#Immigration resources
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
My love for ATLA has been there as my comfort during the dark and anxious times of my life💙. The show was ahead of its time touching on the topic of children battling a war to restore balance to the word in the face of a dictatorship, colonization, and genocide. I think about my favorite character Katara. I love her so much because of her strength, passion, bravery, kindnesses, and resiliency after the genocide of her people making her the last waterbender of her tribe.
I get emotional because as a Mexican-American and the current dehumanization and attacks on our community, where we are experiencing raids and getting pushed out of own land, kidnapped, I think about the warriors of the water tribe and their resiliency.
I think about the beauty in how they have a sense of a community of love that binds them together through the darkest of times. I see connection of the beauty of our people where we look out for eachother, we care for eachother, and refuse to back down and fight back against the colonial oppressor.
We will not sit down with our hands tied. We are descendants of warriors. We know who we are. We are loud and outspoken and won’t tolerate any of the inhume injustices that are inflicted upon us and we will push back because this is rightfully our native land 🦅🐍🌵🤎🪶
So even though it is an animated show, shows and characters can mean so much to people! Katara as a character is a strong indigenous female warrior! She would definitely be fighting along side us in this war and she wouldn’t tolerate any of this tyrannical sh** either!!!🥹🌊🇲🇽 We are warriors, and we are healers of our communities










#atla#katara#atla katara#southern water tribe#immigration#fuck ice#fuck trump#los angeles#indigenous peoples#native land#mexican american#colonization#collective power#anti ice#ice#mexico#immigration resources#resist#avatar the last airbender#avatar#no human being is illegal#chinga la migra
35 notes
·
View notes
Text


posting this to spread the word. know your rights. it's very important to know what you can do and how you can do it. this is from:
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Know Your Rights - Fuck ICE !!
in light of the despicable ICE raids and deportations, here is a link to free, printable Red Cards. Red Cards come in a variety of languages (39 to be exact), and they detail your rights if an officer tries to speak with you. you can slide them under the door if they try to enter your house, or hand them to an officer. many people will print these out themselves and distribute them to community members, but you can also order official cards.
under the current administration, agents might still try to ignore the law (and not be held accountable), but it remains important to share knowledge and make sure everyone feels supported in these times of crisis. it can be hard to remember what to say in the moment, even if you know your rights up and down.
#please share#immigration#immigration resources#fuck ice#ice#red cards#mass deportations#fuck Trump#resources#community resources#Hispanic#refugee#immigrant
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
resources for the incoming USA administration
i compiled a list of resources -- although short -- for those in the united states who are scared for or unsure about these next few years. please always stay strong and connected to your communities. your existence is resistance.
https://linktr.ee/eliasdecaro
if you have any proposals for links to add, feel free to suggest them!
#us politics#usa#fuck trump#us resources#immigration resources#usa elections#us election#united states#usa politics#resources#stay strong#stay safe#deny defend depose#fuck the government#unite and educate yourselves and others further#defund ice
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi all! I know that objectively everything is going to shit rn and this is only skimming the surface of what we can do to help but one of the ways that we can support immigrant communities is making sure that people know where they can turn to for legal support and other resources.
I put together some flyers for resources in different counties in my home state of MD (plus Baltimore City). If you live in this area, feel free to print and distribute where you live. If your county is not represented feel free to reach out and I can make one for your area. So far I have Prince George’s County, MoCo, Frederick, Howard, Anne Arundel and Baltimore City.
If you live in a different state and have resources you’d like to share, feel free to post here too and we can make a master list here.
Feel free to reblog and share for wider reach.
0 notes
Text
ICE raids are happening.
Any immigrants, no matter how long you have been a citizen of the USA, is at risk of being deported either out of the country as a whole or into what are basically concentration camps. Raids starting in Chicago, Illinois. and spreading to other major cities with high POC and Hispanic populations. The US Immigrations and Customs Enforcement (ICE) and Customs and Border Patrol (CBP) have started raiding homes and families in California.
There are no "protected locations" as of January 21, 2025. Hospitals, schools, and churches are all at risk of being raided, where before these places were deemed safe and off limits to raids.
