#Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Also preserved on our archive (Thousands of reports, sources, and resources! Daily updates!)
By Robert Stevens
A COVID wave fuelled by the XEC variant is leading to hospitalisations throughout Britain.
According to the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA), the admission rate for patients testing positive for XEC stood at 4.5 per 100,000 people in the week to October 6—up significantly from 3.7 a week earlier. UKHSA described the spread as “alarming”.
Last week, Dr. Jamie Lopez Bernal, consultant epidemiologist at the UKHSA, noted of the spread of the new variant in Britain: “Our surveillance shows that where Covid cases are sequenced, around one in 10 are the ‘XEC’ lineage.”
The XEC variant, a combination of the KS.1.1 and KP.3.3 variants, was detected and recorded in Germany in June and has been found in at least 29 countries—including in at least 13 European nations and the 24 states within United States. According to a New Scientist article published last month, “The earliest cases of the variant occurred in Italy in May. However, these samples weren’t uploaded to an international database that tracks SARS-CoV-2 variants, called the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID), until September.”
The number of confirmed cases of XEC internationally exceeds 600 according to GISAID. This is likely an underestimation. Bhanu Bhatnagar at the World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe noted that “not all countries consistently report data to GISAID, so the XEC variant is likely to be present in more countries”.
Another source, containing data up to September 28—the Outbreak.info genomic reports: scalable and dynamic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 variants and mutations—reports that there have been 1,115 XEC cases detected worldwide.
Within Europe, XEC was initially most widespread in France, accounting for around 21 percent of confirmed COVID samples. In Germany, it accounted for 15 percent of samples and 8 percent of sequenced samples, according to an assessment from Professor Francois Balloux at the University College London, cited in the New Scientist.
Within weeks of those comments the spread of XEC has been rapid. Just in Germany, it currently accounts for 43 percent of infections and is therefore predominant. Virologists estimate that XEC has around twice the growth advantage of KP.3.1.1 and will be the dominant variant in winter.
A number of articles have cited the comments made to the LA Times by Eric Topol, the Director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in California. Topol warns that XEC is “just getting started”, “and that’s going to take many weeks, a couple months, before it really takes hold and starts to cause a wave. XEC is definitely taking charge. That does appear to be the next variant.”
A report in the Independent published Tuesday noted of the make-up of XEC, and its two parent subvariants: “KS.1.1 is a type of what’s commonly called a FLiRT variant. It is characterised by mutations in the building block molecules phenylalanine (F) altered to leucine (L), and arginine (R) to threonine (T) on the spike protein that the virus uses to attach to human cells.
“The second omicron subvariant KP.3.3 belongs to the category FLuQE where the amino acid glutamine (Q) is mutated to glutamic acid (E) on the spike protein, making its binding to human cells more effective.”
Covid cases are on the rise across the UK, with recent data from the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) indicating a 21.6 percent increase in cases in England within a week.
There is no doubt that the spread of XEC virus contributed to an increase in COVID cases and deaths in Britain. In the week to September 25, there were 2,797 reported cases—an increase of 530 from the previous week. In the week to September 20 there was a 50 percent increase in COVID-related deaths in England, with 134 fatalities reported.
According to the latest data, the North East of England is witnessing the highest rate of people being hospitalised, with 8.12 people per 100,000 requiring treatment.
Virologist Dr. Stephen Griffin of the University of Leeds has been an active communicator of the science and statistics of the virus on various public platforms and social media since the start of the pandemic. He was active in various UK government committees during the height of the COVID-19. In March 2022, he gave an interview to the World Socialist Web Site.
This week Griffin spoke to the i newspaper on the continuing danger of allowing the untrammelled spread of XEC and COVID in general. “The problem with COVID is that it evolves so quickly,” he said.
He warned, “We can either increase our immunity by making better vaccines or increasing our vaccine coverage, or we can slow the virus down with interventions, such as improving indoor air quality. But we’re not doing those things.”
“Its evolutionary rate is something like three or four times faster than that of the fastest seasonal flu. So you’ve got this constant change in the virus, which accelerates the number of susceptible people.
“It’s creating its own new pool of susceptibles every time it changes to something that’s ‘immune evasive’. Every one of these subvariants is distinct enough that a whole swathe of people are no longer immune to it and it can infect them. That’s why you see this constant undulatory pattern which doesn’t look seasonal at all.”
There are no mitigations in place in Britain, as is the case internationally, to stop the spread of this virus. Advice for those with COVID symptoms is to stay at home and limit contact with others for just five days. The National Health Service advises, “You can go back to your normal activities when you feel better or do not have a high temperature”, despite the fact that the person may well still be infectious. Families are advised that children with symptoms such as a runny nose, sore throat, or mild cough can still “go to school or childcare' if they feel well enough.
The detection and rapid spread of new variants disproves the lies of governments that the pandemic is long over and COVID-19 should be treated no differently to influenza.
Deaths due to COVID in the UK rose above 244,000 by the end of September. It is only a matter of time before an even deadlier variant emerges. Last month, Sir Chris Whitty, England’s chief medical officer, told the ongoing public inquiry into COVID-19 “We have to assume a future pandemic on this scale [the global pandemic which began in 2020] will occur… That’s a certainty.”
#mask up#covid#pandemic#wear a mask#public health#covid 19#wear a respirator#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2
145 notes
·
View notes
Text
COVID-19
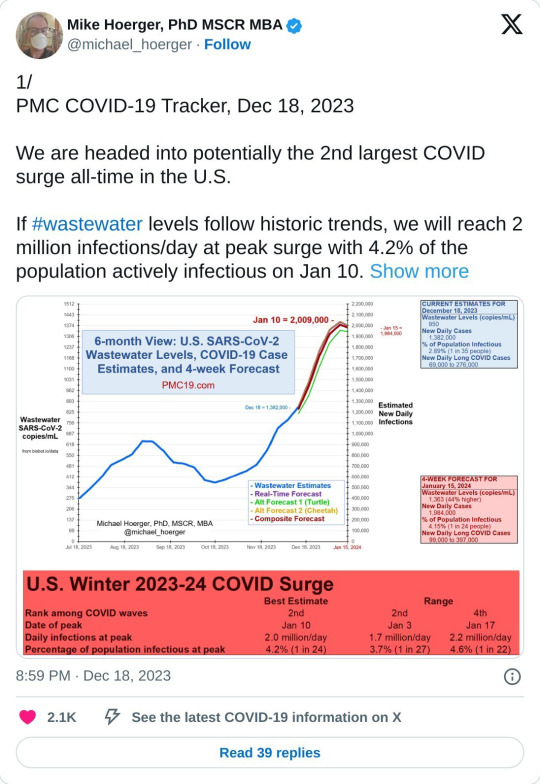
We are currently in the largest COVID surge of all-time in the US.
There is also a new variant that is not protected by the previous vaccine.
Please start back masking and please get the COVID-19 booster (schedule with your local pharmacy).
Wastewater counts are obscenely high right now, belying the official case numbers. Considering that we've stopped collecting or reporting most COVID data, wastewater is the best way we have to judge the actual infection rate now. Wastewater is collected from washing our hands, going the bathroom, etc. We shed COVID into the water system and based on the concentration of COVID in waste water, we can get very accurate estimates of how many people are infected at one time.
We are currently seeing ten million new infections a week, and can expect that to greatly increase within the next three weeks.
* If you've stopped masking, please start again, for your own safety and the safety of your community. Many hospital systems are already trending toward being overwhelmed right now; wear a mask when in crowded, enclosed, or poorly ventilated areas, and keep a safe distance from others, as feasible.
* Avoid unnecessary gatherings where possible.
* Ventilate your spaces well (Corsi-Rosenthal Box).
* Reevaluate casual habits (touching face, respiratory etiquette—covering coughs and sneezes, clean your hands regularly, stay home if you are sick, get tested if you have symptoms, or if you might have been exposed to someone with COVID-19 or influenza)
Please be aware of Long Covid.
COVID impacts the immune system similar to HIV in that it hides in the body and continues to wreak havoc in the various organ system by driving inflammation and disrupting the immune response. It causes neurological, vascular, and immune dysfunction.
Patients with long COVID generally have symptoms that fall into three categories or phenotypes: fatigue, neurocognitive symptoms such as brain fog or headaches, and cardiovascular symptoms such as shortness of breath, heart arrythmias, exercise intolerance, and blood clots. Patients may have more than one type, and some also have symptoms like constipation, diarrhea, or loss of taste and smell that don’t seem to fit neatly into one of the three groups.
This is a period where we need to act with more care. Not a time to panic, but a time to be more cautious.
If you contract COVID, these are some helpful things that work to reduce viral load in the hope of minimising symptoms. And your chance of developing Long Covid:
* Brush & floss as usual
* Mouthwash (CPC (cetylpyridinium chloride, an ingredient in many/most commercial mouthwashes), cooled green tea, salt water)
* Green Tea (drink on an empty stomach if possible; can also be used for swishing/gargling once it has cooled; if green tea isn't doable for you, black tea is an alternative)
* Nasal Spray (if chemicals in nasal spray causing an issue for you, saline nasal spray also an option)
* Vitamin C supplement
* Antihistamines
* Other prophylactics to consider: Nattokinase, Grape Seed Extract, EGCG supplements
* Natto (if this is something you already eat, or would like to try. It's fermented soya beans and is popular in Japan
* Mask & Vaccinate!! A fully vaccinated individual is five times less likely to continue to have any symptoms or ill-effects three months after their initial infection compared to someone who has not been vaccinated.
Not a medical professional but compiled resources from medical professionals and individuals with disabilities including long COVID.
Free Palestine. Free Congo. Free Sudan. Free Tigray. Stop Cop City. Eyes on the Mass Graves in Jackson.
Please SHARE & Please participate in the Global Strike for Palestine 1.21-1.28.

#covid#covid19#long covid#covid isn't over#covid 19#coronavirus#corona#free palestine#free gaza#free congo#free sudan#freepalastine🇵🇸#freedom#black liberation#israel is committing genocide#israel is a terrorist state#end occupation#human rights#hawai'i#land back#decolonization#nakba#jason todd x reader#free tigray#stopcopcity#copcity#congo genocide#save congo#mass graves in jackson#jackson mississippi
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
COVID FLiRT variants KP.3 and XEC: What you need to know
KP.3 was the 'predominant' SARS-CoV-2 variant in the US. It was also spreading in Europe. It's now joined with another variant and become XEC.
Over the European summer, the number of COVID-19 infections rose again, with test positivity for SARS-CoV-2 above 20%. Globally, test positivity was about 10%.
The US also saw a rise in hospitalizations, apparently after a wave of COVID-19 infections in Singapore.
Now, as we in the northern hemisphere move into autumn and winter, there is concern about two new variants.
The first one is known as KP.3 and its sub-variant KP.3.1.1. The second is XEC, a "recombinant" variant which is related to KP.3.
KP.3 is considered a global Variant of Concern (VOC) in the US by The US Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) because KP.3 was "predominant" there in August. VOCs may spread more easily or cause more severe illness.
It's important to note that KP.3 is not a global VOC, only in the US.
The CDC recommended people get an updated 2024–2025 COVID-19 vaccine.
What are the KP.3 and XEC variants?
KP.3 is one of a group of SARS-CoV-2 variants known as FLiRT variants. SARS-CoV-2 is the base virus that causes COVID, the illness.
As the name KP.3 suggests, there are also KP.1 and KP.2 sub-variants. KP.3 became predominant because it is more infectious than other circulating sub-variants.
KP.3 and other FLiRT variants descend from the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2.
Now, think of a family tree: The KP variants are children of the JN.1 variant. And JN.1 is, in turn, a child of omicron variant BA.2.86.
How omicron evolved into the subvariants KP.3. and XEC
This is important to know because of all the major COVID variants, omicron remains dominant, globally. You'll recall, other major variants are alpha, beta, delta, and gamma.
But omicron keeps evolving or mutating into new variants and sub-variants.
XEC the sub-variant is believed to have formed when KP.3 joined with KS.1.1. But we don't know for sure.
As Francois Balloux, Professor of Computational Systems Biology and Director at the UCL Genetics Institute, UK, told the Science Media Centre, "XEC is a likely recombinant between the subvariants KP.3.3 and KS.1.1."
XEC COVID variant in Germany
XEC has been reported as being first detected in Germany in June. But it is yet to appear on the Robert Koch Institute's COVID Dashboard.
As a spokesperson from the Robert Koch Institute implied via email, XEC may never appear on the dashboard because it is "impossible to predict how individual variants will spread."
Since June, the number of XEC cases in Germany has been in double-digits, but the spokesperson did not specify further. The RKI's doesn't even mention XEC on its weekly assessment, published September 18, 2024.
The focus in Germany remains on KP.3.1.1, which is dominant and considered more infectious than previous variants.
In an interview with the DPA news agency, virologist Sandra Ciesek said it was no surprise that KP.3.1.1 was more infectious.
"The virus keeps mutating in search of new ways to infect people […] but that doesn't mean that the variant causes a more severe illness," said Ciesek, who's based at the German Center for Infection Research.
How prevalent are KP.3.1.1, KS.1.1 and XEC? Up to September 3, KP.3.1.1 remains the most dominent variant, according to data provided by GISAID, the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data, and presented by outbreak.info.
KP.3.1.1 was detected worldwide 14,396 times
KP.3.3 was detected worldwide 9,157 times
KS.1.1 was detected worldwide 2,650 times
XEC was detected worldwide 95 times
0 notes
Text
Scientists say a now-dominant strain of the coronavirus could be more contagious than original
from the LA Times:
MAY 5, 20204 AM UPDATED 8:35 PM
Scientists have identified a new strain of the coronavirus that has become dominant worldwide and appears to be more contagious than the versions that spread in the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study led by scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
The new strain appeared in February in Europe, migrated quickly to the East Coast of the United States and has been the dominant strain across the world since mid-March, the scientists wrote.
In addition to spreading faster, it may make people vulnerable to a second infection after a first bout with the disease, the report warned.
The 33-page report was posted Thursday on BioRxiv, a website that researchers use to share their work before it is peer-reviewed, an effort to speed up collaborations with scientists working on COVID-19 vaccines or treatments. That research has been largely based on the genetic sequence of earlier strains and might not be effective against the new one.
Scientists with major organizations working on a vaccine or drugs to combat the coronavirus have told The Times that they are pinning their hopes on initial evidence that the virus is stable and not likely to mutate the way the influenza virus does, requiring a new vaccine every year. The Los Alamos report could upend that assumption.
The mutation identified in the new report affects the now-infamous spikes on the exterior of the coronavirus, which allow it to enter human respiratory cells. The report’s authors said they felt an “urgent need for an early warning” so that vaccines and drugs under development around the world will be effective against the mutated strain.
In many places where the new strain appeared, it quickly infected far more people than the earlier strains that came out of Wuhan, China, and within weeks it was the only strain that was prevalent in some nations, according to the report. The new strain’s dominance over its predecessors suggests that it is more infectious, according to the report, though exactly why is not yet known.
The coronavirus, known to scientists as SARS-CoV-2, has infected more than 3.5 million people around the world and caused more than 250,000 COVID-19 deaths since its discovery late last year.
The report was based on a computational analysis of more than 6,000 coronavirus sequences from around the world collected by the Global Initiative for Sharing All Influenza Data, a public-private organization in Germany. Time and again, the analysis found the new version was transitioning to become dominant.
The Los Alamos team, assisted by scientists at Duke University and the University of Sheffield in England, identified 14 mutations. Those mutations occurred among the nearly 30,000 base pairs of RNA that make up the coronavirus’s genome. The report authors focused on a mutation called D614G, which is responsible for the change in the virus’ spikes.
“The story is worrying, as we see a mutated form of the virus very rapidly emerging, and over the month of March becoming the dominant pandemic form,” study leader Bette Korber, a computational biologist at Los Alamos, wrote on her Facebook page. “When viruses with this mutation enter a population, they rapidly begin to take over the local epidemic, thus they are more transmissible.”
Scientists’ reaction to the study were mixed Tuesday.
Charles Brenner, a professor of biochemistry at the University of Iowa who has conducted research on how cells defend themselves against viruses, called the Los Alamos report a useful paper. Teams around the world working to develop vaccines “would be watching papers like this very carefully.”
Brenner noted that the study did not show the mutation makes people sicker, but found more of the virus present in sick people, “suggesting that it replicates better.” The new strain of the virus is likely to be used for vaccine generation, he said.
Dr. Peter Hotez, co-director of Texas Children’s Hospital Center for Vaccine Development, called the new study “noteworthy” but said its conclusions require further investigation.
“There is a lot of speculation here,” Hotez said. “They have no experimental verification.”
The Los Alamos report contains regional breakdowns of when the new strain of the virus first emerged and how long it took to become dominant.
Italy was one of the first countries to see the new virus in the last week of February, almost at the same time that the original strain appeared. Washington was among the first states to get hit with the original strain in late February, but by March 15 the mutated strain dominated. New York was hit by the original virus around March 15, but within days the mutant strain took over. The team did not report results for California.
May 1, 2020
If the pandemic fails to wane seasonally as the weather warms, the study warns, the virus could undergo further mutations even as research organizations prepare the first medical treatments and vaccines. Without getting on top of the risk now, the effectiveness of vaccines could be limited.
Some of the compounds in development are supposed to latch onto the spike or interrupt its action. If they were designed based on the original version of the spike, they might not be effective against the new coronavirus strain, the study’s authors warned.
“We cannot afford to be blindsided as we move vaccines and antibodies into clinical testing,” Korber wrote on Facebook. “Please be encouraged by knowing the global scientific community is on this, and we are cooperating with each other in ways I have never seen … in my 30 years as a scientist.”
David Montefiori, a Duke University scientist who worked on the report, said it is the first to document a mutation in the coronavirus that appears to make it more infectious.
Although the researchers don’t yet know the details about how the mutated spike behaves inside the body, it’s clearly doing something that gives it an evolutionary advantage over its predecessor and is fueling its rapid spread. One scientist called it a “classic case of Darwinian evolution.”
“D614G is increasing in frequency at an alarming rate, indicating a fitness advantage relative to the original Wuhan strain that enables more rapid spread,” the study said.
Still unknown is whether this mutant virus could account for regional variations in how hard COVID-19 is hitting different parts of the world.
In the United States, doctors had begun to independently question whether new strains of the virus could account for the differences in how it has infected, sickened and killed people, said Alan Wu, a UC San Francisco professor who runs the clinical chemistry and toxicology laboratories at San Francisco General Hospital.
Medical experts have speculated in recent weeks that they were seeing at least two strains of the virus in the U.S., one prevalent on the East Coast and another on the West Coast, according to Wu.
“We are looking to identify the mutation,” he said, noting that his hospital has had only a few deaths out of the hundreds of cases it has treated, which is “quite a different story than we are hearing from New York.”
The Los Alamos study does not indicate that the new version of the virus is more lethal than the original. People infected with the mutated strain appear to have higher viral loads. But the study’s authors from the University of Sheffield found that among a local sample of 447 patients, hospitalization rates were about the same for people infected with either virus version.
Even if the new strain is no more dangerous than the others, it could still complicate efforts to bring the pandemic under control. That would be an issue if the mutation makes the virus so different from earlier strains that people who have immunity to them would not be immune to the new version.
If that is indeed the case, it could make “individuals susceptible to a second infection,” the study authors wrote.
