#GLP-1 receptor
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Semaglutide enhances cognitive abilities and reduces Alzheimer’s pathology in mice and human brain models
A study in *Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy* explored the effects of Semaglutide on Alzheimer's Disease (AD) in mouse and human brain organoid models. Researchers found that Semaglutide improved cognitive function, reduced amyloid plaque and Tau protein levels, and decreased neuroinflammation in APP/PS1 mice. Behavioral tests indicated enhanced learning and memory, while biochemical assessments showed modulation of key neuroprotective pathways. Additionally, Semaglutide increased oxytocin levels in human models, suggesting its therapeutic potential through GLP-1 receptor and oxytocin interaction. These findings point to Semaglutide as a promising candidate in AD treatment, warranting further research.
#Semaglutide#Cognitive enhancement#Alzheimer's disease#APP/PS1 mice#Amyloid plaque reduction#Tau protein#Neuroinflammation#Learning and memory improvement#GLP-1 receptor#Oxytocin interaction#Brain organoid models#Neuroprotective pathways#Alzheimer's pathology#Therapeutic potential#Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy
0 notes
Text









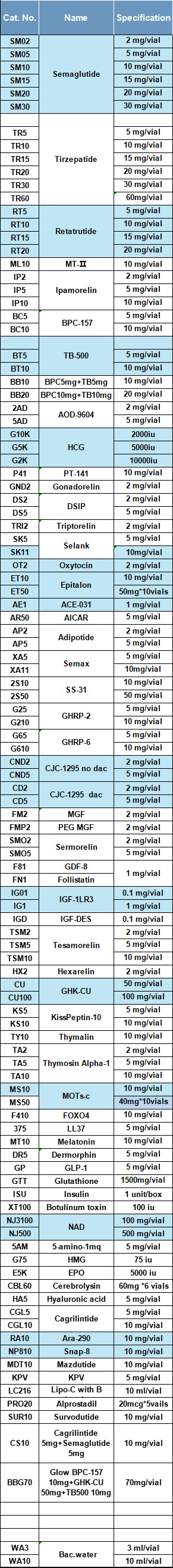






中国供应商,厂家直销,优质多肽,规格齐全,可定制,价格优惠,专线运输。 WhatsApp1: +85246350221 电报: +85246350221/+8615931973545
#retatrutide#lose weight without exercise#lose weight motivation#glp-1 receptor agonists#lose weight at home#glp-1 drugs#lose weight tips#lose weight#glp-1#lose weight fast
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Most foods cause the release of endogenous GLP-1 at physiological levels but this release is diminished in pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RA) give a pharmacological dose of GLP-1 with a good benefit to risk ratio for most patients. Yes these foods have no risks and no side effects but they also have no benefits. Shame on MDLinx!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
High Quality Peptide Factory
Chinese supplier, factory direct sales, high-quality peptides, we have every specification, can be customized, preferential price, dedicated line transportation. WhatsApp1: +85246350221 Telegram: +85246350221



#glp-1#glp-1 drugs#glp-1 receptor agonists#lose weight#lose weight at home#lose weight fast#lose weight motivation#lose weight tips#lose weight without exercise#retatrutide#tirzepatide#Peptide weight loss
0 notes
Text
Expanding access to weight-loss drugs could save thousands of lives a year
Expanding access to new, highly effective weight-loss medications could prevent more than 40,000 deaths a year in the United States, according to a new study led by researchers at Yale School of Public Health and the University of Florida. The findings highlight the critical need to remove existing barriers that are hindering people’s access to effective weight loss treatments and impeding…
0 notes
Text
Exploring Semaglutide and Trizeptride: Contrasting Weight Loss Injections
Discover the differences between Semaglutide and Trizeptride, two innovative GLP-1 receptor agonists for weight loss. Learn about their mechanisms, benefits, and which might be right for your obesity treatment needs in Edwardsville.
#Semaglutide Weight Loss#Trizeptride Weight Loss#GLP-1 Receptor Agonists#Weight Loss Injections#Obesity Treatment Medications#Edwardsville Weight Loss Injections#aesthetic treatments#iv hydration therapy#holistic wellness edwardsville#medical weight loss#natural aesthetic services#iv therapy edwardsville#medical weight loss edwardsville#im injections for wellness#nfuze wellness#iv hydration therapy edwardsville
0 notes
Text
A recent study published in JAMA Network Open investigated the relationship between semaglutide, a medication commonly used for type 2 diabetes (T2D), and the risk of opioid overdose in patients with both T2D and opioid use disorder (OUD).
#psychiatry#doctor#mental health#psychiartist#shrinks in sneakers#mental illness#mental health matters#addiction#GLP-1#glp 1#glp 1 receptor agonists#medical#diabetes#diabetic#opioid#opioid epidemic#opioid crisis
1 note
·
View note
Text
Let's Talk About GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs)
GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs), including Tirzepatide and Semaglutide, are showing promise not just in managing type 2 diabetes but also in addressing inflammatory and neurodegenerative conditions. These medications have demonstrated benefits beyond blood sugar control, such as anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. Research indicates that they may potentially aid in the treatment of…
#Dementia Prevention#Diabetes Medications#GLP-1 Receptor Agonists#health#Inflammation Reduction#life lessons#metabolic health#Neurodegenerative Diseases#Neuroprotection#Science research#Self Improvement#Semaglutide Osteoarthritis#Tirzepatide Benefits#Type 2 Diabetes Treatments
0 notes
Text
https://social.studentb.eu/read-blog/184594_glp-1-receptor-agonist-market-size-analysis-and-forecast-2031.html
The GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market in 2023 is US$ 14.44 billion, and is expected to reach US$ 23.58 billion by 2031 at a CAGR of 6.32%.
#GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market#GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market Scope#GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market Forecast
0 notes
Text
#Wegovy#Weight Loss#Obesity Treatment#GLP-1 Receptor Agonist#Bariatric Medicine#Health and Wellness#Diet and Nutrition#Exercise#Metabolic Health#Body Mass Index (BMI)#Appetite Control#Medical Weight Loss#Lifestyle Changes#Prescription Medication#Weight Management#Healthy Habits#Patient Education#Side Effects#Clinical Trials#Healthcare Providers
1 note
·
View note
Text

