#Mysql Development services
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Magento Developer
Looking for expert Magento developers? Perfection Info offers tailored Magento e-commerce development, including custom themes, seamless integrations, and optimized solutions to boost online sales. Trust their top-rated team for a scalable, secure, and engaging e-commerce platform that meets your business goals.
#php mysql development#e-commerce solution provider from the netherland#graphics design services#shopify developer
0 notes
Text
Looking for professional MySQL Database Development Services Company in India, we deliver fully managed, enterprise-ready MySQL databases, supporting robust application development. Our talented developers build powerful and scalable web applications, ensuring high availability and dynamic scaling for websites with massive data and user volumes.
#MySQL Database Development Services Company in India#MySQL Database Development Services#MySQL Database Development Company#MySQL Database Development#Hire Dedicated MySQL Developer
0 notes
Text
🚀 Explore the Horizon of Virtualization with VPSDime! 🚀
Embark on a seamless journey through the realms of high-performance hosting without burning a hole in your pocket! With VPSDime, you unlock a treasure trove of features tailored to meet the evolving demands of developers and businesses alike. Here’s a sneak peek into what awaits you: 🖥️ Diverse Linux Distribution Support: Dive into a versatile hosting environment with a broad spectrum of…

View On WordPress
#Affordable Hosting#Developer-Friendly Hosting#Global Hosting Solutions#linux hosting#Offloaded MySQL Service#Virtual Private Server#VPSDime
0 notes
Text
Set up your own MySQL database on cloud within clicks! Every developer must try!?
#scloud#cloud computing#virtual machine#cloud services#app development#uhost#udb mysql#database#mysql#programming
0 notes
Text
In this highly competitive web and app development world ensuring data security is the prime concern. Several languages are used for creating different kinds of websites. But there are only a few languages that not only create outstanding websites and web apps but also ensure the high-level security of those websites. Today we are going to discuss about such two widely used programming languages i.e. PHP and MySQL.
To read full post, Visit: https://tech.eastsons.com/blog/how-much-does-it-cost-to-develop-a-php-website-with-mysql
#php website development cost#php website development services#php website development with MySQL#PHP With MySQL Is Use In Web Development
0 notes
Text
#nickoftimewebdesign#nftcreators#nikimoto#blockchain development#WXRP#StreetCode#GCP#Python3#PHP#ASP#AWS#CSS#MYSQL#Apache#Web As A Service#WaaS
0 notes
Text
Web & Mobile App Development

1 note
·
View note
Text
At Naarsoft we strive to get you the best innovative technology solution. We are not just a fastest growing Information Technology & Consulting Services company but also a family of skilled experts who aim to help global brands, enterprises and startups.
Known for trusted quality service
NaarSoft has an excellent team that works on diverse platforms, building projects of excellent quality. When you partner with NaarSoft, you will experience prompt and efficient service.
Innovation to achieve Excellence
Our team is not only technically proficient, but thinks out-of-the-box solutions walking the extra mile in understanding your business challenges & needs to deliver tailor-built, cost-effective, time-saving, and revenue-generating results.
#php web development#PHP Laravel#website development#Portal development services#PHP E-commerce Development#Custom PHP Programming Corporate#JSP (Java Server Pages)#Servlets#EJB#JTA(Java Transaction API)#J2EE Design Patterns#Python#MongoDB#MySQL#No SQL DB#SQL Server#Javscript#Jquery#Azax#Angular#ReactJS#Node JS
1 note
·
View note
Text
BRB... just upgrading Python
CW: nerdy, technical details.
Originally, MLTSHP (well, MLKSHK back then) was developed for Python 2. That was fine for 2010, but 15 years later, and Python 2 is now pretty ancient and unsupported. January 1st, 2020 was the official sunset for Python 2, and 5 years later, we’re still running things with it. It’s served us well, but we have to transition to Python 3.
Well, I bit the bullet and started working on that in earnest in 2023. The end of that work resulted in a working version of MLTSHP on Python 3. So, just ship it, right? Well, the upgrade process basically required upgrading all Python dependencies as well. And some (flyingcow, torndb, in particular) were never really official, public packages, so those had to be adopted into MLTSHP and upgraded as well. With all those changes, it required some special handling. Namely, setting up an additional web server that could be tested against the production database (unit tests can only go so far).
Here’s what that change comprised: 148 files changed, 1923 insertions, 1725 deletions. Most of those changes were part of the first commit for this branch, made on July 9, 2023 (118 files changed).
But by the end of that July, I took a break from this task - I could tell it wasn’t something I could tackle in my spare time at that time.
Time passes…
Fast forward to late 2024, and I take some time to revisit the Python 3 release work. Making a production web server for the new Python 3 instance was another big update, since I wanted the Docker container OS to be on the latest LTS edition of Ubuntu. For 2023, that was 20.04, but in 2025, it’s 24.04. I also wanted others to be able to test the server, which means the CDN layer would have to be updated to direct traffic to the test server (without affecting general traffic); I went with a client-side cookie that could target the Python 3 canary instance.
In addition to these upgrades, there were others to consider — MySQL, for one. We’ve been running MySQL 5, but version 9 is out. We settled on version 8 for now, but could also upgrade to 8.4… 8.0 is just the version you get for Ubuntu 24.04. RabbitMQ was another server component that was getting behind (3.5.7), so upgrading it to 3.12.1 (latest version for Ubuntu 24.04) seemed proper.
One more thing - our datacenter. We’ve been using Linode’s Fremont region since 2017. It’s been fine, but there are some emerging Linode features that I’ve been wanting. VPC support, for one. And object storage (basically the same as Amazon’s S3, but local, so no egress cost to-from Linode servers). Both were unavailable to Fremont, so I decided to go with their Chicago region for the upgrade.
Now we’re talking… this is now not just a “push a button” release, but a full-fleged, build everything up and tear everything down kind of release that might actually have some downtime (while trying to keep it short)!