Peter Pitts, president of the nonpartisan Center for Medicine in the Public Interest, and former FDA associate commissioner, said the emergence of a mutation is not surprising, but it does increase the urgency to protect the public through social isolation and other measures.
“It clearly means that we are up against a wily virus,” he said.
Times staff writer Anita Chabria contributed to this report.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Coronavirus and Unemployment
- The Data set that I have chosen is the ‘Gapminder Data set’.
- The research question that I am going to work on is:
“ Does pandemic sitiuation affect world employment and economy globally”
Hypothesis: There are lots of negative effects on economy and employment during pandemic period
My codebook


The search terms that I used for my literature review are:
- Employment and economy before pandemic
- Obstacles for employment in pandemic
- Quarantine’s effects on Firms and factories
- Economic derogation during quarantine
- Reduction on number of employees
Literature Review Summary:
The Coronavirus has already led to disruption in manufacturing output, foreign travel and consumer demand. If the virus spreads and becomes a pandemic, what will be the likely economic effects?
In short, a global pandemic will have a serious supply-side impact – especially on foreign travel, manufacturing and investment. The uncertainty and decline in travel will also lead to people staying off work, losing income and causing a fall in demand. If it is relatively short-lived, the economy may quickly bounce back. But, if it is prolonged, it could lead to permanent loss of output – with vulnerable groups of workers particularly negatively affected.
Initial estimates on the effects of COVID-19 on the world economy include
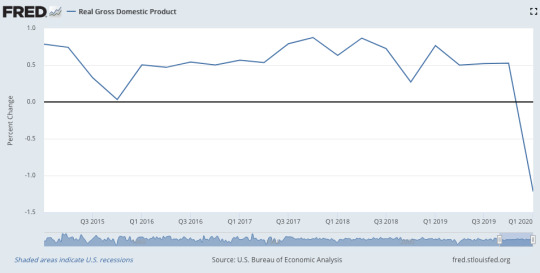
A fall in global GDP of up to 4% below baseline (World Bank April 2020)
A fall in UK GDP of 14% (According to Bank of England)
A fall in US GDP of 10% (Golden Sachs)
Supply-side effects
Reduced manufacturing output. The most effective response to the virus is quarantining and limiting chances for the virus to spread. In China, the high number of cases, led to workers staying at home, either because they have the virus or because they fear to catch it from other workers. This has led to a very significant fall in manufacturing output. In one month, the official China manufacturing index fell to 35.7 (above 50 is expansion, less than 50 is contraction) It is the biggest fall on record.
Knock-on effects. Even for countries or regions not affected by the virus, the global interconnectedness of supply chains means that nearly all manufacturers are affected by the lack of availability of parts. This leads to supply bottlenecks. UK car producers have reported bringing spare parts in suitcases from China. Big companies like Apple, which produce the iPhone in China have warned of supply shortages occuring soon.
Confidence. In a time of uncertainty, firms will cut back on investment and wait until what happens. If the pandemic causes uncertainty for a prolonged period of time, it will cause investment projects to be delayed and even postponed completely.
Lost productivity. A rise in sickness and mortality itself has an economic cost.
Demand-side effect
If travel restrictions are imposed, there will be a big fall in demand for some sectors, especially travel and tourism. Already airlines have issued profit warnings for 2020 and some flights have been cancelled. It will also cause a significant fall in demand for certain tourist sights and related business. For example, the popular tourist city of Venice is completely deserted as people avoid due to the outbreak in Italy. This will be devastating for local business, such as restaurants and gift shops who rely on tourists.
A limited pandemic may have some benefits for local tourist destinations. For example, rather than risk flights, Americans and British holidaymakers may choose to holiday at home, so there could be winners in the domestic tourist industry. But, this relies on the virus being contained in those particular countries. A real pandemic would probably cause a worldwide fall in travel.
Impact on workers. In recent years, there has been a rise in self-employed workers and workers on zero-hour contracts. This means that more workers are vulnerable to having to take time off work. If workers can work at home or get sick pay, their income will be maintained. But, for gig workers like delivery drivers and English language teachers, they could face very low income from travel restrictions and a decline in business.
Confidence. The stock market has seen its biggest contraction since the global credit crunch. With falls of 12%. A falling stock market can cause a decline in consumer wealth and hold back spending as people absorb the negative news. One study suggests falls in the stock market only have a limited effect on reducing GDP growth
“In the case of prolonged falls in share prices of 10 per cent, the QUEST model gives an additional negative output effect in the range of between -0.2 and -0.8, depending on the monetary policy response.” (effects of pandemic)
Limited scope for monetary policy. In western Europe and Japan, interest rates are already very low, there is limited scope for significant interest rate cuts. Even if rates were cut from 1% to 0.5%, it is not clear this would make much difference to the effects of the crisis. Japan has announced stimulus measures to shore up the economy – but given a prolonged period of stagnation it is uncertain whether this will make a significant difference.
Evaluation – How bad would the effects really be?
Liberia, for example, saw GDP growth decline 8 percentage points from 2013 to 2014 during the recent Ebola outbreak in West Africa.
The World Bank estimates that a very serious global influenza pandemic would cost the world economy $800 billion and kill tens-of-millions of people.
Time. An important question is how serious and prolonged is the crisis. If the crisis is less than six months, there is every chance that the economy can rebound with no loss of output. If firms delay production for three months, they build up a backlog of orders, when people return to work, this backlog can be solved due to people working over-time. This can lead to a post-crisis mini-boom.
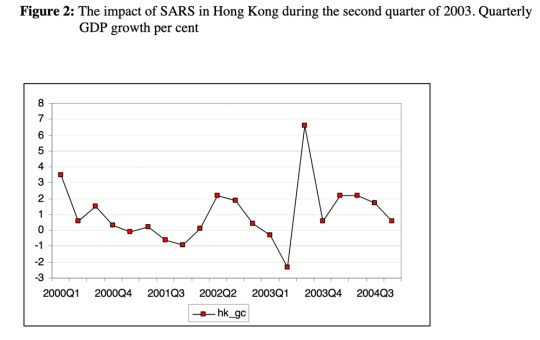
How serious is the pandemic?
A model by the EU commission in 2006, tried to model the effects of a future pandemic on the economy.
Can people work from home? In recent years, we have seen a shift in people working from home. A pandemic crisis would speed up this shift and more firms could encourage people to work from home. This can work for some sectors, but you cannot outsource manufacturing or nursing, supermarket sales. It is clear that any pandemic would hit vulnerable sectors much more.
Can monetary/fiscal policy offset the fall? Usually, if we get a demand-side shock (e.g. fall in confidence), the monetary authorities can cut interest rates to boost demand. The government can pursue fiscal policy to increase public sector investment. This helps to maintain aggregate demand. The problem is that a pandemic is both a demand-side and supply-side shock. If people stay at home because they are sick or because they fear to go to work, demand-side policy cannot deal with that. A tax cut does not particularly help if you are not working or it is difficult to get goods.
How much would economic activity cease? In the beginning of a pandemic, where is highly localised, there is a strong case for strict quarantine, leading to the factory shuts downs we see in China and ghost towns in Italy. However, if the pandemic reaches a tipping point and the virus becomes widespread, severe travel restrictions may not be effective anyway. It is uncertain how people will respond. It may reach a point, where critical industries like foods supply have to continue – regardless of the risk of transmission. The WHO state dealing with a pandemic is not just about the direct health effects on sickness and possible fatalities, but also wider issues such as the potential breakdown of social order. E.g. failure to provide sanitation and food supplies could cause more serious problems than the virus itself.
The Impact Of The Covid-19 Pandemic On Employment Contracts
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to devastate the global economy, employers in large and small businesses are faced with a dreadful conundrum on whether to let their staff go, cut their hours, or declare them redundant.
It is however highly unlikely that most employers, in drafting their contracts of employment, would have contemplated the current circumstances; particularly the level of interruption and disruption to work as we know it, which has been occasioned by the Government's response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Indeed, employers and employees have had to be deal with this unprecedented situation by adopting new ways of meeting their obligations under their employment contracts.
The primary legislation on labour and employment matters in Nigeria is the Labour Act1. The other relevant legislations are the Trade Union Act2, the Trade Disputes Act3, National Industrial Court Act4 and the National Industrial Court Rules, 20075. Nonetheless, the relationship between employers and employees are typically regulated by the contracts of employment which sets out the terms of such employment. It is trite that parties to a contract are bound by its terms and cannot vary the terms and conditions of the contract except with each other's consent6. This principle extends to employer – employee relationship and to the extent that a contract of employment is a contract, the general principles relating to general contracts will apply unless the law provides for a departure from such general principles. Hence, in NEPA v. Adesaaji7, it was held by the Court that in an employer-employee relationship, the parties' relationship is governed by terms and conditions of the contract between them. The foregoing therefore begs the critical question: What options are available to employers considering the impact the pandemic is having on their businesses? In this article we will analyze the options available to employers for addressing their employment issues during this pandemic under the existing legal framework in Nigeria.
Working from Home: The New Normal
As expected, the first reaction by most organizations has been to direct their employees to work remotely, to protect their employees and clients from the spread of the pandemic. This directive may raise the question of whose responsibility it is to provide remote working tools to the employee? This question can be answered from the decision in the case of Gattuso v. Harte-Hanks Shoppers, Inc8, where the California Supreme Court held that the intention of the provision of California Labor Code9 which requires an employer to indemnify its employees for all necessary expenditures or losses incurred as a direct consequence of the discharge of his or her duties, is to "protect employees from suffering expenses in direct consequence of doing their jobs." It is important to note that whilst the above case is from the jurisdiction of the State of California, in the United States of America, the dictum of the Court in Adetoun Oladeji (Nig.) Ltd. v. N.B. Plc10 on the application of foreign judgments in Nigeria as a form of judicial precedent may be instructive in this regard. The court held that, "... decisions of English courts or any foreign court are not binding on Nigerian courts. They are merely of persuasive authority". In addition to this, by virtue of the Third Constitutional Alteration Act of 2010, the National Industrial Court was empowered to apply all labour-related international conventions, treaties and protocols ratified by Nigeria even where they have not been domesticated11. Indeed, section 7(6) of the National Industrial Court Act provides:
"The Court shall, in exercising its jurisdiction or any of the powers conferred upon it by this Act or any other enactment or law, have due regard to good or international best practice in labour or industrial relations and what amounts to good or international best practice in labour or industrial relations shall be a question of fact".
So, if our courts are persuaded by foreign decisions on the issue of who bears the costs of expenses of working from home during the periods of lockdown, Nigerian employers may be required to reimburse employees who had to work from home during the COVID-19 pandemic for their reasonable and necessary home office expenses if they did not do that before now.
Deferment/Reduction of Salaries
Having regard to the current realities especially the inability to do business as we know it, one of the options available to employers may be to vary the terms of their employees' contract such that there is a deferment or reduction of agreed salaries. This approach should be a win-win situation for both parties as on one hand, employees would be able to retain their employments during the pandemic and on the other hand, the employers are able to manage their resources until things return to normal. In the event that this option is considered, an employer is required to notify/engage its employees and obtain prior consent as to when and how the changes would take effect, before implementing same12. In Adebusola Adedayo Omole v. Mainstreet Bank Microfinance Bank Ltd,13 the Court held that it is not acceptable for an employer to engage in unilateral reduction in the wages and salaries of workers as the reduction of the salary of the employee by the employer, without her consent, violated the spirit of section 5(1) of the Labour Act and the ILO Convention14. Furthermore, to avoid any adverse claims on the acceptance of the reduction or deferment, the employer should ensure that the employees communicate their acceptance of the changes in writing. In other words, in communicating the deferment or reduction, the employer should ensure that the notification is communicated in writing and request for a confirmation of acceptance in writing.
However, there may be instances where an employee refuses to give a written consent to such deferment or reduction in salary but continues to receive the reduced salary and does not complain. In that situation, the Court may infer an acquiescence on the part of the employee as in Oyeyemi v. Guardian Global Resources Nigeria Ltd15 where the claimant claimed that the reduction in his salary was without his consent. In dismissing the prayers of the claimant, the court held that even though his consent was required, his silence and continued stay in the employment without any form of protest; whilst receiving the reduced salary for over a year, was an acquiescence to the variation and that his silence for a year was deemed as consent.
Deferment of bonuses and promotions
Another option available to employers is deferment of bonus or promotions. In most companies, bonus determination and application usually form part of the company's policies which are typically incorporated by reference in employment contracts; thereby, becoming binding. In such circumstance, the provision for bonuses and promotions vests a right in an employee and may be recoverable against the employer due to the expectation interest they create for the employee.
The doctrine of legitimate expectation is that where an employer by his actions or inactions, creates a state of affairs that gives an employee an expectation interest which is legitimate and reasonable, then such employer is by law obligated to meet up with such expectation.
The leading and most frequently cited case supporting this approach in employment matters is the case of Toussaint v Blue Cross and Blue Shield16, which came up in the State of Michigan.
The issue before the Supreme Court was whether a voluntary promise, including a discharge-for-cause policy, made by the employer to his employee in a handbook constituted a binding obligation upon the employer. The Court held that such a policy could bind an employer if the 'employer's written policy statements set forth in the manual of personnel gave rise to legitimate expectations'. The court held that when a promise acquires legitimate expectation, the employer's unlawful breach or departure constitutes a breach of contract.
Essentially, for legitimate expectation to give rise to protection, all that has to be proven is that the employer has chosen 'to create an environment in which the employee believes that, whatever the personnel policies and practices, they are established and official at any given time, purport to be fair, and are applied consistently and uniformly to each employee'. Consequently, an employer that makes a voluntary promise in a formal statement that is reasonably capable of creating a legitimate expectation to the employee 'may not treat its promise as illusory'.17
Whilst this is a developing area in Nigerian jurisprudence, the National Industrial Court (NIC) recently applied the principle in the case of Medical and Health Workers Union of Nigeria & Ors v. Federal Ministry of Health18. The Court acknowledged that the practice of skipping salary grade levels by Government can create an expectation interest, which in turn was capable of creating an entitlement or vested right in favour of the complainants who had all the while been beneficiaries of the practice19.
Having said that, it does appear that there is a tendency for the courts to respect the employer's decision where there is genuine reason for the employer to resile such as when the future of the business and its survival is at stake20. The test must therefore be applied on the fact of each case, the context and impact of the promise made by the employer and the degree of business efficiency or need, when considering an employer's decision to revoke its promise.21
Promotions, on the other hand, are not contractual rights, as they are usually conditional upon the employee meeting certain organizational performance-based indexes. Thus, in the case of Sylvester C. Nwoye V. Federal Airports Authority of Nigeria22, it was held that promotion from one level or position in an organization to another is not a right but a privilege, which is earned. Hence, an employer cannot be compelled to promote its employee no matter the good opinion the employee might have of himself.
Paid and Unpaid Leave
Whilst section 18 of the Labour Act23 provides for at least six (6) days of paid annual leave for every 12 months of employment, most employment contracts typically provide for more number of days which can be taken as annual leave by the employee in an organization. Due to the compulsory stay at home directed by Government to curb the spread of the pandemic, many organizations may consider bringing forward the scheduled leave days/period of employees such that the leave days become part of the period now being compulsorily spent at home. This may however not apply to businesses whose employees have been working remotely during the lockdown, as this is likely to be considered an unfair labour practice by the Courts.
Thus, in Akinfemiwa Akinyinka v. More Time CO23 Gas Plant Ltd24 the National Industrial Court held that denial of annual leave to an employee is an unfair labour practice. The Court, in upholding the case of the Claimant held; "We find that the denial of annual leave entitlement to the claimants all through their years of service to the 1st defendant coupled with the 1st defendant's work days is inhuman and so a deprivation of the right to annual leave under section 18 of the Labour Act. This is, therefore, an unfair labour practice which this court cannot close its eyes to. There has been a violation of a legal right which entitles the claimants to an award of general damages and its quantum need not be pleaded or proved".
Declaration of redundancy
In Nigeria, redundancies are governed by the Labour Act, the decisions of the National Industrial Court of Nigeria (NICN), the contracts of the affected employees, organizational policies or employees' handbook, and the provisions of any collective bargaining agreement between an employer and the representatives of a trade union.
The Nigerian labour law acknowledges that an employer reserves the right to pay off any employee whether based on redundancy, idleness etc. or at the end of a project where the employee is engaged. The Labour Act defines redundancy as an "involuntary and permanent loss of employment caused by an excess of manpower".25 No specific rules apply to mass layoff or collective redundancy. Section 20 (1) of the Labour Act provides that in the event of redundancy, employers shall apply the procedure as follows:
informing the trade union or representatives of the employees of the reason for and extent of the anticipated redundancy
applying the principle of 'last in, first out' in determining the employees to be affected by the process, subject to all factors of relative merit, including skill, ability, and reliability; and
negotiating redundancy payments of the affected employees.
Though the definition of excess manpower is not provided in the Labour Act, the courts have considered the acquisition of a company, restructuring, reduction of production line, shortage of raw materials, economic and technological reasons as valid grounds for declaring redundancy.
In Alexander O. Ejah & Ors v Niger Mills Co. Ltd26, the Court reasoned that from the evidence shown, the mass termination of employment of the Defendant's employees arose from a change from a manual to an automated process requiring fewer staff; the disengagement was necessitated by economic and technological reasons, and was thus within the contemplation of the Act as a ground for redundancy. Also, in Peugeot Automobile Nigeria Ltd v Oje27 the Court described redundancy in the following words: "it is a mode of removing of an employee from service when his post is declared 'redundant' by his employee (sic). It is not a voluntary or forced retirement. It is not a dismissal from service. It is not a voluntary or forced resignation. It is not a termination of appointment as is known in public service. It is a form unique only to its procedure where an employee is quietly and lawfully relieved of his post....".
Another insightful decision of the Court in this regard is the case of Okwara Agwu & Ors v. Julius Berger Nigeria Plc28. where the Supreme Court, in dismissing the appeal held that a Court will not compel an unwilling employer to retain employees it does not need, and that the only thing a Court can do is to order for payment of all entitlement of the employees, based on the provisions of the contract of employment. In view of the foregoing, it is recommended that employers be transparent about the redundancy process and inform employees of the intention to declare a redundancy as well as negotiate a disengagement package where necessary.
Termination
In light of current realities and considering the effect of the pandemic on business activities, employers may also, as a last resort, rely on the principle of frustration or contractual force majeure to terminate employments.
Generally, frustration is upheld as a basis for termination where it is established to the satisfaction of the court that due to a subsequent change in circumstances, the contract has become impossible to perform29. Such change in circumstance may include subsequent legal changes, outbreak of war, cancellation by an unexpected event.
The consequence of the occurrence of a frustrating event which makes parties unable to perform their contract such as lockdown directives by governments to flatten the curve of the COVID-19 pandemic is that the contract is terminated immediately and the parties discharged.30
Force majeure provisions, on the other hand, are provisions contained in the employment contract which allows the parties to determine in their contract, such occurrences which may be termed as being beyond their control and described as force majeure events. This is distinct from the principle of frustration in that for force majeure provisions to hold, such events must have been agreed by the parties and their occurrence must be such that they affect the performance of parties' respective obligations under the contract. These events typically include wars, floods, or pandemics such as COVID-19. However, for an employer to rely on a force majeure clause, such clause must specifically mention pandemics, or acts of government which are beyond the reasonable control of the parties.
