#achaemenids
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
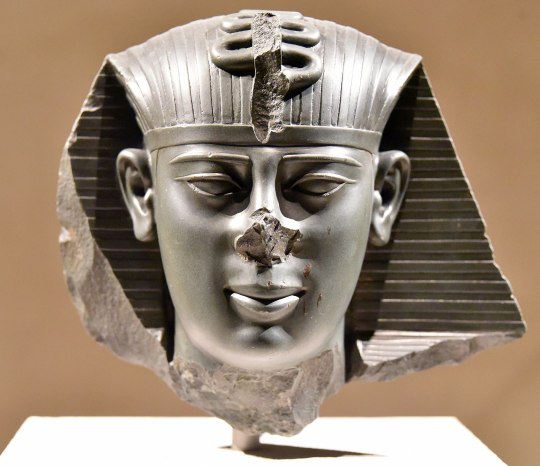

Head of Pharaoh Amasis (Ahmose) II of the 26th Dynasty, 6th century BCE. Amasis II claimed the throne after his predecessor, Apries, fell out of favor with his soldiers following a disastrous expedition against the Greek city-state of Cyrene. Apries formed an alliance with the Neo-Babylonian monarch Nebuchadnezzar II, who sought to install him as a puppet ruler on the Egyptian throne. However, Amasis II defeated both the Babylonians and Apries, solidifying his rule. He passed the throne to his son, Psamtik III, in 526 BCE. Psamtik III's reign was short-lived, as the Persian king Cambyses II invaded and conquered Egypt just one year later.
#egypt#egyptology#ancient egypt#ancient egyptian#egyptian history#egyptian art#persian#persian empire#achaemenids
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The "Daiva (=Demons) Inscription" of Xerxes of Persia

The Old Persian "Daiva inscription" of Xerxes I found at Persepolis
"1. A great god is Ahuramazda, who created this earth, who created yonder sky, who created man, who created happiness for man, who made Xerxes king, one king of many, one lord of many.
2. I am Xerxes, the great king, king of kings, king of countries containing many kinds of men, king in this great earth far and wide, son of king Darius, an Achaemenian, a Persian, son of a Persian, an Aryan, of Aryan stock.
3. King Xerxes says: By the grace of Ahuramazda these are the countries of which I was king apart from Persia. I had lordship over them. They bore me tribute. What was said to them by me, that they did. My law, that held them: Media, Elam, Arachosia, Armenia, Drangiana, Parthia, Aria, Bactria, Sogdia, Chorasmia, Babylonia, Assyria, Sattagydia, Lydia, Egypt, Yaunâ, those who dwell on this side of the sea and those who dwell across the sea, men of Maka, Arabia, Gandara, India, Cappadocia, theDahae, the haoma-drinking Sacae, the Sacae wearing pointed caps, Thrace, men of Âkaufaciyâ, Libyans, Carians, and the Nubians.
4. King Xerxes says: when I became king, there was among these countries one that was in rebellion. Ahuramazda bore me aid. By the grace of Ahuramazda I smote that country and put it down in its place.
And among these countries there was a place where previously demons (daiva) were worshipped. Afterwards, by the grace of Ahuramazda I destroyed that sanctuary of demons, and I proclaimed: 'The demons shall not be worshipped!' Where previously the demons were worshipped, there I worshipped Ahuramazda at the proper time and in the proper manner. And there was other business that had been done ill. That I made good. That which I did, all I did by the grace of Ahuramazda. Ahuramazda bore me aid until I completed the work.
You who may live hereafter, if you should think 'Happy may I be when living, and when dead may I be blessed,' have respect for that law which Ahuramazda has established. Worship Ahuramazda at the proper time and in the proper manner. The man who has respect for that law that Ahuramazda has established and worships Ahuramazda at the proper time and in the proper manner, he both becomes happy while alive and becomes blessed when dead.
5. King Xerxes says: May Ahuramazda protect me from harm, and my house, and this land. This I ask of Ahuramazda. This may Ahuramazda give to me."
Translation of the Old Persian text as found on https://www.livius.org/sources/content/achaemenid-royal-inscriptions/xph/
This important Persian royal inscription has drawn much scholarly attention and various theories have been proposed concerning the identification of the "rebellious land", the 'demons", the "demon-worshipping" country and the "sanctuary of demons" that Xerxes would have destroyed according to the inscription, Athens and her Acropolis being among the candidates.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Gate of Cyrus: From Babylon to Persia
The Discovery of an Achaemenid Architectural Masterpiece

In recent years, archaeologists have made a remarkable discovery near Persepolis: a magnificent gate attributed to Cyrus the Great. This discovery has revolutionized our understanding of Achaemenid architecture and civilization, providing us with valuable insights into this historical period.
