#Kingdom of Ndongo
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
the martyrer than thou syndrome that reblogger had lmao
European history is not white


Someone commented this to a post I reblogged, which message is basically "we shouldn't venerate the Dead White Man HistoryTM and we should elevate other history too, but we still need to learn Dead White Man HistoryTM to understand the world today". It's basically a response to the attitude you sometimes come across in the internet that sees learning about those Dead White MenTM as not worth our time. And this person, who seems to be following this blog because they responded to my reblog, takes it as a personal attack against all white Europeans. For some reason. Well I take these comments as a personal attack against historical understanding.
Firstly, the post clearly didn't say you shouldn't venerate any European history, because not all European history is Dead White Man HistoryTM. Obviously this person thinks European history is white, which is not true, but surely, surely, they know it's not all men? Secondly, what is "west culture"? When did it start? There is not one western culture, not one European culture. The first concept of some shared Europeanness was the Christendom in Middle Ages, but it was not exactly the same as we think of Europe today, because it did not include the pagan areas, but it included a lot of Levant and parts of Central Asia, where there were large Christian areas. And Europe was not "very white" nor was the Christendom. The more modern concept of West was cooked in tandem with race and whiteness during colonial era and Enlightenment, around 17th to 18th centuries. And Europe was certainly not very white then. The western world also includes a lot of colonized areas, so that's obviously not white history. Thirdly, implying that asking white people to apologize for European history (which no one did ask) is as ridiculous as asking black people for African history is... a choice. Black people do exist in a lot of other places than Africa, which white people should be the ones apologizing for, and really white people also have a lot to answer for about African history. Lastly, if you think the quote "anyone who thinks those dead white guys are aspirational is a white supremacist" means you as an European are demanded to apologize for your existence, maybe - as we say in Finland - that dog yelps, which the stick clanks. (I'm sorry I think I'm the funniest person in the world when I poorly translate Finnish sayings into English.)
The thing is, there is no point in European history, when Europe was white, for three reasons. 1) Whiteness was invented in 17th century and is an arbitrary concept that has changed it's meaning through time. 2) Whichever standard you use, historical or current, Europe still has never been all or overwhelmingly white, because whiteness is defined as the in-group of colonialists, and there has always been the internal Other too. In fact the racial hierarchy requires an internal Other. 3) People have always moved around a lot. The Eurasian steppe and the Mediterranean Sea have always been very important routes of migration and trade. I've been meaning to make a post proving exactly that to people like this, since as I've gathered my collection of primary images of clothing, I've also gathered quite a lot of European primary images showing non-white people, so I will use this opportunity to write that post.
So let's start from the beginning. Were the original inhabitants of Europe white? Of course not. The original humans had dark skin so obviously first Europeans had dark skin. Whenever new DNA evidence of dark skinned early Europeans come out (like this study), the inevitable right-wing backlash that follows is so interesting to me. Like what did you think? Do you still believe the racist 17th century theories that white people and people of colour are literally different species? I'm sure these people will implode when they learn that studies (e.g. this) suggest in fact only 10 000 years ago Europeans had dark skin, and even just 5 000 years ago, when Egypt (an many others) was already doing it's civilization thing, Europeans had brown skin (another source). According to the widely accepted theory, around that time 5 000 years ago the Proto-Indo-European language developed in the Pontic-Caspian steppe, which extends from Eastern Europe to Central Asia. These Proto-Indo-Europeans first migrated to Anatolia and then to Europe and Asia. Were they white? Well, they were probably not light skinned (probably had brown skin like the other people living in Europe around that time), the Asian branch of Indo-European peoples (Persians, most Afghans, Bengalis, most Indians, etc.) are certainly not considered white today and a lot of the people today living in that area are Turkic and Mongolic people, who are also not considered white. I think this highlights how nonsensical the concept of race is, but I don't think Proto-Indo-Europeans would have been considered white with any standard.
Around Bronze Age light skin became common among the people in Europe, while in East Asia it had become wide spread earlier. This does not however mark the point when "Europe became white". During the Bronze Age there was a lot of migration back and forth in the Eurasian steppe, and the early civilizations around Mediterranean did a lot of trade between Europe, Africa and Asia, which always means also people settling in different places to establish trading posts and intermarrying. There were several imperial powers that also stretched to multiple continents, like the briefly lived Macedonian Empire that stretched from Greece to Himalayas and Phoenicians from Levant, who didn't built an empire but settled in North Africa, Sicily and Iberia. In Iron Age the Carthaginian Empire, descendants of Phoenician settlers in current Tunisia, build an Empire that spanned most of the western Mediterranean coast. Their army occupying that area included among others Italic people, Gauls, Britons, Greeks and Amazigh people.
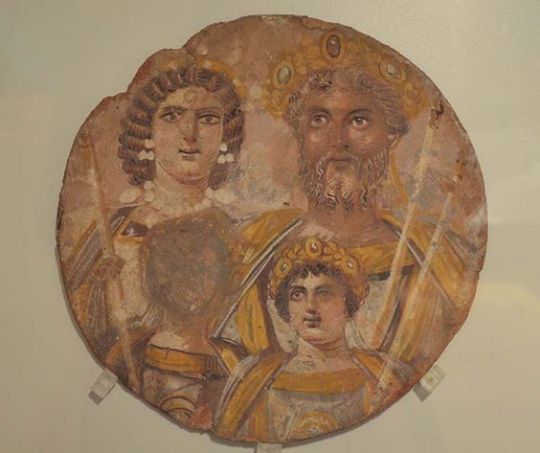
Iron Age also of course saw the rise of the Roman Republic, and later empire, but it was preceded by Etruscans, who populated Tuscan, and possibly preceded the Indo-European presence. However, weather through trade and migration with other Mediterraneans or the continuing presence of darker skin tones of the early Europeans, their art quite often depicts darker skin tones too, like seen below in first two images. Roman Empire at it's height spanned from Babylonia to the British Isles. They recruited soldiers from all provinces and intentionally used stationed them in different areas so they wouldn't be too sympathetic to possible rebels or neighboring enemies. Historical sources mention black Nubian soldiers in British Isles for example. They also built a lot of infrastructure around the empire to ensure protection and easy transportation through trade routes inside the empire. During this time Jewish groups also migrated from Levant to both North-Africa and Europe. Rome even had non-European emperors, like Septimius Severus who originated from Levant and was Punic (descendants of Phoenicians) from his father's side, and who was depicted with darker skin (third picture below). Various ethnicities with differing skin tones are represented all over Roman art, like in the fourth picture below from hunting lodge in Sicily.




