#Madame Roland
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
In one of Madame Roland’s letters there’s a section written by Claude Fauchet (most famous for helping seize the Bastille) complaining about Robespierre losing a manuscript he had given to him. The editor of these letters believes it was lost on Robespierre’s way back from Madame Roland’s salon.

“Robespierre lost my manuscript I had entrusted to him on the establishment of these (popular) societies, and another on the liberty of the press. It was the work of several months. I had the courage, a few days ago, to start again.”
The editor also includes an ad from May 17th in the newspaper Patriote français that Robespierre probably placed offering a reward for any patriots who find the manuscript.

“Manuscript lost. M. Robespierre left, in a carriage he took at 9:30 in the evening, Thursday the 12th, on the quay of Augustins, a manuscript on the indefinite liberty of the press and the popular societies. He requests good citizens who may have heard of it to help him find it. He will give a reward to those who have taken to do so.
He can be reached at Saintonge street, Marais, no. 8 or at M. F. Lantlienas, Guénégaud street, hotel Britannique, suburb of Saint-Germain. The last part of this manuscript was read at the Cercle Social by M. C. Fauchet. We hope that patriots will take an interest in ensuring that it is not lost.”
#do these addresses match up with the places we know he lived/worked?#based on this and what charlotte said it seems like dude got distracted a lot#robespierre#frev#madame roland
114 notes
·
View notes
Text

From left to right: Marie-Anne Pierrette Paulze, Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun, Germaine de Staël, Madame Marie-Jeanne 'Manon' Roland de la Platière, Marie-Anne Charlotte de Corday d'Armont, Olympe de Gouges
In 2022 opera on the women of the French revolution premiered! It is called GIRONDINES! It's an English language opera that premiered with Wilmington Concert Opera and will be having its West Coast premier with Mission Opera!

Album image for the original concert cast album
According to an February 2023 article by Broadway World: "The Original Wilmington Concert Opera Cast Album is now available! It features Kirsten C. Kunkle as Charlotte Corday, Ashley Becker as Olympe de Gouges, Marisa Robinson as Marie Anne Pierrette Paulze Lavoisier, Alyssa Maria Lehman as Manon Roland, Raffaella Lo Castro as Germaine de Staël, Tracy Sturgis as Élisabeth Louise Vigée Le Brun, Thuy Nguyen on Violin, Melissa Brun on Cello, and Sarah Van Sciver on Piano."
I have not yet listened but as someone into frev and opera I am very excited. It also looks like the original concert production may be available to watch on YouTube!

Promo image for the October production
So far it looks like these have been small scale productions, but everything starts somewhere! I need to listen to the music but I wish good things to come
#opera#frev#french revolution#history#Marie-Anne Pierrette Paulze#Countess vom Rumford#Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun#Le Brun#Germaine de Staël#Madame de Staël#de Staël#Marie-Jeanne 'Manon' Roland de la Platière#Madame Roland#Marie-Anne Charlotte de Corday d'Armont#Charlotte Corday#Olympe de Gouges#womens history#herstory#new opera#new theatre#theatre#undescribed#please if anyone has the ability to add image ids for this id appreciate it
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
JUST FOUND OUT MADAME ROLAND AND BUZOT FELL IN LOVE WITH EACH OTHER...AND MONSIEUR ROLAND KNEW?!

Y I K E S

this is kind of sad actually
Also, never tell Danton ANYTHING if you don’t want it to get out al;skddsdfas

#the girondins#madame roland#buzot#danton#camille#the dantonist inability to shut the fuck up strikes again#don't tell danton anything because he WILL tell camille and then camille will tell the world
39 notes
·
View notes
Text