Archaeological excavations at this site have been conducted for ten years by a joint Iranian-Italian team. Using various methods such as carbon-14 dating and the study of inscriptions, archaeologists have reached significant conclusions about the history and function of this gate.
Location of the Gate
The discovered gate is situated in the Tel Ajri site, approximately three kilometers northwest of the Persepolis citadel. This gate was a structure measuring approximately 30 by 40 meters with a height of about 12 meters.
The structure featured a central corridor that formed a rectangular room measuring 8 by 12 meters. Inside this central chamber, there were four seats. The central corridor opened up to the Achaemenid palace complex on both sides.

Structure
A recently discovered gate near Persepolis has provided new insights into Achaemenid architecture and history.Constructed from mud and fired bricks, the gate is adorned with intricate decorations, including lotus flowers, mythological creatures, and religious symbols. Its walls are embellished with colorful panels that reflect the diverse cultural influences of ancient Iran, the Achaemenids, Elamites, and Mesopotamians. Further evidence of the gate’s significance lies in the Babylonian and Elamite inscriptions found within its central chamber
Archaeological investigations led by Alireza Askari Chavardi suggest that the gate was erected after 539 BC, following Cyrus the Great’s conquest of Babylon. The gate's grandeur and symbolic elements point to its ceremonial purpose. While Cyrus was the primary architect of this impressive structure, his son also played a pivotal role, ruling Babylon for eight years before ascending to the Iranian throne in 529 BC.

The Echoes of Ishtar in the Gate of Cyrus
The Gate of Cyrus exhibit striking similarities to the iconic Gates of Ishtar, both featuring intricate brickwork, vibrant colors, and mythological imagery. These shared characteristics suggest a profound influence of Babylonian art and architecture on Achaemenid design.
The discovery of glazed bricks adorned with mushkhushshu (Akk: Mušḫuššu - Cunieform: 𒈲𒍽 MUŠ.ḪUŠ, 'reddish snake') and bull motifs is among the most significant archaeological findings. mushkhushshu, a mythical creature combining the characteristics of a serpent and a dragon, is primarily recognized as a symbol of the god Marduk, the chief deity of the Babylonians.

Discovered fragments of the legendary creature Moshokhoso, matching the original depiction.
Youtube Video
youtube
#cyrus the great#ancient iran#ancient mesopotamia#mesopotamia#archaeology#ancient history#akkadian#persia#persepolis#achaemenids#mushkhushshu#ancient babylonian#babylon#babylonian#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
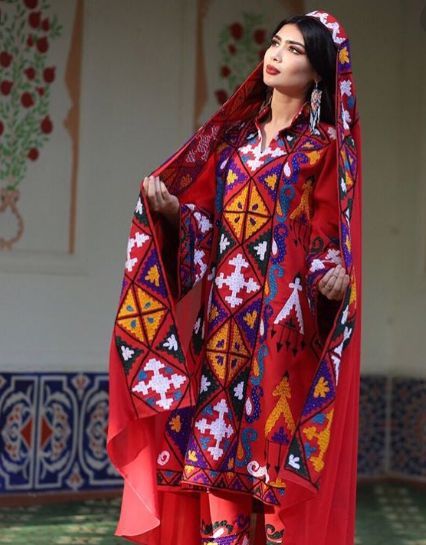



Are Tajiks more related to Iranians/Afghanis or Kazakhs/Mongolians?
Tajiks are an ethnic group primarily found in Central Asia, particularly in modern-day Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Uzbekistan. They speak the Tajik language, which is a dialect of Persian (Farsi) and are generally considered to be closely related to Iranians in terms of language, culture, and history.
Tajiks and Mongols are two distinct ethnic groups with different origins and histories. While there may have been some interaction and influence between the two groups over the centuries, there is no significant genetic or linguistic relationship between them.
The Tajik language is a member of the Iranian branch of the Indo-European language family, which is the same branch as Persian (Farsi). The grammar, syntax, and vocabulary of Tajik are similar to those of Persian, and the two languages are mutually intelligible to a significant extent.
Culturally, Tajiks have been heavily influenced by Persian culture over the centuries, particularly during the period of the Samanid dynasty (9th-10th centuries CE), which was based in what is now modern-day Uzbekistan and Tajikistan. The Samanid rulers were Persian-speaking and promoted Persian culture, literature, and art in their territories, which had a lasting impact on the region.
