#PACS Imaging Software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
PACS Imaging Software | Avanttec Medical Systems
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) have emerged as a game-changer in the ever-evolving healthcare technology landscape. This revolutionary software transforms how medical professionals manage, store, and share medical images within a hospital or healthcare facility. With its seamless integration into existing hospital systems, PACS Imaging Software has become an indispensable tool for teaching and research purposes, propelling the medical field to new heights. PACS Imaging Software, developed by companies like Avanttec Medical Systems, allows healthcare providers to store, retrieve, and distribute medical images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs digitally, eliminating the need for physical films and facilitating seamless access to patient data. The software's ability to integrate with hospital information systems has empowered physicians, radiologists, and other healthcare professionals to access crucial patient information in real time.
0 notes
Text
PACS Solutions: Revolutionizing Radiology Management

In the dynamic realm of healthcare, PACS solutions are catalysts for innovation, reshaping the landscape of radiology management. At the heart of this transformation lies the seamless interfacing of radiology machines with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), ushering in an era of enhanced efficiency and improved patient care.
PACS integration stands as the cornerstone of this revolution. By seamlessly linking radiology machines to the centralized PACS platform, healthcare facilities can streamline their radiology workflow, expediting the process from image acquisition to diagnosis. This integration empowers radiologists with instant access to patient images and data, eliminating the delays associated with traditional film-based systems.
Central to the efficacy of PACS solutions is the swift and secure data transfer capabilities they offer. Through advanced networking technologies, patient images are swiftly transmitted from radiology machines to the PACS server, ensuring rapid availability for analysis and diagnosis. This streamlined PACS connectivity enhances collaboration among healthcare professionals, facilitating prompt decision-making and timely patient care.
Moreover, radiology software plays a pivotal role in optimizing image management within PACS environments. With intuitive interfaces and powerful tools, these software solutions empower radiologists to efficiently organize, analyze, and interpret medical images. From customizable viewing preferences to sophisticated image processing algorithms, radiology software enhances diagnostic accuracy while expediting report generation.
In essence, PACS solutions are reshaping radiology management paradigms, driving operational efficiency and elevating patient care standards. Through seamless interfacing of radiology machines with PACS, healthcare providers can unlock new levels of productivity and precision in medical imaging. As technology continues to evolve, embracing these innovative solutions is paramount for staying at the forefront of modern healthcare delivery.
1 note
·
View note
Text
A few of my thoughts on Careless People, kind of typed out as I read the book:
So I'm reading this partially because it came heavily recommended and partially because I have to for things I'm doing right now. I think many other people enjoy the book more than I did or get more out of it than I do. I think because I am deeply familiar with Silicon Valley culture and the software engineering industry as a whole the cultural internal revelations are less surprising for me, and I have a bit more of a sense of how exactly Wynn-Willams is an unreliable narrator than the completely naive reader. For me, the book is actually hard to move through because of how much Wynn-Williams was so obviously drinking the kool-aid. For all her remarks about the ignorance of the Facebook execs, her own actions and moves are incredibly revealing. She comes across as a white woman with plenty of gaps in her knowledge and understanding of other countries and cultures. She doesn't seem to want to go out of her way to address this lack of knowledge (or at least doesn't describe herself doing so) unless not knowing will produce really serious political consequences/backlash against Facebook that would affect her job. And I understand, she was in a work environment that almost certainly would have left her with very little time to do that due diligence and would have discouraged/devalued it, but that knowledge doesn't make her story any easier to read.
Also I came across a gizmodo article saying that Careless People made Sheryl Sandberg more human and likeable to that particular reader and I was...baffled. Sandberg is explicitly described as someone so obsessed with her image that it has consumed her and based off of the descriptions of Sandberg's behavior and everything I know about her outside of this book I can't say that description rings false.
And now. Highlights. Or lowlights. Or just moments. You can decide.
Sheryl Sandberg being so my-way-or-the-highway about facebook and data and international policy around organ donation that she says "Do you mean to tell me if my four-year-old was dying and the only thing that would save her was a new kidney, that I couldn't fly to Mexico and get one and put it in my handbag"
Mark Zuckerberg trying to show off "fake gangsta handshakes" instead of learning the culturally expected way to bow to South Korean leadership. (everything he does somehow makes him even lamer)
Wynn-Williams not even questioning being sent alone into Myanmar to find a way to get the ear of the junta or being asked to do jail time in South Korea for the sake of the company while she had a 7-month-old child at home until her husband gets mad at her.
Mark wanting to be surrounded by people and gently mobbed (a riot or a peace rally) during a trip to Asia.
This one has been brought up online already but Mark's love of Andrew Jackson, he's collecting wine that was made during Jackson's presidency just because of that love. "Mark explains that Jackson's the greatest president America's ever had, that he was ruthless, populist, an individualist, and that he 'got stuff done.'" (p 142) and of course he ignores the trail of tears and the violence done to native people.
Using Hong Kong users' data explicitly as a bargaining chip while trying to get Facebook into China, and the head of the China policy needing the Nuremberg defense explained to him so they don't just go ahead and suck up to the Chinese gov't praising how they are handling the HK protests.
It really is a clique. More than ideology or competence, many in facebook leadership have simply known each other forever in various ways and continue to look to each other first. "A tiny enmeshed group of people increasingly responsible for shaping the attention of billions. Their preferences turned into policy." (153)
Joel Kaplan (Bush admin joker who clearly has entitlement issues) not knowing that Taiwan is an island and being amazed that PACs are illegal in other countries and contributions to foreign politicians are considered illegal bribery.
Joel also seems to have problems with people expressing legitimate concerns/having real questions about how things are to work and sees it as questioning authority, which. Isn't that such a quintessentially Republican attitude .
"'Sarah stop taking notes,' Sheryl instructs, knowing Kenny's about to tell us how he's going to keep the gravy train going for us. She doesn't want it to be written down. My notes can be subpoenaed. So this part of the meeting will be 'off the books.'" (175) so that the Irish PM can describe how Facebook can keep neatly avoiding taxes.
The sheer number of times they are late to meetings (even ones that are of critical importance to Facebook's future) because of stupid shit like Mark not wanting to get up early and scheduling dumb last-minute meetings with other people that flatter Mark's (or someone else on the management team's) ego.
Mark Zuckerberg asking Xi Jinping to name his unborn child. Xi refusing.
Mark meeting more world leaders and learning about more world issues just makes him care less about the world, actively has him lose interest in playing nice with them or conversing with them.
Passing around toxic strategies from other Silicon Valley companies (like Uber) to combat good faith government interventions interfering with their products.
