#Crude Oil Pipeline
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Uganda Receives First Batch of Pipes for East African Crude Oil Pipeline.
Line pipes arrive in Uganda at Kyotera Main Camp and Pipe Yard 4. Pool. Courtesy image. On Monday, Uganda marked a significant milestone in its crude oil development journey with the arrival of the first batch of coated line pipes for the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP). This delivery, which was made to the main camp and pipe yard located in Kyotera District, highlights the project…
0 notes
Text
East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP)
#tiktok#africa#uganda#france#oil#pipeline#water protectors#water pollution#climate crisis#call to action#collective action#East African Crude Oil Pipeline#EACOP#tanzania
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

#Oil#Weird#unusual#petrolium#crude oil#chevron#Oil sands#oil spill#drill baby drill#drilling rig#deepwater horizon#Kuwaiti oil fires#Chemicals#Ecosystems#Offshore oil platform#pipeline#exxonmobil#exxon#Exxon Valdez#clean up#spills#oil field#BP#OPEC
7 notes
·
View notes
Text


Excerpt from this story from DeSmog Blog:
Last November, a beaming group of staff from MetropolitanRepublic collected their gorilla-shaped trophy at the Silverback Awards, Uganda’s top advertising and public relations gala.
The South African PR agency had won its prize for promoting the “sustainable development” of Uganda’s untapped oil reserves by French oil company TotalEnergies.
MetropolitanRepublic — which is part-owned by British communications giant WPP — described the brief for the award-winning “Action for Sustainability” campaign in its entry to the Silverback Awards: to devise an approach that “squashed all the negative PR” from protests against TotalEnergies’ plans for a 1,443-kilometre pipeline to export oil from Uganda’s Lake Albert via neighbouring Tanzania.
An accompanying video featured photographs of Ugandan anti-pipeline campaigners to illustrate this “backlash” and described them as “haters”.
“How do you launch a successful project off the back of this?” asks the narrator in the video. “Well, you develop a 360 PR campaign that retells your story the way it should be told.”
Now, DeSmog can reveal that Ugandan police or military personnel have arrested, beaten, threatened, or harassed at least eight of the 15 campaigners pictured in MetropolitanRepublic’s award submission video.
These incidents — documented via video taken at protests, interviews with the campaigners, and police records — took place both before and after the video was published on the Silverback website in March.
There is no indication that MetropolitanRepublic’s campaign or the award submission led directly to any specific incidents affecting the activists. Nevertheless, DeSmog found that the agency engaged a network of social media influencers to post hundreds of times in support of TotalEnergies’ plans to mitigate the impact of the pipeline — even as protestors were being beaten and harassed.
“These PR firms are sponsoring our oppression,” said Hillary Innocent Taylor Seguya, one of the campaigners pictured in MetropolitanRepublic’s award submission video. “The more you push misinformation to the rest of the world, the more it means that you don’t care about our rights.”
#East Africa Crude Oil Pipeline#EACOP#Uganda#Tanzania#oil and gas industry#oil pipelines#Africa#MetropolitanRepublic#WPP
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Opponents of a highly controversial oil pipeline under construction in East Africa on Monday demanded an investigation into the Ugandan army's treatment of an environmental activist who was hospitalized after allegedly being severely beaten while he was detained last week.
Stephen Kwikiriza, an activist with the Kampala-based Environmental Governance Institute (EGI), was found dumped on the side of a highway about five hours' drive from the Ugandan capital Sunday night following a weeklong detention by the country's army.
"Unfortunately, he is in poor condition after enduring severe beatings, mistreatment, and abuse throughout the week," EGI said, according toAl Jazeera. "Doctors are conducting various examinations."
Like other climate and environmental campaigners in the movement to stop the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP), Kwikiriza is believed to have been targeted for his activism against the project, which is being built by the French fossil fuel giant TotalEnergies in partnership with the China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC), the Uganda National Oil Company, and others.
The Paris-based International Federation for Human Rights (FIDH) said Kwikiriza was apparently abducted by Ugandan army officers in civilian clothes in what the group called a "particularly worrying escalation of repression."
FIDH said 11 activists have been "kidnapped, arbitrarily arrested, detained, or subjected to different forms of harassment by the Ugandan authorities between May 27 and June 5, 2024," part of what critics call a government campaign targeting StopEACOP campaigners that goes back years.