When it comes to spotting an ICE agent, look for these:
Weirdly neat/well kept hair (shaved heads, side parts, military burs for men; low buns, high ponytails, close cropped bobs for women)
Oversized jacket (long and bulky outerwear makes it easier to hide tools/equipment without being suspicious)
Both hands in pockets
Many undercover agents/cops buy cheap plain clothes off the racks so they aren’t seen in their own clothes. This can make their outfit seem awkward
Sweatshirts with the hood up
Sports apparel (warm up jacket, sweats, etc) with non-sports clothes (jeans, cargo shorts)
Cargo pants/shorts (usually full of items like their badge, flashlight, taser, pepper spray, backup handcuffs, zip ties)
Military or hiking style boots, sometimes chunky sneakers (extra points if none of it matches anything in their outfit)
Outline of a gun in their pants/shirt (easy to see when bending, leaning, or raising arms) (NO NOT SAY ANYTHING)
Overly friendly
Overly inquisitive
“How old are you” and “what do you know about this happening” are both red flags, along with generally odd and personal questions
Don’t fit in
Mismatched pairs in public spaces (usually cops do these things in pairs. They don’t talk to each other or acknowledge each other much, if at all)
DO NOT SAY ANYTHING UNTIL YOU ARE 100% SURE
YOUR BEST BET IS NOT TO SAY ANYTHING UNTIL THE SUSPECT STARTS ACTING OFF AND GETTING PUSHY
COPS ARE NOT OBLIGATED TO TELL YOU THAT THEY ARE UNDERCOVER
COPS CAN AND WILL LIE TO YOU
SCREAM “LA MIGRA” AT THE TOP OF YOUR LUNGS
For protesting:
N95 masks
Respirator/gas mask if you have access to one
Water water water water water (I hate to say it, but disposable one use bottles are best here. If it comes to it, you need to be able to drop and run.) Use for flushing wounds, flushing eyes of tear gas, and of course drinking.
Snacks! You'll be doing a lot of walking and/or running and need to keep that energy up. Trail mix, dried fruit, nuts, granola bars, crackers, jerky/meat sticks, fruit snacks, candy, etc. Think of it like packing your lunchbox for a field trip.
Eyedrops (teargas is a bitch)
Goggles (I bring my old snowboarding goggles)
If you are wearing a t-shirt or have exposed skin, put on fake/temporary tattoos. If you are brought into something and they say you were there, showing a picture of you with the tattoos, show them where that tattoo would be and how there’s nothing there. How would you get rid of a giant flower on your forearm in 2 days anyways?
Wigs fall under the same category as tattoos. The person they're claiming to be you has a blonde bob and you have green hair past your shoulders.It also makes it possible to go with a completely different color without the use of hair dye. This means if they try to arrest you later and try to prove it was you by taking your hair and testing for dye, it won't come back the way they hope. (Thank you @violetrosepetals for this addition!)
Hide your hair. I tuck my hair into my beanie since it’s short. If you have longer hair, try to do the same or tuck it into your shirt. Balaclavas are also a good choice, as they cover both your face and hair.
Power bank
Chargers
Helmet. Any is fine, my personal choice is a skating helmet since they’re rounder and can take more damage, but tactical is also good
Hand sanitizer
Gloves with hard knuckles (tactical gloves). These pack a good punch even if you don't have the correct form. Don't have those? Wrist guards for roller skating/skateboarding work kinda like that too. More of a slapping motion, but still hurt like a bitch. Extra points if they're all scuffed up from use and falls.
Bandanas. Somebody might need one for their face or hair, maybe you need to get dirt off somebody’s face, maybe somebody got injured. They’re great for anything and everything.
Cash (try to stick to cash, your card can be tracked)
Medications if you take them. If you get arrested or happen to somehow be away for longer than expected after the protest, it’s always good to have emergency meds
FIRST AID ALL THE FIRST AID (Tourniquet, Quikclot, chest seal, trauma shears, gauze, bandages, duct tape, and all the usual stuff you’d have in there)
Good shoes. Boots and sneakers are your best choices. Not heels, not platforms, not sandals. Good boots or shoes that won't come off your feet too easily when you run. Steel toed shoes are a great option. Your toes won't be squashed, but also it'll hurt someone a lot more if you start kicking.