The above notwithstanding, it is not enough to have merely described the events which may be regarded as a force majeure event in the contract, an employer who seeks to rely on it, has the duty to prove that the pandemic and the resultant government lockdown has prevented it from being able to physically or legally fulfil its contractual obligations to the employee. However, an employer will not be heard to say that such occurrence has merely created a difficulty to perform, higher cost of performance, or less profits to the business. The employer must be able to prove that:31
such occurrence was reasonably foreseeable at the time of entering the contract
such occurrence is beyond the control of the employer/employee and cannot not be reasonably avoided; and
due to the occurrence of such event, the employer/employee is incapable of performing obligations under the employment contract
CONCLUSION
Whether or not the parties are still able to continue performing their contractual obligations in the face of the current pandemic will depend on pertinent considerations such as:
the nature of the job and ability of the employee and availability of tools for the employee to work remotely
the nature, length, and effect of the force majeure/frustrating event such as the COVID-19 pandemic
whether in the circumstance a reasonable employer could have been expected to wait any longer before taking a decision, and
reasonable adjustments made by the parties to ensure the continued performance of the contract32.
It would be practical for employers to engage their employees before arriving at a decision as this would afford the employer the opportunity to communicate its present predicament to its employees. It is also advisable for the employer to comply with the provisions of the contract of employment for the execution of whatever decision they elect. This may include notice/pay requirement, severance packages, terminal benefits, or consultation with union representatives and compliance with international best practices. It is important to note however that for employers in the oil and gas sector, an approval from the Department of Petroleum Resources ('the DPR') must first be obtained before releasing any Nigerian staff33. The Guidelines defines "release" to include but not limited to, the removal of a worker in a manner that permanently separates the worker from the employer in ways such as by dismissal; retirement; termination; redundancy; release on medical grounds; resignation; death or abandonment of duty post".34 Thus, any employer who wishes to release a worker shall apply in writing to the Director for the Minister's approval stating the manner of staff release, the reasons for the proposed release, the compensation due to the Worker, and any proposed replacement for the Worker.35
On a final note, if disputes arise between employer and employee, it is recommended that such disputes are settled through Alternative Dispute Resolution mechanisms such as mediation, negotiation or arbitration. However, where either party is dissatisfied with the outcome, they may resort to the National Industrial Court of Nigeria (NICN) for adjudication
The links to my literature review:
https://www.mondaq.com/nigeria/employment-and-workforce-wellbeing/938130/the-impact-of-the-covid-19-pandemic-on-employment-contracts
https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/161156/economics/economic-effects-of-a-pandemic/
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/05/coronavirus-unemployment-jobs-work-impact-g7-pandemic/
1 note
·
View note
Link
While a great deal of attention has been paid to the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in the city of Wuhan, which sells live poultry, fish, and several kinds of wild animals to the public, a detailed investigation by the Joint Field Epidemiology Investigation Team, a specialized task force working under the auspices of the Chinese Center for Disease Control (CCDC), found that the COVID-19 epidemic did not originate by animal-to-human transmission in the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, as originally believed, but rather human-to-human transmission totally unrelated to the operation of the market.
Moreover, by analyzing the characteristic of some 27 genomes of the COVID-19 virus provided by the Chinese and published by the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GSAID), research scientists were able to determine that the "most recent common ancestor" for the coronavirus could be dated back to as early as October 1, 2019.
The importance of this date as it relates to the [National Center for Medical Intelligence (NCMI)] is that in mid-October 2019 a delegation of 300 U.S. military athletes arrived in Wuhan to participate in the 2019 Military World games....
The importance of the U.S. military athletes rests in the fact that the NCMI is responsible for conducting threat briefs for all deployments of military personnel world-wide, which meant that a Wuhan-specific Infectious Disease Risk Assessment would have necessarily been prepared in support of this deployment. Infectious Disease Risk Assessments are the bread-and-butter intelligence product produced by the NCMI's Infectious Disease Division, one in which the totality of the medical intelligence collection and analytical capabilities would be utilized.
The production of a Wuhan-specific Infectious Disease Risk Assessment would have created a window of opportunity for the NCMI to have collected the kind of medical intelligence that could have provided early warning about the existence of the coronavirus.
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Viral and host factors related to the clinical outcome of COVID-19
In December 2019, the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by a novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, emerged in Wuhan, Hubei province, China1 and soon spread across the world. In this ongoing pandemic, public health concerns and the urgent need for effective therapeutic measures require a deep understanding of its epidemiology, transmissibility and pathogenesis. Here we analyzed the clinical, molecular and immunological data from 326 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in Shanghai. Genomic sequences of SARS-CoV-2 assembled from 112 quality samples together with sequences in the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID) showed a stable evolution and suggested two major lineages with differential exposure history during the early phase of the outbreak in Wuhan. Nevertheless, they exhibited similar virulence and clinical outcomes. Lymphocytopenia, especially the reduced CD4+ and CD8+ T cell counts upon admission, was predictive of disease progression. High levels of IL-6 and IL-8 during treatment were observed in patients with severe or critical disease and correlated with decreased lymphocyte count. The determinants of disease severity seemed to stem mostly from host factors such as age, lymphocytopenia, and its associated cytokine storm, whereas viral genetic variation did not significantly affect the outcomes.
1 note
·
View note
Photo


China releasing information on COVID-19 and advancing international cooperation on epidemic response
The novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) epidemic is a major public health emergency that has spread the fastest, caused the most extensive infections and been the hardest to contain since the founding of the People's Republic of China in 1949.
Under the strong leadership of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee with Comrade Xi Jinping as the core, China has taken the most comprehensive, the strictest and the most thorough prevention and control measures to battle the epidemic. In their tenacious fight against the coronavirus, 1.4 billion Chinese people have pulled together in tough times and paid a tremendous price and sacrificed a lot.
With the joint efforts of the whole nation, the positive trend in preventing and controlling the epidemic in China has been constantly consolidated and expanded, and the restoration of normal production and everyday life has been quickened.
The pandemic has recently been spreading rapidly across the world, posing a formidable challenge to global public health security. According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), COVID-19 had affected more than 200 countries and regions with over 1.13 million confirmed cases by April 5,2020.
Virus knows no national borders, and the epidemic distinguishes no races. Only with solidarity and by cooperation can the international community prevail over the pandemic and safeguard the common homeland of humanity. Upholding the vision of building a community with a shared future for humanity, China has been timely releasing information on COVID-19 since the onset of the epidemic in an open, transparent and responsible manner, unreservedly sharing with the WHO and the international community its experience in epidemic response and medical treatment, and strengthening cooperation on scientific research. It has also provided assistance to all parties to the best of its ability. All these efforts have been applauded and widely recognized by the international community.
Based on media reports and information from the National Health Commission, scientific research institutions and other departments, Xinhua News Agency sorted out the main facts China has taken in the global joint anti-virus efforts to timely release epidemic information, share prevention and control experience, and advance international exchanges and cooperation on epidemic response.
The following timeline was arranged in chronological order.
Late December 2019
・ The Wuhan Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in central China's Hubei Province detected cases of pneumonia of unknown cause.
Dec. 30, 2019
・ The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission issued an urgent notification to medical institutions under its jurisdiction, ordering efforts to appropriately treat patients with pneumonia of unknown cause.
Dec. 31, 2019
・ The National Health Commission (NHC) made arrangements in the wee hours, sending a working group and an expert team to Wuhan to guide epidemic response and conduct on-site investigations.
・ The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission released a briefing on its website about the pneumonia outbreak in the city, confirming 27 cases and telling the public not to go to enclosed public places or gather. It suggested wearing face masks when going out.
・ Starting Dec. 31, 2019, the Wuhan Municipal Health Commission released briefings on the pneumonia outbreak in accordance with the law.
January 2020
Jan. 1
・ The NHC set up a leading group to determine the emergency response to the epidemic. The group convened meetings on a daily basis since then.
Jan. 2
・ The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (China CDC) and the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS) received the first batch of samples of four patients from Hubei Province and began pathogen identification.
・ The NHC came up with a set of guidelines on early discovery, early diagnosis and early quarantine for the prevention and control of the viral pneumonia of unknown cause.
Jan. 3
・ Starting Jan. 3, China has been regularly informing the WHO, relevant countries and regions and China's Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan about the pneumonia outbreak.
・ China began to inform the United States of the pneumonia outbreak and response measures on a regular basis.
・ The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission updated briefing on its website about the situation of viral pneumonia of unknown cause, reporting a total of 44 cases of viral pneumonia of unknown cause.
・ The NHC organized the China CDC and three other institutions to carry out parallel laboratory testing of the samples for pathogen identification.
・ The NHC and the Health Commission of Hubei Province jointly worked out nine documents on the outbreak, including a trial version of guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of viral pneumonia of unknown cause.
Jan. 4
・ The NHC and relevant health departments in Hubei Province issued a treatment manual for viral pneumonia of unknown cause to all medical institutions in Wuhan City, and provided citywide training.
・ Head of the China CDC talked over phone with director of the U.S.CDC about the pneumonia outbreak. The two sides agreed to keep in close contact for information sharing and technological cooperation.
Jan. 5
・ The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission updated briefing on the situation of viral pneumonia of unknown cause, reporting a total of 59 cases. Laboratory test results ruled out respiratory pathogens, such as influenza, avian influenza, adenovirus, the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus, and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus, as the cause.
・ China informed the WHO about the outbreak updates.
・ The WHO released its first briefing on cases of pneumonia of unknown cause in Wuhan.
Jan. 6
・ The NHC gave a briefing on cases of pneumonia of unknown cause at a national health conference, calling for efforts to strengthen monitoring, analysis and study, and make timely response.
Jan. 7
・ Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, made instructions on epidemic response when presiding over a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee.
・ The China CDC succeeded in isolating the first novel coronavirus strain.
Jan. 8
・ An expert evaluation team from the NHC initially identified a new coronavirus as the cause of the epidemic.
・ Heads of China and U.S. CDCs talked over phone to discuss technological exchanges and cooperation.
Jan. 9
・ An expert team from the NHC made public of the pathogen, saying a new type of coronavirus was initially identified as the cause of the viral pneumonia in Wuhan.
・ China informed the WHO about the epidemic, sharing with the WHO the initial progress in determining the cause of the viral pneumonia in Wuhan.
・ The WHO released on its website a statement regarding a cluster of pneumonia cases in Wuhan, saying that preliminary identification of a novel coronavirus in a short period of time is a notable achievement.
Jan. 10
・ Research institutions including the Wuhan Institute of Virology (WIV) developed testing kits. Wuhan City organized tests of all relevant cases admitted at hospitals in the city.
・ Head of the NHC Ma Xiaowei talked over phone with WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus about the epidemic response.
・ Head of China CDC exchanged information over phone with WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus.
・ The China CDC shared with the WHO the specific primers and probes for detecting the novel coronavirus.
Jan. 11
・ The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission updated briefing on the situation of viral pneumonia of unknown cause.
Jan. 12
・ The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission changed the name of "viral pneumonia of unknown cause "to "pneumonia caused by the novel coronavirus" for the first time in a briefing.
・ The China CDC, the CAMS and the WIV under the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), as designated agencies of the NHC, submitted to the WHO the genome sequence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), which was published by the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID) and shared globally.
・ The NHC shared with the WHO about information on the genome sequence of the novel coronavirus.
Jan. 13
・ The NHC held a meeting to instruct Wuhan authorities to further strengthen social management measures and body temperature monitoring of people at ports and stations, as well as reduce crowd gathering.
・ Delegations from the Hong Kong and Macao special administrative regions and Taiwan visited Wuhan (until Jan. 14.)
・ Wuhan Municipal Health Commission updated the outbreak briefing on its official website, saying Wuhan had reported a total of 41 cases of pneumonia caused by the novel coronavirus as of Jan. 12.
・ The WHO issued on its official website a statement on the discovery of the novel coronavirus cases in Thailand, pointing out that China's sharing of the genome sequence enabled more countries to quickly diagnose patients.
Jan. 14
・ The NHC held a national teleconference, making arrangements for Hubei Province and Wuhan City to strengthen epidemic prevention and control, while ordering the whole country to prepare for epidemic prevention and response.
Jan. 15
・ The NHC unveiled the first version of guidelines on diagnosis and treatment for pneumonia caused by novel coronavirus, along with the guidelines on prevention and control measures.
Jan.16
・ After the optimization of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) diagnostic reagents was complete, Wuhan City took proactive measures to screen all patients treated in fever clinics or under medical observation in 69 secondary or above hospitals.
・ Foreign journalists asked about the epidemic for the first time at a press conference held by the Chinese foreign ministry in Beijing. Foreign ministry spokesperson said that China has timely informed the WHO and other international organizations of the outbreak and kept close communication with them.
Jan. 17
・ The NHC sent seven inspection teams to different provincial-level regions to instruct local epidemic prevention and control work.
Jan. 18
・ The NHC organized and sent a high-level expert team, headed by Zhong Nanshan, to Wuhan City to carry out on-site investigation into the prevention and control work (until Jan. 19).
・ The NHC released the second version of guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment for the pneumonia caused by the novel coronavirus.
Jan. 19
・ The NHC distributed nucleic acid testing reagents to health departments across the country.
・ The China CDC communicated with the U.S. CDC on epidemic prevention and control.
・ Wuhan Municipal Health Commission updated the outbreak briefing on its official website, saying as of Jan. 17, Wuhan had reported a total of 62 confirmed cases, including 19 cases discharged after recovery, eight cases with severe symptoms, and two deaths.
Jan. 20
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Chinese President Xi Jinping, also general secretary of CPC Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, has made important instructions on the outbreak of pneumonia caused by the novel coronavirus in Wuhan City and other places in Hubei Province, stressing the Party committees and governments at all levels must put people's safety and health as the top priority, make thorough plans, take effective measures to curb the spread of the virus, timely release information and deepen international cooperation.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Premier Li Keqiang chaired an executive meeting of the State Council to make further arrangements on the prevention and control work of the pneumonia outbreak caused by the novel coronavirus.
・ A teleconference of the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council was held in Beijing, at which Vice Premier Sun Chunlan stressed local authorities must take their responsibilities, strengthen the prevention and control measures, secure people's health, and maintain normal production and everyday life order.
・ Wuhan Municipal Health Commission updated the outbreak briefing on its official website: as of 10 p.m. on Jan. 19, Wuhan reported a total of 198 cases of pneumonia caused by the novel coronavirus, with 25 cured and discharged cases, three deaths.
・ The NHC held a press conference for the high-level expert team headed by Zhong Nanshan, who on the team's behalf confirmed human-to-human transmission of the novel coronavirus and called on people not to go to Wuhan except for extremely important reasons.
・ The NHC released a statement to classify the novel coronavirus pneumonia as a category B infectious disease under the law on prevention and control of infectious diseases, but take preventive and control measures of category A infectious diseases; the novel coronavirus pneumonia was put under quarantinable infectious disease management according to the Frontier Health and Quarantine Law.
・ The NHC published the second version of guidelines on the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus pneumonia.
・ Researchers from City University of Hong Kong published a genetic analysis on the bioRxiv preprint platform, suggesting what animals that serve as the transmission vehicle of the 2019-nCoV remains to be identified.
Jan. 21
・ The NHC started to update via its official website and its new media platform the epidemic information of the previous day on a daily basis. It had updated 71 times by March 31. Starting on Feb. 3, the English official website of the NHC started releasing epidemic information simultaneously, updating the data for 58 times by March 31.
・ A foreign ministry spokesperson said China will, upon invitation from the WHO, send representatives to attend an International Health Regulations (IHR) Emergency Committee meeting.
・ The People's Government of Guangdong Province held a press briefing on the pneumonia outbreak and epidemic prevention and control measures. Zhong Nanshan told the briefing that "since it is known that the virus can be transmitted from people to people, one thing to do is to strictly quarantine patients and track close contacts, which is probably the most important thing," adding that there has been thus far no targeted and effective drugs against the novel coronavirus.
・ The WHO published a statement on its official website saying on Jan.20-21, a WHO delegation conducted a field visit to Wuhan to learn about the response to 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) and visited the Wuhan Tianhe Airport, Zhongnan hospital, Hubei provincial CDC.
Chinese experts shared with Gauden Galea, the WHO Representative in China, Olowokure Babatunde and other members of the delegation a range of protocols that will be used in developing international guidelines, including case definitions, clinical management, and infection control among others.
・ The China CDC Weekly reported for the first time the epidemiological characteristics of the novel coronavirus, displaying the whole genome sequence of three strains of the virus, in an article titled "Note from the Field: A Novel Coronavirus Genome Identified in a Cluster of Pneumonia Cases-Wuhan, China 2019-2020."
・ Researchers from the Institut Pasteur of Shanghai under the CAS, the Institute of Military Medicine under the Academy of Military Sciences, and the CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences published a paper in the English version of "Science China Life Science," titled "Evolution of the novel coronavirus from the ongoing Wuhan outbreak and modeling of its spike protein for risk of human transmission," evaluating the potential human-to-human transmission capacity of the virus, providing scientific theoretical basis for confirming the source and transmission route of infection as soon as possible and formulating prevention and control strategies.
Jan. 22
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with French President Emmanuel Macron at request.
Macron said that France supports China in actively dealing with the epidemic and is willing to enhance health cooperation with the Chinese side.
Xi said that since the outbreak, China has taken strict measures in prevention, control and treatment, and has been releasing relevant information to the public and keeping the World Health Organization as well as relevant countries and regions informed in a timely manner.
China is willing to work with the international community to effectively tackle the spread of the disease and maintain global health security, Xi said.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with German Chancellor Angela Merkel at request.
Merkel said Germany appreciates China's efforts to respond in a timely manner, stay open and transparent, and actively carry out international cooperation, adding that Germany is willing to provide China with support and assistance.
Xi expressed his gratitude to Germany, stressing that China is willing to strengthen cooperation with Germany, the WHO and the international community.
・ The NHC published the third version of guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia, detailing the use of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference about epidemic and the prevention and control work, advising people outside Wuhan not to go to the city in principle and Wuhan residents not to leave the city without special reasons.
・ At the invitation of the WHO, China attended an International Health Regulations (IHR) Emergency Committee meeting along with other countries affected by the epidemic. Participating countries, the WHO and experts shared information on the epidemic and conducted scientific research and assessment of the epidemic at the meeting.
・ China's NHC received a notification from the United States saying the first confirmed case had been reported in the United States.
・ The China CDC weekly for the first time reported the epidemiological investigation results of the pneumonia caused by the novel coronavirus in Wuhan in an article titled "Note from the Field: An Outbreak of NCIP (2019-nCoV) Infection in China-Wuhan, Hubei Province 2019-2020."
・ Researchers from the MRC-University of Glasgow Centre for Virus Research and the Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University, posted their sequence analysis of the 2019-nCoV on a medical discussion forum Virological, suggesting the novel coronavirus may have originated in bats rather than snakes.
・ The 2019 Novel Coronavirus Resource (2019nCoVR), a database develop by the China National Center for Bioinformation, was officially launched to release worldwide novel coronavirus genome and information on variation analysis.
Jan. 23
・ Wuhan epidemic prevention and control headquarters issued a notice to shut down the city's outbound channels at airports and railway stations starting 10 a.m. on Jan. 23.
・ In an emergency notice, the Ministry of Transport demanded other parts of the country suspend the passenger traffic into Wuhan by road or by waterway.
