#Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The head of the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) has proposed a plan for “lasting peace” in war-torn Sudan as his rival army chief promised victory and no chance of a deal with “traitors”.
Mohamed Hamdan “Hemedti” Dagalo, the head of the RSF, late Sunday published a 10-point plan by the paramilitary group that proposes new negotiations to end a war that began in mid-April, a war he claimed the RSF “did not seek, nor initiate”.
“Efforts to end the protracted crisis must be directed toward achieving a lasting ceasefire, coupled with comprehensive political solutions that address the root cause of Sudan’s wars,” his statement said.
Hemedti floated the idea of a “non-symmetrical federal system” that would represent Sudan’s regional, cultural and ethnic diversity after elections to form a civilian government and end “structural violence” against broad segments of Sudanese citizens.
Crucially, he proposed a new, apolitical and unified Sudanese army built from merging existing forces that would have civilian oversight and conform to internationally recognised foundations.
But the general’s proposals, which are titled Sudan Reborn and appear to be in line with international calls for shaping the country’s future, hardly correspond with the realities on the ground as the devastating war enters its 20th week.
For one, war broke out between the RSF and the Sudanese army shortly before the paramilitary force was supposed to be integrated into the army, which is led by General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan, as part of a plan to restore civilian rule.
The two generals had staged a coup in 2021 that pushed civilian politicians out of the government, which itself came two years after they banded together to end the reign of military commander Omar al-Bashir over Sudan.
On the other hand, Hemedti and the RSF have been documented by the United Nations and prominent human rights organisations and activists to have committed ethnic cleansing as well as systemic sexual violence.
In the western region of Darfur, which was the scene of a genocidal war in the early 2000s involving forces that later evolved into the RSF, there have been widespread reports of killing African community members and rape since the start of the war.
The International Criminal Court has also said it is investigating new war crimes and crimes against humanity in Darfur as the UN has warned that the war “now threatens to consume the entire country”.
More than 4.6 million people have been forced to flee their homes since the start of the war, according to UN figures that say more than one million have fled to neighbouring countries, including Chad and Egypt.
Al-Burhan denounces RSF
In a speech on Monday, al-Burhan denounced the RSF as “traitors” and promised a decisive victory in a speech to soldiers, rejecting calls for a ceasefire.
“We do not make deals with traitors, we do not make deals with anyone who has betrayed the Sudanese people,” al-Burhan told cheering soldiers at the Flamingo Base in Port Sudan on the Red Sea.
Al-Burhan has embarked on a tour of bases in army-controlled regions and is expected to travel to Saudi Arabia and Egypt, prompting some to speculate that a deal was imminent.
“We are dedicating all our time to this war … to ending this rebellion,” al-Burhan said, promising a quick and decisive victory, echoing previous statements from the military leadership.
The RSF “are completely exhausted – just a little effort and they will be finished,” he said.
On Thursday, he had made an appearance outside the army’s general command centre in the capital, Khartoum, for the first time since the war began.
On Sunday, he appeared in Port Sudan, to the northeast of the country, which has been spared the worst of the fighting.
Many ceasefires in Sudan have been repeatedly violated, often immediately after coming into effect, with the two sides blaming each other for undermining the ceasefires.
Riyadh and Washington have for now stopped their mediation efforts as the two sides continue to grapple for military dominance before seriously committing to a long-term peace plan.
0 notes
Text
this will be a bit of a long post but i ask that you please please read the full thing if you want to know more about Sudan- i feel like not enough people ACTUALLY know what's going on in Sudan. a lot of people have a vague idea that a 'war' and genocide is going on, but it's important to know the specifics as well.
there is extremely little coverage of Sudan from non-Sudanese sources, and even those that DO cover it often paint it as a war between two different generals for power over a country- and to a certain extent, without context, that IS what's happening. for those unaware, the two 'warring factions' in Sudan are the official Sudanese military- the SAF (Sudanese Armed Forces) and the RSF (Rapid Support Forces).
in April 2019, during the Sudanese Revolution, Islamist dictator Omar al-Bashir was deposed by the SAF in response to a mass wave of revolutionary organizing, protests, and sit-ins. Immediately after, the TMC (Transitionary Military Council) was established, with SAF general inspector Abdel Fattah al-Burhan being appointed as the chairman. for a brief time, protestors engaged in negotiations with Burhan, and many believed that he was being ernest in his promises of a true civilian democratic government- but it soon became clear to protestors that he was not actually taking their demands seriously, so demonstrations once again intensified. on June 3, 2019, it was under Burhan's command that the Khartoum Massacre was committed, killing 118 protestors while they were participating in a sit-in at the military headquarters in Khartoum.
as the next few months went by, agreements came about to dissolve the TMC and form a Transitional Sovereignty Council based on a draft of a constitutional declaration. it was supposed to be that a military official would be the chairman for 21 months, then transitioning to a civilian chairman for the next 18 months- but Burhan staged a coup in October of 2021, and dissolved the council and effectively turned the Sudanese government back into a military junta, which was the cause of further protesting.
i want to emphasize the crimes and horrors of the SAF because they are often forgotten in these discussions due to the absolute atrocities committed by the RSF. there is no good guy here- both the SAF and the RSF are vying for dictatorial power. so let's talk about the RSF.
headed by genocidal war criminal Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, known more widely as "Hemedti", the RSF formed around 2014 due to reorginization of the Janjaweed militias- which were the militias that formed across the Darfuri regions of southwestern Sudan to suppress demonstrations against Bashir's oppressive and racist regime which carried out the first genocide of Massalit and other ethnically non-Arab peoples across Darfur in the early 2000s. so to be succinct- the RSF has direct roots in dictatorial suppression of Sudanis protesting against ethnic cleansing, genocide, and oppression.
for around a decade, the RSF and SAF were different factions of the Sudanese military- both have their roots and a pattern of supporting dictatorial violence and anti-Black genocide. and, on April 15, 2023, these two dictatorial Arab-colonialist powers began fighting out of the blue. fighting has been most intense around Khartoum, the central state and capital city of Sudan, where now an estimated 35% of its residents have been forced to flee, with the rest trapped in the middle of an active war zone.
the RSF has been actively continuing the genocide of non-Arab Darfuri Sudanis that its predecessor the Janjaweed committed 20 years prior. they have been consistently launching attacks against Massalit villages in Darfur and El Geneina. Recently, they have completely ethnically cleansed several Massalit villages, killing hundreds in each one of them. in addition, they are committing so many other war crimes, like sexual violence, blocking access to humanitarian aid, occupying civilian homes and kicking the residents out, along with blatant ethnic cleansing campaigns, mass murder, and targeting of civilians.
but don't think that this is a 'civil war' as many are calling it. a civil war is an internal dispute, but this is far from that. both the SAF and the RSF are supported by external powers, namely the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Russia, who all provide funding to these groups IN EXCHANGE FOR SUDANESE RESOURCES LIKE GOLD AND OIL. this is, ultimately, not just some random war between two different military groups- it is a war funded by and for foreign colonial powers who have a vested interest in colonizing Sudan for its resources. as an example- the UAE's- and especially Dubai's- infamous gold and jewelry industry, is only made possible by the fact that the UAE illegally smuggles 80% of Sudan's gold- they fund this by sending weapons AND SOLDIERS to the RSF. Several of the gold mines in Sudan are owned and operated by the Russian government.
all of this, both the 'internal' AND the external, colonial aspects of this war and genocide, has led to the world's current WORST humanitarian crisis. not only do LOW estimates place the total murdered in the past year at 150,000, but out of Sudan's population of nearly 47 million, over half (25 million) are in severe need of humanitarian aid, and of those 25 million, over half are children. fighting between the RSF and SAF has lead to severe blockage of aid, and the UN's initial proposed budget of $1.5 billion in April of 2023 has not only not increased to accommodate the severe worsening of the crisis, but ALSO has not even been funded 20%.
2.5 MILLION PEOPLE ARE EXPECTED TO STARVE TO DEATH IN SUDAN BY THIS FUCKING SEPTEMBER. THAT IS LESS THAN 2 MONTHS AWAY.
additionally, due to both western colonization and the Sudanese governments' deliberate cutting of internet access across the entirety of Sudan, there is a huge lack of the proper infrastructure for generating awareness and spreading videos and info from on the ground in Sudan. this means that not only are people unable to effectively crowdfund support to leave, but they are also barred from accessing social media to spread awareness, and they're unable to contact loved ones outside of Sudan most of the time.
also, Sudan is HUGE- in order for displaced people to escape fighting, they usually have to walk, on foot, for hundreds of miles, often across literal deserts, with extremely little access to water. there has also been a surge of internally displaced people dying due to illness and scorpion stings in displacement camps. 70% of Sudan's hospitals have stopped functioning entirely. and even if they DO make it to a neighboring country, most of the options there are just as bad, if not worse- Egypt is extremely anti-Black, and doesn't allow work permits to most Black refugees, meaning they are relegated to being houseless and jobless if they go to Egypt- and westward in Chad, there is also crisis with food and resources, so the government of Chad quite literally can not materially support anymore Sudanese refugees. In South Sudan, there is also conflict, war, and crisis, and in Ethiopia, where the genocide is taking place in Tigray, the government is extremely hostile to Sudanese refugees. there are currently more than 6,000 Sudanese refugees stranded in the forests because of the hostilities they faced while in UNHCR camps.
and everyday that we're not doing something, this genocide, war, and humanitarian crisis is getting worse. doing something starts with being educated. i urge y'all to look more into this, don't just take what i'm saying and roll with it- truly learn and listen to Sudanese activists on this. i highly recommend following these accounts on Instagram:
@/red_maat , @/bsonblast , @/sudansolidaritycollective, @/forsudaneseliberation, @/darfurwomenaction, @/liberatesudan, @/zzeirra, @/yousraelbagir, @/modathirzainalabdeen, @/sdn.world, @/nasalsudan, @/sudanuntold, @/kandakamagazine, and @/almigdadhassan0
IF ANYTHING I'VE SAID IS INACCURATE, PLEASE LET ME KNOW!
i'd like to spread this post for some education. could you reblog this @decolonize-the-left @incorrectmadrigalfamilyquotes @homoidiotic @heritageposts @el-shab-hussein
@fairuzfan @palipunk @silicacid @sissa-arrows @apollos-olives @
@northgazaupdates @our-queer-experience @intersexfairy @genderqueerdykes
#🌌when the stars align ; reigns rambles🌌#sudan#free sudan#keep eyes on sudan#keep eyes on darfur#free darfur#genocide in sudan#stop the genocide
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Orphanage Under Siege
Orphanage Caught Between Civil War
An orphanage is caught between warring factions in the capital of Sudan, and more than sixty children have died inside as help has been unable to reach them. The Al-Mayqoma orphanage in Khartoum, Sudan, is surrounded by homes, markets, and little shops. But since mid-April, it has been at the epicenter of a warzone. The Sudanese military, led by General Abdel-Fattah Burhan, are fighting the…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text