Spare socks. Trust me. You can use them to stop bleeding if it comes to it, but also you can put rocks in there and boom weapon. Also if the socks you're wearing get wet.
As much covering clothing as you can handle. Plain jeans, plain hoodie, plain t-shirt, keep yourself as anonymous as possible. Black and baggy is best.
Photocopy of your ID, not your real one.
Sunscreen!
Make sure your clothes have pockets, even if you have a bag. You want everything to be easily accessible.
Do not wear contact lenses. If tear gas is used, that will make everything so much worse. Wear your glasses or go blind. If you have overly unique or identifiable frames, goggles are your friend here. Get some goggles that will fit over your frames, preferably ones that are tinted.
If you use mobility aids, cover defining features. Logos, brand names, colors, stickers, all of it. Take some old plain t-shirt and tie it around your wheelchair’s backrest. Wrap your wheelchair frame in cling wrap, then duct tape, or plain black self adhering medical tape. Cover stickers on your cane or crutches the same way. Electric chair? You have a little more work, but you can do it. Wrap it up. Same idea. Walker? Same thing. Cover. It. All.
If you are bringing a bag, make sure that bag is as plain as possible. No pins. No patches. No keychains. Except maybe a pride flag so people know which team you're playing on.
Scarf or keffiyeh if you have one. They have many uses!
Write a reliable phone number (of someone who is not at the protest with you) on your body. On the off chance you get arrested, that is your emergency contact.
Pocket knife.
Pepper spray/mace/bear spray
if you get tear gassed, shake around first before using water. Most tear gas is more of a powder and water has a high likelihood of just spreading it around. (Thank you @actually-a-bread-loaf for this addition!)
Tennis rackets also work wonderfully for chucking tear gas canisters back at those throwing them. Anybody asks, you're going out to play tennis with friends later. Baseball bats also work! (Thank you @azul-nova-24 for this addition!)
Anything you can throw. Soup for my family.
IF YOU CAN, LEAVE YOUR PHONE AT HOME
IF YOU HAVE TO TAKE IT WITH YOU, TURN OFF LOCATION SERVICES ON ALL APPS AND TURN OFF BIOMETRICS (FACE ID AND FINGERPRINT) SO YOU CAN ONLY UNLOCK YOUR PHONE WITH YOUR PASSWORD
COPS CAN FORCE YOU TO OPEN YOUR PHONE WITH YOUR FINGERPRINT OR FACE ID
MAKE SURE SOMEBODY KNOWS GENERALLY WHERE YOU ARE
If you see a potential or active raid, take pictures and note the time and location. Post online if you can, as well.
You have the right to remain silent. State that you wish to remain silent. Avoid giving information about anybody's immigration status. You have the right to refuse to sign anything before speaking to an attorney. You have the right to refuse searches of your car, your home, and yourself. Schools do not collect a child's immigration status.
I do not want to scare anybody, but this is what life is right now. That man does not care how long you have been a citizen of this country. If you are not a white, cisgender, heterosexual, Christian male, you are seen as less than by men in power. You are not less than. You are a threat to them, and they are scared. Keep it that way.
Even if you're not currently protesting, it's good to know this just in case. Things are happening very quickly, and there is a very high chance of it changing very quickly within the next four years.
Here's the link to my post on what to bring in terms of first aid.
If you cannot attend protests, that’s fine. Do what’s best for you. Even just reposting information helps.
This is an updated version of this post,
Updated January 27, 2025.
#us news#us politics#american politics#project 2025#fuck trump#donald trump#president trump#trump administration#jd vance#trump#immigrants#immigration#protest#protests#civil rights#class consciousness#informative#information#long post#PSA#public service announcement#resources#the resistance#mass deportations#ice raids#la migra#know your rights
5K notes
·
View notes
Text

If ICE Shows Up at Your Door, Know Your Rights!
Do NOT open the door. ICE does not have the right to enter your home without a valid warrant signed by a judge.
Remain calm. Don’t run and most importantly do not lie about your name, age, immigration status, etc. Anything you say or do can be used against you.
Do not sign anything. Ask to have documents translated. If you do not speak English ask for an interpreter. Have an attorney look over any documents that ICE gives you.