"[Mark] launches into a spiel about Emperor Augustus, his favorite emperor, who led the transformation of Rome from a republic to an empire. He talks about 'offense.' He wants lists of adversaries, whether they're companies, individuals, organizations, or governments. He wants to know how we can use the platform and tools we have to win against these adversaries." (207)
"there are unspoken rules with Sheryl about obedience and closeness. Those closest to Sheryl are rewarded. Marne and Sadie often appear in her unwanted designer clothes; both assumed plum seats on boards that Sheryl had been asked to serve on. [...] Sadie is very conscious of the benefits of being Sheryl's 'little doll,' as she calls it and having Sheryl tell her she loves her." (219) this is after Wynn-Williams says no to Sheryl asking/outright ordering her to "come to bed" on a flight they were sharing. There was anote about how "Sheryl and Sadie had taken turns sleeping in each other's laps, occasionally stroking each other's hair." (218)
Because of Joel Kaplan and increasing Republican influence there, following the 2016 election there is a distinct disdain in a good section of that policy and leadership team for the many people who are worried about Trump and what a Trump presidency meant for the US. "It's hard to ignore the eyerolls exchanged by some of the Republicans on the DC team who forget that their faces are being magnified and projected on the wall." (254-5) Also things like all lives matter graffiti popping up on the Facebook campus. Also somehow people like Elliot are blindsided by the notion that 2016 could have been their fault despite the fact that it OBVIOUSLY was and that Trump used Facebook as intended, as other fringe candidates around the world had to gain traction.
Mark getting annoyed about international governance, " What I take from this is that he's feeling Facebook's rising power globally. He has politicians from around the world wanting to see him and kiss the ring [...] He has this global network, more political capital and more wealth than he can possibly spend, and he's wondering what he can use it for." (259) telling that the way this takes shape for Marky Mark is not in addressing a world need like world hunger but instead in looking at power and thinking hey why isn't that stronger so I can take advantage of it.
Plans to visit Peru for APEC thrown into question because it coincides with Priscilla's ovulation and Mark and Priscilla were going to try for a baby and they're stretching Zika concerns to Lima (ignore the fact that there was basically no Zika in Lima at the time and Wynn-Williams had been sent to Zika ground zero while actively pregnant) and Mark wanted a "tribe" of kids. Operation protect sperm. Ridiculous.
When Mark comes around to Facebook's influence in the election he's struck by the ingenuity of it rather than being upset, despite the fact that there's unsavory stuff like voter suppression that happened as a part of that. Sheryl, similarly, thought it was brilliant rather than horrifying.
"It's like Mark's a kingmaker, and they're there to bend the knee." (272) about John Key, PM of New Zealand, and Peña Nieto, president of Mexico, and Justin Trudeau, president of Canada, and Malcolm Turnbull, PM of Australia. Sickening.
"These leaders are all in the business of getting elected. [...] I'm sure that Trump's election elevated Mark in their eyes. He's the powerbroker and they want to stay in power. They understand that one of their most important assets - their voice - is political capital that is ultimately controlled by Mark" (273) SPINELESS SPINELESS SPINELESS
"I think he's telling me to be quiet, to drop it, to know my place. And I realize that everyone around Mark is like this. No one is going to try to talk him out of [trying to run for president]." (281)
I'm being reminded that I need everyone who's cavalier about the extent of authoritarian rule in China and the repression of human rights advocates and the legitimate threat of violence that the CCP places on people against them to get a grip. Also Facebook was happy to play ball on all of these topics, labeling human rights and minority advocate groups as terrorists, allowing for censorship and surveillance, and spreading CCP propaganda ads as long as it kept them in business with China.
"From the start, the Facebook team agrees that Facebook will store Chinese user data in China under their terms. When other countries have asked for this-Russia, Indonesia, Brazil- Facebook has refused." (310)
"One of Facebook's few supposed red lines is that China will not get any access to the data of users who are located outside China. But, unsurprisingly, the documents tell a different story." (311)
"Another document, titled 'Aldrin Security Risks,' outlines the risks that the Chinese content moderators could feed data on non-Chinese users to the government either directly or by sharing their credentials. This, coupled with espionage reaching further into Facebook's network, was a real concern." (312) really rich knowing that part of the reason for the TT ban was Meta pushing fear about TT's Chinese connections HARD in congress.
"The goal for companies is, as I understand it, to answer the questions Congress has without committing perjury." (317) well that's comforting, isn't it? That they find that hard?
Ha. They were already considering that they might be compared to Nazis back in 2018. Fun. Also Mark lies to Congress and Facebook's stock price rises. Ugh.
"Zhao tells the team about GitHub, a site with very active discussion boards, owned by Microsoft. He tells them that he knows GitHub's leadership and when someone 'started slandering' President Xi, the CAC filed a report with the GitHub CEO, the content was removed, and GitHub let them know it was because of their relationship with the Chinese government." (324) free speech my ass. These tech companies have never been shit.
"Facebook is operating illegally in China. One of American's biggest publicly listed companies is completely indifferent to the rules." (332) it has been the whole time, water is wet, this is what happens when you let the attitudes you saw at the start just keep rolling
In a meeting on gender and diversity issues, a senior man says "When will women focus on work and stop talking about diversity already," (340) which kills a discussion on workplace sexual harassment. "I think many of the employees are fine with that. Most of the company is made up of white and Asian men who don't seem to have a problem with how things have been going. The entitlement in the Facebook offices flows as freely as the prosecco from the Prosecco Tap that's installed in one of the Facebook office kitchens. When there are complaints of gentrification around Facebook's Menlo Park campus, driving up rents and forcing longtime residents out, they post things that could have been lifted from the pages of Atlas Shrugged, like, 'I take exception to think that I am part of the problem, I won't be villainized for my own successes in life.' And, "These people just want our gobs of Money.'" (340-41). I'm deeply familiar with this attitude already, I just need everyone to get how vile and how persistent it is into their heads. It exists EVERYWHERE in tech. You get little oases, little teams where your immediate coworkers respect you and your managers are nice. But upper management and the company as a whole? hah.
"It's us against the outsiders and hates, whether that's the media, academics, or other companies. It's us versus them. And as with nationalism, there's something cleansing in this narrative pushed from the top, something comforting about being in the right, an organized innocence." (342)
"If you want someone to actually influence the policy and political decisions that are ultimately made by Joel and Elliot, they'll have a greater chance of success if they're male, older, white, and a Harvard graduate." (353)
"I've spent a lot of time thinking about what unfolded next in Myanmar, and Facebook's complicity. [...] It was just that Joel Elliot, Sheryl, and Mark didn't give a fuck." (359) yep. it was all fixable and foreseeable and they did jack. Wynn-Williams tried to get people in place to help but was not able to do so (feet were dragged, she was told it was not priority).
Joel's power increased as Trump's did, since Joel cozied up due to his history of Republican connections. "He drops a napkin at the opening night reception and he waits and stares at me till I figure out that he's expecting me to kneel to the ground and pick it up for him." (362) the sexual harassment returns/is really in full force as soon as his power is on the up-and-up again.
7 notes
·
View notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Understanding The Global Specialty PACS Market: Key Findings From The Latest Report
The Specialty Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) Market continues to demonstrate solid growth, with a valuation of USD 3.21 billion in 2023. Industry forecasts project the market will reach USD 5.21 billion by 2032, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.56% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2032.
