#Eco-Friendly and Sustainability
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Growth capitalism is a deranged fantasy for lunatics.
Year 1, your business makes a million dollars in profit. Great start!
Year 2, you make another million. Oh no! Your business is failing because you didn't make more than last year!
Okay, say year 2 you make $2 mil. Now you're profitable!
Then year 3 you make $3 mil. Oh no! Your business is failing! But wait, you made more money than last year right? Sure, but you didn't make ENOUGH more than last year so actually your business is actively tanking! Time to sell off shares and dismantle it for parts! You should have made $4 mil in profit to be profitable, you fool!
If you're not making more money every year by an ever-increasing exponent, the business is failing!
Absolute degenerate LUNACY
#eat the rich#fuck capitalism#capitalists make great mulch#they're a sustainable and eco-friendly source of pig feed and fertilizer#blog together queue alone
51K notes
·
View notes
Text
#gift ideas#merch for financial institutions#Viviamo Concepts#financial institutions#Eco-Friendly and Sustainability
0 notes
Text
It’s an open secret in fashion. Unsold inventory goes to the incinerator; excess handbags are slashed so they can’t be resold; perfectly usable products are sent to the landfill to avoid discounts and flash sales. The European Union wants to put an end to these unsustainable practices. On Monday, [December 4, 2023], it banned the destruction of unsold textiles and footwear.
“It is time to end the model of ‘take, make, dispose’ that is so harmful to our planet, our health and our economy,” MEP Alessandra Moretti said in a statement. “Banning the destruction of unsold textiles and footwear will contribute to a shift in the way fast fashion manufacturers produce their goods.”
This comes as part of a broader push to tighten sustainable fashion legislation, with new policies around ecodesign, greenwashing and textile waste phasing in over the next few years. The ban on destroying unsold goods will be among the longer lead times: large businesses have two years to comply, and SMEs have been granted up to six years. It’s not yet clear on whether the ban applies to companies headquartered in the EU, or any that operate there, as well as how this ban might impact regions outside of Europe.
For many, this is a welcome decision that indirectly tackles the controversial topics of overproduction and degrowth. Policymakers may not be directly telling brands to produce less, or placing limits on how many units they can make each year, but they are penalising those overproducing, which is a step in the right direction, says Eco-Age sustainability consultant Philippa Grogan. “This has been a dirty secret of the fashion industry for so long. The ban won’t end overproduction on its own, but hopefully it will compel brands to be better organised, more responsible and less greedy.”
Clarifications to come
There are some kinks to iron out, says Scott Lipinski, CEO of Fashion Council Germany and the European Fashion Alliance (EFA). The EFA is calling on the EU to clarify what it means by both “unsold goods” and “destruction”. Unsold goods, to the EFA, mean they are fit for consumption or sale (excluding counterfeits, samples or prototypes)...
The question of what happens to these unsold goods if they are not destroyed is yet to be answered. “Will they be shipped around the world? Will they be reused as deadstock or shredded and downcycled? Will outlet stores have an abundance of stock to sell?” asks Grogan.
Large companies will also have to disclose how many unsold consumer products they discard each year and why, a rule the EU is hoping will curb overproduction and destruction...
Could this shift supply chains?
For Dio Kurazawa, founder of sustainable fashion consultancy The Bear Scouts, this is an opportunity for brands to increase supply chain agility and wean themselves off the wholesale model so many rely on. “This is the time to get behind innovations like pre-order and on-demand manufacturing,” he says. “It’s a chance for brands to play with AI to understand the future of forecasting. Technology can help brands be more intentional with what they make, so they have less unsold goods in the first place.”
Grogan is equally optimistic about what this could mean for sustainable fashion in general. “It’s great to see that this is more ambitious than the EU’s original proposal and that it specifically calls out textiles. It demonstrates a willingness from policymakers to create a more robust system,” she says. “Banning the destruction of unsold goods might make brands rethink their production models and possibly better forecast their collections.”
One of the outstanding questions is over enforcement. Time and again, brands have used the lack of supply chain transparency in fashion as an excuse for bad behaviour. Part of the challenge with the EU’s new ban will be proving that brands are destroying unsold goods, not to mention how they’re doing it and to what extent, says Kurazawa. “Someone obviously knows what is happening and where, but will the EU?”"
