#PERSIAN EMPIRE
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
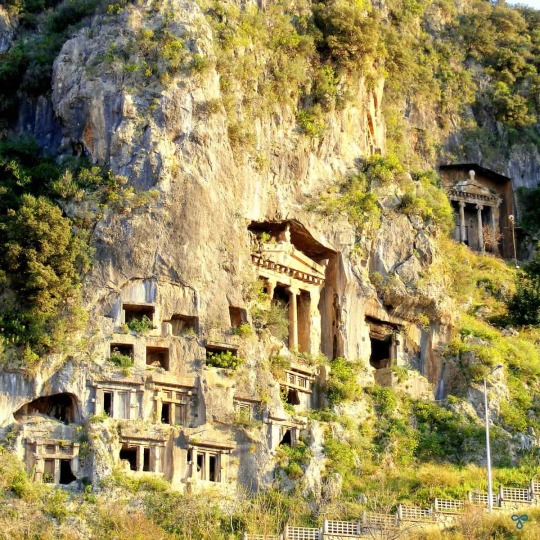

The Lycian Rock Tombs, Fethiye, Türkiye, c. 4th century BCE.
#ancient#ancient history#ancient art#ancient culture#antiquité#antichità#greek art#hellenism#hellenistic#greek history#ancient greek#Lycia#lycian#fethiye#türkiye#achaemenid#achaemenid empire#persian empire#ancient persia#archeology#anatolia#ancient anatolia
156 notes
·
View notes
Text

archers' frieze with palmettos and festoons | c. 522 - 486 BCE | palace of darius i, susa, iran
in the museo internazionale delle ceramiche collection
#ancient art#darius i#achaemenid#iron age#susa#iran#iranian art#persia#persian empire#achaemenid empire
226 notes
·
View notes
Text

Earthenware rhyton in the shape of an ibex head, from Achaemenid Persia (6th or 5th century BCE). Excavated at Gilan, Iran; now in the Tokyo National Museum, Tokyo, Japan.
#art#art history#artifact#artifacts#rhyton#Persia#Persian art#Persian Empire#Achaemenid Empire#earthenware#Tokyo National Museum
398 notes
·
View notes
Text

A Pot With Gold Coins Discovered in Ancient Greek City in Turkey
Archaeologists have discovered a pot of buried treasure overflowing with ancient Greek coins in Turkey.
The gold coins were found inside a room beneath a home in Notion, an ancient Greek city in western Turkey. They feature the figure of a kneeling archer, a design element used for the Persian daric, a gold coin issued by the Persian Empire. The currency was likely minted in Sardis, located 60 miles (97 kilometers) northeast of Notion, according to a statement from the University of Michigan.
Researchers think the mercenaries used the hoard as payment, but it's unclear why they buried it.
"The discovery of such a valuable find in a controlled archaeological excavation is very rare," Christopher Ratté, a professor of ancient Mediterranean art and archaeology at the University of Michigan and director of the Notion Archaeological Survey, the project that led to the discovery the coins, said in the statement. "No one ever buries a hoard of coins, especially precious metal coins, without intending to retrieve it. So only the gravest misfortune can explain the preservation of such a treasure."
A few stylistic clues indicate that the coins were struck sometime during the fifth century B.C. — a time stamp archaeologists are using to help uncover the sequence of events that led to the treasure's burial.

"This hoard will provide a firm date that can serve as an anchor to help fix the chronology of the (entire sequence of coins)," Ratté said. "According to the Greek historian Xenophon, a single daric was equivalent to a soldier's pay for one month."
In the past few years, the site has been a hotbed for artifact finds, including pottery fragments, also from the fifth century B.C., hidden "in earlier walls incorporated into the foundations of the house," which dates to the Hellenistic period, according to the statement.
The Hellenistic period occurred after the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C. and lasted until the conquest of the final Hellenistic kingdom by Rome in 31 B.C. During the sixth century B.C., Notion was incorporated into the Persian Empire along with other Greek cities. In the early fifth century B.C., it was freed from Persian rule for a time, only to be reintegrated into the empire during the fourth century B.C., according to the statement.
Between 430 and 427 B.C., a group of Persian sympathizers, as well as Greek and "barbarian" mercenaries, occupied Notion. During that time, the Athenian general Paches killed pro-Persian mercenaries, prompting Persian sympathizers to be expelled from the city as the Athenians took control, according to the statement.
Ratté said that these events could have led to the burial and eventual loss of the hoard.
By Jennifer Nalewicki.


#A Pot With Gold Coins Discovered in Ancient Greek City in Turkey#Notion#gold#coins#collectable coins#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#persian empire#greek history
237 notes
·
View notes
Text
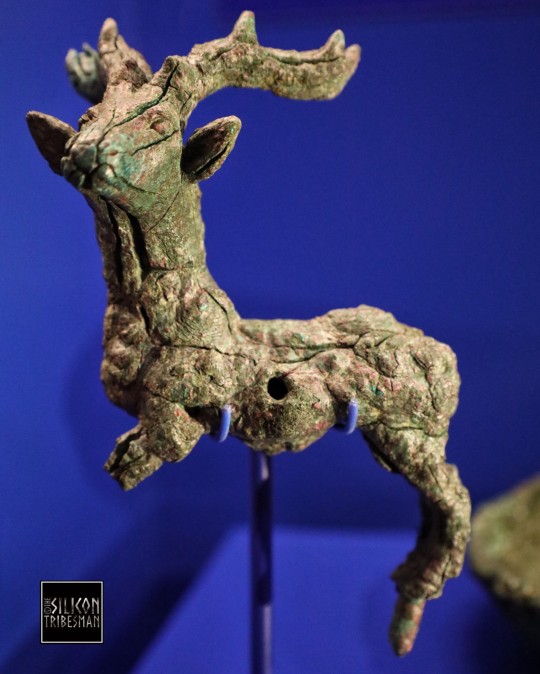

