#National University of Mexico
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
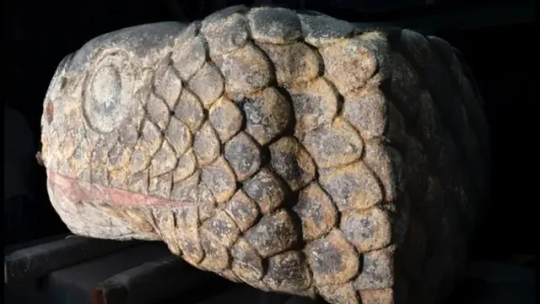
Earthquake Reveals Aztec Snakehead Beneath Mexico City
Researchers are conserving a rare snakehead from the Aztecs that still retains its painted colors from hundreds of years ago.
An earthquake last year revealed a big surprise beneath a law school in modern-day Mexico City: a giant, colorful snakehead from the Aztec Empire.
The snakehead dates back more than 500 years, to when the Aztecs controlled the area, which at the time was part of the flourishing capital of Tenochtitlan. The sculpture was discovered after a magnitude-7.6 earthquake struck Mexico City on Sept. 19, 2022; the seismic event caused damage and changes in the topography, revealing the snakehead beneath a building that was part of a law school at the National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico's National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) said in a Spanish-language statement.
The Aztecs built temples and pyramids and worshipped a number of deities, including Quetzalcoatl, who was often depicted as a snake. However, it's unclear if this sculpture depicts him, the archaeologists said.
The sculpted snake is 5.9 feet (1.8 meters) long, 2.8 feet (0.85 m) wide and 3.3 feet (1 m) high, and it weighs about 1.3 tons (1.2 metric tons), the INAH said. Several colors — including red, blue, black and white — are preserved on the sculpture.

Color was preserved on about 80% of the sculpture's surface. To keep it preserved, an INAH team lifted the snakehead out of the ground with a crane and constructed a humidity chamber around the sculpture. This chamber allows the sculpture to lose humidity gradually, with its color being preserved, María Barajas Rocha, a conservationist with the INAH who worked extensively on the sculpture, said in the statement.
While other snakehead sculptures have been found at Tenochtitlan, this one is particularly important for its preserved colors, said Erika Robles Cortés, an archaeologist with the INAH.

"Thanks to the context in which this piece was discovered, but above all, thanks to the stupendous intervention of the restorers-conservators led by Maria Barajas, it has been possible to stabilize the colors for its preservation in almost all the sculpture, which is extremely important, because the colors have helped us to conceive pre-Hispanic art from another perspective," Robles Cortés told Live Science in an email.
The sculpture's "sheer size is impressive, as well as its artistry," but the survival of the colors is remarkable, said Frances Berdan, a professor emeritus of anthropology at California State University, San Bernardino who was not involved with the excavation. "The survival of black, white, red, yellow, and blue paints is particularly interesting — one gains a good image of the visual impact of such sculptures as they were arrayed about the city center," Berdan said in an email.

In addition to its preserved colors, the snakehead's size is notable, said Bertrand Lobjois, an associate professor of humanities at the University of Monterrey in Mexico who is not involved in the excavation. The "first time I saw this serpent head, I was dazzled by its dimensions," he said in an email.
Lobjois also praised the conservation work that allowed the colors to survive, noting that "the conservation process allows us to appreciate the naturalistic approach of figuration" the Aztec artists used.
This work is ongoing and will continue at the site into next year.
By Owen Jarus.
#Earthquake Reveals Aztec Snakehead Beneath Mexico City#National Autonomous University of Mexico#Quetzalcoatl#sculpture#stone sculpture#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#aztec culture#aztec history#aztec mythology#aztec gods#aztec empire#aztec art
619 notes
·
View notes
Text



Miss Universe Mexico 2023 National Costume
“Guardiana Alebrije”
355 notes
·
View notes
Text
The First Light of Trinity
— By Alex Wellerstein | July 16, 2015 | Annals of Technology