Via NasAlSudan
December 17 2023. #KeepEyesOnSudan #SudanActionWeek
Swipe through to build a foundational understanding of the war, its origins, and the key players involved. For actionable ways to support those in Sudan, check the link in our bio. Stay tuned for more posts this week.
Transcript:
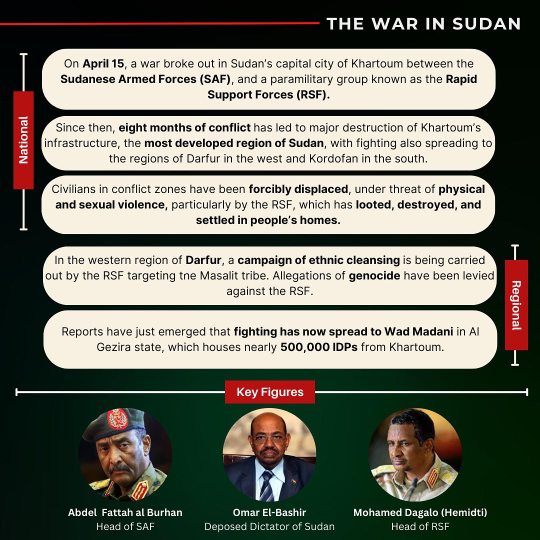
National:
On April 15, a war broke out in Sudan's capital city of Khartoum between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF), and a paramilitary group known as the Rapid Support Forces (RSF).
Since then, eight months of conflict has led to major destruction of Khartoum's infrastructure, the most developed region of Sudan, with fighting also spreading to the regions of Darfur in the west and Kordofan in the south.
Civilians in conflict zones have been forcibly displaced, under threat of physical and sexual violence, particularly by the RSF, which has looted, destroyed, and settled in people's homes.
Regional:
In the western region of Darfur, a campaign of ethnic cleansing is being carried out by the RSF targeting the Masalit tribe. Allegations of genocide have been levied against the RSF.
Reports have just emerged that fighting has now spread to Wad Madani in Al Gezira state, which houses nearly 500,000 IDPs from Khartoum.
Key figures:
Abdel Fattah al Burhan Head of SAF
Omar El-Bashir Deposed Dictator of Sudan
Mohamed Dagalo (Hemidti) Head of RSF

Transcript:
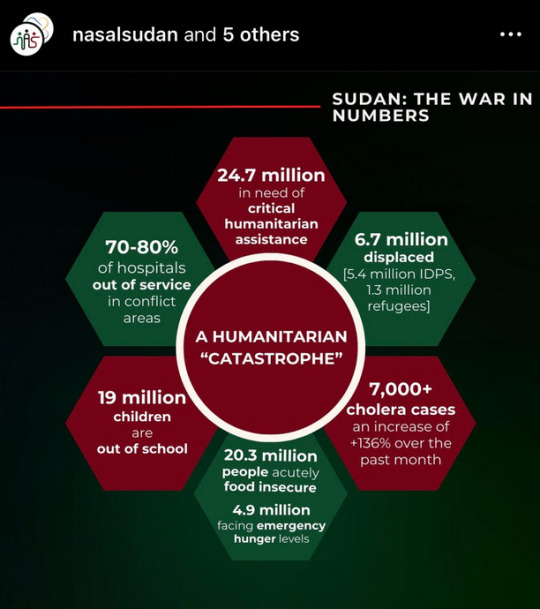
Sudan: the war in numbers
A humanitarian "catastrophe"
24.7 million in need of critical humanitarian assistance
70-80% of hospitals out of service in conflict areas
19 million children are out of school
20.3 million people acutely food insecure. 4.9 million facing emergency hunger levels
6.7 million displaced [5.4 million IDPS, 1.3 million refugees]
7,000+ cholera cases an increase of +136% over the past month

Transcript:
FAQ - THE SAF
QUESTION 01: What is the SAF?
Stands for the Sudanese Armed Forces
Is the de-facto government of Sudan
Is headed by Lt. General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan
QUESTION 02 What is their capacity?
Estimated to have ~200,000 personnel and tactical advantage of airforce
Currently control the relative northern and eastern regions of Sudan with functioning capital in Port Sudan (East)
QUESTION 03 Do they have backing and support?
On the international stage, primarily backed by Egypt
Limited weapons supply from allies
Internally, the SAF is ultimately considered the lesser of two evils

