#NewSpace
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Massu ig 07.09.2023.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Move

I am so excited to announce...that I am moving!!! And this is not no ordinary move. I have found a new space that I can make my own. I am so happy for this new move, I don’t know where to begin. Well, I guess I can start here.
Follow me on the mystical journey as I pack up the old space and journey to my new space. This is my story and experience with “The Spiritual House”.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Rise of Small Satellite Manufacturing: Big Dreams, Tiny Packages
In a world where bigger used to mean better, the space industry is flipping the script—and we’re here for it. 💥 Welcome to the era of small satellites, where innovation is compact, agile, and changing the game for good.
🛠️ What’s the deal with smallsats? Small satellites (aka "smallsats") are spacecraft that weigh under 500 kg. Some are so tiny you could hold them in one hand—like CubeSats, which are built in standardized 10x10x10 cm units! 📦 They're easier (and cheaper) to design, build, and launch.
🌍 Why they matter:
Affordable access to space for startups, universities, and even high school teams 🧑🚀📡
Quicker manufacturing cycles (we’re talking months instead of years!) ⏱️
Ideal for Earth observation, climate monitoring, communications & research 📊🌱
🛠️ Inside the lab: Small satellite manufacturing is a beautiful dance between precision engineering, composite materials, and modular design. 3D printing? Yes. Custom PCBs? Absolutely. Smart propulsion? You bet. The future is efficient and elegant.
🌠 The future is looking up (literally): As mega-constellations fill the sky, and missions multiply, smallsat manufacturing is becoming the backbone of NewSpace. 🚀 It's not just about going to space—it's about doing it smarter, faster, and with a smaller footprint.
📸 Bonus: They look really cool in cleanroom selfies.

#space#satellite#smallsat#CubeSat#aerospace#STEM#engineering#newspace#satelliteengineering#spacetech
0 notes
Video
youtube
SpaceX’s Bandwagon-3: 300th Launch Milestone! #sciencefather #spacex #scientist
SpaceX’s Bandwagon-3 mission 🚀 marked a major milestone as it became the 300th orbital launch from Cape Canaveral’s historic pad 40 🛰️. As part of SpaceX’s expanding rideshare program 🤝, Bandwagon-3 carried a variety of small satellites into orbit, showcasing the company’s continued push toward making space more accessible and efficient 🌍✨. The launch highlights not only the reliability of Falcon 9 💪 but also the transformation of pad 40 into a cornerstone of modern spaceflight 🏗️🌌. With clear skies and a flawless ascent 🌤️⬆️, the mission was a celebratory moment for both SpaceX and the legacy of Cape Canaveral 🚀🇺🇸.
Natural Scientist Awards
Nomination Link: https://naturalscientist.org/award-nomination/?ecategory=Awards&rcategory=Awardee
Visit Our Website 🌐naturalscientist.org
Contact us [email protected]
Get Connected Here:
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/natural-scientist-466a56357/
Blogger: https://naturalaward.blogspot.com/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/natural_scientist/
Pinterest: https://in.pinterest.com/research2805/_profile/
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@NaturalScientistAwards
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=61574191899176
#youtube#sciencefather#naturalscientistawards#researchawards#spacex#bandwagon#rideshare#falcon9#capecanaveral#spaceflight#satellitelaunch#orbital#spacetechnology#elonmusk#spacexlaunch#spaceexploration#aerospaceengineering#astrophysics#orbitalmechanics#satellite#researchanddevelopment#spaceinnovations#newspace#spaceindustry#scientist#researcher
0 notes
Text
https://www.industryarc.com/Research/small-and-medium-satellite-market-research-800681?utm_source=tumbler&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=Raghavarao

#SmallSat#SatelliteTechnology#SpaceInnovation#SpaceTech#NewSpace#SatelliteLaunch#SatelliteCommunication
0 notes
Text
Design research: AeroSpace sidestick
Imagine that you need to press the buttons of the sidestick (joystick) confidently and clearly when your vehicle / lander / spacecraft is being hit and shaken.
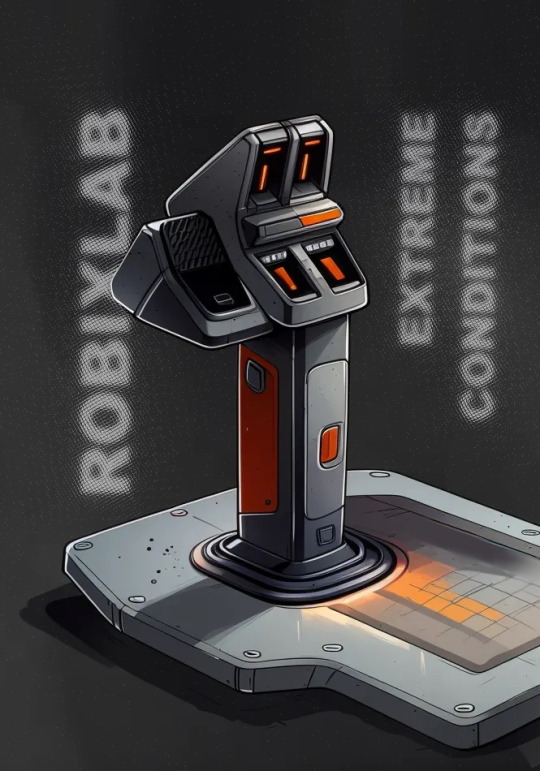