"Speaking up for frontline communities should never lead to this," the StopEACOP movement said on social media following Kwikiriza's release. "We urge human rights organizations to hold Ugandan authorities accountable and ensure human rights and environmental defenders can work safely."
"We also ask TotalEnergies and CNOOC to investigate the injustices done in their names as alleged," the coalition added. "You can still make profits without harming communities or enabling human rights violations."
...
If completed, the $3.5 billion, nearly 900-mile EACOP project is expected to transport up to 230,000 barrels of crude oil per day from fields in the Lake Albert region of western Uganda through the world's longest electrically heated pipeline to the Tanzanian port city of Tanga on the Indian Ocean.
A July 2023 report by Human Rights Watch (HRW) detailed how EACOP has devastated the lives and livelihoods of tens of thousands of people in its path while exacerbating the climate emergency.
"The Ugandan government needs to end its harassment of opponents of oil development in the country, such as the East African Crude Oil Pipeline Project, which has already devastated thousands of people's livelihoods in Uganda and, if completed, will displace thousands of people and contribute to the global climate crisis," HRW senior environmental rights advocate Myrto Tilianaki said in a statement issued during Kwikiriza's detention.
#human rights#enviromentalism#ecology#east africa#East African Crude Oil Pipeline#EACOP#uganda#environmental activism#tanzania#china#China National Offshore Oil Corporation#belt and road initiative
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Oil Theft: Palaces, Religious Centres Are Outlets," Says NNPC
“Oil Theft: Palaces, Religious Centres Are Outlets,” Says NNPC Mosques, Churches, Palace Amongst Others Traced To Oil Theft In recent months, it is no longer news that Oil theft has become major concerns around oil-producing areas. On Saturday, the Nigerian National Petroleum Company Limited (NNPCL) voiced its displeasure over the large amount of illegal oil theft within the country, citing that…
#Barrel#Crude Oil#Mosques#Niger Delta#Nigerian Navy. Relogious Centres< Church#Nigerian President Bola Tinubu#Oil Theft#Palaces#Pipeline Vandalisation
0 notes
Text
Discover comprehensive oil testing services at ITC Labs, your trusted partner in quality and safety. Our oil testing lab offers a wide range of oil and gas testing services including lubricant testing, crude oil analysis, and pipeline testing. With over 36 years of expertise, we ensure accurate and reliable results for automotive oil testing, petrochemical analysis, and more. Our advanced facilities and experienced professionals provide top-notch quality control and assurance. Contact ITC Labs for dependable gas testing services and petrochemical testing. Ensure the safety and efficiency of your operations with our pipeline testing services and petrochemical services.
#oil testing services#oil testing lab#lubricant testing#automotive oil testing#crude oil testing#pipeline testing services
0 notes
Text
Global Crude Transportation Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Increasing Oil and Gas Exploration Activities

The global crude transportation market is estimated to be valued at US$ 21.58 billion in 2023 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 6% over the forecast period 2023-2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights. The market is driven by the increasing oil and gas exploration activities, which require efficient transportation of crude oil from production sites to refineries. Market Overview: The crude transportation market involves the transportation of crude oil through various modes such as pipelines, tankers, and railcars. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth flow of crude oil from production fields to refineries, where it is processed and converted into usable products such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. The demand for crude oil is constantly increasing due to the growing population, urbanization, and industrialization, making efficient transportation a necessity. Market Key Trends: One key trend driving the growth of the crude transportation market is the increased use of pipelines. Pipelines are considered the most efficient and cost-effective mode of transporting crude oil over long distances. They offer several advantages, including higher capacity, lower operating costs, and reduced environmental impact compared to other modes of transportation. For example, the Keystone Pipeline system in North America has a capacity of transporting over 590,000 barrels of crude oil per day. PEST Analysis: Political: The political factors influencing the crude transportation market include government regulations and policies related to energy security, environmental protection, and infrastructure development. For instance, the approval or rejection of major pipeline projects often depends on political factors and public sentiment. Economic: Economic factors such as oil prices, market demand, and economic growth influence the demand for crude transportation services. Higher oil prices incentivize increased production, leading to higher demand for transportation services. Social: Social factors such as growing energy consumption, rising population, and changing consumer preferences impact the crude transportation market. The increasing demand for petroleum products from various industries and households drives the need for efficient transportation. Technological: Technological advancements have significantly improved the efficiency and safety of crude transportation. For example, advanced pipeline monitoring systems and leak detection technologies help prevent accidents and minimize environmental impacts. Key Takeaways: 1: The Global Crude Transportation Market Size is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 6% over the forecast period. This growth can be attributed to increasing oil and gas exploration activities, which drive the demand for efficient transportation solutions. 2: In terms of regional analysis, North America is expected to be the fastest-growing and dominating region in the crude transportation market. The region has a well-developed pipeline infrastructure and is a major producer of crude oil. Furthermore, the shale oil boom in the United States has contributed to the increased demand for crude transportation services. 3: Key players operating in the global crude transportation market include ExxonMobil Corporation, Royal Dutch Shell, Chevron Corporation, BP plc, TotalEnergies SE, ConocoPhillips, China National Petroleum Corporation, Saudi Aramco, Rosneft Oil Company, Valero Energy Corporation, Phillips 66, Marathon Petroleum Corporation, PetroChina Company Limited, Kinder Morgan Inc., and Enbridge Inc. These players are focused on expanding their pipeline networks, investing in advanced technologies, and improving operational efficiency to meet the growing demand for crude transportation.