Historia de Europa by D. Emilio Castelar, 1895
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you happen to know how often it occurred for wives of arrested deputies to share the same fate of their husbands, so either imprisoned, or condemned to death ? Do you have some examples? I'm referring to the years between 92-95. Moreover if it's not too much to ask for, could you also point out the signature of the CSP members who signed such warrants?
That’s a very interesting question, especially since no official studies seem to have been made on the subject. What I’ve found so far (and it wouldn’t surprise me if there’s way more) is:
Félicité Brissot — after the news of her husband’s arrest, Félicité, who had lived in Saint-Cloud with her three children since April 1793, traveled to Chartres. There (on an unspecified date?) she and her youngest son Anacharsis (born 1791) were arrested by the Revolutionary Committee of Saint-Cloud (the two older children had been taken in by other people) which sent her to Paris. Once arrived in the capital, Felicité was placed under surveillance in the Necker hotel, rue de Richelieu, in accordance with an order from the Committee of General Security dated August 9 1793 (she could not be placed under house arrest in her own apartment, since seals had already been placed on it). On August 11 she underwent an interrogation, and on October 13, she was sent from her house arrest (where she had still enjoyed a relative liberty) to the La Force prison. Félicité and her son were set free on February 4 1794, after six months spent under arrest. The order for her release was it too issued by the Committee of General Security, and signed by Lacoste, Vadier, Dubarran, Guffroy, Amar, Louis (du Bas-Rhin), and Voulland. Source: J.-P. Brissot mémoires (1754-1793); [suivi de] correspondance et papiers (1912) by Claude Perroud)
Suzanne Pétion — In a letter to the Convention dated July 26 1793, Carrier reports that ”Péthion's [sic] wife, their son and the wife of another fugitive, were arrested in Homfleurs, we are going to take them to Paris.” On August 9, we find a CGS decree ordering Suzanne and her ten year old son, for the moment under house arrest, to be taken to the Sainte-Pélagie prison. Ten days after that, August 19, the CGS orders the furniture in Suzanne’s apartment to be brought over to her. A year later, August 13 1794, we find a letter from Suzanne to the Committee of Public Safety pleading for the release of her and her son, imprisoned only for sharing the name of a proscribed deputy. But this would appear to have lead nowhere, and the two were instead transported from the Sainte-Pélagie prison to the Maison Desnos. Finally, on December 9 1795, after one year, four months and thirteen days imprisoned, a CGS decree with the signatures of Mathieu, Reverchon, Bourdon, Montmayou, Barras and Comorel on it ordered Suzanne and her son released and their seals lifted immediately.
Louise-Catherine-Àngélique Ricard, widow Lefebvre (Suzanne Pétion’s mother) — According to Histoire du tribunal révolutionnaire de Paris: avec le journal de ses actes (1880) by Henri Wallon, Louise was called before the parisian Revolutionary Tribunal on September 24 1793, accused “of having applauded the escape of Minister Lebrun by saying: “So much the better, we must not desire blood,” of having declared that the Brissolins and the Girondins were good republicans (“Yes,” her interlocutor replied, “once the national ax has fallen on the corpses of all of them”), for having said, when someone came to tell her that the condemned Tonduti had shouted “Long live the king” while going to execution; that everyone would have to share this feeling, and that for the public good there would have to be a king whom the “Convention and its paraphernalia ate more than the old regime”. She denied this when asked about Tonduti, limiting herself to having said: “Ah! the unfortunate.” Asked why she had made this exclamation she responded: ”through a sentiment of humanity.” She was condemned and executed the very same day.
Marie Anne Victoire Buzot — It would appear she was put under house arrest, but was able to escape from there. According to Provincial Patriot of the French Revolution: François Buzot, 1760–1794 (2015) by Bette W. Oliver, ”[Marie] had remained in Paris after her husband fled on June 2 [1793], but she was watched by a guard who had been sent to the Hôtel de Bouillon. Soon thereafter, Madame Buzot and her ”domestics” disappeared, along with all of the personal effects in the apartment. […] Madame Buzot would join her husband in Caen, but not until July 10; and no evidence remains regarding her whereabouts between the time that she left Paris in June and her arrival in Caen. At a later date, however, she wrote that she had fled, not because she feared death, but because she could not face the ”ferocious vengeance of our persecutors” who ignored the law and refused ”to listen to our justification.” I’ve unfortunately not been able to access the source used to back this though…
Marie Françoise Hébert — arrested on March 14 1794, presumably on the orders of the Committee of General Security since I can’t find any decree regarding the affair in Recueil des actes du Comité de salut public. Imprisoned in the Conciergerie until her execution on April 13 1794, so 30 days in total. See this post.
Marie Françoise Joséphine Momoro — imprisoned in the Prison de Port-libre from March 14 to May 27 1794 (2 months and 13 days), as seen through Jean-Baptiste Laboureau’s diary, cited in Mémoires sur les prisons… (1823) page 68, 72, 109.