For example, the oscillation amplitude is 0.01-1.0m , or acceleration is 2/5/10G.
You can't let the joystick out of your hand to work with the buttons, you can't look at the buttons, you have a thick aerospace glove on your hand.
We have designed a handle of sidestick that solves such problems.
1) The buttons are divided into three levels, each of which differs in its geometric location and is easily determined by tactile feels.
2) The buttons are made mechanical - this prevents accidental clicks.
3) They are embedded in the body, and near them there is a finger support - this allows you to prepare for pressing in advance, even with vibrations.
4) The buttons are equipped with touch contact sensors - the finger contact with each button (without pressing) is displayed as an indicator on the dashboard.
Designed by Robixlab, more illustrations about this project: ROBIXLAB (@robixlab) • Instagram
#aerospace#engineering#industrial design#spacecraft#joystick#cockpit#productdesign#newspace#designresearch#uidesign#pilot#interface#research#ergonomics#robixlab
1 note
·
View note
Text





JEUDI 06 JUIN À PARTIR DE 14:30
NOUS AVONS LE PLAISIR DE VOUS
ACCUEILLIR POUR L’EVENT DU 5ETG
83 BOULEVARD LONGCHAMP 13001
|||||||
🧨 super.esx invité.esx 👇🏽
✅ Event 06.06.2024 !
~ 14:30 > ~ 22:30 …….
Espace 🪐 5e étg
83 Bd Longchamp
13001 marseille !!!
Sonnez fort 👉🏿Galtier
✅ Event
4 Lectures + 1 concert 🎵
Les invitéEsx ::
• 16:00
Concert
#MatheusNogueira
• 17:40
Lecture
#LilianeGiraudon
• 18:10
Lecture
#LaurenceDenimal
• 18:40
Lecture
#MarieFrançoiseDeGantès
• 19:10
Lecture
#NadineAgostini
✅ Event
Expositions #12 [+1] plasticienNEsx
Les invitéEsx ::
⭐️ #LilianeGiraudon
⭐️ #AymericLouis
⭐️ #ClaraPerreaut
⭐️ #PatrickLefebvre
⭐️ #FredPradeau
⭐️ #RémiBragard
⭐️ #MarieFrancoiseDeGantes
⭐️ #DavidRaynaudGermain
⭐️ #OdetteMonnier
⭐️ #SaloméDeFontainieu
⭐️ #LaureChaminas
⭐️ #LorraineThomas
& sous réserve
⭐️ #LaurentLeforban
*******
« On peut créer entre les mots et les objets de nouveaux rapports et préciser quelques caractères du langage et des objets, généralement ignorés dans la vie quotidienne ».
Ou encore :
« Parfois le nom d’un objet tient lieu d’une image. Un mot peut prendre la place d’un objet dans la réalité. Une image peut prendre la place d’un mot dans une proposition ».
Et ceci qui n’emporte poin
*******
https://mediterranees.net/histoire_romaine/empereurs_1siecle/neron/racine/acte1.html
*******
c’est à partir
des constellations d’enduits au plafond
cuisine chs salon sallàmanger 2bain ….
du vide dans le couloir où l’aspirateur jaune ne sert jamais
du soleil qui baigne chacune des 8 pièces que je viens de vider
des murs blancs où plus rien n’est accroché depuis que newspace se prépare
que les artistes ont pensé investir l’espace au 5eme etg que je quitte ….
mercis à euxellesx mercis pour leurs œuvres & leurs engagements constants
⭐️
https://uel.unisciel.fr/physique/optigeo/optigeo_ch01/co/apprendre_ch01_07.html
⭐️
« Dans un tableau, les mots sont de la même substance que les images. On voit autrement les images et les mots dans un tableau ».
Magritte de P. Waldberg.
Michel Foucault
1 note
·
View note
Text
Chandrayaan 3 Launch Live Updates: ISRO LVM 3

Chandrayaan 3 Launch Live Updates: ISRO Lunches LVM 3 Successfully The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched its third lunar mission, Chandrayaan-3, on Friday, July 14, 2023. The launch took place at 2:35 p.m. IST from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.

