#HemoglobinA1C
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to Identify Prediabetes: Key Risk Factors and Diagnostic Tests
Prediabetes, a crucial stage often referred to as "borderline diabetes," acts as a silent warning sign. Blood sugar levels are elevated beyond normal but not yet high enough for a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. This window of opportunity empowers you to take action and prevent the progression to full-blown diabetes. This comprehensive guide delves into the key risk factors, unveils the diagnostic tests, and equips you with the knowledge to identify and address prediabetes effectively. Read more: https://bit.ly/45ZE92c

#prediabetes#bloodsugar#BloodSugarControl#dietplan#exercise#weightmanagement#stressmanagement#hemoglobina1c#type1diabetes#type2diabetes
0 notes
Text
Unlocking the Secrets of HbA1c: Understanding the Key to Diabetes Management
Are you curious about the mysterious HbA1c test? Do you want to understand how it relates to diabetes and your overall health? Look no further! In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the world of HbA1c, exploring what it is, how it's measured, and what the results mean for you.
What is HbA1c? HbA1c, or Hemoglobin A1c, is a vital marker for diabetes management. It's a test that measures the average amount of glucose attached to your red blood cells over the past 2-3 months. This attachment is called glycation, and it's a natural process that occurs when glucose enters your bloodstream.
How is HbA1c measured? The HbA1c test is a simple blood test that can be done at your healthcare provider's office or at a lab. It's usually done when you're fasting, and it doesn't require any special preparation. The test measures the percentage of hemoglobin A1c in your blood, which indicates your average glucose levels over the past few months.
What do the results mean? Your HbA1c results can fall into one of three categories:

Normal: Below 5.7%
Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
Diabetes: 6.5% and above
Let's break down what each category means:
Normal: If your HbA1c is below 5.7%, it means your glucose levels are within a healthy range. Keep up the good work!
Prediabetes: If your HbA1c falls between 5.7% and 6.4%, it means you're at risk of developing diabetes. Don't worry; this is a great opportunity to make lifestyle changes and prevent diabetes from developing!
Diabetes: If your HbA1c is 6.5% or higher, it means you have diabetes. Don't panic! With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, you can manage your diabetes and live a healthy life.
Why is HbA1c important? HbA1c is a vital tool for diabetes management because it:
Provides a long-term picture of your glucose levels
Helps diagnose and monitor diabetes
Assists in adjusting treatment plans
Encourages healthy lifestyle choices
Conclusion: HbA1c is a powerful indicator of your glucose levels and overall health. By understanding what HbA1c is, how it's measured, and what the results mean, you'll be better equipped to manage your diabetes and take control of your health. Remember, knowledge is power!
Optimized keywords: HbA1c, Hemoglobin A1c, diabetes management, glucose levels, prediabetes, diabetes diagnosis, healthy lifestyle choices.
Note: This blog post is for informational purposes most effective and need to no longer be considered scientific advice. Consult your healthcare company for customized guidance on diabetes management and HbA1c testing.
#HbA1c#DiabetesManagement#GlucoseLevels#HemoglobinA1c#Prediabetes#DiabetesDiagnosis#HealthyLifestyle#DiabetesAwareness#BloodSugarControl#HealthMonitoring#DiabetesPrevention#HealthTips#WellnessJourney#MedicalTesting#ChronicIllness#Healthcare#PatientEducation#DiabetesCare#PreventDiabetes#HealthyLiving#KnowYourNumbers#LongTermHealth
0 notes
Text
youtube
Glucodyn - Best Vitamins For Diabetes - Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms - Insulin Resistance
#glucodyn#glucodynreview#insulindependentdiabetes#insulinoverdose#bringbloodsugardown#bringbloodsugardownfast#decreasesugarlevel#lowerbloodsugar#lowerbloodsugarfast#lowerbloodsugarlevels#lowerbloodsugarnaturally#loweringbloodsugarnaturally#diabetes#diabetessymptoms#type2diabetes#diabetesmellitus#glucose#insulin#insulinresistance#lowbloodsugarsymptoms#bloodsugarlevels#type2diabetessymptoms#insulinpump#normalglucoselevels#causesofdiabetes#ac1bloodtest#bestvitaminsfordiabetes#diabetesvitamins#hba1c#hemoglobina1c
0 notes
Text
হিমোগ্লোবিন কম হওয়ার কারণ