Seventy years ago, the flash of a nuclear bomb illuminated the skies over Alamogordo, New Mexico. Courtesy Los Alamos National Laboratory
The light of a nuclear explosion is unlike anything else on Earth. This is because the heat of a nuclear explosion is unlike anything else on Earth. Seventy years ago today, when the first atomic weapon was tested, they called its light cosmic. Where else, except in the interiors of stars, do the temperatures reach into the tens of millions of degrees? It is that blistering radiation, released in a reaction that takes about a millionth of a second to complete, that makes the light so unearthly, that gives it the strength to burn through photographic paper and wound human eyes. The heat is such that the air around it becomes luminous and incandescent and then opaque; for a moment, the brightness hides itself. Then the air expands outward, shedding its energy at the speed of sound—the blast wave that destroys houses, hospitals, schools, cities.
The test was given the evocative code name of Trinity, although no one seems to know precisely why. One theory is that J. Robert Oppenheimer, the head of the U.S. government’s laboratory in Los Alamos, New Mexico, and the director of science for the Manhattan Project, which designed and built the bomb, chose the name as an allusion to the poetry of John Donne. Oppenheimer’s former mistress, Jean Tatlock, a student at the University of California, Berkeley, when he was a professor there, had introduced him to Donne’s work before she committed suicide, in early 1944. But Oppenheimer later claimed not to recall where the name came from.
The operation was designated as top secret, which was a problem, since the whole point was to create an explosion that could be heard for a hundred miles around and seen for two hundred. How to keep such a spectacle under wraps? Oppenheimer and his colleagues considered several sites, including a patch of desert around two hundred miles east of Los Angeles, an island eighty miles southwest of Santa Monica, and a series of sand bars ten miles off the Texas coast. Eventually, they chose a place much closer to home, near Alamogordo, New Mexico, on an Army Air Forces bombing range in a valley called the Jornada del Muerto (“Journey of the Dead Man,” an indication of its unforgiving landscape). Freshwater had to be driven in, seven hundred gallons at a time, from a town forty miles away. To wire the site for a telephone connection required laying four miles of cable. The most expensive single line item in the budget was for the construction of bomb-proof shelters, which would protect some of the more than two hundred and fifty observers of the test.
The area immediately around the bombing range was sparsely populated but not by any means barren. It was within two hundred miles of Albuquerque, Santa Fe, and El Paso. The nearest town of more than fifty people was fewer than thirty miles away, and the nearest occupied ranch was only twelve miles away—long distances for a person, but not for light or a radioactive cloud. (One of Trinity’s more unusual financial appropriations, later on, was for the acquisition of several dozen head of cattle that had had their hair discolored by the explosion.) The Army made preparations to impose martial law after the test if necessary, keeping a military force of a hundred and sixty men on hand to manage any evacuations. Photographic film, sensitive to radioactivity, was stowed in nearby towns, to provide “medical legal” evidence of contamination in the future. Seismographs in Tucson, Denver, and Chihuahua, Mexico, would reveal how far away the explosion could be detected.
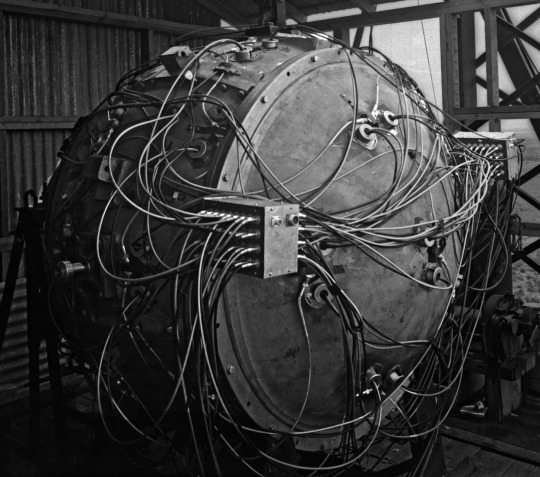
The Trinity test weapon. Courtesy Los Alamos National Laboratory
On July 16, 1945, the planned date of the test, the weather was poor. Thunderstorms were moving through the area, raising the twin hazards of electricity and rain. The test weapon, known euphemistically as the gadget, was mounted inside a shack atop a hundred-foot steel tower. It was a Frankenstein’s monster of wires, screws, switches, high explosives, radioactive materials, and diagnostic devices, and was crude enough that it could be tripped by a passing storm. (This had already happened once, with a model of the bomb’s electrical system.) Rain, or even too many clouds, could cause other problems—a spontaneous radioactive thunderstorm after detonation, unpredictable magnifications of the blast wave off a layer of warm air. It was later calculated that, even without the possibility of mechanical or electrical failure, there was still more than a one-in-ten chance of the gadget failing to perform optimally.