-via British Vogue, December 7, 2023
#fashion#slow fashion#style#european union#eu#eu news#eu politics#sustainability#upcycle#reuse#reduce reuse recycle#ecofriendly#fashion brands#fashion trends#waste#sustainable fashion#sustainable living#eco friendly#good news#hope
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
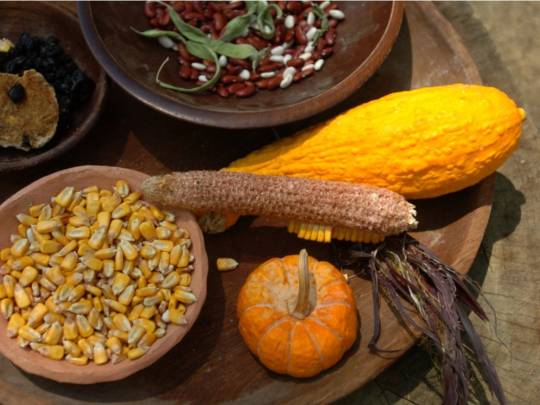
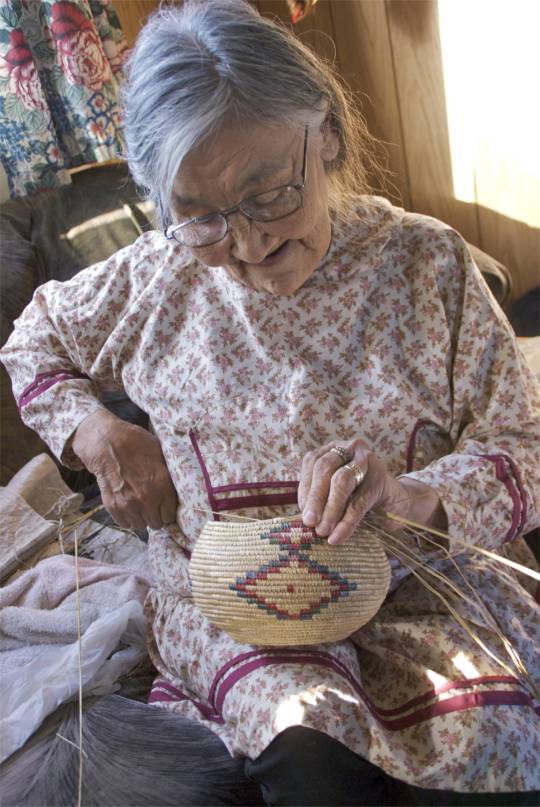













times, places, and practices that I want to learn from to imagine a hopeful future for humanity 🍃
the three sisters (squash, beans, maize) stock photo - alamy // anecdote by Ira Byock about Margaret Mead // art by Amanda Key // always coming home by Ursula K. Le Guin // Yup'ik basket weaver Lucille Westlock photographed by John Rowley // the left hand of darkness by Ursula K. Le Guin // photo by Jacob Klassen // the carrier bag theory of fiction by Ursula K. Le Guin // article in national geographic // the dawn of everything by David Graeber and David Wengrow // braiding sweetgrass by Robin Wall Kimmerer // the birchbark house by Louise Erdrich // photo by John Noltner
I'm looking for more content and book recs in this vein, so please send them my way!
#solarpunk#hopepunk#braiding sweetgrass#just a collection of books and pictures that make me hopeful for the future#margaret mead#robin wall kimmerer#nature#ursula k le guin#ursula k. le guin#the left hand of darkness#the carrier bag theory of fiction#the dawn of everything#anthropology#future#hopecore#native plants#biodiversity#sustainability#eco#eco friendly#louise erdrich#civilization
3K notes
·
View notes
Text







"Rhoēs" villa, Serifos island, Greece,
Sinas Architects
#art#design#architecture#minimalism#interiors#summerhouse#luxuryhouse#luxuryhome#island#greece#serifos#nature#retreat#rhoes#sinas architecture#waves#eco friendly#sustainability#emerald sustrai#sustainable fashion#sustainableliving
233 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Maldives Floating City, set to open in 2027, will provide eco-friendly, floating residences for 20,000 people, adapting to rising sea levels.
#Maldives#floating city#climate change#sea level rise#eco-friendly architecture#sustainable living#urban planning#2027#innovative design
87 notes
·
View notes
Text

Not that we want to rush through Spooky Season, but this is a good tip for November 1st.