Lucile Desmoulins — arrested on April 4 1794 according to a joint order with the signatures of Du Barran (who had also drafted it) and Voulland from the CGS and Billaud-Varennes, C-A Prieur, Carnot, Couthon, Barère and Robespierre from the CPS on it. Imprisoned in the Sainte-Pélagie prison up until April 9, when she was transferred to the Conciergerie in time for her trial to begin. Executed on April 13 1794, after nine days spent in prison. See this post.
Théresa Cabarrus — ordered arrested and put in isolation on May 22 1794, though a CPS warrant drafted by Robespierre and signed by him, Billaud-Varennes, Barère and Collot d’Herbois. Set free on July 30 (according to Madame Tallien : notre Dame de Thermidor from the last days of the French Revolution until her death as Princess de Chimay in 1835 (1913)), after two months and eight days imprisoned.
Thérèse Bouquey (Guadet’s sister-in-law) — arrested on June 17 1794 once it was revealed she and her husband for the past months had been hiding the proscribed girondins Pétion, Buzot, Barbaroux, Guadet and Salles. She, alongside her husband and father and Guadet’s father and aunt, were condemned to death and executed in Bordeaux on July 20 1794. Source: Paris révolutionnaire: Vieilles maisons, vieux papiers (1906), volume 3, chapter 15.
Marie Guadet (Guadet’s paternal aunt) — Condemned to death and executed in Bordeaux on July 20 1794, alongside her brother and his son, the Bouqueys and Xavier Dupeyrat. Source: Charlotte Corday et les Girondins: pièces classées et annotées (1872) by Charles Vatel.
Charlotte Robespierre — Arrested and interrogated on July 31 1794 (see this post). According to the article Charlotte Robespierre et ses amis (1961), no decree ordering her release appears to exist. In her memoirs (1834), Charlotte claims she was set free after a fortnight, and while the account she gives over her arrest as a whole should probably be doubted, it seems strange she would lie to make the imprisonment shorter than it really was. We know for a fact she had been set free by November 18 1794, when we find this letter from her to her uncle.
Françoise Magdeleine Fleuriet-Lescot — put under house arrest on July 28 1794, the same day as her husband’s execution. Interrogated on July 31. By August 7 1794 she had been transferred to the Carmes prison, where she the same day wrote a letter to the president of the Convention (who she asked to in turn give it to Panis) begging for her freedom. On September 5 the letter was sent to the Committee of General Security. I have been unable to discover when she was set free. Source: Papiers inédits trouvés chez Robespierre, Saint-Just, Payan, etc. supprimés ou omis par Courtois. précédés du Rapport de ce député à la Convention Nationale, volume 3, page 295-300.
Françoise Duplay — a CGS decree dated July 27 1794 orders the arrest of her, her husband and their son, and for all three to be put in isolation. The order was carried out one day later, July 28 1794, when all three were brought to the Pélagie prison. On July 29, Françoise was found hanged in her cell. See this post.
Élisabeth Le Bas Duplay — imprisoned with her infant son from July 31 to December 8 1794, 4 months and 7 days. The orders for her arrest and release were both issued by the CGS. See this post.
Sophie Auzat Duplay — She and her husband Antoine were arrested in Bruxelles on August 1 1794. By October 30 the two had been transferred to Paris, as we on that date find a letter from Sophie written from the Conciergerie prison. She was set free by a CPS decree (that I can’t find in Recueil des actes du Comité de salut public…) on November 19 1794, after 3 months and 18 days of imprisonment. When her husband got liberated is unclear. See this post.
Victoire Duplay — Arrested in Péronne by representative on mission Florent Guiot (he reveals this in a letter to the CPS dated August 4 1794). When she got set free is unknown. See this post.
Éléonore Duplay — Her arrest warrant, ordering her to be put in the Pélagie prison, was drafted by the CGS on August 6 1794. Somewhere after this date she was moved to the Port-Libré prison, and on April 21 1795, from there to the Plessis prison. She was transfered back to the Pélagie prison on May 16 1795. Finally, on July 19 1795, after as much as 11 months and 13 days in prison, Éléonore was liberated through a decree from the CGS. See this post.
Élisabeth Le Bon — arrested in Saint-Pol on August 25 1794, ”suspected of acts of oppression” and sent to Arras together with her one year old daughter Pauline. The two were locked up in ”the house of the former Providence.” On October 26, Élisabeth gave birth to her second child, Émile, while in prison. She was released from prison on October 14 1795, four days after the execution of her husband. By then, she had been imprisoned for 1 year, 1 month and 19 days. Source: Paris révolutionnaire: Vieilles maisons, vieux papiers (1906), volume 3, chapter 1.
#frev#french revolution#madame roland is of course here too but she might go in the notlikeothergirls camp in this particular instance#félicité brissot#suzanne pétion#éléonore duplay#élisabeth lebas#charlotte robespierre#théresa cabarrus#lucile desmoulins#marie françoise hébert#everyone: is held in prison from anything from two months to a whole year if not executed before then#charlotte: two weeks…#i mean i’m not surprised but…
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
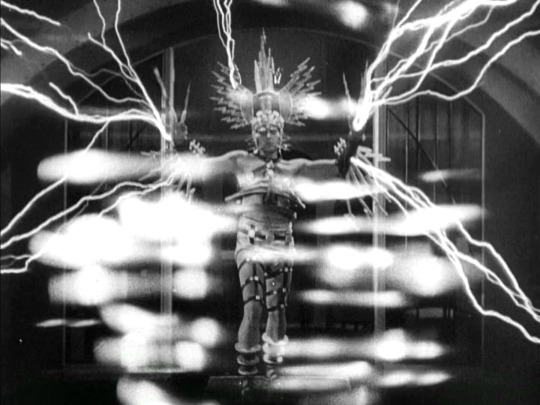
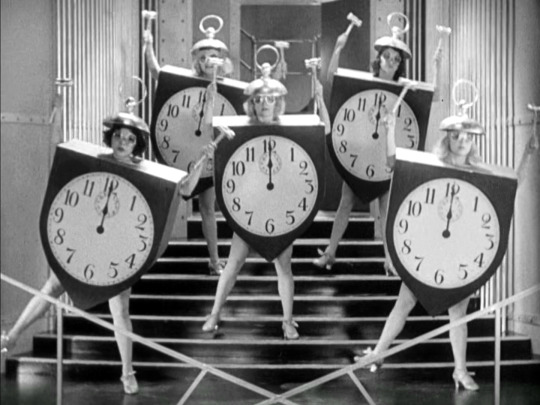
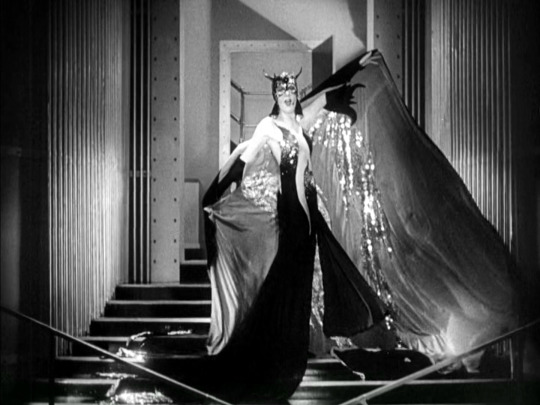
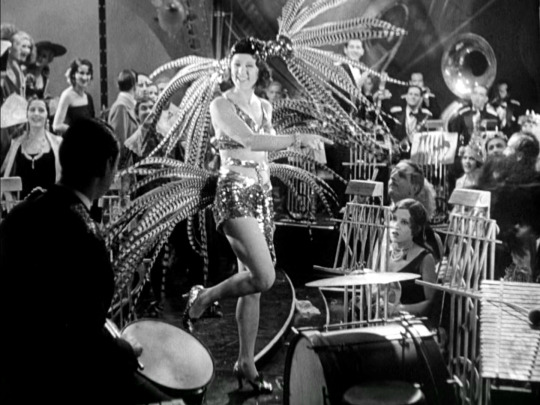
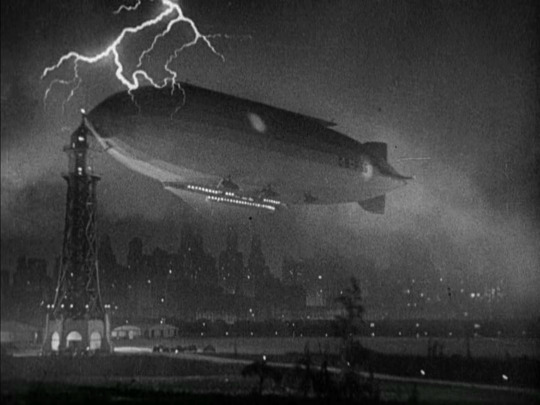
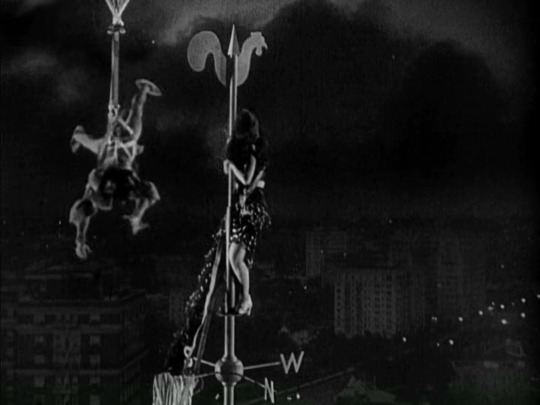