Bronze Stag Statuette from the Persian Empire, 550 to 330 BCE, Ashmolean Museum, Oxford
#stag#bronze statuette#animals#symbols#metalwork#metalworking#ancient living#ancient craft#ancient cultures#persian#persian empire#archaeology#ashmolean#beasts
460 notes
·
View notes
Text


Discovered almost 3 days ago in the south of Iran (shiraz)
Unbelievable! 0_0
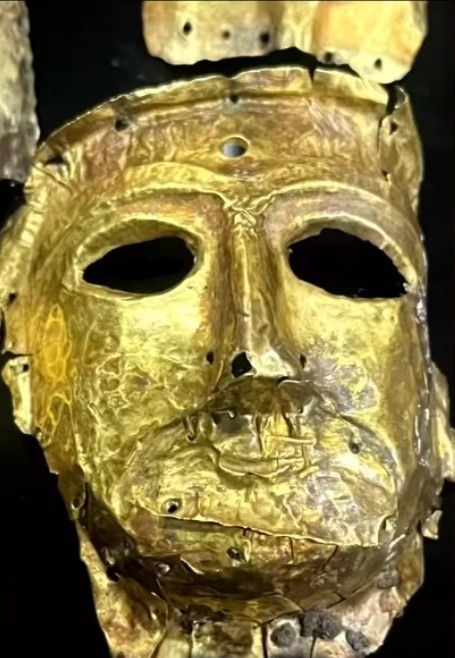

According to archaeologists, these objects(two masks and a few piece of bracelet made of gold) are more than 2000 years old and goes back to the pre-Achaemenid empire period and the late Elam area
#treasure#achaemenid#ancient history#history#mask#braclets#treasures#gold#persian empire#kingdom of heaven#fandom#king baldwin iv#area#baldwin iv#kingdom of heaven 2005#the leper king#kingdom of heaven fandom#art#koh fandom#koh#artists on tumblr#old#iran
103 notes
·
View notes
Text



300 (2006)
#2006#gif#film#movie#comics#300#Zack Snyder#Gerard Butler#King Leonidas#Michael Fassbender#Stelios#Rodrigo Santoro#Xerxes#Lena Headey#Queen Gorgo#Frank Miller#Sparta#Persian Empire#Thermopylae#480 BC
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

#meme#memes#shitpost#shitposting#humor#funny#lol#satire#funny memes#funny humor#fact#facts#funny meme#history#history memes#ancient egypt#persian empire#irony#joke#parody#cats#cat memes
250 notes
·
View notes
Text

Satan, the powerful demotic ruler of the earth who loves giving people moral pop quizzes!😄
🔥🐐🔥
#history#satan#ha-satan#the devil#fallen angel#ancient history#babylonian captivity#helluva boss#christianity#abrahamic religions#jewish history#book of job#angra mainyu#evil#zoroastrianism#persian history#ahurg mazda#demon#helluva boss satan#vivziepop#judaism#demonology#old testament#christian history#ancient#persian empire#king of hell#nickys facts
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
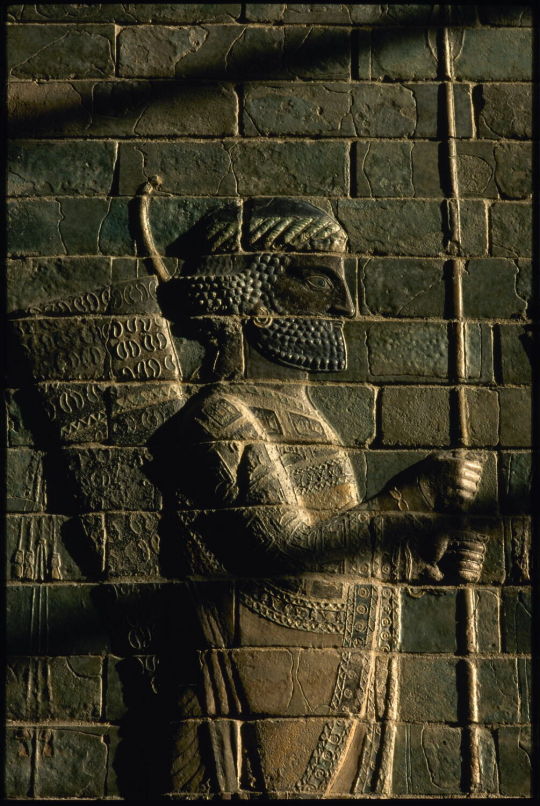




Frieze of archers, Persian Empire (Darius), 522 to 486 BC., siliceous bricks molded with colored glazes, 5 m, Susa, tell of Apadana, palace of Darius, Paris, Louvre museum.
This is the representation of Persians soldiers who certainly formed the close guard of the king. They are heading to the left as well as to the right but their original layout is not known, as well as their location. It is estimated that they were to adorn the walls of an interior courtyard.
This decor is certainly inspired by the processional route of Babylon, created by Nebuchadnezzar II in the previous century. The technique is however different because the Babylonian craftsmen used bricks of clayey and non-siliceous paste.
Darius' archers are accompanied by a glazed decoration with a varied repertoire : winged bulls, genies, palm leaves... There are numerous borrowings from Babylonian vocabulary but here they lose their religious significance and only retain their aesthetic aspect.
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