I built a release plan document and worked through it. The key to the smooth upgrade I want was to make the cutover as seamless as possible. Picture it: once everything is set up for the new service in Chicago - new database host, new web servers and all, what do we need to do to make the switch almost instant? It’s Fastly, our CDN service.
All traffic to our service runs through Fastly. A request to the site comes in, Fastly routes it to the appropriate host, which in turns speaks to the appropriate database. So, to transition from one datacenter to the other, we need to basically change the hosts Fastly speaks to. Those hosts will already be set to talk to the new database. But that’s a key wrinkle - the new database…
The new database needs the data from the old database. And to make for a seamless transition, it needs to be up to the second in step with the old database. To do that, we have take a copy of the production data and get it up and running on the new database. Then, we need to have some process that will copy any new data to it since the last sync. This sounded a lot like replication to me, but the more I looked at doing it that way, I wasn’t confident I could set that up without bringing the production server down. That’s because any replica needs to start in a synchronized state. You can’t really achieve that with a live database. So, instead, I created my own sync process that would copy new data on a periodic basis as it came in.
Beyond this, we need a proper replication going in the new datacenter. In case the database server goes away unexpectedly, a replica of it allows for faster recovery and some peace of mind. Logical backups can be made from the replica and stored in Linode’s object storage if something really disastrous happens (like tables getting deleted by some intruder or a bad data migration).
I wanted better monitoring, too. We’ve been using Linode’s Longview service and that’s okay and free, but it doesn’t act on anything that might be going wrong. I decided to license M/Monit for this. M/Monit is so lightweight and nice, along with Monit running on each server to keep track of each service needed to operate stuff. Monit can be given instructions on how to self-heal certain things, but also provides alerts if something needs manual attention.
And finally, Linode’s Chicago region supports a proper VPC setup, which allows for all the connectivity between our servers to be totally private to their own subnet. It also means that I was able to set up an additional small Linode instance to serve as a bastion host - a server that can be used for a secure connection to reach the other servers on the private subnet. This is a lot more secure than before… we’ve never had a breach (at least, not to my knowledge), and this makes that even less likely going forward. Remote access via SSH is now unavailable without using the bastion server, so we don’t have to expose our servers to potential future ssh vulnerabilities.
So, to summarize: the MLTSHP Python 3 upgrade grew from a code release to a full stack upgrade, involving touching just about every layer of the backend of MLTSHP.
Here’s a before / after picture of some of the bigger software updates applied (apologies for using images for these tables, but Tumblr doesn’t do tables):
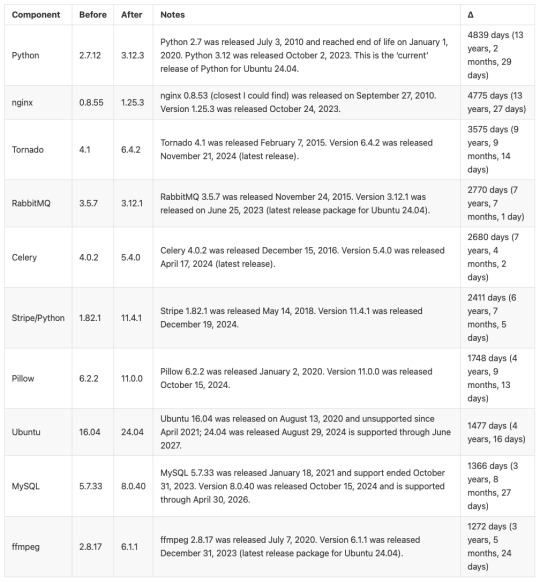
And a summary of infrastructure updates:
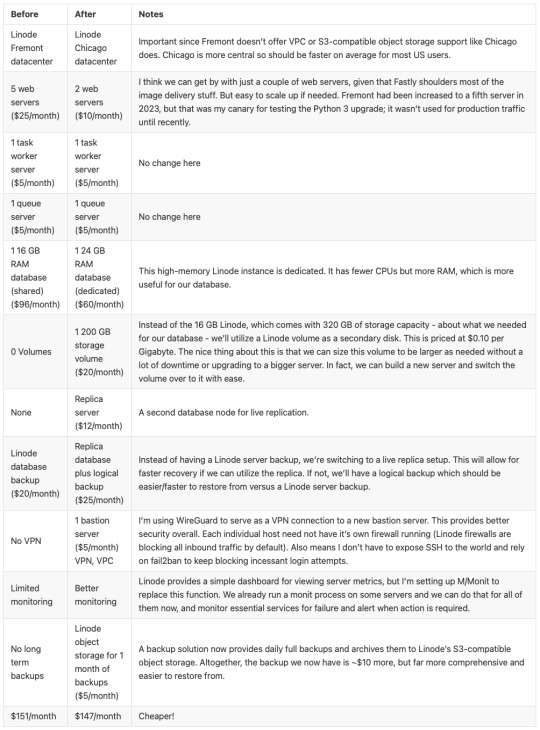
I’m pretty happy with how this has turned out. And I learned a lot. I’m a full-stack developer, so I’m familiar with a lot of devops concepts, but actually doing that role is newish to me. I got to learn how to set up a proper secure subnet for our set of hosts, making them more secure than before. I learned more about Fastly configuration, about WireGuard, about MySQL replication, and about deploying a large update to a live site with little to no downtime. A lot of that is due to meticulous release planning and careful execution. The secret for that is to think through each and every step - no matter how small. Document it, and consider the side effects of each. And with each step that could affect the public service, consider the rollback process, just in case it’s needed.
