#National Space Technology Laboratories
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

"View of the Saturn V S-IC-5 (first) flight stage static test firing at the S-IC-B1 test stand at the Mississippi Test Facility (MTF), Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Begirning operations in 1966, the MTF has two test stands, a dual-position structure for running the S-IC stage at full throttle, and two separate stands for the S-II (Saturn V third) stage. It became the focus of the static test firing program. The completed S-IC stage was shipped from Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) to the MTF. The stage was then installed into the 407-foot-high test stand for the static firing tests before shipment to the Kennedy Space Center for final assembly of the Saturn V vehicle. The MTF was renamed to the National Space Technology Laboratory (NSTL) in 1974 and later to the Stennis Space Center (SSC) in May 1988."
Date: August 1, 1967
NASA ID: 6758560
#S-IC#Apollo 10#Saturn V#SA-505#Rocket#NASA#Apollo Program#National Space Technology Laboratories#NSTL#Test Stand#John C. Stennis Space Center#Stennis Space Center#SSC#Hancock County#Mississippi#Rocketdyne F-1#F-1#Rocket Engine#August#1967#my post
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
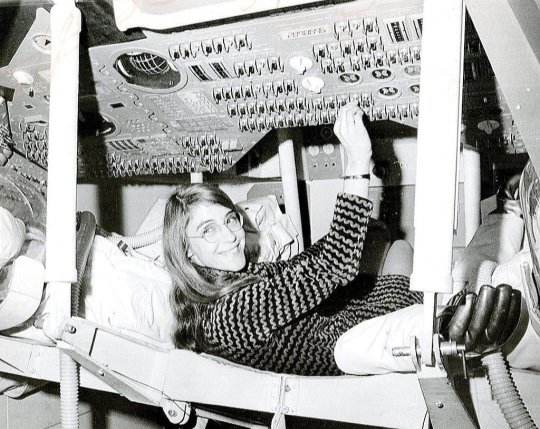
COMPUTER-SOFTWARE ENGINEERING RISING IN THE AMERICAN SPACE PROGRAM.
PIC INFO: Spotlight on American computer programmer Margaret Hamilton (b. 1936), at the MIT Instrumentation Laboratory, during her time as lead flight software engineer for the Apollo space mission, c. 1969.
MINI-BIO: "She and her team wrote the code for the inflight software of the spacecraft, and her work contributed to the safe landing of Apollo 11 on the moon in 1969."
Sources: www.thenation.com/article/archive/peoples-history-of-personal-computing-joy-lisi-rankin-review-silicon-valley-bros & X.
#Margaret Hamilton NASA#Apollo#Margaret Hamilton Software Engineer#Software Engineer#Apollo Mission#Apollo Space Mission#Apollo Program#USA#Apollo 11#1960s#60s#Sixties#Massachusetts Institute of Technology#Computer Scientist#Computer Science#MIT Instrumentation Laboratory#MIT#American Style#United States#1969#Space Program#Margaret Hamilton#NASA#National Aeronautics and Space Administration
4 notes
·
View notes
Text



NEW YORK (AP) — Leap year. It’s a delight for the calendar and math nerds among us.
So how did it all begin and why?
Have a look at some of the numbers, history and lore behind the (not quite) every four year phenom that adds a 29th day to February.
BY THE NUMBERS
The math is mind-boggling in a layperson sort of way and down to fractions of days and minutes.
There’s even a leap second occasionally, but there’s no hullabaloo when that happens.
The thing to know is that leap year exists, in large part, to keep the months in sync with annual events, including equinoxes and solstices, according to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory at the California Institute of Technology.
It’s a correction to counter the fact that Earth’s orbit isn’t precisely 365 days a year.
The trip takes about six hours longer than that, NASA says.
Contrary to what some might believe, however, not every four years is a leaper.
Adding a leap day every four years would make the calendar longer by more than 44 minutes, according to the National Air & Space Museum.
Later, on a calendar yet to come (we’ll get to it), it was decreed that years divisible by 100 not follow the four-year leap day rule unless they are also divisible by 400, the JPL notes.
In the past 500 years, there was no leap day in 1700, 1800 and 1900, but 2000 had one.
In the next 500 years, if the practice is followed, there will be no leap day in 2100, 2200, 2300 and 2500.
The next leap years are 2028, 2032, and 2036.
WHAT WOULD HAPPEN WITHOUT A LEAP DAY?
Eventually, nothing good in terms of when major events fall, when farmers plant and how seasons align with the sun and the moon.
“Without the leap years, after a few hundred years we will have summer in November,” said Younas Khan, a physics instructor at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“Christmas will be in summer. There will be no snow. There will be no feeling of Christmas.”