・ The NHC and other five departments jointly issued a statement on preventing the transmission of the novel coronavirus-caused pneumonia via transportation, requiring efforts for health management of vehicles, trains, planes and other means of transport, as well as key places including stations, airports and docks to prevent to the greatest extent the spread of the epidemic.
・ Researchers from WIV under the CAS, Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital and the Hubei Provincial CDC found that the full-length genome sequences of the 2019-nCoV shares 79.5 percent of SARS-CoV sequence, which was published on the bioRxiv preprint platform.
Jan. 24
・ Researchers from the Beijingbased China-Japan Friendship Hospital, the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital published an article in the Lancet, titled "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China."
・ WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus on social media thanked the Chinese government for its cooperation and transparency, saying that the Chinese government has been successful in isolating and sequencing the virus very quickly and has shared that genetic sequence with the WHO and the international community.
・ The National Microbiology Data Center and the National Pathogen Resources Collection Center jointly established the Novel Coronavirus National Science and Technology Resource Service System, releasing the first electron microscope picture of the virus and strain information.
Jan. 25
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee on the prevention and control of the outbreak of pneumonia caused by the novel coronavirus, making further study of and new arrangements on issues especially related to the treatment of patients.
The meeting decided to set up a CPC Central Committee leading group for the epidemic response work under the leadership of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee.
The CPC Central Committee decided to send guidance groups to Hubei Province and other seriously affected areas to enhance the frontline prevention and control work.
・ The NHC unveiled six guidelines on public prevention for general use, tourism, households, public places, public transport and self observation at home.
・ The NHC replied in a letter to WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, welcoming the WHO to send a group of international experts to cooperate with China to strengthen epidemic prevention and control.
・ Led by the China CDC, several hospitals and research institutes jointly published a paper, titled "The novel coronavirus carried by Chinese pneumonia patients in 2019," revealing their finding of a Betacoronavirus that had never been seen before through whole genome sequencing, which became the seventh member of the coronavirus family that infects human.
Jan. 26
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Chinese Premier Li Keqiang, also a member of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee, and head of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the response to the novel coronavirus outbreak, presided over the leading group's meeting. The meeting made further epidemic prevention and control arrangements according to instructions by Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference to invite the NHC head Ma Xiaowei to brief on the epidemic and introduce the joint prevention and control work.
Ma told the press conference recent clinical results showed that the novel coronavirus has more transmissibility and the epidemic situation is grim and complicated, adding that the country is at a crucial time in the prevention and control of the outbreak.
Ma said that the source of infection is yet to be found and studies are still needed to understand its pathogenicity, adding that the possibility of virus changes over time can't be ruled out.
・ The NHC and relevant departments jointly provided detailed information to the WHO Western Pacific Region on measures taken in Wuhan which may restrict international travel, including the suspended operation of city buses, subways and ferries, as well as public health reasons for the above measures.
Jan. 27
・ A guidance group, sent by the CPC Central Committee and headed by Vice Premier Sun Chunlan, arrived in Wuhan to guide the epidemic prevention and control work in Hubei Province, repeatedly demanding open and transparent release of epidemic information.
・ The NHC released the fourth version of guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing to give briefings on the development of the community-based prevention measures to curb the novel coronavirus epidemic.
Such press conference has been held every day since Jan. 27, releasing updated data on a daily basis, including new confirmed cases, people discharged from hospital, people who had had close contact with infected patients and were discharged from medical observation, severe cases, deaths, suspected cases, people receiving treatment in quarantine, close contacts still under medical observation, accumulative data on the Chinese mainland as well as data reported in the Hong Kong and Macao special administrative regions and Taiwan.
As of March 31, 65 press conferences under the mechanism had been held on a wide range of topics, including the epidemic prevention and control, treatment and scientific research. Officials of 69 departments answered 779 questions raised by Chinese and foreign reporters at the conferences.
・ Head of China's NHC Ma Xiaowei talked over phone with U.S. secretary of health and human services Alex Azar at request, discussing the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus outbreak.
Jan. 28
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping met with WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus in Beijing.
"The epidemic is a devil. We will not let it hide," Xi said, stressing the Chinese government has released information about the epidemic in a timely, open, transparent and responsible manner, actively responded to concerns of all sides, and enhanced cooperation with the international community.
Xi noted that China is ready to work with the WHO as well as the international community to safeguard regional and global public health security.
・ The NHC released the third-edition guidelines on the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus pneumonia.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing on details of medical workers sent from other parts of China to Hubei Province to help fight the epidemic.
・ The Ministry of Foreign Affairs held a briefing for foreign embassies and missions in China on the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus outbreak. The NHC and the foreign ministry briefed on the current situation and China's efforts to prevent and control the epidemic, and answered questions. Foreign diplomats and representatives present made positive comments on the briefing held by the Chinese side, and appreciated the Chinese government's firm and decisive measures in handling the epidemic, as well as the open, transparent and responsible attitude it has shown. They said that they are willing to strengthen communication and coordination with the Chinese side, and cooperate with China in prevention and control efforts to jointly safeguard regional and international health security.
Jan. 29
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the response to the novel coronavirus outbreak to further study the prevention and control of the epidemic, and roll out targeted and enhanced measures to curb the epidemic.
・ Yang Jiechi, a member of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee, also head of the Office of the Foreign Affairs Commission of the CPC Central Committee, spoke over phone with U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo. Pompeo expressed appreciation for China's timely response to U.S. concerns after the epidemic.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing to advise the public on the prevention of the novel coronavirus outbreak.
・ A thesis on the genome sequence of the novel coronavirus by a research team of the WIV of the CAS was formally accepted by the journal Nature.
・ The China CDC published an epidemiological feature analysis of the novel coronavirus pneumonia outbreak in the New England Journal of Medicine.
・ Researchers from the Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine and WIV under the CAS published an article in the Lancet, titled "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study", revealing data regarding clinical features and treatment of novel coronavirus patients.
・ Researchers from the China CDC published a paper in the Lancet, titled "Genomic characterization and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding," analyzing 10 genome sequences of 2019-nCoV obtained from nine confirmed patients in Wuhan.
・ Research team of Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica under the CAS published an article on the bioRxiv preprint platform, revealing research results about drugs by computer-simulated screening.
・ Researchers of the Institute of Automation under the CAS published an article on the medRxiv preprint platform, estimating the development trend of the epidemic based on the daily reported novel coronavirus cases by the China CDC.
Jan. 30
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing on policies to ensure transportation of anti-epidemic materials in the fight against the novel coronavirus outbreak.
・ China's NHC notified the U.S.side that American experts are welcomed to join the China-WHO joint mission. The U.S. side responded the same day and expressed their appreciation.
・ The China CDC published a paper in the New England Journal of Medicine, titled "Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia," revealing the epidemiological characteristics of the 2019-nCoV on the basis of data collected from the first 425 confirmed cases.
Jan. 31
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus outbreak, making arrangements for the transportation for the post-Spring Festival trips while enhancing the epidemic prevention and control.
・ The NHC released guidelines on gathering patients infected with novel coronavirus that show severe symptoms into designated medical institutions for treatment, in order to minimize the fatality rate and increase the recovery rate.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing on the epidemic prevention and control work concerning major groups and by community organizations.
February 2020
Feb. 1
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Chinese Premier Li Keqiang spoke over phone with European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen, noting the Chinese government and people have confidence, resolution and ability to win the battle against the epidemic.
Li said China is willing to strengthen information, policy and technology exchanges, and carry out relevant cooperation with EU and the international community.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing giving briefings on the epidemic prevention and control work concerning pregnant women, infants and nurseries.
Feb. 2
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus outbreak, urging authorities in some provincial-level regions to flexibly arrange their work to battle the epidemic, step up prevention and control efforts and ensure market supply while pledging greater medical supplies support to key areas in Hubei Province.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing providing epidemic prevention guidance for people exposed to public places, public transport and other potential coronavirus risks.
As revealed by China CDC experts at the press conference, the finding of novel coronavirus from fecal samples of confirmed cases showed the virus can exist and replicate in digestive tract, but it needs further epidemiological research to determine whether the virus can transmit through the fecal-oral route or respiratory droplets-formed aerosol.
・ Head of China's NHC Ma Xiaowei sent a letter to the U.S. secretary of health and human services Alex Azar, further exchanging views on bilateral cooperation in health as well as epidemic prevention and control.
Feb. 3
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee to hear briefings from the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus outbreak and from relevant departments, and study epidemic prevention and control work in the near future. Xi's speech was later published on the Qiushi Journal, a flagship magazine of the CPC Central Committee, in its fourth issue of 2020.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference on ensuring supplies of crucial anti-epidemic medical materials and daily necessities. At the press conference, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology said about 60 percent of production capacity of domestic mask manufacturers have been resumed. Though N95 masks were in shortage, the supply would keep on increasing through expanded domestic production and increased international procurement.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing about provision of psychological assistance through online or hotline counseling services amid efforts to prevent and control the epidemic.
・ During the first online press conference of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, a ministry spokesperson gave briefings on donations of epidemic prevention and control supplies China has received. The spokesperson said China attaches great importance to the lives and health of Chinese and foreign nationals in Wuhan, and has timely taken effective measures to address their concerns and needs.
・ The NHC introduced the epidemic situation in China and presented suggestions for further cooperation at a video conference held among senior health officials from China, ASEAN, Japan and the Republic of Korea (ROK).
・ The WHO Executive Board convened its 146th session meeting in Geneva, during which China's deputy permanent representative to the UN Office at Geneva and other international organizations in Switzerland called for concerted efforts from the international community to combat the epidemic.
・ As of Feb. 3, China has given the United States briefings on the epidemic information and control measures in China for 30 times, including sharing with U.S. CDC project manager in China information about China's diagnosis and treatment guidelines, prevention and control guidelines, and the linkage of the novel coronavirus database that China shares with the world in real time.
・ Officials of the China CDC welcomed a U.S. expert from the Columbia University.
・ Researchers from Fudan University, Central Hospital of Wuhan, National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention of China CDC, Wuhan CDC, and the University of Sydney published a paper in the journal Nature, titled "A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China."
Feb. 4
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus outbreak, rolling out measures to improve the admission and cure rates, reduce the infection and fatality rates of patients in Wuhan, and further improve supplies of medical materials and life necessities.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing on the treatment of novel coronavirus-infected patients with severe symptoms.
As revealed by the NHC at the press conference, the number of confirmed cases on the Chinese mainland had reached 20,438 as of Feb. 3, with a total of 425 deaths and a fatality rate of 2.1 percent. The NHC vowed to concentrate resources to improve the admission and cure rates and reduce the infection and fatality rates.
・ Head of the China CDC spoke over phone with director of the U.S.National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to exchange information on the epidemic.
・ The Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Health and Harvard University had first discussion over scientific research cooperation to fight the novel coronavirus epidemic.
・ Researchers from WIV under the CAS and the Institute of Military Medicine under the Academy of Military Sciences released a paper in the journal Cell Research, titled "Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro."
Feb. 5
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that President Xi Jinping presided over the third meeting of the Commission for Overall Law-based Governance of the CPC Central Committee, and delivered an important speech, stressing that under the CPC Central Committee's centralized and unified leadership, ensuring the safety and health of the people should always be prioritized.
Xi, also general secretary of the CPC Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, and head of the Commission for Overall Law-based Governance of the CPC Central Committee, called for greater legislative, law enforcement, judicial and law observance efforts to strengthen the capacity to carry out law-based epidemic prevention and control. Excerpts of Xi's speech at the meeting were published by the Qiushi Journal in its fifth issue of 2020.
・ President Xi Jinping met with Cambodian Prime Minister Samdech Techo Hun Sen in Beijing, saying a friend in need is a friend indeed as the Cambodian people stand with the Chinese people at this special moment.
Xi said Cambodian King Norodom Sihamoni and his mother, former Queen Norodom Monineath Sihanouk, had specially extended sympathy and support to the Chinese side.
The Cambodian prime minister had expressed strong support to China on many occasions and even made a special tour to China, which demonstrated unbreakable friendship and mutual trust between the two nations and showcased the essence of building a community of shared future of the two countries, Xi said.
・ The NHC made revisions and published the fifth edition of guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of the novel coronavirus patients.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing on the latest development of work involving production, dispatch and imports of medical supplies, and briefing on the fifth-edition guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of the novel coronavirus patients.
・ While meeting with a delegation of Russian experts on epidemic prevention, a Chinese foreign ministry official said China is committed to maintaining global public health security and conducting international cooperation in epidemic prevention and control in the principles of openness and transparency. The epidemic prevention exchanges and joint research between the two countries will definitely help win the fight against the epidemic.
・ While meeting with French Ambassador to China Laurent Bili, a Chinese foreign ministry official briefed him on the latest situation of the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus pneumonia outbreak, saying that the life and health of French citizens in China are guaranteed and it is hoped that France will view and support the Chinese side's work in a rational, calm and scientific manner.
・ Chinese foreign ministry hosted the second briefing on the novel coronavirus pneumonia outbreak for diplomatic missions in China. The briefing was held online and attended by representatives of more than 180 diplomatic missions. Officials from the NHC and the foreign ministry gave briefings on the epidemic situation and the containment measures taken by the Chinese government, and answered questions of concern to the diplomatic envoys.
Feb. 6
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping spoke over phone with Saudi King Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud at request, noting China will keep on working with Saudi Arabia and other countries to jointly handle the epidemic, and maintain public health security in the region and around the world in openness and transparency.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus outbreak, making arrangements of more targeted measures to enhance epidemic prevention and control, and resume production and ensure market supply step by step.
・ While meeting with Ambassador of the United Kingdom to China Barbara Janet Woodward, a Chinese foreign ministry official briefed on the latest development of prevention and control of the novel coronavirus pneumonia outbreak, and stressed that China has the confidence and capability to win this battle. The life and health of all the foreign nationals, including the British people, are guaranteed.
・ A Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson said at a regular press conference that the Chinese government puts people's lives and health as its top priority. Acting with openness, transparency and a high sense of responsibility, it has been timely sharing information, enhancing international cooperation, putting in place a nationwide scheme to pool national resources and take the strictest and most thorough measures to fight the outbreak. The ministry started to update cases of the novel coronavirus pneumonia at the regular press conferences.
Feb. 7
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping spoke over phone with U.S. President Donald Trump at request, stressing that China is dedicated to safeguarding the lives and health of not only its own people but also people all over the world.
With an open, transparent and responsible attitude, China has kept the WHO as well as relevant countries and regions, including the United States, posted on the epidemic, and invited WHO and other experts to conduct field visits in Wuhan, Xi said.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held publishing measures to enhance epidemic prevention and control in key regions, and improve the admission and cure rates and reduce the infection and fatality rates.
・ While meeting with Head of the Delegation of the European Union to China Nicolas Chapuis, a Chinese foreign ministry official briefed on the latest development of the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus outbreak, saying China will continue to share information and data with the EU and the international community in an open, transparent and responsible manner and strengthen cooperation in the field of public health.
・ Experts of the China CDC joined the WHO informal expert conference call and epidemiology working group expert conference call.
Feb. 8
・ The NHC gave briefings on China's anti-epidemic efforts and measures at the first meeting of the APEC health working group.
・ The NHC gave briefings to Chinese diplomatic missions overseas on the country's plans for the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus outbreak, diagnosis and treatment, monitoring, epidemiological probe and laboratory testing.
・ Chinese, U.S. health authorities had another discussion over arrangements regarding the participation of American experts in the China-WHO joint mission.
Feb. 9
・ Chinese Premier Li Keqiang talked over phone with German Chancellor Angela Merkel, exchanging views over the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus outbreak.
Li said China is open, transparent and highly responsible in epidemic prevention and control work, releasing information to the Chinese people and the international community in a timely manner.
"The measures we have taken have gone far beyond the requirements of the International Health Regulations and the recommendations of the WHO," Li said.
Li said he hopes that the international community, including Germany, can stay rational, support China's efforts in containing the epidemic, maintain normal bilateral exchanges, and strengthen international cooperation on public health security, adding he hopes that the German side can provide China with necessary convenience so that China can purchase medical supplies from Germany through commercial channels.
Feb. 10
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that President Xi Jinping, also general secretary of the CPC Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, made an inspection tour in Beijing on the epidemic prevention and control. Xi said the situation at the moment remains very serious, calling on Party committees and governments at all levels to firmly follow the CPC Central Committee's decisions and arrangements on epidemic prevention and control.
Xi urged strict enforcement of the general requirements of firm confidence, sticking together in tough times, scientific prevention and control and carrying out targeted policies.
Calling for persistent efforts, Xi said with firmer confidence, more indomitable will and more decisive measures, and by firmly relying on the people, China will resolutely contain the spread of the epidemic, and win the people's all-out war against the epidemic.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the prevention and control of the novel coronavirus outbreak, making arrangements to further increase the production and supply of key medical prevention and control materials, and strengthen the deployment of medics and development of drugs against the novel coronavirus.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing on measures to enhance epidemic prevention and control at the grassroots level.
・ The Ministry of Commerce held the first online press conference, giving briefings on the supply of daily necessities in the battle against the epidemic. The weekly news conferences had been held for seven consecutive weeks as of March 31, taking many epidemic-related questions, such as about the consumer market, resumption of work and production as well as foreign trade and investment.
・ An advance squad of the WHOled team arrived in Beijing.
Feb. 11
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping spoke over phone with Indonesian President Joko Widodo at request, noting China has been safeguarding the lives and health of the Chinese people and fulfilling responsibility for the cause of global public health by upholding the vision of building a community with a shared future for mankind.
Xi said China will continue to strengthen cooperation on the prevention and control of the epidemic with Indonesia and other countries in an open and transparent manner to safeguard regional and global public health security.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Qatari Emir Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani at request, stressing that China has been safeguarding the Chinese people's lives and health while actively contributing to global public health security.
Xi said China is willing to maintain close communication with Qatar, timely provide updates on the latest situation of the epidemic, ensure the life and health of the Qatari nationals in China so as to safeguard the health and safety of the people of both countries.
・ Experts of the China CDC participated in a WHO-coordinated research and innovation forum, held on Feb. 11-12 in Geneva, either in person or online. The forum, co-hosted by WHO and the Global Research Collaboration for Infectious Disease Preparedness, attracted more than 400 participants, including leading scientists from virus-related disciplines, representatives of countries with confirmed COVID-19 cases and those of public health agencies. Soumya Swaminathan, WHO chief scientist, hailed the contribution made by Chinese researchers attending the forum.
・ The China-WHO joint mission held the first meeting, discussing and reaching initial agreement on issues including the principle in determining the list of members, priorities of field visits and agenda of the mission.
・ Experts from the China and U.S.CDCs held a conference call, discussing and sharing epidemic prevention and control information.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing on measures to enhance epidemic prevention and control in rural regions.
・ Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the China CDC for the first time used transgenic mice to study the pathogenicity of the novel coronavirus, and published an article in the bioRxiv platform. This may facilitate the development of therapeutics and vaccines.
Feb. 12
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee to hear the report of the central leading group on the prevention and control work to the COVID-19 outbreak, analyze the epidemic situation, and study measures to strengthen prevention and control work.
・ Specialists from the NHC joined a China-EU teleconference on COVID-19 related technical exchanges, introducing the latest developments of the epidemic, prevention and control measures, and the situation of international cooperation.