The scientists were prepared to cancel the test and wait for better weather when, at five in the morning, conditions began to improve. At five-ten, they announced that the test was going forward. At five-twenty-five, a rocket near the tower was shot into the sky—the five-minute warning. Another went up at five-twenty-nine. Forty-five seconds before zero hour, a switch was thrown in the control bunker, starting an automated timer. Just before five-thirty, an electrical pulse ran the five and a half miles across the desert from the bunker to the tower, up into the firing unit of the bomb. Within a hundred millionths of a second, a series of thirty-two charges went off around the device’s core, compressing the sphere of plutonium inside from about the size of an orange to that of a lime. Then the gadget exploded.
General Thomas Farrell, the deputy commander of the Manhattan Project, was in the control bunker with Oppenheimer when the blast went off. “The whole country was lighted by a searing light with the intensity many times that of the midday sun,” he wrote immediately afterward. “It was golden, purple, violet, gray, and blue. It lighted every peak, crevasse, and ridge of the nearby mountain range with a clarity and beauty that cannot be described but must be seen to be imagined. It was that beauty the great poets dream about but describe most poorly and inadequately.” Twenty-seven miles away from the tower, the Berkeley physicist and Nobel Prize winner Ernest O. Lawrence was stepping out of a car. “Just as I put my foot on the ground I was enveloped with a warm brilliant yellow white light—from darkness to brilliant sunshine in an instant,” he wrote. James Conant, the president of Harvard University, was watching from the V.I.P. viewing spot, ten miles from the tower. “The enormity of the light and its length quite stunned me,” he wrote. “The whole sky suddenly full of white light like the end of the world.”
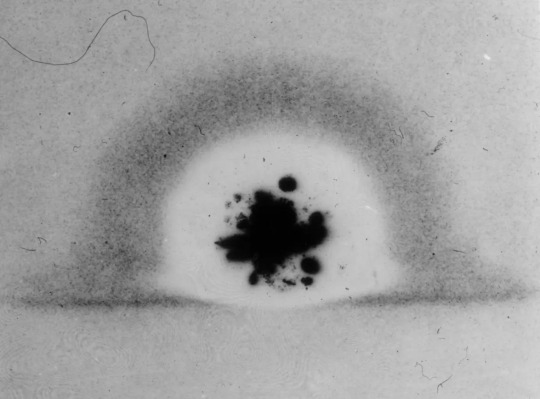
In its first milliseconds, the Trinity fireball burned through photographic film. Courtesy National Archives and Records Administration
Trinity was filmed exclusively in black and white and without audio. In the main footage of the explosion, the fireball rises out of the frame before the cameraman, dazed by the sight, pans upward to follow it. The written accounts of the test, of which there are many, grapple with how to describe an experience for which no terminology had yet been invented. Some eventually settle on what would become the standard lexicon. Luis Alvarez, a physicist and future participant in the Hiroshima bombing, viewed Trinity from the air. He likened the debris cloud, which rose to a height of some thirty thousand feet in ten minutes, to “a parachute which was being blown up by a large electric fan,” noting that it “had very much the appearance of a large mushroom.” Charles Thomas, the vice-president of Monsanto, a major Manhattan Project contractor, observed the same. “It looked like a giant mushroom; the stalk was the thousands of tons of sand being sucked up by the explosion; the top of the mushroom was a flowering ball of fire,” he wrote. “It resembled a giant brain the convolutions of which were constantly changing.”
In the months before the test, the Manhattan Project scientists had estimated that their bomb would yield the equivalent of between seven hundred and five thousand tons of TNT. As it turned out, the detonation force was equal to about twenty thousand tons of TNT—four times larger than the expected maximum. The light was visible as far away as Amarillo, Texas, more than two hundred and eighty miles to the east, on the other side of a mountain range. Windows were reported broken in Silver City, New Mexico, some hundred and eighty miles to the southwest. Here, again, the written accounts converge. Thomas: “It is safe to say that nothing as terrible has been made by man before.” Lawrence: “There was restrained applause, but more a hushed murmuring bordering on reverence.” Farrell: “The strong, sustained, awesome roar … warned of doomsday and made us feel that we puny things were blasphemous.” Nevertheless, the plainclothes military police who were stationed in nearby towns reported that those who saw the light seemed to accept the government’s explanation, which was that an ammunition dump had exploded.
Trinity was only the first nuclear detonation of the summer of 1945. Two more followed, in early August, over Hiroshima and Nagasaki, killing as many as a quarter of a million people. By October, Norris Bradbury, the new director of Los Alamos, had proposed that the United States conduct “subsequent Trinity’s.” There was more to learn about the bomb, he argued, in a memo to the new coördinating council for the lab, and without the immediate pressure of making a weapon for war, “another TR might even be FUN.” A year after the test at Alamogordo, new ones began, at Bikini Atoll, in the Marshall Islands. They were not given literary names. Able, Baker, and Charlie were slated for 1946; X-ray, Yoke, and Zebra were slated for 1948. These were letters in the military radio alphabet—a clarification of who was really the master of the bomb.
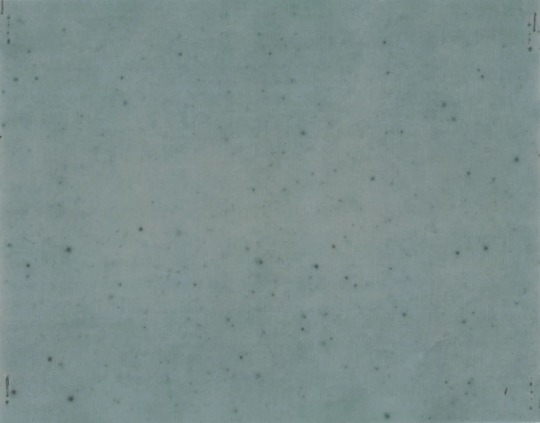