Madam Satan (1930)
#madam satan#madam satan 1930#cecil b demille#kay johnson#reginald denny#lillian roth#roland young#1930s#1930#filmedit#film#cinema#movies
107 notes
·
View notes
Text










Madam Satan (1930) Cecil B. DeMille
January 27th 2025
#madam satan#1930#cecil b. demille#kay johnson#reginald denny#roland young#lillian roth#elsa peterson#ann dvorak#pre-code
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

2 notes
·
View notes
Text









GUAN XIAOTONG 关晓彤 in Roland Mouret Resort 2025 | Madame Figaro Born to Shine Fashion Event in Beijing
Guan Xiaotong: more photos here Madame Figaro Event: more photos here
#guan xiaotong#关晓彤#chinese actress#black dress#cnladies#madame figaro event#roland mouret resort 2025#roland mouret
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
flaubert'in hiçbir şeyden zevk almamasına yol açan ve ruhunu öldürecek kadar dolduran o köklü, özel, sert ve ardı arkası kesilmeyen sıkıntı anları.
roland barthes - yas günlüğü
#roland barthes#yas günlüğü#gustave flaubert#madame bovary#kitap#edebiyat#blogger#felsefe#kitaplar#blog#kitap kurdu#kitaplık#jose luis borges#friedrich nietzsche#oğuz atay#tutunamayanlar#tehlikeli oyunlar#lale müldür#selim ileri#selçuk baran#charles bukowski#ekmek arası#emrah serbes#kürk mantolu madonna#sabahattin ali#felsefe blog#charles baudelaire#paris sıkıntısı
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
I've seen the phrase "real/true yearners" used in a shitpost exactly once and since then it hasn't left my brain.
10/10
#like yessss I'll integrate that into my vocabulary#true yearners know that getting what you want is never the goal#true yearners know that love is a religion and a graveyard and a knife in the back and the sword of a knight#true yearners know the knight never gets the lady#true yearners know the pain is the goal#true yearners know that love is a ballad true yearners know that Roland was a fool and a role model#true yearners know why Orpheus looked back yes true yearners know Madame Bovary is one of them and they are her#anyway
1 note
·
View note
Text


Almost out of nowhere Roland spends 3 pages describing her body, face, accomplishments etc. only for it to be lead up to Camille slander lol
#it’s the first time him or any frev guy is mentioned too#at the beginning of frev she was pretty close to Robespierre and talked to Danton#so I’m surprised she never met Camille#left in the part where she compares him to an old coxcomb cause it’s funny to me#frev#madame roland#camille desmoulins#camille#The Private Memoirs of Madame Roland
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
The trouble with Stravaigin'
This pic is currently making the rounds on Tumblr and X, and for all the good reasons (thank you @mariaae, for bringing it here):
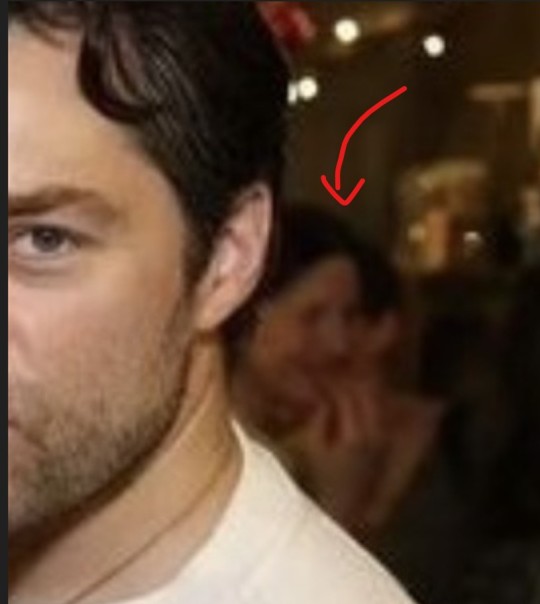