WHO CAME UP WITH LEAP YEAR?
The short answer: It evolved.
Ancient civilizations used the cosmos to plan their lives, and there are calendars dating back to the Bronze Age.
They were based on either the phases of the moon or the sun, as various calendars are today. Usually they were “lunisolar,” using both.
Now hop on over to the Roman Empire and Julius Caesar.
He was dealing with major seasonal drift on calendars used in his neck of the woods. They dealt badly with drift by adding months.
He was also navigating a vast array of calendars starting in a vast array of ways in the vast Roman Empire.
He introduced his Julian calendar in 46 BCE.
It was purely solar and counted a year at 365.25 days, so once every four years an extra day was added.
Before that, the Romans counted a year at 355 days, at least for a time.
But still, under Julius, there was drift. There were too many leap years.
"The solar year isn’t precisely 365.25 days. It’s 365.242 days," said Nick Eakes, an astronomy educator at the Morehead Planetarium and Science Center at the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill.
Thomas Palaima, a classics professor at the University of Texas at Austin, said adding periods of time to a year to reflect variations in the lunar and solar cycles was done by the ancients.
The Athenian calendar, he said, was used in the fourth, fifth and sixth centuries with 12 lunar months.
That didn’t work for seasonal religious rites. The drift problem led to “intercalating” an extra month periodically to realign with lunar and solar cycles, Palaima said.
The Julian calendar was 0.0078 days (11 minutes and 14 seconds) longer than the tropical year, so errors in timekeeping still gradually accumulated, according to NASA. But stability increased, Palaima said.
The Julian calendar was the model used by the Western world for hundreds of years.
Enter Pope Gregory XIII, who calibrated further. His Gregorian calendar took effect in the late 16th century.
It remains in use today and, clearly, isn’t perfect or there would be no need for leap year. But it was a big improvement, reducing drift to mere seconds.
Why did he step in? Well, Easter.
It was coming later in the year over time, and he fretted that events related to Easter like the Pentecost might bump up against pagan festivals.
The pope wanted Easter to remain in the spring.
He eliminated some extra days accumulated on the Julian calendar and tweaked the rules on leap day.
It’s Pope Gregory and his advisers who came up with the really gnarly math on when there should or shouldn’t be a leap year.
“If the solar year was a perfect 365.25 then we wouldn’t have to worry about the tricky math involved,” Eakes said.
WHAT’S THE DEAL WITH LEAP YEAR AND MARRIAGE?
Bizarrely, leap day comes with lore about women popping the marriage question to men.
It was mostly benign fun, but it came with a bite that reinforced gender roles.
There’s distant European folklore.
"One story places the idea of women proposing in fifth-century Ireland, with St. Bridget appealing to St. Patrick to offer women the chance to ask men to marry them," according to historian Katherine Parkin in a 2012 paper in the Journal of Family History.
Nobody really knows where it all began.
In 1904, syndicated columnist Elizabeth Meriwether Gilmer, aka Dorothy Dix, summed up the tradition this way:
“Of course people will say ... that a woman’s leap year prerogative, like most of her liberties, is merely a glittering mockery.”
The pre-Sadie Hawkins tradition, however serious or tongue-in-cheek, could have empowered women but merely perpetuated stereotypes.
The proposals were to happen via postcard, but many such cards turned the tables and poked fun at women instead.
Advertising perpetuated the leap year marriage game. A 1916 ad by the American Industrial Bank and Trust Co. read thusly:
“This being Leap Year day, we suggest to every girl that she propose to her father to open a savings account in her name in our own bank.”
There was no breath of independence for women due to leap day.
SHOULD WE PITY THE LEAPLINGS?
Being born in a leap year on a leap day certainly is a talking point. But it can be kind of a pain from a paperwork perspective.
Some governments and others requiring forms to be filled out and birthdays to be stated stepped in to declare what date was used by leaplings for such things as drivers licenses, whether February 28 or March 1.
Technology has made it far easier for leap babies to jot down their February 29 milestones, though there can be glitches in terms of health systems, insurance policies, and with other businesses and organization that don’t have that date built in.
There are about 5 million people worldwide who share the leap birthday out of about 8 billion people on the planet.
Shelley Dean, 23, in Seattle, Washington, chooses a rosy attitude about being a leapling.
Growing up, she had normal birthday parties each year, but an extra special one when leap years rolled around.
Since, as an adult, she marks that non-leap period between February 28 and March 1 with a low-key “whew.”
This year is different.
“It will be the first birthday that I’m going to celebrate with my family in eight years, which is super exciting, because the last leap day I was on the other side of the country in New York for college,” she said. “It’s a very big year.”

#Leap Year#calendar#equinoxes#solstices#Jet Propulsion Laboratory#California Institute of Technology#NASA#National Air & Space Museum#Julius Caesar#julian calendar#Pope Gregory XIII#gregorian calendar#Elizabeth Meriwether Gilmer#Dorothy Dix#leaplings
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Improving Climate Predictions By Unlocking The Secrets of Soil Microbes
— By Julie Bobyock, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory | February 5, 2024
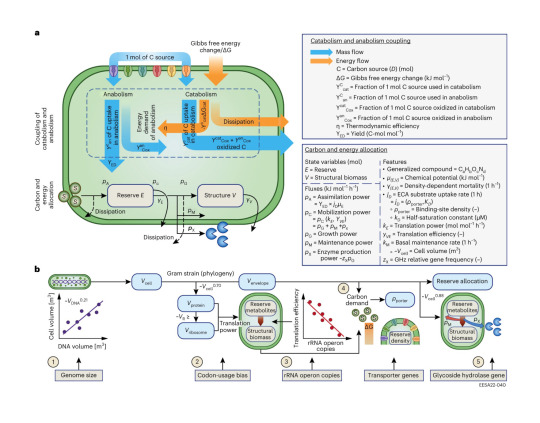
Overview of DEBmicroTrait. Credit: Nature Microbiology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41564-023-01582-W
Climate models are essential to predicting and addressing climate change, but can fail to adequately represent soil microbes, a critical player in ecosystem soil carbon sequestration that affects the global carbon cycle.
A team of scientists led by the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has developed a new model that incorporates genetic information from microbes. This new model enables the scientists to better understand how certain soil microbes efficiently store carbon supplied by plant roots, and could inform agricultural strategies to preserve carbon in the soil in support of plant growth and climate change mitigation.
"Our research demonstrates the advantage of assembling the genetic information of microorganisms directly from soil. Previously, we only had information about a small number of microbes studied in the lab," said Berkeley Lab Postdoctoral Researcher Gianna Marschmann, the paper's lead author.
"Having genome information allows us to create better models capable of predicting how various plant types, crops, or even specific cultivars can collaborate with soil microbes to better capture carbon. Simultaneously, this collaboration can enhance soil health."
This research is described in a new paper that was recently published in the journal Nature Microbiology. The corresponding authors are Eoin Brodie of Berkeley Lab, and Jennifer Pett-Ridge of Lawrence Livermore National Lab, who leads the "Microbes Persist" Soil Microbiome Scientific Focus Area project.
Seeing the Unseen: Microbial Impact on Soil Health and Carbon
Soil microbes help plants access soil nutrients and resist drought, disease, and pests. Their impacts on the carbon cycle are particularly important to represent in climate models because they affect the amount of carbon stored in soil or released into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide during the process of decomposition.
By building their own bodies from that carbon, microbes can stabilize (or store) it in the soil, and influence how much, and for how long carbon remains stored belowground. The relevance of these functions to agriculture and climate are being observed like never before.
However, with just one gram of soil containing up to 10 billion microorganisms and thousands of different species, the vast majority of microbes have never been studied in the lab. Until recently, the data scientists had to inform these models came from only a tiny minority of lab-studied microbes, with many unrelated to those needing representation in climate models.
"This is like building an ecosystem model for a desert based on information from plants that only grow in a tropical forest," explained Brodie.
The World 🌎 Beneath Our Feet 🦶🦶
To address this challenge, the team of scientists used genome information directly to build a model capable of being tailored to any ecosystem in need of study, from California's grasslands to thawing permafrost in the Arctic. With the model using genomes to provide insights into how soil microbes function, the team applied this approach to study plant-microbiome interactions in a California rangeland. Rangelands are economically and ecologically important in California, making up more than 40% of the land area.
Research focused on the microbes living around plant roots (called the rhizosphere). This is an important environment to study because, despite being only 1-2% of Earth's soil volume, this root zone is estimated to hold up to 30-40% of Earth's carbon stored in soils, with much of that carbon being released by roots as they grow.
To build the model, scientists simulated microbes growing in the root environment, using data from the University of California Hopland Research and Extension Center. Nevertheless, the approach is not limited to a particular ecosystem. Since certain genetic information corresponds to specific traits, just as in humans, the relationship between the genomes (what the model is based on) and the microbial traits is transferable to microbes and ecosystems all over the world.
The team developed a new way to predict important traits of microbes affecting how quickly they use carbon and nutrients supplied by plant roots. Using the model, the researchers demonstrated that as plants grow and release carbon, distinct microbial growth strategies emerge because of the interaction between root chemistry and microbial traits.
In particular, they found that microbes with a slower growth rate were favored by types of carbon released during later stages of plant development and were surprisingly efficient in using carbon—allowing them to store more of this key element in the soil.
The Root of the Matter
This new observation provides a basis for improving how root-microbe interactions are represented in models, and enhances the ability to predict how microbes impact changes to the global carbon cycle in climate models.
"This newfound knowledge has important implications for agriculture and soil health. With the models we are building, it is increasingly possible to leverage new understanding of how carbon cycles through soil. This in turn opens up possibilities to recommend strategies for preserving valuable carbon in the soil to support biodiversity and plant growth at scales feasible to measure the impact," Marschmann said.
The research highlights the power of using modeling approaches based on genetic information to predict microbial traits that can help shed light on the soil microbiome and its impact on the environment.
#Biology 🧬 🧪#Ecology#Cell & Microbiology 🧫#Nanotechnology#Physics#Earth 🌍#Astronomy 🪐 🔭 & Space#Chemistry 🧪 ⚛️#Other Sciences#Medicine 💊#Technology#Phys.Org#Julie Bobyock | Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory 🥼 🧪#Almeda County | California | USA 🇺🇸
0 notes
Text
Top Ukrainian female Scientists, Doctors, Mathematicans, Economists, Artists, Athletes, Leaders, Astronauts, Military Leaders, etc.
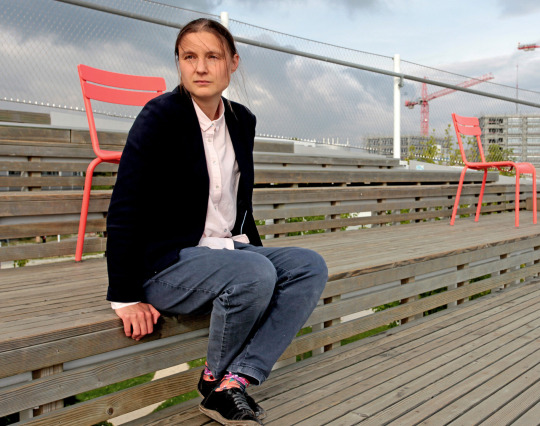