Chandrayaan 3 lunch live updates Chandrayaan-3 is a robotic mission that consists of a propulsion module, a lander module, and a rover. The propulsion module will transport the lander and rover from the injection orbit to the lunar orbit up to 100 kilometers. The lander will then descend to the lunar surface, where it will deploy the rover. The main purpose of Chandrayaan-3 is to create and showcase innovative technologies essential for missions between planets. The mission will also conduct scientific experiments to study the lunar surface and its environment. The launch of Chandrayaan-3 was a major milestone for India's space program. It is the first time that India has attempted to land a spacecraft on the moon's south pole, which is a region that has not been explored by any other country. The success of Chandrayaan-3 is a testament to the hard work and dedication of the ISRO team. It is also a significant achievement for India, which is now one of the few countries in the world that has the capability to land a spacecraft on the moon.
Here are some additional details about the mission Chandrayaan 3:

Chandrayaan 3 lunch live updates

Chandrayaan 3 lunch live updates

Chandrayaan 3 lunch live updates

Chandrayaan 3 lunch live updates

Chandrayaan 3 lunch live updates

Chandrayaan 3 lunch live updates - The propulsion module is based on the PSLV-C39 launch vehicle. - The lander module is named Vikram, after the father of India's space program, Vikram Sarabhai. - The rover is named Pragyan, which means "wisdom" in Sanskrit. - The mission is expected to last for one year. The launch of Chandrayaan-3 was met with widespread praise and congratulations from around the world. Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi tweeted that the launch was a "moment of pride" for India. He also said that the mission would "further our understanding of the moon and its mysteries." The success of Chandrayaan-3 is a major boost for India's space program. It is a sign that India is a major player in the global space race. The mission is also a source of inspiration for Indians around the world. It shows that India is capable of achieving great things. The launch of Chandrayaan-3 was met with widespread praise from the scientific community. Dr. S. Somanath, the chairman of ISRO, said that the launch was a "major accomplishment" for the Indian space program. He added that the mission would "help us to better understand the moon and its evolution." The success of Chandrayaan-3 is a testament to the hard work and dedication of the scientists and engineers at ISRO. It is also a reminder of India's growing capabilities in the field of space exploration.
India Successfully launched Chandrayaan 3
- India successfully launched its third lunar mission, Chandrayaan-3, on July 14, 2023. - The mission aims to soft-land a lander and rover on the lunar surface. - The launch is a significant milestone for India's space program and is expected to provide valuable scientific data about the moon. - The success of Chandrayaan-3 is a testament to the hard work and dedication of the scientists and engineers at ISRO. - The Chandrayaan-3 mission is a follow-on to the Chandrayaan-2 mission, which launched in 2019. Chandrayaan-2 was the first Indian mission to soft-land on the moon, but the lander failed to deploy the rover. - The Chandrayaan-3 lander is named Vikram, after Vikram Sarabhai, the father of the Indian space program. The rover is named Pragyan, which means "wisdom" in Sanskrit. - The Chandrayaan-3 mission is equipped with a variety of scientific instruments to study the lunar surface, including: - A spectrometer to study the composition of the lunar surface - A camera to image the lunar surface - A magnetometer to measure the magnetic field of the moon - A seismometer to measure the seismic activity of the moon - The Chandrayaan-3 mission is expected to provide valuable data about the moon's evolution, its composition, and its potential for resources. - The success of Chandrayaan-3 will further cement India's position as a leading spacefaring nation. - Chandrayaan 3 has developed & designed by ISRO.