Feb. 13
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Malaysian Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad at request, noting that China has taken strong measures in response to the epidemic in a way that not only assumes the responsibility for the health of its people, but also contributes to the cause of global public health, which has been fully recognized by the WHO and other countries in the world.
Xi said China will continue to strengthen cooperation with Malaysia and other ASEAN countries on prevention and control of the epidemic in an open and transparent manner to jointly safeguard regional public health security.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the prevention and control of the COVID-19 outbreak, making arrangements to take category-specific prevention and control measures, optimize diagnosis and treatment, and accelerate the development of drugs for the scientific prevention and control efforts.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held on the new category of clinically diagnosed COVID-19 cases.
As revealed at the press conference, the new category was created in Hubei Province to define suspected cases with pneumonia-related computerized tomography (CT) scan results as confirmed cases to facilitate early standardized treatment and further improve the recovery rate.
China is strengthening efforts to treat the 13,332 clinically diagnosed cases in Hubei to reduce the number of severe cases and the death rate.
The WHO supported the adoption of the new category, believing it helpful in providing patients with faster clinical care, while citing the resulting rise in confirmed cases not meaning a major change in the trajectory of the epidemic.
・ The U.S. department of health and human services sent a letter to China's NHC to communicate the arrangements of bilateral cooperation in health and epidemic prevention and control.
・ Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Health and Harvard Medical School jointly formed a COVID-19 research team, co-chaired by Chinese respiratory expert Zhong Nanshan and the dean of Harvard Medical School. The team works in four major fields including rapid detection and diagnosis, clinical treatment, drug screening and vaccine development.
Feb. 14
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that President Xi Jinping, also general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, chairman of the Central Military Commission and the head of the CPC Central Committee for Deepening Overall Reform, presided over the 12th meeting of the central committee for deepening overall reform and made an important speech.
Xi stressed safeguarding people's life and health is a major mission of the Party in governing the country, urging efforts to win the battle against the epidemic with scientific and accurate measures, strengthen areas of weakness, and close the loopholes exposed in the current epidemic.
Xi demanded improvement in the mechanism for major epidemic prevention and control and the national public health emergency management system. Excerpts of Xi's speech at the meeting was published by the Qiushi Journal in its fifth issue of 2020.
・ Michael Ryan, executive director of the WHO health emergencies program, refuted remarks by Lawrence Kudlow, the director of the White House National Economic Council, that described the Chinese government's response to the epidemic outbreak as lacking transparency.
Ryan said the remarks did not accord with the facts, as the Chinese government actively cooperated with the WHO and displayed a high level of transparency.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held announcing China's daily new confirmed COVID-19 cases outside Hubei had been dropping for 10 consecutive days.
Feb. 15
・ Chinese State Councilor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi made a speech at the 56th Munich Security Conference, introducing China's decisive measures to combat the COVID-19 epidemic and the notable results it has achieved.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference in Wuhan, briefing the work of epidemic prevention and control and medical treatment in Hubei Province. It was the first of such conferences held in the province by the office amid the epidemic outbreak. The office held three press conferences in Beijing and Wuhan that day.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference in Beijing on epidemic prevention and control related to the return trips of the Spring Festival travel rush.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing updating progress in drug development and scientific research related to the COVID-19.
As revealed at the press conference, seven types of detection reagents have been approved to tap the market, while staged progress has been made in drug screening and treatment, vaccine development and animal model construction.
Feb. 16
・ The China-WHO joint expert team started a nine-day field visit in China, scheduled to inspect cities including Beijing, Chengdu, Guangzhou, Shenzhen and Wuhan.
The team consists of 25 experts from China, Germany, Japan, Republic of Korea (ROK), Nigeria, Russia, Singapore, the United States and WHO.
Foreign experts include senior WHO adviser Bruce Aylward, Tim Eckmanns, researcher with the Robert Koch Institute, Dale Fisher, professor at the National University of Singapore, Chikwe Ihekweazu, head of the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control, Cliff Lane, researcher with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the United States, Jong-Koo Lee, associate professor at Seoul National University College of Medicine, Natalia Pshenichnaia, Aleksandr Semenov, Hitoshi Takahashi, scientist with the National Institute of Infectious Diseases of Japan, Maria van Kerkhove, head of WHO's emerging diseases and zoonosis unit, and Weigong Zhou.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing updating the country's prevention and control situation.
As revealed at the press conference, as of Feb. 15, the proportion of severe and critical cases among all confirmed COVID-19 cases had dropped significantly in China (including Wuhan and Hubei Province).
Feb. 17
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on response to the COVID-19 outbreak, making arrangements to continue the treatment of COVID-19 patients and ensure market supply in Hubei Province, particularly in Wuhan City, and advance orderly resumption of work and production while enhancing epidemic prevention and control.
・ During a working consultation with Estonian officials in Tallinn, the capital of Estonia, a senior official from the Chinese foreign ministry introduced China's progress in prevention and control of the COVID-19, saying China has confidence, ability and certainty to win the battle against the epidemic.
・ At a press conference in Beijing, a Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson introduced China's efforts in sharing information and anti-epidemic cooperation with Japan.
Feb. 18
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with French President Emmanuel Macron at request, noting China not only safeguards the lives and health of the Chinese people, but acts in a highly responsible manner for global public health security.
Xi said China has always been open and transparent in its cooperation with France and other countries to deal with the epidemic, adding that China stands ready to work with France to boost practical cooperation in the health sector and jointly safeguard regional and global public health security.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with British Prime Minister Boris Johnson at request, noting that by upholding the idea of building a community with a shared future for mankind, China is not only responsible for the safety and health of its people, but also committed to the cause of safeguarding international public health.
China has made enormous efforts, and has effectively contained the global spread of the virus, Xi said, adding that the Chinese side will continue to cooperate with Britain and all other countries in an open and transparent manner.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing announcing that the daily new confirmed cases nationwide dropped below 2,000 for the first time on Feb. 17, with that outside Hubei Province below 100 for the first time. Daily death across the country also fell below 100 for the first time.
・ The China-WHO joint expert team traveled to Guangdong and Sichuan provinces for a three-day field investigation on the COVID-19 outbreak.
・ An official of the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs introduced China's progress in prevention and control of the COVID-19 epidemic when meeting with Albanian officials at Tirana, the capital of Albania.
・ An official of the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs met with Greg Gilligan, the new chairman of the American Chamber of Commerce in China, saying the impact of the COVID-19 epidemic is temporary, and the long-term trend of China's economic development has not changed. China welcomes U.S.enterprises to continue their business in China and hopes to strengthen cooperation with the chamber and its members, the official said.
・ China's NHC replied in a letter to U.S. department of health and human services, further communicating on arrangements for bilateral cooperation on health and epidemic control.
Feb. 19
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee to hear reports on the epidemic prevention and control work, and coordinate epidemic control and economic and social development. The meeting decided to submit the relevant measures to the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee for further review.
・ The Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs held the third briefing on epidemic prevention and control online. Ambassadors and diplomats from more than 180 foreign missions in China attended the briefing. China's foreign ministry updated the situation of the COVID-19 outbreak in China and the country's efforts in epidemic prevention and control. The Foreign Affairs Office of the People's Government of Beijing Municipality introduced the latest epidemic control arrangements related to people returning to Beijing from abroad amid the outbreak, which was closely followed by foreign missions in China. Officials from the education and foreign ministries answered questions relevant to foreign students and employees in China.
Feb. 20
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Pakistani Prime Minister Imran Khan at request, stressing facts have proved once again that China and Pakistan are true friends and good brothers that share weal and woe. Xi said China will take good care of its Pakistani brothers and sisters in the country like its own citizens.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with President of the Republic of Korea Moon Jae-in at request, stressing China's forceful prevention and control measures are not only aimed at safeguarding the lives and health of the Chinese people, but also contributing to the world's public health cause. Xi said China will continue to strengthen communication and cooperation with the Republic of Korea and other countries in an open and transparent manner, so as to tackle the epidemic together and promote the health and well-being of people across the world.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping replied in a letter to Bill Gates, co-chair of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, expressing his appreciation toward the foundation's act in supporting China's prevention and control work against the COVID-19 epidemic. Xi called for unity and cooperation in the international community to fight the disease.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on response to the COVID-19 outbreak, making arrangements on further improving protection for frontline medics, accelerating effective applications of drugs and continuing to advance orderly resumption of work and production while enhancing epidemic prevention and control measures in a scientific way.
・ Chinese State Councilor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi attended a special China-ASEAN foreign ministers' meeting, introducing China's progress in epidemic prevention and control.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference in Hubei Province, briefing epidemic prevention and control work organized by the guidance group sent to the province by the CPC Central Committee.
・ When asked at a press conference whether the novel coronavirus is a biological weapon, a spokesperson of the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs said: "What we need in the face of an epidemic is science, rationality and cooperation. We must seek the triumph of science over ignorance, dispel rumors with truth, and replace prejudice with cooperation. We hope the international community, while fighting COVID-19 together, will continue to combat conspiracy theories and other 'political viruses'."
・ Clinical medical experts from China and ASEAN held a video conference to exchange ideas on treatment guidelines and rescue experience on COVID-19 patients.
Feb. 21
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, chaired a meeting of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee on the prevention and control of the COVID-19 and the coordination between the epidemic control and economic and social development.
The meeting called for deepening opening up and international cooperation, enhancing communication and coordination with China's economic and trade partners, and giving priority to helping the leading enterprises that have a significant influence in the global supply chain to resume production and supply to maintain the stability of the global supply chain.
Efforts will be made to make good use of export credit insurance and encourage key export enterprises to resume operation as soon as possible, according to the meeting.
The meeting also highlighted active international cooperation in epidemic prevention and control from the perspective of building a community with a shared future for humanity.
・ The NHC released the fifth version of guidelines on the prevention and control of the COVID-19.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing announcing the daily number of newly cured and discharged COVID-19 patients on Feb.20 in Wuhan outnumbered that of new confirmed cases for the first time, and the daily number of newly cured and discharged COVID-19 patients nationwide surpassed 2,000 for the first time.
Feb. 22
・ The China-WHO joint expert team arrived in Hubei Province for a two-day field investigation on the COVID-19 outbreak.
The experts visited Tongji Hospital, the Wuhan Sports Center that was converted into a temporary hospital, and the provincial CDC to learn about epidemic prevention and control as well as medical treatment. They also talked with officials and experts in the province.
Feb. 23
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Chinese President Xi Jinping stressed unremitting efforts on the prevention and control of the COVID-19 and coordination in advancing economic and social development.
Xi, also general secretary of the CPC Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, made the remarks when delivering an important speech at a meeting in Beijing to advance the work on coordinating the prevention and control of the COVID-19 and economic and social development.
The epidemic situation remains grim and complex and it is now a most crucial moment to curb the spread, Xi noted, asking Party committees and governments at all levels to continue to make unremitting efforts in various prevention and control work and resume work and production in an orderly manner.
Efforts should be made to turn pressure into impetus, turn crises into opportunities, restore the work and life order step by step, Xi said, adding measures should be consolidated to stabilize the employment, finance, foreign trade, foreign capital, domestic investment, and expectations, and intensify policy adjustments to fully unleash the huge potential and strong momentum of China's development and strive to achieve the goals and tasks for economic and social development this year, Xi said.
Xi's speech on the meeting was published that day.
Feb. 24
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on response to the COVID-19 outbreak, helping Wuhan City to further enhance epidemic prevention and treatment and making arrangements on region-and category-based differentiated prevention and control strategies.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing announcing China's daily number of new COVID-19 infections had remained below 1,000 for the five consecutive days.
The number of existing confirmed cases had dropped for nearly a week, while the daily number of newly cured and discharged COVID-19 patients was no less than that of new confirmed infections in all provincial-level regions.
・ An official with the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs talked over phone respectively with ambassadors of Brazil, Chile, Mexico, Colombia, Peru, Trinidad and Tobago and Costa Rica to China, briefing foreign missions on China's epidemic prevention and control work.
・ The China-WHO joint expert team held a press conference in Beijing, during which team members said China's unprecedented public health responses to the COVID-19 outbreak have yielded notable results in slowing the spread of the epidemic and blocking human-to-human transmission of the virus, preventing or at least delaying hundreds of thousands of cases.
・ The China CDC published a paper on The Journal of the American Medical Association, titled "Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China", to describe and analyze the epidemiological characteristics of the 72,314 cases of infection reported through Feb. 11 on the Chinese mainland.
・ The Lancet published an article coauthored by WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus and WHO chief scientist Soumya Swaminathan. The article said Chinese doctors quickly identified the novel coronavirus during the flu season and shared genome sequencing information of the virus with international counterparts through the global scientific research network, which laid the foundation for follow-up scientific research. China's unremitting efforts in preventing and controlling the COVID-19 not only wins precious time for other countries, but also "paves the way "for the international scientific community to jointly deal with the epidemic.
Feb. 25
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi Sheikh Mohammed bin Zayed Al Nahyan at request, noting that the Chinese government has always acted with an open, transparent and responsible attitude, timely shared information, actively addressed the concerns of various parties, and boosted cooperation with the international community.
Xi said China will continue to take effective measures to safeguard the life and health of citizens of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and all other foreign nationals in the country, and stands ready to work with the UAE to maintain close communication on the latest development of the COVID-19 and share experience in epidemic prevention and control.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed at request, noting that African countries and people's various support for China's battle against the COVID-19 outbreak has vividly illustrated the brotherly friendship of sharing weal and woe and helping each other between China and Africa. Xi said African countries are also facing many challenges in epidemic prevention and control, and China is willing to provide them with more medical supplies that are urgently needed, including test kits.
China also stands ready to accelerate the implementation of the health care initiative of the eight major initiatives unveiled during the Beijing Summit of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation, promote the construction of the Africa CDC, and strengthen China-Africa cooperation in public health and disease prevention and control, Xi said.
・ China's NHC shared updated technical guidelines on COVID-19 response with a number of countries and regional organizations.
・ When meeting with Laurent Bili, the French ambassador to China, an official of the Chinese foreign ministry introduced the latest situation of China's notable achievements in fighting COVID-19, stressing that under the strong leadership of President Xi Jinping, the Chinese people are united and have full confidence, capacity and certainty to win the battle against the epidemic.
・ A Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson said at a press briefing that China is willing to share information and experience with Japan and the Republic of Korea in fighting COVID-19 outbreak and offer support and assistance to them according to their needs.
Feb. 26
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. The meeting was briefed by the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the prevention and control work of COVID-19 epidemic, analyzed the current situation and made arrangements for prevention and control measures in the near future.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing on the COVID-19 outbreak in prisons.
An official from the ministry of justice told the press that as of Feb.25, five prisons in Hubei, Zhejiang and Shandong provinces had reported 555 confirmed COVID-19 cases and another 19 suspected cases, four severe confirmed cases, adding that no inmates have thus far died of the virus.
・ Experts from the China CDC participated in the WHO's informal expert consultation teleconference on COVID-19.
・ At a regular press conference, a Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson briefed reporters on COVID-19 infection among foreigners in China.
Feb. 27
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping held talks with Mongolian President Khaltmaa Battulga in Beijing, stressing that by upholding the vision of a community with a shared future for humanity, China is making every effort not only to protect the lives and health of its own people but also to contribute to global public health security.
With an open, transparent and responsible attitude, the Chinese government has actively stepped up international cooperation to fight the outbreak, and China's efforts have been highly affirmed and recognized by the WHO and the international community, Xi said, adding China will continue to work with Mongolia and other countries to fight the epidemic and safeguard regional and global public health security.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the prevention and control work of the COVID-19 epidemic, making further arrangements to reduce mortality and ensure the sufficient supply of daily necessities, demanding more detailed prevention and control measures for vulnerable groups and urging strengthened international cooperation.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing, saying that upon the WHO's notice, COVID-19 cases had been reported in some other countries, and the epidemic is spreading quite quickly in a few countries. China would attach equal importance to joint control measures to effectively prevent imported and exported cases, and strengthen cooperation with relevant international organizations and countries to jointly contain the epidemic.
・ The second China-EU special teleconference on COVID-19 was held for health experts from both sides to have in-depth exchanges on epidemic prevention and control measures, diagnosis and screening, and treatment guidelines.
Feb. 28
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Cuban President Miguel Diaz-Canel at request, stressing that by upholding the vision of a community with a shared future for mankind and with an attitude of openness, transparency and responsibility, China has timely shared information with the WHO and the international community, actively responded to the concerns of various sides, and strengthened international cooperation in the anti-epidemic fight to prevent it from spreading around the world.
The WHO and the international community have spoken highly of China's prevention and control work, Xi said, adding that China is willing to continue exchanges and cooperation with Cuba in the fields of medicine and epidemic prevention and control.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Chilean President Sebastian Pinera at request, noting that the Chinese nation has experienced many ordeals in its history, but has never been overwhelmed.
Xi said the impact of the epidemic on China's economy is temporary and generally manageable, and the fundamentals of China's long-term sound economic growth remain unchanged.
While making unrelenting, solid and meticulous efforts in epidemic prevention and control, China will roll out a series of policies and measures to gradually restore orderly production and life and ensure realization of this year's economic and social development goals, Xi said.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference in Hubei Province on the progress of the epidemic prevention, control work and medical treatment in Hubei under the direction by the guidance team sent by the CPC Central Committee to the province.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing about the prevention, control work and treatment of COVID-19.
As revealed by the NHC at the press conference, the number of newly confirmed COVID-19 cases in Hubei outside Wuhan and that outside Hubei have both dropped to single-digit figures for the first time on Feb. 27. Efforts should not be slackened in prevention and control in communities, medical treatment and other aspects to prevent the epidemic from rebounding.
・ China's NHC participated in the video conference of the Greater Mekong Sub-region's Working Group on Health Cooperation to discuss the challenges and technical needs of epidemic prevention and control.
・ Research teams led by academicians Zhong Nanshan and Li Lanjuan, and researchers from Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital, the Central Hospital of Wuhan, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, the Chinese University of Hong Kong and other institutions jointly published a paper on the New England Journal of Medicine, titled "Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China", analyzing the data of 1,099 COVID-19 patients' treatment.
・ Research teams from Peking Union Medical College and the China CDC published a paper titled "The Pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 in hACE2 Transgenic Mice," which develops an animal model for COVID-19 and helps promote the development of vaccines and drugs.
Feb. 29
・ Voluntary medical experts from the Red Cross Society of China arrived in Iran.
・ The WHO-China Joint Mission published a report about its field study trip on COVID-19 in China. According to the report, in the face of a previously unknown virus, China has rolled out perhaps the most ambitious, agile and aggressive disease containment effort in history. As striking, has been the uncompromising rigor of strategy application that proved to be a hallmark in every setting and context where it was examined. Achieving China's exceptional coverage with and adherence to these containment measures has only been possible due to the deep commitment of the Chinese people to collective action in the face of this common threat. At a community level this is reflected in the remarkable solidarity of provinces and cities in support of the most vulnerable populations and communities.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing about the treatment of COVID-19 and the recovery of patients.
March 2020
March 1
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing about the effective prevention and control in accordance with the law of the imported COVID-19 cases.
March 2
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Chinese President Xi Jinping, also general secretary of the CPC Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, made an inspection tour of the scientific research work for the prevention and control of the COVID-19 epidemic in Beijing.
