help. Having a single pollinator for all agriculture in the world is terrible, both for the industry and the bees. Stop supporting it.
3. Wool. Sheep have been selectively bred over time to produce lots of wool and not naturally shed it so they are required to be sheared. Does shearing hurt sheep? No, if you take your time with it. Do factory wool farms take their time? No, they don't. Also, there is this weird sentiment that vegans are only wearing clothes made of synthetic fibres and ruining the world with microplastics. Most vegans are also environmentalists, they care about the planet. I think you'd be more likely to find a hardcore vegan wearing clothes made of things like hemp than someone who isn't vegan. As well as that, why are vegans held to a higher moral standard than other people when it comes to synthetic fibres? I would put money on the fact that most people have clothes that have some percentage of nylon or polyester in them. No one is wearing clothes made of just cotton or just wool.
4. Eggs. So modern chickens have been selectively bred to overproduce eggs. Their ancestors would lay 12-14 eggs a year, most chickens will lay around 250 eggs a year. This wreaks havoc on their poor bodies that end up calcium and protein deficient - think about the amount they are losing to produce 250 eggs a year. If you keep chickens, I believe the humane thing to do is to let them sit on their eggs for a few days to not disrupt the brood behaviour, and then feed the eggs back to them so that they can recoup the nutrients and minerals they have lost. By harvesting their eggs, you contribute to their pain. You contribute to this system. The best thing to do is to stop breeding chickens. I'd love if we could un-selectively breed them back to what they used to be, like some people have done with dogs like pugs.
Ultimately, veganism is about reducing harm. I truly do understand why people encourage you to support local farmers and not large chain brands (and you definitely should), but as the world is today, buying animal products does contribute to animal suffering and it does contribute to climate change.
Vegans of tumblr, listen up. Harvesting agave in the quantities required so you dont have to eat honey is killing mexican long-nosed bats. They feed off the nectar and pollinate the plants. They need the agave. You want to help the environment? Go back to honey. Your liver and thyroid will thank you, as well. Agave is 90% fructose, which can cause a host of issues. Bye.
#long post#veganism#turning my anon off for a bit because last time i made a vegan post i got lots of hate#im always up for a discussion like nothing is gospel#but you wont shake my belief that veganism is best for animals and nature and the planet
251K notes
·
View notes
Text
Vegan Pasta Market Drivers and Trends Shaping the Industry's Future Outlook and Growth Dynamics
The vegan pasta market has gained significant momentum in recent years, driven by rising consumer interest in plant-based diets, health-conscious eating, and sustainability. With growing awareness of the environmental impact of animal-based food production, the demand for vegan alternatives continues to surge. The market is projected to experience robust growth in the coming years, supported by various drivers and trends that are shaping the industry's future.

Increasing Demand for Plant-Based Products
One of the key drivers of the vegan pasta market is the growing consumer preference for plant-based foods. As more people adopt vegan, vegetarian, and flexitarian diets, the demand for vegan alternatives to traditional products like pasta has skyrocketed. Consumers are becoming increasingly aware of the health benefits associated with plant-based foods, including lower cholesterol levels, improved digestion, and reduced risk of chronic diseases. Vegan pasta, made from plant-based ingredients such as chickpeas, lentils, and quinoa, provides an appealing and nutritious option for those seeking healthier meal alternatives.
Health and Wellness Trends
Health-conscious consumers are increasingly looking for food options that align with their wellness goals. Vegan pasta, often high in fiber and protein, is seen as a healthier choice compared to traditional pasta made from refined wheat. The gluten-free trend also contributes to the rise in popularity of vegan pasta, as many plant-based pasta options cater to individuals with gluten sensitivities. Additionally, vegan pasta is typically free from artificial preservatives, colors, and flavors, which appeals to consumers seeking cleaner, more natural foods. As the demand for healthier food options continues to grow, vegan pasta's popularity is expected to follow suit.
Sustainability and Ethical Consumerism
Environmental concerns and ethical considerations are also driving the growth of the vegan pasta market. The food industry is increasingly prioritizing sustainability, with consumers seeking products that have a lower carbon footprint. Plant-based foods, including vegan pasta, require fewer natural resources such as water and land to produce compared to animal-based products. Moreover, the production of vegan pasta typically generates less greenhouse gas emissions, which aligns with the growing interest in reducing environmental impact. This focus on sustainability is particularly prominent among millennials and Gen Z, who are more likely to support eco-friendly brands and products.