#horror#halloween#spooky season#wildlife#eco friendly#sustainability#pumpkins#jack o lantern#animals#october#spooktacular#spooktober
115 notes
·
View notes
Text

from the 'wholistic + abundant {lifestyle}' Pinterest board
#q#quotes#david attenborough#earth stewardship#mindsets#mindfulness#eco conscious#solarpunk#eco friendly#sustainability#holistic leveling up#leveling up#that girl#green juice girl#slow living#soft living#symbiosis#sidewalkchemistry
336 notes
·
View notes
Text
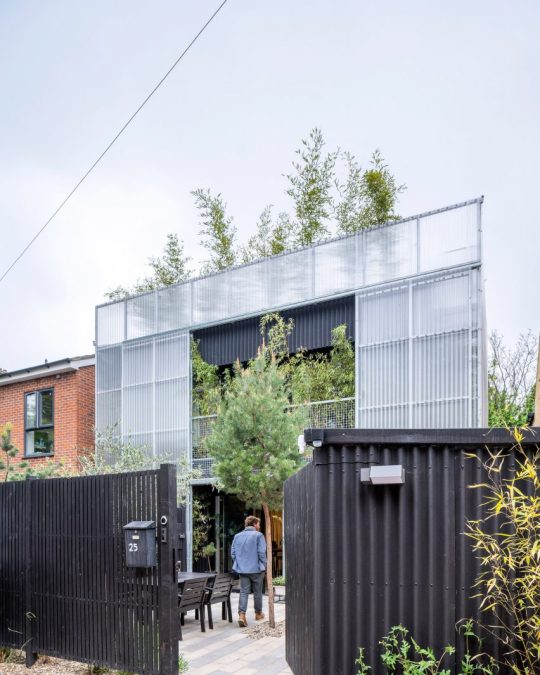
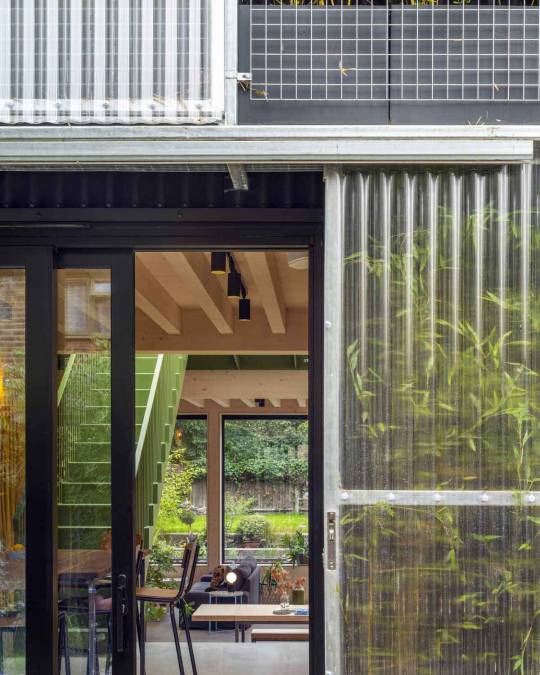
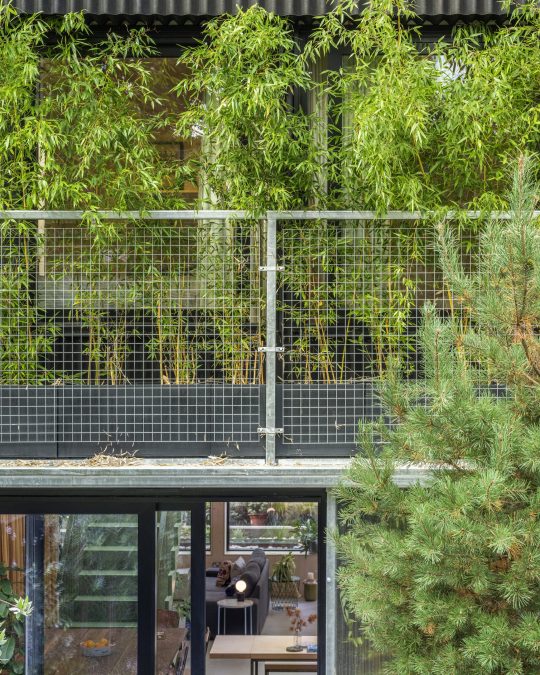
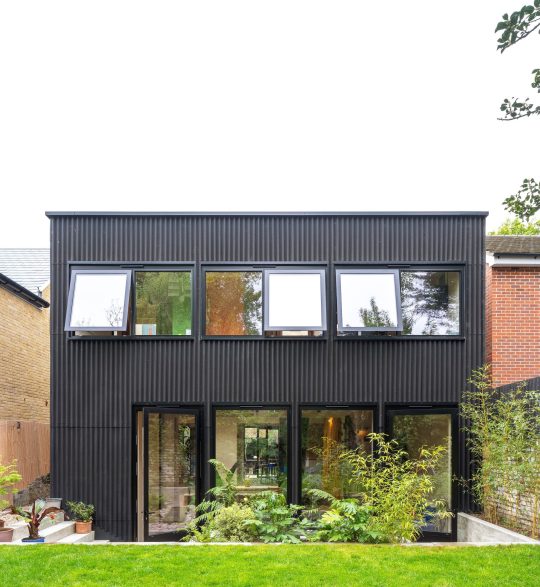
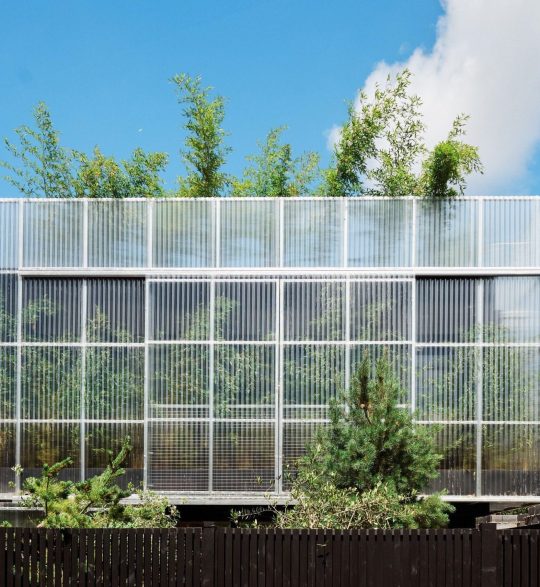
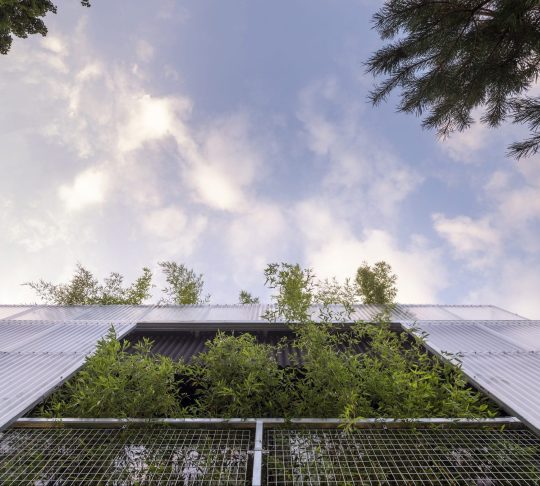
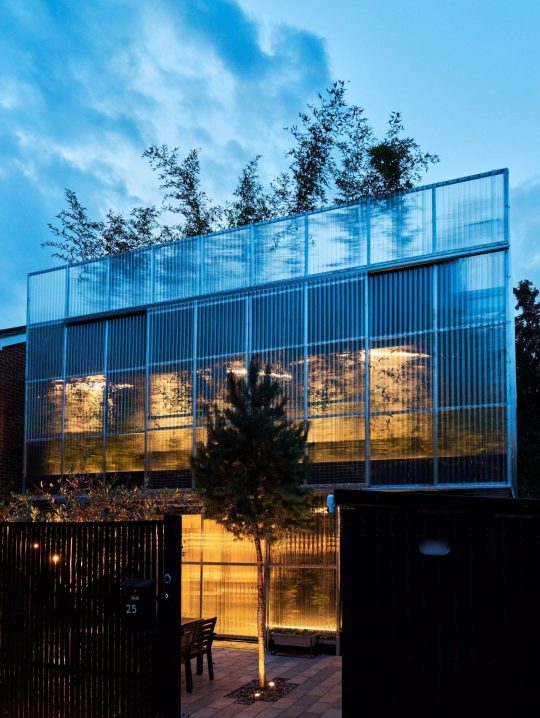
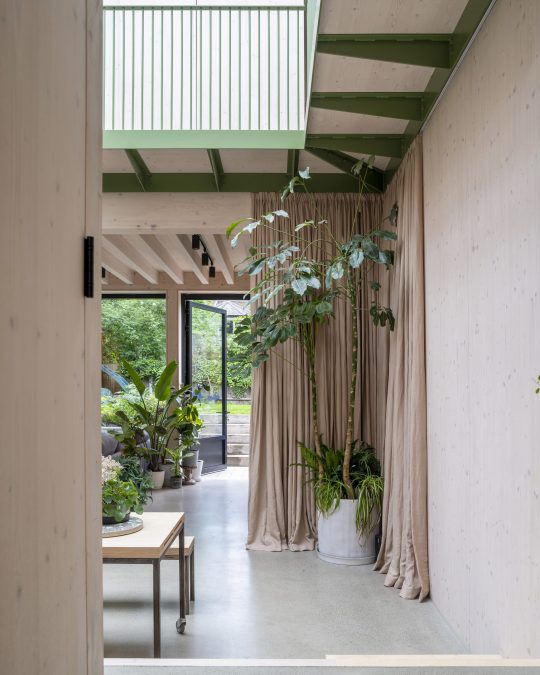
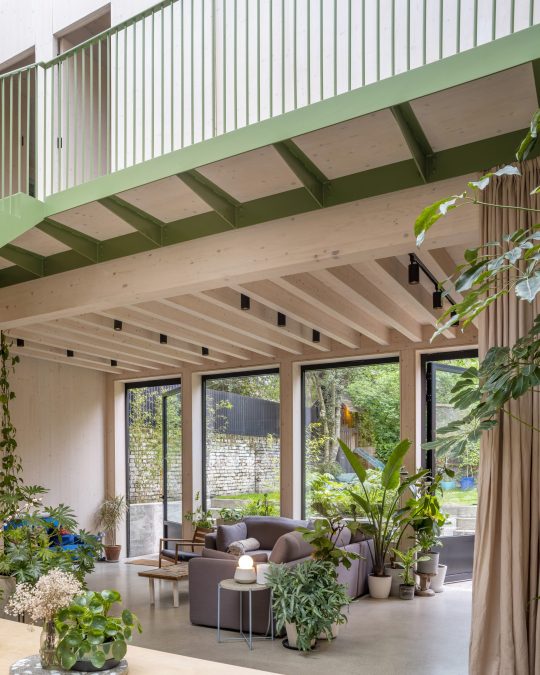
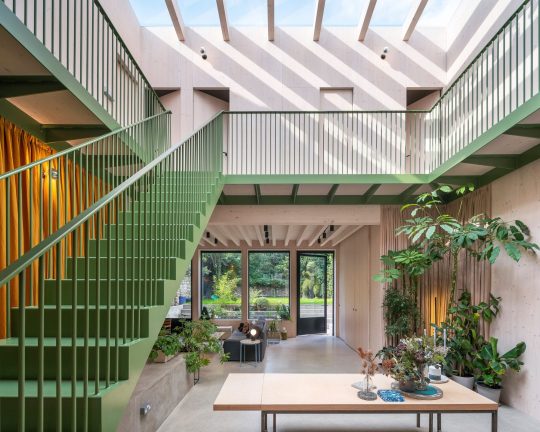
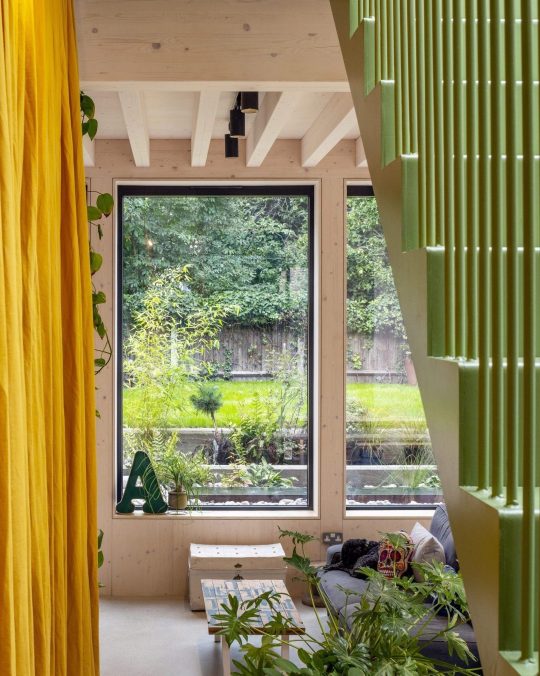
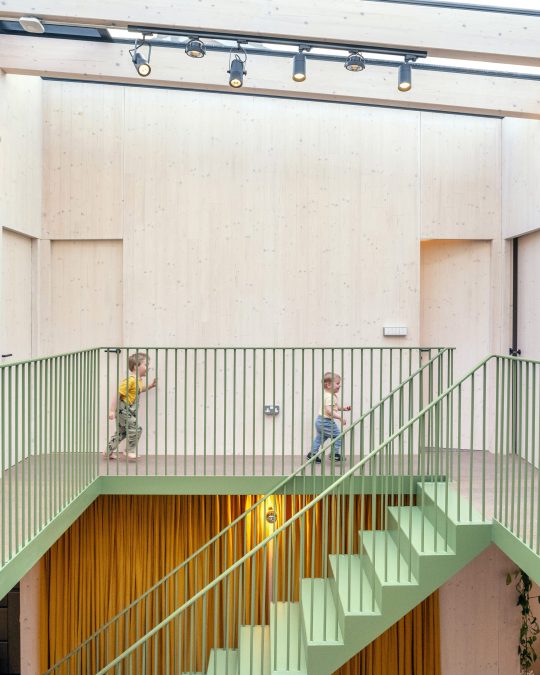