At this time, the server migration is complete and things are running smoothly. Hopefully we won’t need to do everything at once again, but we have a recipe if it comes to that.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tech Skill For Computer Science Students
Technical Skills for Computer Science Students
Software Development
MERN Stack
Python-Django Stack
Ruby on Rails ( RoR )
LAMP ( Linux, Apache Server, MySql, PHP )
.Net Stack
Flutter Stack ( For mobile app )
React Native Stack ( Cross Platform mobile app development )
Java Enterprise Edition
Serverless stack - "Cloud computing service"
Blockchain Developer
Cyber Security
DevOps
MLOps
AL Engineer
Data Science
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Text
What Is Linux Web Hosting? A Beginner's Guide
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, the choice of web hosting can significantly impact your online presence. One of the most popular options available is Linux web hosting. But what exactly does it entail, and why is it so widely preferred? This beginner’s guide aims to demystify Linux web hosting, its features, benefits, and how it stands against other hosting types.
Introduction to Web Hosting
Web hosting is a fundamental service that enables individuals and organisations to make their websites accessible on the internet. When you create a website, it consists of numerous files, such as HTML, images, and databases, which need to be stored on a server. A web host provides the server space and connectivity required for these files to be accessed by users online.
There are several types of web hosting, each designed to cater to different needs and budgets. Shared hosting is a cost-effective option where multiple websites share the same server resources. Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting offers a middle ground, providing dedicated portions of a server for greater performance and control. Dedicated hosting provides an entire server exclusively for one website, ensuring maximum performance but at a higher cost. Cloud hosting uses multiple servers to balance the load and maximise uptime, offering a scalable solution for growing websites.
Web hosting services also include various features to enhance the performance and security of your website. These can range from basic offerings like email accounts and website builders to more advanced features like SSL certificates, automated backups, and DDoS protection. The choice of web hosting can significantly influence your website’s speed, security, and reliability, making it crucial to choose a solution that aligns with your specific requirements.
Understanding the different types of web hosting and the features they offer can help you make an informed decision that suits your needs. Whether you are running a personal blog, a small business website, or a large e-commerce platform, selecting the right web hosting service is a critical step in establishing a successful online presence.
What Is Linux Web Hosting?
Linux web hosting is a type of web hosting service that utilises the Linux operating system to manage and serve websites. Renowned for its open-source nature, Linux provides a stable and secure platform that supports a wide array of programming languages and databases, making it a favoured choice amongst developers and businesses. This hosting environment typically includes support for popular technologies such as Apache web servers, MySQL databases, and PHP scripting, which are integral to modern website development.
One of the distinguishing features of Linux web hosting is its cost-effectiveness. As an open-source system, Linux eliminates the need for costly licensing fees associated with proprietary software, thereby reducing overall hosting expenses. This makes it an attractive option for individuals and organisations operating on a budget.
Moreover, Linux is celebrated for its robust performance and high stability. Websites hosted on Linux servers experience less downtime and faster loading times, which are critical factors for maintaining user engagement and search engine rankings. The operating system’s extensive community of developers continuously works on updates and improvements, ensuring that Linux remains a cutting-edge choice for web hosting.
Linux web hosting also offers considerable flexibility and customisation options. Users have the freedom to configure their hosting environment to meet specific needs, whether they are running simple static websites or complex dynamic applications. This versatility extends to compatibility with various content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal, which often perform optimally on Linux servers.
In summary, Linux web hosting provides a reliable, secure, and cost-effective solution that caters to a diverse range of web hosting requirements. Its compatibility with essential web technologies and its inherent flexibility make it a preferred choice for many web developers and site owners.
Key Benefits of Linux Web Hosting
Linux web hosting offers several compelling advantages that contribute to its widespread adoption. One of its primary benefits is cost-effectiveness. The open-source nature of Linux eliminates the need for expensive licensing fees, allowing users to allocate their resources more efficiently. This makes it an ideal choice for individuals and organisations with budget constraints. Additionally, Linux is celebrated for its high stability and robust performance. Websites hosted on Linux servers often experience minimal downtime and faster loading speeds, which are essential for maintaining user engagement and achieving favourable search engine rankings.
Another significant benefit is the extensive community support that comes with Linux. The active community of developers and enthusiasts continuously works on updates, patches, and security enhancements, ensuring that Linux remains a secure and reliable platform for web hosting. This ongoing development also means that any issues or vulnerabilities are promptly addressed, offering peace of mind for website owners.
Flexibility is another key advantage of Linux web hosting. The operating system supports a wide range of programming languages, including PHP, Python, and Ruby, making it suitable for various types of web applications. Additionally, Linux servers are highly customisable, allowing users to configure their environment to meet specific needs, whether they are running simple static sites or complex dynamic applications.
Moreover, Linux web hosting is highly compatible with popular content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal. This compatibility ensures that users can easily deploy and manage their websites using these platforms, benefiting from their extensive plugin and theme ecosystems.
Lastly, Linux's superior security features are worth noting. The operating system is inherently secure and offers various built-in security measures. When combined with best practices such as regular updates and strong passwords, Linux web hosting provides a highly secure environment for any website.
Understanding Linux Distributions in Web Hosting
Linux comes in a variety of distributions, each tailored to meet specific needs and preferences. Among the most popular for web hosting are Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian. Ubuntu is celebrated for its ease of use and extensive community support, making it a great choice for those new to Linux. CentOS, a favourite in enterprise environments, offers impressive stability and long-term support, which ensures a dependable hosting experience. Debian stands out with its robust package management system and commitment to open-source principles, providing a reliable and secure foundation.
Each distribution brings its own strengths to the table. For example, Ubuntu’s frequent updates ensure access to the latest features and security patches, while CentOS’s extended support cycles make it a solid choice for those requiring a stable, long-term hosting environment. Debian’s extensive repository of packages and minimalistic approach offers flexibility and customisation, catering to the needs of experienced users.