In terms of history, the lands inhabited by Tajiks were historically part of the greater Iranian cultural and political sphere, with ties to various Persian empires and dynasties such as the Achaemenids, Parthians, Sassanids, and Safavids. The region was also influenced by Islamic culture and traditions, which further connected it to the wider Iranian world.
Tajiks and Iranians share a close linguistic, cultural, and historical relationship, with the Tajik people being considered a branch of the greater Iranian cultural and linguistic family.
#tajiks#mongols#asia#central asia#persian#perisan culture#ethnic#achaemenids#parthians#sassanids#uzbekistan#samanid#indo european#kemetic dreams#ethnic diversity#ethnic studies
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Learn about Iran's rich 2,500 year history and why it's so important in today's world. From Persepolis to modern day Iran, this video dives deep into the country's past and its impact on global affairs.Join us as we delve into Iran's rich 2,500 year history and explore why it is so important today. From the ancient city of Persepolis to modern-day politics, this video will give you insight into Iran's past and present.
#iranianhistory#HistoryofIran#PersianEmpire#CyrustheGreat#Achaemenids#AlexandertheGreat#ParthianEmpire#SasanianEmpire#ArabConquest#IslamicPersia#SafavidDynasty#ConstitutionalRevolution#PahlaviDynasty#MohammadRezaShah#IranianRevolution#AyatollahKhomeini#IslamicRepublic#IranIraqWar#PersianCulture#Youtube
0 notes
Text
History is so beautiful and stunning and amazing if you dont believe me go look at persepolis or mycenae or newgrange or think about the fact that throughout time billions and billions of people have looked at the same stars as you and found delight in the same world and made art and talked and lived their lives and like we have so many examples of this and each and every one is wonderful
#history#i cant believe i didnt think of it here but pompeii#i dont know what else to tag this#the specific thing im thinking of is the achaemenid empire#which im obsessed with#achaemenids#art#i thought of more tags#newgrange is so cool though#i love it
1 note
·
View note
Text
Obviously the description above should be understood as meaning that the emblem of Ahura Mazda is the figure above the sphinxes, not that the sphinxes were the emblems of Ahura Mazda.
For the rest, it is interesting how both Greeks and Persians took the Egyptian figure of the sphinx and adapted it artistically and culturally to express their needs for symbols and their artistic tastes.

Polychrome glazed brick panel with sphinxes —emblem of the god Ahura Mazdā— from the palace of the Persian king Darius I at Susa (Babylonian: Šušim; now Shush, Iran) ~ ca.510 BC Louvre Museum
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Achaemenid Empire, Persia, Now Iran: Cyrus II of Persia commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Persian Achaemenid Empire… The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of 5.5 million square kilometres. The empire spanned from the Balkans and Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Valley to the southeast. Wikipedia
#Persia 500 BCE#Achaemenid Empire#Cyrus the Great#Achaemenid dynasty#First Persian Empire#Iranian empire#Modern-day Iran#Asia
328 notes
·
View notes
Text


Silver bowl with gold appliques, Achaemenid Iran, 6th century BC
from The Miho Museum, Kyoto
701 notes
·
View notes
Text

relief of lion attacking a bull | c. 550-330 BCE | achaemenid, present-day iran
in the university of Chicago institute for the study of ancient cultures’ collection
375 notes
·
View notes
Text
"BMCR 2009.10.48
Ancient Greece and Ancient Iran: Cross-Cultural Encounters. 1st International Conference (Athens, 11-13 November 2006)
Seyed Mohammad Reza Darbandi, Antigoni Zournatzi, Ancient Greece and Ancient Iran: Cross-Cultural Encounters. 1st International Conference (Athens, 11-13 November 2006). Athens: National Hellenic Research Foundation; Hellenic National Commission for UNESCO; Cultural Center of the Embassy of the Islamic Republic of Iran, 2008. xxix, 377. ISBN 9789609309554. €60.00 (pb).
Review by
Margaret C. Miller, University of Sydney. [email protected]
[Authors and titles are listed at the end of the review.]
The volume commemorates a landmark occasion, when the national research centres of Iran and Greece collaborated in a multi-national interdisciplinary conference on the history of exchange between Iran and Greece. Its nearly 400 pages reflect a strong sense of its symbolic importance. Papers span the Achaemenid through the Mediaeval periods and address the theme of exchange from the perspective of many disciplines — history, art, religion, philosophy, literature, archaeology. The book thus brings together material that can be obscure outside the circle of specialists, and in a manner that is generally accessible; the wide range of topics and periods included is a strength. Excellent illustrations often in colour enhance the archaeological contributions, as does inclusion of hitherto unpublished material.