Eurasian steppe continued to be important source of migration and trade between Europe and Asia. Scythians, Iranic nomadic people, were important for facilitating the trade between East Asia and Europe through the silk road during the Iron Age. They controlled large parts of Eastern Europe ruling over Slavic people and later assimilating to the various Slavic groups after loosing their political standing. Other Iranic steppe nomads, connected to Scythian culture also populated the Eurasian steppe during and after Scythia. During the Migration Period, which happened around and after the time of Western Rome, even more different groups migrated to Europe through the steppe. Huns arrived from east to the Volga region by mid-4th century, and they likely came from the eastern parts of the steppe from Mongolian area. Their origins are unclear and they were either Mongolic, Turkic or Iranic origin, possibly some mix of them. Primary descriptions of them suggests facial features common in East Asia. They were possibly the nomadic steppe people known as Xiongnu in China, which was significant in East and Central Asia from 3rd century BCE to 2nd century CE until they moved towards west. Between 4th and 6th centuries they dominated Eastern and Central Europe and raided Roman Empire contributing to the fall of Western Rome.
After disintegration of the Hun Empire, the Huns assimilated likely to the Turkic arrivals of the second wave of the Migration Period. Turkic people originate likely in southern Siberia and in later Migration period they controlled much of the Eurasian steppe and migrated to Eastern Europe too. A Turkic Avar Khagenate (nation led by a khan) controlled much of Eastern Europe from 6th to 8th century until they were assimilated to the conquering Franks and Bulgars (another Turkic people). The Bulgars established the Bulgarian Empire, which lasted from 7th to 11th in the Balkans. The Bulgars eventually adopted the language and culture of the local Southern Slavic people. The second wave of Migration Period also saw the Moor conquest of Iberia and Sicily. Moors were not a single ethnic group but Arab and various Amazigh Muslims. Their presence in the Iberian peninsula lasted from 8th to 15th century and they controlled Sicily from 9th to 11th century until the Norman conquest. During the Norman rule though, the various religious and ethnic groups (which also included Greeks and Italic people) continued to live in relative harmony and the North-African Muslim presence continued till 13th century. Let's be clear that the Northern Europe was also not white. Vikings also got their hands into the second wave migration action and traveled widely to east and west. Viking crews were not exclusively Scandinavians, but recruited along their travels various other people, as DNA evidence proves. They also traded with Byzantium (when they weren't raiding it) and Turkic people, intermarried and bought slaves, some of which were not white or European. A Muslim traveler even wrote one of the most important accounts of Vikings when encountering them in Volga.
By this point it should already be clear that Medieval Europe was neither white, but there's more. Romani people, who originate from India and speak Indo-Aryan language, arrived around 12th century to Balkans. They continued to migrate through Europe, by 14th century they were in Italy, by 15th century in Germany and by 16h century in Britain and Sweden. Another wave of Romani migration from Persia through North-Africa, arrived in Europe around 15th century. Then there's the Mongol Empire. In 13th century they ruled very briefly a massive portion of the whole Eurasian continent, including the Eastern Europe. After reaching it's largest extent, it quickly disintegrated. The Eurasian Steppe became the Golden Horde, but lost most of the Eastern-Europe, except Pontic-Caspian Steppe. They ruled over Slavs, Circissians, Turkic groups and Finno-Ugric groups till early 15th century. The Mongolian rulers assimilated to the Turkic people, who had been the previous rulers in most of the steppe. These Turkic people of the Golden Horde came to be known as Tatars. Golden Horde eventually split into several Tatar khagenates in 15th century, when the khagenates, except the Crimean Khagenate, were conquered by the Tsardom of Moscovy. Crimean Khagenate was annexed by the Russian Empire in 1783. Crusades were a movement from Europe to Levant, but they also meant intermarriage in the the Crusader kingdoms especially between the European and Levant Christians, and some movement back and froth between these kingdoms and Europe, trade and a lot of movement back after the Crusader kingdoms were defeated in 13th century. Generally too trade across the Mediterranean sea was extensive and led to migration and intermarriage.
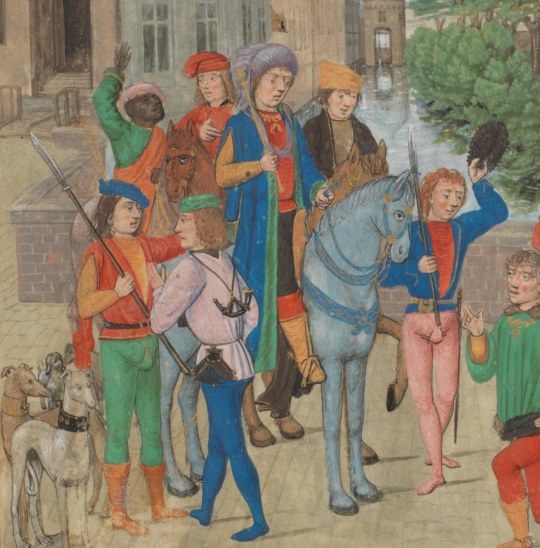
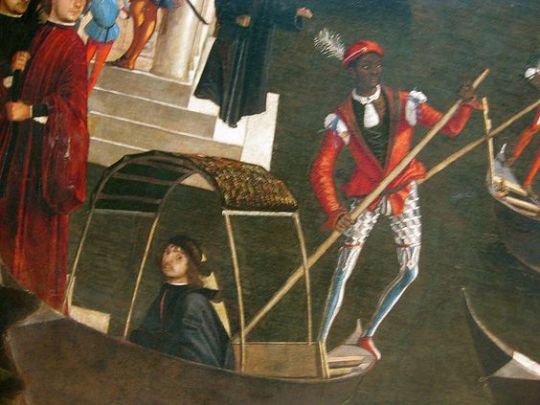
And here's some example of people of colour in Medieval European art, shown as part of the majority white European societies. First is from a 15th century French manuscript depicting Burgundy court with dark skin courtier and lady in waiting. Second one is from a Flemish manuscript from 15th century of courtiers, including a black courtier, going for a hunt. Third is a 15th century Venetian gondolier with dark skin.



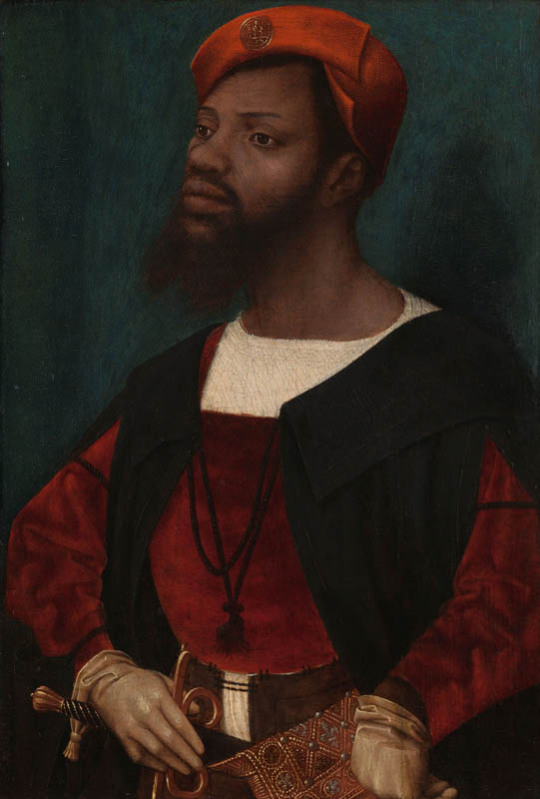
In Renaissance Era Europe was only increasing it's trade and therefore had even more connections outside Europe. The first picture below is Lisbon, which had strong trade relationship with Africa, depicted in late 16th century. People with darker skin tones were part all classes. Second image is an Italian portrait of probably a seamstress from 16th century. Third one is a portrait of one of the personal guards of the Holy Roman Emperor. Fourth image is a portrait of Alessandro de' Medici, duke of Florence, who was noted for his brown complexion, and the modern scholarly theory is that his mother was a (likely brown) Italian peasant woman.