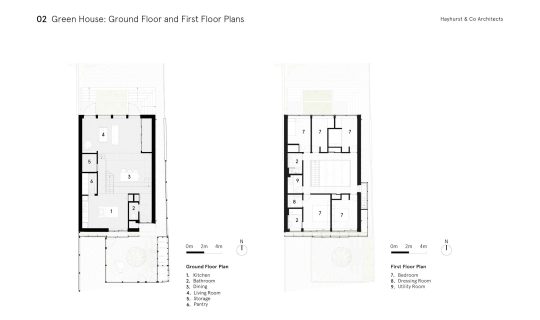

Green House, Tottenham, London, United Kingdom,
Hayhurst and Co
#art#design#architecture#minimal#nature#interior design#minimalism#green house#london#tottenham#hayburst & Co#bamboo#polycarbonate#screen#facade#low cost#lost energy#eco-friendly#sustainability#sustainable architecture#gif#architecture gif
345 notes
·
View notes
Text
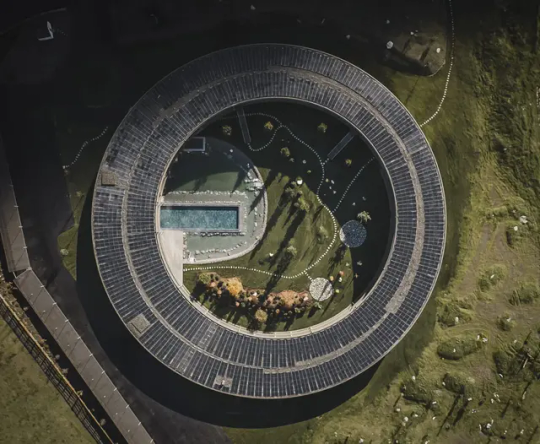









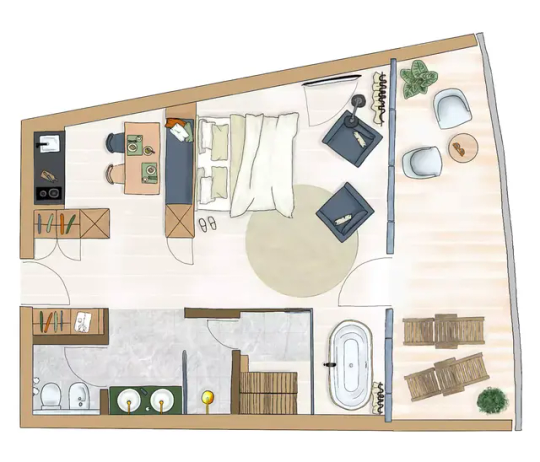





OLM Nature Escape - Eco Aparthotel,
A Design Boutique Hotel Sand in Taufers, Italy
Andreas Gruber Architekten AGA
#art#design#architecture#travels#boutique hotel#interior design#luxury lifestyle#luxury hotel#interiors#luxury hotels#escape#nature#eco friendly#spa#welness#italy#aparthotel#taufers#andreas gruber#sustainable architecture#green architecture
106 notes
·
View notes
Text
my mother (jokingly) called me a tradwife the other day because I asked for fiber arts stuff for Christmas 😅 we then had to explain to my dad what a tradwife is.