How does Retatrutide Work when We Using it, how Magic!
Retatrutide works
Depending on which cell receptors they bind to, different receptor agonists play distinct roles in our bodies. Retatrutide, as previously stated, stimulates three receptor agonists: GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon. To gain a better grasp of retatrutide mechanism of action, you should first learn about receptor agonists. Here’s how each one works in our bodies and why they help with weight loss:
GLP-1 (Glucagon-like Peptide-1):
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) emerges as an intestinal peptide hormone that our body generates in response to meal consumption. This hormone assumes a versatile role, with its primary significance lying in the regulation of food intake and hunger sensations. As we partake in a meal or a snack, the elevation of our blood glucose levels triggers the release of GLP-1, setting in motion the stimulation of insulin secretion from the pancreas
Insulin, a pivotal hormone manufactured by our body, functions as the key to unlocking cellular entry for glucose originating from dietary intake. The cells’ reliance on glucose as their chief energy source for fundamental processes underscores the critical role of insulin. Its role extends to the meticulous management of blood sugar levels and its implications for weight management. The absence of sufficient insulin erects barriers to glucose ingress into cells, not only impeding nutrient absorption but also leading to escalated blood sugar levels. Consequently, surplus glucose metamorphoses into adipose tissue, contributing to weight gain.
GLP-1 orchestrates the promotion of insulin secretion from the pancreas while simultaneously orchestrating the curtailment of glucose release from the liver. Beyond its contributions to glucose moderation, GLP-1 orchestrates a deliberate deceleration of gastric emptying, inducing a protracted digestive journey. This translates to a hastened sense of satiety and contentment following meals. Furthermore, GLP-1 exercises its influence on the brain’s hunger center, instigating a reduction in the sensation of appetite. These dual facets of GLP-1’s influence work in concert to quell hunger, akin to the mechanisms of appetite suppressants like Phentermine, often employed to foster weight loss endeavors.
GIP (Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide):
Just as GLP-1, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) belongs to the family of incretin hormones. Hence, both these peptide hormones exhibit strikingly similar behaviors. This hormone is generated within the small intestine following a meal, where it homes in on the pancreatic beta cells, effectively triggering the discharge of insulin. This action contributes to the regulation of post-meal blood sugar levels. Nevertheless, GIP’s sojourn within our system is brief; it undergoes breakdown in approximately 7 minutes. GIP receptor agonist medications, exemplified by Mounjaro, are designed to sustain elevated GIP levels in our bloodstream, extending its presence. This hormone induces a gradual-paced gastric emptying process while concurrently curbing appetite. Its influence extends to both the brain and the digestive system. That is why the stomach is one of the best place to inject Tirzepatide for weight loss.
Glucagon receptor:
Glucagon, an additional hormone of paramount significance, assumes a pivotal role in the orchestration of blood sugar levels. Analogous to GLP-1 and GIP, its origin lies within the pancreas, although it emanates from a distinct variety of cells known as alpha cells. In stark contrast to the aforementioned hormones, glucagon operates in a manner diametrically opposed. When our blood sugar levels begin to ebb, prompted by factors such as fasting or slumber, glucagon initiates the conversion of glycogen—the reserved form of sugar—into glucose, thus providing our body with a readily accessible fuel source. Although insulin and glucagon wield divergent effects, they collaborate in tandem to uphold optimal sugar levels. Insulin channels sugar into glycogen, while glucagon undertakes the converse.
How does glucagon contribute to weight loss? Our system stockpiles surplus glucose from dietary intake as both glycogen and adipose tissue. During prolonged intervals devoid of carbohydrate consumption—during periods of sleep, adherence to a low-calorie regimen, or intermittent fasting, for instance—glucagon emerges as a vital player, endeavoring to engineer glucose generation. This process commences by dismantling glycogen reserves; once this reservoir is depleted, glucagon turns its focus to the disintegration of fat stores, converting them into a usable energy source.
#polypeptide#weight loss#polypeptide.ltd#retatrutide weight loss#tirzepatide#tirzepatide injection#tirzepatide weight loss#semaglutide#GLP-1#Glucagon receptor
1 note
·
View note
Text
Chinese supplier, factory direct sales, high-quality peptides, we have every specification, can be customized, preferential price, dedicated line transportation. WhatsApp1: +85246350221 Telegram: +85246350221
#glp-1#glp-1 drugs#glp-1 receptor agonists#lose weight#lose weight at home#lose weight fast#lose weight motivation#lose weight without exercise#lose weight tips#retatrutide
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Probably launch early next year. Pricing strategy for a generic daily glp-1 ra will be interesting.
0 notes
Text
6 Week Belly Ozempic Weight Loss Before and After
In a world where countless weight loss methods promise quick fixes, finding an approach that not only delivers results but also targets that stubborn belly fat can feel like an elusive quest. But what if we told you that a 6 Week Belly Ozempic Weight Loss Before and After challenge could be the key to your long-awaited transformation? Hold on tight because we are about to go on a journey that…