The Ukrainian mathematician Maryna Viazovska who won Fields Medal — the highest honor for a mathematician.
Selected few famous Ukrainian scientists
We decided to talk about outstanding Ukrainian women who've changed and continue to change the world of science to show that girls can do anything.
Maryna Viazovska, a mathematician
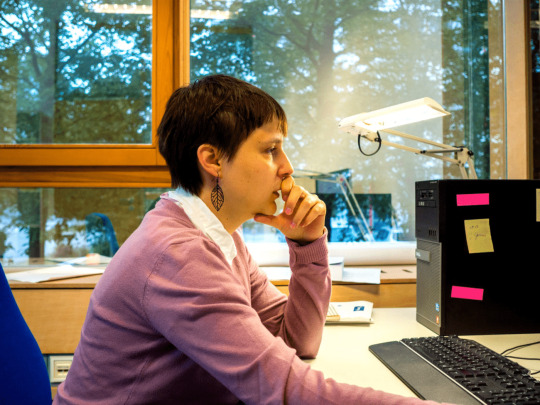

Ukrainian scientist, doctor of natural sciences. Ukrainian mathematician Maryna Viazovska, who currently works at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, received the Salem Prize 2016, which is extremely prestigious for mathematicians. The commission awarded the prize to Maryna Viazovska for her world-class discovery. Ukrainian solved a problem that scientists have been working on for more than 400 years, i.e. packing spheres in 8-dimensional space, and co-authored the one in 24-dimensional space. Previously, the problem of packing spheres was solved only for spaces with three or fewer dimensions.
Yuliia Bezvershenko, a physicist

Ukrainian scientist in theoretical physics, popularizer of science, public figure, Ph.D. of physic and mathematical sciences, Yuliia Bezvershenko is included in the list of TOP-20 Ukrainian women in STEM for 2018-2019. Yuliia deals with mathematical methods applied to the problems of dynamics of quantum systems in external fields and control of quantum systems. She is convinced and proves that one can practice theoretical physics with passion.
According to Yuliia, at one time she heard an important thing from her mentor: you can be yourself in any field! Therefore, one shouldn't be afraid of stereotypes and prejudices of others.
If you're a girl, a woman, no matter where, no matter how old you are, and your heart is in science, don't be afraid. Go there boldly. After all, nothing will stop a woman, ready to work and conduct scientific discoveries.
Mariia Bailiak, a biologist

Doctor of Biological Sciences, Associate Professor of Biochemistry and Biotechnology in Vasyl Stefanyk Precarpathian National University. Scientist Mariia Bailiak studies biochemistry and researches the influence of various plants and substances on the aging process. Mariia Bailiak's discoveries concern, for instance, the increase of stress resistance and the general condition of living organisms (and therefore, us and you, and it's good news: stress resistance doesn't hurt anyone), and anti-aging substances. Thanks to her intensive work, Mariia is in the Top 10 successful Ukrainian women scientists.
Olha Brovarets, a biophysicist