Make a family plan. If you have children, identify a caretaker.
Record. If you witness someone being detained by ICE, you have the right to record as long as you do not interfere with the arrest. Pictures, videos, and any information you can gather, can help verify an immigration raid and also help someone’s immigration case.
DOWNLOAD THIS GRAPHIC: https://maketheroadny.org/we-protect-us/
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
List of cities in the U.S. that are suspected to have ICE raids in the next week
Chicago
Los Angeles
Denver
New York
Miami
Boston
Washington DC
San Antonio
Dallas
Phoenix
Seattle
Detroit
Newark
That being said, make sure to know and exercise your rights. This post outlines what is needed to detain someone, and what to do if you are detained by ICE.
Raids are suspected to continue in large metropolitan cities, with a focus on cities that are considered ‘sanctuary cities’, I will update the list if more places are suspected to be raided. Stay safe everyone
ACLU guide to immigrant rights
#us politics#us government#united states#democrat#politics#donald trump#immigration#ice raids#U.S. resources#uspol#chicago#los angeles#new york#Denver#Miami#Boston#washington dc#san antonio#arizona
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Waking up every day has been heavy. Undergoing functional freeze and dissociation. Feeling grief, anger, anxiety, fear, yet also hope. We are being attacked and being stolen from our families in our own land. Unless we are safe, nothing else really matters. We are not criminals.We matter. We are sacred. We are community. We have pride in who we are ❤️ Resources below for my fellow Angelenos.
And thank you to those who have spoken up.🇲🇽🤎❤️🩹










#los angeles#fuck ice#immigration#anti ice#mexico#fuck trump#mexican american#native land#anti ice protests#🇲🇽##mental heath awareness#ice raids#immigration resources#protest#resist#mexican pride
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Naming International POC Characters: Do Your Research.
This post is part of a double feature for the same ask. First check out Mod Colette's answer to OP's original question at: A Careful Balance: Portraying a Black Character's Relationship with their Hair. Below are notes on character naming from Mod Rina.
~ ~ ~
@writingraccoon said:
My character is black in a dungeons and dragons-like fantasy world. His name is Kazuki Haile (pronounced hay-lee), and his mother is this world's equivalent of Japanese, which is where his first name is from, while his father is this world's equivalent of Ethiopian, which is where his last name is from. He looks much more like his father, and has hair type 4a. [...]
Hold on a sec.
Haile (pronounced hay-lee), [...] [H]is father is this world’s equivalent of Ethiopian, which is where his last name is from.
OP, where did you get this name? Behindthename.com, perhaps?
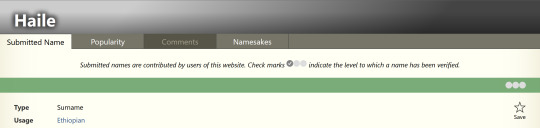
Note how it says, “Submitted names are contributed by users of this website. Check marks indicate the level to which a name has been verified.” Do you see any check marks, OP?
What language is this, by the way? If we only count official languages, Ethiopia has 5: Afar, Amharic, Oromo, Somali, & Tigrinya. If we count everything native to that region? Over 90 languages. And I haven't even mentioned the dormant/extinct ones. Do you know which language this name comes from? Have you determined Kazuki’s father’s ethnic group, religion, and language(s)? Do you know just how ethnically diverse Ethiopia is?
~ ~ ~
To All Looking for Character Names on the Internet:
Skip the name aggregators and baby name lists. They often do not cite their sources, even if they’re pulling from credible ones, and often copy each other.
If you still wish to use a name website, find a second source that isn’t a name website.
Find at least one real life individual, living or dead, who has this given name or surname. Try Wikipedia’s lists of notable individuals under "List of [ethnicity] people." You can even try searching Facebook! Pay attention to when these people were born for chronological accuracy/believability.
Make sure you know the language the name comes from, and the ethnicity/culture/religion it’s associated with.
Make sure you understand the naming practices of that culture—how many names, where they come from, name order, and other conventions.
Make sure you have the correct pronunciation of the name. Don’t always trust Wikipedia or American pronunciation guides on Youtube. Try to find a native speaker or language lesson source, or review the phonology & orthography and parse out the string one phoneme at a time.