Get Free Sample Report on Specialty PACS Market
As diagnostic imaging becomes an increasingly integral part of modern medicine, the demand for specialized, efficient, and secure image management systems has never been higher. Specialty PACS are designed to meet the unique needs of specific medical disciplines such as cardiology, oncology, ophthalmology, orthopedics, dentistry, and pathology—going far beyond the capabilities of general radiology PACS.
A Growing Need for Specialized Image Management
In today’s healthcare landscape, clinical disciplines increasingly rely on high-resolution imaging for diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring. Specialty PACS provide focused functionalities tailored to individual specialties, offering intuitive user interfaces, 3D viewing tools, and advanced analytics. These systems enable faster workflows, improved diagnostic accuracy, and seamless integration with existing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems.
The growth of the market is largely being driven by:
The increasing volume of diagnostic imaging procedures worldwide
Rising prevalence of chronic diseases that require regular imaging (e.g., cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes-related complications)
Technological advancements in imaging modalities and PACS software
A growing shift toward value-based care and the need for operational efficiency
Key Market Drivers
Rising Imaging Volumes Across Specialties As non-invasive imaging becomes a first-line diagnostic tool, the volume of specialty-specific scans is growing. Fields such as cardiology and oncology increasingly depend on CT, MRI, PET, and ultrasound technologies, requiring specialized PACS platforms to store, manage, and analyze the resulting data efficiently.
Technological Innovations and AI Integration Today’s PACS solutions are incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to help clinicians detect abnormalities more quickly, automate repetitive tasks, and assist in decision-making. Specialty PACS, tailored for specific disciplines, are benefiting from these innovations more rapidly due to their focused nature and clear clinical use cases.
Expansion of Telehealth and Remote Diagnostics Telemedicine growth post-pandemic has pushed providers to adopt solutions that allow remote image sharing, review, and reporting. Cloud-based Specialty PACS solutions are enabling remote access to patient imaging data, supporting collaboration between multidisciplinary teams and improving patient outcomes.
Regulatory Push for Interoperability Global regulatory bodies are pushing for better data integration and standardization across systems. Specialty PACS systems that support interoperability with Hospital Information Systems (HIS), EHRs, and other imaging modalities are gaining traction, especially in developed healthcare markets.
Key Market Segmentation
By Type
By Component
By Deployment Model
By End-User
Key Players and Their Specialty PACS Products
Merge PACS, Merge Eye Care PACS, Merge Oncology PACS
Centricity PACS, Centricity Universal Viewer, Centricity Imaging
IntelliSpace PACS, Philips Digital Pathology Solution, Philips Ophthalmology PACS
Synapse PACS, Synapse 3D, Synapse Mobility
syngo PACS, syngo.via, syngo.plaza
IntelePACS, InteleRad RIS, InteleViewer
PowerPACS, PowerServer PACS, PowerWeb
eRAD PACS, eRAD Cloud PACS, eRAD RIS
Oracle PACS Solutions, Oracle Healthcare Imaging Suite
Sectra PACS, Sectra Enterprise Imaging, Sectra Breast Imaging PACS
McKesson Radiology PACS, McKesson Cardiology PACS
Enterprise Imaging PACS, Agfa Xero PACS
Carestream Vue PACS, Carestream Radiology PACS
NovaPACS, NovaCloud PACS
Challenges and Opportunities
While the market shows promising growth, it is not without its challenges:
High initial implementation costs
Data security and privacy concerns
Integration complexities with legacy systems
However, these challenges are increasingly being addressed by cloud-based solutions, subscription pricing models, and improved vendor support services.
Opportunities lie in:
Expanding to emerging economies with rapidly developing healthcare systems
Enhancing AI-driven analytics for diagnostics and decision support
Offering mobile and tablet-compatible PACS platforms for improved clinician access.
Make Enquiry about Specialty PACS Market
Conclusion
The Specialty PACS Market is set for sustained growth, reflecting the healthcare industry’s increasing reliance on precision imaging and specialty-specific diagnostics. With the market expected to grow from USD 3.21 billion in 2023 to USD 5.21 billion by 2032, healthcare providers, technology companies, and investors alike have a strong incentive to engage with and innovate within this evolving landscape.
As imaging technology continues to advance and patient care becomes more personalized, Specialty PACS will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of diagnostic medicine.
About US
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President Of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#Specialty PACS Market#Specialty PACS Market Trend#Specialty PACS Market Share#Specialty PACS Market Growth#Healthcare Data Storage Market.
0 notes
Text
2025 March Gear and Software Loadout
…and it is almost the end of month of March…how time is flying! Here is an update to my current setup (some have respective links to Amazon that help defray the hosting costs and get me more funding to purchase cool, new gear). If you all have any questions about the items below, please feel free to reach out as I am always glad to share my thoughts. I also added a rather silly AI generated image to the post…one of these days it will get it right!
The changes plus the detailed list are below:
Added:
Password Manager - Apple Passwords
Terminal App - Ghostty
RSS Reader - Tapestry
Calendar Support Application - ItsyCal
Time Support Application - Clocker
Recording/Streaming Application - Ecamm Live
Removed:
Drafts
The New Reeder
macOS Applications
Task Manager - Reminders
Text Editor - BBEdit
Terminal App - Ghostty
Automation App - Hazel
Online Backup Service - Backblaze
Backup Application - Carbon Copy Cloner
Calendar Support Application - ItsyCal - A great little app that hides in the menu bar and provides a quick overview of the day.
Time Support Application - Clocker - Since I have friends in a multitude of different timezones, this application helps me get a nice, concise overview so I don’t bug them when they are sleeping!
Recording/Streaming - Ecamm Live
iOS/iPadOS Applications
Podcast App - Castro
Camera App - Halide
Video Recording App - Kino
Object Scanning App - Scan Thing
Document Scanning App - Simple Scan
iOS/iPadOS/macOS Applications
Password Manager - Apple Passwords - I have fully moved over to the Apple Passwords application as it makes my life easier when I need to share credentials with my family.
Package Tracking App - Parcel
Calendar App - Calendar.app
Recipe Manager - Mela
RSS Reader - Tapestry
Read Later Application - Goodlinks
Email Application - Mail.app
Note-Taking App - Tot, Apple Notes
Mastodon Application - Ivory
Social Media - Threads
Social Media - Bluesky
Mind-Mapping Software - Mind Node
Remote Control Application - Screens 5
Hardware
Keyboard - HHKB Studio
Dock - OWC Thunderbolt Pro Dock
Laptop - 14" MacBook Pro
iPad - iPad Mini
3D Printer - Creality K1C - A Prusa Core One is on order and won’t arrive until the end of March.
Watch - Apple Watch Series 10 Black Aluminum 46mm with Cellular
Phone - iPhone 16 Pro Max
Inkjet Printer - Epson 4850
Charger - Anker MagGo 3-in-1 Charging Stand
Charger - Anker MagSafe Compatible MagGo UFO 3-in-1 Charger
Automation - Elgato Stream Deck Neo
Lighting - Elgato Key Light Neo
Game Capture - Elgato Game Capture Neo
Webcam with Smarts - Obsbot Tiny 2
Camera - Fujifilm X-M5
Trackball - Ploopy Adept - Ploopy makes some great hardware that can be easily repaired and doesn’t get in the way of your day to day activities.
