#Native plant
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


New bloom today! California manroot is blooming!
8 notes
·
View notes
Note
Question for y'all and the solarpunk network at large, I guess:
do you know of a tool that helps with native plant recommendations that takes climate changes in the region into account?
I've been working through soil repair and am finally ready to start planting deliberately, but a lot of the recommendations for my area seem to be focused on what the area was like 10 years ago.
Hey, thanks for asking! We're not aware of any resources like that, unfortunately - if anyone following can help out, that would be great!
#solarpunk#Solarpunk Presents Podcast#question#Q&A#native plant#plant identifier#soil repair#climate change#zoning#regional climate changes#plants#gardening#plantblr
15 notes
·
View notes
Photo
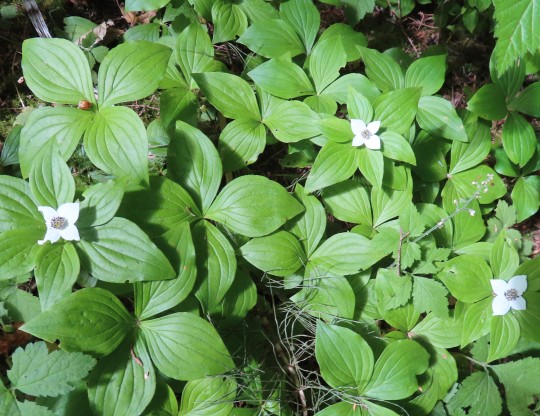



Cornus canadensis (Canadian bunchberry)
About a month ago I was talking to a neighbor about her pink dogwood tree and she showed me a four petaled, white flower in her garden. She said it had just “shown up” last year and wondered if this was a dogwood too. “Oh no,” I said, “dogwoods are either shrubs or small trees. I’ve never seen a dogwood growing as a groundcover before.”
Of course this conversation raised an element of doubt and as soon as I got home I opened my copy of Plants of Coastal British Columbia (revised edition) and there it was on page 320, Cornus canadensis. A week later I was walking the forest trails in Stanley Park and I found it all over the place.
This wildflower is native to Canada, Greenland, Northern China, North Korea, Japan, parts of Siberia and a number of US states. Although most dogwoods are shrubs and small trees, two species, Canadian bunchberry and Alaskan bunchberry (Cornus × unalaschkensis) grow between four and eight inches tall.
#flowers#photographers on tumblr#Canadian bunchberry#dogwood#native plant#fleurs#flores#fiori#blumen#bloemen#Stanley Park#Vancouver
88 notes
·
View notes
Text
I need to find a small twinky person or smthn to take pictures of big trees with. I’m 6ft 2 and probably 280 pounds, so the trees don’t look as big as they should



10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Common Violet
Sometimes you must bend down and look closely to find the little gems
Viola sororia Native to Eastern North America Stemless Spreads by stolons and forms small colonies Flowers white with purple veining only occasionally Downy, wide-heart-shaped leaves Stops blooming in hot summer weather Great ground cover

View On WordPress
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

Triumph over frostbite! This red Rhodie got hit hard by frostbite at the beginning of spring, and yet it has not only survived but is starting to bloom!
#rhododendron#red flowers#native plant#frostbite#late freeze#PNW#photozoi#original photo#5-2024#nature
9 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Queen Anne's Lace A lovely pollinator plant
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
On the Way to the Opera

View On WordPress
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Celebrating Indigenous Peoples' Day in LA (Tongva / Los Angeles Region)
This month, I am hiking to fundraise for the National Parks Conservation Association (NPCA)! Support the journey here: Through Venmo: https://account.venmo.com/u/twiichiiThrough NPCA Fundraiser: https://give.npca.org/fundraiser/5852280 Hi all, how are you doing? It may be fall, but I hope you all are rising! Autumn is the perfect season to rest and connect with loved ones in community. It’s…
#Art#counselor#culture#garden#healing#Health#healthy#hike#hiker#hiking#indigenous#international#justice#meadow#mental health#mountain#national monument#national park#national parks#native plant#natural#naturalist#nature#nature journaling#nps#nursery#pacific crest trail#pass#passes#peaks
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The VERY Hungry Caterpillar 🐛