The volume commences with a brief section on what might be called Greek textual evidence (Tracy, Petropoulou, Tsanstanoglou), followed by papers on interaction in Sasanian through mediaeval Persia (Azarnoush, Alinia, Venetis, Fowden), four papers discussing Achaemenid, Seleucid and Parthian history (Weiskopf, Ivantchik, Tuplin, Aperghis), aspects of the archaeology of Persepolis and Pasargadae (Stronach, Talebian, Root, Palagia), and ends with essays on the receptivity to Achaemenid culture in the material culture of the western empire and fringes: Cyprus, Turkey, Greece (Zournatzi, Lintz, Summerer, Paspalas, Ignatiadou, Sideris, Triantafyllidis), followed by a paper on traces of Greek material culture in the archaeology of (Seleucid) Iran (Rahbar). The wealth of vehicles, contexts and levels of exchange attested through the ages is both eye-opening and exciting. While there is unfortunately little attempt at globalizing synthesis or theoretical modelling, the analytical methods and collections of data in the individual contributions will aid future work in the area.
Stephen Tracy starts the volume with a synchronic analysis of the ways in which first Aeschylus, then Homer, play upon the prejudices of their audience against ” barbaroi” and then show the human quality of the enemy. In Persai, the Athenians are anonymous in contrast with the delineated personalities of the Persian royal family; in the Iliad, Achilles is “not very likeable” but learns humanity from the sorrow of Priam. Both poets focus on common humanity that transcends short-term hostilities.
Angeliki Petropoulou offers a detailed analysis of Herodotus’ account of the death of Masistios and subsequent mourning (Hdt. 9.20-25.1). Herodotus played up the heroic quality of Masistios’ death, stressing his beauty and height, qualities appreciated by both Greeks and Persians. The fact that Masistios seems to have gained the position of cavalry commander in the year before his death, coupled with the likelihood that his Nisaian horse with its golden bridle was a royal gift, suggests he had been promoted and rewarded for bravery.
Kyriakos Tsantsanoglou discusses the Derveni papyrus’ mention of magoi (column VI.1-14). Though the papyrus dates 340-320, the text was composed late fifth century BC, making the apparently Iranian content especially important. Both the ritual described and the explanation for it cohere with elements known from later Persian sources as features of early Iranian religious thought. While the precise vehicles of transmission of such knowledge to the papyrus are unknowable, the papyrus is the first certain documentation of the borrowing of Iranian ideas in Greek (philosophical) thought.
On the Iranian side exchange of religious ideas is documented by Massoud Azarnoush in the iconography of a fourth-century AD Sasanian manor-house he excavated at Hajiabad 1979.1 Moulded stucco in the form of divine figures included dressed and naked females identified with Anahita. The very broad shoulders of the Hellenistically dressed Anahita fit an Iranian aesthetic; the closest parallel for the slender naked females is found not in the cognate Ishtar type but in the Aphrodite Pudica type. Reliefs of naked boys, of uncertain relationship with Anahita, have attributes of fertility cult in the (Dionysian?) bunches of grapes they hold and in the ?ivy elements of their headdress.
Sara Alinia offers a brief but fascinating account of the development of state-sponsored religion hand-in-hand with state-sponsored persecution of religious elements that were deemed to be affiliated with another state: the Christian Late Roman Empire and the Zoroastrian Sasanian Empire. She documents the rise of religion as a tool of inter-state diplomacy and vehicle for inter-state rivalry; religion was but one facet of the political antagonism between the two.
Evangelos Venetis studies the cross-fertilization between Hellenistic and Byzantine Greek romance and Iranian pre-Islamic and Islamic romantic narrative. Persian elements are found in Hellenistic romance; Hellenistic themes contribute to Persian epics. The fragmentary nature of texts ranging 2nd -11th/14th c. AD and the lack of intermediary texts are serious impediments which may yet be overcome. The Alexander Romance, known in Iran from a Sasanian translation, contributed to the form and detail of the Shahname, as well as to other Persian epics.
Garth Fowden outlines the complex history of the creation, translation, wide circulation and impact of the pseudo-Aristotelian texts on religious thought. Aristotle’s works were translated into Syriac in the 6th c. and in the mid 8th c. into Arabic. Arab philosophers, attracted to the idea of Aristotle as counsellor of kings, updated him. Owing to his remoteness in time, “Aristotle” offended neither Muslim nor Christian. The Letters of Alexander, Secret of Secrets and al-Kindi’s sequel of Metaphysics, the Theology of Aristotle, contributed significantly to the philosophical underpinnings of both Muslim and Christian theology; the last remains an important text in teaching at Qom.