Audio Hardware
Microphone - Rode Podcaster White
Speaker - Beats Pill
Speaker - 3x HomePod mini
Microphone - Rode NT-USB Mini - Microphone for recording on the go!
Gaming
Emulator - Retroid Pocket 4 Pro
Emulator - Retroid Pocket Mini
Gaming with Friends - Helldivers 2
Universal Controller - 8BitDo Ultimate Bluetooth Controller
Storage/Bags/Cases
Daily Carry Backpack - Alpaka Elements Backpack Pro X-Pac VX42
Travel Backpack - Peak Design Travel Backpack
Tech Pouch - Peak Design Tech Pouch
Stationary
Pen - Tactile Turn Pens
Pen - Leuchtturm1917 Drehgriffel
Kitchen/Cooking
Indoor Grill - Ninja Foodi Indoor Grill
Pressure Cooker - Ninja Foodi Pressure Cooker
Convection Oven - Ninja Foodi Convection Oven
Coffee Maker - Fellow Aiden
Coffee Grinder - Baratza Fortè AP Coffee Grinder
MISC
Car Error Code Scan Tool - BlueDrive OBDII Scan Tool
Hosting Service - Hetzner
Universal Remote - Sofabaton Remote
Cell Service - US Mobile and T-Mobile

0 notes
Text
Title: Nandico PACS: The Ultimate DICOM Reader for Medical Imaging Professionals
In the fast-evolving world of medical imaging, efficient and accurate image viewing is crucial for healthcare professionals. One of the essential tools in this field is a DICOM reader, which allows radiologists, physicians, and technicians to access and analyze medical images in the DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) format. Nandico PACS stands out as a leading solution in this domain, providing a seamless and user-friendly experience for handling medical imaging data.
What is a DICOM Reader?
A DICOM reader is a software application that enables healthcare professionals to view, manipulate, and store medical images obtained from different imaging modalities such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds. The DICOM format is the industry standard for storing and transmitting medical images, ensuring interoperability between various imaging systems and healthcare providers.
A good DICOM reader must be fast, reliable, and feature-rich to cater to the needs of modern radiology and medical diagnostics. Nandico PACS provides all these essential functionalities, making it an ideal choice for healthcare professionals worldwide.
Why Choose Nandico PACS as Your Preferred DICOM Reader?
1. User-Friendly Interface
Nandico PACS is designed with an intuitive interface that simplifies navigation and image interpretation. The clean layout and accessible tools allow users to quickly load and analyze medical images without a steep learning curve. Whether you are a seasoned radiologist or a new medical imaging technician, Nandico PACS ensures a hassle-free experience.
2. Advanced Image Processing Tools
The software offers a range of advanced image processing features, including:
Zoom and Pan – Allows users to focus on specific areas of interest.
Windowing and Leveling – Adjust contrast and brightness for enhanced image clarity.
Annotations and Measurements – Enable accurate diagnosis with text notes and distance measurement tools.
Multi-Planar Reconstruction (MPR) – Converts 2D images into 3D representations for a comprehensive analysis.
These features make Nandico PACS an essential tool for professionals who need precision in their imaging assessments.
3. Seamless Integration with PACS
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) are vital for storing and managing medical images. Nandico PACS is fully compatible with existing PACS infrastructure, ensuring smooth image retrieval and storage without workflow disruptions. The ability to integrate seamlessly with other hospital and clinic systems improves efficiency and data accessibility.
4. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Nandico PACS is designed to work on various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. This cross-platform functionality ensures that healthcare facilities can deploy the software without worrying about hardware and system compatibility issues.
5. Cloud-Based and On-Premises Solutions
Depending on the needs of the healthcare facility, Nandico PACS offers both cloud-based and on-premises solutions:
Cloud-Based PACS – Allows remote access to medical images from any location, enabling telemedicine and collaboration between healthcare professionals.
On-Premises PACS – Ensures data security and fast access to locally stored medical images.
With these flexible deployment options, medical institutions can choose the best setup for their specific requirements.
6. Compliance with Industry Standards
Regulatory compliance is critical in the medical industry. Nandico PACS is fully compliant with DICOM standards, HIPAA regulations, and other relevant medical data protection guidelines. This ensures that patient data remains secure and accessible only to authorized personnel.
7. Cost-Effective and Scalable
Nandico PACS is an affordable solution for healthcare institutions of all sizes. Whether you're a small clinic or a large hospital, the software can scale according to your needs. With flexible licensing models and minimal upfront costs, it offers excellent value for money compared to traditional medical imaging systems.
Applications of Nandico PACS in Medical Imaging
Radiology
Nandico PACS is widely used in radiology departments for viewing X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. Its advanced tools help radiologists make precise diagnoses and provide better patient care.
Orthopedics
In orthopedics, accurate imaging is crucial for diagnosing fractures and joint conditions. The DICOM reader in Nandico PACS enables orthopedic specialists to assess bone structures with high precision.
Cardiology
For cardiologists, echocardiograms and cardiac MRIs are essential diagnostic tools. Nandico PACS supports these modalities, ensuring detailed visualization of the heart and vascular system.
Dentistry
Dental professionals rely on medical imaging for diagnosing oral conditions and planning treatments. Nandico PACS facilitates the review of dental X-rays and CBCT scans with ease.
Telemedicine
With the rise of telemedicine, Nandico PACS enables remote consultations by allowing doctors to access medical images securely from anywhere. This improves patient care, especially in underserved areas.
Conclusion
A reliable DICOM reader is a must-have for any healthcare professional dealing with medical imaging. Nandico PACS offers an exceptional solution with its intuitive interface, powerful image processing tools, seamless PACS integration, and cross-platform compatibility. Whether you are a radiologist, cardiologist, or any medical professional requiring high-quality imaging, Nandico PACS is the ideal choice for efficient and accurate medical image analysis.
By choosing Nandico PACS, you ensure better patient care, improved workflow efficiency, and compliance with industry standards—all at an affordable cost. Experience the future of medical imaging with Nandico PACS today!
0 notes
Text
PACS Imaging Software | Avanttec Medical Systems Chennai
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare technology, Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) have emerged as a game-changer. This revolutionary software is transforming the way medical professionals manage, store, and share medical images within a hospital or healthcare facility. With its seamless integration into existing hospital systems, PACS Imaging Software has become an indispensable tool for teaching and research purposes, propelling the medical field to new heights. PACS Imaging Software, developed by companies like Avanttec Medical Systems, allows healthcare providers to store, retrieve, and distribute medical images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs digitally, eliminating the need for physical films and facilitating seamless access to patient data. The software's ability to integrate with hospital information systems has empowered physicians, radiologists, and other healthcare professionals to access crucial patient information in real time.