Irradiated Kodak X-ray film. Courtesy National Archives and Records Administration
By 1992, the U.S. government had conducted more than a thousand nuclear tests, and other nations—China, France, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union—had joined in the frenzy. The last aboveground detonation took place over Lop Nur, a dried-up salt lake in northwestern China, in 1980. We are some years away, in other words, from the day when no living person will have seen that unearthly light firsthand. But Trinity left secondhand signs behind. Because the gadget exploded so close to the ground, the fireball sucked up dirt and debris. Some of it melted and settled back down, cooling into a radioactive green glass that was dubbed Trinitite, and some of it floated away. A minute quantity of the dust ended up in a river about a thousand miles east of Alamogordo, where, in early August, 1945, it was taken up into a paper mill that manufactured strawboard for Eastman Kodak. The strawboard was used to pack some of the company’s industrial X-ray film, which, when it was developed, was mottled with dark blotches and pinpoint stars—the final exposure of the first light of the nuclear age.
#Hiroshima | Japan 🇯🇵 | John Donne | Manhattan Project | Monsanto#Nagasaki | Japan 🇯🇵 | Nuclear Weapons | Second World War | World War II#The New Yorker#Alex Wellerstein#Los Alamos National Laboratory#New Mexico#J. Robert Oppenheimer#John Donne#Jean Tatlock#University of California Berkeley#Jornada del Muerto | Journey of the Dead Man#General Thomas Farrell#Nobel Prize Winner Physicist Ernest O. Lawrence#Luis Alvarez#US 🇺🇸#China 🇨🇳#France 🇫🇷#Soviet Union (Now Russia 🇷🇺)#Alamogordo | New Mexico#Eastman Kodak#Nuclear Age
39 notes
·
View notes
Text