After a rather busy week and an even busier week-end, it's certainly nice to check in for this 👆.
Funny how the dunces across the street dub this a 'wrap party combo' of sorts. Oh, come on, are you that stupid, people?
Jamie Roy's OG post is absolutely clear with this regard:
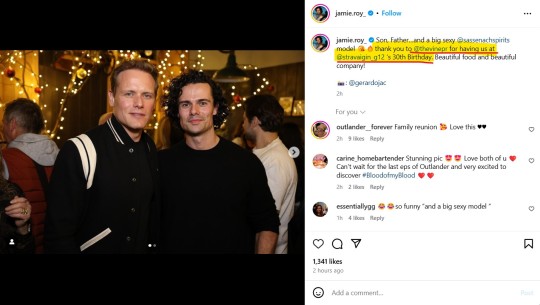
'Thank you @thevinepr for having us at @stravaigin_g12's 30th Birthday.' An event that is directly linked to this very recent Stravaigin's announcement, that has to do exclusively with S's spirits' business:
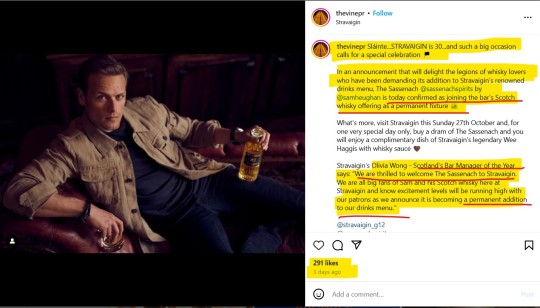
'In an announcement that will delight the legions of whisky lovers who have been demanding its addition to Stravaigin’s renowned drinks menu, The Sassenach @sassenachspirits by @samheughan is today confirmed as joining the bar’s Scotch whisky offering as a permanent fixture 🥃. (...)
Stravaigin's Olivia Wong - Scotland's Bar Manager of the Year says: “We are thrilled to welcome The Sassenach to Stravaigin. We are all big fans of Sam and his Scotch whisky here at Stravaigin and know excitement levels will be running high with our patrons, as we announce it is becoming a permanent addition to our drinks menu.'
Note to self: this is something Marple 'forgot' to post about, despite her all-consuming obsession for S. Without this information, the rest was presented as just another heavy drinking sesh. Tss, shame on you, madam! Is this where you're at? Lying to your readers, in an attempt to demonstrate: a) S is a highly-functioning alcoholic (by your reasoning, half of the UK might be, ROFLMAO) and b) Ashley Hearn is a lazy, entitled idiot, who spends her time in bars chatting and drinking with her buddies?
Lying by omission is either a mortal sin (when made with the purpose of hurting someone's reputation) or a venial one (when 'in jest', like the Screeching Banshees pretend to do). But I have no idea if that woman is a Catholic, nor do I care. Either way, it's unsavory as fuck. So long for playing it Switzerland, in here.
All of the above to emphatically (LOL for ages) say that this event has nothing to do with Outlander. This has everything to do with Sam Roland Heughan and his own, local business network. This is exactly why Jamie Roy was thanking the organizing PR firm (more on this, a bit later in this post).There were zero reasons for C to be there that night, something that has been confirmed by fans on X:
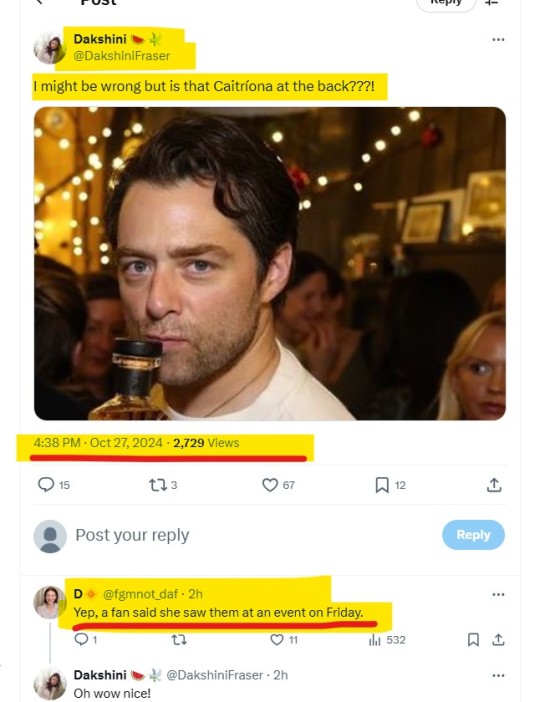
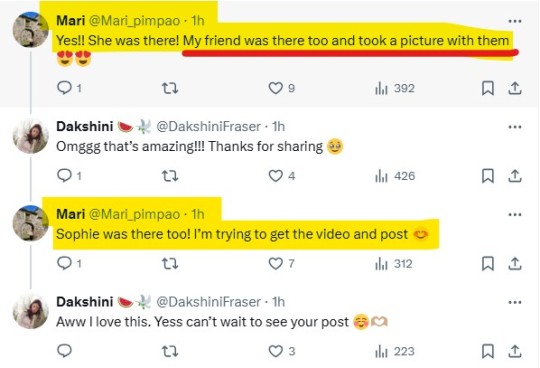
Interesting: 'took a picture with them'. In the context, people were wondering if there were pics with the Two of Them, not the rest of the cast. But hey, didn't you know? THEY CAN'T STAND EACHOTHER, NEVER COULD!
And there we go, we have the arrival video (why does it always have to be Brazilian fans directly or indirectly involved? that is a mystery on par with who killed JFK, LOL):
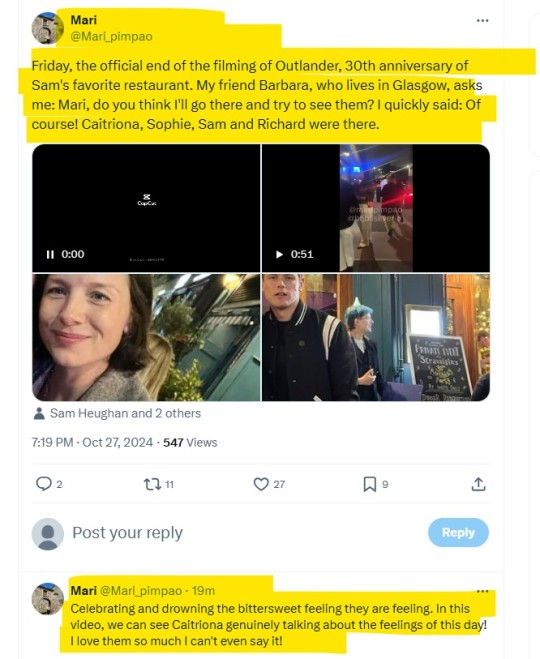
And here we have it, courtesy of @maripimpao, the OG X poster (https://x.com/Mari_pimpao/status/1850588095046971487?t=p3_lv013WuINhA085ayr4A&s=19).
... S arriving separately, as predictible, probably on his own (fucking Tumblr doesn't let me upload more than one video, but you'll find everything on the X page above), then C and Skeleton (God, that girl must KNOW stuff!) together - not surprised at all, either:
A normal convo ensues, C stating that she feels 'both happy and sad' because Friday was their last day ever on set. I was very surprised by her genuine warmth, to be honest, as I wasn't expecting it, but it is in line with public lore on her being spotted before by fans.
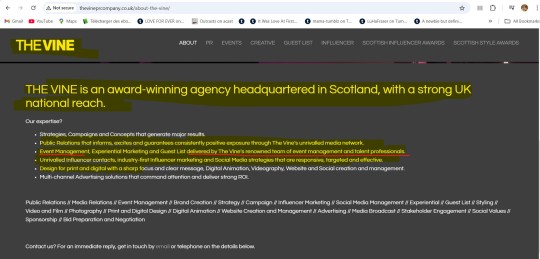
A word on The Vine PR company. This is one of the biggest PR firms in Scotland and even the UK, with a very nice portfolio of clients, partners and events they manage on the regular:
Oh...
And re-oh...
So, there should come as no surprise to find, among The Vine's clients (for whom it managed flagship events), two of LVMH's portfolio companies/brands: Moët & Chandon and Glenmorangie. I also remember being ridiculed, as writing fanfic, by both Marple and her minions. Well, eat crow now, I have been announcing it for a year, already, for both of them. Not once, but three times in a row.
One...
Two...
Third time's a charm/Jamais deux sans trois:
Business-wise, this is about the amount of time it takes to make things of this amplitude happen. Wait, I forgot that business was bound to flounder, sweet Baby Jesus on a motorbike!
On top of it all, I have some very inconvenient, yet rhetorical questions (for the people across the street, a rhetorical question is supposed to make a point, not wait for an answer):
What about McTavish's spirits business? Still in promo mode, bought medals, and all the tralala? Hmmm.
What about Tony McGill? Why isn't he seen at any event at all, in the music business or otherwise, like ever? Isn't he supposed to manage (Media Manager, my 🦶) a Scottish band? Where was he, on Friday night? How does he even do business? Hmmm.
Oh, FFS.