0 notes
Text
Secure Medical Image Sharing Made Simple: A Free PACS Solution Guide
As healthcare facilities increasingly collaborate to provide comprehensive patient care, the need for efficient and secure medical image sharing has never been more critical.
Fortunately, implementing a PACS viewer free solution can help healthcare providers streamline their workflow while maintaining strict security standards.
In this guide, we'll walk through everything you need to know about setting up a secure cross-facility image sharing system.

PACS Fundamentals
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) form the backbone of modern medical imaging. Before diving into implementation, let's understand the key components:

Why Free PACS Viewers? While premium PACS solutions can cost upwards of $50,000, free alternatives have evolved to offer robust features. According to recent healthcare IT surveys, over 65% of small to medium-sized facilities now utilize some form of free PACS viewing solution.
Selecting the Right Free PACS Viewer
When choosing a free PACS viewer, consider these essential features:
Must-Have Features:
DICOM compatibility
Multi-modality support
Cross-platform functionality
Active development community
Regular security updates
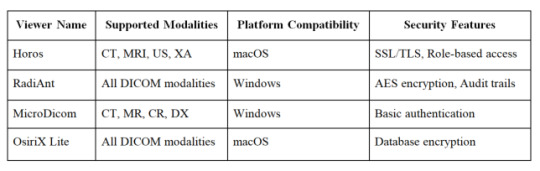
Here's a comparison of popular free PACS viewers:
Security Requirements and Compliance
HIPAA Compliance is Non-Negotiable Your implementation must adhere to strict security protocols:
Data Encryption
Use AES-256 encryption for stored images
Implement TLS 1.3 for data in transit
Regular encryption key rotation
2. Access Control
Multi-factor authentication
Role-based access control (RBAC)
Detailed audit logging
Key Security Statistics:
Healthcare data breaches cost an average of $429 per record
60% of breaches involve unauthorized access
Regular security audits reduce breach risks by 50%
Implementation Steps
1. Network Infrastructure Setup
Required Components:
- Dedicated VLAN for PACS traffic
- Hardware firewall
- VPN for remote access
- Load balancer (for high availability)
2. Server Configuration
Begin with proper server hardening:
Operating System Security
Apply latest security patches
Disable unnecessary services
Implement host-based firewall rules
Database Setup
Separate database server
Regular automated backups
Encryption at rest
3. PACS Viewer Installation
Step-by-Step Process:
Download the chosen free PACS viewer
Verify checksum for software integrity
Install on designated workstations
Configure initial security settings
Test basic functionality
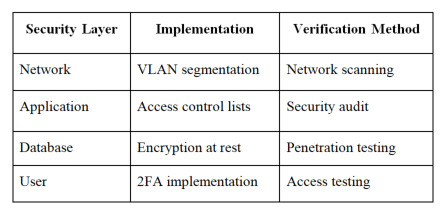
4. Security Implementation
Critical Security Measures:
Best Practices and Maintenance
Daily Operations
Regular Maintenance Tasks:
System health checks
Security log review
Backup verification
User access audits
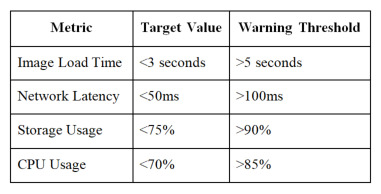
Performance Optimization
Monitor these key metrics:
Image retrieval time
System response time
Network latency
Storage utilization
Recommended Performance Thresholds:
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Image Loading Problems
Common Solutions:
Clear viewer cache
Verify network connectivity
Check file permissions
Validate DICOM compatibility
Connection Issues
Follow this troubleshooting flowchart:
Verify network status
Check VPN connectivity
Validate server status
Review firewall rules
Staff Training and Documentation
Essential Training Components:
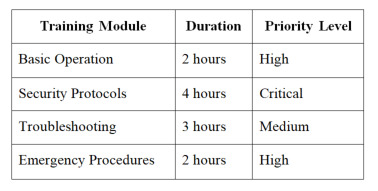
0 notes
Text
Cloud Computing in Healthcare: Adoption Trends & Competitive Landscape
The global healthcare cloud computing market size is anticipated to reach USD 45.1 billion by 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.7% from 2024 to 2030. The associated benefits of data analytics and increase in demand for flexible & scalable data storage by healthcare professionals is expected to drive the demand for these services over the forecast period.
Healthcare organizations are digitalizing their IT infrastructure and deploying cloud servers to improve features of systems. These solutions help organizations in reducing infrastructure cost & interoperability issues and aid in complying with regulatory standards. Hence, rising demand from health professionals to curb IT infrastructure costs and limit space usage are anticipated to boost market growth over the forecast period.
Increase in government initiatives undertaken to develop and deploy IT systems in this industry is one of the key drivers of this market. Moreover, increase in partnerships between private & public players and presence of a large number of players offering customized solutions are some of the factors anticipated to drive demand in the coming years.
Healthcare Cloud Computing Market Report Highlights
Nonclinical information systems dominated the market and accounted for a market share of 50.7% in 2023. It can be attributed to the larger penetration of cloud computing services for various applications such as fraud management, financial management, healthcare information exchange, and others.
Private cloud dominated the market and accounted for a market share of 37.6% in 2023. Private clouds enable healthcare organizations to maintain high levels of security, access control, and customization.
Private deployment model dominated the overall market owing to its benefits and ease of usage
Healthcare providers dominated the market and accounted for a market share of 57.0% in 2023. It can be attributed to the rising number of hospital connections over the cloud impacting the demand of the SaaS model.
Pay-as-you-go dominated the market and accounted for a market share of 55.0% in 2023. It can be attributed to the various benefits it provides such as the less initial investment.
North America healthcare cloud computing market dominated in 2023. This can be attributed to the increasing geriatric population and the growing prevalence of various chronic diseases in this region.
Healthcare Cloud Computing Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the healthcare cloud computing market on the basis of the type, deployment, pricing model, service model, end-use, and region:
Healthcare Cloud Computing Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Clinical Information Systems
EMR
PACS, VNA, and Image Sharing Solutions
PHM
Telehealth
LIMS
PIS
RIS
Other CIS
Nonclinical Information Systems
RCM
Billing and Accounts Management
Financial Management
HIE
Fraud Management
Supply Chain Management
Other NCIS
Healthcare Cloud Computing Deployment Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Private cloud
Hybrid cloud
Public cloud
Healthcare Cloud Computing Pricing Model Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Pay-as-you-go
Spot Pricing
Healthcare Cloud Computing Service Model Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Software-as-a-service
Infrastructure-as-a-service
Platform-as-a-service
Healthcare Cloud Computing End-use Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Healthcare Providers
Healthcare Payers
Healthcare Cloud Computing Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million; 2018 - 2030)
North America
US
Canada
Mexico
Europe
UK
Germany
France
Italy
Spain
Denmark
Sweden
Norway
Asia Pacific
Japan
China
India
Australia
South Korea
Thailand
Latin America
Brazil
Argentina
MEA
South Africa
Saudi Arabia
UAE
Kuwait
Key Players in the Healthcare Cloud Computing Market
Amazon Web services
Microsoft
Google Inc
athenahealth
CareCloud, Inc.