According to ISRO about Chandrayaan 3
Chandrayaan-3, India's lunar mission, consists of a Lander module, Propulsion module, and Rover. Its objective is to develop and demonstrate new technologies for interplanetary missions. The Lander will soft land on the lunar surface and deploy the Rover for in-situ chemical analysis. Both the Lander and Rover have scientific payloads for experiments. The Propulsion Module carries the Lander to the lunar orbit and separates from it. The mission objectives include safe landing, Rover mobility, and scientific experiments. Advanced technologies in the Lander include altimeters, velocimeters, inertial measurement, propulsion system, navigation and guidance, hazard detection, and landing leg mechanism. The GSLV-Mk3 launcher will place the module in an elliptic parking orbit.
Countries which has successfully landed a spacecraft on the Moon
There are only 3 countries that have successfully landed a spacecraft on the Moon: - United States: The United States was the first country to successfully land a spacecraft on the Moon, with the Apollo 11 mission in 1969. There were a total of 6 crewed Apollo missions that landed on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. - Soviet Union: The Soviet Union was the second country to successfully land a spacecraft on the Moon, with the Luna 9 mission in 1966. There were a total of 15 successful uncrewed Soviet Moon missions, including 3 that returned samples of lunar soil to Earth. - China: China became the third country to successfully land a spacecraft on the Moon, with the Chang'e 3 mission in 2013. The Chang'e 3 mission also deployed a rover, Yutu, which was the first rover to operate on the far side of the Moon. Other countries, such as India, Japan, and the European Space Agency, have sent spacecraft to the Moon, but they have not yet successfully landed on the surface. In addition to these countries, there are a number of private companies that are developing spacecraft that could one day land on the Moon. These companies include SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Moon Express. Read the full article
#3#Chandrayaan#Chandrayaan3#Dhawan#Liveupdates#Mangalyaan#NASA#new#NewDelhi#Newspace#SatishDhawan#Space#Spaceagency#Telangana#Yaan
0 notes
Link
space law and governance—a framework designed to ensure that humanity’s expansion into the stars remains peaceful, sustainable, and fair.
#spacesustainability#ArtemisAccords CosmicGovernance NewSpace OuterSpaceTreaty SpaceCommerce SpaceDebris SpaceEconomy SpaceEnvironment SpaceExploration SpaceInno
0 notes
Text
Defence Ministry funds 77 projects under Technology Development Fund
Ministry of Defence Technology Development Fund: India’s Ministry of Defence’s Technology Development Fund (TDF) scheme has already sanctioned a total of 77 projects with a combined value exceeding $3.6 million (INR 300 crore). These projects have successfully yielded 27 new defence technologies, said the government on Wednesday. The aim of MoD‘s Technology Development Fund is to promote…
#ChiStats Labs Private Limited#Combat Robotics#Defence Budget#Defence Ministry&039;s TDF Scheme#DRDO#Ministry of Defence#NewSpace Research and Technologies Private Limited#Technology Development Fund
0 notes
Text
77 defence projects get funding under DRDO's TDF Scheme
77 defence projects get funding under DRDO's TDF Scheme
Ministry of Defence Technology Development Fund: India’s Ministry of Defence’s Technology Development Fund (TDF) scheme has already sanctioned a total of 77 projects with a combined value exceeding $3.6 million (INR 300 crore). These projects have successfully yielded 27 new defence technologies, said the government on Wednesday. The aim of MoD‘s Technology Development Fund is to promote…
#ChiStats Labs Private Limited#Combat Robotics#Defence Budget#Defence Ministry&039;s TDF Scheme#DRDO#Ministry of Defence#NewSpace Research and Technologies Pvt. Ltd#Technology Development Fund
0 notes
Text