Colonialism begun in the Renaissance Era, but the wide spread colonial extraction and slavery really got going in the 17th century. Racial hierarchy was developed initially to justify the trans-Atlantic slave trade specifically. That's why the early racial essentialism was mostly focused on establishing differences between white Europeans and black Africans. Whiteness was the default, many theories believed humans were originally white and non-whites "degenerated" either through their lives (some believed dark skin was basically a tan or a desease and that everyone was born white) or through history. Originally white people included West-Asians, some Central-Asians, some North-Africans and even sometimes Indigenous Americans in addition to Europeans. The category of white inevitably shrank as more justifications for atrocities of the ever expanding colonial exploitation were required. The colonial exploitation facilitated development of capitalism and the industrial revolution, which led to extreme class inequality and worsening poverty in the European colonial powers. This eventually became an issue for the beneficiaries of colonialism as worker movements and socialism were suddenly very appealing to the working class.
So what did the ruling classes do? Shrink whiteness and give white working classes and middle classes justifications to oppress others. Jews and Roma people had long been common scapegoats and targets of oppression. Their oppression was updated to the modern era and racial categories were built for that purpose. The colonial powers had practiced in their own neighborhoods before starting their colonial projects in earnest and many of those European proto-colonies were developed to the modern colonial model and justified the same way. In 19th century, when racial pseudoscience was reaching it's peak, Slavs, others in Balkan, the Irish (more broadly Celts), Sámi (who had lost their white card very early), Finns, Southern Italians, the Spanish, the Southern French and Greeks all were considered at least not fully white. The Southern Europeans and many Slavs were not even colonized (at least in the modern sense, though with some cases like Greeks it's more complicated than that), but they looked too much and were culturally too similar to other non-white Mediterraneans, and they were generally quite poor. In many of these cases, like Italians, the French and Slavs, it was primarily others belonging in the same group, who were making them into second class citizens. All this is to highlight how very malleable the concept of race is and that it's not at all easy to define the race of historical people.
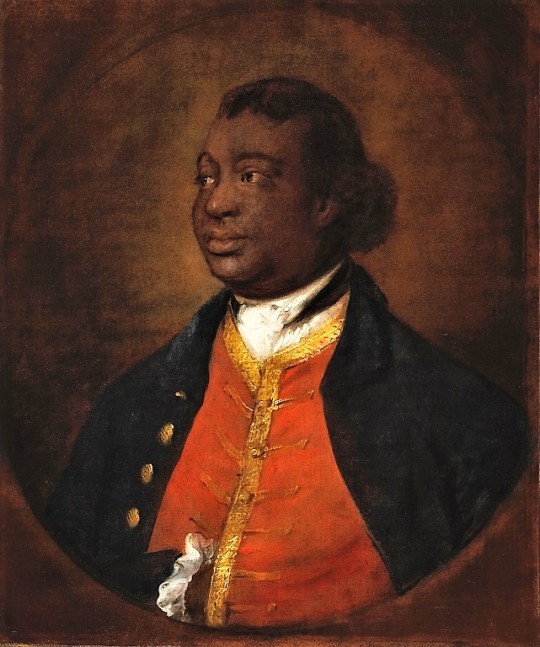
However, even if we would go with the racial categories of today, Europe was still far from being all white in this period. You had Roma, who certainly are not included in whiteness today, and European Jews, whose whiteness is very conditional, descendants of Moors in Southern Europe and Tatars and Turks in Eastern Europe and Turkey, which today is often not thought of as part of Europe, but historically certainly was. And then colonialism brought even more people into Europe forcibly, in search of work because their home was destroyed or for diplomatic and business reasons. There were then even more people of colour, but they were more segregated from the white society. Black slaves and servants are very much represented in European art from 17th century onward, but these were not the only roles non-white people in Europe were in, which I will use these examples to show. First is a Flemish portrait of Congo's Emissary, Dom Miguel de Castro, 1643. Second is a 1650 portrait of a Moorish Spanish man Juan de Pareja, who was enslaved by the artist as artisanal assistant, but was freed and became a successful artist himself. Third is a 1768 portrait of Ignatius Sancho, a British-African writer and abolitionist, who had escaped slavery as a 20-year-old. Fourth painting is from 1778 of Dido Elizabeth Belle, a British gentlewoman born to a slave mother who was recognized as a legitimate daughter by her father, and her cousin. The fifth portrait is of an unknown woman by (probably) a Swiss painter from late 18th century. Sixth is a 1760s Italian portrait of a young black man.



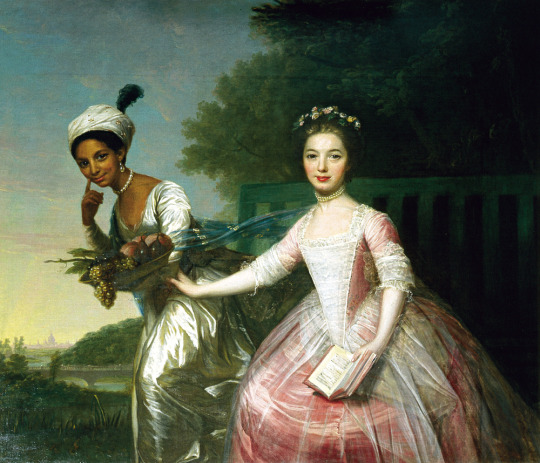
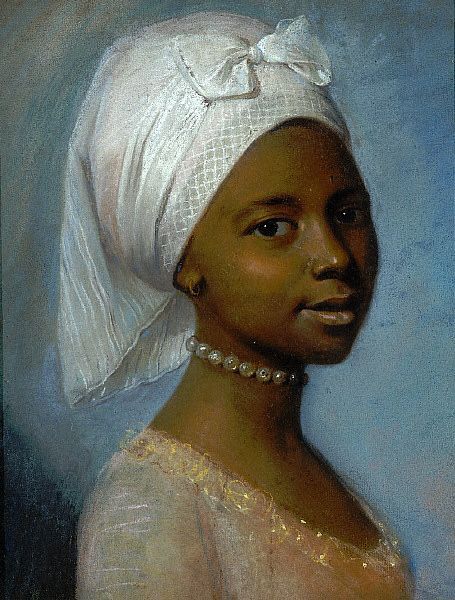