Siemens Healthineers AG
Salesforce, Inc.
Oracle (Cerner Corporation)
Epic Systems Corporation
Order a free sample PDF of the Healthcare Cloud Computing Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes
Text
Why Medical Professionals Rely on DICOM Publishing Systems in Secure Patient Data Management
INTRODUCTION
In today's fast-paced medical environment, image management and other patient data safety are more of a priority now than ever. Medical practitioners are constantly involved with sensitive data, and for both patient safety and regulatory compliance, safe handling is inevitable.
However, with the ever-increasing volume of medical data, many healthcare facilities are now dealing with issues such as data breaches, inefficiencies in sharing patient information, and the risk of human error when managing medical images. This may delay diagnosis, compromise patient safety, and lead to costly mistakes.
It is here where DICOM publishing systems come in. Allowing a reliable and secure DICOM solution would be one way by which doctors have the chance to streamline workflow, protect patient data, and be in strict compliance with strictest healthcare regulations that may bring an improvement regarding the quality of care and outcomes.
1. What is DICOM and why does it matter?
DICOM is the worldwide standard for the storage and transmission of medical imaging data. This allows medical images, including X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, to be stored and shared across healthcare systems in a consistent and interoperable format.
The DICOM format also enables interoperability among various medical devices, systems, and software so that health care providers can gain easy access to the images and patient data quickly. It is an important aspect in medical fields where speedy diagnosis with proper precision is required while procuring timeliness.
2. Data Security using DICOM Publishing Systems
One of the most significant reasons doctors and medical practitioners use DICOM publishing systems is the security offered to sensitive patient data. The fact that health care data are prime targets for cyberattacks and data breaches has placed a top priority on securing medical images and the related patient information.
The DICOM publishing systems have strong encryption and access controls to protect the data. It allows access and modification of information about patients who are authorized for it while at the same time maintaining a history of all operations done on the data.
3. Streamlining Workflow and Minimizing Human Errors
In medicine, time is of the essence. DICOM publishing systems remove the manual procedure of publishing and distributing medical images, thereby decreasing the reliance on those tasks that involve human error.
Manual entry of data, poor image formatting, and even transportation of images all contribute to a mistake that delays care for patients. The DICOM systems help in streamlining some of these activities to ensure proper publication of images, making them readily available on relevant platforms without even a single moment of delay. This reduces the administrative workload and a medical practitioner can have more time to care for their patients.
4. Easy and Fast Sharing of Data Between Systems
The other significant advantage of DICOM publishing systems is that they facilitate the easy sharing of medical images between healthcare institutions, imaging centers, and different medical professionals.
Imaging data has to be easily and promptly transferred between different hospitals, clinics, or any other healthcare institutions if a patient requires treatment from several locations or gets a second opinion. DICOM publishing systems facilitate smooth interoperability among various PACS so that images are made accessible to all permitted users in all locations.
5. Patient Data Integrity
Data integrity is a critical characteristic of medical images. Unlike any other data, medical images should be maintained at their original, high-quality state, so that patients receive accurate diagnoses. Over time, if left unmanaged, images degrade in quality, and the results become faulty.
DICOM publishing systems ensure images are preserved without degradation. They maintain the integrity of medical images because they guarantee no file corruption and provide dependable long-term storage, meaning that images can be stored and retrieved without compromising the quality therefore, health providers can make appropriate decisions based on accurate data.
Conclusion
In today's fast-paced healthcare environment, DICOM publishing systems are crucial for the secure management of patient data. They help medical professionals maintain the integrity, security, and efficiency of medical image management, ensuring that healthcare providers can make informed decisions and deliver timely, high-quality care.
DICOM systems are a necessity for healthcare facilities interested in developing improved data management practices through automation of image publishing, compliance with health care regulations, and protection of patient data. In the changing face of the healthcare industry, DICOM publishing systems will be one of the cornerstones of digital transformation, aiding providers in their delivery of better patient outcomes.
If your healthcare facility is yet to adopt a DICOM publishing system, now is when to update it to improve your data management, patient care, and security.
0 notes
Text
Global Cardiology Information System (CIS) Market Size: Analysis Of Market Segmentation And Trends
The Cardiology Information System (CIS) Market was valued at USD 1.09 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to USD 2.24 billion by 2031, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.4% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2031. The rising demand for advanced healthcare IT infrastructure, increased focus on reducing clinical errors, and the growing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases are driving the global CIS market forward.
Get Free Sample Report on Cardiology Information System (CIS) Market Size
As cardiology departments across the globe look to enhance their diagnostic and treatment capabilities, Cardiology Information Systems have emerged as essential tools to support clinicians with workflow efficiency, data management, and informed decision-making.
What is a Cardiology Information System?
A Cardiology Information System (CIS) is a specialized software platform designed to manage clinical, administrative, and diagnostic data in cardiology departments. It facilitates the storage, retrieval, analysis, and sharing of cardiac-related patient information, including imaging, test results, electrocardiograms (ECGs), echocardiograms, and catheterization lab data.
CIS enables cardiologists and healthcare providers to streamline their operations by integrating with hospital information systems (HIS), picture archiving and communication systems (PACS), and electronic health records (EHRs). With real-time access to data, clinicians can improve accuracy, minimize redundant testing, and enhance patient care.
Key Market Drivers
Rising Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of death worldwide. With aging populations and lifestyle changes contributing to the surge in heart-related conditions, there is an urgent need for advanced cardiac care management tools. CIS solutions help in early detection, better tracking of patient histories, and clinical decision support.
Growing Adoption of Healthcare IT and Digitalization Healthcare providers are rapidly embracing digital tools to manage patient data efficiently and comply with government mandates. CIS platforms are a key part of this digital transformation, helping hospitals and specialty clinics digitize workflows, reduce paperwork, and improve communication among care teams.
Integration with Imaging and Diagnostic Tools Cardiology relies heavily on imaging and diagnostic data. Modern CIS systems integrate seamlessly with PACS and diagnostic imaging devices, enabling clinicians to access high-quality visuals and patient history from a single platform. This integration improves diagnostic precision and reduces turnaround times.
Need for Workflow Efficiency and Cost Reduction Hospitals and cardiology practices face increasing pressure to reduce operational costs while maintaining high standards of care. CIS platforms offer automation, data analytics, and intelligent reporting features that enhance workflow efficiency and resource management.
Supportive Government Initiatives and Regulations Governments in regions like North America and Europe are investing in healthcare IT infrastructure and encouraging the adoption of interoperable systems to improve population health management. Such policies are further accelerating the growth of the CIS market.
Market Segmentation
The Cardiology Information System Market is segmented based on component, mode of deployment, end user, and region.
By Component: The market includes software, services, and hardware. The software segment holds the largest share, driven by increasing demand for integrated, cloud-based platforms. Services such as maintenance, training, and technical support are also witnessing robust growth.