Transcript:
FAQ - THE RSF
QUESTION 01 What is the RSF?
Stands for the Rapid Support Forces
Paramilitary group originating from the Janjaweed, Arab tribal militias armed by al-Bashir in 2003 to fight against ethnically African rebel groups in Darfur + carried out 2003 genocide
Is headed by General Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo (Hemidti)
QUESTION 02 What is their capacity?
Estimated to have 100,000 to 150,000 troops
Winning the ground fight in Khartoum and control 4/5 states in Darfur
QUESTION 03 Do they have backing and support?
On the international stage, primarily backed by the UAE
Have steady weapons supply chain and diversified financial profile with critical assets in UAE and Russia
Transcript:
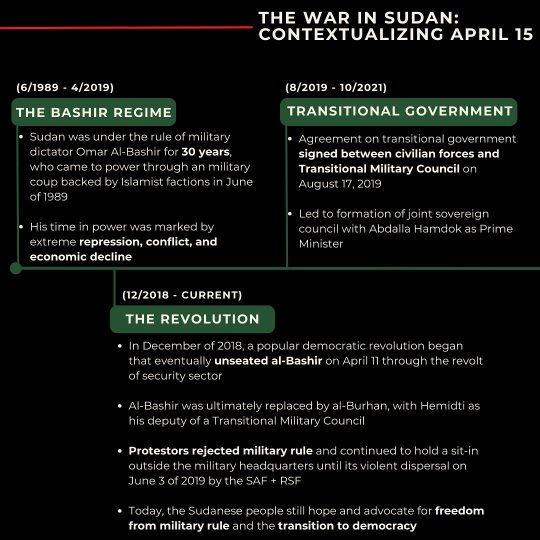
THE WAR IN SUDAN: CONTEXTUALIZING APRIL 15
(6/1989 - 4/2019) THE BASHIR REGIME
Sudan was under the rule of military dictator Omar Al-Bashir for 30 years, who came to power through an military coup backed by Islamist factions in June of 1989
His time in power was marked by extreme repression, conflict, and economic decline
(12/2018 CURRENT) THE REVOLUTION
In December of 2018, a popular democratic revolution began that eventually unseated al-Bashir on April 11 through the revolt of security sector
Al-Bashir was ultimately replaced by al-Burhan, with Hemidti as his deputy of a Transitional Military Council
Protestors rejected military rule and continued to hold a sit-in outside the military headquarters until its violent dispersal on June 3 of 2019 by the SAF + RSF
Today, the Sudanese people still hope and advocate for freedom from military rule and the transition to democracy
(8/2019-10/2021) TRANSITIONAL GOVERNMENT
Agreement on transitional government signed between civilian forces and Transitional Military Council on August 17, 2019
Led to formation of joint sovereign council with Abdalla Hamdok as Prime Minister
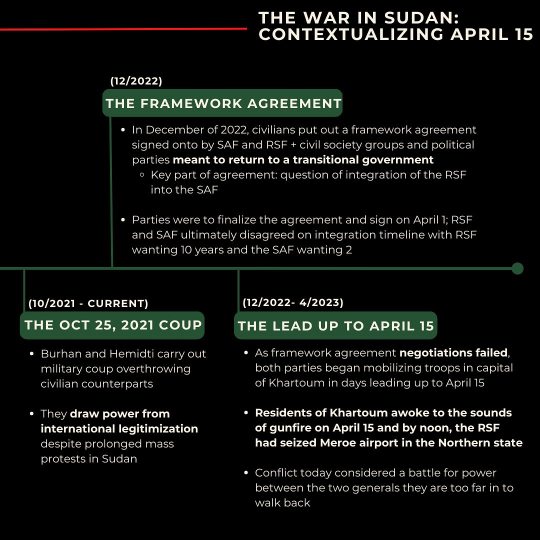
Transcript:
(10/2021 CURRENT)THE OCT 25, 2021 COUP
Burhan and Hemidti carry out military coup overthrowing civilian counterparts
They draw power from international legitimization despite prolonged mass protests in Sudan
(12/2022) THE FRAMEWORK AGREEMENT
In December of 2022, civilians put out a framework agreement signed onto by SAF and RSF + civil society groups and political parties meant to return to a transitional government
Key part of agreement: question of integration of the RSF into the SAF
Parties were to finalize the agreement and sign on April 1; RSF and SAF ultimately disagreed on integration timeline with RSF wanting 10 years and the SAF wanting 2
(12/2022-4/2023) THE LEAD UP TO APRIL 15
As framework agreement negotiations failed, both parties began mobilizing troops in capital of Khartoum in days leading up to April 15
Residents of Khartoum awoke to the sounds of gunfire on April 15 and by noon, the RSF had seized Meroe airport in the Northern state
Conflict today considered a battle for power between the two generals they are too far in to walk back

Transcript:
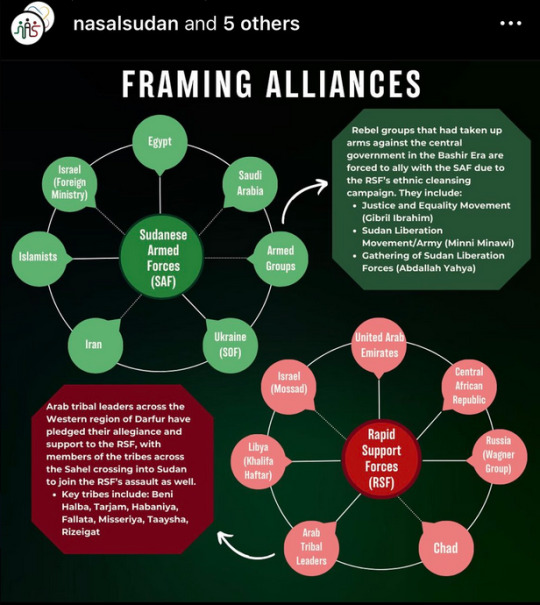
FRAMING ALLIANCES
Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF):
Egypt
Israel (Foreign Ministry)
Islamists
Iran
Saudi Arabia
Ukraine (SOF)
Armed Groups
Rebel groups that had taken up arms against the central government in the Bashir Era are forced to ally with the SAF due to the RSF's ethnic cleansing campaign. They include:
Justice and Equality Movement (Gibril Ibrahim)
Sudan Liberation Movement/Army (Minni Minawi)
Gathering of Sudan Liberation Forces (Abdallah Yahya)
Rapid Support Forces (RSF):
Israel (Mossad)
Libya (Khalifa Haftar)
United Arab Emirates
Central African Republic
Russia (Wagner Group)
Chad
Arab Tribal Leaders
Arab tribal leaders across the Western region of Darfur have pledged their allegiance and support to the RSF, with members of the tribes across the Sahel crossing into Sudan to join the RSF's assault as well.
Key tribes include: Beni Halba, Tarjam, Habaniya, Fallata, Misseriya, Taaysha, Rizeigat

Transcript:
IS THERE AN END IN SIGHT?
THE STATE OF NEGOTIATIONS
Effort: JEDDAH TALKS [MAY]
Parties involved: Externally: United States, Saudi Arabia Internally: SAF, RSF
Outcome: Discussed humanitarian ceasefire; signed Jeddah Declaration of Commitment to Protect the Civilians of Sudan - Failed
Effort: INTERGOVERNMENTAL AUTHORITY ON DEVELOPMENT (IGAD) [JULY]
Parties Involved: Externally: Kenya, Ethiopia, Djibouti, South Sudan Internally: RSF
Outcome: Proposed peacekeeping troops to ensure humanitarian corridor - Rejected
Effort: CAIRO TALKS (NEIGHBORING COUNTRIES) [JULY]
Parties Involved: Externally: Egypt, Ethiopia, South Sudan, Chad, Eritrea, CAR, Libya Internally: SAF, RSF
Outcome: Discussed lasting ceasefire, safe humanitarian passage, political dialogue framework - Failed
Effort: JEDDAH TALKS [OCTOBER]
Parties Involved: Externally: United States, Saudi Arabia Internally: SAF, RSF
Outcome: Discussed lasting ceasefire, safe humanitarian passage, political dialogue framework - Failed
Effort: IGAD + AFRICAN UNION (AU) [DECEMBER]
Parties Involved: Externally: IGAD, EU, UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, United States Internally: SAF (Burhan in person), RSF
Outcome: Agreed to a face-to-face meeting in late December and ceasefire; SAF later issued a retraction - Ongoing

Transcript:
The conflict in Sudan calls for the collective support of all to raise awareness about the war and aid the Sudanese people on the ground, especially when we live in nations that have been complicit in the oppression of the Sudanese people. Explore the options below and share with others. For more information, check the link in our bio.
WHAT CAN YOU DO?
EDUCATE YOURSELF
Deepen your knowledge about Sudan, empowering yourself with insights into the complexities of the situation.
DONATE
Extend a helping hand to Sudan by generously donating to individuals or grassroots organizations on the ground.
CONTACT YOUR REPS.
Amplify your impact by contacting your representatives, advocating for positive change.
#sudan#keep eyes on sudan#KeepEyesOnSudan#Sudan Action Week#SudanActionWeek#i hope the way i formatted it is good#i saw a few hours ago that rsf retreated from wad madani outskirts
370 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let's talk about Sudan-
TRANSCRIPT UNDER CUT