Lead study Mexican author Luis Rodríguez, a professor emeritus at the Institute of Radio Astronomy and Astrophysics at the National Autonomous University of Mexico
In 2023, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) helped identify hundreds of free-floating "rogue" planets that don't orbit a parent star. Now, astronomers have found that a pair of these planets may be producing enigmatic, hard-to-interpret radio signals.
The rogue planets spotted by JWST lie in the Orion Nebula, a long-time observational hotspot for astronomers. In total, they number over 500. This discovery bonanza was possible thanks to JWST's ability to pick up infrared radiation emitted by these relatively young planets.
Bizarrely, though, about 80 of these planets exist as pairs. Similar in mass to Jupiter, the planets orbit each other at distances ranging from 25 to 400 times the distance between Earth and the sun. These tangoing duos, called Jupiter-mass binary objects (JuMBOs), pose a huge mystery for astronomers, because the existence of these worlds challenges current theories of planet formation. Some scientists think these objects may not even be planets but rather previously unknown entities that are larger than planets but smaller than brown dwarfs, which are sometimes called "failed stars" because they blur the line between planets and stars.
The JWST data showed that JuMBOs generated infrared radiation, but the new study's authors wanted to see if these dancing objects produced radio waves. That's because different classes of cosmic objects produce distinct patterns of radio emissions. For instance, planets like Jupiter spew several types of radio signals, including gigahertz-frequency emissions thousands of times higher-pitched than an FM signal, partly because of their magnetic fields.
Spotting such signatures from the JuMBOs could help resolve their identity. The observations could also explain "why some objects have detectable radio emission and others do not," lead study author Luis Rodríguez, a professor emeritus at the Institute of Radio Astronomy and Astrophysics at the National Autonomous University of Mexico, told Live Science in an email.
To find radio wave "snapshots" of the Orion Nebula where the JuMBOs reside, the scientists combed through archives of observations maintained by the U.S. National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO). They found just one pair that apparently emits radio waves: JuMBO 24. Itself an oddity among the oddball objects, it's the heaviest of the JuMBOs, and also the one with the tightest space between its component planets.
A decade's worth of data the research team collated showed that the radio waves remained steady but strong, with a power of roughly a quarter of a ton of TNT and frequencies of 6 to 10 gigahertz. The radio waves also weren't circularly polarized, meaning they lacked spiral, twisting electric fields, the team reported in their study, published Jan. 8 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
But these features aren't what astronomers expect of signals created by planets." Circular polarization is an unambiguous indicator of the presence of magnetic fields," Rodríguez said. Without this, the team can't say definitively that the signals come from JuMBO 24 (assuming the planets have magnetic fields). Besides, radio emissions from other exoplanets are more variable and less intense.
Even if JuMBO 24 isn't a pair of planets but rather another type of cosmic duo, the signals are unusual. Signals from brown dwarfs are very different from the newly identified radio beams. The beams' brightness and frequency even ruled out the possibility of pulsars, the rapidly spinning cores of dead stars that produce pulses of radio waves at regular intervals.
The researchers also estimated the likelihood that the signals originate from an object behind JuMBO 24 and found it to be exceedingly slim, at just 1 in 10,000. And, in case you were wondering, the signals probably don't originate from aliens. "The fact that both components emit at similar levels favors a natural mechanism," Rodríguez said.
With the research at an impasse, the team is applying to the NRAO's Very Large Array in New Mexico to collect data from free-floating planets. Until then, the radio signals will remain a mystery.
#🇲🇽#STEM#Luis Rodríguez#mexican scientists#astronomy#science#Institute of Radio Astronomy and Astrophysics#National Autonomous University of Mexico#James Webb Space Telescope#JWST#radio signals#planets#orion nebula#Jupiter-mass binary objects#JuMBOs#brown dwarfs#jupiter#JuMBO 24#The Astrophysical Journal Letters#pulsars#mexican#latino#hispanic
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
nightmare shift today
#it was national overdose awareness day. and boy was i aware of the overdoses !!!#went thru 8 naloxone kits in 8 hours#i got off at 3am and went to the gym and then realized i took the spare van keys home w me by accident so i had to bike back to work#in time for the morning shift team . and then i went to a diner at 6am and the waiter tried to chat me up#except within the first 5 minutes he expressed disapproval for universal basic income and said 'at least where i'm from in mexico kids will#do tricks or dance or work to get handouts from people' like bro what . no#anyways it was funny. at first i wasn't sure but then he mentioned that he's single and gets off at 7am like 5 different ways#it's now 8am and i'm going to bed so i can do it all over again in 9h <3#pegasus speaks
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