By Deployment Mode: CIS solutions can be deployed via on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid models. Cloud-based systems are rapidly gaining popularity due to their scalability, remote accessibility, and reduced upfront costs, especially among small to mid-sized hospitals.
By End User: Hospitals, specialty clinics, diagnostic centers, and academic institutions are the primary users of CIS. Large hospitals lead the market due to their ability to invest in comprehensive digital systems and manage higher patient volumes. However, ambulatory cardiac care centers are expected to grow steadily as outpatient procedures become more common.
KEY PLAYERS:
Some of the major key players are as follows: GE Healthcare, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, CREALIFE Medical Technology, Honeywell Life Care Solution, Lumedx, Esasote, Cerner Corporation, Fujifilm Medical Systems, McKesson Corporation, Digisonics, Inc., Merge Healthcare Inc, Philips Healthcare, Cisco Systems and Other Players.
Make Enquiry about Cardiology Information System (CIS) Market Size
Future Outlook
As the demand for value-based and personalized care continues to rise, Cardiology Information Systems will play an increasingly central role in how cardiac care is delivered. The integration of artificial intelligence, predictive analytics, and machine learning is expected to enhance CIS platforms, offering clinicians deeper insights and more proactive patient management tools.
With increasing global focus on early diagnosis, efficient data handling, and patient-centered care, the CIS market is expected to witness strong momentum throughout the forecast period. Healthcare stakeholders investing in advanced information systems today are well-positioned to lead in the cardiology care of tomorrow.
About US
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President Of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#Cardiology Information System (CIS) Market Size#Cardiology Information System (CIS) Market Size Trend#Cardiology Information System (CIS) Market Size Share#Cardiology Information System (CIS) Market Size Growth#Cardiology Information System (CIS) Market.
0 notes
Text
India VNA & PACS Market to Reach $341.6 Million by 2031
Meticulous Research®, a premier global market research firm, has released a report titled “India VNA & PACS Market—Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast (2024-2031).��� This report projects that the Indian VNA & PACS market will reach $341.6 million by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 9.9% from 2024 to 2031.
Download Sample Report @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/download-sample-report/cp_id=4961
The growth of this market is driven by several factors, including advancements in diagnostic imaging technologies, rising awareness and demand for high-quality healthcare, increasing adoption of medical imaging equipment, and the growing need for a filmless environment. Additionally, the surge in health IT and EHR adoption, alongside a rising geriatric population, further fuels this growth.
Key opportunities lie in the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging and the burgeoning telehealth market. However, the market also faces challenges such as inadequate infrastructure and high out-of-pocket expenses due to limited insurance coverage. Notably, the shift towards cloud-based solutions and the establishment of diagnostic imaging centers are emerging trends within the Indian VNA & PACS market.
Key Players:
The competitive landscape of the Indian VNA & PACS market features both large and small players, including:
The key players operating in the India VNA & PACS market are GE HealthCare Technologies Inc. (U.S.), Siemens Healthineers AG (Germany), Fujifilm Holdings Corporation (Japan), Agfa-Gevaert NV (Belgium), Carestream Health, Inc. (U.S.), Koninklijke Philips N.V. (Netherlands), Amrita Technologies (India), SoftTeam Solutions Pvt Ltd. (India), Medsynaptic Pvt. Ltd. (India), INFINITT Healthcare Co., Ltd. (South Korea), and Merative L.P. (U.S.). The PACS market is segmented by Procurement Model and Delivery Mode, while the VNA market is segmented similarly. The combined market analysis includes segmentation by Type, Imaging Modality, Vendor Type, and End User.
The PACS segment is expected to dominate, capturing over 79.2% of the market share in 2024, largely due to its extensive use in cardiology and radiology for replacing traditional film methods.
Browse in Depth @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/india-vna-and-pacs-market-4961
In terms of procurement models, departmental PACS is projected to lead the market share in 2024, driven by increased imaging data usage across various medical fields.
On-premise PACS will also hold a significant market share due to advantages like quicker data access and enhanced data security. Similarly, the Enterprise VNA segment is anticipated to be the largest due to its benefits in data exchange and technology management.
Among imaging modalities, Computed Tomography (CT) is set to dominate, facilitating better integration and access within healthcare facilities.
By vendor type, independent software vendors are expected to maintain a strong position, responding to the growing demand for efficient medical imaging solutions. The hospital segment is projected to lead in end users, supported by rising admissions and the need for comprehensive image data management.
Request for Customization Report @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/request-customization/cp_id=4961
Key Questions Answered in the Report-
What is the value of revenue generated by the sale of VNA & PACS in India market?
At what rate is the demand for VNA & PACS projected to grow for the next five to seven years in India?
What is the historical market size and growth rate for the India VNA & PACS market?
What are the major factors impacting the growth of the VNA & PACS market in India?
What are the major opportunities for existing players and new entrants in the market?
Which procurement model, delivery mode, imaging modality, vendor type, end user, and segments create major traction for the manufacturers in this market?
What are the key geographical trends in this market? Which countries are expected to offer significant growth opportunities for the manufacturers operating in the India VNA & PACS market?
Who are the major players in the India VNA & PACS market? What are their specific product offerings in this market?
What recent developments have taken place in the India VNA & PACS market? What impact have these strategic developments created on the market?
Contact Us: Meticulous Research® Email- [email protected] Contact Sales- +1-646-781-8004 Connect with us on LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/company/meticulous-research
0 notes
Text
Impact of AI on Radiology Practices
The integration of AI in radiology practices has far-reaching implications for healthcare delivery and patient care. Some of the notable impacts include:
Streamlining Workflow and Reducing Turnaround Time
AI-powered tools can automate repetitive tasks, such as image analysis and report generation, leading to a more efficient workflow and reduced turnaround time for radiological examinations. This can contribute to faster diagnosis and treatment planning for patients.
Facilitating Personalized Treatment Plans for Patients
AI technologies can analyze large volumes of patient data, including imaging studies, genetic information, and clinical records, to support the development of personalized treatment plans. By leveraging predictive analytics and decision support systems, radiologists can tailor interventions to individual patient needs.
You can learn more about DICOM Anonymisation Software
Redefining the Role of Radiologists in the Healthcare Ecosystem
AI integration in radiology is reshaping the role of radiologists from image interpreters to strategic decision-makers. Radiologists are increasingly becoming collaborators in multidisciplinary care teams, leveraging AI insights to provide comprehensive patient management and treatment strategies.
You can learn more about PACS System Radiology
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Radiology
While the potential benefits of AI in radiology are substantial, there are also challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for successful integration. Some of the key concerns include:
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
The use of AI in radiology relies on access to vast amounts of sensitive patient data, raising concerns about data privacy, security, and compliance with regulatory standards such as HIPAA. Safeguarding patient information and ensuring secure data transmission and storage are critical considerations in AI integration.