Michael N. Weiskopf argues that Herodotos’ account of the Persian treatment of Ionia after the Ionian revolt constitutes “imperial nostalgia” — the popular memory of how good things were under a past regime, in the context of a new regime. Herodotos 6.42-43, stressing the administrative efficiency and fairness of Artaphernes’ arrangements, allows a reading of Mardonios’ alleged imposition of democratic constitutions (so dissonant with the subsequent reported governing of Ionian states) as imperial nostalgia, to be contrasted with the inconsistent and unfair treatment of the Ionians by the Athenians of Herodotos’ own day.
Askold I. Ivantchik publishes two Greek inscriptions from Hellenistic Tanais in the Bosporos (and reedits a third). Evidently private thiasos inscriptions, they confirm that the city was already in 2nd or 1st century BC officially divided into two social (presumably ethnic) groups: the Hellenes and the Tanaitai, presumably Sarmatians, on whose land the city was founded in the late 3rd century BC. A thiasos for the river god Tanais includes members with both Greek and Iranian names, showing that private religious thiasoi were an important vehicle for breaking down social barriers between the two populations of the city.
Two papers offer contrasting interpretations of the evidence for Seleucid retention of Achaemenid institutions. That there were parallels between structures of the different periods is uncontested; the question is whether the parallels signify a deliberate programme of Seleucid self-presentation as the “heirs of the Achaemenids.” Christopher R. Tuplin argues that acquisition of the empire involved adoption of the Achaemenid mantle in some contexts and maintenance of those structures that worked, but that the balance of evidence suggests no conscious policy of continuation, and considerable de facto alteration of attitude and form. He suggests that the evidence of continuity of financial (taxation) structures — a major part of Aperghis’ argument — is ambiguous, at best. The treatment and divisions of territory, most notably the “shift of centre of gravity” from Persis to Babylonia, argue more for disruption than continuity.
G. G. Aperghis gives the case for a deliberate Seleucid policy of continuation of many Achaemenid administrative practices. He points to the retention of the satrapy as basis of administrative organization; use of land-grants (albeit to cities rather than individuals); continuing royal support of temples; maintenance of the Royal Road system (n.b. two Greek milestones, one illustrated in this volume by Rahbar); the retention of two separate offices relating to financial oversight. He suggests that the double sealing of transactions in the Persepolis Fortification Tablets metamorphosed into the double monogram on Seleucid coinage. Further field work in Iran, like that outlined by Rahbar (see below), will settle such contested matters as whether the many foundations of Alexander had any local impact. At present, Tuplin offers the more persuasive case.
David Stronach, excavator of Pasargadae, gives his considered opinion on the complex nexus of issues relating to the date of Cyrus’ constructions at Pasargadae. Touching upon the East Greek and Lydian contribution to early Achaemenid monumental architecture in stone and orthogonal design principles, Cyrus’ conquest chronology and the Nabonidus Chronicle, Darius’ creation of Old Persian cuneiform, the elements of the Tomb of Cyrus, and new evidence confirming the garden design, he argues that the chronology of the constructions at Pasargadae indirectly confirms the date of the conquest of Lydia around 545.
Mohammad Hassan Talebian offers a diachronic analysis of Persepolis and Pasargadae, starting with a survey of the Iranian and Lydian elements in their construction. Modern interventions include the ill-informed and damaging activities of Herzfeld and Schmidt at Persepolis in the 1930s, the stripping away of the mediaeval Islamic development of the Tomb of Cyrus, and the damage to the ancient city of Persepolis in preparation for the 2500-anniversary celebrations in 1971. Recent surveys in the region compensate to some degree. Talebian urges the importance of attention to all periods of the past rather than a privileged few.
Margaret Cool Root continues her thought-experiment in exploring how a fifth-century Athenian male might have viewed Persepolis.2 Sculptural traits such as the emphasis on the clothed body and nature of interaction between individuals would have seemed to the hypothetical Athenian to embody a profoundly effeminate culture. Yet Root’s study of the Persepolis Fortification Tablet sealings, their flashes of humour and playfulness in their utilisation on the tablets, reveals a world in which oral communication — idle chit-chat — perhaps bridged the cultural divide. She concludes that a visiting Greek might well have learned how to read the imagery like an Iranian.