Glimpses of Shige's first IG live because he was just adorable 🫠💚
0 notes
Text
Space Technology Opportunity in India

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
Introduction:
Entrepreneurship in space technology in India has been gaining momentum in recent years. The Indian government has been actively promoting the development of the space sector, and private companies are playing an increasingly important role.
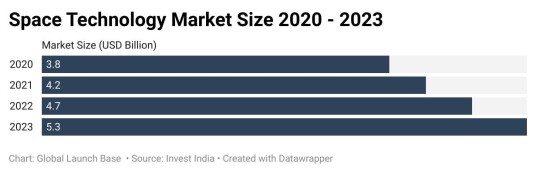
As the nation liberalizes its space sector, a diverse array of players are contributing to the burgeoning space ecosystem. Entrepreneurs are venturing into satellite manufacturing, pushing the boundaries of launch services, delving into space exploration, and exploring innovative solutions for satellite-based communication. The landscape is further enriched by collaborative efforts between private entities, government agencies, and academic institutions, fostering a dynamic environment for research and development.
In this context, it's crucial to explore the challenges and opportunities that define the entrepreneurial spirit in India's space technology sector. Regulatory hurdles, infrastructure development, and the need for sustained investments are among the challenges that entrepreneurs face. However, with increasing investor interest, a robust policy framework, and a commitment to fostering innovation, India's entrepreneurial ventures in space technology are poised to shape the nation's narrative in the cosmic domain. This dynamic interplay of public and private entities is not only propelling India's space capabilities but is also contributing to the global discourse on the commercialization and exploration of space.
Here are some key aspects of entrepreneurship in space technology in India:
Government Initiatives:New Space Policy: The Indian government has introduced policies to encourage private sector participation in space activities. The New Space India Limited (NSIL) was established to promote, commercially exploit, and transfer technologies developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).Liberalization: The government has liberalized the space sector, allowing private companies to undertake a wide range of space-related activities, including satellite launches, space exploration, and satellite communication services. (ISRO) Initiatives: Antrix Corporation: Antrix is the commercial arm of ISRO, and it collaborates with private players for the commercialization of space-related products and services.: SEED is a program initiated by ISRO to promote startups in the space sector by providing them with opportunities for collaboration and technology transfer.: NSIL is a central public sector enterprise (CPSE) under the Department of Space. It plays a crucial role in commercializing space products, technical consultancy services, and transfer of technologies.: ISRO has been actively engaging with startups, providing them access to its facilities, expertise, and technology.: The Department of Space in India oversees the country's space program. It may introduce schemes and programs to support space technology startups and entrepreneurs. (AIM): AIM, a flagship initiative of the NITI Aayog, supports innovation and entrepreneurship in various sectors. It may have programs and funding opportunities that space technology startups can explore. (NIF): NIF supports grassroots innovations and may provide support to startups working on innovative space technologies.
Private Space Companies:Startups: Several startups in India are focusing on various aspects of space technology. Some are involved in satellite manufacturing, launch services, data analytics from space, and more.Launch Services: Companies like Agnikul Cosmos, Skyroot Aerospace, and Pixxel are working on developing small satellite launch vehicles to provide cost-effective and flexible launch options.
Space Exploration and Research: Interplanetary Missions: ISRO has been actively involved in space exploration, and private companies are expressing interest in participating in future interplanetary missions.Research and Development: Private entities are engaging in research and development activities, contributing to advancements in satellite technology, propulsion systems, and other space-related technologies.
Satellite Manufacturing:Private Satellite Manufacturers: Companies like Exseed Space and Bellatrix Aerospace are involved in the manufacturing of satellites, catering to various purposes such as communication, Earth observation, and scientific research.
Communication Services:Telecommunication Satellites: Private companies are exploring opportunities to provide satellite-based communication services. This includes both broadband internet services and other communication solutions.
Funding and Investments:Investor Interest: The space technology sector in India has attracted attention from investors. Funding rounds for space startups have been on the rise, indicating confidence in the potential growth of the industry.
Collaborations and Partnerships:
Industry-Academia Collaboration: Partnerships between private companies, government organizations, and academic institutions are fostering innovation and research in the space sector.
The Indian space technology ecosystem is evolving, and with continued government support, entrepreneurial ventures in space technology are expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of the Indian space industry.
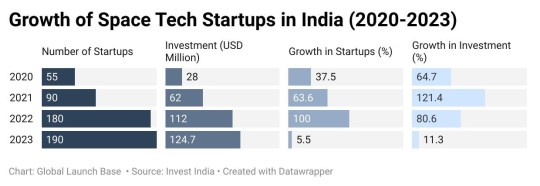
The number of space tech startups in India has witnessed explosive growth, increasing by almost five times in just five years. Investments in the sector have also seen a sharp rise, from $17 million in 2019 to an estimated $124.7 million in 2023.
Commercialization of Space Activities: With India's proven track record in satellite launches and space technology, there is a substantial potential for the commercialization of space activities. The burgeoning demand for satellite-based services, including communication, arth observation, and navigation, opens up opportunities for private entities to actively participate in the space industry. As the cost of space access continues to decrease, private companies can explore ventures such as satellite manufacturing, space tourism, and satellite-based applications, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