Transcript: What is happening in Sudan? The war, its origins, and the key players involved.
The war in Sudan
On April 15, a war broke out in Sudan's capital city of Khartoum between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF), and a paramilitary group known as the Rapid Support Forces (RSF). Since then, eight months of conflict has led to major destruction of Khartoum's infrastructure, the most developed region of Sudan, with fighting also spreading to the regions of Darfur in the west and Kordofan in the south.
Civilians in conflict zones have been forcibly displaced, under threat of physical and sexual violence, particulary by the RSF, which has looted, destroyed, and settled in people's homes.
In the western region of Darfur, a campaign of ethnic cleansing is being carried out by the RSF targeting the Masalit tribe. Allegations of genocide have been levied against the RSF.
Reports have just emerged that fighting has now spread to Wad Madani in AI Gazira state, which houses nearly 500,00 IDPs from Khartoum.
Key Figures: Abdel Fattah al Burhan (head of SAF), Omar El-Bashir (deposed dictator of Sudan), Mohamed Dagalo (Hemidti) (head of RSF)
Sudan: the war in numbers
24.7 million in need of critical humanitarian assistance 6.7 million displaced [5.4 million IDPS, 1.3 million refugees] 7,000+ cholera cases an increase of +136% over the past month 20.3 million people acutely food insecure- 4.9 million facing emergency hunger levels 19 million children are out of school 70-80% of hospitals out of service in conflict areas
FAQ - THE SAF
What is the SAF?
stands fro the Sudanese Armed Forces
is the de-facto government of Sudan
is headed by Lt. General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan
What is their capacity?
estimated to have aprox. 200,000 personnel and tactical advantage of airforce
currently control of relative northern and eastern regions of Sudan with functioning capital in Port Sudan (East)
Do they have backing and support?
on the international stage, primarily backed by Egypt
limited weapons supply from allies
internally, the SAF is ultimately considered the lesser of two evils
FAQ - THE RSF
What is the RSF?
stands fro Rapid Support Forces
paramilitary group originating from the Janjaweed, Arab tribal militias armed by al-Bashir in 2003 to fight against ethnically African rebel groups in Darfur + carried out 2003 genocide
is headed by General Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo (Hemidti)
What is their capacity?
estimated to have 100,000 to 150,000 troops
winning the ground fight in Khartoum and control 4/5 states in Darfur
Do they have backing and support?
on the international stage, primarily backed by the UAE
have steady weapons supply chain and diversified financial profile with critical assets in UAE and Russia
The war in Sudan: contextualizing April 15
6/1989 - 4/2019 - The Bashir Regime Sudan was under the rule of military dictator Omar Al-Bashir for 30 years, who came to power through an military coup backed by Islamist factions in June of 1989 His time in power was marked by extreme repression, conflict, and economic decline
12/2018 - current - The revolution In December of 2018, a popular democratic revolution began taht eventually unseated al-Bashir on April 11 through the revolt of security sector Al-Bashir was ultimately replaced by al-Burhan, with Hemidti as his deputy of a Transitional Military Council Protestors rejected military rule and continued to hold a sit-in outside the military headquarters until its violent dispersal on June 3 of 2019 by the SAF + RSF Today, the Sudanese people still hope and advocate for freedom from the military rule and the transition to democracy
8/2019 - 10/2021 - Transitional Government Agreement on transitional government signed between civilian forces and Transitional Military Council on August 17, 2019 Led to formation to joint sovereign council with Abdalla Hamdok as Prime Minister
10/2021 - Current - The Oct 25, 2021 Coup Burhan and Hemidti carry out military coup overthrowing civilian counterparts They draw power from international legitimization despite prolonged mass protests in Sudan
12/2022- The Framework Agreement In December of 2022, civilians put out a framework agreement signed onto by SAF and RSF + civil society groups and political parties meant to return to a transitional government - key part of agreement: question of integration of the RSF into the SAF Parties were to finalize the agreement and sign on April 1; RSF and SAF ultimately disagreed on the integration timeline with RSF wanting 10 years and the SAF wanting 2
12/2022-4/2023 - The Lead up to April 15 As framework agreement negotiations failed, both parties began mobilizing troops in capital of Khartoum in days leading up to April 15 Residents of Khartoum awoke to the sounds of gunfire on April 15 and by noon, the RSF had seized Meroe airport in the Northern state Conflict today considered a battle of power between the two generals they are too far in to walk back
Framing alliances
Sudnese Armed Forces (SAF):
Saudi Arabia
armed groups- rebel groups that had taken up arms against the central government in the Bashir Era are forced to ally with the SAF due to the RSF's ethnic cleansing campaign. They include: Justice and Equality Movement (Gibril Ibrahim), Sudan Liberation Movement/Army (Minni Minawi), Gathering of Sudan Liberation Forces (Abdallah Yahya)
Ukraine (SOF)
Iran
Islamists
Israel (Foreign Ministry)
Egypt
Rapid Support Forces (RSF):
United Arab Emirates
Central African Republic
Russia (Wagner Group)
Chad
Arab Tribal Leaders- Arab tribal leaders across the Western region of Darfur have pledged their allegiance and support to the RSF, with members of the tribes across the Sahel crossing into Sudan to join the RSF's assault as well. Key tribes include: Beni Halba, Tarjam, Habaniya, Fallata, Misseriya, Taaysha, Rizeigat
Libya (Khalifa Haftar)
Israel (Mossad)
Is there an end in sight? The state of negotiations
Effort- Jeddah Talks [May] Parties Involved- Externally: United States, Saudi Arabia. Internally: SAF, RSF Outcome: discussed humanitarian ceasefire; signed Jeddah Declaration of Commitment to Protect the Civilians of Sudan- FAILED
Effort- Intergovernmental authority on development (IGAD) [July] Parties Involved- Externally: Kenya, Ethiopia, Djibouti, South Sudan . Internally: RSF Outcome: proposed peacekeeping troops to ensure humanitarian corridor-REJECTED
Effort- Cairo talks (neighboring countries) [July] Parties Involved- Externally: Egypt, Ethiopia, South Sudan, Chad, Eritrea, CAR, Libya. Internally: SAF, RSF Outcome: discussed lasting ceasefire, safe humanitarian passage, political dialogue framework-FAILED
Effort- Jeddah talks [October] Parties Involved- Externally: United States, Saudi Arabia . Internally: SAF, RSF Outcome: discussed lasting ceasefire, safe humanitarian passage, political dialogue framework-FAILED
Effort- IGAD + African Union (AU) [December] Parties Involved- Externally: IGAD, EU, UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, United States. Internally: SAF (Burhan in person), RSF Outcome: agreed to face-to-face meeting in late December and ceasefire; SAF later issued a retraction-ONGOING
What can you do?
The conflict in Sudan calls for the collective support of all to raise awareness about war and aid the Sudanese people on the ground, especially when we live in nations that have been complicit in the oppression of the Sudanese people. Explore the potions below and share with others. Educate yourself- deepen your knowledge about Sudan, empowering yourself with insights into the complexities of the situation. Donate- extend a helping hand to Sudan by generously donation to individuals or grassroots organizations on the ground.
Contact your reps- amplify your impact by contacting your representatives, avocating for positive change
226 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sudan’s rival generals have ignored warnings of mass starvation. In more than a year of brutal war, the two military factions have weaponized humanitarian aid.
Sudan’s de facto leader, military chief Abdel Fattah al-Burhan, has blocked aid into at least half of the country under the control of the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) headed by Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, known as Hemeti. Meanwhile, the RSF is obstructing trucks into places held by the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF). Local volunteers running soup kitchens have been targeted and killed by the RSF, particularly in Khartoum, Sudanese aid workers told FP.
The conflict has created the world’s largest hunger and internal displacement crises. The fighting has pushed 25 million people, more than half the nation’s population, into acute hunger and forced about 11 million people to flee their homes, including 2.3 million who fled abroad. More than two million Sudanese could die by the end of this year, aid agencies warn.
In areas where there is food available, extortion and attacks on traders at checkpoints have raised prices. Women have recounted having sex with SAF soldiers in exchange for food. Reports of torture, rape, the use of children under 15 in the fighting, and ethnic-based massacres by the RSF and armed militias have surged over the past year.
“People are dying of hunger in the capital,” said Mathilde Vu, the Norwegian Refugee Council’s advocacy advisor in Sudan. “We are looking at the risk of starvation being used as a weapon of war. … This needs to be monitored. The policymakers already have a tool for that. The U.N. Security Council resolution about conflict and hunger, and what they need to put in place is a monitoring of that.”
Both sides in Sudan’s nearly 17-month civil war have committed “harrowing” abuses that may amount to war crimes, a U.N.-mandated mission reported on Friday, calling for a countrywide arms embargo. Sudan’s military government rejected a proposal by U.N. experts to deploy a peacekeeping force to protect civilians.
Compounding the situation, the humanitarian response is critically underfunded. A $2.7 billion U.N. appeal has been just 32 percent funded. Much of that funding has come from the United States. However, aid agencies say local volunteers on the ground need to be better supported since a cease-fire is highly unlikely in the immediate future.