#mother nature#caterpillar#monarch caterpillars#monarch butterfly#milkweed#native plant#happy#nom nom
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Planet's Fucked: What Can You Do To Help? (Long Post)
Since nobody is talking about the existential threat to the climate and the environment a second Trump term/Republican government control will cause, which to me supersedes literally every other issue, I wanted to just say my two cents, and some things you can do to help. I am a conservation biologist, whose field was hit substantially by the first Trump presidency. I study wild bees, birds, and plants.
In case anyone forgot what he did last time, he gagged scientists' ability to talk about climate change, he tried zeroing budgets for agencies like the NOAA, he attempted to gut protections in the Endangered Species Act (mainly by redefining 'take' in a way that would allow corporations to destroy habitat of imperiled species with no ramifications), he tried to do the same for the Migratory Bird Treaty Act (the law that offers official protection for native non-game birds), he sought to expand oil and coal extraction from federal protected lands, he shrunk the size of multiple national preserves, HE PULLED US OUT OF THE PARIS CLIMATE AGREEMENT, and more.
We are at a crucial tipping point in being able to slow the pace of climate change, where we decide what emissions scenario we will operate at, with existential consequences for both the environment and people. We are also in the middle of the Sixth Mass Extinction, with the rate of species extinctions far surpassing background rates due completely to human actions. What we do now will determine the fate of the environment for hundreds or thousands of years - from our ability to grow key food crops (goodbye corn belt! I hated you anyway but), to the pressure on coastal communities that will face the brunt of sea level rise and intensifying extreme weather events, to desertification, ocean acidification, wildfires, melting permafrost (yay, outbreaks of deadly frozen viruses!), and a breaking down of ecosystems and ecosystem services due to continued habitat loss and species declines, especially insect declines. The fact that the environment is clearly a low priority issue despite the very real existential threat to so many people, is beyond my ability to understand. I do partly blame the public education system for offering no mandatory environmental science curriculum or any at all in most places. What it means is that it will take the support of everyone who does care to make any amount of difference in this steeply uphill battle.
There are not enough environmental scientists to solve these issues, not if public support is not on our side and the majority of the general public is either uninformed or actively hostile towards climate science (or any conservation science).
So what can you, my fellow Americans, do to help mitigate and minimize the inevitable damage that lay ahead?
I'm not going to tell you to recycle more or take shorter showers. I'll be honest, that stuff is a drop in the bucket. What does matter on the individual level is restoring and protecting habitat, reducing threats to at-risk species, reducing pesticide use, improving agricultural practices, and pushing for policy changes. Restoring CONNECTIVITY to our landscape - corridors of contiguous habitat - will make all the difference for wildlife to be able to survive a changing climate and continued human population expansion.
**Caveat that I work in the northeast with pollinators and birds so I cannot provide specific organizations for some topics, including climate change focused NGOs. Scientists on tumblr who specialize in other fields, please add your own recommended resources. **
We need two things: FUNDING and MANPOWER.
You may surprised to find that an insane amount of conservation work is carried out by volunteers. We don't ever have the funds to pay most of the people who want to help. If you really really care, consider going into a conservation-related field as a career. It's rewarding, passionate work.
At the national level, please support:
The Nature Conservancy
Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation
Cornell Lab of Ornithology (including eBird)
National Audubon Society
Federal Duck Stamps (you don't need to be a hunter to buy one!)
These first four work to acquire and restore critical habitat, change environmental policy, and educate the public. There is almost certainly a Nature Conservancy-owned property within driving distance of you. Xerces plays a very large role in pollinator conservation, including sustainable agriculture, native bee monitoring programs, and the Bee City/Bee Campus USA programs. The Lab of O is one of the world's leaders in bird research and conservation. Audubon focuses on bird conservation. You can get annual memberships to these organizations and receive cool swag and/or a subscription to their publications which are well worth it. You can also volunteer your time; we need thousands of volunteers to do everything from conducting wildlife surveys, invasive species removal, providing outreach programming, managing habitat/clearing trails, planting trees, you name it. Federal Duck Stamps are the major revenue for wetland conservation; hunters need to buy them to hunt waterfowl but anyone can get them to collect!
THERE ARE DEFINITELY MORE, but these are a start.
Additionally, any federal or local organizations that seek to provide support and relief to those affected by hurricanes, sea level rise, any form of coastal climate change...
At the regional level:
These are a list of topics that affect major regions of the United States. Since I do not work in most of these areas I don't feel confident recommending specific organizations, but please seek resources relating to these as they are likely major conservation issues near you.
PRAIRIE CONSERVATION & PRAIRIE POTHOLE WETLANDS
DRYING OF THE COLORADO RIVER (good overview video linked)