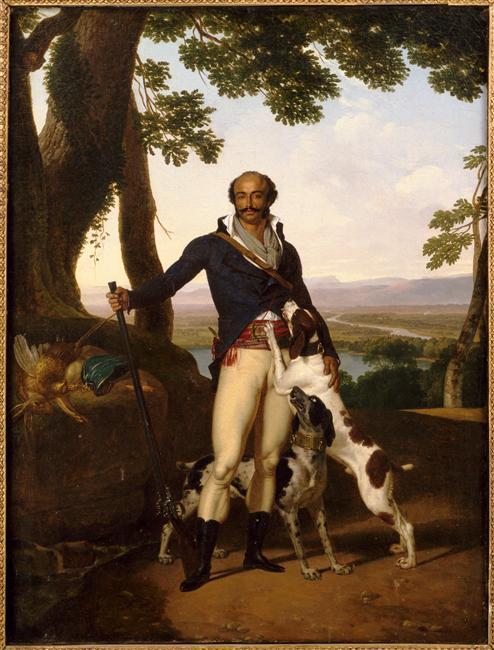
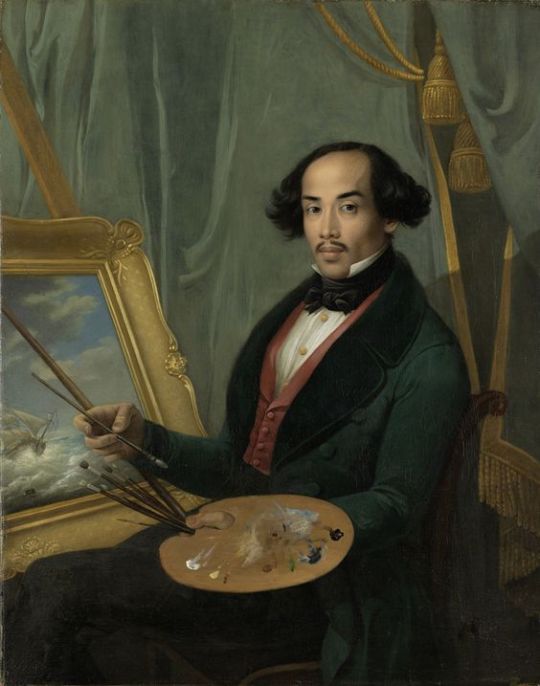
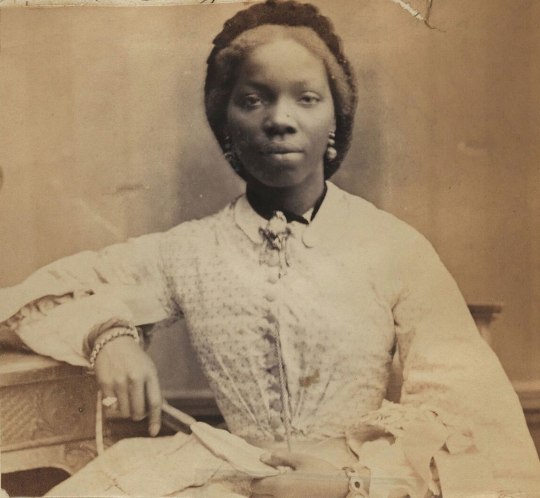
In late 18th century England abolished slavery in British Isles first, then in early 19th century in the whole British Empire, thanks to the continuous campaign of free Black people and some white allies, notably Quakers. Around the same time slavery was abolished in France (briefly till Napoleon got to power) after the French revolution. This meant there were a lot more free black people in Europe after that. In 18th century the Europeans, British especially, were colonizing Asia as much they could, which meant that in 19th century there started to also be a lot more Asian, especially Indian people in Europe. First picture below is of Thomas Alexander Dumas, who was son of a black slave woman and a white noble French man and became a general in the French revolutionary army. His son was one of the most well-known French authors, Alexander Dumas, who wrote The Count of Monte Cristo and The Three Musketeers. Second portrait is of Jean-Baptiste Belley, a Senegalese former slave, who became French revolutionary politician. Third portrait is from 1810 of Dean Mahomed, an Indian-British entrepreneur, who established the first Indian restaurant in London. Forth is Arab-Javanese Romantic painter Saleh Syarif Bustaman, who spend years in Europe. Fifth is a 1862 photo of Sara Forbes Bonnetta, originally named Aina, princess of Edbago clan of Yoruba, who was captured into slavery as a child, but later freed and made Queen Victoria's ward and goddaughter. She married a Nigerian businessman, naval officer and statesman, James Pinson Labulo Davies (sixth picture).






So any guesses on at what point was that "very white Europe" when the "west culture" begun? It kinda seems to me that it never actually existed.
#People forget that Dumas father was literally the first black man to become a brigadier general in Francs#“Slavery is an all black thing; and wealth / nobility an all white thing” ALLOW ME TO DIFFER. Wealth and slavers wasn’t an all race thing.#Also the “we need to make queen Charlotte black because there are not enough black royals / noblemen” is wrong#Like what about the kings and emperors of Haiti? The kingdom of Ndongo?#Also Indian royalty is sooo erased from Hollywood and when represented is soooo stereotypical
201 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nzinga Mbande: Warrior Queen of Angola
Nzinga Ana de Sousa Mbande (c. 1583 – 17 December 1663) was a southwest African ruler who ruled as queen of the Ambundu Kingdoms of Ndongo (1624–1663) and Matamba (1631–1663), located in present-day northern Angola. Born into the ruling family of Ndongo, her father Ngola Kilombo Kia Kasenda was the king of Ndongo. She is remembered in Angola as the Mother of Angola, the fighter of negotiations,…

View On WordPress
#African History#African Leaders#Ambundu Kingdoms of Ndongo#Angola History#central africa history#Nzinga Ana de Sousa Mbande
1 note
·
View note
Text
Okay, Shōgun was amazing. Can FX/hulu produce an African historical epic drama next? Hire African writers, actors, directors, etc and tell an authentic story set in a historical African state/kingdom/empire (Ndongo, Matamba, Mali Empire, Kingdom of Benin, the Zulu Kingdom, etc) and aimed at a global audience!
76 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Portuguese Angola
Portuguese Angola in southwest Africa was the first European colony on that continent. While settlement from 1571 proved problematic in the interior, the Portuguese did obtain a large number of slaves which they shipped to their Atlantic island colonies and to Portuguese Brazil right up to the end of the Atlantic slave trade in the 19th century.
With the capital at Luanda on the coast, the Portuguese struggled against the kingdoms of Kongo, Ndongo, and Matamba to gain control of the interior. The Angolan Wars saw shifting tribal allegiances thwart the relatively small number of Afro-Portuguese, but help from Brazil, eager to maintain the flow of slaves, proved crucial. The decolonization process in the mid-20th century was one of the most bloody and shambolic in Africa, and civil war continued long after independence was gained in 1975.
The Portuguese in West Africa
The Portuguese arrived in West Africa, and from the late 15th century they began to explore further south. Following the Portuguese colonization of São Tomé and Principe in 1486, the Europeans were looking for slaves to work on their sugar plantations. The Portuguese settlers on São Tomé and Principe had already been in trade contact with the mainland, searching for gold, pepper, and ivory. The main trading partner was the Kingdom of Kongo (c. 1400 - c. 1700), which controlled a booming regional slave trade. Through the 16th century, slaves from Kongo (and also the Kingdom of Benin) were transported to the Portuguese islands and to their colonies in the North Atlantic like Madeira.
The Portuguese had bought African slaves with cotton cloth, silk, mirrors, knives, and glass beads, but they got the idea to launch their own slave-capturing expeditions in Africa’s interior and cut out the Kongolese middlemen. The Kongo kings were not pleased with this development, and they were increasingly alarmed at the effects of European culture and the Christian religion on their subjects. As relations soured, the Portuguese began to look for another trade partner further down the coast of Africa.
Exploring further south in the mid-16th century, the Europeans came into contact with a new kingdom, or rather a loose confederation of Kimbundu tribes, then known as Ndongo, probably formed c. 1500. Its ruler was called the Ngolo, which derives from the local word for iron - ngola - and from which the name Angola derives. The Portuguese attempted to create a new slave industry partnership with Ndongo and even involved the kingdom in a war with their northern neighbours, the Kingdom of Kongo. Ndongo had already defeated Kongo in a battle in 1556 and so seemed a good candidate to satisfy Portugal's ambitions in the region.
Continue reading...
20 notes
·
View notes
Photo