Princess Grace and Prince Rainier of Monaco at the celebration of the 2,500th anniversary of the founding of the Persian Empire in October 1971.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Countries that are no more: Achaemenid Empire (550BC-330BC)
It was not the first empire of Iranian peoples, but it arose as probably the greatest in terms of influence and became the measure by which all subsequent Iranian empires tended to compare themselves and its influence on culture, government & civil infrastructure would influence others beyond the span of its territory and the span of time. This is the Achaemenid Empire.
Name: In Old Persian it was known as Xšāça or the "The Kingdom or the Empire", it was named the Achaemenid Empire by later historians. Named after the ruling dynasty established by its founder Cyrus the Great who cited the name of his ancestor Haxāmaniš or Achaemenes in Greek as progenitor of the dynasty. It is sometimes also referred to as the First Persian Empire. The Greeks simply referred to it as Persia, the name which stuck for the geographic area of the Iranian plateau well into the modern era.
Language: Old Persian & Aramaic were the official languages. With Old Persian being an Iranian language that was the dynastic language of the Achaemenid ruling dynasty and the language of the Persians, an Iranian people who settled in what is now the southwestern Iranian plateau or southwest Iran circa 1,000 BC. Aramaic was a Semitic language that was the common and administrative language of the prior Neo-Assyrian & Neo-Babylonian Empires which centered in Mesopotamia or modern Iraq, Syria & Anatolian Turkey. After the Persian conquest of Babylon, the use of Aramaic remained the common tongue within the Mesopotamian regions of the empire, eventually becoming a lingua franca across the land. As the empire spread over a vast area and became increasingly multiethnic & multicultural, it absorbed many other languages among its subject peoples. These included the Semitic languages Akkadian, Phoenician & Hebrew. The Iranian language of Median among other regional Iranian languages (Sogdian, Bactrian etc). Various Anatolian languages, Elamite, Thracian & Greek among others.
Territory: 5.5 million kilometers squared or 2.1 million square miles at its peak circa 500BC. The Achaemenid Empire spanned from southern Europe in the Balkans (Greece, Bulgaria, European Turkey) & northwest Africa (Egypt, Libya & Sudan) in the west to its eastern stretches in the Indus Valley (Pakistan) to parts of Central Asia in the northeast. It was centered firstly in the Iranian Plateau (Iran) but also held capitals in Mesopotamia (Iraq). Territory was also found in parts of the Arabian Peninsula & the Caucausus Mountains.
Symbols & Mottos: The Shahbaz or Derafsh Shahbaz was used as the standard of Cyrus the Great, founder of the empire. It depicts a bird of prey, typically believed to be a falcon or hawk (occasionally an eagle) sometimes rendered gold against a red backdrop and depicts the bird holding two orbs in its talons and adorned with an orb likewise above its head. The symbolism was meant to depict the bird guiding the Iranian peoples to conquest and to showcase aggression & strength coupled with dignity. The imperial family often kept falcons for the pastime of falconry.
Religion: The ancient Iranian religion of Zoroastrianism served as the official religion of the empire. It was adopted among the Persian elite & and had its unique beliefs but also helped introduce the concept of free-will among its believers, an idea to influence Judaism, Christianity & Islam in later centuries. Despite this official religion, there was a tolerance for local practices within the subject regions of the empire. The ancient Mesopotamian religion in Babylon & Assyria, Judaism, the Ancient Greek & Egyptian religions & Vedic Hinduism in India was likewise tolerated as well. The tolerance of the Achaemenids was considered a relative hallmark of their dynasty from the start. Famously, in the Old Testament of the Bible it was said that it was Cyrus the Great who freed the Jews from their Babylonian captivity and allowed them to return to their homeland of Judea in modern Israel.
Currency: Gold & silver or bimetallic use of coins became standard within the empire. The gold coins were later referred to as daric and silver as siglos. The main monetary production changes came during the rule of Darius I (522BC-486BC). Originally, they had followed the Lydian practice out of Anatolia of producing coins with gold, but the practice was simplified & refined under the Achaemenids.
Population: The estimates vary ranging from a low end of 17 million to 35 million people on the upper end circa 500BC. The official numbers are hard to determine with certainty but are generally accepted in the tens of millions with the aforementioned 17-35 million being the most reasonable range based on available sources.