Ukrainian biophysicist, Doctor of Physic and Mathematical Sciences, winner of the Scopus Awards Ukraine in the nomination "Best team of scientists who achieved significant scientific results without Western collaborations" and the President of Ukraine Award for Young Scientists, and a leading researcher in the Department of Molecular and Quantum Biophysics Institute of Molecular Biology and Genetics of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine. Olha is the youngest doctor habilitatus in Ukraine; she became a doctor at 29. Olha is now 34 years old and she continues to study biophysics: her discoveries give an understanding of the mechanisms of cancer and many other diseases caused by mutations. It was Olha who calculated the pattern of mutations in DNA leading to cancer and many other diseases.
Nana Voitenko, a biologist

Professor, Doctor of Biological Sciences, neurobiologist, head of the department of sensory signaling of the Bohomolets Institute of Physiology of NAS of Ukraine. Nana Voitenko has been researching pain for more than 20 years. What do we know about pain? For most people on Earth, pain is something they'd like to get rid of as soon as possible if they feel it. Nana Voitenko deals with the nature of pain, as it occurs and spreads in the human's central and peripheral nervous systems. In the laboratory, Voitenko and her colleagues managed to develop an experimental treatment that affects only those cells involved in pain syndromes. Besides, Nana Voitenko is actively promoting science: she's a lecturer at the "Days of Science" initiative, was a lecturer at TED-x Kyiv in 2013, and the organizer of the "Week of Knowledge about the Brain." Science is close, and it's accessible to everyone.
Ella Libanova, an economist

Scientist in socioeconomics, demography, and labor economics, academician of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Doctor of Economics, Professor, Honored Economist of Ukraine. Ella Libanova is an academician-secretary of the economics department of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine and, by the way, the first and only female member of the presidium of the National Academy of Sciences for 102 years of its work. She teaches social statistics at the Faculty of Economics of the Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv; introduced a method for measuring human development at the region level, used by the State Statistics Service of Ukraine for annual calculations.
Nina Virchenko, a mathematician

Professor of the Department of Mathematical Analysis and Probability Theory, Doctor of Physic and Mathematical Sciences Nina Virchenko is one of the most famous Ukrainian mathematicians. She is the author of more than 500 scientific and methodological works, including 20 books published in Ukrainian, Russian, English, and Japanese. Nina Virchenko is recognized not only in Ukraine but also abroad; she's a member of the Australian, American, Belgian, Edinburgh, London mathematical societies. In the end, it's not surprising, because mathematics knows no boundaries and recognizes all the achievements, wherever you obtain them.
Nina Virchenko's fate wasn't easy: at 18 in 1948, she was sentenced to 10 years in the Gulag camps for preparing a "political conspiracy, revolt" and participating in the "Ukrainian-nationalist gang." Years in the camps didn't stop the future doctor from achieving her dreams. In 1964, she defended her Ph.D. and her Dr. habil. dissertation in Kyiv in 1988.
Nataliia Vynohrad, an epidemiologist

Epidemiologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences, Nataliia Vynohrad manages the Department of Epidemiology of Lviv National Medical University. She's an expert of the World Health Organization in responding to epidemic threats and the Ministry of Health of Ukraine on epidemiology, an adviser to the Ministry of Emergencies of Ukraine on anti-epidemic protection and biosafety. Agree, you can't find a more relevant profession in 2020-2021. Once an ordinary girl from a village in the Khmelnytskyi region, and now the author of 305 scientific papers, and 8 copyright certificates for inventions and patents of Ukraine, proves that nothing is impossible for a girl who knows what she wants.
Nataliia Polonska-Vasylenko, a historian

From the early 20th century until the end of her life in the 1970s, our first heroine studied the history and archeology of Ukraine, both in Ukraine and later in exile in Germany and the Czech Republic. In a historically troublesome time for Ukraine, she became one of the leading representatives of the state school in Ukrainian historiography, that is, she promoted the idea of independence and continuity of the Ukrainian historical process. Nataliia Polonska-Vasylenko is the author of almost 200 scientific works on the history of Zaporizhzhia and Southern Ukraine, which remain relevant to this day.
Valentyna Radzymovska, a biologist

One of the most prominent names in our history is Valentyna Radzymovska, a professor, doctor of medical and physiological sciences, founder of the Ukrainian school of physiologists and biochemists, and a public figure. The Soviet authorities repressed Valentyna Radzymovska for her political activities and participation in the Union for the Liberation of Ukraine in the 1930s. However, it didn't prevent her from becoming the author of more than 60 works on biochemistry, pathophysiology, pediatrics, psychoneurology, physiology, and phthisiology. Like the previous scientist in our article, she left Ukraine in 1945, emigrating first to Germany and then to the United States.
Radzymovska contributed hugely to the study of tuberculosis and its treatment in children.
Nina Morozhenko, a physicist

Although the sun is the closest star to us, it still hides many fascinating mysteries. Ukrainian astronomer, helio physicist, doctor of physic and mathematical sciences, author of 56 scientific works, Nina Morozhenko devoted her entire life to studying the structure of our guide light and the processes taking place on it. After all, everything happening on the Sun affects many areas of human activity. Without studying the sun, it's impossible to understand not only what the future holds for our civilization but also what is happening in space, i.e. on the distant stars the humanity is so eager to reach. Nina Morozhenko's scientific works on solar prominences were the first in the world and gave rise to scientific research by helio physicists from many countries. The Ukrainian researcher's significant contribution to the physics of the sun once again demonstrates that physics isn't a purely "male" science.
201 notes
·
View notes
Text
WHEN WILL WE BECOME A TYPE 1 CIVILIZATION??
Blog#453
Wednesday, November 13th, 2024.
Welcome back,
Human civilization has achieved some incredible things during its short reign on this planet. We’ve been to the Moon, we can create vaccines to fight-off pandemics and we’re even on the cusp of having flying cars. Oh, and we’ve had quite the effect on our planet’s climate. Not exactly an achievement to be proud of, but at least it shows that we’re a big deal, right?

Wrong. We’re not even a “Type 1” civilization and we won’t be until about 2371 according to NASA scientists. Even then it’s not inevitable; we could be on the cusp of being filtered-out of existence if we can’t stop destroying our own planet.
A paper published online and supported by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory states that to reach even the basic level of a “Kardashev Type 1 civilization” we must do two things:

Develop more advanced technology and share it with all responsible nations.
Make renewable energy accessible to all parts of the world.
We’re talking governments and private businesses, and we’re talking cooperation. Otherwise, warn the authors, humanity cannot avoid the “Great Filter” and will not reach the status of a basic civilization.