1 note
·
View note
Text
Age-Related A1C Levels: Understanding Normal Blood Sugar Ranges
Hey there, health enthusiast! You’ve just stumbled upon the Well Health Hub, your go-to spot for top-tier tips and deep-dives into all things health! This time around, we’re chatting about blood sugar – it’s a bit like mastering a complex dance, so strap in! From the nitty-gritty of what normal blood sugar levels look like, to why they’re your new best friend, and of course, the secrets to…

View On WordPress
#A1CTesting#BloodSugar#BloodSugarControl#ChronicCondition#DiabetesCare#diabetesmanagement#DiabetesPrevention#GlucoseLevels#HealthScreening#HemoglobinA1C
0 notes
Photo

It is not too late to honor your body. You have what it takes to create sustainable health and fitness. There are no quick fixes. Learn & Listen to your body. Your body will respond in some way. #Achieve #Believe #sustainability #hemoglobina1c #diabetes #prediabetes #coach #mentor #nurse #lifestyle #integrativenutritionhealthcoach #instituteforintegrativenutrition #integrativemedicine #journey #mission #healtheducation #globalissues #accountability #teacher #class #children #obesity #power #quotes #tuesday #nutrition #food #family #positivepsychology #behavior https://www.instagram.com/p/BrPmaQJF5hH/?utm_source=ig_tumblr_share&igshid=m46skz386ki6
#achieve#believe#sustainability#hemoglobina1c#diabetes#prediabetes#coach#mentor#nurse#lifestyle#integrativenutritionhealthcoach#instituteforintegrativenutrition#integrativemedicine#journey#mission#healtheducation#globalissues#accountability#teacher#class#children#obesity#power#quotes#tuesday#nutrition#food#family#positivepsychology#behavior
0 notes
Text
Insulin Pump Therapy
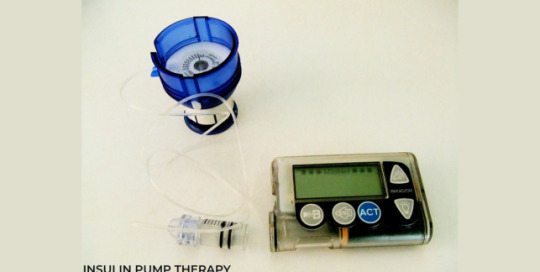
How does insulin pump therapy work?
The insulin pump is a battery-operated device with a quick-acting insulin reservoir that provides both basal (background) and quick-acting insulin doses. Importantly, newer technology now enables for programmable memory, variable basal rates, and easy titration and bolusing methods.
An insulin pump, also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin therapy, is a medical device used to provide insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Depending on the design, the device configuration may differ. A typical pump consists of the following components:
1. The nozzle (including controls, processing module, and batteries)
2. A disposable insulin reservoir (inside the pump)
3. A disposable infusion set that includes a cannula for subcutaneous (under the skin) insertion and tubing to link the insulin reservoir to the cannula.
When used in combination with blood glucose monitoring and carbohydrate counting, an insulin pump offers an alternative to several daily insulin injections using insulin syringes or an insulin pen. It allows for more flexible insulin management.
The insulin pumps can be worn on straps under the cloths, pockets, belts or attached with adhesives on the stomach or arm.
Why are insulin pumps used?
People with diabetes don’t produce enough insulin on their own. Instead, patients must rely on insulin shots to keep their blood sugar under control. Pumps provide a constant supply of insulin, reducing the number of needle poke. They’re also a wonderful alternative for kids or anyone who forgets to take their insulin shots. Insulin pumps are more convenient than insulin pen injections for certain people because they stay linked to the body.
Who can use insulin pumps?
It is a personal choice whether or not to use an insulin pump. You should consider using an insulin pump if you:
1. Food absorption takes longer than usual.
2. When you exercise, you may want to halt your insulin dosages.
3. Have severe hypoglycemic responses.
4. You have diabetes and are thinking about starting a family.
For young persons with Type 1 diabetes, insulin pumps can be a useful alternative. Even for children and those who have problems keeping to an insulin injection schedule, a pump can provide a consistent supply of insulin.
What happens while using insulin pumps?
In an insulin pump, insulin is delivered in one of two ways:
1. Insulin dosages are given in small, regular increments (basal insulin).
2. Insulin spikes around mealtimes (bolus insulin).
Even if you’re using an insulin pump, you should still monitor your blood sugar levels. The average person checks their blood sugar four times every day. Alternatively, you might utilize a continuous glucose monitor.