Favorite list of royal women | Regnant queens (who crowed herself queen without her husbands)
Been a queen regnant is not always easy specially when you are married but mor common than one would think. Here four of my favorite queen that were married and despite what society, and often the husband himself, thought decided that her lands by heritage or conquest were only hers to rule.
i. [1081-1116] Called The Reckless, Urraca was one of the most powerful reigning Queens of her time having inherithed the kingdom of León. Upon the death of her first husband she was convinced to marry Alfonso of Aragon the most successful warrior king of the Iberian Peninsula. It went horribly wrong. Personalities clashed and Alfonso emprisoned Urraca at one point. With Galicia rebelling and the Almoravides menace the spouses still went to war againts each other. Finally they separate and while Urraca still has a long way ahead and could keep most of her lands for herself.
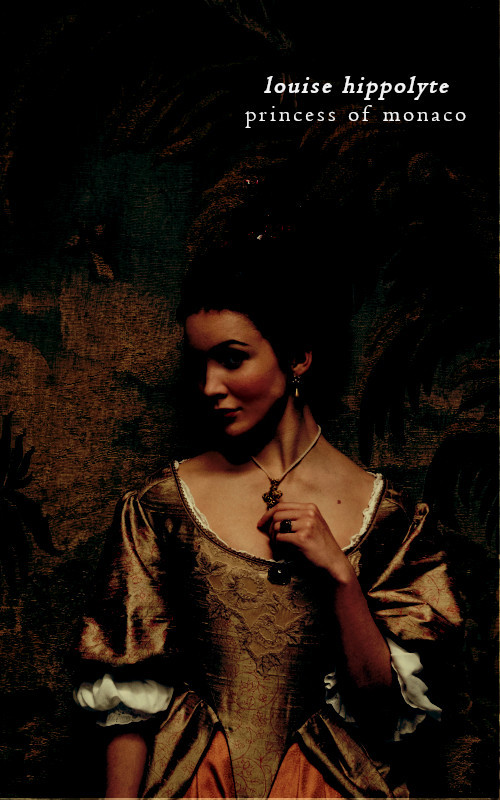
ii. [1697-1731] Louise Hyppolite was at her time of birth the last Grimaldi. Monaco was under French control and it was decided that man from the French King family will be Louise’s husband and rule along with her. She was married and had to leave her land with her husband. Described as shy and submissive she did not enjoy her time at Versailles. When her father was ill she came back alone to Monaco and when he died she crowned herself Princess of Monaco with the people enthusiastic support naming her firstborn heir. There is no much her husband could do and though she ruled fr a short time she did it as the sole Princess.
iii. [1717-1780] Maria Theresia’s father Emperor Charles VI of the Roman Empire, did not prepared her to rule as he was convinced that her husband would rule for her. However, she had other plans and when her father died Maria Theresa, a 23 years old set to stablish her right as a moanrch against Prussia and most of Europe. She manage to gain ruling experience and be a monarch for 40 years. Though she deeply loved her husband she did not let him rule in her name and even refused to kneel in front of him when he was elected Holy Roman Emperor as she was of highest ruler. She was Sovereign of Hungary and Bohemia and Archduchess of Austria on her own right her husband being the consort.
iv. [1583-1663] Njinga was Queen of Ndongo after her father and brother. At the time with the Portuguese slave trade Njinga became a symbol of resistance to the Europeans. In order to gain power in the center of the region she married an Imbangala leader and learned the techniques and strategies of his people. However when she set to conquer the kingdom of Matamba and ruled there as the Queen as Matamba had tradition of female rulers. As she gained influence she was recognized as one of the great queens of the region at the time.
#historical women#women in history#maria theresia#njinga of ndongo and matamba#urraca of leon#louise hyppolite of monaco#maria theresa of austria#history
147 notes
·
View notes
Text
Please reblog for a bigger sample size!
If you have any fun fact about Angola, please tell us and I'll reblog it!
Be respectful in your comments. You can criticize a government without offending its people.
44 notes
·
View notes
Text

A nganga (pl. banganga or kimbanda) is a spiritual healer, diviner, and ritual specialist in traditional Kongo religion. These experts also exist across the African diaspora in countries where Kongo and Mbundu people were transported during the Atlantic slave trade, such as Brazil, the southern United States, Haiti and Cuba.

Nganga means "expert" in the Kikongo language. The Portuguese corruption of the meaning was "fetisher."��It could also be derived from -ganga, which means "medicine" in Proto-Bantu. As this term is a multiple reflex of a Proto-Bantu root, there are slight variations on the term throughout the entire Bantu-speaking world