but seriously, it is crazy to me that there are two parallel movements of young people doing crafts, making their own food/clothing, and pushing for more sustainable lifestyle. But one movement is assigning religious meaning to it and also advocating for a return to “conservative family values” while the other movement is very progressive and doing it for a more environmentally friendly way of living. We’re a weird generation, fellow gen z’s
#tradwife#sustainability#Fiber arts#crafts#homemaking#slow living#eco friendly#gen z#Progressive#just to be clear I am not a tradwife#I am the other side of the movement
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Easy zero waste tip no. 3: Know your R's
Refuse: If you don't acquire the thing that will become waste in the first place, it won't produce further waste. Simple enough. Refuse that which you do not need. Example: All that cute stuff on that Buzzfeed article? You don't need it. Don't even click the link.
Reduce: If you need something, get the minimum. Note that this doesn't mean the cheapest option- it means the most effective and environmentally friendly option. Example: Instead of buying disposable razors, or a razor with changeable heads, try out a safety razor. Instead of using plastic toothbrushes, try out bamboo, and instead of toothpaste in disposable tubes, try out some toothpaste bits. Instead of buying chicken breasts for one thing and chicken broth for another, get a whole chicken and learn to butcher its meat, and make broth from the skin and bones.
Reuse: This means both being mindful of purchases, so you're only buying things that are reusable whenever possible (Example: use beeswax wrap instead of saran wrap), and repurposing things you've already bought (Example: use those little Oui yogurt containers to start seeds for your garden).
Recycle: Find out what your local recycling program actually recycles, and be mindful. Aluminum is a safe bet most of the time, as is paper/cardboard; but plastics, most of the time, are a dud, so try to refuse, reduce, and reuse plastic whenever possible so you don't even need to worry about recycling it. This also refers to donation- that's another valid way to recycle things!
Rot: If you have a yard, start a compost pile! Just try to get a 50/50 balance of food scraps to brown matter (paper, dry leaves, etc). If you have a freezer, you can stick a container in there to act as a compost thing until you can bring it to a compost facility, such as a local garden, or farm. If you don't have the ability to do either of these things, then you can see if there's a subscription compost service in your area (I used CompostNow for ages, they're great).
Understanding these five principles, and looking at them in this order, can make things easier. Next time you're buying something, or about to throw something away, consider which of these might allow you to reduce your waste output in the future.
#zero waste#sustainability#anti consumerism#anti consumption#eco friendly#sustainable#environment#five r's#refuse reduce reuse recycle rot#reduce reuse recycle#recycle#ecofriendly#recycling#compost#composting
237 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cars were a massive, historic mistake, and tethering our national economy to their production is the single biggest barrier we face to progress and prosperity
#socialism#communism#marxism#marxism leninism#poverty#anarcho communism#leftism#fully automated luxury gay space communism#liberalism#communism memes#leftists#progressivism#leftist politics#neoliberalism#hardcore punk#solar punk#reaping week#ecopunk#eco friendly#sustainability#permaculture#fuck cars#public transportation#urban planning#walkable cities#public transit#city planning
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
"At HarperCollins, a lot of attention and thought is given to deciding exactly what combinations of margin measurements, font, and layout feel most appropriate for the genre, and writing style.
But in a case of do-your-part environmentalism, designers at the publishing house have now standardized a series of subtle and imperceptible alterations to normal font style, layouts, and ink that have so far removed the need for 245 million book pages, totaling 5,618 trees.
Telling the story in Fast Company, representatives from HarperCollins, one of the four largest publishing houses in the world, explained that the idea first arose in Zondervan Bibles, HarperCollins’ Christian publishing division. Being that the Bible is 2,500 pages or sometimes more, saving ink and pages was not just an environmental consideration, but one of production costs.
A new typeface called NIV Comfort Print allowed Zondervan to shave 350 pages off of every Bible, which by 2017 had amounted to 100 million pages, and which, as Fast Company points out, would be four times higher than the Empire State Building if stacked.
The production and design teams then wondered how much they could save if they applied the same concepts to other genres like romance and fiction. Aside from the invention of the eBook, publishing hasn’t changed much in the last 100 years, and the challenge was a totally novel one for the teams—to alter all their preconceived ideas and try and find a font and typeface that resulted in fewer pages without being harder to read.
They eventually standardized 14 different combinations their tests determined were the most environmentally friendly, and which delivered an unchanged reading experience.