The pump calculates how much bolus insulin you need based on the information you provide about your food consumption and blood sugar levels. After that, the pump will suggest a bolus dose to you and will wait for your consent before administering it. Furthermore, some pumps alter baseline dosages automatically based on glucose readings from a continuous glucose monitor.
What are the advantages of insulin pumps?
1. There will be fewer needle sticks needed. When you change your infusion set on a pump, you’ll need one shot every few days.
2. A pump is more precise than injections and can help you regulate your blood sugar levels better.
3. Because you must take bigger quantities of insulin at once, injections have a higher risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). A pump decreases the danger by providing a constant supply of insulin. This is especially useful at night, when too much insulin might cause a nocturnal hypoglycemia response.
4. It has the potential to lower your hemoglobinA1C levels.
5. It’s simpler to dose for meals and snacks.
6. It’s simpler to schedule workouts. With an insulin pump in place, you don’t have to eat large amounts of carbohydrates before you work out to maintain glucose levels.
7. It’s less difficult to bolus. If your schedule causes you to eat at odd hours or skip a meal every now and again, a pump might help you adjust more readily. Bolus insulin may be delivered to cover a meal with the easy touch of a button because pumps employ fast-acting insulin.
8. It aids in the management of elevated blood sugar in the early morning, often known as the “dawn phenomenon.”
What are disadvantages of insulin pumps?
1. You run the danger of infection if you don’t replace the insertion site of the cannula (the tube that contains the needle) every two or three days.
2. More frequent blood sugar checks: This is especially important during the first several months of using the pump. The only way to know if your basal rate and bolus are operating properly is to test frequently. If you’re using an insulin pump, you should be willing and able to check your glucose levels four times a day with a finger-prick blood test. Separate continuous glucose monitors are used by certain pumps, such as a sensor-augmented pump, for convenience.
3. Increased risk of high glucose levels: Disconnecting from the pump for an extended period of time or failing to check blood glucose levels on a regular basis might result in high glucose levels, which can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis.
4. Weight gain: Patients with greater initial basal insulin levels have a higher risk of gaining weight. Furthermore, insulin is a fat-producing hormone. As a result, the more insulin you inject, the more weight you’ll acquire.
5. Price: Insulin pumps are costly, and insurance may or may not cover the expense.
In order to seek proper guidance on any diabetes related problems,
Contact No. +91 88847 22267 E-mail: [email protected]
or visit our website Diabetes Reversal Clinic.
0 notes
Text
Juniper Publishers-Open Access Journal of Case Studies
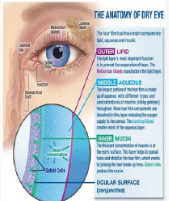
The Incidence of Dry Eye Disease Related to Long Term Diabetes Mellitus Tip 2
Authored by Nora Burda
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Dry eye; Goblet cell; HbA1c level; Tear meniscus
Abbreviations: DM: Diabetes Mellitus; DES: Dry Eye Syndrome; TUBT: Tear Break Up Time; BVCA: Best Corrected Visual Acuity; SPK: Superficial Punktate Keratitis; MGD: Meiboimian Gland Dysfunction; MG: Meiboimian Gland
Introduction
Diabetes is a disease that affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin effectively to control blood sugar (glucose) levels. DM is a chronic metabolic disorder usually genetic [1,2]. The global diabetes mellitus evidence predicts that 6.4% of the world population are affecting 286 million adults in 2010 by 2030 is predicted to increase about 7.6% affecting about 439 million of adults [2]. People with diabetes frequently develop dry eye syndrome [3]. It is estimated that over 50% of people with type 2 diabetes have dry eye [4]. Patients will complain of eye irritation, excessive tearing, fatigue, red eye, gritty sensation, increased watering of the eyes, dryness and blurred vision [5,6].
The causes of dry eye are so many, but the main cause is a disturbance of the tear film due to either decreased tear production or excessive evaporation of tears. MGD occurs when the normal function of the MG becomes compromised because of gland blockages that occur over time, resulting in inadequate oil production into the tear [7]. If the MG malfunctions, the lipid layer may be reduced, allowing rapid evaporation of the tear complex [7-9]. Research shows that most cases of dry eye associated with diabetes are caused by insufficient production of tears due to “autonomic neuropathy. The condition is affecting the nerves that control the lacrimal gland secretion damaging the production of tear film that normally produce moisture to keep the eyes well lubricated [10,11]. When the transparent and sensitive cornea is no longer adequately lubricated, the cells of the cornea become damaged and free nerve endings are exposed. The exposure of the nerve endings leads towards symptoms of dry eye.