Selecting the right Linux distribution largely depends on your specific requirements and technical expertise. If you prioritise user-friendliness and a wealth of resources for troubleshooting, Ubuntu might be the ideal pick. On the other hand, if you need a rock-solid, stable platform for an enterprise-level application, CentOS could be more appropriate. For those seeking maximum control and a commitment to open-source principles, Debian is a compelling option.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances of these distributions will enable you to choose a Linux environment that aligns with your web hosting needs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Linux Hosting vs Windows Hosting: A Comparative Analysis
When evaluating Linux hosting against Windows hosting, several critical factors come into play. Cost is a significant differentiator; Linux hosting is generally more affordable due to its open-source nature, which eliminates the need for expensive licensing fees. In contrast, Windows hosting often incurs additional costs related to proprietary software licenses.
Compatibility is another important aspect to consider. Linux hosting is renowned for its compatibility with a broad array of open-source software and applications, including popular content management systems like WordPress, Joomla, and Magento. These platforms typically perform better on Linux servers due to optimised server configurations. On the other hand, Windows hosting is the go-to option for websites that rely on Microsoft-specific technologies such as ASP.NET, MSSQL, and other .NET frameworks.
Performance and stability are also crucial elements in this comparison. Linux hosting often provides superior uptime and faster loading speeds due to the lightweight nature of the Linux operating system. The robust performance of Linux servers is further enhanced by the active community that continuously works on optimisations and security patches. Windows hosting, while also reliable, can sometimes be more resource-intensive, potentially affecting performance.
Customisation and control levels differ significantly between the two. Linux offers greater flexibility and customisation options, allowing users to tweak server settings and configurations extensively. This level of control is particularly beneficial for developers who need a tailored hosting environment. Conversely, Windows hosting is typically easier to manage for those familiar with the Windows operating system but may offer less flexibility in terms of customisation.
Security measures also vary between Linux and Windows hosting. Linux is often praised for its strong security features, which are bolstered by a large community dedicated to promptly addressing vulnerabilities. While Windows hosting is secure, it may require more frequent updates and maintenance to ensure the same level of protection.
Common Use Cases for Linux Web Hosting
Linux web hosting is versatile and caters to a broad range of applications, making it a popular choice across various sectors. One of the most common use cases is hosting blogs and personal websites, particularly those built on platforms like WordPress. The open-source nature of Linux and its compatibility with PHP make it an ideal environment for WordPress, which powers a significant portion of the web.
E-commerce websites also benefit greatly from Linux web hosting. Solutions like Magento, PrestaShop, and OpenCart often perform better on Linux servers due to their need for a robust, secure, and scalable hosting environment. The flexibility to configure server settings allows online store owners to optimise performance and ensure a smooth shopping experience for their customers.
Content Management Systems (CMS) such as Joomla and Drupal are another prime use case. These systems require reliable and flexible hosting solutions to manage complex websites with large amounts of content. Linux's support for various databases and scripting languages ensures seamless integration and optimal performance for CMS-based sites.
Developers frequently turn to Linux web hosting for custom web applications. The operating system supports a variety of programming languages, including Python, Ruby, and Perl, making it suitable for a wide array of development projects. Its command-line interface and extensive package repositories allow developers to install and manage software efficiently.
Additionally, Linux web hosting is commonly used for educational and non-profit websites. The low cost and high reliability make it a practical choice for schools, universities, and charitable organisations that need a dependable online presence without breaking the bank.
Setting Up a Linux Web Hosting Environment
Setting up a Linux web hosting environment can be straightforward with the right approach. Begin by selecting a reputable hosting provider that offers Linux-based plans. After signing up, you'll typically be granted access to a control panel, such as cPanel or Plesk, which simplifies the management of your hosting environment. Through the control panel, you can manage files, databases, email accounts, and more.
Next, if you're using a content management system (CMS) like WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal, you can often find one-click installation options within the control panel. This feature makes it easy to get your website up and running quickly. Additionally, ensure that you configure your domain name to point to your new hosting server, which usually involves updating your domain's DNS settings.
For those who prefer more control or are comfortable using the command line, you can manually set up your web server using SSH access. This method allows you to install and configure web server software like Apache or Nginx, as well as databases such as MySQL or PostgreSQL.
Regardless of the setup method you choose, it's crucial to secure your server from the outset. This includes setting up a firewall, enabling SSH key authentication for secure access, and regularly updating all software to protect against vulnerabilities. Regularly monitoring your server's performance and security logs can help you stay ahead of potential issues, ensuring a stable and secure hosting environment for your website.
Security Best Practices for Linux Web Hosting
Securing your Linux web hosting environment is paramount to safeguarding your website against potential threats. Begin by ensuring your server software and all installed applications are up to date. Regular updates often include patches for security vulnerabilities, making this a critical step. Utilise strong, unique passwords for all user accounts, and consider employing SSH key authentication for added security when accessing your server remotely.
Setting up a firewall is another essential measure. Tools like iptables or firewalld can help you configure firewall rules to control incoming and outgoing traffic, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorised access. Implementing intrusion detection systems (IDS), such as Fail2Ban, can provide an additional layer of security by monitoring and blocking suspicious activities.
Consider deploying an SSL certificate to encrypt data transmitted between your server and users' browsers. This not only enhances security but also boosts user trust and can improve your search engine rankings. Additionally, limit the use of root privileges; create separate user accounts with the necessary permissions to minimise potential damage in the event of a breach.
Regularly backup your data to mitigate the impact of data loss due to hardware failure, cyber-attacks, or human error. Automated backup solutions can simplify this process, ensuring your data is consistently protected. Monitoring your server's logs can also be invaluable for identifying unusual activity early. Tools like Logwatch or the ELK Stack can assist in log management and analysis, enabling you to take swift action if anomalies are detected.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Setting up and maintaining a Linux web hosting environment can present various challenges, especially for those new to the platform. One frequent issue is navigating the command line, which can be daunting for beginners. Engaging with online tutorials, forums, and communities like Stack Overflow can be invaluable for learning the basics and troubleshooting problems. Another common challenge is software incompatibility. Ensuring your web applications are compatible with the Linux distribution you choose is crucial; consulting documentation and support resources can help mitigate these issues.