Government: The government of the Achaemenid Empire was a hereditary monarchy ruled by a king or shah or later referred to as the ShahanShah or King of Kings, this is roughly equivalent to later use of the term Emperor. Achaemenid rulers due the unprecedented size of their empire held a host of titles which varied overtime but included: King of Kings, Great King, King of Persia, King of Babylon, Pharaoh of Egypt, King of the World, King of the Universe or King of Countries. Cyrus the Great founded the dynasty with his conquest first of the Median Empire and subsequently the Neo-Babylonians and Lydians. He established four different capitals from which to rule: Pasargadae as his first in Persia (southwest central Iran), Ecbatana taken from the Medians in western Iran's Zagros Mountains. The other two capitals being Susa in southwest Iran near and Babylon in modern Iraq which was taken from the Neo-Babylonians. Later Persepolis was made a ceremonial capital too. The ShahanShah or King of Kings was also coupled with the concept of divine rule or the divinity of kings, a concept that was to prove influential in other territories for centuries to come.
While ultimate authority resided with the King of Kings and their bureaucracy could be at times fairly centralized. There was an expansive regional bureaucracy that had a degree of autonomy under the satrapy system. The satraps were the regional governors in service to the King of Kings. The Median Empire had satraps before the Persians but used local kings they conquered as client kings. The Persians did not allow this because of the divine reverence for their ShahanShah. Cyrus the Great established governors as non-royal viceroys on his behalf, though in practice they could rule like kings in all but name for their respective regions. Their administration was over their respective region which varied overtime from 26 to 36 under Darius I. Satraps collected taxes, acted as head over local leaders and bureaucracy, served as supreme judge in their region to settle disputes and criminal cases. They also had to protect the road & postal system established by the King of Kings from bandits and rebels. A council of Persians were sent to assist the satrap with administration, but locals (non-Persian) could likewise be admitted these councils. To ensure loyalty to the ShahanShah, royal secretaries & emissaries were sent as well to support & report back the condition of each satrapy. The so called "eye of the king" made annual inspections of the satrapy to ensure its good condition met the King of Kings' expectations.
Generals in chief were originally made separate to the satrap to divide the civil and military spheres of government & were responsible for military recruitment but in time if central authority from the ShahanShah waned, these could be fused into one with the satrap and general in chiefs becoming hereditary positions.
To convey messages across the widespread road system built within the empire, including the impressive 2,700 km Royal Road which spanned from Susa in Iran to Sardis in Western Anatolia, the angarium (Greek word) were an institution of royal messengers mounted on horseback to ride to the reaches of the empire conveying postage. They were exclusively loyal to the King of Kings. It is said a message could be reached to anywhere within the empire within 15 days to the empire's vast system of relay stations, passing message from rider to rider along its main roads.
Military: The military of the Achaemenids consisted of mostly land based forces: infantry & cavalry but did also eventually include a navy.
Its most famous unit was the 10,000-man strong Immortals. The Immortals were used as elite heavy infantry were ornately dressed. They were said to be constantly as 10,000 men because for any man killed, he was immediately replaced. Armed with shields, scale armor and with a variety of weapons from short spears to swords, daggers, slings, bows & arrows.
The sparabara were the first line of infantry armed with shields and spears. These served as the backbone of the army. Forming shield walls to defend the Persian archers. They were said to ably handle most opponents and could stop enemy arrows though their shields were vulnerable to enemy spears.
There was also the takabara light infantry and though is little known of them it seems they served as garrison troops and skirmishers akin to the Greek peltast of the age.
The cavalry consisted of four distinct groups: chariot driven archers used to shoot down and break up enemy formations, ideally on flat grounds. There was also the traditional horse mounted cavalry and also camel mounted cavalry, both served the traditional cavalry functions and fielded a mix of armor and weapons. Finally, there was the use of war elephants which were brought in from India on the empire's eastern reaches. These provided archers and a massive way to physically & psychologically break opposing forces.
The navy was utilized upon the empire's reaching the Mediterranean and engaged in both battles at sea and for troop transport to areas where troops needing deploying overseas, namely in Greece.
The ethnic composition of Achaemenid military was quite varied ranging from a Persian core with other Iranian peoples such as the Medians, Sogdian, Bactrians and Scythians joining at various times. Others including Anatolians, Assyrians, Babylonians, Anatolians, Indians, Arabs, Jews, Phoenicians, Thracians, Egyptians, Ethiopians, Libyans & Greeks among others.
Their opponents ranged from the various peoples they conquered starting with the Persian conquest of the Medians to the Neo-Babylonians, Lydians, Thracians, Greeks, Egyptians, Arabs & Indians and various others. A hallmark of the empire was to allow the local traditions of subjugated areas to persist so long as garrisons were maintained, taxes were collected, local forces provided levies to the military in times of war, and they did not rebel against the central authority.