International Collaborations: Collaborations with other space-faring nations present a promising avenue for India to augment its space capabilities. Joint ventures, knowledge exchange, and technology transfer can accelerate innovation and enhance the efficiency of space missions. ISRO has already established itself as a reliable partner for international launches, and expanding collaborative efforts can lead to shared resources, reduced costs, and a more diversified approach to space exploration. As India continues to engage in global partnerships, it can leverage collective expertise for ambitious endeavors beyond Earth's orbit.
Innovation in Space Technology: Investments in research and development (R&D) can catapult India into the forefront of space innovation. Emphasis on cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, advanced materials, and propulsion systems can revolutionize space missions. The development of reusable launch vehicles, like the ongoing efforts in creating a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), can significantly reduce launch costs, making space exploration more sustainable. Encouraging a culture of innovation, fostering collaboration between academia and industry, and providing incentives for R&D initiatives can fuel breakthroughs in space technology.
Space Applications for Sustainable Development: Leveraging space technology for sustainable development on Earth is an untapped frontier. Utilizing satellite data for precision agriculture, disaster management, environmental monitoring, and resource mapping can contribute to addressing pressing global challenges. By integrating space-based solutions into sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and urban planning, India can harness the power of space technology for inclusive and sustainable development, bringing tangible benefits to its citizens and contributing to global initiatives.
Expansion of Interplanetary Exploration: Building on the success of Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), India has the potential to expand its interplanetary exploration efforts. Initiatives for exploring other celestial bodies, such as Venus or asteroids, can contribute to humanity's understanding of the solar system and beyond. A strategic focus on ambitious interplanetary missions can position India as a key player in the broader scientific community and foster international collaboration in the exploration of the cosmos.
Trending Technologies in India's Space Industry:
Nanotechnology: The integration of nanotechnology in space technology has the potential to revolutionize spacecraft design, materials, and instrumentation. Nanosatellites, with their miniaturized components, are becoming increasingly popular for cost-effective and innovative space missions. India can leverage nanotechnology for lightweight yet robust spacecraft, enhancing mission efficiency and scientific capabilities.
Companies: Nano-Tech SpA, Kalva Nanotech
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are playing a pivotal role in data analysis, image processing, and autonomous decision-making in space missions. India can explore AI applications for real-time data interpretation, automated navigation, and predictive maintenance of spacecraft. Incorporating machine learning algorithms into Earth observation data analysis can significantly enhance the understanding of environmental changes.
Companies: Aadyah Aerospace, Blue Sky Analytics
Quantum Computing: Quantum computing holds the promise of solving complex computational problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers. In the space sector, quantum computing can be utilized for optimizing mission trajectories, simulating quantum systems, and enhancing the security of communication channels. India's focus on quantum computing research can contribute to advancements in space-related computations.
Companies: QpiAI, BosonQ
3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: The adoption of 3D printing in space technology can revolutionize the manufacturing process, enabling the production of complex and lightweight structures. India can benefit from 3D printing for rapid prototyping, cost-effective manufacturing of satellite components, and even on-demand production during long-duration space missions.
Companies: Agnikul Cosmos, EOS India
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent data management, making it applicable to space-based applications such as satellite communication, data storage, and secure information sharing. By incorporating blockchain, India can enhance the security and integrity of space-related data and transactions.
Companies: SpaceTime Labs, Aryaka Networks
Solar Sail Technology: Solar sails, propelled by the pressure of sunlight, offer a sustainable and efficient means of propulsion for spacecraft. This technology can be harnessed for deep-space exploration, enabling missions to travel vast distances with minimal fuel requirements. India's exploration programs can benefit from research and development in solar sail technology for extended-duration missions.
Companies: Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST), IIT Bombay - Aerospace Engineering Department
Hyperspectral Imaging: Hyperspectral imaging involves capturing a wide range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. This technology is instrumental in Earth observation, resource mapping, and environmental monitoring. India can explore the integration of hyperspectral imaging in its satellite payloads for enhanced remote sensing capabilities.
Companies: Pixxel, Paras Defence & Space Technologies Ltd
Internet of Things (IoT) for Space: The application of IoT in space technology involves connecting devices and sensors on satellites and spacecraft to gather and transmit data. This interconnected network can facilitate efficient communication, data collection, and collaborative decision-making during space missions. India can explore IoT applications for enhanced space situational awareness and mission coordination.