Famine was declared in Zamzam camp housing about 500,000 displaced people near the besieged city of El Fasher, the state capital of North Darfur—areas where the RSF is blocking aid trucks. There’s a realistic chance of famine in 16 other areas, Vu said, but precise figures are hard to confirm. Last month, the SAF agreed to open the Adré border crossing from landlocked Chad into Sudan, for a period of three months. But international aid agencies told FP that the SAF has made things difficult through lengthy authorizations ensuring only a trickle of shipments gets in.
U.S. envoy for Sudan Tom Perriello visited Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Turkey this week in the latest attempt by the Biden administration to expand humanitarian access in Sudan, following failed peace talks in Geneva. The conflict risks turning into a forever war, in which various external actors seize the opportunity to extend their influence. Turkey, Egypt, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Russia have been accused of arming warring parties.
While such negotiations are essential, U.S. attention and pressure should also focus on other regional powers with a vested interest in the conflict such as Eritrea and Ethiopia. Foreign mercenaries from Chad, Mali, Niger, the Central African Republic, and Libya are believed to be fighting in Sudan.
Pressuring regional powers could engage local armed militias allied to the warring parties in ultimately ensuring access to places like El Fasher. “It will create more of a buffer than two guys signing an agreement in Jeddah” and then breaking it, Vu said. “You cannot bypass the regional powers. … They really are the ones who have the leverage. It’s very important that Western powers engage them so that they have a constructive role in this crisis rather than a harmful one,” she added. Even if Burhan and Hemeti signed a peace deal, many of the local armed groups involved would likely not abide by it.
Both generals have held meetings with several African leaders, while the African Union has been largely absent in peace negotiations. More recently, Burhan held meetings with Eritrea’s president, Isaias Afwerki, and Ethiopia’s prime minister, Abiy Ahmed, at the China-Africa summit.
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
The United Nations food agency warned Sudan’s warring parties Friday that there is a serious risk of widespread starvation and death in Darfur and elsewhere in Sudan if they don’t allow humanitarian aid into the vast western region. Leni Kinzli, the World Food Program’s regional spokesperson, said at least 1.7 million people in Darfur were experiencing emergency levels of hunger in December, and the number “is expected to be much higher today.” “Our calls for humanitarian access to conflict hotspots in Sudan have never been more critical,” she told a virtual U.N. press conference from Nairobi. Sudan plunged into chaos in mid-April 2023, when long-simmering tensions between its military led by Gen. Abdel Fattah Burhan, and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces commanded by Mohammed Hamdan Dagalo, broke out into street battles in the capital, Khartoum. Fighting has spread to other parts of the country, especially urban areas and the Darfur region. The paramilitary forces, known as the RSF, have gained control of most of Darfur and are besieging El Fasher, the only capital in Darfur they don’t hold, where some 500,000 civilians had taken refuge. Kinzli said WFP’s partners on the ground report that the situation in El Fasher is “extremely dire” and it’s difficult for civilians wanting to flee the reported RSF bombings and shelling to leave. She said the violence in El Fasher and surrounding North Darfur is exacerbating the critical humanitarian needs in the entire Darfur region, where crop production for staple cereals like wheat, sorghum and millet is 78% less than the five-year average. On top of the impact of escalating violence, Kinzli said, “WFP is concerned that hunger will increase dramatically as the lean season between harvests sets in and people run out of food.”
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://t.co/J3fEqiIOIk
Since June 2019, Sudan has been caught in a whirlwind of revolution, descending into a profound economic and political crisis. The initial optimism that followed President Omar H. al-Bashir's ousting has led to chaos, influenced by powerful international actors with their respective political agendas. The geopolitical quagmire is further complicated by the involvement of neighbouring countries.
Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed's (PhD) recent visit to Port Sudan, where he met with Abdel Fattah al-Burhan (Gen.), the head of the Sudanese army and the Saudi- and Egyptian-backed Sovereign Council of Sudan, evidenced Ethiopia’s vested interests. The visit should be particularly important given Abiy’s prior engagement with Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) leader, whom he hosted in Addis Abeba in December 2023 to advocate for peace in Sudan.
Ethiopia's economic ties with Sudan are substantial. The slowdown in the 211.5 million dollar investment circuit between Khartoum and Addis Abeba has adversely affected both countries. Small businesses along the Sudan-Ethiopia border have borne the brunt of the ongoing conflict. Prime Minister Abiy’s visit can be seen as an effort to stabilise these economic ties and promote peace for mutual benefit. However, if influenced by Western countries or Saudi Arabia, Abiy’s administration may face political backlash from its ally, the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
The role of international players was evident early on. The UAE was among several countries, including the United States (US), Israel, Saudi Arabia and Egypt, that expressed solidarity with the Sudanese people. Saudi Arabia and the UAE notably provided three billion dollars in economic aid to Al-Burhan’s leadership, signalling their approval of the political shift in Khartoum. However, the situation in Sudan soon deteriorated into an ongoing civil war, leading to accusations of ethnic cleansing and further international scrutiny.
Sudan's civil war, however, extends beyond regional dynamics. Recent reports have uncovered the involvement of external actors in perpetuating the conflict.
In May this year, American Senator Ben Cardin, chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, raised concerns about a UN Panel of Experts' report from the previous year, which provided evidence of the UAE supplying weapons to the RSF, a group notorious for its brutal tactics. US Ambassador to the UN, Linda Thomas-Greenfield, echoed these concerns, calling for “external actors" to stop "fueling and prolonging this conflict and enabling these atrocities by funnelling weapons into Sudan.”
Abu Dhabi has been working vigorously to clear its name in response to these accusations. Through diplomatic channels and humanitarian aid, the UAE has sought to counter allegations of its involvement in the Sudanese civil war. Hundreds of millions of dollars have been funnelled to humanitarian organisations operating in Sudan through various UN agencies, a move seen by many as an attempt by Abu Dhabi to portray itself as a force for good amidst the chaos.
Despite these efforts, a recent UN report has further implicated the UAE. The report exposed that the RSF, supported by Abu Dhabi, committed international crimes by receiving and laundering gold illegally exported from Sudan. The UAE has vehemently denied any involvement in Sudan’s political turmoil or illegal gold trade practices, calling the allegations a political mockery of its humanitarian generosity.
While these revelations add layers of complexity, the international community’s response remains lacklustre. The US and the UN have the political and diplomatic clout to influence the situation, but the resolution of Sudan’s crisis ultimately lies in the hands of its people. The international community can only play a supportive role in the Sudanese-led efforts to resolve the political disorder, providing the necessary space and resources for Sudan to shape its destiny.
Although belatedly, the Addis Abeba-based African Union (AU) has also begun addressing the dire humanitarian situation in Sudan. The Chairperson of the AU High-Level Panel on Sudan, Mohamed Ibn Chambas (PhD), has begun to speak out about the severe impacts of the ongoing civil war. However, stronger official condemnations from the AU were expected, holding all groups and countries involved in the war accountable.
Ironically, Sudan’s revolution is no longer a story of a failed uprising but an ongoing civil war marked by international intrigue and regional power struggles.
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nearly 500 days of violence and conflict have left Sudan in the wake of a humanitarian crisis many say is one of the largest in the world.
Almost 52,000 people have been killed or wounded and tens of millions displaced since April 2023, when a battle for power erupted between Sudan’s army, led by Gen. Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) headed by his former deputy, Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo.
The magnitude of the crisis is apparent from the repeated warnings by aid groups and even the UN, which has gone as far as to say that Sudan is now at a “cataclysmic breaking point”. [...]
“Ukraine is of vital interest for the security of Europe – Sudan is not … This alone explains why Ukraine receives all the West’s attention, and not Sudan. This reasoning is similar, looking at Israel.”
Various other factors for this lack of attention to Sudan include the UN’s waning influence in global affairs and a growing unwillingness of Western countries to directly intervene in the internal affairs of other nations, he said. [...]
Continue Reading.
Tagging: @vague-humanoid
Note from the poster @el-shab-hussein: the article makes it clear how any Western interventionism comes from a place of desiring control and power, not help for those who need it.
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