In the Kingdom of Kongo and the Kingdom of Ndongo, expert healers, known as banganga, underwent extensive training to commune with the ancestors in the spiritual realms and seek guidance from them. They possessed the skill to communicate with the ancestors in the spiritual realm, or Ku Mpémba, as well as divining the cause of illness, misfortune and social stress and preparing measures to address them, often by supernatural means and sacred medicine, or minkisi.
They were also responsible for charging a nkisi, or physical objects intended to be the receptacle for spiritual forces that heal and protect its owner. When Kongo converted to Christianity in the late fifteenth century, the term nganga was used to translate Christian priest as well as traditional spiritual mediators. In modern Kongo Christianity, priests are often called "Nganga a Nzambi" or "priests of God."[citation needed] The owner and operator of an nkisi, who ministered its powers to others, was the nganga.
An English missionary describes how an nganga looks during his healing performance:
Thick circles of white around the eyes, a patch of red across the forehead, broad stripes of yellow are drawn down the cheeks, bands of red, white, or yellow run down the arms and across the chest.... His dress consists of the softened skins of wild animals, either whole or in strips, feathers of birds, dried fibres and leaves, ornaments of leopard, crocodile or rat's teeth, small tinkling bells, rattling seedpods...
This wild appearance was intended to create a frightening effect, or kimbulua in the Kongo language. The nganga's costume was often modeled on his nkisi. The act of putting on the costume was itself part of the performance; all participants were marked with red and white stripes, called makila, for protection.
The "circles of white around the eyes" refer to mamoni lines (from the verb mona, to see). These lines purport to indicate the ability to see hidden sources of illness and evil.
Yombe nganga often wore white masks, whose color represented the spirit of a deceased person. White was also associated with justice, order, truth, invulnerability, and insight: all virtues associated with the nganga.
The nganga is instructed in the composition of the nkondi, perhaps in a dream, by a particular spirit. In one description of the banganga's process, the nganga then cuts down a tree for the wood that s/he will use to construct the nkondi. S/he then kills a chicken, which causes the death of a hunter who has been successful in killing game and whose captive soul subsequently animates the nkondi figure. Based on this process, Gell writes that the nkondi is a figure an index of cumulative agency, a "visible knot tying together an invisible skein of spatio-temporal relations" of which participants in the ritual are aware
#nganga#african#afrakan#kemetic dreams#africans#afrakans#african culture#afrakan spirituality#african american#african spirituality#nkondi#nkisi#central africa#gells#spatio temporal
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Black American Freedom Fighters"
/*
"Black American Freedom Fighters" By Gregory V. Boulware WordPress, 2013
"What is a man who does not try and make the World better?" 'Black American Freedom Fighters' “And wo, wo, will be to you if we have to obtain our freedom by fighting… I declare to you, while you keep us and our children in bondage, and treat us like brutes, to make us support you and your families, we cannot be your friends!" https://www.academia.edu/113880204/Black_American_Freedom_Fighters
The 1619 Project Further information: Slavery in the colonial history of the United States The 1619 Project was launched in August 2019 to commemorate the 400th anniversary of the arrival of the first enslaved Africans in the British colony of Virginia. In 1619, a group of "twenty and odd" captive Africans arrived in the Virginia Colony. An English privateer operating under a Dutch letter of marque, White Lion, carried 20–30 Africans who had been captured in joint African-Portuguese raids against the Kingdom of Ndongo in modern-day Angola, making its landing at Point Comfort in the English colony of Virginia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_1619_Project
'The BookMarketingNetwork' http://thebookmarketingnetwork.com/profiles/blogs/black-american-freedom-fighters
"What Is A Man Who Does Not Try and Make the World Better?" ~'Black American Freedom Fighters'~ https://blackamericanfreedomfighters.blogspot.com/ http://hbcu.com/content/246227/black-american-freedom-fighters https://boulwareenterprises.wordpress.com/2013/02/15/black-american-freedom-fighters/
“Twitter” https://twitter.com/#!/AuthorBoulwareG
Academia: https://www.google.com/search?q=Black+American+Freedom+fighters%2C+Gregory+V.+Boulware&rlz=1C1GCEA_enUS1090US1090&oq=Black+American+Freedom+fighters%2C+Gregory+V.+Boulware&gs_lcrp=EgZjaHJvbWUyBggAEEUYOTIGCAEQRRhAMgYIAhBFGEDSAQoyODQzN2owajE1qAIAsAIA&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8#ip=1
*/

#Woke#Academia#Freedom#TheUSConstitution#Emmancipation#History#Yahuah#BlackHistory#Herstory#Tubal#DEI#MLK#BLM#TYT#MeidasTouch#Kemetic#EyesOnThePrize#PBS#WordPress#LinkedIn#Blogger#PhiladelphiaTribune#Philosophy#Boulware#Yahweh#Yahshua#Yahushua#Hebrew#TheSeedOfMan#Falasha
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here's my list of forgotten/cool women from history. Please take it, reblog it with more, spread it, learn about them, make books about them:
Lucy (slave used for experimentations on the uterus)
Nightwitches from WW2
Grace Hopper
Mary Anning
Maria Mitchell
Ada Lovelace
Kate Warne
Agnes Barre
Flora Tristan
Olympe de Gouges
Eleanor Roosevelt
Bessie Smith
Sylvia Plath
Sweet Tee
Lady D (the rapper)
The Sequence
Lady B
Rachel Carson
Baya
Tahireh
Lalla Fatma N'Soumer
Rosalind Franklin
Miriam Makeba
Alexandra David Néel
Suzanne Noël
Helena Rubinstein
Katherine Switzer
Jeanne Barret
Sophie Germain
Katherine Johnson
Margaret Hamilton
Hedy Lamarr
Betty Snyder Holberton
Kathleen McNulty Mauchly Antonelli
Marilyn Wescoff Meltzer
Frances Bilas Spence
Ruth Lichteman Teitelbaum og Jean Jennings Bartik
Valerie Thomas
Karen Sparck Jones
Dr Shirley Ann Jackson
Radia Perlman
Stacy Horn
Dr Betty Harris
Beulah Louise Henry
Elizabeth "Jake" Feinler
Empress Zenobia of the Palmyrene Empire
Surya Bonaly
Dolly Parton
Mary Wollstonecraft
Mary Shelley
Queen Nzinga of Ndongo Kingdom
Queen Yaa Asantewa Ashanti
Empress Candace of Ethiopia
Queen Sarraounia Mangou of Aznas Kingdom
Dona Beatriz
Mileva Marić
Matoaka
Janet Sobel
Claudette Colvin
Marsha P. Johnson
Marian Anderson
Madam CJ Walker
Frida Kahlo
Mirka Mora
Dahomey Amazons
The 40 Elephants
Diamond Alice
Maggie Bailey
Julie d'Aubigny
Bessie Coleman
Policarpa Salavarrieta
Annie Oakley
Anna Julia Cooper
Sojourner Truth
Ida B. Wells
Shirley Chisholm
Mary Church Terrell
Audre Lorde
Harriet Tubman
Maria W. Stewart
Angela Davis
Florynce Kennedy
Jocelyn Bell
Alice Ball
Lise Meitner
Chien Shiung Wu
Marie Tharp
Elizabeth Blackwell
Amanirenas
Wu Zetian
40 notes
·
View notes
Text

August 1, 1619, “20 and odd” Angolans, kidnapped by the Portuguese, arrive in the British colony of Virginia and are then bought by English colonists. The arrival of enslaved Africans in the New World marks the beginning of two and a half centuries of slavery in North America.
Founded at Jamestown in 1607, the Virginia Colony was home to about 700 people by 1619. The first enslaved Africans to arrive there disembarked at Point Comfort, in what is today known as Hampton Roads. Most of their names, as well as the exact number who remained at Point Comfort, have been lost to history, but much is known about their journey.
They were kidnapped by Portuguese colonial forces, who sent captured members of the native Kongo and Ndongo kingdoms on a forced march to the port of Luanda, the capital of modern-day Angola. From there, they were ordered on the slave ship San Juan Bautista, which set sail for Veracruz in the colony of New Spain. As was quite common, about 150 of the 350 captives aboard the ship died during the crossing.. Αs it approached its destination, the ship was attacked by two privateer ships, the White Lion and the Treasurer. Crews from the two ships stole up to 60 of the Bautista’s ενslaveδ. It was the White Lion that docked at Virginia Colony's Point Comfort and traded some of the prisoners for food on August 20, 1619. #africanhistory365 #africanexcellence
2 notes
·
View notes
Text