156 notes
·
View notes
Text
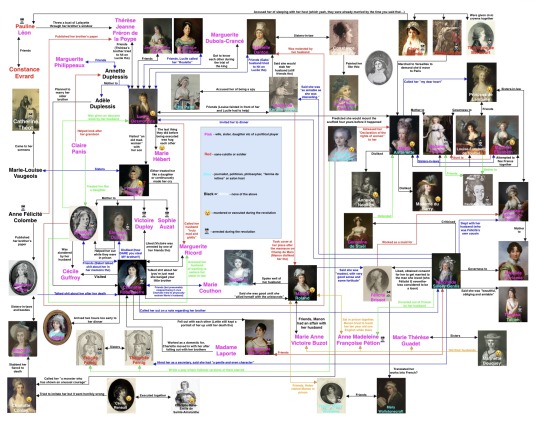
I decided to try this but for the girlies instead.
Are you sure want to click on ”keep reading”?
For Pauline Léon marrying Claire Lacombe’s host, see Liberty: the lives of six women in Revolutionary France (2006) by Lucy Moore, page 230
For Pauline Léon throwing a bust of Lafayette through Fréron’s window and being friends with Constance Evrard, see Pauline Léon, une républicaine révolutionnaire (2006) by Claude Guillon.
For Françoise Duplay’s sister visiting Catherine Théot, see Points de vue sur l’affaire Catherine Théot (1969) by Michel Eude, page 627.
For Anne Félicité Colombe publishing the papers of Marat and Fréron, see The women of Paris and their French Revolution (1998) by Dominique Godineau, page 382-383.
For the relationship between Simonne Evrard and Albertine Marat, see this post.
For Albertine Marat dissing Charlotte Robespierre, see F.V Raspail chez Albertine Marat (1911) by Albert Mathiez, page 663.
For Lucile Desmoulins predicting Marie-Antoinette would mount the scaffold, see the former’s diary from 1789.
For Lucile being friends with madame Boyer, Brune, Dubois-Crancé, Robert and Danton, calling madame Ricord’s husband ”brusque, coarse, truly mad, giddy, insane,” visiting ”an old madwoman” with madame Duplay’s son and being hit on by Danton as well as Louise Robert saying she would stab Danton, see Lucile’s diary 1792-1793.
For the relationship between Lucile Desmoulins and Marie Hébert, see this post.
For the relationship between Lucile Desmoulins and Thérèse Jeanne Fréron de la Poype, and the one between Annette Duplessis and Marguerite Philippeaux, see letters cited in Camille Desmoulins and his wife: passages from the history of the dantonists (1876) page 463-464 and 464-469.
For Adèle Duplessis having been engaged to Robespierre, see this letter from Annette Duplessis to Robespierre, seemingly written April 13 1794.
For Claire Panis helping look after Horace Desmoulins, see Panis précepteur d’Horace Desmoulins (1912) by Charles Valley.
For Élisabeth Lebas being slandered by Guffroy, molested by Danton, treated like a daughter by Claire Panis, accusing Ricord of seducing her sister-in-law and being helped out in prison by Éléonore, see Le conventionnel Le Bas : d'après des documents inédits et les mémoires de sa veuve, page 108, 125-126, 139 and 140-142.
For Élisabeth Lebas being given an obscene book by Desmoulins, see this post.
For Charlotte Robespierre dissing Joséphine, Éléonore Duplay, madame Genlis, Roland and Ricord, see Mémoires de Charlotte Robespierre sur ses deux frères (1834), page 76-77, 90-91, 96-97, 109-116 and 128-129.
For Charlotte Robespierre arriving two hours early to Rosalie Jullien’s dinner, see Journal d’une Bourgeoise pendant la Révolution 1791–1793, page 345.
For Charlotte Robespierre physically restraining Couthon, see this post.
For Charlotte Robespierre and Françoise Duplay’s relationship, see Mémoires de Charlotte Robespierre sur ses deux frères (1834) page 85-92 and Le conventional Le Bas: d’après des documents inédits et les mémoires de sa veuve (1902) page 104-105
For the relationship between Charlotte Robespierre and Victoire and Élisabeth Lebas, see this post.
For Charlotte Robespierre visiting madame Guffroy, moving in with madame Laporte and Victoire Duplay being arrested by one of Charlotte’s friends, see Charlotte Robespierre et ses amis (1961)
For Louise de Kéralio calling Etta Palm a spy, see Appel aux Françoises sur la régénération des mœurs et nécessité de l’influence des femmes dans un gouvernement libre (1791) by the latter.
For the relationship between Manon Roland and Louise de Kéralio Robert, see Mémoires de Madame Roland, volume 2, page 198-207
For the relationship between Madame Pétion and Manon Roland, see Mémoires de Madame Roland, volume 2, page 158 and 244-245 as well as Lettres de Madame Roland, volume 2, page 510.
For the relationship between Madame Roland and Madame Buzot, see Mémoires de Madame Roland (1793), volume 1, page 372, volume 2, page 167 as well as this letter from Manon to her husband dated September 9 1791. For the affair between Manon and Buzot, see this post.
For Manon Roland praising Condorcet, see Mémoires de Madame Roland, volume 2, page 14-15.
For the relationship between Manon Roland and Félicité Brissot, see Mémoires de Madame Roland, volume 1, page 360.
For the relationship between Helen Maria Williams and Manon Roland, see Memoirs of the Reign of Robespierre (1795), written by the former.
For the relationship between Mary Wollstonecraft and Helena Maria Williams, see Collected letters of Mary Wollstonecraft (1979), page 226.
For Constance Charpentier painting a portrait of Louise Sébastienne Danton, see Constance Charpentier: Peintre (1767-1849), page 74.
For Olympe de Gouges writing a play with fictional versions of the Fernig sisters, see L’Entrée de Dumourier à Bruxelles ou les Vivandiers (1793) page 94-97 and 105-110.
For Olympe de Gouges calling Charlotte Corday ”a monster who has shown an unusual courage,” see a letter from the former dated July 20 1793, cited on page 204 of Marie-Olympe de Gouges: une humaniste à la fin du XVIIIe siècle (2003) by Oliver Blanc.
For Olympe de Gouges adressing her declaration to Marie-Antoinette, see Les droits de la femme: à la reine (1791) written by the former.
For Germaine de Staël defending Marie-Antoinette, see Réflexions sur le procès de la Reine par une femme (1793) by the former.
For the friendship between Madame Royale and Pauline Tourzel, see Souvernirs de quarante ans: 1789-1830: récit d’une dame de Madame la Dauphine (1861) by the latter.
For Félicité Brissot possibly translating Mary Wollstonecraft, see Who translated into French and annotated Mary Wollstonecraft’s Vindication of the Rights of Woman? (2022) by Isabelle Bour.
For Félicité Brissot working as a maid for Louise Marie Adélaïde de Bourbon, see Mémoires inédites de Madame la comptesse de Genlis: sur le dix-huitième siècle et sur la révolution française, volume 4, page 106.
For Reine Audu, Claire Lacombe and Théroigne de Méricourt being given civic crowns together, see Gazette nationale ou le Moniteur universel, September 3, 1792.
For Reine Audu taking part in the women’s march on Versailles, see Reine Audu: les légendes des journées d’octobre (1917) by Marc de Villiers.
For Marie-Antoinette calling Lamballe ”my dear heart,” see Correspondance inédite de Marie Antoinette, page 197, 209 and 252.
For Marie-Antoinette disliking Madame du Barry, see https://plume-dhistoire.fr/marie-antoinette-contre-la-du-barry/
For Marie-Antoinette disliking Anne de Noailles, see Correspondance inédite de Marie Antoinette, page 30.
For Louise-Élisabeth Tourzel and Lamballe being friends, see Memoirs of the Duchess de Tourzel: Governess to the Children of France during the years 1789, 1790, 1791, 1792, 1793 and 1795 volume 2, page 257-258
For Félicité de Genlis being the mistress of Louise Marie Adélaïde de Bourbon’s husband, see La duchesse d’Orléans et Madame de Genlis (1913).
For Pétion escorting Madame Genlis out of France, see Mémoires inédites de Madame la comptesse de Genlis…, volume 4, page 99.
For the relationship between Félicité de Genlis and Louise de Kéralio Robert, see Mémoires de Madame de Genlis: en un volume, page 352-354
For the relationship between Félicité de Genlis and Germaine de Staël, see Mémoires inédits de Madame la comptesse de Genlis, volume 2, page 316-317
For the relationship between Félicité de Genlis and Théophile Fernig, see Mémoires inédits de Madame la comptesse de Genlis, volume 4, page 300-304
For the relationship between Félicité de Genlis and Félicité Brissot, see Mémoires inédites de Madame la comptesse de Genlis, volume 4, page 106-110, as well as this letter dated June 1783 from Félicité Brissot to Félicité Genlis.
For the relationship between Félicité de Genlis and Théresa Cabarrus, see Mémoires de Madame de Genlis: en un volume (1857) page 391.
For Félicité de Genlis inviting Lucile to dinner, see this letter from Sillery to Desmoulins dated March 3 1791.
For Marinette Bouquey hiding the husbands of madame Buzot, Pétion and Guadet, see Romances of the French Revolution (1909) by G. Lenotre, volume 2, page 304-323
Hey, don’t say I didn’t warn you!
#french revolution#frev#marie antoinette#pauline léon#claire lacombe#théroigne méricourt#reine audu#charlotte robespierre#éléonore duplay#élisabeth duplay#élisabeth lebas#lucile desmoulins#louise de kéralio#félicité de genlis#félicité brissot#mary wollstonecraft#manon roland#madame royale#charlotte corday#albertine marat#simonne evrard#catherine théot#madame élisabeth#sophie condorcet#françoise duplay#cécile renault#gabrielle danton#louise sebastien danton#theresa tallien#theresa cabarrus
199 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi!
I really enjoy your posts about d'Eon; she's so fascinating. I'm definitely not an expert on her, but I'm very interested! One article I read said that, in her unfinished memoirs, she used both male and female pronouns. Is this a) even true, given some of the clearly wrong historical writing you've cited before, and b) if it is true, what do you think about it?
So I don't speak French. D'Eon's unfinished memoirs were originally written in French and I'm working with an English translation. This makes any discussion of gendered language in her memoirs a bit more difficult as there are words that are gendered in French but gender neutral in English and vice versa. Helpfully the translation by Roland A. Champagne, Nina Ekstein and Gary Kates notes when the masculine or feminine form is being used. However I'm still answering this question based on a translation not d'Eon's original words.