14 September 2023








#alien corpses#UFO#ufologist#Jaime Maussan#Autonomous National University of Mexico (UNAM)#DNA#US Congress#Mexico#Cusco#Peru#Ryan Graves#Americans for Safe Aerospace#ufology#UFO conspiracy theory
3 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
New Year's Song: Angels They Will Always Be: Hind Rajab, Sidra Hassouna & 17 Thousand More Children! By É. Roscha (Feat.)
#youtube#us universities#usa#mexico#canada#francesca albanese#united nations#us politics#human rights#free palestine#save palestine#i stand with palestine#palestinian genocide#all eyes on palestine#brazil#gaza genocide#genocide#stop the genocide#seresta#serenata#hind rajab#sidra hassouna#poetry
0 notes
Text
youtube
#missolatino#miss universe venezuela#missosology#miss grand international#มิสยูนิเวิร์สไทยแลนด์ 2024#hector cermeño#miss universe indonesia#miss universe 2024#youtube#miss universe mexico 2024 preliminar#Masculinity with Responsibility#Mustafa Galal Elezali#Cao Xuân Tài#Daniel Georgievski#Jin Kyu Kim#Aditya Khurana#Jin Wook Kim#Sergio Alejandro Azuaga Piñango#National costume competition#International male beauty pageant#swimwear competition#Mister Universe competition#Candidates#Official Candidates#Swimwear#Portraits#Pageant#Pageantry#International Pageantry#Male Pageant
1 note
·
View note
Text
Why we should learn from Mexican feminists
#school: university of texas el paso#publication: the prospector#year: 2023#genre: opinion#subject matter: national#subject matter: texas#subject matter: el paso#subject matter: mexico
0 notes
Video
youtube
Mexico Top University IQ Test #iqtest #freeiqtest #quiz #quiztime #quizg...
#youtube#IQ Test available for National Autonomous University of Mexico Tecnologico de Monterrey Monterrey Institute of Technology and Higher Educati
0 notes
Text
Royal and Pontifical University of Mexico, born in 1551, shaped by imperial whims, survived closures, and morphed into the National University. A saga of conquest, commitment, and bureaucratic flair unfolds over 471 years.
0 notes
Text
Art Sense Ep. 115: Museums of Tomorrow Roundtable
In April of this year, the Museums of Tomorrow Roundtable brought nearly two dozen museum directors from around the world together in Silicon Valley to discuss the evolving role of technology in museums. As dialogs between museum directors and technology leaders in Silicon Valley evolved, it became apparent that planning for the use of artificial intelligence had become a critical need.
On today’s episode, I’m honored to be joined by four museum executives who are an active part of these conversations about the future of museums:
Thomas P Campbell Director and CEO of the Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco
Seb Chan Director & CEO at the Australian Centre for the Moving Image in Melbourne, Australia
Amanda de la Garza Director General of Visual Arts at the National Autonomous University of Mexico in Mexico City and head of its University Museum of Contemporary Art
Suhanya Raffel Executive Director, M+ Museum in Hong Kong
#2023#Seb Chan#Suhanya Raffel#Amanda de la Garza#Thomas P Campbell#Australian Centre for the Moving Image#Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco#Visual Arts at the National Autonomous University of Mexico#M+
0 notes
Text
Atomic Secrets: The Scientists Who Built The Atom Bomb 💣
Science and the military converged under a cloak of secrecy at Los Alamos National Laboratory. As part of the Manhattan Project, Los Alamos — both its very existence and the work that went on there — was hidden from Americans during World War II.
Many of the thousands of scientists on the project were not officially aware of what they were working on. Though they were not permitted to talk to anyone about their work, including each other, by 1945 some had figured out that they were in fact building an atomic bomb.
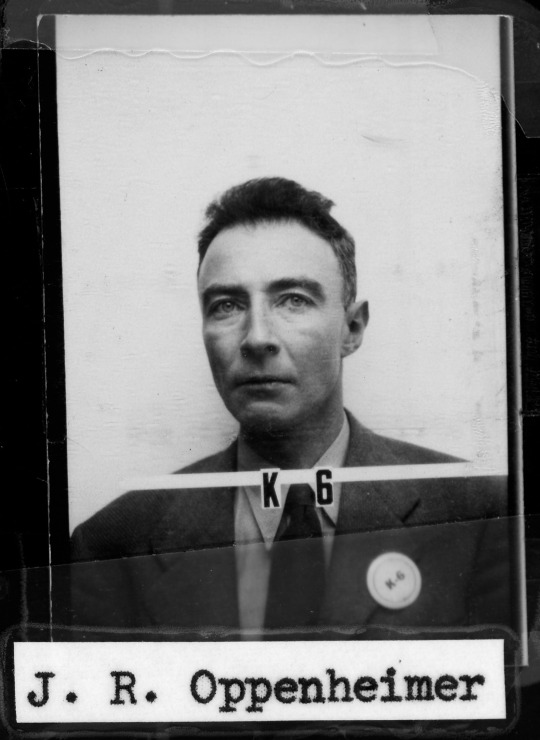

In 1943 J. Robert Oppenheimer was named the director of the Bomb Project at Los Alamos, a self-contained area protected -- and completely controlled -- by the U.S. Army. Special driver's licenses had no names on them, just ID numbers. Credit: Courtesy of the Los Alamos National Laboratory Archives

Robert Oppenheimer's wife Kitty was not above scrutiny. All who were affiliated with the project -- and their spouses -- were thoroughly screened and had a security file with the FBI. Credit: Courtesy of the F.B.I.
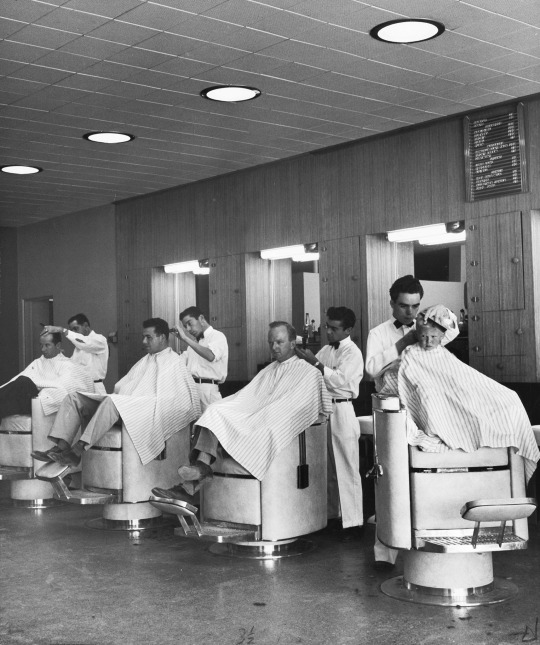

Less than a year after Oppenheimer proposed using the remote desert site for the laboratory, Los Alamos was already home to a thousand scientists, engineers, support staff… and their families. By the end of the war the population was over 6,000, and the compound included amenities like this barber shop. Credit: Time Life/Getty Images