Xi stressed the COVID-19 research must be taken as a major and pressing task, calling for pooling talents and resources of multiple fields under the united leadership and synergy, accelerating the research and development pace on the basis of adhering to science and ensuring safety, to overcome key and difficult issues in epidemic prevention and control as soon as possible to provide strong scientific and technological support for winning the anti-epidemic war. Xi's speech was published by the Qiushi Journal in its sixth issue of 2020.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on COVID-19 response work, making arrangements of prevention and control work for the next stage, to enhance the caring for the community workers at the response frontline and coordinate the work of epidemic prevention and control and spring farming.
・ A Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson answered questions on imported cases from Russia at a press conference.
March 3
・ China's NHC unveiled the seventh version of guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19, which made modifications and improvements in the transmission routes, clinical features and diagnostic criteria, and emphasized the integration of traditional Chinese and western medicine in treating the disease.
・ Received by China's NHC, Hala Zayed, Egyptian President's special envoy and Egypt's Minister of Health and Population, visited China and met Chen Zhu, vice chairman of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress and president of the Red Cross Society of China.
March 4
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee to analyze major tasks in preventing and controlling the COVID-19 epidemic while stabilizing economic and social development.
・ China's NHC sent letters to the health authorities or organizations of Japan, Iran, the Republic of Korea, Italy, Singapore and Pakistan to express concerns on the current COVID-19 outbreak in these countries and hopes to enhance information sharing and technical cooperation.
・ China's foreign ministry and NHC jointly held a multilateral video conference on COVID-19 with experts from six countries including Azerbaijan and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, to have in-depth exchanges on areas including prevention and control measures, diagnosis and screening, and laboratory testing.
・ The State Council Information Office held a simultaneous press conference in Beijing and Wuhan, linking frontline Chinese experts in Wuhan who introduced the treatment of COVID-19 with reporters in Beijing via video. The whole meeting was in English.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing about promoting production and ensuring supply of important medical treatment equipment for epidemic prevention and control.
・ A research team from Westlake Institute for Advanced Study published an article in the journal Science, titled "Structural Basis for the Recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 by Full-Length Human ACE2", which successfully analyzed for the first time the full-length three-dimensional structure of ACE2, the cellular receptor for the new coronavirus.
・ Experts from China CDC participated in a COVID-19 response teleconference by the WHO's Global Preparedness Monitoring Board.
・ Zhong Nanshan held a video conference with head of the European Respiratory Society to introduce China's anti-epidemic achievements and experience.
March 5
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on COVID-19 response work, ordering more targeted and effective prevention and control measures, demanding the implementation of solid measures to care for the medical personnel fighting on the frontline against COVID-19, and urging efforts to better guarantee the minimum living standard for those people in need.
・ China's foreign ministry and NHC held a video conference with health experts from Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, Armenia, Turkmenistan and the secretariat of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization to share China's anti-epidemic experience.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference in Beijing on international cooperation in combating the COVID-19 outbreak.
An NHC official told the press conference that China had conducted multiple exchanges with the heads of international and regional organizations such as the WHO and health departments of relevant countries, and received a special visit of Egypt's Minister of Health and Population, the special envoy of Egyptian President.
China has timely shared with the world the whole gene sequence, primers and probes of the coronavirus, and shared diagnosis and treatment guidelines and other technical documents with more than 100 countries and over 10 international and regional organizations around the world, said the official.
China has also carried out timely technical exchanges with international and regional organizations, such as the WHO, ASEAN and APEC, as well as Japan, Russia, Germany, the United States and other countries through expert discussions and teleconferences to share China's epidemic prevention and control experience and guidelines, said the official.
An official with Chinese foreign ministry introduced China's international cooperation in fighting the COVID-19 outbreak and answered questions from reporters.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing about the COVID-19 epidemic.
・ As revealed by the NHC at the press conference, two imported cases of novel coronavirus infection were reported on the Chinese mainland on March 4, bringing the accumulated number of imported cases to 20.
From March 5, China began reporting on a daily basis the newly imported COVID-19 cases on the previous day and the total imported cases from overseas.
・ A joint research team from Southern University of Science and Technology and the Third People's Hospital of Shenzhen published an article on bioRxiv, titled "Viral Architecture of SARS-CoV-2 with Post-Fusion Spike Revealed by Cryo-EM", revealing the overall structure of the novel coronavirus.
March 6
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that President Xi Jinping, also general secretary of the CPC Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, attended a symposium on securing a decisive victory in poverty alleviation in Beijing and made an important speech. Xi urged Party committees and governments at all levels to advance the fight against poverty in greater determination and intensity, overcome the impact of the COVID-19 to clinch a complete victory in eradicating poverty and accomplish the great cause that is of tremendous importance both for the Chinese nation and humanity. Xi's speech was published in full text on the same day.
・ China shared with ASEAN, Japan, ROK, Yemen, Iran, Iraq, the United Arab Emirates, EU and other countries and regions videos of press conferences of China's clinical experts.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference in Hubei Province on the progress of the prevention, control, and treatment of COVID-19.
"We made public the information of epidemic prevention and control timely to let the society see the truth," said Ding Xiangyang, deputy secretary-general of the State Council.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing about the latest situation of COVID-19 scientific and technological research and development.
・ NHC spokesperson told the press that among 17 new confirmed cases of COVID-19 reported on March 5 on the Chinese mainland, 16 cases were imported from outside the mainland, warning that China faces rising risk of imported COVID-19 cases.
・ China will continue to deepen international cooperation, timely share information and experience with the WHO and relevant countries, and jointly fight the epidemic, the spokesperson said.
・ The Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson answered questions of reporters, addressing some media's claim that the novel coronavirus is "made in China."
・ According to the spokesperson, the traceability of the virus is still in progress. "Though the first case of COVID-19 was detected in China, it does not necessarily mean that it originated from China. We should jointly oppose 'information virus' and 'political virus.'"
March 7
・ The NHC released the sixth version of guidelines on the prevention and control of COVID-19.
・ A Chinese medical team dispatched by the Red Cross Society of China arrived in Iraq, carrying China-aided COVID-19 prevention supplies.
・ China's NHC shared with Chile the latest version of the guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19 and other technical information, expressing its willingness to conduct technical exchanges online. The commission also shared with key countries and regions the English version of the seventh version of the diagnosis and treatment guidelines.
・ China announced a donation of 20 million U.S. dollars to the WHO to support its international cooperation in the fight against COVID-19.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference in Wuhan City at which members of the guidance group sent by the CPC Central Committee introduced the progress of the COVID-19 prevention and treatment.
March 8
・ The NHC released a manual on prevention and control of COVID-19 for rural residents, which provides guidance and help for them to understand, prevent and control the coronavirus, and improve their self-prevention awareness and personal protection.
・ The NHC instructed medical teams aiding foreign countries to carry out capacity-building in local areas, hold online training on the COVID-19 prevention and control for these teams, along with exercises on the epidemic prevention and control for the medical teams aiding Mozambique, Burkina Faso and Sierra Leone.
March 9
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the COVID-19 response work, making arrangements for deepening international cooperation on epidemic prevention and control, curbing the cross-border spread of the epidemic and pushing for substantial results in relevant work.
・ Chen Zhu, vice chairman of the National People's Congress (NPC) Standing Committee and head of the Red Cross Society of China, held a China-Italy video seminar on the COVID-19 prevention and control at the emergency command center of the China CDC.
・ A spokesperson for the Ministry of Foreign Affairs said at a routine press conference in Beijing that while overcoming its own difficulties, China is willing to provide masks and other medical protection materials to relevant countries to support them in fighting the COVID-19 epidemic and jointly deal with and eventually win the battle.
March 10
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that President Xi Jinping, also general secretary of the CPC Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, went to Wuhan to inspect the prevention and control work at the critical moment of fighting COVID-19.
Xi stressed that the epidemic prevention and control situation in Hubei and Wuhan has seen positive changes and achieved important results in stages through hard work, but the task of the epidemic prevention and control remains arduous.
Xi pointed out that the public must keep a clear mind and be more cautious at this moment, making persistent efforts and great achievements and continuing to take the epidemic prevention and control as the current top priority and the most important work.
Xi also stressed that the whole country must not be careless or weary, and should pay close attention to all kinds of prevention and control work to resolutely win the battles against the coronavirus in Hubei and Wuhan.
Xi's speech was published by the Qiushi Journal in its seventh issue of 2020.
・ China's NHC and the foreign ministry held a TV and telephone conference with 10 South Pacific island countries to exchange the COVID-19 prevention and control technologies, organized experts to introduce China's prevention and control measures and phased achievements, shared disease information, prevention and control experience, and addressed foreign concerns.
・ The NHC recommended experts to participate in the formulation of the WHO gene sequencing guidelines.
March 11
・ The NHC and the foreign ministry jointly held the third China-EU teleconference on the exchange of the COVID-19 prevention and control technologies.
・ The NHC coordinated experts to attend the WHO's conference in America to introduce China's experience in the COVID-19 prevention and control.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing about the COVID-19 epidemic.
As revealed at the press conference, China has seen the daily number of newly confirmed cases and newly suspected cases of COVID-19 ease to double-digit for five consecutive days. Apart from Wuhan, there were two newly confirmed cases in the last five days in China. The overall epidemic situation remained at a relatively low level and the prevention and control situation continued to improve.
However, there are still a large number of confirmed cases in Hubei and Wuhan, and the task of the epidemic prevention and control remains arduous. The rapid development of epidemic abroad also brings uncertainties, according to the press conference.
・ A research team from the China CDC published a paper in the JAMA network, titled "Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Different Types of Clinical Specimens", discovering the cytokine change map and prognosis rule in patients infected with COVID-19 for the first time.
・ Experts from the China CDC were invited to attend 2020 online Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections organized by the International Antiviral Society-USA.
March 12
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres at request, stressing that the hard work of the Chinese people has bought precious time and made important contributions to the prevention and control of the COVID-19 epidemic in countries in the world.
Xi noted that China is willing to share its prevention and control experience with relevant countries, carry out joint research and development of drugs and vaccines, and is providing assistance to some countries where the epidemic has spread.
Xi said China supports the UN and the WHO in mobilizing the international community to strengthen policy coordination and increase resource investment, especially to help developing countries with weak public health systems to prepare for prevention and response.
Xi also said China has announced a donation of 20 million U.S. dollars to the WHO to support its international efforts to combat the epidemic.
Xi stressed that the international community should step up its efforts to effectively carry out international cooperation in joint prevention and control, so as to pool strong synergy in the fight against the epidemic; and that the international community must foster a sense of community with a shared future for mankind, support each other, work together to deal with risks and challenges and build a better planet.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on COVID-19 response work, calling for better region-and category-based measures to prevent and control the COVID-19, ensure supplies according to the changing epidemic situation, and taking more precise and targeted measures to guard against imported and exported cases of infection across the border.
・ The Second Sherpa Meeting of the G20 Riyadh Summit was held in Saudi Arabia, to discuss COVID-19 and its impact on people worldwide and the global economy. A special statement by the sherpas (personal representatives) of the leaders of the G20 on international response to the coronavirus pandemic was issued after the meeting.
・ Heads of China, Japan and ROK CDCs held a conference call on the COVID-19 prevention and control technologies, during which the three parties introduced the current situation of the epidemic prevention and control in their respective countries and exchanged views on specific technical issues.
・ China and the WHO held an international briefing via video chat in Beijing on China's experience in preventing and controlling COVID-19. Representatives of relevant countries' embassies in China and international organizations attended the briefing. Representatives of the WHO Western Pacific Region and relevant countries attended the meeting remotely via video chat.
China and the WHO jointly released the latest English versions of the diagnosis and treatment guidelines and prevention and control guidelines at the briefing.
・ The first batch of Chinese medical experts carrying China-assisted medical supplies arrived in Italy to help with its epidemic prevention and control efforts.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing about the COVID-19, saying the epidemic peak in China has passed as a whole, with the number of new cases declining continuously, and the epidemic situation remaining at a relatively low level.
・ A Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson said that China and Europe have maintained close communication and cooperation since the COVID-19 outbreak, and that China's NHC and CDC have set up a special joint expert group to deal with the epidemic with the European Commission's Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety and the ECDC.
March 13
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping sent messages to the European Council President Charles Michel and European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen, extending sincere sympathies to the EU and the people in all its member countries over the recent outbreak of the novel coronavirus disease.
China firmly supports the European side in combating the COVID-19 epidemic. China is willing to provide assistance to help the European side win the fight against the epidemic at an early date. Upholding the concept of a community with a shared future for mankind, China stands ready to strengthen coordination and cooperation with the European side within bilateral and international frameworks to jointly safeguard global and regional public health security and protect the lives and health of people of both sides and in other countries around the world, Xi said.
・ China and the ROK established a joint prevention and control cooperation mechanism to deal with the epidemic and held the first video conference.
Led by the foreign ministries of these two countries, with the participation of health, education, customs, immigration, civil aviation and other departments, the mechanism aims to implement the important consensus of the heads of these two countries, strengthen communication and coordination between the two sides, carry out joint prevention and control, overcome the epidemic jointly, improve the health and well-being of these two countries' people, and safeguard and promote bilateral exchanges and cooperation.
・ China and 17 central and eastern European countries (CEEC) held a video conference of experts on the COVID-19 prevention and control, during which officials of the China's foreign ministry, NHC, and Chinese experts in disease control, civil aviation, customs and other fields shared information on the fight against the epidemic and exchanging prevention and control experience with government officials and experts from Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia and Czech Republic and other CEEC members.
・ Experts from University of Science and Technology of China and its first affiliated hospital published an article, titled "Pathogenic T cells and inflammatory storm in severe COVID-19 patients."
March 14
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Chinese President Xi Jinping recently sent a message of sympathy to Italian President Sergio Mattarella, expressing sincere sympathies on behalf of the Chinese government and people to the Italian government and people on the recent COVID-19 epidemic in Italy.
Xi stressed that the Chinese government and its people firmly support Italy's fight against the COVID-19 outbreak at this difficult time, and China is willing to cooperate with Italy and offer assistance.
Xi noted that mankind is a community with a shared future and that only through unity and coordination can humanity tackle various global risks and challenges.
Xi said as long as the two countries and the broader international community make joint efforts, they will certainly overcome the current difficulties and prevail over the epidemic at an early date, so as to protect the well-being of people in both countries and across the world.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping recently sent a message of sympathy to Iranian President Hassan Rouhani, expressing heartfelt sympathies on behalf of the Chinese government and people to the Iranian government and people over the epidemic.
Xi noted that the Iranian government and people have provided sincere and friendly support and help for China's fight against the epidemic.
Meanwhile, to help Iran beat the disease, China has offered Iran a batch of anti-epidemic supplies and sent a team of voluntary health experts, Xi said.
Xi stressed that China stands ready to step up cooperation with Iran to contain the epidemic and will continue to provide as much assistance as it can for Iran in the latter's fight against the COVID-19 outbreak, adding he is confident that the Iranian government and people will surely win the battle against the outbreak.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping recently sent a message of sympathy to President of the Republic of Korea Moon Jae-in, expressing heartfelt sympathies on behalf of the Chinese government and people to the ROK government and people in ROK over the epidemic.
Xi noted that epidemics know no borders, and all countries worldwide are part of a community with a shared future, and the Chinese government and people empathize with the ROK in its struggle against the epidemic and related difficulties.
Xi said China will continue to provide as much assistance as it can to the ROK to support the latter's fight against the COVID-19 outbreak, the Chinese side stands ready to join hands with the ROK to win the fight against the epidemic at an early date, so as to protect the lives and health of the people of the two countries and the wider world.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing about the COVID-19 epidemic risk categorization, saying the vast majority of counties on the Chinese mainland have been thus far low-risk through the monitoring of high, medium and low-risk counties. Relevant provinces, municipalities and autonomous regions have published lists of high, medium and low-risk counties.
March 15
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing saying all the new local confirmed cases of COVID-19 came from Wuhan.
As revealed at the press conference, no new local confirmed cases have been reported in cities other than Wuhan for 10 consecutive days. The number of local new confirmed cases in provinces other than Hubei has been in single-digit since Feb. 27 and zero new local confirmed cases has been reported for three consecutive days.
March 16
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Giuseppe Conte, Italian Prime Minister at request. Xi pointed out that China is willing to work with Italy to contribute to international cooperation in fighting the epidemic and building a "healthy Silk Road," believing that the traditional friendship and mutual trust will be further deepened and the all-round cooperation between China and Italy will usher in a broader prospect through this joint fight against the epidemic.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on COVID-19 response work, making further arrangements to improve prevention and control measures and speed up work and manufacturing resumption in all aspects and restore normal economic and social order.
・ The State Council Information Office held press conferences in English simultaneously in Beijing and Wuhan. Experts from the medical team of Peking Union Medical College Hospital aiding Hubei answered questions from foreign media on issues related to the treatment of COVID-19 patients with severe symptoms.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference in Hubei on the scientific treatment of COVID-19 patients with severe symptoms.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing about the prevention and control measures China adopted according to law to guard against imported COVID-19 cases.
March 17
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping held talks with Pakistani President Arif Alvi in Beijing, noting that the COVID-19 epidemic is erupting in many places around the world at present, and all countries should join hands to fight the epidemic.
Upholding the vision of a community with a shared future for mankind, China has timely released the epidemic information and shared prevention and treatment experience openly, transparently and responsibly, Xi said, adding China is willing to make more contributions to prevent the spread of the epidemic worldwide and will continue to provide support and assistance to Pakistan.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Spanish Prime Minister Pedro Sanchez at request, stressing that China's prevention and control measures have achieved positive results and have stepped out of the most difficult and most arduous stage through the hard work of the whole country.
Xi said as the epidemic has spread in many countries, China is willing to carry out international cooperation with other countries and provide assistance within its capabilities.
Xi hoped that the international community will work together to turn crises into opportunities, resist the impact of the epidemic with open and cooperative practical actions, and jointly safeguard international health security.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing to introduce the latest research and development of vaccines and detection reagents.
・ China, Japan, and the ROK held a teleconference among heads of their COVID-19 response departments. The three parties introduced the epidemic situation and measures in their respective countries and exchanged in-depth views on strengthening cooperation in the epidemic prevention and control. They believed that they should jointly prevent the spread of the epidemic and strengthen joint prevention and control.
・ China began supplying 14 kinds of domestic test kits to 11 countries, with the first batch of test kits donated by China to Cambodia arrived in Phnom Penh.
March 18
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee to analyze the situation of the COVID-19 epidemic prevention and control as well as the economy at home and abroad, and make arrangements for coordinating the epidemic prevention and control with key work of economic and social development.
Xi urged closer cooperation with the international community on epidemic prevention and control, stressing China will keep its close cooperation with the WHO to strengthen the analysis and prediction of the changes in the global epidemic situation, improve strategies and policies to cope with imported risks, boost exchanges and cooperation with other countries on epidemic response, and continue to offer assistance to the best of China's ability.
・ Chinese Premier Li Keqiang talked over phone with European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen, saying under the current circumstances, China stands firmly with the EU and supports its anti-epidemic efforts.
Li said China will facilitate its procurement of medical supplies through commercial channels, adding that China is also ready to actively carry out international cooperation to jointly protect the health of the humankind.
・ Chinese Premier Li Keqiang spoke over phone with Bulgarian Prime Minister Boiko Borisov at request.
Li said China is willing to enhance exchanges of anti-epidemic experience with Bulgaria, provide assistance within China's capability to help it contain the spread of COVID-19, and provide necessary facilitation to the Bulgarian side in its procurement of medical supplies through commercial channels.