Economy: Because of the efficient and extensive road system within the vast empire, trade flourished in a way not yet seen in the varied regions it encompassed. Tax districts were established with the satrapies and could be collected with relative efficiency. Commodities such as gold & jewels from India to the grains of the Nile River valley in Egypt & the dyes of the Phoenicians passed throughout the realm's reaches. Tariffs on trade & agricultural produce provided revenue for the state.
Lifespan: The empire was founded by Cyrus the Great circa 550BC with his eventual conquest of the Median & Lydian Empires. He started out as Cyrus II, King of Persia a client kingdom of the Median Empire. His reign starting in 559BC. Having overthrown and overtaken the Medians, he turned his attention Lydia and the rest of Anatolia (Asia Minor). He later attacked the Eastern Iranian peoples in Bactria, Sogdia and others. He also crossed the Hindu Kush mountains and attacked the Indus Valley getting tribute from various cities.
Cyrus then turned his attention to the west by dealing with the Neo-Babylonian Empire. Following his victory in 539BC at the Battle of Opis, the Persians conquered the Babylonia with relative quickness.
By the time of Cyrus's death his empire had the largest recorded in world history up to that point spanning from Anatolia to the Indus.
Cyrus was succeeded by his sons Cambyses II and Bardiya. Bardiya was replaced by his distant cousin Darius I also known as Darius the Great, whose lineage would constitute a number of the subsequent King of Kings.
Darius faced many rebellions which he put down in succession. His reign is marked by changes to the currency and the largest territorial expansion of the empire. An empire at its absolute zenith. He conquered large swaths of Egypt, the Indus Valley, European Scythia, Thrace & Greece. He also had exploration of the Indian Ocean from the Indus River to Suez Egypt undertaken.
The Greek kingdom of Macedon in the north reaches of the Hellenic world voluntarily became a vassal of Persia in order to avoid destruction. This would prove to be a fateful first contact with this polity that would in time unite the Greek-speaking world in the conquest of the Achaemenid Empire. However, at the time of Darius I's the reign, there were no early indications of this course of events as Macedon was considered even by other Greek states a relative backwater.
Nevertheless, the Battle of Marathon in 490BC halted the conquest of mainland Greece for a decade and showed a check on Persia's power in ways not yet seen. It is also regarded as preserving Classical Greek civilization and is celebrated to this day as an important in the annals of Western civilization more broadly given Classical Greece & in particular Athens's influence on western culture and values.
Xerxes I, son of Darius I vowed to conquer Greece and lead a subsequent invasion in 480BC-479BC. Xerxes originally saw the submission of northern Greece including Macedon but was delayed by the Greeks at the Battle of Thermopylae, most famously by Spartan King Leonidas and his small troop (the famed 300). Though the Persians won the battle it was regarded as a costly victory and one that inspired the Greeks to further resistance. Though Athens was sacked & burnt by the Persians, the subsequent victories on sea & land at Salamis & Plataea drove the Persians back from control over Greece. Though war would rage on until 449BC with the expulsion of the Persians from Europe by the Greeks.
However, the Greeks found themselves in a civil war between Athens & Sparta and Persia having resented the Athenian led coalition against their rule which had expelled them from Europe sought to indirectly weaken the Greeks by supporting Greek factions opposed to Athens through political & financial support.
Following this reversal of fortune abroad, the Achaemenid Empire not able to regain its foothold in Europe, turned inward and focused more on its cultural development. Zoroastrianism became the de-facto official religion of the empire. Additionally, architectural achievements and improvements in its many capitals were undertaken which displayed the empire's wealth. Artaxerxes II who reigned from 405BC-358BC had the longest reign of any Achaemenid ruler and it was characterized by relative peace and stability, though he contended with a number of rebellions including the Great Satraps Revolt of 366BC-360BC which took place in Anatolia and Armenia. Though he was successful in putting down the revolt. He also found himself at war with the Spartans and began to sponsor the Athenians and others against them, showcasing the ever dynamic and changing Greco-Persian relations of the time.
Partially for safety reasons, Persepolis was once again made the capital under Artaxerxes II. He helped expand the city and create many of its monuments.
Artaxerxes III feared the satraps could no longer be trusted in western Asia and ordered their armies disbanded. He faced a campaign against them which suffered some initial defeats before overcoming these rebellions, some leaders of which sought asylum in the Kingom of Macedon under its ruler Philip II (father of Alexander the Great).