Atomic Bomb Project employees having lunch at Los Alamos. Though food was often in scant supply, residents made the best of life in their isolated community by putting on plays and organizing Saturday night square dances. Some singles’ parties in the dormitories reportedly served a brew of lab alcohol and grapefruit juice, cooled with dry ice out of a 32-gallon GI can. Credit: Copyright Bettmann/CORBIS
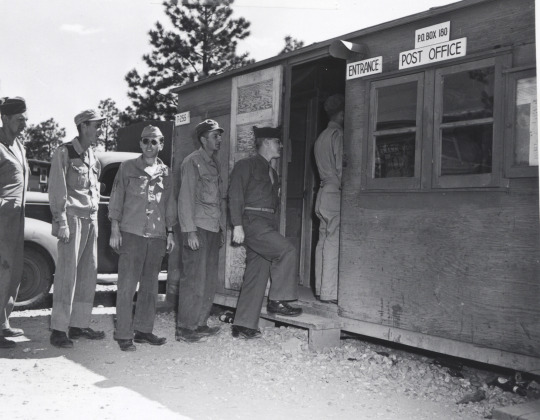

Completely self-contained, the Los Alamos facility did not officially exist in its early years except as a post office box. Scientists’ families were mostly kept in the dark about the nature of the project, learning the truth only after the bomb was dropped on Hiroshima. Credit: Courtesy of the Los Alamos National Laboratory Archives

Credited with inventing the cyclotron, University of California-Berkeley physicist Ernest Lawrence (squatting, center) looks on as Robert Oppenheimer points out something on the 184” particle accelerator. Harvard University supplied the cyclotron that was used to develop the atomic bomb. Credit: Copyright CORBIS
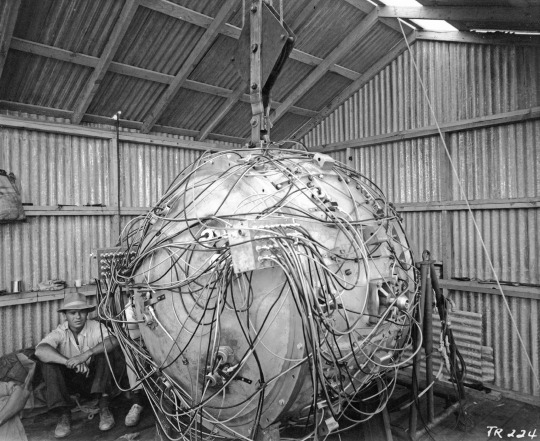

The Trinity bomb was the first atomic bomb ever tested. It was detonated in the Jornada del Muerto (Dead Man’s Walk) Desert, near Alamogordo, New Mexico, on July 16, 1945. The test was a resounding success. The United States would drop similar bombs on Japan just three weeks later. Credit: Courtesy of the Los Alamos National Laboratory Archives

Oppenheimer and General Leslie Groves inspect the melted remnants of the 100-foot steel tower that held the Trinity bomb. Ensuring that the testing of a bomb with unknown strength would remain completely secret, the government chose a location that was so remote they had to import their water from over 150 miles away. Credit: Copyright CORBIS

Oppenheimer and General Leslie Groves stand in front of a map of Japan, just five days before the bombing of Hiroshima. Credit: Copyright CORBIS

Though there was no evidence that Oppenheimer had betrayed his country in any way, several officials called his loyalty into question in the Cold War environment of 1954. After being subjected to months of hearings, “the most famous physicist in the world” eventually lost his government security clearance. Credit: Reprinted courtesy of TIME Magazine
#Atomic Secrets#Scientists#Atomic Bomb#American 🇺🇸 Experience#NOVA | PBS#Los Alamos National Laboratory#Manhattan Project#World War II#J. Robert Oppenheimer#Katherine Oppenheimer#New Mexico#Hiroshima | Nagasaki#University of California-Berkeley#Harvard University#Jornada del Muerto (Dead Man’s Walk) Desert 🐪#Alamogordo New Mexico#General Leslie Groves#Japan 🇯🇵#TIME Magazine
21 notes
·
View notes
Text