Suggestions for web sources:
Wikipedia! Look for: “List of [language] [masculine/feminine] given names,” “List of most common [language] family names,” “List of most common surnames in [continent],” and "List of [ethnicity] people."
Census data! Harder to find due to language barriers & what governments make public, but these can really nail period accuracy. This may sound obvious, but look at the year of the character's birth, not the year your story takes place.
Forums and Reddit. No really. Multicultural couples and expats will often ask around for what to name their children. There’s also r/namenerds, where so many folks have shared names in their language that they now have “International Name Threads.” These are all great first-hand sources for name connotations—what’s trendy vs. old-fashioned, preppy vs. nerdy, or classic vs. overused vs. obscure.
~ ~ ~
Luckily for OP, I got very curious and did some research. More on Ethiopian & Eritrean naming, plus mixed/intercultural naming and my recommendations for this character, under the cut. It's really interesting, I promise!
Ethiopian and Eritrean Naming Practices
Haile (IPA: /həjlə/ roughly “hy-luh.” Both a & e are /ə/, a central “uh” sound) is a phrase meaning “power of” in Ge’ez, sometimes known as Classical Ethiopic, which is an extinct/dormant Semitic language that is now used as a liturgical language in Ethiopian churches (think of how Latin & Sanskrit are used today). So it's a religious name, and was likely popularized by the regnal name of the last emperor of Ethiopia, Haile Selassie (“Power of the Trinity”). Ironically, for these reasons it is about as nationalistically “Ethiopian” as a name can get.
Haile is one of the most common “surnames” ever in Ethiopia and Eritrea. Why was that in quotes? Because Ethiopians and Eritreans don’t have surnames. Historically, when they needed to distinguish themselves from others with the same given name, they affixed their father’s given name, and then sometimes their grandfather’s. In modern Ethiopia and Eritrea, their given name is followed by a parent’s (usually father’s) name. First-generation diaspora abroad may solidify this name into a legal “surname” which is then consistently passed down to subsequent generations.
Intercultural Marriages and Naming
This means that Kazuki’s parents will have to figure out if there will be a “surname” going forward, and who it applies to. Your easiest and most likely option is that Kazuki’s dad would have chosen to make his second name (Kazuki’s grandpa’s name) the legal “surname.” The mom would have taken this name upon marriage, and Kazuki would inherit it also. Either moving abroad or the circumstances of the intercultural marriage would have motivated this. Thus “Haile” would be grandpa’s name, and Kazuki wouldn’t be taking his “surname” from his dad. This prevents the mom & Kazuki from having different “surnames.” But you will have to understand and explain where the names came from and the decisions dad made to get there. Otherwise, this will ring culturally hollow and indicate a lack of research.
Typically intercultural parents try to
come up with a first name that is pronounceable in both languages,
go with a name that is the dominant language of where they live, or
compromise and pick one parent’s language, depending on the circumstances.
Option 1 and possibly 3 requires figuring out which language is the father’s first language. Unfortunately, because of the aforementioned national ubiquity of Haile, you will have to start from scratch here and figure out his ethnic group, religion (most are Ethiopian Orthodox and some Sunni Muslim), and language(s).
But then again, writing these characters knowledgeably and respectfully also requires figuring out that information anyway.
~ ~ ~
Names and naming practices are so, so diverse. Do research into the culture and language before picking a name, and never go with only one source.
~ Mod Rina
#asks#language#languages#linguistics#east africa#african#immigration#ethiopian#names#naming#research#resources#writeblr#character names#character name ideas#rina says read under the cut. read it
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
attention if you're in Chicago or know people who are
Trump's incoming administration is planning a mass deportation on this coming Tuesday, January the 21st. This has been reported in the Wall Street Journal, with reports of up to 200 officers preparing to be sent there. The administration plans to "make an example" of sanctuary cities such as Chicago.

Below are resources, one national and one specific to Illinois, for immigrants:
#us politics#immigration#i don't think i'm the best person to make this post#but i haven't found anything to reblog#so please if anyone has anything to add or change or something please do so#or tag recs for wider reach?#resources#chicago
487 notes
·
View notes
Text
IMMIGRANT RIGHTS RESOURCES (forwarding from a friend -- share widely)
Hope you are having a blessed day! With the help of a friend, I have compiled a list of resources that provide info in several different languages regarding immigrant rights. I am sharing these links to resources with you and others because we never know who will come into our orbit that might need help or the orbit of others dear to us. This is by no means a complete list but it useful and helpful nonetheless.