As defined in 1964 by Nikola Kardashev, a Soviet astronomer, a Type 1 civilization is able to store and use all the energy available on its planet. We’re not even close to that. He actually defined three types of civilizations to aid those searching for signs of life elsewhere in our galaxy and beyond:
Type 1 or “planetary” civilization: has harnessed all major forms of energy available from its home planet and also includes the energy received by the home world from its parent star.

Type 2 or “stellar” civilization: can obtain and store all the energy its parent star releases, probably through things like Dyson spheres. Power consumption is ten orders of magnitude more than a Type 1 civilization.
Type 3 or “galactic” civilization: can access and control much of the energy the entire galaxy generates. Any civilization that can do that can probably also manipulate space-time itself, creating wormholes to enable travel to any point in the Universe, say the authors.
Originally published on https://www.forbes.com
COMING UP!!
(Saturday, November 16th, 2024)
"HOW MANY GALAXIES ORBIT THE MILKY WAY??"
#astronomy#outer space#alternate universe#astrophysics#universe#spacecraft#white universe#space#parallel universe#astrophotography
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
The International Space Station (ISS) will be retired in 2030 after more than 32 years of continuous service. Naturally, there are questions regarding what will replace this station, which has served as a bastion for vital research and inter-agency cooperation in space. In the past, China has indicated that their Tiangong ("heavenly palace") space station will be a successor and rival to the ISS, offering astronauts from other nations an alternative platform to conduct research in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). As part of this plan, China recently announced plans to double the size of Tiangong in the coming years. This announcement was shared last Wednesday, October 4th, during the 74th International Astronautical Congress (IAC 2023) in Baku, Azerbaijan. According to the China Academy of Space Technology (CAST), three new modules will be added to Tiangong, which currently consists of the Tianhe Core Cabin Module (CMM) and two Laboratory Cabin Modules (LCM)—Wenhian ("Quest for the Heavens") and Mengtian ("Dreaming of the Heavens"). This expansion will be accompanied by extending the station's operational lifetime. According to the statement made by CAST, Tiangong will be in service for more than 15 years, 10 more years than previously announced. This means that China intends to keep Tiangong operational until 2037 or later, several years after the ISS is decommissioned and deorbited. As of the penning of this article, the station has been fully operational since late 2022 (a total of 894 days) and has been occupied for the past 764 days. The station has hosted 15 taikonauts (a maximum of three at a time) at orbital altitudes of 340 to 450 km (210 and 280 mi).
Continue Reading.
231 notes
·
View notes
Text
The bifacial solar cell, developed at the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), harvests reflected sunlight hitting the back of the device, offering an unconventional route to producing higher energy yields for less space and cost. Typical advances to solar cell efficiency rates centre on iterative improvements to the side facing the Sun. This new approach could boost the energy harvesting capabilities of solar panels beyond their theoretical limit. “This perovskite cell can operate very effectively from either side,” said Kai Zhu, a scientist at the Chemistry and Nanoscience Center at NREL who led the research. Current solar cell technologies, which use silicon as the semiconductor material, have an efficiency rate of around 26 per cent – higher than the 23 per cent achieved in lab tests by the front side of the new panel. The back side of the panel, however, achieves an efficiency of about 91-93 per cent of the front, which offers up to 20 per cent more power overall when harvesting reflected sunlight.
249 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Fabio Giuseppe Carlo Carisio
VERSIONE IN ITALIANO
«A primary objective of DARPA’s Biological Technologies Office (BTO) is to better ensure the health, and thereby the force readiness, of the country’s military service community. The COVID-19 pandemic, which rapidly spread worldwide from an initial outbreak in China at the end of 2019, highlights one of the most perilous vulnerabilities to deployed military personnel and civilians: lack of protection and medical countermeasures (MCMs) against endemic and emerging biothreats. DARPA’s investments in this space led. directly, with the biotechnology firm Moderna as a contracted performer on the program, to a first-ever human clinical trial with an RNA vaccine in 2019».
DARPA’s ADEPT Project on SARS Viruses
The project is called ADEPT (subtitle Advancing National Security Through Fundamental Research), it is signed by DARPA, that is, the very powerful military agency of the Pentagon: the Department of Defense of the United States of America.
DARPA is the acronym for Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. It is one of the most powerful and secret military research centers in the world that controls various biological laboratories at Fort Detrick, the best-equipped bacteriological weapons development center in the world.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
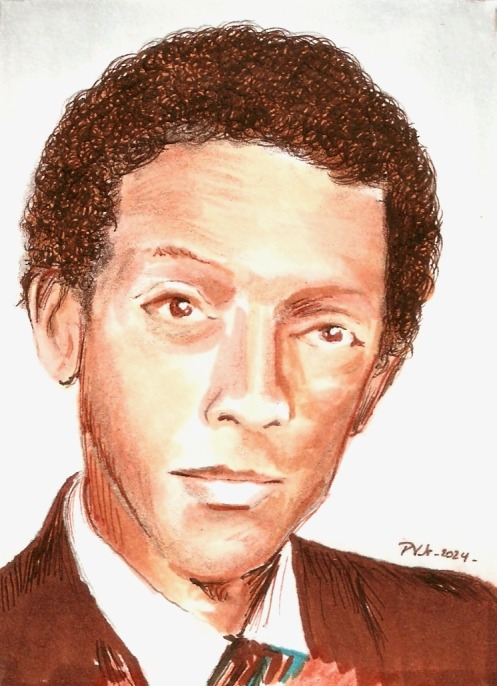