Security configuration can also be a complex task. Implementing best practices such as setting up firewalls, regular updates, and using strong authentication methods requires a good understanding of Linux security principles. Managed hosting services can offer a solution here by handling these technical aspects for you, allowing you to focus on your website content.
Resource management is another area where users might struggle. Monitoring server performance and managing resources effectively ensures your website runs smoothly. Utilising monitoring tools and performance optimisation techniques can help you stay ahead of potential issues. Lastly, when it comes to server backups, regular, automated solutions are essential to prevent data loss and minimise downtime. Being proactive in addressing these challenges will ensure a more seamless and secure Linux web hosting experience.
Popular Control Panels for Linux Web Hosting
Control panels are invaluable for simplifying the management of your Linux web hosting environment. Among the most popular are cPanel, Plesk, and Webmin. cPanel is renowned for its intuitive interface and extensive feature set, making it a favourite among users who need a straightforward yet powerful management tool. Plesk offers robust functionality and supports both Linux and Windows servers, providing versatility for those who manage multiple server environments. Webmin stands out as a free, open-source option that allows comprehensive server management through a web interface, catering to those who prefer a customisable and cost-effective solution. Each control panel brings unique strengths, helping to streamline tasks such as file management, database administration, and security configurations.
Choosing the Right Linux Web Hosting Provider
Choosing the right Linux web hosting provider involves several key considerations. Firstly, evaluate the quality of customer support offered. Responsive and knowledgeable support can be invaluable, especially when troubleshooting technical issues or during the initial setup phase. Check if the provider offers 24/7 support and multiple contact methods such as live chat, email, and phone.
Another crucial factor is the security measures in place. Opt for providers that offer robust security features, including regular backups, SSL certificates, firewalls, and DDoS protection. These features help safeguard your website against potential threats and ensure data integrity.
Reliability and uptime guarantees are also vital. Aim for providers that offer at least a 99.9% uptime guarantee, as frequent downtimes can significantly affect your website’s accessibility and user experience. Additionally, look into the provider’s data centre infrastructure and redundancy measures, which can impact overall performance and reliability.
Scalability is another important aspect to consider. As your website grows, you’ll need the flexibility to upgrade your hosting plan seamlessly. Check if the provider offers scalable solutions, such as easy transitions to VPS or dedicated hosting, without causing disruptions to your site.
Lastly, consider the hosting plans and pricing structures available. While cost-effectiveness is a significant benefit of Linux web hosting, ensure the plans align with your specific needs. Compare the features, storage, bandwidth, and other resources included in different plans to find the best value for your money.
Reading customer reviews and seeking recommendations can also provide insights into the provider’s reputation and service quality. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose a Linux web hosting provider that meets your requirements and supports your online endeavours effectively.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Linux web hosting stands out as an optimal choice for both beginners and seasoned web developers. Its open-source nature provides an affordable, highly customisable, and secure environment, suitable for a diverse range of websites, from personal blogs to large e-commerce platforms. The extensive community support ensures ongoing improvements and prompt resolution of issues, contributing to its reliability and performance. Choosing the right hosting provider is crucial; look for robust security measures, excellent customer support, and scalability to accommodate your website's growth. By leveraging the strengths of Linux web hosting, you can build a resilient and efficient online presence that meets your specific needs and goals.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Comprehensive Guide to Web Development, Data Management, and More
Introduction
Everything today is technology driven in this digital world. There's a lot happening behind the scenes when you use your favorite apps, go to websites, and do other things with all of those zeroes and ones — or binary data. In this blog, I will be explaining what all these terminologies really means and other basics of web development, data management etc. We will be discussing them in the simplest way so that this becomes easy to understand for beginners or people who are even remotely interested about technology. JOIN US
What is Web Development?
Web development refers to the work and process of developing a website or web application that can run in a web browser. From laying out individual web page designs before we ever start coding, to how the layout will be implemented through HTML/CSS. There are two major fields of web development — front-end and back-end.
Front-End Development
Front-end development, also known as client-side development, is the part of web development that deals with what users see and interact with on their screens. It involves using languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create the visual elements of a website, such as buttons, forms, and images. JOIN US
HTML (HyperText Markup Language):
HTML is the foundation of all website, it helps one to organize their content on web platform. It provides the default style to basic elements such as headings, paragraphs and links.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets):
styles and formats HTML elements. It makes an attractive and user-friendly look of webpage as it controls the colors, fonts, layout.
JavaScript :
A language for adding interactivity to a website Users interact with items, like clicking a button to send in a form or viewing images within the slideshow. JOIN US
Back-End Development
The difference while front-end development is all about what the user sees, back end involves everything that happens behind. The back-end consists of a server, database and application logic that runs on the web.
Server:
A server is a computer that holds website files and provides them to the user browser when they request it. Server-Side: These are populated by back-end developers who build and maintain servers using languages like Python, PHP or Ruby.
Database:
The place where a website keeps its data, from user details to content and settings The database is maintained with services like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB. JOIN US
Application Logic —
the code that links front-end and back-end It takes user input, gets data from the database and returns right informations to front-end area.

Why Proper Data Management is Absolutely Critical
Data management — Besides web development this is the most important a part of our Digital World. What Is Data Management? It includes practices, policies and procedures that are used to collect store secure data in controlled way.
Data Storage –
data after being collected needs to be stored securely such data can be stored in relational databases or cloud storage solutions. The most important aspect here is that the data should never be accessed by an unauthorized source or breached. JOIN US
Data processing:
Right from storing the data, with Big Data you further move on to process it in order to make sense out of hordes of raw information. This includes cleansing the data (removing errors or redundancies), finding patterns among it, and producing ideas that could be useful for decision-making.