D'Eon's memoirs are written in first person so the majority of the pronouns she uses for herself are first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine).
Other characters use either he/him or she/her pronouns for d'Eon but this reflects that characters perspective not d'Eon's personal pronouns. For example in a scene set in Russia the Comte de Vorontsov confronts d'Eon about her double life, using feminine pronouns for Mademoiselle d'Eon and masculine pronouns for Captain d'Eon:
This young lady remarked to Madame Vorontsov and to my niece the Princess Asthoff that she remembers very well that Mademoiselle d'Eon has a small wine-colored birthmark on her left cheek near her ear, that at the convent in Meaux she wore gold-drop earrings, and that if Captain d'Eon has this wine-colored birthmark on his left cheek and that if he has pierced ears, you can be sure that this is the Demoiselle d'Eon whom I knew in the convent. (p20)
D'Eon pretty consistently seems to use feminine language for herself when speaking in the present tense. She uses the words "woman", "girl", "maiden", "daughter", the titles "mademoiselle" and "chevalière" and "she/her" pronouns at points when she slips into third person.
However when talking in the past tense she sometimes describes herself in the masculine. She was a "man" but is now a "woman". She will sometime talk about her past self in third person referring to "him" as her "brother". After Mademoiselle Bertin dresses d'Eon in woman's clothes for the first time d'Eon says to her:
You have killed my brother the dragoon. That leaves me with a heavy heart. (p61)
D'Eon's describes her transition as a death and rebirth. A few weeks before d'Eon was to be presented at the Court of Versailles as a woman she returns home to Tonnerre. Still wearing men's clothes she gets into an argument with her mother who believes she should start wearing women's clothes immediately. But d'Eon is reluctant, avoiding it. At one point in the argument d'Eon tells her mother she must resign herself to "the imminent death of your pitiful dragoon" as "he" only has a few weeks left in men's clothes. Their argument ends with the following passage:
In tears, my mother said to me: "You are still my dear daughter sitting in the darkness and the shadow of death. But you will be reborn, my daughter, without fear or reproach, to live and die peacefully by your mother, who loves and will always cherish you. For your salvation and our mutual happiness, I have long prayed for the misfortune that befalls you." She wiped her tears against my face and returned to her room. I hid my face under the covers in order not to see or hear anything. I was even troubled by my own presence in he darkness of night. (p41)
While d'Eon describes the loss of her "brother" the dragoon as painful she ultimately sees it as something that is necessary and positive:
Mademoiselle d'Eon has only one more step to take to bury her brother the captain of the dragoons with the full honors of War ... Tomorrow without fail I will inform Mademoiselle Bertin of my return to Paris and tell her to bring with her feathered aides-de-camp to deplume me and to sew the dragoon's skin to that of a girl who is worn out from bitter disappointment with her own skin. This girl has the greatest need of her help to be trimmed, readied, and fitted out by her skillful hand in order that I may walk with unworried assurance along the narrow path of virtue, as is befitting a Christian maiden (p56)
The death of the dragoon captain gives life to the Christian maiden:
In my regiment I sought only the rough and tumble. But in my convent I find only remedies and healing. Thus by a natural tendency I find it impossible to reconcile Mademoiselle d'Eon with her brother, the dragoon captain. The brother is imperfect, the sister perfect. How can one reconcile between the imperfect and the perfect? (p72)
Her life as Geneviève d’Eon brings her joy:
At present I am living in profound peace; and my joy is so great that I praise God in three languages so that a greater number of people may partake of the happiness of the angels in this life while awaiting the crown of ordinary martyrs, Nunc Genofeva d'Eon est nomen meum; quam suave et dulce est laetitia mea! [My name is now Geneviève d’Eon; how delightful and how sweet is my joy!] (p87)
However she doesn't always refer to her pre-transition self in the masculine. D'Eon presents herself as a woman who was raised as a boy by her parents: "I had been educated as a boy, and I dressed as one." (p7) She describes her past self as a "foolish girl who was tricked to go along like a foolish ewe." (p3)
One interesting example of d'Eon's use of gendered language is her invention of the word "demoiseau". One of the translators Roland A. Champagne describes it as a "masculine version of demoiselle" and explains "We translated demoiseau as "pretty boy" in order to capture the lexical proximity of demoiseau to damoiseau ("fop")." Champagne concludes that "d'Éon constructed in a neutral gender the demoiseau to live as a masculine woman beyond the codes of the Ancien Regime." (Decoding "The Maiden of Tonnerre": Translating Gender from the Eighteenth Century)
Champagne is correct to say that d'Eon lived as a "masculine woman" but I think he might be making too much of this one word considering the context. The word "demoiseau" comes from the following exchange between d'Eon and Bertin:
Mademoiselle d'Eon. Alas, at court everything is beautiful. To please the court, does a former dragoon captain have to become a pretty boy [demoiseau]? Mademoiselle Bertin. Yes, absolutely, when the so-called "boy" is discovered to be in fact a girl by the systems of justice both in England and in France. (p64)
So I don't think d'Eon necessarily identified as a "demoiseau" but perhaps I'm missing something in translation.
The part I struggle with the most is words that are gender neutral in English but gendered in French. Without being familiar with French it's difficult for me to understand what the use of masculine and feminine forms of words means in context. Take the following passage for example:
Neither my body nor my mind was worn out from studying when my father took(m) me to Paris at the age of thirteen. At that point, I knew only how to read and write, and not well at that. I, however, fell into the hands(f) of my uncle and aunt who made(m) me feel ashamed(m) of my ignorance and who motivated me to study. Furthermore, they alerted and warned me that if I revealed the truth of my sex I would be locked away(f) in a convent forever. (p4)
In "my father took(m) me" took is masculine. Does that mean that d'Eon is masculine, her father is masculine or the act of taking is masculine? What about "made(m) me feel ashamed(m) of my ignorance" is d'Eon masculine or is her shame masculine? If her sex if revealed she will be "locked away(f) in a convent". Why is the word away feminine?
One thing that I particularly found interesting is that the pronoun "me" is sometimes marked as feminine, sometimes masculine, but most often not marked as either. So we have:
The Revolution made me(m) so rich that today I do not have the means to buy ink or paper.
And then just a few paragraphs later:
I would just as soon suffer childbirth as to be doing this painful work of writing, which I have begun because of the destitution to which the Revolution has reduced me(f).
Then a few paragraphs latter:
I am no longer a disciple of this world since my wonderful conversion, which separated me(f) completely from the body of the dragoons and from the sin of my uniform and which finally stripped away the old man in order to make of me a totally new being before Our Lord, in the eyes of men, in front of the Queen's ladies-in-waiting as well as the Daughters of Holy Mary, and in the hopes of the fortune reserved for me in heaven. The knowledge of that fortune has filled me(m) with complete wisdom and spiritual intelligence so that I might bring to fruition every good action and so that I might behave as befits a Christian woman not only before the world but also before the Lord, since during my novitiate I was washed(f), probed(f), tested(f), corrected(f), corroborated(f), strengthened(f), and rooted(f) in every way, which I endured, in complete patience and spiritual tranquility, the Lord having erased my obligations, which consisted of military orders, orders contrary to my spirit, and which He completely abolished and replaced with my new obligation to live and die in the essential purity of my innocent dress, no longer thinking of those things here below but only about those on high. (p136-137)
The switching back and forth between "me(m)" and "me(f)" is interesting but I honestly have no idea what it means.
If I ignore all the little "f"s and "m"s the gendered language seems pretty clear and consistent. D'Eon is a woman who was raised as a boy. She is feminine in the present tense but sometimes masculine in the past tense. But I can't just ignore the fact that I'm reading a translation. That would not be a honest analysis of her memoirs. I'd love if someone who is familiar with French went through her writing and really analysed her use of gendered language. I'm unfortunately restricted by the limits of working with a translation.
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reflections on the Comments of Maximilien Robespierre and Manon Roland on Condorcet