The entire African continent was an extremely civilized place by their own rich cultures, the time the first European travellers began discovering and later destroying her people and cultures.
“When they arrived in the Gulf of Guinea and landed at Vaida (in West Africa) the captains were astonished to find streets well laid out, bordered on either side for several leagues by two rows of trees; for days they travelled through a country of magnificent fields, inhabited by men clad in richly coloured garments of their own weaving! Further south in the Kingdom of the Congo, a swarming crowd dressed in `silk` and `velvet`; great States well-ordered, and down to the most minute details; powerful rulers, flourishing industries-civilized to the marrow of their bones. And the condition of the countries on the eastern coast- Mozambique, for example- was quite the same.”Leo Frobenius, `Histoire de la Civilisation Africaine`, quoted in Anna Melissa Graves, `Africa, the Wonder and the Glory,US, Black Classic Press, (originally 1942),pg4.
Portuguese missionaries wrote of the Kongo…” a well-organized political system with taxes and rates, there was a brilliant court,(and) a great civil service. The state constructed roads, imposed tolls, supported a large army and had a monetary system-of…shells, of which the Mani Congo…had a monopoly. The Congo Kingdom even had a few satellite states, for example the state of the Ngola (ie Ndongo) in present-day Angola. The original kingdom was about the size of France and Germany put together”.
“There is no doubting…the existence of an expert metallurgical art in the ancient Kongo; only the competition of objects from abroad and the slow deterioration brought about its decline. A further proof is provided by recent ethnographic documents. The Bakongo were aware of the toxicity of lead vapours. They devised preventative and curative methods, both pharmacological (massive doses of pawpaw and palm oil) and mechanical (exerting of pressure).
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nganga - Wikipedia
A nganga (pl. banganga or kimbanda) is a spiritual healer, diviner, and ritual specialist in traditional Kongo religion.[1] These experts also exist across the African diaspora in countries where Kongo and Mbundu people were transported during the Atlantic slave trade, such as Brazil, the southern United States, Haiti and Cuba.

Etymology
Nganga means "expert" in the Kikongo language. The Portuguese corruption of the meaning was "fetisher."[2] It could also be derived from -ganga, which means "medicine" in Proto-Bantu. As this term is a multiple reflex of a Proto-Bantu root, there are slight variations on the term throughout the entire Bantu-speaking world.[citation needed]
Central Africa

Inyanga from Johannesburg, South Africa
In the Kingdom of Kongo and the Kingdom of Ndongo, expert healers, known as banganga, underwent extensive training to commune with the ancestors in the spiritual realms and seek guidance from them.[2] They possessed the skill to communicate with the ancestors in the spiritual realm, or Ku Mpémba, as well as divining the cause of illness, misfortune and social stress and preparing measures to address them, often by supernatural means and sacred medicine, or minkisi.[2]
They were also responsible for charging a nkisi, or physical objects intended to be the receptacle for spiritual forces that heal and protect its owner. When Kongo converted to Christianity in the late fifteenth century, the term nganga was used to translate Christian priest as well as traditional spiritual mediators.[3] In modern Kongo Christianity, priests are often called "Nganga a Nzambi" or "priests of God."[citation needed] The owner and operator of an nkisi, who ministered its powers to others, was the nganga.[4]
An English missionary describes how an nganga looks during his healing performance:
Thick circles of white around the eyes, a patch of red across the forehead, broad stripes of yellow are drawn down the cheeks, bands of red, white, or yellow run down the arms and across the chest.... His dress consists of the softened skins of wild animals, either whole or in strips, feathers of birds, dried fibres and leaves, ornaments of leopard, crocodile or rat's teeth, small tinkling bells, rattling seedpods...[4][5]
This wild appearance was intended to create a frightening effect, or kimbulua in the Kongo language. The nganga's costume was often modeled on his nkisi. The act of putting on the costume was itself part of the performance; all participants were marked with red and white stripes, called makila, for protection.[4]
The "circles of white around the eyes" refer to mamoni lines (from the verb mona, to see). These lines purport to indicate the ability to see hidden sources of illness and evil.[4]
Yombe nganga often wore white masks, whose color represented the spirit of a deceased person. White was also associated with justice, order, truth, invulnerability, and insight: all virtues associated with the nganga.[citation needed]
The nganga is instructed in the composition of the nkondi, perhaps in a dream, by a particular spirit. In one description of the banganga's process, the nganga then cuts down a tree for the wood that s/he will use to construct the nkondi. S/he then kills a chicken, which causes the death of a hunter who has been successful in killing game and whose captive soul subsequently animates the nkondi figure.[6] Based on this process, Gell writes that the nkondi is a figure an index of cumulative agency, a "visible knot tying together an invisible skein of spatio-temporal relations" of which participants in the ritual are aware.[7]

Southern Africa
A n'anga, close to Great Zimbabwe
In South Africa, the inyanga has a medicinal role, in contrast to the sangoma, who deals with divination and the ancestral spirits, however, the distinction has become blurred in some areas and many traditional healers tend to practice both arts.[8][9] In Swahili, mganga refers to a qualified physician or traditional healer.[citation needed]
Among the Shona people of Zimbabwe, a n'anga is a traditional healer who uses a combination of herbs, medical/religious advice and spiritual guidance to heal people. In Zimbabwe, N'angas are recognized and registered under the ZINATHA (Zimbabwe National Traditional Healer's Association).[10][11]
They are believed to have religious powers to tell fortunes, and to change, heal, bless or even kill people. Traditionally N’angas were people’s main source of help in all matters of life. They have existed for decades well before the British colonial era. Guerrilla leaders are said to have consulted with N’angas during the Rhodesian Bush War.[12]
Even today, N'angas are consulted by the people for advice and healing of many illnesses. Sometimes N'angas refer their patients to western medical practitioners and hospitals in case of emergency or illness they cannot cure with the help of their healing spirit.[13]
The Americas
In the United States, nganga, who acted as spiritual leaders, played a key role in Hoodoo practices, which combined Kongo religion, Christianity and indigenous American herbal knowledge.[2]
In Cuba, the term nganga refers to a clay pot or iron cauldron that is kept in the homes of Palo diviners, called paleros. Similar to mojo bags in the United States, these banganga contained items from important places in nature and spiritual items, such as forest dirt, volcanic ash, and the hair, ashes or bones of an ancestor. They were seen as means to honor Nzambi, the mpungo and mfumbi (ancestral spirits), and the forces of nature.[14]
Many inverted positions of capoeira, including bananeira, aú, rabo de arraia, and others, are believed to have originated from the use of handstand by nganga imitating their ancestors, who walked on their hands in the spirit world.
#Nganga - Wikipedia#Kongo#Palo#Paleros#Nganga#Banganga#Indigenous African Religions#Palo Mayombe#African Traditional Religion
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The first large political entity in the area, known to history as the Kingdom of Kongo, appeared in the thirteenth century and stretched from Gabon in the north to the river Kwanza in the south, and from the Atlantic in the west to the river Cuango in the east. Mbanza Kongo, the capital, had a population of 50,000 people. South of this kingdom were various important states, of which the Kingdom of Ndongo, ruled by the ngola (king), was most significant. Modern Angola derives its name from the king of Ndongo.
Their wealth came mainly from agriculture. Power was in the hands of the Mani, aristocrats who occupied key positions in the kingdom and who answered only to the all-powerful King of the Kongo. Mbanza was the name given to a territorial unit administered and ruled by a Mani; Mbanza Kongo, the capital, had a population of over fifty thousand in the sixteenth century.
In the century before Portuguese exploration of West Africa, the Kongo Kingdom developed in West Central Africa. In the three hundred years from the date the kingdom was founded by Ne Lukeni Kia Nzinga until its destruction in 1665 by the Portuguese, Kongo was an organized stable, politically centralized society based upon a subsistence economy. The Kongo is significant in exploring the historic contexts of African American heritage because the majority of all Africans enslaved in the Southern English colonies were from West Central Africa.
https://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/angola/kongo.htm
#quote#Kingdom of Kongo#Congo#Angola#West Africa#Africa#African history#DRC#Portugal#maps#cartography#Zaire#Central Africa
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
NZINGA // QUEEN OF THE AMBUNDU KINGDOMS
“She was a West African ruler who served as queen of the Ambundu Kingdoms of Ndongo and Matamba, located in present day northern Angola. She received military and political training as a child and demonstrated an aptitude for defusing political crises as an ambassador to the Portuguese Empire. She later assumed power over Ndongo after the deaths of her father and brother and would go onto conquer Matamba. She ruled during a period of rapid growth in the African slave trade and enroachment of the Portuguese Empire into South West Africa, in attempts to control the slave trade. She fought for independence and stature of her kingdoms in a reign that lasted 37 years.”