Furthermore, by keeping blood sugar levels as firmly controlled as possible is the first step in preventing dry eye syndrome at diabetes patients. The high blood glucose HbA1c more than 6.4 % lead to autonomic neuropathy affecting the tear gland but also affects the quality of our tears by increasing the amount of glucose in the tears layers and disrupting their normal chemical composition [12,13]. The tear fluid contains water, lipids, mucin, lactoferrin, lysozyme, lipocalin, imunoglobulins, glucose, urea, sodium potassium, lacritin [14].
Three layers are components of tear film: the aqueous layer, the mucus layer and the lipid layer. Also the goblet cells of conjunctiva plays very important role by producing and secreting mucin lubricating the ocular surface [7].
Insufficient tear production and changes in osmolarity promote high concentrations of proteins within the tears inducing apoptosis of surface epithelium and a vicious cycle of increased expression of inflammatory cytokines from ocular surface [7]. The condition gets even worse by apoptosis and decreased mucin production by goblet cells [15] (Figure 1&2).
Purpose
The purpose of the study is to prescribe and analyze the correlation of Dry Eye with diabetes related to duration of primary disease.
Methods
A total number of 98 non selective patients, diagnosed with Diabetes Mellitus Tip II, sent for routine examination from Endocrinologist, underwent ocular examinations. 50 male and 45 female, aged from 42-84 years old.
History of disease, duration of diabetes, age, sex, the level of hemoglobinA1c equal or over than 6.5 % (for the past 3 months) was obtained by reviewing the medical records from the Endocrinology Department and direct patient interview. Visual acuity with correction BVCA, OSDI questionnaire for classification of DES. Slight- lamp examination, tear meniscus at inferior lid margin, tear film break-up time (BUT) test, corneal sensitivity test, Schirmmer Test to evaluate the tear film secretion from the lacrimal gland, Rose Bengal stain test for the conjunctiva goblet cells malfunction, fluoresceine corneal dye test to evaluate the corneal epithelial involvement. Also tear film measurement performing Schirmmer’s test in 5 min time to evaluate the amount of tear film production from Lacrimal Gland, cotton-swab test for the corneal sensitivity damage and peripheral neuropathy. Tear film break up time test measurement was performed using fluorescein strips.
Visual acuity was evaluated by using Snellen’s chart. Slit lamp (Nidek SL-450) examination was performed with particular attention to lid margin, bulbar and tarsal conjunctiva, cornea and conjunctiva to detect any abnormality of meiboimian Gland Disfunction and also the presence of Superficial Punktate keratitis or any involvement ̷ reduction of Golbet cells production. In addition the patient complains of tearing photophobia, red eye, itching, foreign body sensation, increased watering of the eyes, dryness and blurred vision was obtained. The duration of primary disease was recorded and divided in three groups of patients: duration onset of DM -5 years, duration of 5-10 years and more than 10 years of duration (Figure 3-5).
Results
From our research the results are as follows. 64 patients were diagnosed with Dry Eye Syndrome of varying degrees from mild to very severe according to OSDI questionnaire, 28 male / 36 female. The diagnosis was made by having two or more positive tests performed as mentioned above and patient’s complaints. In addition, at those subjects diagnosed with DES, 5 patients represent pinpoint corneal dye with fluorosceini (SPK), 8 of them where positive to corneal cotton swab test, 16 of them resulted positive to Schirmer test less than 10 mm in 5 min, 14 of them was showing TBUT test less than 9 sec, presence of positive tear meniscus was seen in 15 patients, Rose Bengal staining of conjunctiva was detected in 6 patients, MGD was noticed at 12 subjects. Regarding the duration of Diabetes in our study the findings where : 21 patients were diagnosed with DM during the period of 5 years of duration, 31 of the patients were diagnosed with DM since 5-10 years ago, 46 of them had Type2 more than 10 years.
With insight at the group with 5 years of duration there was a low number of patients presenting very mild dry eye at 11 patients, at group with 5-10 years of duration of DM there were about 20 patients presenting mild and severe dry eye, considering that the group included patient with DM more than 10 years of duration; 31 patients were presenting severe to very severe DES (Figure 6&7).