・ The second group of Chinese medical experts arrived in Italy, carrying nine tonnes of medical supplies donated by China, including ventilators, infusion pumps, monitors and testing reagents.
・ China and Africa held a video conference on COVID-19 epidemic prevention and control. Attendees of the online meeting were about 300 officials, health experts from 24 African countries, including health ministers from Ethiopia, Kenya and Liberia, and WHO representatives in some countries.
・ China and Mongolia held a video meeting on the COVID-19 epidemic, at which China shared its anti-epidemic technologies and experience in epidemic prevention and control, had in-depth exchanges in epidemic situation, prevention and control measures, screening and diagnosis, and treatment guidelines.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing announcing that Chinese mainland reported for the first time on March 17 no new suspected domestic cases of COVID-19. Hubei Province had seen no new confirmed cases for 13 consecutive days in cities and prefectures outside Wuhan.
・ Zhong Nanshan said at a press conference in Guangzhou that China has proved the effectiveness of containment measures in high outbreak regions and public prevention and control measures in other regions.
March 19
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping spoke over phone with Russian President Vladimir Putin at request, reaffirming that China stands ready to work with Russia and other countries to step up international cooperation against the COVID-19 epidemic for the vision to build a community with a shared future for humanity.
Xi called for closer international cooperation in epidemic prevention and control, experience sharing on containment and treatment, and facilitation of joint research, to cope with the common threat and challenge, and safeguard global public health security.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the COVID-19 epidemic response, making arrangements to optimize prevention and control measures, precisely curb cross-border transmission of COVID-19, and actively promote the orderly resumption of work and production.
・ An inspection team of the National Supervisory Commission released the report of an investigation into issues related to doctor Li Wenliang, an ophthalmologist with the Central Hospital of Wuhan. Following the report, Wuhan Public Security Bureau decided to revoke the previous reprimand letter and apologized to Li's family over the mistake.
・ China's foreign ministry and NHC jointly held a China-Europe video meeting with 18 European countries including Britain, France, Germany, Italy, Spain and Switzerland, introducing China's experience of COVID-19 outbreak prevention and control for European officials and medical specialists.
・ The NHC held a meeting with the Embassy of Japan in China to exchange views in building clinical and epidemic prevention mechanism of joint response to COVID-19 epidemic.
Shanghai Municipal Health Commission and Health Commission of Anhui Province held video meetings with specialists from Costa Rica and South Sudan, respectively, to exchange on epidemic prevention and control.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing saying that no new confirmed and suspected COVID-19 cases were reported for the first time on the Chinese mainland on March 18.
No new death was reported outside Hubei Province, and the number of severe cases dropped by two. No new confirmed local cases had been reported outside Hubei on the Chinese mainland for seven consecutive days, as revealed by the press conference.
The risk of imported COVID-19 cases was on the rise due to the rapid spread of the epidemic globally, thus the task to prevent imported risk must be implemented, according to the press conference.
・ Specialists from the China CDC participated in a teleconference with the WHO and the Global Outbreak Alert and Response Network (GOARN) to introduce China's experience on COVID-19 prevention and control.
・ Zhong Nanshan attended an international sharing and exchange meeting on epidemic prevention and control experience, calling for high attention to 100 the spread of novel coronavirus in a number of countries, saying it's crucial to carry out early detection, early quarantine, early diagnosis and early treatment to control the epidemic.
March 20
・ Upon the initiative of China, Chinese State Councilor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi held a special video conference on COVID-19 with ROK Foreign Minister Kang Kyung-wha and Japanese Foreign Minister Toshimitsu Motegi. They had an in-depth exchange of views on joint response to the epidemic.
・ China's NHC and foreign ministry held a video meeting with 19 countries from Europe and Asia to provide a platform for specialists to exchange and share technologies for the prevention and control of the COVID-19 epidemic.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing, announcing that no new confirmed or suspected COVID-19 cases were reported on the Chinese mainland on March 19. It was the first time of such zero report on the Chinese mainland since it started the nationwide battle against the coronavirus.
・ Specialists from the China CDC attended a teleconference organized by the WHO on COVID-19 vaccine research.
March 21
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Chinese President Xi Jinping recently sent a message of sympathy to Spanish King Felipe VI, expressing sincere sympathies on behalf of the Chinese government and people to the Spanish government and people over the recent COVID-19 outbreak in Spain.
Xi noted that China firmly supports Spain's efforts and measures in fighting the epidemic, and stands ready to share prevention and control experience as well as diagnostic and treatment guidelines, and provide assistance and support within its capacity.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping recently sent a message of sympathy to Serbian President Aleksandar Vucic, expressing sincere sympathies on behalf of the Chinese government and people to the Serbian government and people over the recent COVID-19 outbreak in Serbia.
Xi stressed that China firmly supports Serbia's efforts against the epidemic, and will provide Serbia with assistance in protective equipment and medical instruments, and help it purchase urgently needed supplies in China.
China will also send a group of medical experts to help it better contain the COVID-19 epidemic, so as to protect the life, health and well-being of the Serbian people.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping recently sent a message of sympathy to German Chancellor Angela Merkel, stressing China firmly supports Germany's endeavor in combating the epidemic and is willing to provide assistance within its capacity if there is a need from the German side.
Xi noted by upholding the vision of building a community with a shared future for mankind, China stands ready to continue sharing information and experience with Germany, and strengthening cooperation in such areas as epidemic prevention and control, treatment of patients, and vaccine research and development, so as to jointly protect the health and well-being of people not only in both countries but in the rest of the world.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping recently sent a message of sympathy to French President Emmanuel Macron, noting the Chinese government and people firmly support France's efforts against the COVID-19 epidemic, and stand ready to boost cooperation with France and jointly win the battle through mutual support and help.
Xi said China is willing to make concerted efforts with France to enhance international cooperation in epidemic prevention and control, support the UN and the WHO playing a core role in improving global public health governance, and build a community of common health for mankind.
March 22
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing underscoring the importance of implementing prevention and control measures in quarantine, transfer, treatment and isolation to curb the imported COVID-19 cases as the pandemic is affecting more than 180 countries and regions.
・ A Chinese medical team carrying ventilators, medical masks, test kits and other medical materials arrived in Serbian to help it battle the novel coronavirus.
March 23
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with French President Emmanuel Macron, introducing upon request the situation of the COVID-19 epidemic prevention and control in China.
Xi stressed both China and France shoulder the arduous responsibility of safeguarding international and regional public health security, suggesting that both countries carry out sincere cooperation to promote joint research programs, strengthen cooperation in frontier health and quarantine inspection, support the work of the WHO, jointly help African countries enhance epidemic prevention and control, and strive to build a community of common health.
Xi said China stands ready to work with France to encourage all relevant parties to step up coordination and cooperation within such frameworks as the UN and G20, engage in joint prevention and containment, improve global health governance, help developing countries and other countries in need with capacity-building, and cushion the epidemic's impact on the world economy.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Egyptian President Abdel-Fattah al-Sisi, noting facts have shown once again that mankind is a community that shares weal and woe. All countries must unite and work together to jointly cope with the COVID-19 epidemic.
Xi said by upholding the vision of a community with a shared future for humanity, China will work with other countries to step up international cooperation in epidemic prevention and control, jointly address common threats and challenges, and safeguard global public health security.
Noting that Egypt is also facing the urgent task of battling the epidemic, Xi said China is willing to share with Egypt the epidemic-related information, experience on prevention and treatment, and medical research results, and provide it with medical supplies to support its prevention and control efforts to jointly beat the disease.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with British Prime Minister Boris Johnson, introducing upon request China's epidemic prevention and control measures. Xi stressed that China hopes Britain will enhance coordination with China to minimize the risk of the epidemic's spread while ensuring necessary flow of people and trade.
Xi called on all nations to push forward cooperation within the frameworks of the UN and G20, enhance the exchange and sharing of information and experience, boost collaboration in scientific research, support the WHO in playing its due role, improve global health governance, increase macro-economic policy coordination so as to stabilize the market, maintain economic growth, safeguard people's well-being, and keep the global supply chains open, stable and safe.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee on the COVID-19 epidemic response, making arrangements to prevent imported infections and COVID-19 rebound at home according to changes in the epidemic situation, actively advance the resumption of work and production in order while keep prevention and control effective.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing, announcing Hubei Province and Wuhan City had reported zero new confirmed and suspected case for five straight days, with the number of existing confirmed cases declining continuously. A health official told the press conference that zero report of new cases does not mean there is no risk, thus it's still arduous to prevent and control the epidemic.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference in Hubei, introducing the importance and effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in treating COVID-19. Zhang Boli, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering noted that TCM had remarkably reduced the proportion of patients with mild symptoms turning to severe cases.
・ A team of Chinese medical experts carrying a batch of medical materials aided by China arrived in Cambodia to help it fight the COVID-19.
March 24
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Kazakh President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, noting that in the battle against the current global public health crisis, the urgency and significance of building a community with a shared future for humanity have become even greater. Only with solidarity and cooperation can the international community prevail over the pandemic and safeguard the planet.
Xi said China is ready to work with Kazakhstan and other countries to strengthen international cooperation against the pandemic and safeguard global public health security.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Polish President Andrzej Duda, reiterating China's firm support to the Polish government and people in combating the COVID-19 epidemic. Xi noted China had held a video conference of health experts with Poland and other Central and Eastern European countries (CEECs) to timely share information and relevant measures on epidemic prevention and control.
Xi said by upholding the vision of a community with a shared future for humanity, China is willing to enhance cooperation with other countries to fight the epidemic and safeguard global public health security.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Brazilian President Jair Bolsonaro at request, noting that the COVID-19 broke out in many parts of the world and was spreading rapidly and the top priority now is for countries to strengthen cooperation.
Xi said by upholding the vision of building a community with a shared future for mankind, and with an open, transparent and responsible attitude, China has timely released epidemic information and shared experience in prevention, control and treatment with the WHO and the international community without reserve, and doing its best to provide assistance for other parties.
Xi stressed that the international community has already recognized that China made enormous sacrifices in the fight against COVID-19 and bought precious time for the world.
・ Chinese authorities and experts interacted via a video conference with health professionals across Latin America and the Caribbean states, sharing COVID-19 prevention and control experience. Attendees were about 200 officials and experts from 25 countries and representatives from the WHO, UNICEF, Pan American Health Organization and Inter-American Development Bank.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing with disease control specialists and medical experts introducing the COVID-19 prevention, control and clinical diagnosis information. As revealed at the press conference, spreading risks of sporadic COVID-19 cases and imported cases still exist, thus the prevention and control work should not be taken lightly.
March 25
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, presided over a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee to hear reports of the epidemic prevention and control and the current economic situation, and study responsive measures.
The meeting decided to submit the measures to the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee for further review.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with German Chancellor Angela Merkel, stressing China firmly supports Germany in its fight against the COVID-19 epidemic and is willing to continue to provide assistance within China's capacity.
Xi said that the Chinese and German experts have already had video exchanges, and German experts have also travelled to China with the WHO expert team.
Xi said China is willing to share with Germany its experience in prevention, control and treatment, strengthen cooperation in vaccine and drug research and development, and contribute to the health and well-being of both peoples and global public health security.
In the battle against the outbreak, the strength of solidarity and cooperation between China and Germany, between China and the EU, have displayed positive energy, Xi said, adding China is ready to work with Germany and other sides to step up coordination and advocate the spirit of sharing the same boat and jointly fight the epidemic, so as to shore up confidence in the international community.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing asking for efforts to strictly prevent imported infections and epidemic rebound at home.
・ A new PCR lab assisted and built by China was inaugurated in Baghdad, Iraq, to increase the testing capacity to contain COVID-19 in the war-torn country.
・ Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Health plans to sign with American pharmaceutical company Gilead Sciences on China-led evaluation research of medicine Remdesivir.
March 26
・ Via video link in Beijing, Chinese President Xi Jinping delivered a speech titled "Working Together to Defeat the COVID-19 Outbreak "at the Extraordinary G20 Leaders' Summit.
Stressing the outbreak is spreading worldwide and the situation is disturbing and unsettling, Xi said it's imperative for the international community to strengthen confidence, act with unity and work together in a collective response to win the battle against such a major infectious disease for humanity.
Guided by the vision of building a community with a shared future for mankind, China will be more than ready to share its good practices, provide assistance in its capacity to countries hit by the growing outbreak, and contribute to the stability of the world economy, Xi said.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping wrote in a reply letter to WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, saying China has always supported the global COVID-19 containment efforts with concrete actions, and has offered assistance to the WHO and other international organizations, as well as more than 80 countries. Xi said China will continue to provide support for the international community in combating COVID-19 epidemic.
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee COVID-19 response work, calling for strict implementation of measures to prevent the rebound of the epidemic within the country and efforts to step up measures to guard against risks of imported cases by land and water.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing announcing that 23 provincial-level regions reported confirmed imported cases of COVID-19 on March 25.
As revealed by the press conference, pressure remains huge to prevent the spread of the epidemic, and people should prepare for more persistent prevention and control efforts.
・ China's third medical team carrying ventilators, medical monitors, masks and other medical supplies arrived in Italy via chartered flight to help Italy fight the COVID-19 outbreak.
・ China held a video meeting on COVID-19 pandemic with medical experts and health officials from the West Asian and North African countries. About 200 participants from the Gulf Cooperation Council and 16 countries including Egypt, Algeria, Palestine, Lebanon, Kuwait and Qatar joined the online meeting.
・ According to the data of China International Development Cooperation Agency, China has thus far provided four batches of anti-pandemic aid for 89 countries and four international organizations, while the fifth batch of aid program was being developed.
March 27
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, chaired a meeting of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee to analyze the COVID-19 response and economic performance.
The meeting made new arrangements on coordinating the COVID-19 response and economic and social development.
China will deepen exchange and cooperation with the WHO and continue to provide assistance within its ability to other countries, according to the meeting.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with Saudi King Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud, stressing viruses respect no national borders, and only by cooperation and with a collective response can the international community prevail over them.
Xi said the G20 major economies should uphold the vision of building a community with a shared future for mankind, and strengthen unity, coordination and cooperation to resolutely stem the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic and stabilize the world economy with all their strength.
Xi noted that with the king's presiding, G20 leaders successfully held an extraordinary summit on COVID-19 on March 26, and reached important consensus on fighting the pandemic in solidarity and stabilizing the world economy, which has sent a positive signal to the international community.
Xi stressed that China is ready to maintain close communication with Saudi Arabia and strengthen the momentum of G20 cooperation.
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping talked over phone with U.S. President Donald Trump at request, stressing that China has been timely sharing information on COVID-19 in an open, transparent and responsible manner with the WHO and countries including the United States since the onset of the epidemic. China, Xi said, wasted no time in releasing such information as the genetic sequence of the coronavirus, and has also been sharing experience on COVID-19 prevention, containment and treatment without reserve, and providing as much support and assistance as it can for countries in need.
Xi said China will continue to do so, and work with the international community to prevail over the pandemic.
・ Chinese Premier Li Keqiang talked over phone at request over the COVID-19 pandemic with Croatian Prime Minister Andrej Plenkovic, whose country holds the rotating EU presidency, and with Austrian Chancellor Sebastian Kurz, respectively.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing announcing that the number of the close contacts under medical observation had been increasing for seven consecutive days, with the number reported on March 26 jumping 78 percent than that on March 19.
The combination of emergency and normalized measures should be improved to accurately prevent and control the domestic epidemic and take strict precautions against the virus spreading.
・ China's NHC head Ma Xiaowei attended a COVID-19 pandemic information briefing held by the WHO, sharing experience of fighting against the virus and answering questions from other countries. More than 500 people from the countries like Russia, Brazil, Egypt and Qatar attended the online meeting.
March 28
・ A Chinese medical expert team carrying medical supplies arrived in Pakistan to help it fight COVID-19.
・ Invited by the European Respiratory Society, Wang Chen, vice president of the Chinese Academy of Engineering and also a medical specialist of respiratory and critical disease, attended a video connection and shared the health policies of the COVID-19 prevention and control with European physicians and health administrators.
March 29
・ Chinese President Xi Jinping, also general secretary of the CPC Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, made an inspection tour for COVID-19 control and work resumption in east China's Zhejiang Province from March 29 to April 1, according to a Xinhua News Agency report.
Xi called for the full implementation of the decisions and arrangements by the CPC Central Committee, while coordinating efforts for COVID-19 prevention and control, and economic and social development.
・ Under the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council, a press conference was held in Beijing announcing that local transmission of COVID-19 has been basically blocked on the Chinese mainland, and China will continue efforts to guard against the dual risks of sporadic domestic cases and imported cases.
・ A team of Chinese medical experts carrying medical supplies, such as treatment machines, protective materials, traditional Chinese and western medicines, arrived at Laos to assist the country's fight against the COVID-19 outbreak.
March 30
・ Xinhua News Agency reported that Li Keqiang presided over a meeting of the leading group of the CPC Central Committee COVID-19 response work, urging efforts to consolidate prevention and control measures to focus on the prevention and control of cases of infections that show no symptoms.
・ The International Department of CPC Central Committee and the secretariat of the International Conference of Asian Political Parties (ICAPP) standing committee co-hosted an online seminar about jointly fighting against the COVID-19, aiming to promote the exchange and dialogue among Asian political parties in epidemic prevention and control via online communication, and boosting experience sharing and cooperation among Asian countries.
・A team of Chinese medical and scientific experts carrying test kits, medical protective equipment, medicines and other China-donated medical supplies arrived in Caracas, capital of Venezuela, to help fight COVID-19.
・ Invited by the American College of Chest Physicians, Chinese medical experts attended a network forum of COVID-19 with their American counterparts and shared experience in fighting against the virus.
・ Upgraded by Chinese enterprises, Zimbabwe's main COVID-19 quarantine and treatment center, Wilkins Hospital, was completed and delivered to Zimbabwe.
・ China's NHC head Ma Xiaowei talked over phone with the U.S.secretary of health and human services Alex Azar on the implementation of principles agreed by the heads of state of China and the United States in a telephone conversation on March 27, sharing China's latest epidemic prevention and control situation and exchanging views for further cooperation.
March 31
・ Chinese Premier Li Keqiang talked over phone with Algerian Prime Minister Abdelaziz Djerad at request, saying the COVID-19 epidemic is spreading in the Middle East region and China feels keenly for it. Li said China stands firmly with Algeria, and is willing to provide support within its capacity and share its anti-virus experience.
・ Chinese Premier Li Keqiang talked over phone with Irish Prime Minister Leo Varadkar at request, saying China firmly supports Ireland's efforts in the fight against the disease, and is willing to provide Ireland with necessary assistance within its capacity. Li said China is also ready to facilitate Ireland's procurement and transportation of medical supplies from China, enhance exchanges of experience on epidemic prevention and treatment, and carry out cooperation in medical research and development.
・ The State Council Information Office held a press conference in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, and answered questions about the COVID-19 epidemic prevention and control, treatment of severe patients, resumption of normal medical order in the province and international cooperation of epidemic prevention and control.
・ A Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson told a press conference in Beijing that the Chinese government had provided material assistance including medical masks, N95 masks, protective suits, nucleic acid testing reagent and ventilators to 120 countries and four international organizations.