Innovation in Product Development
As the vegan pasta market expands, manufacturers are continually innovating to meet consumer preferences and differentiate their products. There has been a surge in the development of new vegan pasta varieties made from alternative grains and legumes, offering a broader range of textures, flavors, and nutritional benefits. For example, pasta made from red lentils, edamame, and black beans has become popular for its high protein and fiber content. In addition, the rise of pasta with added functional ingredients, such as spirulina, turmeric, and flaxseeds, has further contributed to the market's growth by catering to consumers looking for functional and nutrient-dense food options.
Global Market Expansion
The vegan pasta market's growth is not limited to one region but is becoming a global trend. While North America and Europe lead the market, the demand for vegan products is rapidly increasing in other regions, including Asia and Latin America. The rise of veganism in countries like China, India, and Brazil has created new opportunities for vegan pasta manufacturers to tap into previously untapped markets. As global consumers become more conscious of their dietary choices, the demand for plant-based food products, including pasta, is expected to rise, contributing to the overall expansion of the market.
Conclusion
The vegan pasta market is experiencing significant growth, driven by health-conscious consumers, sustainability efforts, and continuous product innovation. As the market continues to evolve, it will likely benefit from ongoing trends in plant-based eating, ethical consumerism, and the demand for healthier, more sustainable food options. Manufacturers who can successfully tap into these trends and offer a diverse range of vegan pasta products will be well-positioned to thrive in this dynamic and rapidly expanding market.
Request Sample PDF Report : https://www.pristinemarketinsights.com/get-free-sample-and-toc?rprtdtid=NjIw&RD=Vegan-Pasta-Market-Report
#VeganPastaMarket#VeganPastaMarketTrends#VeganPastaMarketInsights#VeganPastaMarketGrowth#VeganPastaMarketForecast#VeganPastaMarketOpportunities
0 notes
Text
Plant-based Seafood Market Hindrances to Expansion
The plant-based seafood market has shown promising growth due to increasing consumer demand for healthier, sustainable food options. However, despite the positive outlook, the market faces several growth hindrances that could impede its expansion. Addressing these challenges is essential for unlocking the full potential of the plant-based seafood sector.
1. Limited Consumer Awareness
One of the primary obstacles to the growth of the plant-based seafood market is limited consumer awareness. While plant-based food alternatives have gained popularity, seafood alternatives are still relatively unknown to many consumers. Many people are unaware of the health benefits, environmental advantages, and ethical considerations associated with plant-based seafood. Without proper education and awareness campaigns, many consumers continue to view traditional seafood as a better option, hindering the adoption of plant-based alternatives.
2. Taste and Texture Concerns
Replicating the taste and texture of traditional seafood has been a significant challenge in the plant-based seafood market. Seafood is known for its unique flavor profile and delicate texture, which are difficult to mimic using plant-based ingredients. While companies are making strides with innovations in plant-based seafood products, such as plant-based fish fillets, shrimp, and crab cakes, these offerings are often considered inferior in taste and texture compared to their traditional counterparts. Until these issues are addressed, consumer acceptance of plant-based seafood remains limited.

3. High Production Costs
Plant-based seafood products tend to be more expensive than traditional seafood. The cost of production, which includes sourcing quality plant proteins, developing new manufacturing processes, and using specialized ingredients, leads to higher retail prices. For many consumers, this price difference makes plant-based seafood less attractive, particularly in regions where seafood is affordable and widely consumed. Without price parity or cost reductions, plant-based seafood may remain a niche offering, limiting its broader market appeal.
4. Supply Chain and Ingredient Availability
The availability of key ingredients for plant-based seafood is a significant challenge. Many of the ingredients used to replicate seafood textures and flavors, such as seaweed, algae, and plant proteins, are not always readily available in sufficient quantities. The limited sourcing of high-quality ingredients can lead to inconsistent product availability, higher costs, and potential supply chain disruptions. As the market grows, companies will need to develop more reliable sourcing methods and supply chain strategies to keep up with increasing demand.
5. Regulatory Challenges
Regulatory frameworks for plant-based seafood are still evolving, with many regions lacking clear guidelines for labeling and ingredient disclosure. In some countries, plant-based products may be subject to different regulations than traditional seafood, which can complicate product development and market entry. Manufacturers face uncertainty around health claims, ingredient labeling, and packaging requirements. Until standardized regulations and clearer guidelines are established, plant-based seafood companies will continue to face regulatory barriers that can slow down market growth.
6. Competition from Traditional Seafood
The plant-based seafood market competes directly with the traditional seafood industry, which is well-established and deeply ingrained in consumer culture. Despite the growing demand for plant-based products, traditional seafood remains a staple in many diets due to its established culinary use, nutritional benefits, and consumer familiarity. To overcome this competition, plant-based seafood must offer a compelling value proposition in terms of taste, price, and sustainability.