PROTECTION OF ESTUARIES AND SALTMARSH, ESPECIALLY IN THE DELAWARE BAY AND LONG ISLAND (and mangroves further south, everglades etc; this includes restoring LIVING SHORELINES instead of concrete storm walls; also check out the likely-soon extinction of saltmarsh sparrows)
UNDAMMING MAJOR RIVERS (not just the Colorado; restoring salmon runs, restoring historic floodplains)
NATIVE POLLINATOR DECLINES (NOT honeybees. for fuck's sake. honeybees are non-native domesticated animals. don't you DARE get honeybee hives to 'save the bees')
WILDLIFE ALONG THE SOUTHERN BORDER (support the Mission Butterfly Center!)
INVASIVE PLANT AND ANIMAL SPECIES (this is everywhere but the specifics will differ regionally, dear lord please help Hawaii)
LOSS OF WETLANDS NATIONWIDE (some states have lost over 90% of their wetlands, I'm looking at you California, Ohio, Illinois)
INDUSTRIAL AGRICULTURE, esp in the CORN BELT and CALIFORNIA - this is an issue much bigger than each of us, but we can work incrementally to promote sustainable practices and create habitat in farmland-dominated areas. Support small, local farms, especially those that use soil regenerative practices, no-till agriculture, no pesticides/Integrated Pest Management/no neonicotinoids/at least non-persistent pesticides. We need more farmers enrolling in NRCS programs to put farmland in temporary or permanent wetland easements, or to rent the land for a 30-year solar farm cycle. We've lost over 99% of our prairies to corn and soybeans. Let's not make it 100%.
INDIGENOUS LAND-BACK EFFORTS/INDIGENOUS LAND MANAGEMENT/TEK (adding this because there have been increasing efforts not just for reparations but to also allow indigenous communities to steward and manage lands either fully independently or alongside western science, and it would have great benefits for both people and the land; I know others on here could speak much more on this. Please platform indigenous voices)
HARMFUL ALGAL BLOOMS (get your neighbors to stop dumping fertilizers on their lawn next to lakes, reduce agricultural runoff)
OCEAN PLASTIC (it's not straws, it's mostly commercial fishing line/trawling equipment and microplastics)
A lot of these are interconnected. And of course not a complete list.
At the state and local level:
You probably have the most power to make change at the local level!
Support or volunteer at your local nature centers, local/state land conservancy non-profits (find out who owns&manages the preserves you like to hike at!), state fish & game dept/non-game program, local Audubon chapters (they do a LOT). Participate in a Christmas Bird Count!
Join local garden clubs, which install and maintain town plantings - encourage them to use NATIVE plants. Join a community garden!
Get your college campus or city/town certified in the Bee Campus USA/Bee City USA programs from the Xerces Society
Check out your state's official plant nursery, forest society, natural heritage program, anything that you could become a member of, get plants from, or volunteer at.
Volunteer to be part of your town's conservation commission, which makes decisions about land management and funding
Attend classes or volunteer with your land grant university's cooperative extension (including master gardener programs)
Literally any volunteer effort aimed at improving the local environment, whether that's picking up litter, pulling invasive plants, installing a local garden, planting trees in a city park, ANYTHING. make a positive change in your own sphere. learn the local issues affecting your nearby ecosystems. I guarantee some lake or river nearby is polluted
MAKE HABITAT IN YOUR COMMUNITY. Biggest thing you can do. Use plants native to your area in your yard or garden. Ditch your lawn. Don't use pesticides (including mosquito spraying, tick spraying, Roundup, etc). Don't use fertilizers that will run off into drinking water. Leave the leaves in your yard. Get your school/college to plant native gardens. Plant native trees (most trees planted in yards are not native). Remove invasive plants in your yard.
On this last point, HERE ARE EASY ONLINE RESOURCES TO FIND NATIVE PLANTS and LEARN ABOUT NATIVE GARDENING:
Xerces Society Pollinator Conservation Resource Center
Pollinator Pathway
Audubon Native Plant Finder
Homegrown National Park (and Doug Tallamy's other books)
National Wildlife Federation Native Plant Finder (clunky but somewhat helpful)
Heather Holm (for prairie/midwest/northeast)
MonarchGard w/ Benjamin Vogt (for prairie/midwest)
Native Plant Trust (northeast & mid-atlantic)
Grow Native Massachusetts (northeast)
Habitat Gardening in Central New York (northeast)
There are many more - I'm not familiar with resources for western states. Print books are your biggest friend. Happy to provide a list of those.
Lastly, you can help scientists monitor species using citizen science. Contribute to iNaturalist, eBird, Bumblebee Watch, or any number of more geographically or taxonomically targeted programs (for instance, our state has a butterfly census carried out by citizen volunteers).
In short? Get curious, get educated, get involved. Notice your local nature, find out how it's threatened, and find out who's working to protect it that you can help with. The health of the planet, including our resilience to climate change, is determined by small local efforts to maintain and restore habitat. That is how we survive this. When government funding won't come, when we're beat back at every turn trying to get policy changed, it comes down to each individual person creating a safe refuge for nature.
Thanks for reading this far. Please feel free to add your own credible resources and organizations.
#us election#climate change#united states election#resources#native plants#this took 3 hours to write so maybe don't let it flop? i know i write long posts. i know i follow scientists on here#that study birds and corals and other creatures#i realize i did not link sources/resources for everything. i encourage those more qualified to add things on. i need to go to work
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
If you live in East TN then check out Native Plant Rescue Squad!