Companies: Agnikul Cosmos
As India looks to the future, embracing these trending technologies will be crucial for maintaining its competitive edge in space exploration and satellite technology. By actively incorporating these innovations into its space programs, India can not only enhance mission success but also contribute to the global advancement of space technology. Collaborations with research institutions, startups, and the private sector will play a vital role in driving these technological advancements in India's space industry.
Challenges and the Way Forward:
Despite its successes, India's space program faces challenges such as increased competition, budget constraints, and the need for continuous innovation. To overcome these challenges, sustained government support, collaboration with private entities, and a focus on skill development in the space sector are crucial.
Increased Global Competition: The space industry is becoming increasingly competitive with the emergence of new players and the commercialization of space activities. To stay ahead, India must continuously innovate, streamline its processes, and invest in cutting-edge technologies. Developing a robust ecosystem for space startups and fostering public-private partnerships can enhance India's competitiveness in the global space market.
Budget Constraints: Despite commendable achievements, budget constraints pose a challenge for sustaining and expanding India's space endeavors. A consistent and increased allocation of funds to ISRO, along with exploring innovative funding mechanisms, will be crucial. Engaging with the private sector for joint ventures and commercial space activities can help alleviate financial constraints and promote economic sustainability in the long run.
Human Resource Development: The growth of India's space program necessitates a skilled workforce capable of handling complex missions. Investing in education and training programs in collaboration with academic institutions can ensure a steady supply of skilled professionals in fields such as aerospace engineering, astrophysics, and data sciences. This will not only address the current workforce requirements but also fuel future innovations in space technology.
Technological Advancements: Rapid technological advancements globally require India to stay at the forefront of innovation. Embracing emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and advanced propulsion systems will be essential. Establishing research and development centers dedicated to space technology innovation can facilitate the integration of these advancements into future missions.
Space Debris Management: The increasing number of satellites and space missions contribute to the growing issue of space debris. India needs to actively participate in international efforts to address space debris management, adopting sustainable practices in satellite design and end-of-life disposal. Research into debris removal technologies and international collaboration on space traffic management will be pivotal in ensuring the long-term sustainability of space activities.
Climate Change Monitoring: With the rising global concerns about climate change, space technology plays a crucial role in monitoring environmental indicators. India can take a leadership role in developing satellite-based solutions for climate monitoring, disaster response, and sustainable resource management. This requires a dedicated focus on Earth observation satellites, advanced sensors, and data analytics.
Enhanced Space Diplomacy: Strengthening space diplomacy is essential for India to expand its global influence in the space arena. Engaging in collaborative space missions, sharing scientific knowledge, and participating in international forums will enhance India's standing as a responsible space-faring nation. Forming strategic partnerships with countries interested in space exploration can open up new avenues for cooperation and joint missions.
Conclusion:
India's journey in space technology has been nothing short of remarkable, with ISRO consistently pushing the boundaries of innovation. As the nation continues to invest in space exploration, the opportunities for growth, collaboration, and technological advancements are boundless. The future holds exciting possibilities for India's space technology sector, positioning the country as a key player in the global space community.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#ISRO - Indian Space Research Organization#NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)#SEED(Social Entrepreneurship Empowerment Development)#Atal Innovation Mission Official#National Innovation Foundation - India#Nano-Tech SpA#Kalva Nanotech#AADYAH Aerospace Private Limited#Blue Sky Analytics#QpiAI#BosonQ Psi (BQP)#AgniKul Cosmos#EOS#Spacetime Labs#Aryaka#Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology#Aerospace Engineering Association IIT Bombay#Pixxel#Paras Defence & Space Technologies Ltd.#AgniKul Cosmos hashtag#SpaceTechnologyInIndia hashtag#IndianSpaceProgram hashtag#ISROOpportunities hashtag#SpaceIndustryGrowthIndia hashtag#SpaceResearchOrganizationsIndia hashtag#SatelliteTechnologyOpportunities hashtag#IndianSpaceExploration hashtag#ISROAchievements hashtag#SpaceScienceCareersIndia hashtag#SpaceTechnologyTrends hashtag
0 notes
Text
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
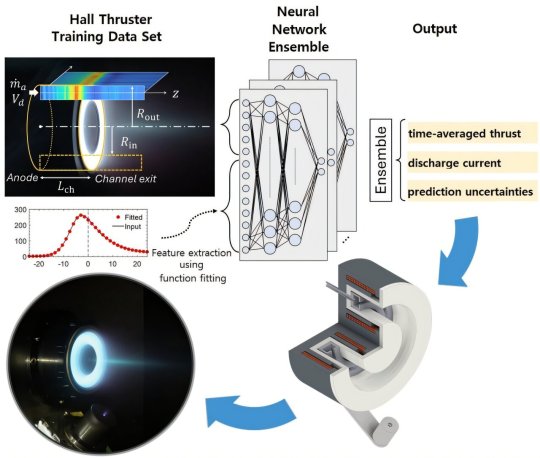
AI technique predicts Hall thruster power for spacecraft with high accuracy
A Hall thruster is a high-efficiency propulsion device using plasma that is used for various difficult space missions, such as SpaceX's constellation satellites, Starlink and NASA's asteroid probe, Psyche, and is one of the core space technologies.
KAIST researchers will be verifying the performance of the Hall thruster for CubeSats developed using artificial intelligence techniques by loading it onto the CubeSat K-HERO during the fourth launch of Nuri scheduled for November of this year.
Professor Wonho Choe of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering developed an artificial intelligence technique that can predict the thrust performance of Hall Effect ion thrusters (i.e., Hall thrusters), which are engines for satellites or space probes, with high accuracy. The study is published in the journal Advanced Intelligent Systems.