#Crude Transportation Market#Crude Transportation Market Insights#Crude Transportation Market Demand#Crude Transportation Market Forecast#Crude Transportation Market Analysis#Crude Transportation#pipelines#oil tankers#transportation#power generation#coherent market insights
0 notes
Text
"More than three-quarters of UK universities have pledged to exclude fossil fuel companies from their investment portfolios, according to campaigners.
The move, which is part of a wider drive to limit investment in fossil fuels, follows years of campaigning by staff and students across the higher education sector.
The student campaign group People & Planet announced on Friday that 115 out of 149 UK universities had publicly committed to divest from fossil fuels – meaning £17.7bn-worth of endowments are now out of reach of the fossil fuel industry.
Laura Clayson, from People & Planet, said it would have been unthinkable a decade ago that so many institutions had formally refused to invest in fossil fuels.
“That we can celebrate this today is down to the generations of students and staff that have fought for justice in solidarity with impacted communities. The days of UK universities profiteering from investments in this neo-colonial industry are over.”
People & Planet set up the Fossil Free universities campaign in 2013. As part of its efforts the group has highlighted the “struggles and voices” of communities on the frontline of the climate crisis in an attempt to bring home the real-world impact of investment decisions made by UK universities.
Clayson said: “The demand for fossil-free came from frontline communities themselves and it is an act of solidarity from global north organisers campaigning on this … We have a responsibility to speak the lived experiences of the communities resisting these inequalities into megaphones at protests and in negotiations within university boardrooms, to highlight their stories of struggle in spaces so often detached from the reality of everyday life on the frontlines.”
One of the projects highlighted by the campaign is the proposed East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) – a mega project that would stretch almost 900 miles from the Lake Albert region of Uganda to the coast in Tanzania, and release vast amounts of planet-heating carbon.
The pipeline is being built in spite of local opposition, and there are reports that protesters and critics have been met with state violence. Hundreds of student organisers have been involved in the struggle.
Ntambazi Imuran Java, the lead coordinator at the Stop EACOP Uganda campaign, said its members appreciated the efforts of UK students to bring an end to universities’ fossil fuel investments.
“[This] supports those who have worked tirelessly to stop deadly extraction projects like EACOP … Regardless of the arrests and violations on the activists, students’ activists and communities, we continue to demand for the Uganda authorities to stop the project and instead invest in renewables.”
People & Planet said four UK institutions – Birmingham City University, Glasgow School of Art, Royal Northern College of Music and the University of Bradford – had recently incorporated fossil fuel exclusions into their ethical investment policies, meaning 115 out of 149 UK universities have publicly committed to divest from fossil fuels.
Later this month, the group will group will unveil its latest university league table that ranks institutions by their ethical and environmental performance. Campaigners say they will then increase pressure on the remaining 34 UK universities yet to go fossil-free."