Data Security:
Another important part of data management is the security of it. It refers to defending data against unauthorized access, breaches or other potential vulnerabilities. You can do this with some basic security methods, mostly encryption and access controls as well as regular auditing of your systems.
Other Critical Tech Landmarks
There are a lot of disciplines in the tech world that go beyond web development and data management. Here are a few of them:
Cloud Computing
Leading by example, AWS had established cloud computing as the on-demand delivery of IT resources and applications via web services/Internet over a decade considering all layers to make it easy from servers up to top most layer. This will enable organizations to consume technology resources in the form of pay-as-you-go model without having to purchase, own and feed that infrastructure. JOIN US
Cloud Computing Advantages:
Main advantages are cost savings, scalability, flexibility and disaster recovery. Resources can be scaled based on usage, which means companies only pay for what they are using and have the data backed up in case of an emergency.
Examples of Cloud Services:
Few popular cloud services are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. These provide a plethora of services that helps to Develop and Manage App, Store Data etc.
Cybersecurity
As the world continues to rely more heavily on digital technologies, cybersecurity has never been a bigger issue. Protecting computer systems, networks and data from cyber attacks is called Cyber security.
Phishing attacks, Malware, Ransomware and Data breaches:
This is common cybersecurity threats. These threats can bear substantial ramifications, from financial damages to reputation harm for any corporation.
Cybersecurity Best Practices:
In order to safeguard against cybersecurity threats, it is necessary to follow best-practices including using strong passwords and two-factor authorization, updating software as required, training employees on security risks.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) represent the fastest-growing fields of creating systems that learn from data, identifying patterns in them. These are applied to several use-cases like self driving cars, personalization in Netflix.
AI vs ML —
AI is the broader concept of machines being able to carry out tasks in a way we would consider “smart”. Machine learning is a type of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that provides computers with the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. JOIN US
Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: some common applications include Image recognition, Speech to text, Natural language processing, Predictive analytics Robotics.
Web Development meets Data Management etc.
We need so many things like web development, data management and cloud computing plus cybersecurity etc.. but some of them are most important aspects i.e. AI/ML yet more fascinating is where these fields converge or play off each other.
Web Development and Data Management
Web Development and Data Management goes hand in hand. The large number of websites and web-based applications in the world generate enormous amounts of data — from user interactions, to transaction records. Being able to manage this data is key in providing a fantastic user experience and enabling you to make decisions based on the right kind of information.
E.g. E-commerce Website, products data need to be saved on server also customers data should save in a database loosely coupled with orders and payments. This data is necessary for customization of the shopping experience as well as inventory management and fraud prevention.
Cloud Computing and Web Development
The development of the web has been revolutionized by cloud computing which gives developers a way to allocate, deploy and scale applications more or less without service friction. Developers now can host applications and data in cloud services instead of investing for physical servers.
E.g. A start-up company can use cloud services to roll out the web application globally in order for all users worldwide could browse it without waiting due unavailability of geolocation prohibited access.
The Future of Cybersecurity and Data Management
Which makes Cybersecurity a very important part of the Data management. The more data collected and stored by an organization, the greater a target it becomes for cyber threats. It is important to secure this data using robust cybersecurity measures, so that sensitive information remains intact and customer trust does not weaken. JOIN US
Ex: A healthcare provider would have to protect patient data in order to be compliant with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) that is also responsible for ensuring a degree of confidentiality between a provider and their patients.
Conclusion
Well, in a nutshell web-developer or Data manager etc are some of the integral parts for digital world.
As a Business Owner, Tech Enthusiast or even if you are just planning to make your Career in tech — it is important that you understand these. With the progress of technology never slowing down, these intersections are perhaps only going to come together more strongly and develop into cornerstones that define how we live in a digital world tomorrow.
With the fundamental knowledge of web development, data management, automation and ML you will manage to catch up with digital movements. Whether you have a site to build, ideas data to manage or simply interested in what’s hot these days, skills and knowledge around the above will stand good for changing tech world. JOIN US
#Technology#Web Development#Front-End Development#Back-End Development#HTML#CSS#JavaScript#Data Management#Data Security#Cloud Computing#AWS (Amazon Web Services)#Cybersecurity#Artificial Intelligence (AI)#Machine Learning (ML)#Digital World#Tech Trends#IT Basics#Beginners Guide#Web Development Basics#Tech Enthusiast#Tech Career#america
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pinball Machine: Cloud-Connected Retro Sandbox Gameplay

Pinball Machines
Google cloud frequently take for granted how simple it is to link apps with a wide range of robust cloud services in today’s cloud-centric world. Nonetheless, integration remains difficult in a great number of legacy systems and other restricted situations.
When creating Backlogged Pinball, a unique pinball game that created as a demonstration for integrating cloud services in unusual locations, they took on this difficulty head-on. A real pinball machine called Backlogged Pinball can be connected to the cloud for a number of purposes, such as updating leaderboards and tracking information about finished and ongoing games.
In order to concentrate on game coding and cloud integration, built it on the foundation of a commercially available programmable pinball machine. The computer’s software environment was constrained, though, as it was using a sandboxed version of the.NET Framework 3.5, which was initially made available 17 years ago. In practice, this meant that were unable to install tools like gcloud to facilitate communication with the cloud and utilize any of the current Google cloud SDKs that were available for C#.
There’s a catch
It knew wanted to use the cloud for logging of game events and results, databases for high scores and game statistics, and a custom service to modify the game experience on the fly. However, creating software for such a limited setting came with a number of difficulties that you may be familiar with:
Limited library support: There are plenty of excellent libraries available to assist you in connecting to cloud services if you have complete control over your stack. However, there are instances when you are unable to choose where your software runs. Finding appropriate libraries to connect Google cloud pinball machine to the desired cloud services proved to be challenging.