Around 1,300 people, mostly civilians belonging to the Massalit tribe, were slaughtered in Sudan’s West Darfur over three days earlier this month by the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) and its allied Arab militias, witnesses, local activists and human rights defenders have told Middle East Eye.
The massacres in Ardamata, an area on the northeast outskirts of West Darfur’s state capital el-Geneina, were committed after the RSF, a paramilitary force, expelled Sudanese soldiers from a military base in the suburb during battles from 2 to 6 November.
For the second time in a matter of months, the streets of el-Geneina and its surroundings have been left filled with corpses.
Witnesses said the scenes were reminiscent of June, when Arab militias and RSF fighters killed more than 500 people in what human rights organizations described as ethnic cleansing against the Massalit, a Black African tribe.
After Sudan’s war broke out on 15 April between the RSF and the Sudanese military, Darfur has been the scene of some of the most ferocious fighting, alongside Khartoum.
Between 2003-2005, Darfur endured a vicious conflict, in which the government of then-president Omar al-Bashir armed thousands of Arab tribesmen, creating a militia known as the Janjaweed, which he used against Darfuri rebel groups that had revolted against Khartoum in response to longstanding neglect of the region’s Black African population.
Around 300,000 people were killed in the war, which is often described as genocidal and brought war crimes charges against several men leading it from the International Criminal Court, as the Janjaweed targeted Darfur’s Black population, driving millions from their homes.
Today, the backbone of the RSF’s paramilitary forces, including its leader, Mohammed Hamdan Dagalo, better known as Hemeti, is made up of Arab tribesmen from Darfur and its surroundings who used to be Janjaweed fighters.
According to Human Rights Watch researcher Mohamed Osman, the Massalit community, as well as other non-Arab communities, have been targeted by the RSF and its allied militias in el-Geneina since June.
Click the link in our bio for more on this story
✍️: MEE/Mohammed Amin
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sudan updates as of 7/19/2024