7. Perceptions of Plant-based Foods
Although plant-based foods are on the rise, many consumers still associate plant-based alternatives with being less satisfying or having an artificial taste. Additionally, there is a perception that plant-based seafood may lack the nutritional benefits of real seafood. Overcoming these perceptions and proving the health and taste benefits of plant-based seafood alternatives is essential to boosting consumer adoption.
Conclusion
While the plant-based seafood market shows great potential, growth will be impeded by challenges related to consumer awareness, taste and texture issues, production costs, ingredient availability, regulatory barriers, and competition from traditional seafood. Addressing these hindrances through innovation, education, and strategic partnerships will be key to accelerating growth and expanding the market for plant-based seafood products.
0 notes
Text
Plant Based Meal Kits Market Drivers: Key Factors Behind the Rising Global Demand for Sustainability
The plant-based meal kits market has been witnessing exponential growth globally, driven by shifting consumer preferences, technological advancements, and increasing awareness of sustainability. As the demand for healthier, eco-friendly, and convenient meal options rises, several factors have emerged as pivotal drivers for this market. This article explores the key market drivers fueling the growth of plant-based meal kits and highlights their influence on the industry.

1. Shifting Consumer Preferences Towards Plant-Based Diets
One of the most significant drivers of the plant-based meal kits market is the growing consumer inclination toward plant-based diets. With heightened awareness of health issues, ethical concerns surrounding animal welfare, and environmental sustainability, more consumers are adopting vegetarian, vegan, and flexitarian lifestyles. This trend is particularly strong among millennials and Gen Z, who prioritize health and environmental consciousness in their purchasing decisions.
Research reveals that plant-based diets can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like obesity, diabetes, and heart conditions. This health awareness has encouraged many to seek plant-based meal kits that offer balanced nutrition and easy preparation.
2. Rising Environmental Awareness and Sustainability Concerns
The environmental benefits of plant-based diets are another critical driver for this market. Livestock farming contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water usage. As global concerns about climate change escalate, consumers are opting for plant-based meal kits as a sustainable alternative.
Meal kit companies are leveraging eco-friendly packaging, locally sourced ingredients, and carbon-neutral production practices to attract environmentally conscious customers. This alignment with sustainable practices not only appeals to consumers but also contributes to the overall growth of the market.
3. Convenience and Time-Saving Solutions
The busy lifestyles of modern consumers have increased the demand for convenient meal solutions. Plant-based meal kits address this need by offering pre-portioned ingredients and easy-to-follow recipes. This eliminates the need for time-consuming meal planning, grocery shopping, and preparation.
Additionally, the growing prevalence of meal kit subscriptions ensures that customers receive fresh, ready-to-cook ingredients regularly. This level of convenience has resonated with consumers, particularly those who want to adopt plant-based diets without sacrificing time or effort.
4. Innovations in Product Offerings
Innovation in the plant-based meal kits market is a significant driver of its growth. Companies are investing heavily in developing new recipes, flavors, and meal options that cater to diverse tastes and dietary requirements. From gluten-free and high-protein options to allergen-free and organic offerings, brands are expanding their portfolios to reach a broader audience.
Technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence for personalized meal recommendations and the use of food science to create plant-based meat alternatives, have further boosted the appeal of meal kits.
5. Increased Marketing and Awareness Campaigns
Marketing efforts and awareness campaigns play a vital role in driving the plant-based meal kits market. Companies are actively promoting the benefits of plant-based diets through social media, influencer partnerships, and educational initiatives. These campaigns focus on the health, environmental, and ethical advantages of choosing plant-based options.
Collaborations with fitness influencers, celebrity endorsements, and strategic advertising have successfully captured consumer interest. Moreover, the increased visibility of plant-based meal kits in retail stores and online platforms has made them more accessible, further driving market adoption.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the plant-based meal kits market is poised for growth, challenges such as higher costs, limited access in rural areas, and competition from traditional meal kits persist. However, these obstacles also present opportunities for innovation and expansion, as companies explore ways to reduce costs, expand delivery networks, and improve customer experience.
Conclusion The plant-based meal kits market is thriving due to several key drivers, including shifting dietary preferences, sustainability concerns, convenience, product innovation, and effective marketing campaigns. As more consumers embrace plant-based diets, the market is expected to grow exponentially, creating opportunities for businesses to innovate and expand their offerings. With the right strategies, the industry can continue to meet the demands of health-conscious and eco-aware consumers worldwide.
0 notes