"I had no role models because nobody ever publicized them, not that they didn't exist. George Washington Carver and Percy Julian and others had preceded me in science, but nobody ever publicized their accomplishments, and, therefore, many of the minority students didn't know that they had a future in science because they figured it was something that was not for them."
After a bit of time away from this project to make room for convention appearances and other shows, I now return to the subject with a look at the life and accomplishments of physicist George Robert Carruthers, on this, what would have been his 85th birthday.
Born in 1939 Cincinnati, Carruthers's father was himself a civil engineer at Wright-Patterson AFB, but the family soon moved to the more rural location of Milford, Ohio. Carruthers was described as quiet and focused --intensely interested in space travel stories and comic books (my people!), and a devourer of the science articles in Collier's magazine (even penning a fan letter to Dr. Werner Von Braun, to which he received an unexpected and encouraging personal reply). At the age of ten Carruthers built his first telescope, constructed from lenses he obtained by mail order. After George's father died in 1952, the family moved to Chicago but his fascination with spaceflight did not diminish. Encouraged by wonderfully observant teachers, he eventually graduated from the University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign in 1960, then earned his MS in in nuclear engineering in 1962, and then landed his PhD in aeronautical and astronautical engineering in 1964.
While working towards his PhD, Carruthers worked as a researcher and teaching assistant, studying plasma and gases. In 1964, Carruthers took a postdoctoral appointment with the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) in Washington, D.C., focusing on far ultraviolet astronomy. In 1969 he received a U.S. patent for inventing a form of image converter; an instrument that detects electromagnetic radiation in short wavelengths. In 1970 his invention recorded the first observation of molecular hydrogen in outer space (which he described as "a very big deal at the time.")
Far and away (literally), Dr. Carruthers's greatest contribution to science is his development and construction of an ultraviolet electronographic telescope, which became the first (and to date still the only) astronomical instrument sent to the surface of the Moon; more properly known as the Far Ultraviolet Camera/Spectrograph. The camera was brought along on the Apollo 16 mission in 1972, set up to observe the Earth's geocorona (outermost atmosphere) from a vantage point never before possible. A short time later a variation on this very same camera was brought aboard Skylab to photograph the near approach of Comet Kohoutek, the first instance of a comet being recorded in ultraviolet. A flight backup of the Apollo 16 instrument, along with the original mission film canister, stood for many years as part of the lunar lander exhibit at the National Air & Space Museum, until it was later transferred to a more protected exhibit to guard against corrosion.
Dr. Carruthers's success and notoriety from the Apollo mission led to his creation of the Science & Engineers Apprentice Program, offering disadvantaged high school students the opportunity to work with scientists at the Naval Research Laboratory. His research into ultraviolet spectroscopy continued --in 1991 one of his ultraviolet cameras was used in multiple experiments aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-39). He retired from the NRL in 2002 and in 2003, was inducted into the National Inventor Hall of Fame. In 2013 was awarded the National Medal for Technology and Innovation by President Barack Obama. Dr. Carruthers died on Christmas Day, 2020.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
'The Amazon rainforest entered the dry season already with a water deficit due to the 2023 drought,' says expert
The extreme drought stems from the 2023 El Niño and the loss of Amazon rainforest areas

“The drought is killing the coffee plantations,” laments family farmer Gersi de Souza, a resident of Acrelândia in Acre state, one of the 3,978 Brazilian municipalities affected by the current drought. “Last year, we were already in a tough situation. And the situation has become more complicated this year,” he says. This is the worst drought in 70 years in Brazil, according to data from the National Center for Monitoring and Alerts of Natural Disasters (CEMADEN, in English) of the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation.
Researchers interviewed by Brasil de Fato believe that the phenomenon results from the influence of El Niño, which affected Brazil in 2023, and growing deforestation in the Amazon, which intensified during the Bolsonaro administration. “From 2019 to 2022, we lost 50,000 km² of primary forest, apart from secondary forest,” explains Luciana Gatti, coordinator of the greenhouse gas laboratory at the National Institute for Space Research (INPE, in Portuguese). Primary forests are the native forests of a biome, while secondary forests are those that have grown in a previously deforested area. “We haven’t recovered the 50,000 square kilometers of forest lost, and we haven’t zeroed out deforestation either,” she warns.
El Niño, characterized by the warming of the waters of the Pacific Ocean, has reduced rainfall in the Amazon rainforest, bringing a dry summer to the region in 2023. “We saw fish deaths, dolphins, riverine populations, and Indigenous peoples isolated and having difficulty accessing high-quality water and transportation,” says Helga Correa, a conservation specialist at the NGO WWF Brasil. In 2024, the drought in the Amazon came earlier than expected, without the biome recovering from the previous drought. “We didn’t have enough rain in the wet season, and we entered the dry season with a water deficit,” she explains.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#environmentalism#environmental justice#amazon rainforest#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

Space Shuttle Main Engine Lifted onto Test Stand A-1
"Space Shuttle Main Engine or SSME, weighing 6339 pounds, is lifted onto Test Stand A-1 at the National Space Technology Laboratories, marking the beginning of a new test phase. The huge stand is 238 feet tall -- the equivalent of a 16-story building. Following completion of facility activation and engine checkout by the NSTL team, the test program commenced May 19, 1975."
Date: 1975
Boeing Images: BI230657
#Space Shuttle Main Engine#SSME#Rocketdyne RS-25#RS-25#Rocket Engine#Space Shuttle#Orbiter#NASA#Space Shuttle Program#National Space Technology Laboratories#NSTL#Test Stand#John C. Stennis Space Center#Stennis Space Center#SSC#Hancock County#Mississippi#May#1975#my post
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
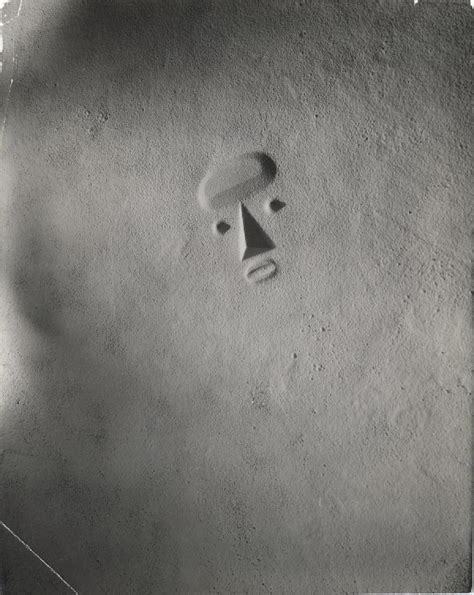