Meanwhile, Egypt had effectively become independent from central Achaemenid rule and Artaxerxes III reinvaded in around 340BC-339BC. He faced stiff resistance at times but overcame the Egyptians and the last native Egyptian Pharaoh Nectanebo II was driven from power. From that time on ancient Egypt would be ruled by foreigners who held the title Pharaoh.
Artaxerxes III also faced rebellion from the Phoenicians and originally was ejected from the area of modern coastal Lebanon, Syria & Israel but came back with a large army subsequently reconquered the area including burning the Phoenician city of Sidon down which killed thousands.
Following Artaxerxes III's death his son succeeded him but a case of political intrigue & dynastic murder followed. Eventually Darius III a distant relation within the dynasty took the throne in 336BC hoping to give his reign an element of stability.
Meanwhile in Greece, due to the military reforms and innovations of Philip II, King of Macedon, the Greek speaking world was now unified under Macedon's hegemony. With Philip II holding the title of Hegemon of the Hellenic League, a relatively unified coalition of Greek kingdoms and city-states under Macedon premiership that formed to eventually invade Persia. However, Philip was murdered before his planned invasion of Asia Minor (the Achaemenid's westernmost territory) could commence. His son Alexander III (Alexander the Great) took his father's reforms and consolidated his hold over Greece before crossing over to Anatolia himself.
Darius III had just finished reconquering some rebelling vestiges of Egypt when Alexander army crossed over into Asia Minor circa 334BC. Over the course of 10 years Alexander's major project unfolded, the Macedonian conquest of the Persian Empire. He famously defeated Persians at Granicus, Issus and Gaugamela. The latter two battles against Darius III in person. He took the King of Kings family hostage but treated them well while Darius evacuated to the far eastern reaches of his empire to evade capture. He was subsequently killed by one of his relatives & satraps Bessus, whom Alexander eventually had killed. Bessus had declared himself King of Kings though this wasn't widely recognized and most historians regard Darius III, the last legitimate ShahanShah of Achaemenids.
Alexander had taken Babylon, Susa & Persepolis by 330BC and effectively himself was now ruler of the Persian Empire or at least its western half. In addition to being King of Macedon & Hegemon of the Hellenic League, he gained the titles King of Persia, Pharaoh of Egypt & Lord of Asia. Alexander would in time eventually subdue the eastern portions of the Achaemenid realm including parts of the Indus Valley before turning back to Persia and Babylon where he subsequently became ill and died in June 323BC at age 32. Alexander's intentions it appears were never to replace the Achaemenid government & cultural structure, in fact he planned to maintain and hybridize it with his native Greek culture. He was in fact an admirer of Cyrus the Great (even restoring his tomb after looting) & adopted many Persian customs and dress. He even allowed the Persians to practice their religion and had Persian and Greeks start to serve together in his army. Following his death and with no established successor meant the empire he established which essentially was the whole Achaemenid Empire's territory in addition to the Hellenic world fragmented into different areas run by his most trusted generals who established their own dynasties. The Asian territories from Anatolia to the Indus (including Iran and Mesopotamia) gave way to the Hellenic ruled Seleucid Empire while Egypt became the Hellenic ruled Ptolemaic Kingdom. The synthesis of Persian and Greek cultures continued in the Seleucid and Greco-Bactrian kingdoms of antiquity.
The Achaemenid Empire lasted for a little over two centuries (550BC-330BC) but it casted a long shadow over history. Its influence on Iran alone has persisted into the modern age with every subsequent Persian Empire claiming to be its rightful successor from the Parthian & Sasanian Empires of pre-Islamic Iran to the Safavids of the 16th-18th century and the usage of the title Shah until the last Shah's ejection from power in the 1979 Islamic Revolution. Even the modern Islamic Republic of Iran uses Achaemenid imagery in some military regiments and plays up its importance in tourism and museums as a source of pride to Persian (Farsi) & indeed Iranian heritage. Likewise, its form of governance and the pushing of the concept of divine rights of kings would transplant from its Greek conquerors into the rest of Europe along with various other institutions such as its road & mail system, tax collection & flourishing trade. Its mix of centralized & decentralized governance. Its religious & cultural tolerance of local regions even after their conquest would likewise serve as a template for other empires throughout history too. The Achaemenid Empire served as a template for vast international & transcontinental empires that would follow in its wake & surpass its size & scope of influence. However, it is worth studying for in its time, it was unprecedented, and its innovations so admired by the likes of Alexander the Great and others echo into the modern era.
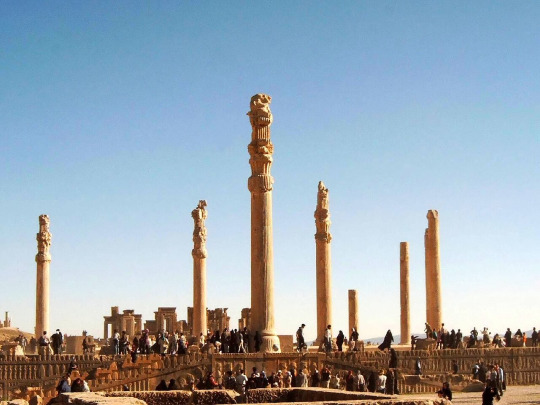
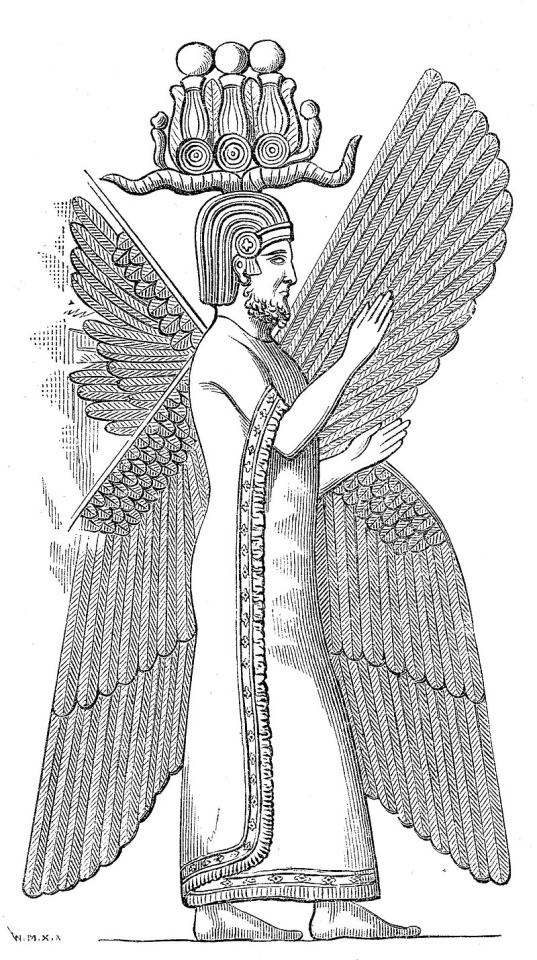
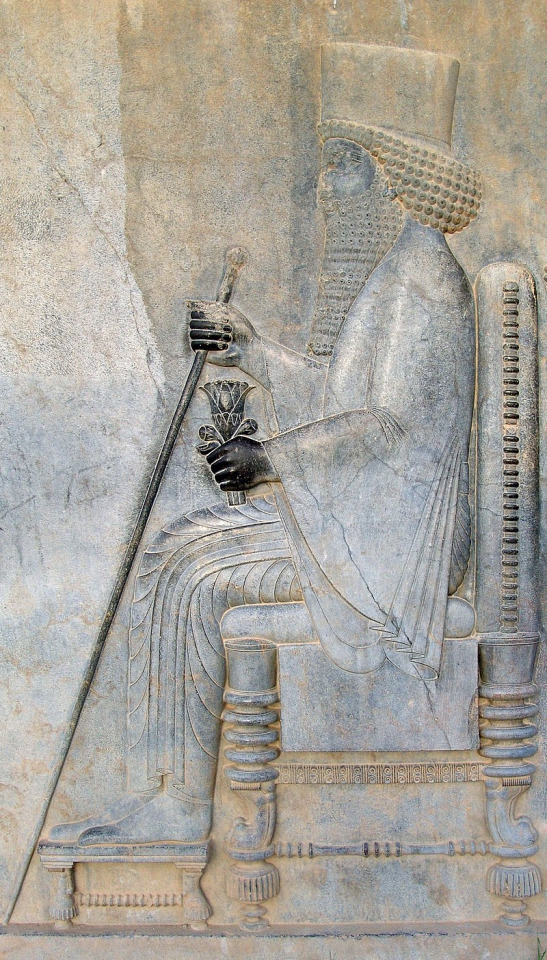
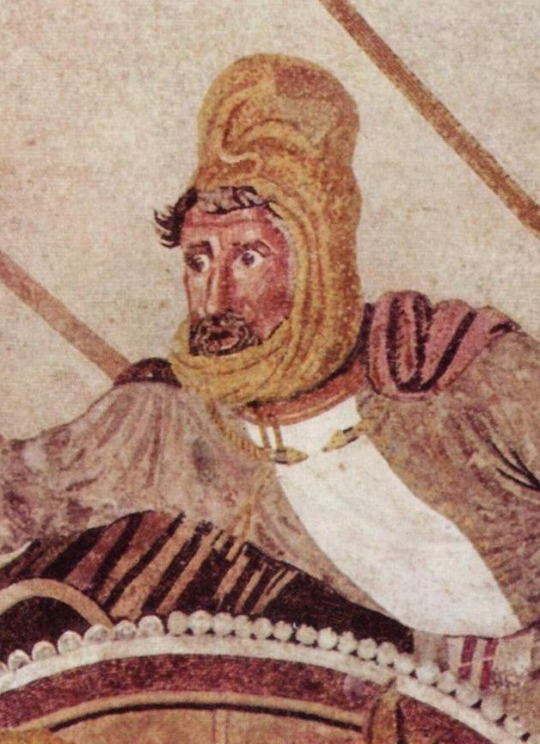