Conclusion
This study, the Dry Eye Syndrome showed to have a high correlation with Diabetes Mellitus Tip II (about56.9%). Prevalence and severity of Dry Eye was significantly higher at patients with longer duration of diabetes (46.9%)) and poor glycaemic control, less high at the patients with no longer duration of primary disease. Dry Eye seems to be an important contributing factor related to corneal abnormalities by disrupting the normal chemical composition of the tear film layers. In our study we have shown that the Age and Sex seem to not play an important role in this condition. Good glycaemic control is very important and decisive for prevention of the DES.
Discussion
To conclude, everything depends on blood sugar levels (HbA1c). The higher the attention monitoring the blood sugar level consists in our first step in preventing dry eye syndrome associated with diabetes [12]. More often, the patients are unaware that their blood glucose is out of control, which is fundamental for the treatment at diabetes related to dry eye syndrome [16]. Educating the patients by sharing our knowledge of primary disease DM, the proper treatment, the appropriate monitoring, the diet instructions the exercises and follow up by Endocrinologist is the key to improve the quality of their life style [2] and to reduce the risk for developing DES as much as possible.
Subsequently, it is very important to achieve a good collaboration among physicians to detect early the DM Type 2, to receive the proper management and treatment options for the patient [17]. Compliance of the patients is also a very important factor to learn how to live with diabetes and to present regularly for follow-up. The DM is a chronic disease hence either the DES remain chronic disease as well, for that reason is still very difficult to manage both conditions [15]. New modalities need to be developed though collaborative research and further studies need to be undertaken to treat the DES and the primary disease DM constantly (Figure 8).
For more Open Access Journals in Juniper Publishers please click on: https://juniperpublishers.business.site/ For more articles in Open Access Journal of Case Studies please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/jojcs/ To know more about Open Access Journals Publishers To read more…Fulltext please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/jojcs/JOJCS.MS.ID.555571.php
#Juniper Publishers#Juniper Publishers Group#Surgical case reports#Virology#immunology#eye#Cardiology#case studies
0 notes
Link
Böbrek yetersizliği nedir? Böbreklerin ana görevleri vücudun su, elektrolit ve mineral içeriğini düzenlemek, metabolizma sonucu ortaya çıkan atık maddelerle yabancı maddeleri vücuttan uzaklaştırmak ve bir takım enzimleri ve hormonları üretmek ve salgılamaktır. Böbreklerin çok çeşitli hastalıklara bağlı olarak bu görevlerini kısmen veya tamamen yapamaz hale gelmesi böbrek yetersizliği olarak tanımlanır. Böbrek yetersizliği iki şekilde ortaya çıkar: Akut böbrek yetersizliği genellikle geçicidir ve kalıcı hasar bırakmaz. Çoğunlukla ilaçlara bağlı olarak veya cerrahi girişimlerden sonra gelişir. Geçici süreyle diyaliz ihtiyacına neden olabilir. Kronik böbrek yetersizliği ise uzun süreli, ilerleyici ve kalıcı böbrek hasarına neden olur. En çok şeker hastalığına, tansiyon yüksekliğine ve nefrit denilen böbreklerin çoğunlukla nedeni belli olmayan bağışıklık sistemiyle ilişkili iltihabi hastalıklarına bağlı olarak gelişir. Bununla birlikte böbrek yetersizliğine yol açabilen 50 ye yakın neden bilinmektedir. Gerek akut gerekse kronik böbrek yetersizliğinde her iki böbrek birden etkilenir. Eğer kişi doğuştan veya sonradan tek böbrekli değilse sadece bir böbreği tutan hastalıklar genellikle böbrek yetersizliğine neden olmazlar. Bu bölümde kronik böbrek hastalığından bahsedilecektir. Üç aydan uzun süren böbrek süzme fonksiyonundaki azalma kronik böbrek hastalığı olarak isimlendirilir. Böbreğin