Sculpture to Be Seen From Mars, 1947
A ten-mile-long earthwork depicting an abstract human face, Noguchi’s Sculpture to Be Seen From Mars was, as the artist himself once put it, “a requiem for all of us who live with the atomic bomb” and alternatively “a flight of the imagination.” Prompted by the World War II atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, which horrified Noguchi—“he often spoke of his fear of atomic annihilation,” Hayden Herrera writes in Listening to Stone—he began thinking about end-of-mankind scenarios. “It was in 1945, wasn’t it, when we dropped the atomic bomb?” Noguchi once reflected. “All of us were concerned about our place on earth, and that it might be rather precarious.”
For Noguchi, the monumental work was intended to be “an eternal reminder to the rest of the solar system that the planet earth, seemingly bent on self-destruction, once had its civilizations,” writes Friedman in the Imaginary Landscapes catalogue, hailing it as the artist’s “most impressive memorial to the futility of war.” The work, as Friedman points out, was also Noguchi’s way of showing his respect and reverence for ancient and indigenous monumental forms, such as the pre-Columbian geometric earthworks in the Andes. “‘Earth sculpture’ is nothing new,” Noguchi said. “It’s just a new name for an old thing.”
The earthwork also connected to Noguchi’s ongoing interest in outer space and the cosmos. When the art critic Lucy Lippard asked Noguchi to use a photograph of the project in her 1983 book Overlay, paralleling contemporary art with prehistoric sites and symbols, Noguchi replied, “I recently saw a reproduction of a face which was found in the landscape of Mars taken by the Viking Satellite. I think it would be very appropriate to show this version along with mine. I have written to the Mars Research Laboratory asking for this image and will send it to you if you are interested.” The connection of rocks across the universe was not lost on the artist. “Ultimately,” Noguchi told Calvin Tomkins in The New Yorker in 1980, “I like to think that when you get to the furthest point of technology, when you get to outer space, what do you find to bring back? Rocks!”
An incredibly moving, visionary concept that, as Friedman notes, in many ways preceded the land art and conceptual art movements that would emerge and flourish in the second half of the twentieth century, Noguchi’s memorial to mankind was intended for “some desert, some unwanted area.” It was, as the artist put it, “a sculpture just to be seen from the air so that, when you come to a landing, you will see the sculpture there.” That Noguchi was concurrently working on the Jefferson National Expansion Memorial suggests he was balancing both a belief in America’s future technological prospects and an acknowledgment of the bleak potential for mankind to destroy the planet and itself. Sculpture to Be Seen From Mars is today only memorialized in a single photograph of a model Noguchi had formed out of sand.
#Sculpture to Be Seen From Mas#Isamu Noguchi#40s#earthwork#land art#monument#landscape#sculpture#mars#atomic bomb#hiroshima#war trauma#my upl#it reminds me of The Martian Chronicles so much...
9 notes
·
View notes
Text


Texas A&M researcher awarded NASA grant to study Martian dunes
Texas A&M University doctoral student Lauren Berger is using a prestigious NASA grant to study Mars' dune formations and uncover secrets about the planet’s environment and wind patterns
Sand dunes on Mars might hold the key to understanding the planet’s mysterious environment, and Texas A&M Geology & Geophysics Ph.D. student Lauren Berger is ready to unlock their secrets. Recently awarded a prestigious grant from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), Berger is diving into a project that could reveal new insights into the Red Planet’s wind patterns, atmospheric conditions and more. The FINESST (Future Investigators in NASA Earth and Space Science and Technology) grant supports innovative research in earth and planetary sciences.
Berger’s project, Insights into the Martian Environment Through Pattern Analysis of Compound Dunes, focuses on studying dune formations on Mars using high-resolution images captured by NASA's orbiting cameras. These “compound dunes”—dunes with smaller dunes layered on top—are well-documented on Earth but remain unexplored on Mars.
“The shape and pattern of these aeolian bedforms—geologic features shaped by wind—can tell us so much about the environment,” Berger explained. “By comparing compound dunes on Mars to those on Earth, we can uncover similarities and differences that could help us better understand the Martian surface and atmosphere.”
This groundbreaking research is supported by the FINESST program, which awarded funding to only 156 projects out of 1,120 submissions. With such a competitive selection process, winning this grant is both rare and significant.
“Lauren is a passionate and dedicated student,” said Dr. Julia Reece, Berger’s adviser and an assistant professor in the Department of Geology & Geophysics. “The FINESST grant is a great accomplishment for which she can be proud. It will allow her to focus on her research, strengthen her relationship with NASA, and grow as a leader in earth and planetary sciences.”
Berger, originally from New York, developed her passion for geology and wind-shaped landscapes during her undergraduate years at Occidental College in Los Angeles, where she earned a degree in geology. As part of her studies, she interned at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, mapping sand ripples on Mars. Her experiences with the National Park Service and NASA fueled her curiosity about aeolian bedforms, leading her to Texas A&M, where she found a program that matched her passion for studying planets and began working with Dr. Ryan Ewing, who now works at NASA’S Johnson Space Center.
As part of her research at Texas A&M with the FINESST grant, Berger’s first step is to identify all the compound dunes on Mars. Using high-resolution images from NASA's Context Camera and High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment, she will study their shapes and compare them to similar dunes on Earth to better understand how they form and what they reveal about the Martian environment.
“After years of looking at sand ripples as hazards for the Perseverance Rover, which is a NASA robot exploring Mars and searching for signs of past life, I wanted to dive deeper into the science behind them,” Berger said.
Dr. Marion Nachon, the principal investigator for the research project and an associate research scientist in the department, has been a key mentor for Berger throughout her work. Nachon emphasizes how rare and valuable the FINESST grant is for young researchers, offering a unique opportunity to advance their careers.
“With this highly competitive FINESST grant award, Lauren is getting an exceptional opportunity to pursue her growth as a motivated and promising scientist,” Nachon said. “She’s reaching for the stars and planets!”
TOP IMAGE: Lauren Berger stands next to a glacier in Iceland during the 2021 SAND-E Mission (Semi-Autonomous Navigation for Detrital Environments), which explored Mars-like terrain to examine how sediments change upriver versus downriver and to test rover science operations and navigation in those environments. Credit Lauren Berger
LOWER IMAGE: Lauren Berger collects grain-size samples of sand outside the Algodones Dune Field in California. Credit Lauren Berger
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just ordered this after having added it to wish list last year. Insomnia, pain, it was the perfect time to order a book with money I really needed to save for the upcoming heating bill. ;D But, hey, book was about 20% off, got free shipping, and there was a seven dollar gift card balance I didn't know I had that amazon applied to it. I'm going to call it a wise order. ;D