For instance, they were aware that in order to power a real-time display of every event occurring in the game, needed to add entries into a Firestore database. Although Firestore has excellent SDKs, they were unable to handle anything prior to the 8.-year-old.NET Framework 4.6.2. Google could have been able to use a TCP connection to access a conventional relational database, but didn’t want to be restricted in Google cloud options for cloud services and tools. Building a real-time web application with MySQL instead of Firestore, which is built from the ground up to push data to the browser in real-time, is obviously far less viable.
Difficult deployment process: You may wish to add new features and cloud integrations, but updating your on-device software may be challenging due to various constraints. Google cloud had to use a USB stick to manually install every version of game while it was being developed because third-party developers. Testing, deploying, and shipping new versions of your code is slowed down by this type of restriction, which is never good. In a contemporary, adaptable cloud platform, adding new features is far simpler.
In essence, discovered that utilizing contemporary cloud services in an unpredictable legacy setting was difficult.
Flipper-ing the script
Initially, it seemed impossible to incorporate all of the services desired into the code that would operate on the pinball machine. However, what if there was an alternative? What if it gave the pinball machine a single simple integration and transformed it into a service? They might then arrange the outcomes in a contemporary cloud environment and have it send a message each time something occurred in the game.
Google cloud concluded that Pub/Sub would be a great approach to accomplish this. It offered a simple method of transferring data to the cloud via a single interface. It was really a simple HTTP POST with any message format desired.Image credit to Google cloud
It created a unique Pub/Sub messaging mechanism to accomplish this. To manage authentication and message delivery via the REST API, created a lightweight Pub/Sub framework just for the pinball machine. This made it incredibly simple to submit events anytime a player struck a target, fired a ball, or even pressed a flipper button. Visit GitHub to view a condensed version of that code!
Google cloud team processed these events in real time on the cloud side by using numerous Cloud Run subscribers. Additionally, stored data and powered visualizations using Firestore.
Jackpot! Benefits of the cloud
There were many benefits of pushing integration complexity into the cloud:
One interface: Authentication alone might be a blog entry in and of itself, so creating own Pub/Sub client was no easy feat. But when it was finished, it was finished! After it was operational, Google could concentrate on employing whichever contemporary client libraries and tools desired to process every event in the cloud.
Real-time updates: At Google Cloud Next, assisted users in creating custom Cloud Run services that can process pinball machine, send messages back to the machine, and receive them. You could theoretically alter the game while a friend was playing it because it took less than a minute to build and deploy these services!
Rich insights from data: In the end, they had a detailed record of every event that took place throughout a game. Playtest-based scoring adjustments and development-related troubleshooting were greatly aided by this.
Leaping ahead
The next version of Backlogged Pinball is already in the works, and it will include features hadn’t initially thought of. For instance, its’re including AI-driven Gameplay and player-style-based recommendations. Instead of struggling with dependencies on a historical system, nearly all of the work will be done in a contemporary cloud environment because of this adaptable cloud-based design.
Furthermore, any limited environment can benefit from the lessonsz learnt from this project. You can overcome the constraints of your environment and realize the full potential of the cloud by utilizing Pub/Sub messaging and embracing a cloud-first mindset, regardless matter whether it’s an embedded system, an Internet of Things device, or an outdated server running older software.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#PinballMachine#Cloudcomputing#Gameplay#Sandbox#pinball#game#SDKs#RetroSandbox#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#govindhtech
1 note
·
View note
Text
java full stack
A Java Full Stack Developer is proficient in both front-end and back-end development, using Java for server-side (backend) programming. Here's a comprehensive guide to becoming a Java Full Stack Developer:
1. Core Java
Fundamentals: Object-Oriented Programming, Data Types, Variables, Arrays, Operators, Control Statements.
Advanced Topics: Exception Handling, Collections Framework, Streams, Lambda Expressions, Multithreading.
2. Front-End Development
HTML: Structure of web pages, Semantic HTML.
CSS: Styling, Flexbox, Grid, Responsive Design.
JavaScript: ES6+, DOM Manipulation, Fetch API, Event Handling.
Frameworks/Libraries:
React: Components, State, Props, Hooks, Context API, Router.
Angular: Modules, Components, Services, Directives, Dependency Injection.
Vue.js: Directives, Components, Vue Router, Vuex for state management.
3. Back-End Development
Java Frameworks:
Spring: Core, Boot, MVC, Data JPA, Security, Rest.
Hibernate: ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) framework.
Building REST APIs: Using Spring Boot to build scalable and maintainable REST APIs.
4. Database Management
SQL Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL (CRUD operations, Joins, Indexing).
NoSQL Databases: MongoDB (CRUD operations, Aggregation).
5. Version Control/Git
Basic Git commands: clone, pull, push, commit, branch, merge.
Platforms: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket.
6. Build Tools
Maven: Dependency management, Project building.
Gradle: Advanced build tool with Groovy-based DSL.
7. Testing
Unit Testing: JUnit, Mockito.
Integration Testing: Using Spring Test.
8. DevOps (Optional but beneficial)
Containerization: Docker (Creating, managing containers).
CI/CD: Jenkins, GitHub Actions.
Cloud Services: AWS, Azure (Basics of deployment).
9. Soft Skills
Problem-Solving: Algorithms and Data Structures.
Communication: Working in teams, Agile/Scrum methodologies.
Project Management: Basic understanding of managing projects and tasks.
Learning Path
Start with Core Java: Master the basics before moving to advanced concepts.
Learn Front-End Basics: HTML, CSS, JavaScript.
Move to Frameworks: Choose one front-end framework (React/Angular/Vue.js).
Back-End Development: Dive into Spring and Hibernate.
Database Knowledge: Learn both SQL and NoSQL databases.
Version Control: Get comfortable with Git.
Testing and DevOps: Understand the basics of testing and deployment.