süzme görevi altta yatan nedene ve kişiden kişiye büyük değişkenlik göstererek aylar veya yıllar içinde azalabilir. Risk faktörleri nelerdir? Yaş arttıkça böbrek hastalığı riski artar. Bazı tip böbrek hastalıkları genetiktir (Örneğin polikistik böbrek hastalığı). Kan basıncı kontrol altında tutulamayan tansiyon hastalarında ve kan şekeri kontrol altında tutulamayan şeker hastalarında böbrek hastalığı gelişme riski ve böbrek hastalığı varlığında hastalığın ilerleme hızı yüksektir. Sık antiromatizmal olan veya olmayan ağrı kesici kullanımı, boğaz infeksiyonları, şişmanlık ve sigara diğer önemli risk faktörleridir. Hastalık nasıl seyreder? Böbrekler hasta oldukları halde görevlerini iyi bir şekilde sürdürürler. Diyet, ilaç tedavisi ve düzenli takip ile risk faktörleri azaltılır ve ortaya çıkan sorunlar düzeltilir. Buna rağmen kronik böbrek yetersizliği olanların çoğunda hastalık 2-10 yıl içinde diyaliz veya organ naklini gerektirecek şekilde son dönem böbrek yetersizliği safhasına ulaşır. Böbrek yetersizliği seyrinde hedefler, karşılaşılan sorunlar nelerdir? Amaç son dönem böbrek yetersizliğine giden süreci mümkün olduğu kadar geciktirmektir. Öncelikle böbrek yetersizliğine neden olan durum tedavi edilir. Hastalığı ilerleten faktörlerin kontrol altına alınması tedavinin köşe taşıdır. Tuz ve protein alımının kısıtlanması suretiyle diyet ayarlanır. Kan basıncı kontrol altına alınır. Hedef kan basıncı 130/80 mmHg nin altıdır. Şeker hastalarında açlık, tokluk kan şekerleri ve hemoglobinA1c kontrol altına alınır. Hedef HbA1c düzeyi % 7 nin altıdır. Kolesterol yüksekliği tedavi edilir. Hedef LDL-Kolesterol düzeyi 100 mg/dL nin altıdır. Sigara yasaklanır. Böbrek yetersizliğinin seyri sırasında pek çok sisteme ait problemler ortaya çıkabilir. Bunlar arasında su ve elektrolit bozuklukları, kalp ve damar hastalıkları, iştahsızlık, bulantı, kusma, gastrit, ülser ve kanama gibi mide barsak problemleri, kansızlık, kanamaya eğilim ve infeksiyonlara karşı duyarlılık artması gibi hematolojik sorunlar, kalsiyum ve fosfor metabolizması bozukluğuna bağlı üremik kemik hastalığı, halsizlik, baş ağrısı, huzursuz bacak ve kramp gibi nörolojik sorunlar, beslenme bozukluğu, protein düşüklüğü, infertilite, cinsel fonksiyon bozukluğu ve amenore gibi endokrin ve metabolizma bozuklukları ve ciltte kuruma, pullanma ve kaşıntı gibi dermatolojik sorunlar sayılabilir. Bu sorunların çözümü için etkili tedavi yöntemleri mevcuttur ve zaman içinde daha da iyileştirilmektedir. Son dönem böbrek yetersizliği nedir? Böbrek yetersizliği çok ilerlediği zaman ise son dönem böbrek yetersizliği olarak isimlendirilir. Bu dönemde şu belirtiler ortaya çıkar; Aşırı yorgunluk ve iştahsızlık hali Ellerde, yüzde ve ayaklarda şişlik Ciddi tansiyon yüksekliği Bulantı ve kusma Nefes darlığı Uyuma güçlüğü Bu belirtiler ortaya çıktığı zaman hızla böbreğin görevlerini yerine getirecek tedavi yöntemleri uygulanmalıdır. Başlıca iki seçenek vardır: Diyaliz: Özel zarlar vasıtası ile kandaki zararlı maddeleri süzmek ve böylece kanı temizlemektir. Diyaliz iki şekilde uygulanabilir: Hemodiyaliz Periton diyalizi Böbrek nakli: Vücuttaki zararlı artıkları temizlemek için yeni bir böbrek yerleştirme işlemidir. İki ayrı tür vericiden yapılabilir: Canlıdan böbrek nakli Kadavradan böbrek nakli. Alternatif Tıp ve Alternatif Tedavi, bitkisel ürünler, sifamarket
0 notes
Text

Glucodyn - Best Vitamins For Diabetes - Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms - Insulin Resistance
#glucodyn#glucodynreview#insulindependentdiabetes#insulinoverdose#bringbloodsugardown#bringbloodsugardownfast#decreasesugarlevel#lowerbloodsugar#lowerbloodsugarfast#lowerbloodsugarlevels#lowerbloodsugarnaturally#loweringbloodsugarnaturally#diabetes#diabetessymptoms#type2diabetes#diabetesmellitus#glucose#insulin#insulinresistance#lowbloodsugarsymptoms#bloodsugarlevels#type2diabetessymptoms#insulinpump#normalglucoselevels#causesofdiabetes#ac1bloodtest#bestvitaminsfordiabetes#diabetesvitamins#hba1c#hemoglobina1c