Nicolas Condorcet (1743-1794)
A long time ago, I found on the excellent site Les Amis de Robespierre what Madame Roland and Robespierre thought of Condorcet. Here is the link: Les Amis de Robespierre. I will translate the thoughts of the different protagonists from this article and give my personal opinion.
Robespierre's Opinion on Condorcet: Condorcet and Robespierre often attacked each other on the issue of war in 1792. Robespierre said about Condorcet’s articles that he knows "nothing worse and more treacherous." After the arrest of the Girondins, when Condorcet fled, Robespierre apparently said, "This coward Caritat, who, like his friend Brissot, fled national justice, and who no less deserved it," and "The coward Condorcet began to fear the responsibility for his liberty-destroying impostures." A few days after the last statement, Condorcet died, either by suicide, from understandable stress, or, some say, possibly murder (I personally doubt the third hypothesis, but I mention it nonetheless).
In his speech on May 7, 1794, when Robespierre spoke about religion and morality based on republican principles, he released new cutting remarks against Condorcet: "A timid conspirator, despised by all parties," and whose writings are described as "the treacherous jumble of his mercenary rhapsodies." Such violent and cutting words against Condorcet. Yet, on the insult of cowardice, someone else who was initially allied with Robespierre before becoming an enemy would join him in this term.
Manon Roland's Opinion on Condorcet: The woman who was called muse of the Gironde had harsh words for Condorcet in her memoirs. She described him as "weak of heart and health," and added, "A brief note on Condorcet, « whose spirit will always be on the level of the greatest truths, but whose character will never be above fear." She concluded about him, "Such men should be left to write and never employed."
My Reflections: I thought these were heavy words. Of course, Condorcet also said very harsh things, and it must be said that my boundless admiration for him when I was very young (especially since the activist he was for gender equality could only please the future feminist in me) was greatly tempered when I read his equally cutting speech about Robespierre. Speaking of Robespierre in this way: "He talks about God and Providence; he calls himself a friend of the poor and the weak; he gets followed by women and weak-minded people. He gravely receives their adoration and homage, disappears with danger, and is seen only when danger is past. Robespierre is a priest and will never be anything else," I need not say more about what irritated me when he spoke of women this way. Firstly, there were many politically active women who did not follow Robespierre or necessarily the ideals of Condorcet. Should we, for example, speak of Albertine Marat who declared to Alphonse Esquiros, "She then spoke to me about Robespierre with bitterness. 'There was nothing in common,' she added, 'between him and Marat. Had my brother lived, the heads of Danton and Camille Desmoulins would not have fallen.'" Even if I slightly disagree with this part that if Marat had survived, Danton's head would not have fallen (Danton being a very corrupt character and Marat starting to doubt him greatly, especially according to the excellent biography of Danton written by Frédériche Bluche), we are far from admiration for Robespierre from an important revolutionary activist like Marat's sister. And this is just one example among many. We can profoundly disagree with men and women for their political convictions, but what makes feminism and above all gender equality is not imposing a woman's way of life, whether it be thoughts or convictions. I will make a provocation by paraphrasing Voltaire to transpose what I mean: "I disapprove of what you say, but I will defend to the death your right to say it." Although personally being cowardly, I would not do it to the death, this exactly reflects what a feminist person should be. And clearly, Condorcet did not respect this part, which makes his conception of gender equality totally imperfect (to put it mildly) by lumping many women together with Robespierre's speech and mocking their political convictions. I feel with him that as long as these women were in agreement with him, it was acceptable, but as soon as they had different political convictions, he cataloged and despised them.
However, do I agree with what Manon Roland and Robespierre said about him? Is everything to be discarded from Condorcet?
Regarding Robespierre, let's not forget that he was an adversary of Condorcet, so it should be taken with a LOT of caution. And let’s not forget that when Robespierre made his speeches, he himself committed acts that can be easily criticized.
Regarding Manon Roland, let’s not forget that Condorcet had positions that were quite difficult to situate within the Girondins and Montagnards split. The group we will call the Girondins did not like to be called that way, and there were more political dissensions between them, and Condorcet did not share all the positions of the Brissotins. So, her words should also be taken with some caution, and she too has things to be blamed for.
But let’s think, would a coward have moderated his criticisms on the moderation of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen and the Constitution of 1791? Because he publicly showed strong criticism.
He was a fervent opponent of the death penalty and stuck to his principles to the end. While some Girondins tried to spare Louis XVI not out of abolitionist conviction or royalism – most were republicans, including some before their time, like Manon Roland – but to not further legitimize the day of August 10, 1792, Condorcet voted against the death penalty out of conviction, whereas Robespierre, who had been an opponent of the death penalty, voted for the death of Louis XVI, rejecting the reprieve. However, he also felt that Louis XVI’s high treason deserved an exemplary punishment, being one of the few to demand that he be condemned to the galleys. He also advocated very early for the rights of Black people. Furthermore, what hastened Condorcet’s end was his condemnation of the arrest of the Brissotins – although his end was accelerated by the fact that he fled, which led to his death sentence in the summer of 1793. To my eyes, a coward would not have condemned the arrest of the Brissotins publicly. He would not have voted in contradiction to his own camp for his convictions (on this point, there is a certain parallel to be made with Robespierre facing the Constituent Assembly of 1789-1791, as Robespierre often intervened against a large majority to make his political ideas and those of so many others triumph).
Of course, I find it unfortunate that in popular culture, Condorcet is often forgiven for his mistakes because he also made mistakes that endangered the French Revolution, particularly the question of war, or what he said about women when he attacked Robespierre. His Panthéonization, for me, is deserved given that he, along with others, advocated generous ideas, and in his biography by historian Antoine Resche, “a public instruction project which, if it was not taken into account under the Revolution, laid the foundations of the school as it has been conceived since the Third Republic, that is, necessarily widespread education, by degrees,” but it is unfortunate that popular culture forget, especially Louis Michel Le Peletier, who proposed a mixed, free, and compulsory primary project defended by Robespierre. When speaking of revolutionaries defending the rights of female citizens, Condorcet is highlighted but not Charles Gilbert Romme, Guyomar, Charlier, and many others. Even more so, we forget revolutionary women like Théroigne de Méricourt, Pauline Léon, Claire Lacombe, Simone Evrard, Albertine Marat, Marie-Anne Babeuf, and many others, as the list is long.
In conclusion, what do I think of Condorcet now that you know that my admiration for him as a teenager has long been greatly tempered and that he is not among my favorite revolutionaries? Well, I still have a fondness for him, a recognition, and a admiration for him like for other revolutionaries, including Manon Roland and Robespierre, although they are not in my top 20 either and not my favorites characters of the frev. They were, fundamentally, complex people caught in a complex period who made, of course , grave and even unforgivable mistakes, but as was said on Tumblr, faultless revolutionaries are quite rare ( (even if there are people in my eyes who are indefensible or rotten like Fouché, Carrier, Tallien, Barras, Charles X, etc.) especially during these during this hellish period of civil war, external and former leaders like Louis XVI who betrayed his people or émigrés who were ready to do anything to destroy the necessary gains of the revolution. . And they are still considered today in a period that is a victim of a black legend that must be constantly combated .
P.S : Forgive me is there was an article Tumblr about what said Manon Roland and Robespierre about Condorcet I checked but I might have missed it
32 notes
·
View notes