Olga Palagia argues that the most famous Greek artefact found at Persepolis, the marble statue of “Penelope”, was not booty but a diplomatic gift from the people of Thasos: its Thasian marble provides a workshop provenance. The “Polygnotan” character, seen also in the Thasian marble “Boston Throne,” possibly from the same workshop, suits the prestige of the gift: Thasos’ great artist, the painter Polygnotos, is also attested as a bronze sculptor. A putative second Penelope in Thasos, taken to Rome in the imperial period with the “Boston Throne,” would have served as model for the Roman sculptural versions.
Antigoni Zournatzi offers the first of a series of regional studies documenting receptivity to Persian culture in the western empire and beyond, with a look at Cyprus. Earlier scholarship focused on siege mound and palace design; receptivity can be tracked in glyptic, toreutic, and sculpture. Western “Achaemenidizing” seals may be Cypriote; Persianizing statuettes may reflect local adoption of Persian dress (or Persian participation in local ritual). The treatment of beard curls on one late 6th century head may reflect Persian sculptural practice. Zournatzi suggests that Cypro-Persian bowls and jewellery were produced not for local consumption but to satisfy tribute requirements.
Yannick Lintz announces a project to compile a comprehensive corpus of Achaemenid objects in western Turkey, an essential step in any attempt to understand the period in the region.3 Particular challenges lie in matters of definition, both of “Achaemenid” and “west Anatolian” traits. The state of completion of the database is not clear; one is aware of a volume of excavated material in museums whose processing and publication was interrupted and can only wish her well in what promises to be a massive undertaking.
Lâtife Summerer continues her publication of the Persian-period Phrygian painted wooden tomb at Tatarli in western Turkey with discussion of the different cultural elements of its iconographic programme.4 The friezes of the north wall especially present Anatolian traditions; the east wall friezes of funerary procession and battle (between Persians and nomads) offer a mix of Persian and Anatolian. New Hittite evidence clinches as Anatolian the identification of the cart with curved top familiar in Anatolo-Persian art; it carries an effigy of the deceased. Alexander von Kienlin’s appendix expands the cultural mix presented by the tomb with his demonstration that its Lydian-style dromos was an original feature.
Stavros Paspalas raises questions about the vehicles and route of cultural exchange between the Persian Empire and Macedon through analysis of Achaemenid-looking lion-griffins on the façade of the later fourth century tomb at Aghios Athanasios. He identifies a pattern of specifically Macedonian patronage of Achaemenid imagery also in southern Greece in the fourth century in such items as the pebble mosaic from Sikyon and the Kamini stele from Athens. Enough survives to suggest independent local Macedonian receptivity to Persian ideas rather than a secondary derivation through southern Greece.
Despina Ignatiadou summarises succinctly the growing corpus of Achaemenidizing glass and metalware vessels in 6th-4th century BC Macedon. Three foreign plants lie behind the forms of lobe and petal-decoration on phialai, bowls, jugs, and beakers: the central Anatolian opium poppy, the Egyptian lotus (white and blue types) and the Iranian/Anatolian (bitter) almond. The common denominator is their medicinal and psychotropic qualities; Ignatiadou suggests that their appearance on vessels has semiotic value and that such drugs were used in religious and ritual contexts along with the vessels that carry their signatures, perhaps especially in the worship of the Great Mother.
Athanasios Sideris outlines the range of issues related to understanding the role of Achaemenid toreutic in documenting ancient cultural exchange: production ranges between court, regional, and extra-imperial workshops, not readily distinguishable. The inclusion of little-known material from Delphi and Dodona enriches his discussion of shape types. He works toward identification of local workshops, both within and without the empire, based especially on apparent local preferences in surface treatment. The geographical range of production is one area that will benefit from further international research collaboration.5
Pavlos Triantafyllidis focuses on the wealth of material from Rhodes, both sanctuary deposits and well-dated burials, that attests a history of imports from Iran and the Caucasus even before the Achaemenid period. Achaemenid-style glass vessels start in the late 6th century with an alabastron and petalled bowl, paralleled in the western empire, and carry on through the fourth century. An excavated fourth-century glass workshop created a series of “Rhodio-Achaemenid” products that dominated Rhodian glassware through the early third century. This microcosmic case study brilliantly exemplifies a much broader phenomenon.