0 notes
Text
What is Normal A1C by Age? Understanding Blood Sugar Control Across Different Age Groups
Hello, everyone! Today, we’re going to delve into the world of diabetes management and unravel the mysteries of A1C levels. This little test holds significant importance when it comes to monitoring our blood sugar, regardless of our age. So, buckle up and join me on this enlightening journey! Understanding A1C: The Glycated Hemoglobin Test Let’s start with the basics. A1C acts as a time…
View On WordPress
#A1CTesting#BloodSugar#BloodSugarControl#ChronicCondition#DiabetesCare#diabetesmanagement#DiabetesPrevention#GlucoseLevels#HealthScreening#HemoglobinA1C
0 notes
Text
Understanding Normal HbA1c Levels by Age: A Comprehensive Guide
Hello health-conscious individuals! We at Well Health Hub, are thrilled to guide you through a comprehensive exploration into the world of HbA1c levels. Our mission is to illuminate the significance of HbA1c in understanding and managing diabetes, a common yet complex health condition. Get ready as we dive deep into the sea of knowledge surrounding HbA1c, its indispensable role in detecting and…

View On WordPress
#A1CTesting#BloodSugar#BloodSugarControl#ChronicCondition#DiabetesCare#diabetesmanagement#DiabetesPrevention#GlucoseLevels#HealthScreening#HemoglobinA1C
0 notes
Text
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels and Diabetes Control
Today, we’re about to take a deep dive into the vast and fascinating ocean of blood sugar levels, diabetes control, and age-based A1C levels. We’ve set our sights on not just meeting your expectations, but exceeding them, by offering you a meticulously researched guide that’s chock-full of need-to-know details. So, get comfy, grab a cup of your favorite brew, and let’s get started! First off,…

View On WordPress
#A1CTesting#BloodSugar#BloodSugarControl#ChronicCondition#DiabetesCare#diabetesmanagement#DiabetesPrevention#GlucoseLevels#HealthScreening#HemoglobinA1C
0 notes
Text
What is normal A1C by age?
In the whirlwind of our modern world, caring for our health has become a front-and-center concern. One key piece of that puzzle? It’s A1C, the golden ticket to understanding your blood sugar health. A1C paints a vivid picture of our average blood sugar levels over three months, acting as a cornerstone for both monitoring and diagnosing diabetes. Ready to take a deep dive into the fascinating…

View On WordPress
#A1CTesting#BloodSugar#BloodSugarControl#ChronicCondition#DiabetesCare#diabetesmanagement#DiabetesPrevention#GlucoseLevels#HealthScreening#HemoglobinA1C
0 notes
Text
A1C Unveiled: The Complete Guide to Mastering Diabetes Control
Welcome to the world of diabetes management, where the A1C test takes center stage. This test, widely recognized and embraced, provides a valuable window into your average blood glucose levels over the past few months. By understanding the significance of A1C, its connection to diabetes, how to interpret the results, and practical steps for achieving optimal levels, you’ll gain the tools to…

View On WordPress
#A1CTesting#BloodSugar#BloodSugarControl#ChronicCondition#DiabetesCare#diabetesmanagement#DiabetesPrevention#GlucoseLevels#HealthScreening#HemoglobinA1C
0 notes
Text
Understanding A1C Levels: The Ultimate Guide to Managing Your Blood Sugar like a Pro
Living with diabetes ain’t no walk in the park, my friend. It requires keeping a close eye on those blood sugar levels of yours if you want to stay in tip-top shape. Now, there’s a nifty little tool called the A1C test that can give you some valuable insights into your long-term blood glucose control. In this all-encompassing guide, we’re going to dive deep into the nitty-gritty of A1C levels,…
View On WordPress
#A1CTesting#BloodSugar#BloodSugarControl#ChronicCondition#DiabetesCare#diabetesmanagement#DiabetesPrevention#GlucoseLevels#HealthScreening#HemoglobinA1C
0 notes