Hall thrusters have high fuel efficiency, so they can greatly accelerate satellites or spacecraft using less propellant (fuel), and can generate large thrust relative to the power consumed. Based on these advantages, it is widely used for various missions, such as maintaining formation flight of satellite clusters in space environments where propellant conservation is important, orbital deorbit maneuvers for reducing space debris, and providing propulsion for deep space exploration such as comet or Mars exploration.
Recently, as the space industry has expanded in the era of Newspace, space missions are becoming more diverse and the demand for Hall thrusters is increasing accordingly. In order to quickly develop high-efficiency Hall thrusters optimized for each unique mission, a technique to accurately predict the performance of the thruster from the design stage is essential.
However, existing methods have limitations such as not being able to precisely handle the complex plasma phenomenon occurring in the Hall thruster or being limited to specific conditions, resulting in low performance prediction accuracy.
The research team developed a highly accurate thruster performance prediction technique based on artificial intelligence that drastically reduces the time and cost required for repetitive work of designing, manufacturing, and testing the Hall thruster.
Professor Choe's team, which started the first domestic electric thruster development research in 2003 and has been leading related research and development, introduced an artificial neural network ensemble structure based on 18,000 Hall thruster learning data generated using a self-developed electric thruster computer analysis tool and applied it to predicting thrust performance.
The computer analysis tool developed to secure high-quality learning data models plasma physics and thrust performance. The accuracy of the computer analysis tool was verified to be high, with an average error of less than 10% compared to approximately 100 experimental data performed with 10 Hall thrusters developed for the first time in Korea by the research team.
The artificial neural network ensemble model operates as a digital twin model that can predict thruster performance in a short period of time, within a few seconds, with high accuracy depending on the design variables of the Hall thruster.
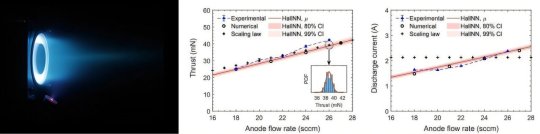
In particular, it can analyze in detail the changes in performance indicators such as thrust and discharge current according to design variables such as fuel flow rate and magnetic field that were difficult to analyze with previously known scaling laws.
The research team showed that the AI neural network model developed this time showed an average error of less than 5% for the 700W and 1kW class Hall thrusters developed in-house, and an average error of less than 9% for the 5kW class high-power Hall thruster developed by the US Air Force Research Laboratory. This study proved that the AI prediction technique developed can be widely applied to Hall thrusters of various power sizes.
Professor Choe said, "The AI-based performance prediction technique developed by the research team has high accuracy and is already being used to analyze the thrust performance of Hall thrusters, which are engines for satellites and spacecraft, and to develop high-efficiency, low-power Hall thrusters. This AI technique can be applied not only to Hall thrusters, but also to the research and development of ion beam sources used in various industries such as semiconductors, surface treatment, and coating."
In addition, Professor Choe explained, "The Hall thruster for the cube satellite developed using AI techniques in collaboration with Cosmo Bee Co., Ltd., an electric propulsion specialist and a laboratory startup of the research team, will be installed on the 3U (30x10x10 cm) cube satellite K-HERO in the 4th launch of Nuri scheduled for November of this year to verify its performance in space."
The results of this study, in which Ph.D. student Jaehong Park of KAIST Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (Space Exploration Engineering Interdisciplinary Major) participated as the first author, were recognized for their innovation by being selected as the journal's front cover paper.
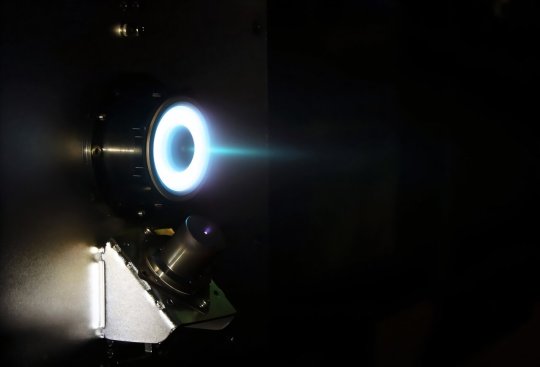
TOP IMAGE: The AI-based technique to predict Hall Effect Ion Source developed by the research team can predict the performance of the thrust according to design variables with high accuracy, rendering it highly useful in the development of high-efficiency Hall thrusters. Credit: Adapted from Advanced Intelligent Systems (2024). DOI: 10.1002/aisy.202400555
CENTRE IMAGE: The operation of a 150 W-class low-power Hall thruster for (ultra)small satellites that is being developed by the research team of Professor Wonho Choe of KAIST in collaboration with Cosmobee, an electric propulsion specialist company founded by the laboratory. This Hall thruster is scheduled to be installed on the CubeSat, K-HERO, that will be launched into space through the 4th launch of Nuriho in the 4th quarter of 2025 to perform in-orbit verification. Credit: The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
LOWER IMAGE: The photo on the left shows the Hall thruster in operation in the Electric Propulsion Vacuum Chamber at KAIST, and the graphs to the right show the results of thrust and discharge current according to the anode flow rate. In the graph, the red line represents the results predicted by the AI model, and the blue dots represent the experimental results. Credit: Adapted from Advanced Intelligent Systems (2024). DOI: 10.1002/aisy.202400555
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
it's kind of funny to me how there are all these plans by newspace companies for new space hotels and private space stations and spacecraft and stuff but at the same time there's this rapidly growing and incredibly rich body of research that basically unanimously states "microgravity is insanely bad for the human body"
5 notes
·
View notes