Mehdi Rahbar outlines and illustrates archaeological material, some not previously published, that will be fundamental in future discussions of Seleucid Iran. The as of yet limited corpus includes: modulation of Greek forms perhaps to suit a local taste (Ionic capital from the temple of Laodicea, Nahavand, known from an 1843 inscription of Antiochus III; fragmentary marble sculpture of Marsyas?), amalgam of Iranian and Greek (milestone in Greek with Persepolitan profile), Greek import (Rhodian stamped amphora handle ΝΙΚΑΓΙΔΟΣ from Bisotun);6 and Iranian adoption of Greek decorative elements (vine leaves, grapes, and acanthus patterns, for which compare Azarnoush’s stucco).
The volume concludes with a brief overview of ancient Iranian-Greek relations and their modern interpretation by Shahrokh Razmjou.
The inclusion of the texts of the introductory and concluding addresses made on the occasion of the conference in particular allow the reader to comprehend its aims: hopes of exchange in the modern world through assessing exchange in the past. A number of the papers make it very clear that collaboration between specialists of “East” and “West” in both textual and archaeological research could yield great gains for all periods of history and modes of analysis. The conference and its publication, therefore, succeed at a variety of levels.
Editing such a volume must have been a real challenge and it is to the credit of authors and editors that throughout the whole volume, I found only a handful of minor infelicities and typographical errors, none of which obscure meaning.7
Contents: Stephen Tracy, “Europe and Asia: Aeschylus’ Persians and Homer’s Iliad” (1-8) Angeliki Petropoulou, “The Death of Masistios and the Mourning for his Loss” (9-30) Kyriakos Tsantsanoglou, “Magi in Athens in the Fifth Century BC?” (31-39) Massoud Azarnoush, “Hajiabad and the Dialogue of Civilizations” (41-52) Sara Alinia, “Zoroastrianism and Christianity in the Sasanian Empire (Fourth Century AD)” (53-58) Evangelos Venetis, “Greco-Persian Literary Interactions in Classical Persian Literature” (59-63) Garth Fowden, “Pseudo-Aristotelian Politics and Theology in Universal Islam” (65-81) Michael N. Weiskopf, “The System Artaphernes-Mardonius as an Example of Imperial Nostalgia” (83-91) Askold I. Ivantchik, “Greeks and Iranians in the Cimmerian Bosporus in the Second/First Century BC: New Epigraphic Data from Tanais” (93-107) Christopher Tuplin, “The Seleucids and Their Achaemenid Predecessors: A Persian Inheritance?” (109-136) G. G. Aperghis, “Managing an Empire—Teacher and Pupil” (137-147) David Stronach, “The Building Program of Cyrus the Great at Pasargadae and the Date of the Fall of Sardis” (149-173) Mohammad Hassan Talebian, “Persia and Greece: The Role of Cultural Interactions in the Architecture of Persepolis-Pasargadae” (175-193) Margaret Cool Root, “Reading Persepolis in Greek—Part Two: Marriage Metaphors and Unmanly Virtues” (195-221) Olga Palagia, “The Marble of the Penelope from Persepolis and its Historical Implications” (223-237) Antigoni Zournatzi, “Cultural Interconnections in the Achaemenid West: A Few Reflections on the Testimony of the Cypriot Archaeological Record” (239-255) Yannick Lintz, “Greek, Anatolian, and Persian Iconography in Asia Minor : Material Sources, Method, and Perspectives” (257-263) Latife Summerer, “Imaging a Tomb Chamber : The Iconographic Program of the Tatarli Wall Paintings” (265-299) Stavros Paspalas, “The Achaemenid Lion-Griffin on a Macedonian Tomb Painting and on a Sicyonian Mosaic” (301-325) Despina Ignatiadou, “Psychotropic Plants on Achaemenid Style Vessels” (327-337) Athanasios Sideris, “Achaemenid Toreutics in the Greek Periphery” (339-353) Pavlos Triantafyllidis, “Achaemenid Influences on Rhodian Minor Arts and Crafts” (355-366) Mehdi Rahbar, “Historical Iranian and Greek Relations in Retrospect” (367-372) Shahrokh Razmjou, “Persia and Greece: A Forgotten History of Cultural Relations” (373-374)
Notes
1. The site is fully published in: M. Azarnoush, The Sasanian manor house at Hajiabad, Iran (Florence 1994).
2. The first appears as “Reading Persepolis in Greek: gifts of the Yauna,” in C. Tuplin, ed., Persian Responses: Political and Cultural Interaction with(in) the Achaemenid Empire (Swansea 2007) 163-203.