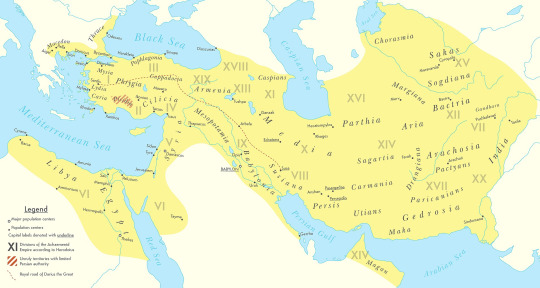









#military history#antiquity#iran#greece#ancient greece#classical greece#ancient ruins#ancient iran#ancient persia#achaemenid#persia#zoroastrianism#alexander the great#cyrus the great#xerxes#artwork#government#history#persian empire#ancient egypt
110 notes
·
View notes
Text
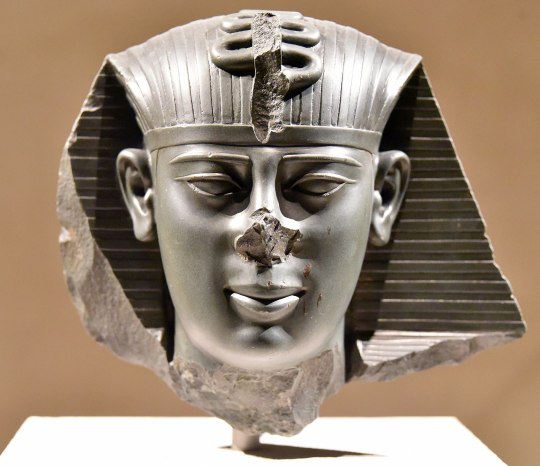

Head of Pharaoh Amasis (Ahmose) II of the 26th Dynasty, 6th century BCE. Amasis II claimed the throne after his predecessor, Apries, fell out of favor with his soldiers following a disastrous expedition against the Greek city-state of Cyrene. Apries formed an alliance with the Neo-Babylonian monarch Nebuchadnezzar II, who sought to install him as a puppet ruler on the Egyptian throne. However, Amasis II defeated both the Babylonians and Apries, solidifying his rule. He passed the throne to his son, Psamtik III, in 526 BCE. Psamtik III's reign was short-lived, as the Persian king Cambyses II invaded and conquered Egypt just one year later.
#egypt#egyptology#ancient egypt#ancient egyptian#egyptian history#egyptian art#persian#persian empire#achaemenids
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Stater, minted 380/379 BCE at Tarsus in Cilicia, of Pharnabazus II, former satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia under the Achaemenid dynasty of Persia and a major figure in the internecine conflicts of the Greek city-states during the late 5th/early 4th centuries. The coin shows the complex intermingling of Greek and Near Eastern cultures characteristic of Anatolia under Achaemenid rule. On the obverse, Ba'al of Tarsus is shown seated, holding a lotus-tipped scepter and wearing the Greek chlamys. On the reverse, a bearded man wears a helmet in Attic style. Both sides are inscribed in Aramaic, which served as the lingua franca of the Near East under the Achaemenids. Photo credit: Classical Numismatic Group, Inc. http://www.cngcoins.com
#history#ancient history#classics#tagamemnon#Persian Empire#Achaemenid#coins#ancient coins#Persian coins#numismatics#ancient numismatics#artifacts#artefacts
104 notes
·
View notes
Text