Immigrant Rights Resources
Flyers regarding immigrant rights if ICE raids the home, workplace or arrest them in the street.
https://www.aila.org/library/know-your-rights-handouts-if-ice-visits-public
Red Cards (template to be printed and laminated) are small cards that immigrants can carry in their language which would have course of action if they get stoped but also in the back it explains to the ice agent in English that the person being stopped is instituting their rights under the la which applies to them.
https://www.masslegalservices.org/content/red-card-templates
https://www.ilrc.org/red-cards-tarjetas-rojas
National Immigration Law Center Press Release:
https://www.nilc.org/press/nilc-statement-on-reports-that-trump-plans-to-revoke-policy-safeguarding-schools-churches-from-ice/
Undocumented Immigrants’ Rights Under the United States Constitution
https://www.accessiblelaw.untdallas.edu/post/undocumented-immigrants-rights-under-the-united-states-constitution
Daily Immigration News Clips 2025
https://www.aila.org/library/daily-immigration-news-clips-january-14-2025
Also here are some local immigrant rights groups throughout MA that could be helpful to people (depending on geography)
Massachusetts Immigrant rights groups!
https://miracoalition.org/
https://www.ifsi-usa.org/
https://braziliancenter.org/
https://www.truealliancecenter.org/8203achievements.html
https://bcnc.net/
https://cct-newbedford.org/
my addition: https://www.beyondbondboston.org/
#human rights#immigration#immigrants#immigrant rights#chinga la migra#fuck ice#massachusetts#resources#we protect us
264 notes
·
View notes
Text

Impossible Exodus: Iraqi Jews in Israel
By Orit Bashkin (2017, Standford University Press)
Between 1949 and 1951, 123,000 Iraqi Jews immigrated to the newly established Israeli state. Lacking the resources to absorb them all, the Israeli government resettled them in maabarot, or transit camps, relegating them to poverty. In the tents and shacks of the camps, their living conditions were squalid and unsanitary. Basic necessities like water were in short supply, when they were available at all. Rather than returning to a homeland as native sons, Iraqi Jews were newcomers in a foreign place. Impossible Exodus tells the story of these Iraqi Jews' first decades in Israel. Faced with ill treatment and discrimination from state officials, Iraqi Jews resisted: they joined Israeli political parties, demonstrated in the streets, and fought for the education of their children, leading a civil rights struggle whose legacy continues to influence contemporary debates in Israel. Orit Bashkin sheds light on their everyday lives and their determination in a new country, uncovering their long, painful transformation from Iraqi to Israeli. In doing so, she shares the resilience and humanity of a community whose story has yet to be told.
#palestine#israel#gaza#resources books#i'll make an updated pinned post later and share some passages#rn i'm reading about how - upon first arriving in israel - iraqi immigrants were sprayed with pesticide at the airport...
1K notes
·
View notes
Text







Share!!!
#pedro pascal#usa#usa politics#donald trump#trump#fuck trump#trump administration#immigrant resources#immigration#pascalispunk#ice raids
204 notes
·
View notes
Text
need help compiling a list of crisis lines and resources
can anyone help me?
i'm working on a video about my thoughts about things post-election.
in the desctiption, i wanna include links/numbers for crisis lines (especially for marginalized groups, but also for anyone in general), as well as some links to organizations/charities that people can check out if they want to help out (especially for LGBTQ+/BIPOC/women/disabled/immigrants/impoverished people in the US, and possibly also for Palestine and Ukraine.)
can you help me compile a list?
(if you can find me an already made google doc or carrd or something similar with all these on it that'd be even better but if not i totally get it)
#politics cw#lgbtq+#bipoc#disability#women's rights#immigrant rights#social justice#palestine#ukraine#mental health#resources#charity#activism
61 notes
·
View notes
Text

Warrant Poster by Make the Road New York
Get more resources here and please share!!
264 notes
·
View notes