In a landmark move to position Mexico as a global leader in science and technology, President Claudia Sheinbaum announced the creation of the National Center for Semiconductor Design “Kutsari”. The initiative, named after the Purépecha word for “sand,” symbolizes the raw material used in semiconductor production and underscores Mexico’s ambition to become a key player in the high-tech industry.
The Kutsari Project will unite scientists and researchers from leading public institutions, including the National Institute of Astrophysics, Optics, and Electronics (INAOE), the Center for Research and Advanced Studies (CINVESTAV), the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM), and the National Polytechnic Institute (IPN). Headquartered in Puebla, Jalisco, and Sonora, the center will focus on designing cutting-edge semiconductors for industries such as automotive, medical equipment, and household appliances.
To support this effort, the Mexican government will reform the Federal Law for the Protection of Industrial Property (LFPPI) to streamline patent processes, reducing approval times from over four years to three. A provisional patent system will also be introduced to protect innovations and prevent plagiarism.
The project is part of the broader Plan Mexico, which aims to strengthen domestic production and attract foreign investment. By 2027, the Kutsari Center aims to consolidate its design capabilities, with plans to expand into semiconductor manufacturing and assembly by 2030. An Accelerated Training Program will also be launched to develop skilled designers and support public and private sector collaboration.
“This initiative is a testament to Mexico’s scientific talent and our commitment to innovation,” said President Sheinbaum. “We are not just designing semiconductors; we are building a future where Mexico is a global technological power.”
#🇲🇽#mexico#STEM#Claudia Sheinbaum#National Center for Semiconductor Design#kutsari#semiconductor#national institue of astrophysics optics and electronics#INAOE#Center for Research and Advanced Studies#CINVESTAV#National Autonomous University of Mexico#UNAM#National Polytechnic Institute#IPN#puebla#jalisco#sonora#plan mexico
0 notes
Text
Miss Universe National Costume 2024, Part 2!
Splitting this off into a new post so I'm not clogging up everyone's dash quite as much.

Miss Malta is some sort of environmental protection Sailor Scout. I think the giant bow would look better on the back of the skirt but otherwise this is solid.

It has just come to my attention that I skipped over Miss Albania and several other A/B countries, back at the beginning. I sincerely apologize! She went to all this trouble putting together a Fifth Element cruise ship passenger costume, and I nearly missed it.

Miss Armenia, in what even I have to admit would be a legit Princess Leia fit.

Miss Bahrain, adding some green to her Gold And Vaguely Historical look, along with what is either a comically large prop chalice or an upside-down lamp.

Miss Bangladesh appears to believe that adding two plush tigers from the toy store around the corner from the pageant venue will conceal the fact that she is just wearing a tiger-print evening dress. Miss Bangladesh is incorrect.

Miss Belgium. Girl. No.

Miss Belize let the seventh-grade art class do her whole costume, which was a bold choice.
Okay, I think that's everyone I missed! Back to alphabetical order. And I should have to rely less on shitty screenshots, now. Some countries were benefiting from the low resolution, tbh.

Kind of feel like Miss Maldives had a luggage mishap and she's just wearing the outfit she packed for a slightly dressy dinner.

Miss Martinique's costume would honestly have looked better in the shitty screencap version. The construction is... bad. It's bad.

Feel like we're in a little bit of slump here. Miss Mauritius did not stick enough butterfly appliqués to her gown to conceal that it is, in fact, just a regular evening gown.

Slump officially over! We are so back. Everyone say thank you, Miss Mexico.

I would like this better if it had just committed to the giant skirt and not felt the need to make it a Sexy Miniskirt look. Sorry, Miss Moldova.

Miss Mongolia wanted to stand out from all the other gold armor on stage, so she decided to a) wear cooler armor and b) bring a bow and arrow instead of a sword. Great work, Miss Mongolia.

Starting to feel like I'm picking on the smaller countries that probably don't have a huge pageant culture or the budget for really elaborate costumes, but on the other hand Miss Montenegro's costume is super low-effort AND the fabrics look cheap, so what am I supposed to do?

Okay, this looks like a pretty standard Miss Universe Sexy Bird, yes? Well, THIS is how Miss Myanmar entered the stage:


She had to fight her way out of that thing! God only knows what the visibility was like in there.

I think the hat is doing most of the heavy lifting to keep Miss Namibia's costume from being Just An Evening Dress, sadly.

Oh, yikes. It's more obvious in motion but Miss Nepal's bodice looks like it's made of craft foam and it fits real weird. The rest of it looks a little like she got together with Miss Cyprus and a pile of tablecloths for a sewing bee last night, I'm sorry to say.

Miss Netherlands has chosen a Tribute to Delft. I think if I were in charge of this costume I would do a much fuller skirt that falls from the waist, instead of the weird trumpet-skirt-with-hoop we've got here. And, obviously, I would make the windmill on the bodice actually spin.

It looks like she's having some issues keeping the wings and peplum in place, but I really like Miss New Zealand's costume from a design perspective. It at least slightly resembles the bird it's supposed to be (New Zealand fantail) and I think the feather pattern is meant to be in a Maori art style.

Miss Nicaragua is a Sexy Cathedral, which I think might be a Miss Universe first and is definitely a big old step closer to drag.
Okay, pausing here to get the next batch ready.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

"Palestinian resistance is not terrorism"
Stencil seen in the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM) in Mexico City
4K notes
·
View notes