Local governments had donated medical supplies to more than 50 countries. And the Chinese enterprises donated medical supplies to more than 100 countries and international organizations.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Headlines
U.S. economy deteriorating faster than anticipated as 80 million Americans are forced to stay at home (Washington Post) The U.S. economy is deteriorating more quickly than was expected just days ago as extraordinary measures designed to curb the coronavirus keep 84 million Americans penned in their homes and cause the near-total shutdown of most businesses. The resulting economic meltdown, which is sending several million workers streaming into the unemployment line, is outpacing the federal government’s efforts to respond. With each day, an unprecedented stoppage gathers force as restaurants, movie theaters, sports arenas and offices close to shield themselves from the disease.
Dramatic slowdown in growth predicted (Wall Street Journal) Analysts now project U.S. growth could shrink at rates far worse than the 2008 global recession, ending weeks of cautious optimism about the economy’s ability to withstand the fallout from the coronavirus. Analysts at Goldman Sachs yesterday said they expect U.S. growth to contract 24% in the second quarter, a rate nearly five times as large as the bank’s previous forecast of a 5% decline. Goldman said a decrease of that magnitude would far outpace the largest quarterly drop in gross domestic product on record--during the first quarter of the 1958 recession, when the U.S. economy contracted 10%. “The sudden stop in U.S. economic activity in response to the virus is unprecedented, and the early data points over the last week strengthen our confidence that a dramatic slowdown is indeed already underway,” the bank said in its report.
Italy virus cases soar again; NY eyes temporary hospitals (AP) The coronavirus pandemic took an increasingly bleak toll Saturday in the U.S. and Europe, producing staggering caseloads in New York and Italy and setting off a desperate scramble to set up thousands of additional hospital beds at convention centers and college campuses. Italy, at the heart of western Europe’s rampaging outbreak, announced 793 new deaths and 6,557 new cases. In New York, Gov. Andrew Cuomo said state officials were scouring the globe for desperately needed medical supplies as confirmed coronavirus cases soared above 10,000 statewide. The state is reviewing four possible locations for temporary hospitals, which would be operated by the Army Corps of Engineers.
As virus grips nation, advocates move to halt evictions (AP) On Wednesday, President Donald Trump announced a proposed $1.5 trillion package that he said includes “immediate relief to renters and homeowners” by suspending evictions and foreclosures for 60 days. But, it turns out, the vast majority of renters will not be covered by the protections. That’s because the Department of Housing and Urban Development’s plan only covers single-family homes with loans through the Federal Housing Administration--roughly 8 million homeowners, most of whom are not under foreclosure, according to HUD. That compares to the roughly 43 million households who rented in 2019, according to the U.S. Census. Roughly half rent their home from an individual investor, while the other half rent from a business or multi-unit property owner. The ones renting from a business will not receive any protections, according to HUD’s proposal. While housing advocates praised the Trump administration package as an “important first step,” they said that by excluding renters, an often economically vulnerable population, it does not go nearly far enough.
The drive-in, relic of yesterday, finds itself suited to now (AP) The drive-in theater, long a dwindling nostalgia act in a multiplex world, is experiencing a momentary return to prominence. With nearly all of the nation’s movie theaters shuttered due to the coronavirus pandemic, some drive-in owners think they’re in a unique position to give moviegoers a chance to do something out of the house while keeping distance from others. This weekend, some drive-ins aren’t the only show in town. They’re the only show in the country.
Guatemala orders eight-day curfew to fight coronavirus (Reuters) Guatemala’s President Alejandro Giammattei on Saturday ordered an eight-day curfew starting Sunday as part of measures aimed at containing the coronavirus, which has infected 17 people in the Central American nation.
Brazil’s densely packed favelas brace for coronavirus (Washington Post) In Liberia, the 2014 outbreak of Ebola was fueled by conditions in the slums of Monrovia. In India, influenza propagates more rapidly in the poorest neighborhoods, which then feed back into the city at large. And in Brazil, even the mosquito-borne disease of Zika was far more concentrated in the favelas of the north, around the city of Recife. Now in the global war against the coronavirus, analysts believe some of the most important battles will be fought in the poorest parts of the developing world, with far fewer tools and far less capacity for isolation than higher-income countries. “The strategy being pushed in the United States and China and Korea, there is no strategy for that there,” said Madhav Marathe, a division director of the University of Virginia’s Biocomplexity Institute. “Once a disease enters a slum, it’s very hard to do social distancing. Once it’s in slum, it’s very hard to protect them.”
Much of Europe is now on lockdown. But can authorities actually enforce those rules? (Washington Post) In a time when Europeans and Americans have been told to practice “social distancing” and to remain at home, people were still out and about in France and across Europe. They were shopping in proximity at bustling market stalls, running in large numbers down public promenades and, in some cases, scoffing at various government restrictions designed to keep them safe. Over the past week, a number of European governments have urged their citizens to take coronavirus seriously by imposing strict limits on movement outside the home. The question now is how governments can actually enforce those rules, with so many people seemingly willing to break them.
China, on virus PR offensive, sends masks and experts abroad (AP) As the fight against a new virus shifts to Europe and beyond, China is supplying millions of masks and other desperately needed items to struggling governments, hoping to build political ties and defuse criticism that it allowed the disease to spread early on. Serbia’s president plans to be at the airport this weekend to welcome a shipment of medical supplies from his “brother and friend,” Chinese leader Xi Jinping. Xi’s government has flown gloves and protective clothing to Liberia. It is sending 100,000 test kits to the Philippines. More than 10 flights carrying millions of masks and other supplies are bound for the Czech Republic this week. It’s part of an effort by the Communist Party to reshape the narrative, from one of early missteps to a nation that acted decisively to bring the outbreak under control. China is touting its deliveries of ventilators and masks overseas and dispatching its medical experts to share the lessons of its success.
Australia’s Bondi Beach closed after crowds defy coronavirus rules (Reuters) Australian officials closed Sydney’s iconic Bondi Beach on Saturday after thousands of people flocked there in recent days, defying social distancing orders to prevent the spread of the coronavirus, amid an unusually warm autumn spell.
Israeli leader offers to step down next year in unity deal (AP) Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu says he is ready to step down next year as part of a proposed power-sharing agreement with his chief rival meant to steer the country through the coronavirus crisis and end a year-long political deadlock.
Thousands of Americans stranded abroad as money, patience run out (Washington Post) Daniel Rico was relaxing in his pajamas in a hotel room after a day biking through Peru’s Sacred Valley when his phone rang. The Peruvian president was about to make an announcement related to the coronavirus pandemic, his tour guide said. Rico went online and saw that Peru’s borders would close in roughly 24 hours.
Minutes later, the 33-year-old financial analyst from New Jersey and a handful of other foreigners were being driven hastily in the dark along winding Incan roads. But when Rico arrived at the Cusco airport at 2 a.m. Monday morning, he found thousands of other travelers clamoring to leave and no available tickets. Skirmishes broke out as people pushed to the front of the line, he said.
Rico and nine other Americans are now stuck in a hotel in downtown Cusco, where a 15-day quarantine is enforced by soldiers with face masks and rifles. A police officer recently shoved Rico against a wall, he said, and threatened to arrest him for going out to buy groceries.
“Things are getting bad here,” said Rico, whose wife is worriedly waiting for him at home. “Fly me to Texas or Louisiana. Drop me in Wyoming, and I’ll rent a car. But we need to get out of this country.”
From Cusco to Casablanca to Cape Town, thousands of Americans like Rico are currently stuck overseas as the rapidly expanding pandemic has caused a cascade of countries to close their borders.
As their money, medications and patience runs out, Americans have watched in mounting frustration as other countries have quickly evacuated their citizens. Feeling abandoned by their government, thousands have turned to social media for help and solace, joining online groups with names like “Americans Stuck in Peru,” “American Citizens Stranded In Guatemala” and “Stay Strong, Quarantine On.”
Their sense of panic deepened on Thursday when the State Department announced American citizens overseas should return to the United States immediately “unless they are prepared to remain abroad for an indefinite period.”
The announcement, coupled with the initial lack of a plan to help Americans come home, has drawn criticism from lawmakers whose inboxes are filling with emails from furious constituents trapped overseas.
“This is a source of great frustration,” Sen. Chris Van Hollen (D-Md.) told The Washington Post. “This administration has made a mess of this by failing to take the necessary actions. We’ve been working for weeks to try to get these Americans who are stranded abroad a way to get home. We’ve watched as other countries have chartered airlines to get their citizens out.”
1 note
·
View note
Text
Investigadores del Malbrán lograron secuenciar el genoma completo SARS –COV-2
🌎 #Nacionales | #Ciencia | #Salud | #Coronavirus 📬 Investigadores del #InstitutoMalbrán lograron secuenciar el #genoma completo #SARSCOV2 💻
[su_pullquote]Científicos y técnicos de la Administración Nacional de Laboratorios e Institutos de Salud (ANLIS), Doctor Carlos G. Malbrán, lograron secuenciar de forma exitosa el genoma completo SARS COV-2, lo que será útil para asegurar la calidad del diagnóstico, complementar la vigilancia epidemiológica y contribuir al desarrollo de una vacuna representativa.[/su_pullquote] Los expertos del In…
View On WordPress
#Administración Nacional#Alemania#ANLIS#Argentina#coronavirus#COVID-19#Doctor Carlos G. Malbrán#ecuenciación Genómica#GISAID#Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data#Instituto Malbrán#Institutos de Salud#laboratorios#pandemia#SARS COV-2#virus de la influenza#virus humanos
0 notes
Text
Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Resistance After Antiviral Treatment - Published Sept 26, 2024
Key Points Question Is there an increased frequency of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral resistance in individuals receiving antiviral therapy?
Findings In this cohort study with 156 participants, nirmatrelvir resistance mutations were detected more often in individuals who were treated with nirmatrelvir, especially those who were immunosuppressed, compared with untreated individuals. However, all mutations were present at relatively low frequencies, appeared transiently, and were unlikely contributors to instances of virologic rebound.
Meaning In this study, the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 strains with resistance to nirmatrelvir after treatment was rare, irrespective of virologic rebound.
Abstract Importance Previous studies have identified mutations in SARS-CoV-2 strains that confer resistance to nirmatrelvir, yet how often this resistance arises and its association with posttreatment virologic rebound is not well understood.
Objective To examine the prevalence of emergent antiviral resistance after nirmatrelvir treatment and its association with virologic rebound.
Design, Setting, and Participants This cohort study enrolled outpatient adults with acute COVID-19 infection from May 2021 to October 2023. Participants were divided into those who received antiviral therapy and those who did not. The study was conducted at a multicenter health care system in Boston, Massachusetts.
Exposure Treatment regimen, including none, nirmatrelvir, and remdesivir.
Main Outcomes and Measures The primary outcome was emergent SARS-CoV-2 antiviral resistance, defined as the detection of antiviral resistance mutations, which were not present at baseline, were previously associated with decreased antiviral efficacy, and emerged during or after completion of a participant’s treatment. Next-generation sequencing was used to detect low frequency mutations down to 1% of the total viral population.
Results Overall, 156 participants (114 female [73.1%]; median [IQR] age, 56 [38-69] years) were included. Compared with 63 untreated individuals, the 79 who received nirmatrelvir were older and more commonly immunosuppressed. After sequencing viral RNA from participants’ anterior nasal swabs, nirmatrelvir resistance mutations were detected in 9 individuals who received nirmatrelvir (11.4%) compared with 2 of those who did not (3.2%) (P = .09). Among the individuals treated with nirmatrelvir, those who were immunosuppressed had the highest frequency of resistance emergence (5 of 22 [22.7%]), significantly greater than untreated individuals (2 of 63 [3.1%]) (P = .01). Similar rates of nirmatrelvir resistance were found in those who had virologic rebound (3 of 23 [13.0%]) vs those who did not (6 of 56 [10.7%]) (P = .86). Most of these mutations (10 of 11 [90.9%]) were detected at low frequencies (<20% of viral population) and reverted to the wild type at subsequent time points. Emerging remdesivir resistance mutations were only detected in immunosuppressed individuals (2 of 14 [14.3%]) but were similarly low frequency and transient. Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data analysis showed no evidence of increased nirmatrelvir resistance in the United States after the authorization of nirmatrelvir.
Conclusions and Relevance In this cohort study of 156 participants, treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations were commonly detected, especially in individuals who were immunosuppressed. However, these mutations were generally present at low frequencies and were transient in nature, suggesting a low risk for the spread of nirmatrelvir resistance in the community with the current variants and drug usage patterns.
#mask up#covid#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#wear a respirator#still coviding
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
The coronavirus is speaking.
Eric Topol is a professor of molecular medicine at Scripps Research.
It's saying it's not done with us.
There's no sugar-coating it: The world has let its guard down on covid-19. And the virus's latest dominant form, XBB.1.5, makes clear that we're doing so just as the virus finds new ways to hurt us.
The new dominant strain shows that the virus is always evolving to spread more quickly and infect us more efficiently. That should serve as a wake-up call for the country to re-invest in new vaccines, treatments and pandemic monitoring.
The XBB strain is the first fast-spreading recombinant variant — meaning it is a fusion of two omicron lineages. Its original version led to a wave of infections in Singapore. Then it added two critical mutations to become XBB.1.5, which was first detected in New York.
These two mutations maintain the high level Of immune escape Of XBB, while also adding more infectivity advantage, giving the virus better ability to attach itself to the receptors that gets it into our cells. The variant identified has rapidly become dominant throughout the Northeast and is destined to do so across the country in the weeks ahead.
What's more, it is picking up steam in many European and Asian countries. This tells us that XBB.1.5 is no slouch. It is outcompeting a soup of new omicron variants that have arisen in recent months.
While there is no indication that XBB.1.5 is more pathogenic or virulent, its ability to spread seems striking, given how quickly it rose to dominance in New York and contiguous states. XBB.1.5 now comprises well beyond 75 percent of infections in New York, Connecticut, New Jersey and Massachusetts. Hospitalizations have risen among seniors to levels only the first omicron wave surpassed.
Of course, it is hard to solely attribute this to XBB.1.5, given the population's waning immunity, less frequent use of masks and other mitigation measures, and indoor gatherings during the holiday season. But the spike in hospitalizations in these states is significantly greater than in other regions in the country. And it is people 65 and older who, along with the immunocompromised, are the most vulnerable.
What can be done to defend against XBB.1.5? It is essential to get boosted, as new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show. Those who are 65 and older who received the bivalent vaccine are 80 percent less likely to be hospitalized. Furthermore, there is evidence that the bivalent vaccine — even though it targeted the earlier BA.5 variant — helps induce neutralizing antibodies and broaden immunity against XBB.1.5. Beyond boosters, the use of high-quality masks, rapid testing before gatherings, distancing, air ventilation and filtration will all help protect against infections.
Americans can take some comfort in the combined immunity from the country's massive numbers of infections, reinfections, vaccinations and boosters. That should blunt the effect of XBB.1.5. Still, we have already seen the levels of covid hospitalizations in the United States reach their highest level in almost II months, and we're not done with this wave yet. The implications of XBB.1.5 are also much bigger than just this formidable variant. The virus is talking to us, and it is telling us it has many more ways to evolve. It is revealing that it not only can fake out or elude our immune response, but can also get better at penetrating our cells. What will happen next? Will we see a whole new family of variants arise that are distinct from the omicron family? It is entirely possible.
And we're not ready for it. Genomic surveillance around the world has dropped 90 percent since early 2022, as reflected by sequenced samples deposited at the Global Initiative on Sharing Avian Influenza Data. That's unacceptable. China is in the midst of a covid crisis with unmitigated spread, and it could become a breeding ground for functionally important variants in the months ahead.
Worse, there's no coordinated, high-priority, accelerated or even funded efforts — either in the United States or globally — to develop the next-generation vaccines that will block infections, such as universal, variant-proof vaccines with extended duration of protection. Nor do we have drugs to replace the monoclonal antibodies that no longer work or for Paxlovid, in case resistance emerges to that treatment.
We've moved from complacency to frank capitulation at just the wrong time. If XBB.1.5 is telling us one thing, it's that we can't be oblivious. We're all tired, but we're up against a force that isn't. We have the intelligence, resourcefulness and ingenuity to finally get ahead of the virus, but politics and unwillingness to invest is holding us back. We cannot afford that gridlock.
0 notes
Text
Genetic diversity and spread dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 variants present in African populations
Preliminary report; The dynamics of COVID-19 disease have been extensively researched in many settings around the world, but little is known about these patterns in Africa. 6139 complete nucleotide genomes from 51 African nations were obtained and analyzed from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) and Global Initiative on Sharing Influenza Data (GISAID) databases to examine genetic diversity and spread dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 lineages circulating in Africa. We investigated their diversity using several clade and lineage nomenclature systems, and used maximum parsimony inference methods to recreate their evolutionary divergence and history. According to this study, only 193 of the 2050 Pango lineages discovered worldwide circulated in Africa after two years of the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak, with five different lineages dominating at various points during the outbreak. We identified South Africa, Kenya, and Nigeria as key sources of viral transmissions between Sub-Saharan African nations because they had the most SARS-CoV-2 genomes sampled and sequenced. These results shed light on the evolutionary dynamics of the circulating viral strains in Africa. Genomic surveillance is one of the important techniques in the pandemic preparedness toolbox and to better understand the molecular, evolutionary, epidemiological, and spatiotemporal dynamics of the COVID-19 pandemic in Africa, genomic surveillance activities across the continent must be expanded. The effectiveness of molecular surveillance as a method for tracking pandemics strongly depends on continuous and reliable sampling, speedy virus genome sequencing, and prompt reporting and we have to improve in all these aspects in Africa. Additionally, the pandemic breakout revealed that current land-border regulations aimed at limiting virus's international transmission are ineffective and a lot needs to be done to implement and improve our African land-borders as far as epidemiology is concerned in order to contain such outbreaks in the future. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.08.17.504290v1?rss=1%22&utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr Read more ↓
0 notes
Text
Circula en 4 estados la subvariante BA.2 de ómicron de COVID-19, entre ellos Veracruz
Circula en 4 estados la subvariante BA.2 de ómicron de COVID-19, entre ellos Veracruz
El Instituto Nacional de Medicina Genómica (Inmegen) detectó siete casos de la subvariante BA.2 de ómicron de COVID-19 en México. Según el reporte que se compartió en GISAID (Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data) los casos están en la Ciudad de México, Veracruz, Jalisco y Quintana Roo. De acuerdo con Milenio, los casos datan desde el inicio de enero, lo que demuestra que ha circulado…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Ómicron avanza en México; reportan más de 5 mil casos en 28 estados
#Nacional Ómicron avanza en México; reportan más de 5 mil casos en 28 estados.
07 DE FEBRERO 2022.- Los casos de coronavirus en México siguen subiendo y las autoridades de salud piden a la población no bajar la guardia ante la presencia de la nueva variante de covid-19 ómicron, de la cual ya se tiene reporte de 5 mil 309 casos distribuidos en 28 entidades. De acuerdo con la plataforma Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID), los casos de la variante ómicron…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
New 'variant Under Investigation' of Omicron Identified!
New ‘variant Under Investigation’ of Omicron Identified!
In total, 40 countries have uploaded 8,040 BA.2 sequences to the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID) since November 17, 2021, and at this point, it is not possible to determine where the sub-lineage may have originated, it added. The first sequences were submitted from the Philippines, and most samples have been uploaded from Denmark (6,411), while other countries that have…

View On WordPress
0 notes