Resources
Books:
Effective Java by Joshua Bloch.
Java: The Complete Reference by Herbert Schildt.
Head First Java by Kathy Sierra & Bert Bates.
Online Courses:
Coursera, Udemy, Pluralsight (Java, Spring, React/Angular/Vue.js).
FreeCodeCamp, Codecademy (HTML, CSS, JavaScript).
Documentation:
Official documentation for Java, Spring, React, Angular, and Vue.js.
Community and Practice
GitHub: Explore open-source projects.
Stack Overflow: Participate in discussions and problem-solving.
Coding Challenges: LeetCode, HackerRank, CodeWars for practice.
By mastering these areas, you'll be well-equipped to handle the diverse responsibilities of a Java Full Stack Developer.
visit https://www.izeoninnovative.com/izeon/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Power of Amazon Web Services: Top AWS Services You Need to Know
In the ever-evolving realm of cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has established itself as an undeniable force to be reckoned with. AWS's vast and diverse array of services has positioned it as a dominant player, catering to the evolving needs of businesses, startups, and individuals worldwide. Its popularity transcends boundaries, making it the preferred choice for a myriad of use cases, from startups launching their first web applications to established enterprises managing complex networks of services. This blog embarks on an exploratory journey into the boundless world of AWS, delving deep into some of its most sought-after and pivotal services.

As the digital landscape continues to expand, understanding these AWS services and their significance is pivotal, whether you're a seasoned cloud expert or someone taking the first steps in your cloud computing journey. Join us as we delve into the intricate web of AWS's top services and discover how they can shape the future of your cloud computing endeavors. From cloud novices to seasoned professionals, the AWS ecosystem holds the keys to innovation and transformation.
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): The Foundation of Scalability At the core of AWS's capabilities is Amazon EC2, the Elastic Compute Cloud. EC2 provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud, allowing you to run virtual servers, commonly referred to as instances. These instances serve as the foundation for a multitude of AWS solutions, offering the scalability and flexibility required to meet diverse application and workload demands. Whether you're a startup launching your first web application or an enterprise managing a complex network of services, EC2 ensures that you have the computational resources you need, precisely when you need them.
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service): Secure, Scalable, and Cost-Effective Data Storage When it comes to storing and retrieving data, Amazon S3, the Simple Storage Service, stands as an indispensable tool in the AWS arsenal. S3 offers a scalable and highly durable object storage service that is designed for data security and cost-effectiveness. This service is the choice of businesses and individuals for storing a wide range of data, including media files, backups, and data archives. Its flexibility and reliability make it a prime choice for safeguarding your digital assets and ensuring they are readily accessible.
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service): Streamlined Database Management Database management can be a complex task, but AWS simplifies it with Amazon RDS, the Relational Database Service. RDS automates many common database management tasks, including patching, backups, and scaling. It supports multiple database engines, including popular options like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server. This service allows you to focus on your application while AWS handles the underlying database infrastructure. Whether you're building a content management system, an e-commerce platform, or a mobile app, RDS streamlines your database operations.
AWS Lambda: The Era of Serverless Computing Serverless computing has transformed the way applications are built and deployed, and AWS Lambda is at the forefront of this revolution. Lambda is a serverless compute service that enables you to run code without the need for server provisioning or management. It's the perfect solution for building serverless applications, microservices, and automating tasks. The unique pricing model ensures that you pay only for the compute time your code actually uses. This service empowers developers to focus on coding, knowing that AWS will handle the operational complexities behind the scenes.
Amazon DynamoDB: Low Latency, High Scalability NoSQL Database Amazon DynamoDB is a managed NoSQL database service that stands out for its low latency and exceptional scalability. It's a popular choice for applications with variable workloads, such as gaming platforms, IoT solutions, and real-time data processing systems. DynamoDB automatically scales to meet the demands of your applications, ensuring consistent, single-digit millisecond latency at any scale. Whether you're managing user profiles, session data, or real-time analytics, DynamoDB is designed to meet your performance needs.
Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud): Tailored Networking for Security and Control Security and control over your cloud resources are paramount, and Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) empowers you to create isolated networks within the AWS cloud. This isolation enhances security and control, allowing you to define your network topology, configure routing, and manage access. VPC is the go-to solution for businesses and individuals who require a network environment that mirrors the security and control of traditional on-premises data centers.
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service): Seamless Communication Across Channels Effective communication is a cornerstone of modern applications, and Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service) is designed to facilitate seamless communication across various channels. This fully managed messaging service enables you to send notifications to a distributed set of recipients, whether through email, SMS, or mobile devices. SNS is an essential component of applications that require real-time updates and notifications to keep users informed and engaged.
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service): Decoupling for Scalable Applications Decoupling components of a cloud application is crucial for scalability, and Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service) is a fully managed message queuing service designed for this purpose. It ensures reliable and scalable communication between different parts of your application, helping you create systems that can handle varying workloads efficiently. SQS is a valuable tool for building robust, distributed applications that can adapt to changes in demand.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands as a colossus, offering a diverse array of services that address the ever-evolving needs of businesses, startups, and individuals alike. AWS's popularity transcends industry boundaries, making it the go-to choice for a wide range of use cases, from startups launching their inaugural web applications to established enterprises managing intricate networks of services.
To unlock the full potential of these AWS services, gaining comprehensive knowledge and hands-on experience is key. ACTE Technologies, a renowned training provider, offers specialized AWS training programs designed to provide practical skills and in-depth understanding. These programs equip you with the tools needed to navigate and excel in the dynamic world of cloud computing.
With AWS services at your disposal, the possibilities are endless, and innovation knows no bounds. Join the ever-growing community of cloud professionals and enthusiasts, and empower yourself to shape the future of the digital landscape. ACTE Technologies is your trusted guide on this journey, providing the knowledge and support needed to thrive in the world of AWS and cloud computing.
8 notes
·
View notes