View On WordPress
#6 Week Belly Ozempic Weight Loss Before and After#Before and After Transformation#Belly fat reduction#Fitness Journey#GLP-1 receptor agonists#Health and wellness#Healthy lifestyle tips#Ozempic weight loss#weight loss#Weight loss challenges
1 note
·
View note
Text
Navigating The Future: Trends And Challenges In The GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market

The GLP-1 receptor agonist market, a critical segment of the pharmaceutical industry, is poised for significant transformations as it continues to address the needs of patients with type 2 diabetes. This dynamic market has seen impressive growth and innovation, but it also faces unique challenges that warrant attention and proactive strategies. Combination Therapies: Combination therapies, involving the use of GLP-1 receptor agonists in conjunction with other diabetes medications, are becoming more common. This approach can provide synergistic effects and better blood sugar control, offering patients comprehensive treatment strategies.
Personalized Treatment: The concept of personalized medicine is gaining traction in the GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market. Advances in genetics and molecular biology are enabling healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to individual patients' needs, maximizing the effectiveness of these medications.
Digital Health Solutions: The integration of digital health solutions, such as mobile apps and wearable devices, is transforming how patients and healthcare professionals manage diabetes. These technologies can assist with medication adherence, track blood sugar levels, and provide real-time insights into patients' health status.
Affordability and Access: Despite the market's growth, affordability and access to GLP-1 receptor agonists remain challenges for many patients. Developing cost-effective options and collaborating with healthcare systems to improve access will be crucial to ensuring equitable treatment for all. Long-term Safety and Efficacy: While the cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists are well-established, the long-term safety and efficacy of these medications require continuous monitoring. Post-market surveillance and research are essential to identify any potential adverse effects over extended periods.
Patient Education: Educating patients about the benefits, proper usage, and potential side effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists is vital. Empowering patients to make informed decisions about their treatment can improve adherence and overall treatment outcomes.
As the GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market navigates the future, collaboration among pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, regulators, and patient advocacy groups will be instrumental. By working together, these stakeholders can overcome challenges and capitalize on emerging trends to improve the lives of individuals with type 2 diabetes.
In conclusion, the GLP-1 receptor agonist market's journey is one of growth, innovation, and adaptation. While trends like personalized treatment and digital health solutions hold promise, addressing challenges related to affordability, safety, and patient education remains crucial. Through sustained efforts and a patient-centered approach, the market can continue to evolve and positively impact the lives of millions affected by type 2 diabetes.
0 notes
Text
Diabetes Medicine: An In-depth Guide to Managing Diabetes
Looking for detailed information on diabetes medicine? This extensive article covers all aspects of effective diabetes management, including a wide range of treatments and medications. Gain insights from experts and real-life experiences. Introduction: Recognizing the Vitality of Diabetes Medicine Diabetes, a pervasive chronic condition afflicting millions worldwide, arises from impaired blood…
View On WordPress
#alcohol and smoking#Allergic Reactions#Blood Sugar Control#Blood Sugar Monitoring#combination therapy#Diabetes Management#diabetes medicine#Diabetes treatment#DPP-4 inhibitors#Drug Interactions#gastrointestinal issues#GLP-1 Receptor Agonists#healthcare professional#Healthcare provider#Healthy Diet#hypoglycemia#Insulin therapy#Long-term Complications#managing diabetes#Medication adherence#meglitinides#metformin#Missed dose#natural alternatives#pregnancy and diabetes medicine#Regular exercise#SGLT2 Inhibitors#stress management#Sulfonylureas#thiazolidinediones
0 notes