Integration with Existing Healthcare Systems and Processes
Integrating AI technologies into existing radiology workflows and healthcare systems can present technical and logistical challenges. Compatibility with electronic health record (EHR) systems, interoperability with imaging devices, and seamless integration into clinical practice are essential for the successful adoption of AI in radiology.
Addressing the Potential for Algorithmic Bias and Errors
AI algorithms are susceptible to biases and errors, particularly when trained on imbalanced or incomplete datasets. Ensuring the fairness and reliability of AI-driven diagnostic tools is crucial to mitigate the risk of misdiagnosis or inaccurate clinical recommendations.
You can learn more about Radiology Teaching Files
0 notes
Text
Sneak Peek into the Evolution of Video Game Development.
Video Games have come a long way from their pixelated beginnings due to technological advancements. Central to this transformation is CGI (Computer-Generated Imagery), which has made it possible to create visually stunning images, animations, and special effects using the latest cutting-edge tools and technologies. With rapid advancements in technology, 3D artists and game developers have pushed the boundaries of visual storytelling and developed captivating visual masterpieces.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fascinating history and evolution of CGI in video games.
A Brief Overview of the History of Video Games
The history of video games can be traced back to the days of arcade games and home consoles that relied on Pixel Art. Arcade games like Pong, Boot Hill, and Gotcha featured simple and monochromatic pixel graphics. As technology evolved, games like Namco’s Galaxian, Pac-Man, Space Invaders, and Super Mario Bros. used more attractive visuals with vibrant colours and different shapes. However, they had limited colour palettes, low resolutions, simple and block graphics, and relied on sprites and tiles for creating characters and environments.
Further came the era of 16-bit consoles like Super Nintendo and Sega Genesis. These consoles offered more colours, larger sprites, and visual effects. Games such as Final Fantasy VI, Sonic the Hedgehog, and Donkey Kong Country showcased this new generation of consoles with detailed sprites, vibrant colours, and immersive worlds.
A major shift in game development came with CGI. This technology enabled detailed and realistic graphics in video games to enhance the overall gaming experience and engage them. Developers began using 3D computer graphics software Maya to create stunning 3D animations, realistic environments, and characters.
The Evolution of CGI in Video Gaming

Computer-generated imagery (CGI) is the use of computer software to create realistic characters, objects, and environments. Visionaries like Ivan Sutherland and Ed Catmull set the stage for this breakthrough in 3D graphics technology. Further, pioneering artists like Manfred Mohr and Vera Molnar integrated algorithms that changed the boundaries of visual storytelling.
Besides video games, CGI made an indelible impact on film production, with Steven Spielberg’s “Jurassic Park” (1993) becoming an iconic movie with its introduction of lively and animated dinosaurs. CGI was utilized in James Cameron’s Titanic (1997), the Matrix (1999), and Avatar (2009) to produce stunning visuals that changed the way stories were visually narrated. Pixar’s Toy Story (1995) won the hearts of audiences due to its astounding use of CGI and became the first fully CGI movie.
The 8-bit 2D Era (1972-1984)
Video games utilized basic 2D sprite-based graphics
Resolution of Arcade games: 320*240 pixels
Resolution of NES games: 256*240 pixels
Sega Master System; 256*192 pixels
Backgrounds designed by repeating tile patterns
Sprites: 8*8 or 16*16 block
Limited colours. Only 2-16 colours for full screen
Bright solid colours
Sharp pixelation
The 16-bit Era (1985-1994)
Detailed sprite-based graphics and visual effects
16-bit consoles
Larger sprites, Higher resolution, Multiple colours
New features like Scaling, Rotation, Parallax effects, Dynamic lighting, Transparency effects, and liquid physics
Super NES: 256×224 to 512×448 pixels
Sega Genesis: 320×224 to 640×448 pixels
Animation-based Gameplay
The 3D Graphics Era (1993-1996)
Introduction of consoles like PlayStation and Nintendo 64 and 3D-capable GPU chips
3D-capable GPU chips for real-time polygon rendering
Development of gameplay mechanics like platforming, puzzle-solving, and exploration
Low polygon counts, low-resolution textures, No lighting or shading effects
Game: Starfox (SNES) utilised simple 3D models and environments at 3–15 FPS.
Virtua Fighter (Arcade) used basic texture-mapped 3D characters
Super Mario 64 (N64) became the first fully 3D Mario game with free camera control
The 6th Generation Era (1997-2005)
Introduction of home consoles like Dreamcast, PS2, and Xbox.
High polygon counts, advanced lighting and shading, and texture filtering through mipmapping.
Resolutions: 640*480 and beyond.
Development of detailed normal maps, early per-pixel lighting, and shadow techniques like heat haze and reflective water.
The Cinematic Pre Rendered Graphics Era (1997-2006)
Utilizing FMW (full motion video), pre rendered CGI backgrounds, Quick Time Events (QTEs), and 3D rendered backgrounds.
Live-action video clips popularized by Night Trap (1992)
Scripted in-game actions for visual spectacle
Games: Resident Evil, Final Fantasy VII, and Soul Calibur
HD Gaming (2005)
Introduction of Xbox 360, PF3, and modern PCs
HD 720p and 1080p gaming
High-definition resolutions, Advanced lighting engines, photorealistic textures, real-time shadow mapping, and HDR lighting
Complex engines like Unreal 3 for dynamic lighting
Higher memory budgets for photorealistic textures
Detailed normal and specular maps for high-complexity
Filters like cinematic tone mapping, depth of field, motion blur, and more
The Current State of CGI in Video Games
Photogrammetry for realistic environments
PBR – Physically based rendering for realistic materials and lighting
Ray tracing for reflections, shadows, and lighting effects
Introduction of 4K gaming with PlayStation 4 Pro, Xbox One X, PlayStation 5, Xbox Series X
Advanced rendering techniques like ray tracing, and global illumination.
Character realism with motion capture and facial animation.
Integration of AR in Video Gaming with AR headsets like HoloLens
Games: The Last of Us Part II, Red Dead Redemption 2, Cyberpunk
Convergence of video games in films, animation, and VR
The Future of Video Gaming
With the evolution of CGI, video games will be more realistic, immersive, and engaging than ever.
More realistic lighting, shadows, and reflections with Ray tracing and 8K resolution.
AI tools will be more adopted to generate environments and characters.
Games will approach photorealism, creating completely lifelike experiences.
More immersive Virtual reality gaming with Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR headsets
Integrating AI, machine learning, and real-time rendering
Cloud gaming and cloud computing.
The Best CGI Animation Studio
In this digital era, it is important to hire a CGI animation studio for your multimedia needs like animated 3D series: TV or Web, shorts, films, commercials, live-action videos, or anything else. CGI is a groundbreaking technology that has the potential to change the game for you with more audience engagement, higher downloads, and licensing.
Prismart is one of the best CGI animation studios in New Delhi and has been catering to clients for over a decade. The company has a dedicated team of 150+ professionals, all experts in their respective fields, who are driven to hard work and results. The company is known for its fastest turnarounds, affordable budget, transparency, and client satisfaction.
0 notes