-via The Guardian, December 2, 2024
#united kingdom#uk#europe#scotland#wales#northern ireland#universities#fossil fuels#climate action#carbon emissions#climate crisis#climate change#sustainability#hope posting#good news#hope#divestment#fossil fuel divestment
531 notes
·
View notes
Text
im obviously a big fan of factory automation games like Satisfactory and Factorio for a lot of reasons but as an engineer the funniest one is how they make non-engineer players understand through firsthand experience immutable engineering and capitalist truisms like "wait it's really easy and profitable to just scale up incrementally forever as long as you assume resources are infinite and you outsource the labor of physically building everything", or "processing crude oil into fuel and plastics is complicated and requires tearing up a lot of the environment with trains and pipelines", or "trains rule and i need more of them", or "what the fuck why do i need so many fucking screws"
245 notes
·
View notes
Text
In November 2023, news broke that a number of Western energy companies, including British Petroleum (BP), were granted gas exploration licences in occupied Palestinian waters by the Israeli Ministry of Energy. While it will take years before these sites are converted into reliable sources of gas, activist groups in the US and Britain have protested these business deals, brokered in the shadow of an ongoing genocide. The motivation for Israel’s genocidal, Western-backed siege on Gaza cannot be reduced to the exploitation of its marine gas fields. The ongoing genocide should be understood as part of the logic of US imperialism and its proxy state which enacts its interests in the region: the Zionist settler colonial project, which seeks to ethnically cleanse all of historic Palestine, seize natural resources, and use and export its fuel supplies for the consolidation of its military and economic power. Indeed, our protests against BP’s gas licences are not in isolation. Like other activist groups in Turkey and Colombia, we campaign against energy companies partnering with Israeli businesses to supply fuel to Israel. For this reason, we situate BP’s gas licence within its larger role in fuelling Israel. BP is the operator and largest shareholder of the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan (BTC) oil pipeline, which is supplying Israel with 28% of its oil during its genocide. In this investigation we explore BP’s colonial history and the supply chain of the BTC pipeline. We also delve into the social licences that facilitate BP’s operations abroad. Social licences are a commercial and metaphorical concept describing corporations' process of acquiring public approval as an added layer of legitimacy for their ongoing profit-driven, colonial business practices. Focusing on the BTC pipeline reveals how Zionist settler-colonialism is central to the continued extraction of oil in the Middle East, and global uneven accumulation, where wealth is concentrated in the Global North. The liberation of Palestine and regional anti-Zionist resistance must therefore be central to the larger struggle against capitalism and for a just transition. Organising from the imperial core against the Zionist occupation of Palestine then becomes about much more than just holding the perpetrators of genocide to account. It is part of the bigger fight against imperialism – which exterminates populations and ecologies for the continued flow of value to the Global North.
9 September 2024
253 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump Plans To Revive Keystone XL Pipeline Project on Day One
It’s been quite some time since we covered the Keystone XL Pipeline, a proposed extension of the existing Keystone Pipeline System designed to transport crude oil from Alberta, Canada, to Nebraska.
The project’s goal was to expand the pipeline system’s capacity by allowing the transport of up to 830,000 barrels of oil per day over a distance of approximately 1,210 miles. The aim was to provide a more direct route for Canadian oil, and provisions were included for adding American-produced oil from the Bakken formation in Montana and North Dakota.
The last time we reported on this Keystone KL, it included a review of the number of jobs that were not created because Biden terminated this project (initially authorized by President-elect Donald Trump.)
The report, which the Department of Energy (DOE) completed in late December without any public announcement, says the Keystone XL project would have created between 16,149 and 59,000 jobs and would have had a positive economic impact of between $3.4-9.6 billion, citing various studies. A previous report from the federal government published in 2014 determined 3,900 direct jobs and 21,050 total jobs would be created during construction which was expected to take two years.
Now, people familiar with the incoming administration’s plans indicate that Trump will revive the project on Day One.
Trump believes declaring the 1,200-mile Canada-to-Nebraska crude project back on the table would drive the pro-oil message he delivered in his campaign, said people involved in the transition team discussions about the idea. Trump also wants to show he can defy President Joe Biden, who reversed Trump’s initial 2017 approval of the project, which was strongly opposed by the climate movement. “It’s on the list of things they want to do first day,” said one of the people familiar with Trump’s plan, who was granted anonymity because they were not authorized to talk to the media. …During his latest presidential campaign, Trump railed against Biden’s decision to revoke the Keystone XL permit. “Why does Biden go in and kill the Keystone [XL] pipeline and approve the single biggest deal that Russia’s ever made, Nord Stream 2, the biggest pipeline anywhere in the world going to Germany and all over Europe?” Trump said during his debate with Vice President Kamala Harris, referring to the gas line that was hit by sabotage in 2022. “Because they’re weak and they’re ineffective.”