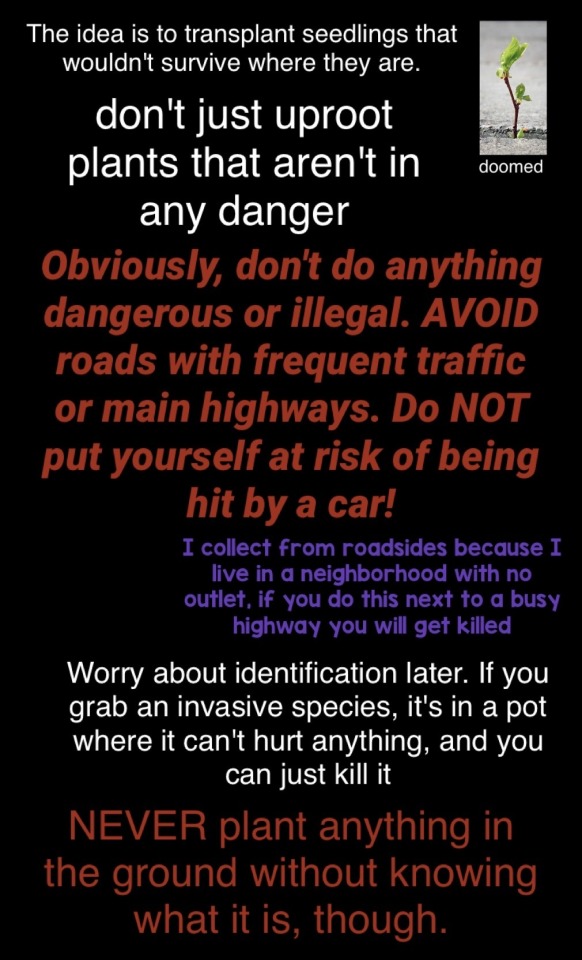




as promised, the transplanting tutorial
most sources make transplanting sound incredibly difficult, but transplanting young seedlings from areas with sparse dirt, like a driveway or roadside, is actually incredibly easy and can get you some great stuff. Once I worked out the method, i've had a very high survival rate
it took me like a month of trial and error to figure this out so you don't have to.
Feel free to repost, no need for credit
#east tn#east tennessee#southern appalachia#native plant gardening#native plant#native plant rescue squad#guerilla gardening#gardening#native plants
28K notes
·
View notes
Text
#tiktok#andrew_the_arborist#urban gardening#urban landscape#ecofriendly#native wildflowers#eco friendly#eco lawn#native plants#garden#gardening
100K notes
·
View notes
Text

16.12.23, Cyclamen persicum flowering, Jabal Faqqua'a (or Mount Gilboa)
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
Mosquito Repellant Native Plant // More Powerful Than DEET (Edible Berries Too) American Beautyberry
This type of bush grows like WEEDS around my property. The birds feed off of them and with Their droppings the bushes pop up all around. Long ago, in a far different Blog group, a person in S.C. was commenting that This type of bush was dyeing out. I replied back, laughing and told her that in my area that type of bush must not be in the same fad, because they grow so Wild and Crazy here.
Every few yrs., when the berries would be heavier than normal, I’d take a limb of them to work and many people from My County would ask What kind of plant is That ?!!! It surprised me that natives from this county didn’t even know what it was/is. They grow Very large.
The leaves can be used to repel mosquitos and ticks. You just pick some and rub them onto your clothing and hat.
This yr. due to a very odd summer, for the first time that I’ve ever noticed, the majority of the plants on my property are Not putting out berries. The Old saying is that the heavier the berries, the colder the winter. Well, I guess that means that I’m going to have a Very Mild winter. . . . We’ll see ?
0 notes