Twitter: Source | Donate: GFM

Twitter: Source | Full article at Source

Donate: GFM | Twitter: Source

Donate: GFM | Twitter: Source

Twitter: Source
Alt won’t fit in alt tab:
DVS welcomes the discussions of the UN Secretary- General's Envoy, Mr. Ramatane Lamamra, with the RSF delegation regarding opening humanitarian paths to deliver aid to Sudanese civilians. This step is appreciated, but it requires the participation of the SAF and the commitment of the parties to open the paths. It also calls on the UN to put pressure on the parties to end the war in Sudan.
الأمم المتحدة
United Nations
Office of the Personal Envoy of the Secretary-General for Sudan مكتب المبعوث الشخصي للأمين العام للأمم المتحدة الى السودان Statement of the Personal Envoy of the Secretary-General for Sudan, Ramtane Lamamra, after the conclusion of the Geneva Proximity Talks 19 July 2024, Geneva
In Resolution 2724 (2024), the Security Council mandated me to use my good offices with the parties to the conflict in Sudan, complementing and coordinating regional peace efforts. Security Council Resolution 2736 (2024) reiterated the Council's concern over the situation in Sudan. It urged the parties to de-escalate in and around El Fasher, to allow and facilitate unfettered humanitarian access across the country and ensure the protection of civilians. It further called on the parties to the conflict to seek an immediate cessation of hostilities, leading to a sustainable resolution of the conflict, through dialogue.
Resolution 2736 (2024) also requested the Secretary-General, in consultation with the Sudanese authorities and regional stakeholders, to make further recommendations for the protection of civilians in Sudan, building on the existing mediation and good offices mechanisms.
To contribute to these recommendations, and building on my previous engagements with the parties, I addressed letters to General Abdel-Fattah al-Burhan, Chairperson of the Sovereign Council and Commander of the Sudanese Armed Forces, and General Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, Commander of the Rapid Support Forces, inviting them to nominate senior delegations to discuss the following issues:
1) measures to be undertaken to ensure the distribution of humanitarian assistance to all the Sudanese population in need;
2) options to ensure the protection of civilians across Sudan.
I invited the delegations appointed by both parties to travel to Geneva, Switzerland, to participate in discussions in "proximity format", in which I would separately engage the delegation of each party, supported by a United Nations integrated technical team providing relevant expertise. These discussions took place from 11 to 19 July 2024. During this period, my team held a total of around 20 sessions with the parties' delegations, including technical and plenary meetings. We interacted with each of the delegations in the context of their respective mandates.
Throughout these engagements, the delegations expressed their positions on key issues of concern, in light of their responsibilities, allowing us to deepen our mutual understanding. We then explored avenues to address these issues to contribute to alleviating the suffering of the civilian population in Sudan. I am encouraged by the willingness of the parties to engage with me on these critical matters, as well as by the commitments made to respond to some specific requests we presented to them.
The humanitarian situation in Sudan remains catastrophic and is deteriorating every day. Urgent action is needed to ensure that humanitarian assistance safely reaches all those in need and to guarantee the protection of all civilians in Sudan. I count on the parties to promptly translate their willingness to engage with me into tangible progress on the ground. The United Nations will continue to make every effort to support the civilian population throughout the country.
The discussions held in Geneva are an encouraging initial step in a longer and complex process. Although unilateral commitments by the parties do not constitute agreements with the UN, I welcome the commitments announced today by one of the two parties to enhance humanitarian assistance and the protection of civilians. I intend to remain in close contact with the leadership of the two parties, to follow up on the implementation of commitments and to engage them on critical issues. I remain at their disposal for the desirable continuation of this process. I urge both parties to step up their engagement for peace for the sake of the Sudanese people and the future of the country.