Greece Returns 1,055 Ancient Coins to Turkey
Greece on Thursday returned a hoard of over 1,000 stolen ancient coins to Turkey in the first repatriation of its kind between the historic rivals and neighbors, Agence France-Presse reported.
The move came a few months after Turkey publicly supported Greece in its long quest to reclaim the Parthenon Marbles from the British Museum in London.
Greek Culture Minister Lina Mendoni said the hoard of 1,055 silver coins had been seized by Greek customs guards on the border with Turkey in 2019.
“These coins had been illegally imported,” Mendoni said at a ceremony at the Numismatic Museum, which specializes in currency and medal collections, in Athens.
Greeks are “particularly sensitive” to repatriation issues, she said.
“All illegally exported antiquities from whichever country should return to their country of origin,” Mendoni added.
Turkish Culture Minister Mehmet Nuri Ersoy said the operation was the first repatriation from Greece.
Greek and Turkish experts determined that the coins were part of a stock hidden in Asia Minor between the late 5th and early 4th century BCE, she added.
While research is ongoing, it is possible the hoard was secreted in modern-day Turkey during the Persian Wars expeditions of Athenian general Cimon, a veteran of the 480 BCE Battle of Salamis, she added.



Broadly used
Most of the cache were tetradrachms — ancient large silver coins — originally minted in Athens and used broadly in the eastern Mediterranean, said Museum Numismatologist Vassiliki Stefanaki, a coinage expert.
Stamped with the image of an owl, the Athenian relics were also used locally to pay tribute to the Persian Empire, and Persian governors used them to reward their troops, she said.
Other coins came from Cyprus, the islands of Aegina and Milos, from Asia Minor cities founded by Greek settlers, the Iron Age kingdom of Lydia, and Phoenicia in modern-day Lebanon, officials said.
Mendoni on Thursday also thanked Turkey for supporting Greece’s campaign to secure the return of the Parthenon Marbles from London.
The British Museum has long maintained that the Marbles were removed from the Acropolis in Athens by royal decree granted to Lord Elgin, the British ambassador to the Ottoman Empire.
But in June, Zeynep Boz, the head of the Turkish Culture Ministry’s anti-smuggling committee, told a UNESCO meeting in Paris that no such document had been found in Ottoman archives.
Her statement was “decisive” in favor of Greece’s position, Mendoni said Thursday.
Ersoy through a translator said Turkey wanted “with all its heart” to see the Marbles return to Athens.
“The Greek people should have them, they belong to them,” he said.
Boz, who attended Thursday’s ceremony in Athens, told Agence France-Presse that the timing of the coins’ return by Greece was not related to her report in June.
The five-year delay was caused by the time required by the Greek justice system to authorize the coins’ repatriation, she said.


#Greece Returns 1055 Ancient Coins to Turkey#silver#silver coins#ancient coins#ancient artifacts#tetradrachms#Persian Empire#archaeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#looted#stolen
80 notes
·
View notes
Text
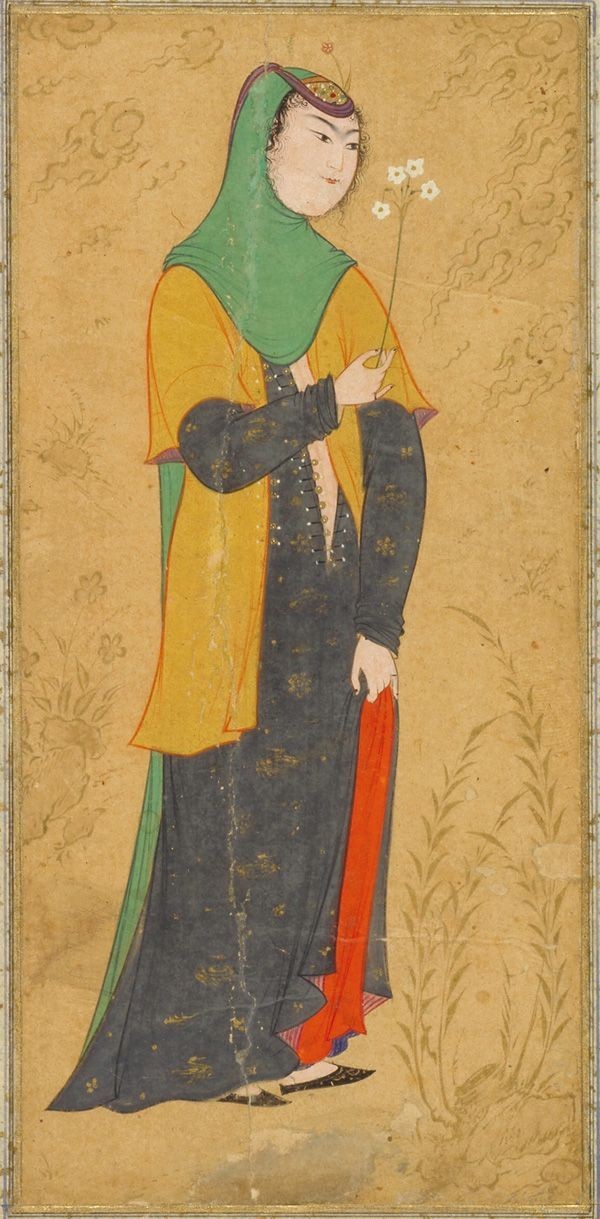

Woman with a spray of flower, 1595, perisan art, Ispahan
#persian#persian art#farsi#islamic#islamic art#floral#iran#iranian#flower#illumination#Illustration#book illustration#art#colour#colourful art#16th century#oriental#oriental art#persian empire#modesty#persian clothing#historical#traditional#Isfahan#ispahan
36 notes
·
View notes