Nuclear Rockets: To the Moon and Mars Paperback – April 16, 2023 by Manfred "Dutch" von Ehrenfried (Author) 4.0 out of 5 stars (2) See all formats and editions So why is NASA refocusing its efforts on Nuclear Thermal Propulsion now, when chemical propulsion is so well established for human spaceflight? The reason is that future proposed flights are getting much longer and studies have shown that long-duration, weightless spaceflight has a lot of deleterious effects on the human body. When considering a flight to Mars takes a minimum of 2-3 years roundtrip, anything we can do to shorten the total mission time is highly desirable; if not mandatory. The longer the mission, the more exposure to galactic cosmic radiation, solar particles and coronal mass ejections, medical problems, and potential emergencies. A first-generation nuclear cryogenic propulsion system could propel human explorers to Mars more efficiently than conventional spacecraft, reducing the crews' exposure to harmful space radiation and other effects of long-term space missions. It could also transport heavy cargo and science payloads. A nuclear rocket engine uses a nuclear reactor to heat hydrogen to very high temperatures, which expands through a nozzle to generate thrust. Nuclear rocket engines generate higher thrust and are more than twice as efficient as conventional chemical rocket engines; just what’s needed for the crew to better survive the long-duration missions to Mars. In 1959, NASA replaced the Air Force in the development of the nuclear rocket and the mission changed from a nuclear missile to a nuclear rocket for long-duration space flight. Working with the DOE National Laboratories they worked on various research projects for 17 years including the Rover, NERVA, Kiwi, Pewee, and Phoebus rockets. In the late 1960s, the rising cost of the Vietnam War put increased pressure on budgets. It was determined that the Apollo program did not need nuclear rockets. Over the years, Congress support for the nuclear thermal propulsion projects including the Saturn upper stage, lunar and Mars missions, and the "Grand Tour" of the Solar System waned; nuclear rocket efforts were canceled in 1973. Now, there is renewed interest in picking up from those early efforts to produce nuclear rockets using state-of-the-art technology for deep space missions. NASA, DOD, and DARPA have teamed up to let contracts to many aerospace companies in order to define the best designs for nuclear thermal propulsion and nuclear fission power for surface energy applications. This book covers the past and present efforts that will lead to supporting near future cis-lunar and Mars missions. " Publisher : Independently published (April 16, 2023) Language : English Paperback : 270 pages ISBN-13 : 979-8377421252 Item Weight : 1.22 pounds Dimensions : 6.69 x 0.64 x 9.61 inches
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

a terra incognita introduction
cast: jake ✗ fem.reader
synopsis: as the world entered the middle of the 21st century, many things have changed for the better or for worse in the newly united korea peninsula: the preparation for the succession of the new conglomerates of the past decade, the uprising of deviant androids, and the new layer of life shield by walls of codes. in the middle of it, two beings are trying to understand each other and the situation of the world they live in; an unknown territory
genre: cyberpunk, cyber noir, psychological thriller, science fiction, dystopian future, politics and philosophies regarding artificial intelligence and humanity, romance, drama, angst, mature content (war and revolution, explicit smut)
based on: video game cyberpunk 2077 (2020) and detroit: become human (2018), anime serial experiments lain (1998), and tv show succession (2018-2023)
masterlist

united korea
the united republic of korea (known as "united korea") is an east asia nation on the korean peninsula. as a result of the reunification agreement back in 2025 of the former north and south korea, the state has now prospered in terms of sociopolitical and economic issues from the korean war. it now excels technologically as one of the firsts in the world to introduce commercialized androids along with other east asian countries such as japan and china. in the aftermath of the social media collapse and the cyber world war of 2027-2030, the private conglomerates of the state have released a new way to connect to the information superhighway.
FLAG

(flag link to r/alternatehistory on reddit)
INFORMATION
capital cities: neo seoul | neo pyongyang
population: 65.5 million
language: korean | english | japanese | chinese
>> HISTORY
>> GEOGRAPHY
>> GOVERNMENT
>> SOCIETY
>> ECONOMY
>> MILITARY
>> MAJOR CITIES
neo seoul
one of the capital cities of united korea and the former capital of south korea, neo seoul is a metropolis for the state's bustling life from the most traditional to the most modern. neo seoul is known for six districts that are divided by the han river flowing in the middle, known as the division of north seoul and south seoul
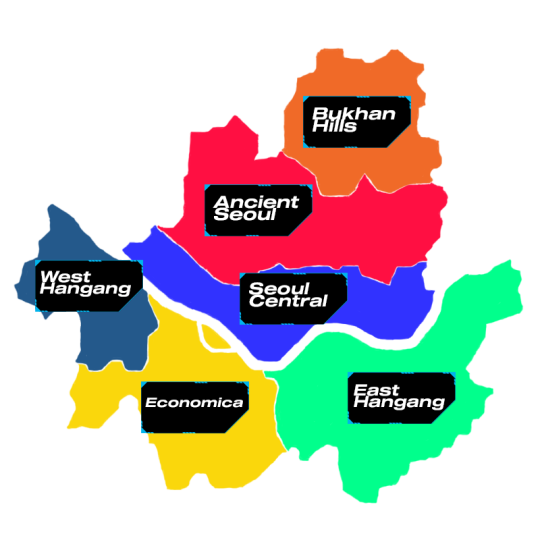
north seoul encapsulates the traditional side of neo seoul and the center for the city's and state's government administration
south seoul lies the center of neo seoul's economy where conglomerates build their headquarters. a distinct living cost gap can be seen to compare those living in the north and those in the south where it is connected to incheon, a major city of transportation with its international seaports and airport
neo pyongyang
one of the capital cities of united korea and the former capital of north korea, neo pyongyang is the capital of the parliament of united korea. it's located on the taedong river kilometers upstream from the yellow sea. it is known as the city where the declaration of unification was signed along with its establishment as half of the capitals of the unified countries. much of the population of neo pyongyang are citizens coming from the southern of the peninsula as they migrate to fill in the spaces and utilize materials. it is also a growing industrial hub where conglomerates built their factories, along with kaesong.
with the rise of deviancies from androids made by shim laboratories, journalists have made observations and assume that neo pyongyang is the main hub of the rebellion between androids and their creator (as one human equates to two androids), creating unrest between the two parties. yet, they also say that neo pyongyang is a better refuge for deviant androids than neo seoul.

taglist: @raeyunshm @endzii23 @fluffyywoo @camipendragon @hiqhkey @wccycc @cha0thicpisces @y4wnjunz @yeehawnana @beansworldsstuff @kimipxl @blurryriki @reallysmolrenjun @frukkoneeeeg
© writingmochi on tumblr, 2021-2025. all rights reserved
#enhypen imagines#enhypen smut#enhypen x reader#enhypen scenarios#enhypen angst#enhypen fanfiction#jake x reader#rsc: t.i.#cr: jake#cs: enhypen#sc: regina
37 notes
·
View notes