4 notes
·
View notes
Text
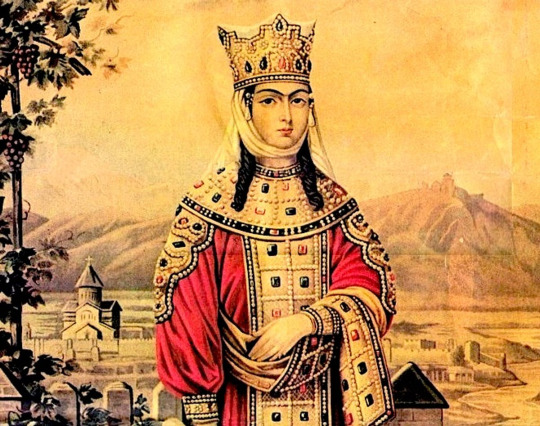
HORSES NEIGHED AND FIRES CRACKLED as Queen Tamar of Georgia walked among her troops on the eve of battle in July 1203. Her enemies outnumbered her soldiers nearly two to one. Still, the queen did not waver as she spoke words of courage to the assembled army. In a show of humility, she stood before them barefoot while wearing lavish garments full of religious symbolism to inspire a righteous bravery in all who saw her. As she finished her rousing speech, hardy, battle-worn soldiers stood, raised their spears, and shouted, “To our king!” The next day, the Georgian army decimated their foe.
In the late 12th and early 13th centuries, Tamar the Great ushered in Georgia’s golden age. She expanded borders, oversaw massive architectural projects, and helped define the kingdom’s unique identity at the crossroads of East and West. She sat on war councils and, as one chronicler wrote, “took counsel with them, not like a helpless person, or a woman, and did not neglect the dictates of reason.”

As father/daughter historians Jonathan and Emily Jordan demonstrate in their book, War Queens: Extraordinary Women Who Ruled the Battlefield, Tamar was far from history’s only warrior queen. The pair recently launched a new podcast with Diversion Audio (also called War Queens) where they dig into all the twists and bloody turns of Tamar’s story alongside other battle-hardened queens.
Atlas Obscura sat down with Emily Jordan to talk about why Italian philosopher Niccolò Machiavelli had it out for her favorite fortress-seizing countess, an African queen who went toe-to-toe with Portuguese enslavers, and why so often these women’s stories go overlooked.
. . .
Who is your favorite person you highlight in the book or on the podcast? And why?
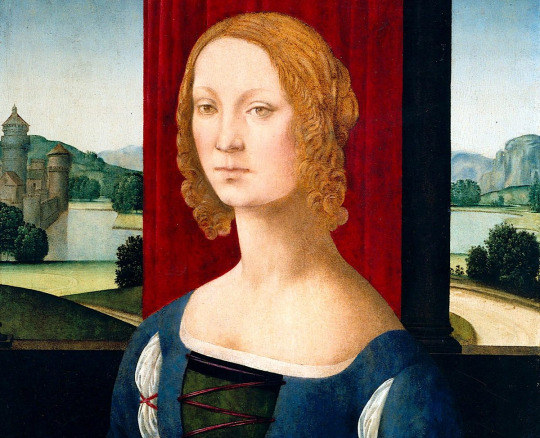
I think in terms of courage, I’d have to say Caterina Sforza. She’s really just an incredible Renaissance woman. She learned all about medicine, botany. She got to interact with Botticelli and Da Vinci. She went to people during times of plague with medicines that she created and studied. My favorite story about her is when her husband’s political interests were compromised when the pope died. Her husband was a paranoid, vicious man, but his family member was the pope. And when the pope passed away, that got Caterina thinking, “We may not be confirmed as the ruler of this city, of Imola.”
So she rides down to Rome, while pregnant, in her early twenties, and she takes hold of this great fortress, Castel Sant’Angelo. The cardinals have to cross in front of the castle on this big bridge to get over to Vatican City. So she points the cannons right at them and says. “Rome, hold up. Stop. I’m in charge.” She stops all of Rome and stops the cardinals from electing a new pope until they confirm her and her husband’s titles. The fact that she did this in her early twenties while pregnant is insane to me.

Did any of these war queens have experience in battle?
Queen Njinga Mbandi of Ndongo-Matamba [two African kingdoms located in present-day Angola] is by far the most physically capable of all the women we write about. Very few of our women really had a lot of hand-to-hand combat experience; Caterina Sforza had a little bit. But Njinga [sometimes spelled “Nzinga”] would charge into battle with her people. She lived during the 17th century and was the leader of her tribe. She had an older brother who was in power before her, but she was a better hand-to-hand combat fighter, leader, and diplomat, so she kind of takes charge. She was this amazing chameleon and takes on different types of cultures in order to unite her people.
She was trained to do this martial art. It’s linked to the Brazilian art of capoeira where you almost do dances as exercises, jumping side to side out of the way of arrows and bullets. Certain scholars even claim that a part of the art, called ginga [pronounced and sometimes spelled “jinga”], is named after her. Their main weapon was a form of battle axe, and she was really well-trained with that axe as well.
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo

In 1482, when the Portuguese first landed in what is now northern Angola, they encountered the Kingdom of the Kongo, which stretched from modern Gabon in the north to the Kwanza River in the south. Mbanza Kongo, the capital, had a population of 50,000 people. South of this kingdom were various important states, of which the Kingdom of Ndongo, ruled by the ngola (king), was most significant. Modern Angola derives its name from the king of Ndongo. The Portuguese gradually took control of the coastal strip throughout the 16th century by a series of treaties and wars. The Dutch occupied Luanda fro…
0 notes