90 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The Longest And Most Profitable Crude Oil Pipeline Companies In North America
by u/st0ckholme
170 notes
·
View notes
Text
---


Native American tribes from Michigan, Wisconsin and Ontario have come together to call for an end to the Line 5 pipeline.
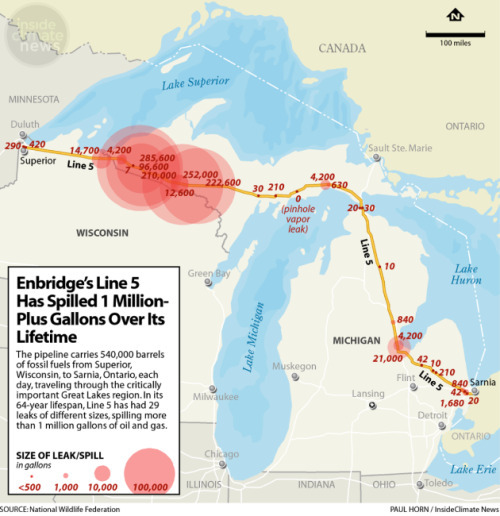
The Enbridge Line 5 crude oil pipeline, first constructed in 1953, stretches from Wisconsin through 645 miles of Michigan and ends in Sarnia, Ontario. Part of the pipeline travels underwater through the Straits of Mackinac.
In recent years, the pipeline's continued operation has become a source of controversy. Many tribal nations and communities claim that the pipeline goes through their traditional territories. The Straits area in particular is considered a place of significant cultural and historical importance to many native groups, including the Anishinaabe. According to tribal leaders, the pipeline poses a major and direct threat to the ecosystems along its path.
“The Straits of Mackinac are [...] sacred from both a cultural and historical perspective in the formation of the Anishinaabe people,” said Austin Lowes, chairperson of the Sault Ste. Marie Tribe of Chippewa Indians, in a statement. “Protecting the Straits is also a matter of the utmost environmental and economic importance — both to our people and the state of Michigan.”
Tribal leaders and other environmental groups have publicly opposed the pipeline for many years and have called for the pipeline to be shut down.
Supporters of the pipeline point out that it transports 540,000 barrels of light crude oil and natural gas liquids through Line 5 on a daily basis. [...]
In an effort to address safety concerns, Enbridge has proposed an underwater tunnel to house the portion of Line 5 that runs under the Straits of Mackinac. [...] Critics of the tunnel project say no oil should be transported through the Straits at all, as a spill could have a devastating impact on more than 700 miles of Great Lakes shoreline. [...]
Previous attempts to shut down the pipeline have been stopped through various means, mostly the 1977 Transit Pipeline Treaty between Canada and the United States.
The latest attempt saw 51 tribal organizations from Wisconsin, Michigan and Ontario submit a report to the United Nations Human Rights Council. This report, dated April 4, claims that the Government of Canada is violating the human rights of Indigenous peoples through its continuous support for Line 5.
The report was submitted to be considered during Canada's upcoming Universal Periodic Review, conducted by the United Nations. As a United Nations member state, Canada is required to be evaluated for its human rights record on a regular basis.
Canada's Universal Periodic Review will take place this year on Nov. 6-17.
The 51 different tribal organizations that signed the report include: The Anishinabek Nation, which represents 39 First Nations throughout the province of Ontario, Sault Ste. Marie Tribe of Chippewa Indians, Bad River Band of the Lake Superior Tribe of Chippewa Indians, Bay Mills Indian Community, Grand Traverse Band of Ottawa & Chippewa Indians, Hannahville Indian Community, Lac Vieux Desert Band of Lake Superior Chippewa Indians, Little River Band of Ottawa Indians, Little Traverse Bay Bands of Odawa Indians, Match-e-be-nash-she-wish Band of Pottawatomi Indians, Nottawaseppi Huron Band of Potawatomi, Saginaw Chippewa Indian Tribe and Red Cliff Band of Lake Superior Chippewa.
---
Headline and text by: Brendan Wiesner. “Michigan, Wisconsin and Canadian tribes come together to fight Line 5.” Yahoo! News. 8 April 2023. Article originally appeared on The Sault News with the title “Great Lakes tribes send report to United Nations to fight Line 5.” [Some paragraph breaks and contractions added by me.]