Twitter: Source

Twitter: Source

Twitter: Source
(Id/alt in alt tab)
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
The US has accused the Sudanese paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) of committing genocide and imposed sanctions on its leader. US Secretary of State Antony Blinken on Tuesday said Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, also known as Hemedti, was being punished for his role in "systematic" atrocities against the Sudanese people during the 20-month conflict. He said the RSF and allied militias were responsible for the murder of "men and boys - even infants", as well as brutal sexual violence against women on ethnic grounds. The militias have also targeted fleeing civilians and murdered innocent people escaping the conflict, Blinken said. "Based on this information, I have now concluded that members of the RSF and allied militias have committed genocide in Sudan," he said. In response, the RSF accused the US of double standards and failing to effectively address the ongoing crisis. "The decision… expresses the failure of the [US President Joe] Biden administration to deal with the Sudanese crisis and the double standards it followed [with regards to the crisis]," Hemedti's adviser, El-Basha Tbaeq, said in a post on his X account. He added that this may complicate the Sudanese crisis and hinder negotiations to address the root causes of the conflict. The RSF has been fighting the Sudanese military since April 2023, and there has been a growing outcry about its conduct during the war. The US had previously determined that the RSF and other militias had engaged in war crimes, crimes against humanity, and ethnic cleansing in the western Darfur region, where the group has been accused of targeting and killing non-Arabs.
continue reading
Remember folks, it's only genocide if it's committed by people we dislike.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the final days of Ramadan, before Mecca's Grand Mosque, Sudan's de facto president and army chief, General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan knelt in prayer beside Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed Bin Salman. Al-Burhan had arrived in the kingdom just two days after his troops dealt a significant blow to the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF), recapturing the capital Khartoum after two years of civil war. Missing from the frame was the United Arab Emirates (UAE), the Gulf power that has backed al-Burhan’s rivals in Sudan’s civil war with arms, mercenaries, and political cover. The scene captured the essence of a deepening rift between Saudi Arabia and the UAE — once allies in reshaping the Arab world, now architects of competing visions for Sudan and the region.
For two years, Sudan has been enveloped in chaos. The conflict that erupted in April 2023 between the Sudanese Armed forces (SAF) and the RSF, led by General Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo "Hemedti," has inflicted immense suffering: an estimated 150,000 killed, allegations of mass atrocities staining both sides but particularly the RSF in Darfur, 12 million displaced, and over half the population facing acute food insecurity.
Khartoum, once a symbol of confluence, bears deep scars — widespread destruction, looted homes, and streets haunted by the unburied dead. It was against this backdrop of devastation and military gains that al-Burhan made his trip across the Red Sea.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
After getting off his helicopter, he kissed the ground then pumped his fist in the air in victory. General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan made a triumphant return to Khartoum on March 26, to celebrate regaining control over the capital, “liberated” from the grip of the paramilitaries.
The army chief had been forced to flee the megapolis nearly two years ago, at the start of the war opposing his Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) led by his former ally Mohammed Hamdan Dagalo, also known as "Hemedti".
The bloody power struggle has left tens of thousands of people dead and over 10 million displaced.
Forced to change course, RSF retreated across Khartoum on Wednesday, using the Jebel Awliya bridge, the last escape route from the greater Khartoum region. Scenes of joy erupted in various areas of the city following the militia’s retreat.
General al-Burhan ‘back to business’
Launched in September, the Sudanese army’s offensive in Khartoum is a turning point in its war against RSF. The militia controlled certain strategic sites in the capital, including the international airport, the presidential palace and several military bases.
“Abdel Fattah al-Burhan’s return to the presidential palace is a very important symbol within the country as well as abroad,” said Marc Lavergne, Sudan expert with the Paris-based French National Centre for Scientific Research. “He claims to be the legitimate leader of the country, and he is showing the world that he is back to business.”
His return was long awaited. When the war began, the military-led government was forced to move to Port Sudan, the country’s principal port on the Red Sea, located 700 kilometres north-east of the capital.
The Sudanese army struggled to stem RSF’s advance. Besides controlling their historic bastion of Darfur, the militia managed to extend their presence across northern and southern Khartoum. The RSF in 2023 inflicted a particularly humiliating defeat on the army by capturing the city of Wad Madani, the capital of Sudan’s central Al-Jazirah state. The army reversed this defeat by reconquering the megapolis of 400,000 inhabitants in January 2025.
The paramilitary fighters lose ground
The change in the balance of power in favour of the Sudanese army is because the paramilitary fighters are “losing steam”, said Lavergne. “The Rapid Support Forces are not professional soldiers with a real hierarchy and logistical organisation. They wanted to hit hard and fast; they took control over large territories without being able to run them.”
Since the start of the war, serious acts of violence have been attributed to both sides. The army is accused of carrying out indiscriminate bombings, killing numerous civilians. A strike this week in Tora, in Darfur state, killed several hundred people, according to witnesses.
Accused of numerous massacres, the RSF is considered even more brutal than the Sudanese army. “These are looters who exploit the territories they manage to capture,” said Lavergne.
The RSF’s methods have tarnished their image and weakened their capacity to recruit among the population. The RSF are also confronted by desertions, like that of the war chief Abu Aqla Kikl, who changed sides and joined the Sudanese army in October 2024.
Fear in Darfur
The balance of power between the two warring sides in Sudan has long been relatively stable, despite the Sudanese army’s notable advantage of possessing military aviation. More established in urban combat, the RSF also possesses an arsenal of drones and missiles provided by the United Arab Emirates, their main supporter, although Abu Dhabi denies any implication in the conflict.
Pressured by losses suffered on the ground, Hemedti embarked on a regional diplomatic tour in Uganda, Ethiopia and Kenya. In a quest for legitimacy, he even announced the creation of a “parallel government” during a February visit to Nairobi, to govern the areas under RSF control. The initiative was firmly rejected by SAF leader Burhan who accused Kenyan President William Ruto of supporting his rival.
“The eastern African countries that hosted Hemedti could have maybe weighed in his favour during a negotiation phase. Yet on the military side, I don’t see how RSF could inverse the balance [of power] today,” said Lavergne.
While in Khartoum the army is celebrating the end of fighting, certain observers fear that RSF’s retreat to Darfur, which it still controls, will provoke a new wave of violence against the non-Arab communities, which are often targeted by the paramilitary forces. The United States accused the RSF and allied militias in January of committing genocide, through the systematic murder of “men and boys – even infants – on an ethnic basis”.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
On a sunny April afternoon in 2006, thousands of people flocked to the National Mall in Washington, D.C., for a rally with celebrities, Olympic athletes, and rising political stars. Their cause: garner international support to halt a genocide in Sudan’s Darfur region.
“If we care, the world will care. If we act, then the world will follow,” Barack Obama, then the junior Illinois senator, told the crowd, speaking alongside future House Speaker Nancy Pelosi. That same week, then-Sen. Joe Biden introduced a bill in Congress calling on NATO to intervene to halt the genocide in Sudan. “We need to take action on both a military and diplomatic front to end the conflict,” he said.
Flash-forward 18 years, and the prospect of genocide again looms in Sudan amid an explosive new civil war. But this time, there are no rallies, no A-list celebrities, no calls for outside military intervention. Few world leaders pay anything more than lip service to condemning the atrocities.
Fighting between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the rival Rapid Support Forces (RSF) paramilitary group has killed tens of thousands of people and displaced some 9 million since the conflict began in April 2023. The United States accused both sides of committing war crimes and atrocities and concluded that the RSF and its allied militias have committed ethnic cleansing.
Western officials and aid workers working on Sudan say they are vexed, and horrified, by the lack of international attention and resources the conflict is receiving—particularly compared to the global response to the conflict in 2006, which was the progenitor of the current conflagration.
If this trend continues and there is no forceful international crisis response, they warn, Sudan will likely collapse into a failed state and could face full-fledged genocide once again.
“You can’t help but watch the level of focus on crises like Gaza and Ukraine and wonder what just 5 percent of that energy could have done in a context like Sudan and how many thousands, tens of thousands of lives it could’ve saved,” said Alan Boswell, an expert on the region at the International Crisis Group.
The top general of the SAF, Gen. Abdel Fattah al-Burhan, and the head of the RSF, Mohamed Hamdan “Hemeti” Dagalo, jointly seized power from a transitional government in a coup in 2021. Tensions between the rival sides escalated and finally erupted into war in April 2023.
In the 13 months since, the RSF has entrenched its positions around the national capital of Khartoum, forcing the SAF to relocate its headquarters to the coastal city of Port Sudan. The RSF has made steady gains in seizing control of Darfur and advancing southward and eastward against SAF forces. The SAF still controls territories around Khartoum and up the Nile River, a vital strategic route to Egypt; along the Red Sea coast; and the eastern borders with Ethiopia and Eritrea.
The conflict has also expanded into a full-fledged regional proxy war. Egypt and Saudi Arabia, as well as Riyadh’s arch regional rival Iran, back the SAF, while the United Arab Emirates is reportedly funneling arms and military supplies to the RSF. The RSF also reportedly receives support from Chad and from Russia through its affiliated mercenary groups.
The focal point of the conflict now is on El Fasher, the capital of North Darfur and the center of fighting. The RSF has taken control of vast swaths of western and southern Sudan in its war against the SAF. El Fasher is the last SAF stronghold in Darfur, occupying a strategically important position for trade routes from neighboring Libya and Chad.
The RSF recently began its advance on El Fasher where an estimated 2 million to 2.8 million civilians have sought to take refuge from the fighting. (Precise figures are hard to come by.)
“The risk of genocide exists in Sudan. It is real, and it is growing every single day,” Alice Nderitu, the U.N. special advisor on the prevention of genocide, warned in a U.N. Security Council meeting last week.
A lengthy report from Human Rights Watch documented how the RSF and allied militias committed widespread atrocities, including mass rape, child murder, and massacres of civilians when it captured the Sudanese city of El Geneina last year. U.S. and U.N. officials and human rights experts warn that the same will likely happen if the RSF takes control of El Fasher, but on a much wider scale. The United States and aid groups have accused the SAF of blocking vital food aid from entering the country and RSF forces of looting humanitarian stocks, exacerbating the crisis and pushing regions of the country closer to famine.
“The potential fatality generation here is off the charts,” said Nathaniel Raymond, executive director of the Humanitarian Research Lab at Yale’s School of Public Health who runs a research project that monitors the conflict in Sudan. “What will happen when the RSF takes El Fasher? Exactly what is happening in every other place they control.”
“There is Hiroshima- and Nagasaki-level casualty potential,” he added, referring to the U.S. atomic bombs dropped on Japan in World War II that killed up to 225,000 people.
Aid organizations and officials who work on Sudan have long decried the relative inattention the conflict in Sudan gets compared to Ukraine or the war in Gaza. Some 20 million people—or 10 times the population of Gaza—are at risk of famine in various regions of Sudan. “Very few people who don’t work on Sudan know that Darfur is on the brink of famine,” Boswell said. “Obviously, everyone knows about the risk of famine in Gaza.”
U.S. President Joe Biden’s own social media posts about Gaza versus Sudan provide another, albeit imperfect, window into the attention each conflict receives. Biden tweeted about Israel or Gaza at least 107 times in the six months since the Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas attacks that started the Israel-Hamas war. Since the war in Sudan began over a year ago, he has tweeted about Sudan four times—three of which were about the evacuation of the U.S. Embassy in Khartoum right after fighting broke out.
Aid groups are strained for resources to tackle the humanitarian crisis caused by the war. In February, Doctors Without Borders warned that in one refugee camp alone in North Darfur, one child was dying every two hours of malnutrition. In April, on the conflict’s first anniversary, aid groups said the international humanitarian response plan to aid the Sudanese was only 6 percent funded. At a donor conference that month in Paris, countries pledged $2 billion more—though that is still only about half of what aid groups estimate the country needs.
Biden appointed a special envoy for Sudan in February—Tom Perriello, a former U.S. representative from Virginia and State Department veteran. Most experts have cheered Perriello’s new push to hold cease-fire talks in the months since and engage U.S. lawmakers on Capitol Hill to bring more levers of U.S. power and financing to bear on Sudan, but they also fear his efforts may be too little, too late for the civilians trapped in El Fasher.
“It will be very hard to deescalate the situation, though everyone should try. But there is an aura of inevitability that this is all going to blow up,” Boswell said. “The degree of mobilization from all sides is hard to walk down.”
Diplomatic and aid officials working on Sudan have some theories on why the atrocities in Darfur and across the country are receiving such little attention now compared to the 2000s, but none gives a full answer.
In 2006, the United States was still reaching the heights of its post-9/11 “war on terror” campaign. Sudan, under former dictator Omar al-Bashir, had given safe haven to Osama bin Laden as he built up al Qaeda’s global terror network, and “bashing Bashir and his genocide in Darfur couched nicely with [counterterrorism] priorities” of the U.S. government at the time, said Nicole Widdersheim, a former senior National Security Council official now with Human Rights Watch.
The memories of failed and successful international interventions to halt genocide—Rwanda in 1994 and the Balkans later that decade, respectively—were still relatively fresh in the minds of policymakers. The costly Western campaigns in Afghanistan, Iraq, and Libya that later exposed the shortcomings and blowback of military interventions were still underway.
It also preceded the current era of great-power competition, where Washington is intensely focused on countering Russia and China. Sudan also competes with the ongoing wars in Gaza and Ukraine for international attention and humanitarian resources. Others suggested racism built into Western foreign policy played a part. “It’s seen as yet ‘another war in Africa like all the others,’” said one official dryly. Not one single factor can explain it all, experts concluded.
“Gaza is taking up the always limited American public interest and activism on a foreign crisis, but to be fair, there was nearly no public activism or engagement on the Sudan war before” the Israel-Hamas war, Widdersheim said.
Experts say the relative inattention Sudan has gotten from the top echelons of the White House and other Western powers that could have influence in pressuring the warring sides in Sudan to sit for peace talks has led to the current protracted state of the war.
Biden hosted Kenyan President William Ruto for a state visit this week, where the two called on “the warring parties in Sudan to facilitate unhindered humanitarian access and immediately commit to a ceasefire” toward the end of a lengthy joint statement but did not elaborate further. U.S. Agency for International Development Administrator Samantha Power and U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations Linda Thomas Greenfield have also been outspoken about urging an end to the conflict in Sudan.
Successive cease-fire talks in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, over the past year, brokered by the United States and Saudi Arabia, failed to clinch any lasting deal. Those talks were led on the U.S. side not by a top White House official or Secretary of State Antony Blinken, but by the assistant secretary of state for African affairs, Molly Phee.
Behind-the-scenes efforts by some members of Congress in December 2023 to appoint a special presidential envoy on Sudan—one who would report directly to the White House, rather than an envoy reporting to the assistant secretary of state—were unsuccessful, multiple officials and congressional aides said, speaking on condition of anonymity to discuss internal administration dynamics. Perriello was appointed two months later.
Perriello in mid-April said that cease-fire talks would resume in Jeddah “within the next three weeks,” but so far those talks have yet to materialize. Several current and former officials familiar with the matter, who spoke on condition of anonymity to speak candidly, said the talks in Jeddah could resume in June, by which point the RSF could have already captured El Fasher from the mostly cutoff SAF forces.
“The need to start formal peace talks in Jeddah is absolutely urgent, and the United States is working exhaustively with partners to make that happen,” said a State Department spokesperson. “But we are not waiting for formal talks to begin—rather, we have accelerated our diplomatic engagements to align international efforts to end this war, mitigate the humanitarian crisis, and prevent future atrocities.”
Cease-fire talks have worked in limited ways in the past, such as when the United States got both sides to briefly stop fighting in Khartoum so it could evacuate its embassy in April 2023. “When the right leverage is put on the table at the right time to get the RSF and SAF to stop fighting, it can be done,” said Kholood Khair, a Sudanese policy analyst and founding director of Confluence Advisory, a Sudan-focused think tank. “The international community has just chosen not to deploy that same leverage this time around.”
Khair added that the Jeddah talks format has failed before, and it will likely fail again. “The concern is that because of the laziness and complicity of the international community at this point, you don’t have any diplomats who are looking for a new way of doing things. Jeddah in many ways is blocking the start of any new diplomatic efforts or other good ideas that could be effective.”
“Diplomats are fixated on Jeddah now, simply because it’s already there,” Khair said.
As Perriello engaged in frenetic diplomacy, he has also publicly marveled at how little attention the scale of the conflict and death in Sudan is receiving on the international stage.
“One of the things that to me captures just how invisible and horrific this war is, is that we don’t have a credible death count,” Perriello said during a congressional hearing in front of the 21-member Senate Foreign Relations Committee this month. “We literally don’t know how many people have died—possibly to a factor of 10 or 15. The number was earlier 15,000 to 30,000. Some think it’s at 150,000,” he said. During the course of Perriello’s hearing, senators cycled out of the room due to scheduling conflicts, often leaving only one senator in the room and 20 empty seats.
48 notes
·
View notes