3. Deniz Kaptan is similarly compiling a corpus of Achaemenid seals and sealings in Turkish museums.
4. Other studies: “From Tatari to Munich. The recovery of a painted wooden tomb chamber in Phrygia”, in I. Delemen, ed., The Achaemenid Impact on Local Populations and Cultures (Istanbul 2007), 129-56; “Picturing Persian Victory: The Painted Battle Scene on the Munich Wood”, in A. Ivantchik and Vakhtang Licheli, edd., Achaemenid Culture and Local Traditions in Anatolia, Southern Caucasus and Iran: New Discoveries (Leiden/Boston 2007: Ancient Civilizations from Scythia to Siberia 13), 3-30.
5. Considerable progress is being made, e.g., in Georgia: V. Licheli, “Oriental Innovations in Samtskhe (Southern Georgia) in the 1st Millennium BC,” and M. Yu. Treister, “The Toreutics of Colchis in the 5th-4th Centuries B.C. Local Traditions, Outside Influences, Innovations,” both Ivantchik / Licheli, edd., Achaemenid Culture and Local Traditions in Anatolia (previous note), 55-66 and 67-107.
6. For early 2nd c. date of this fabricant, see Christoph Börker and J. Burow, Die hellenistischen Amphorenstempel aus Pergamon: Der Pergamon-Komplex; Die Übrigen Stempel aus Pergamon (Berlin 1998), cat. no. 274-286; one example has a context of ca. 200 BC.
7. Except possibly the misprint on p. 357, line 8 up, where “second century” should presumably be “second quarter” (of the fourth century)."
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

~ Man and woman in loving embrace.
Place of origin: Iraq, Nippur
Period: Achaemenid Period
Date: 450 B.C.
Culture: Near Eastern
Medium: Terracotta
#ancient#ancient art#history#museum#archeology#ancient sculpture#ancient history#archaeology#man and woman in a loving embrace#man#woman#love#hug#embrace#nippur#iraq#near east#near eastern#achaemenid#450 b.c.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Earthenware rhyton in the shape of an ibex head, from Achaemenid Persia (6th or 5th century BCE). Excavated at Gilan, Iran; now in the Tokyo National Museum, Tokyo, Japan.
#art#art history#artifact#artifacts#rhyton#Persia#Persian art#Persian Empire#Achaemenid Empire#earthenware#Tokyo National Museum
381 notes
·
View notes
Text

return trip to the Throne Hall at Persepolis
#nanashi mumei#hololive#holocouncil#persepolis#achaemenid persia#needed a good ol hatching exercise to lift my spirits...#comic#wlart#williamleonard
393 notes
·
View notes
Text

Mania (active during the 5th to early 4th century BCE) served as the governor of Aeolis and led armies as a vassal of the Achaemenid Empire.
Her husband, Zenis of Dardanus, had governed Aeolis for the satrap (provincial governor) Pharnabazus II. When Zenis died of illness, Mania petitioned Pharnabazus, who had initially planned to appoint a man as her husband's successor. However, Mania sought the position for herself. According to Xenophon, she approached Pharnabazus with a large retinue and many gifts, both for him and to win favor with his concubines and the influential men at his court.
Her request was granted, and Mania became “mistress of the province”. She governed effectively and led successful military campaigns. She expanded her territory, capturing the cities of Larisa, Hamaxitos, and Kolonai with a force of Greek mercenaries. Mania also accompanied Pharnabazus twice in battle. Impressed by her abilities, he rewarded her and sometimes sought her counsel.
Polyaenus praised her as an exceptional general:
“She always went to battle drawn in a chariot; she gave out orders while in action, formed her lines, and rewarded every man who fought well, as she saw he deserved. And – what has scarcely happened to any general, except herself – she never suffered a defeat.”
Mania was over 40 years old (c.399 BCE) when she was murdered by her son-in-law Meidias, who reportedly claimed that “it was a disgraceful thing for a woman to be the ruler while he was in a private station.” Meidias also killed Mania’s 17-year-old son.
He then asked Pharnabazus to grant him control of the territory, but Pharnabazus rejected his gifts, stating that “he would not wish to live if he failed to avenge Mania.” Eventually, Mania’s cities were seized by the Spartan general Dercylidas. Meidias thus gained nothing in murdering Mania.
Here is the link to my Ko-Fi. Your support would be much appreciated!
Further reading:
Polyaenus, Stratagems in war
Xenophon, Hellenica
#mania#history#women in history#historyedit#women's history#ancient history#ancient world#warrior women#female generals#Achaemenid Empire#historical figures#4th century BCE#5th century BCE
136 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Persian Satrapies during Achaemenid Dinasty (~360 BC) - Based on "Die Satrapienverwaltung Im Perserreich Zur Zeit Darius' III"
59 notes
·
View notes