Context:
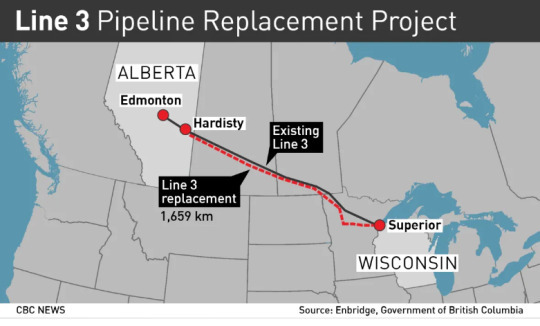
Line 3 brings oil from Alberta to Lake Superior. Then, Line 5 brings the fossil fuel from the Duluth area to the Detroit/Windsor area in Ontario.
709 notes
·
View notes
Text
Having grown up on a farm in Uganda, I have seen the damage of the climate crisis firsthand. My family lived in a small village near the banks of Lake Victoria, the second largest freshwater lake in the world, and my childhood was spent climbing trees, planting seeds, and eating fruit straight from the trees. We grew bananas, guavas, beans, cassava, sugarcane, and coffee. It sounds idyllic but I remember the first time I realised climate change would affect us—it was a rainy season unlike any we had seen before. For days and nights heavy rain battered the fields and strong winds bent and broke the crops until they were unsavable. Not only did the rains affect us financially, but I missed months of my schooling because flooding blocked the roads and I couldn’t get to school.
Burning fossil fuels, which releases carbon pollution into the air and causes our world to overheat, is the number one cause of the climate chaos we’re facing. 2024 may be even hotter than 2023, resulting in even more catastrophic weather.
But there is still hope. Those with power must act now, and the insurance industry holds more power than most to slow the crisis and protect our future. Without insurance, fossil fuel projects can’t operate. If insurance companies updated their policies and refused to insure new fossil fuel projects, there would be no new oil pipelines, liquefied natural gas terminals, or dirty coal mines. If they focused instead on insuring clean, safe energy and a just transition, our communities and our world would be safer for current and future generations.
The insurance industry’s role is to protect and manage risk, but right now it is failing spectacularly at both. Instead of protecting communities, it’s adding fuel to the fire by continuing to insure new fossil fuel projects. The East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) is a prime example. This proposed pipeline would run 1,443 kilometers between Hoima in Uganda and Tanga in Tanzania, but the project has stalled as it has not yet secured full insurance and financing due to the many human and environmental rights abuses associated with it. These include the harassment and imprisonment of peaceful protesters, the disturbing of sacred burial grounds, and the forcible removal of communities to make way for the pipeline. If EACOP gets insured and goes ahead, it will cross 200 rivers and pass through Lake Victoria’s water basin. Over 40 million people depend on the lake for survival, as well as countless animal species; if the pipe leaks and spills oil into the water, what will happen to them?
The corporations behind EACOP say it will “unlock East Africa’s potential,” but let’s be clear: It is neocolonialism at its best, and the only ones who will gain are the foreign companies set to profit. EACOP will irrevocably damage East Africa’s biodiversity, displace thousands of people, destroy their livelihoods and communities, and unleash 32.3 million metric tons of carbon into the atmosphere per year, setting off a climate bomb that will make our world overheat to devastating levels. The International Energy Agency has stated that there can be no new oil pipelines if we are to save the future, and yet insurance companies including AIG, Tokio Marine, Chubb, Hiscox, and Lloyd’s of London still refuse to rule out insuring EACOP.
#enviromentalism#ecology#pipeline#crude oil#climate change#climate crisis#east africa#uganda#tanzania#neocolonialism#East African Crude Oil Pipeline#EACOP#insurance companies
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Oil Theft to End Soon, Vows CDS, Christopher Musa
Oil Theft to End Soon, Vows CDS, Christopher Musa As joint security operation seeks to end the menace He assures the public that oil theft in the region deterring the Nation’s economic growth and expansion, will be laid to rest in three months. Chief Of Defense Staff, General Christopher Musa This assurance came after the Federal Government has ordered the security operatives to curb the illegal…
#Christopher Musa#Criminal Activities#Crude Oil Theft#DIA#DSS#Kayode Egbetokun#Mele Kyari#Niger Delta Region< Pipeline Vandalisation#NNPc#Oil Production#The Army#The Police#The President
0 notes