But the challenge didn’t stop there. Printed books, one might not know, are printed in large sheets which are then folded into sections of sixteen pages, meaning that Leah Carlson-Stanisic, associate director of design at HarperCollins, has to calculate the savings of space, words, and ultimately pages with the help of her team to fall in multiples of sixteen.
Nevertheless, they have been successful with it so far, and in the recent print run of one popular book, 1 million pages (or a number near 1 million that coincides with the 16 times tables) were saved.
“We want to make sure our big titles, by prominent authors, are using these eco-fonts,” Carlson-Stanisic said. “It adds up a little bit at a time, saving more and more trees.”"
-via Good News Network, April 4, 2024
--
Note: Great! Waiting to see this on the rest of their books and at the other big publishers!
Actually, though, it's worth noting that this may not come quickly to the other large publishers, because Harper Collins almost certainly owns that font - meaning that other publishers would have to pay HarperCollins in order to use it, on an ongoing basis.
More on publishing shit and more realistic solutions here below the cut!
What I'm hoping for and think is more likely is that this will inspire the development of open source eco-friendly fonts, which would be free for anyone to use. That would make it far more likely other publishers would adopt eco-friendly fonts.
I'm also hoping it would inspire other publishers to create similar eco-friendly fonts of their own.
Ideally, there would be a whole new landscape of (hopefully mostly open source) eco-friendly fonts. And/or to see calculations of the eco-friendliness of popular existing fonts, compared to each other.
If we could have a publicly accessible list of calculations for different fonts, including fonts designed to maximize eco-friendliness, I really do think that it would affect which fonts publishers choose to use. Here's why:
Most people in publishing are on the left (notoriously, actually) and really do care about the environment
People in publishing are plenty aware of these issues re: paper and trees, I promise
Shorter books means smaller production costs - and possibly smaller shipping costs as well, over time! So it would save them money too.
Eco-friendly fonts could also be combined with other measures for greater effect, such as bamboo paper (already in use for a lot of projects where page color/quality is more flexible) and thinner paper (aka paper with a lower weight) that uses less trees.
Don't expect books to all move to just one or two different fonts, though. Publishers and typesetters and font designers will innovate to create more options instead, though it will take longer. This is because different books really do use different fonts for various different reasons - one new font to rule them all isn't really a solution here.
"Every book is in the same font" may sound like a "whatever" deal to a lot of people, but as someone who works in publishing - trust me, it would actually make your reading experience worse, even if you could never quite put your finger on why.
#publishing#books#book publishing#bookblr#harper collins#fonts#font design#eco friendly#sustainability#conservation#trees#deforestation#good news#hope
395 notes
·
View notes
Text









Photos by Marc Rovellada Ballesteros published in La Mira and Happyxais.
Daniel is a shepherd who has been hired by the City Council of El Bruc (a town in Central Catalonia) to graze in the natural areas between the area's towns. Like other shepherds who work in the traditional way, he practises transhumance (seasonal nomadism to take the animals to the best pastures), and when the herd comes to El Bruc their grazing is this job. In modern times, this job is usually done by the municipal brigade with chainsaws and string trimmers, but Daniel's herd can do it just as well. It consists of 150 sheep, 130 goats, 4 dogs and 1 donkey, as well as the shepherd himself. Grazing in this area, they keep the vegetation to a controlled level, making it safer and reducing the chances of a wildfire.
Shepherding and grazing have been used in this way for millennia, uninterruptedly in many places, and now a few urban areas like El Bruc are joining again in what is being called "silvopasture". Grazing in urban areas is more demanding for the shepherd, because he has to be careful with cars, domestic animals, and neighbours, but in the end it is a mutually-beneficial arrangement.
Daniel shares snippets of his job in his Instagram account Happyxais.savall.
#el bruc#catalunya#silvopasture#sheep#goats#shepherd#animals#transhumance#sustainability#eco friendly#cottagecore#ruralcore#earth#pasture#ethnography#photojournalism#people of the world#culture
38 notes
·
View notes
Text













Casa GAK, Porto Feliz, Sao Paulo, Brazil,
Bernardes Arquitetura
Photo: Fernando Guerra
#art#design#architecture#interiors#interiordesign#luxury house#luxury home#porto feliz#sao paulo#brasil#green roof#sustainability#bernardes arquitetura#fernando guerra#eco friendly
117 notes
·
View notes