#Communication Satellite
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Satellite Manufacturing Market - Forecast(2024 - 2030)
Satellite Manufacturing Market Overview
The Global Satellite Manufacturing Market is estimated to reach $24.0 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 3.2% during 2021-2026. Satellite are launched into the space to provide various services such as telemetry, remote sensing satellite, automatic identification system, surveillance, communication and others. Major drivers for satellite manufacturing market growth are surge in utilization of satellites for military surveillance and other defense applications. There is a requirement of more data bandwidth and reliable communication infrastructure to the military for meeting the growing demand from UAVs and modern equipment. Surge in satellite based telemetry and geostationary applications, development of all-electric propulsion systems for use in sun-synchronous orbit satellites along with the growth in R&D space activities are driving the growth of the market.
Report Coverage
The report: “Satellite Manufacturing Market – Forecast (2021-2026)”, by Industry ARC covers an in-depth analysis of the following segments of the Satellite Manufacturing Market.
By Type– Communication Satellite, Remote Sensing Satellite, Navigation Satellite, Geocentric Orbit type satellites, Global Positioning System, Geostationary Satellites, Drone Satellite, Ground Satellite, Polar Satellite, Nano Satellites, CubeSats, SmallSats
By Size– Large, Medium, Mini, Micro, Nano, Pico, Femto
By Orbit Location– LEO Satellites, Sun-Synchronous Orbit Satellites, GEO Satellites
By Application- Military & Government, Commercial
By Geography - North America (U.S, Canada, Mexico), South America(Brazil, Argentina and others), Europe(Germany, UK, France, Italy, Spain, Russia and Others), APAC(China, Japan India, SK, Australia and Others), and RoW (Middle east and Africa)
Request Sample
Key Takeaways
The rise in adoption of satellites in Military and Space applications along with increased R&D activities are driving the growth of the market.
Military sector is witnessing a significant growth of the market owing to the requirement of advanced communication systems for completing their missions and tracking the exact position and movement of their solders.
North America is witnessing a significant growth of the market owing to the presence of one of the biggest space research organization “NASA” in which R&D activities are majorly performed along with the new policies organized by the government related to the satellites in the Military and Defense sector.
Satellite Manufacturing Market Segment Analysis - By Type
By Type the market is segmented into Communication Satellite, Remote Sensing Satellite, Navigation Satellite, Geocentric Orbit type satellites, Global Positioning System, Geostationary Satellites, Drone Satellite, Ground Satellite, Polar Satellite, Nano Satellites, CubeSats, SmallSats. Communication satellite are dominating the market at 24.5% in 2020 owing to its large use in television, telephone, radio, internet and military applications. Communication satellite uses radio frequencies and microwave frequencies to allow communication between separated geographical points on the Earth. Communication satellites are used in variety of applications such as long-distance telephone transmission, gathering intelligence in military, navigation of ships and aircrafts, weather forecasting and others owing to which it has a demand in the market. These factors have boosted the market growth.
Inquiry Before Buying
Satellite Manufacturing Market Segment Analysis - By Application
By Application the market is segmented into Military & Government, Commercial. Military & Government is witnessing a significant growth in the market. Military and Government sector is witnessing a significant growth in the market at 3.9% CAGR through 2026. In Military and government the satellites are used for intelligence gathering, military communications, and navigation purposes. The private and commercial satellites have become a significant provider of satellite services in the military applications. A continuous picture of location and movements of the solders are provided to the commanders through the combination of GPS –derived positioned data and advanced communication along with variety of space and airborne sensors. These factors are driving the growth of the market.
Satellite Manufacturing Market Segment Analysis - By Geography
By Geography the Satellite Manufacturing Market is dominated by North America with a market share 42.6% in 2020. Presence of robust framework for designing and manufacturing of satellites is one of the predominant factors driving the market in this region. The presence of the major key players and most advanced technological developments in this region is also boosting the growth of the market. On December 2919, National Defense Authorization acts was signed by President Trump. This act created a Space Force and is responsible for organizing, training, and equipping space forces command for the U.S military. The presence of one of the biggest space research organization “NASA” has also propelled the manufacturing of satellites with advanced technology which are involved in the R&D activities. These factors are driving the market in North America.
Schedule a Call
Satellite Manufacturing Market Drivers
Surge in use of satellites in Military applications:
Surge of satellites in military applications have resulted in the development of small bodyguard satellite and space based laser defenses to protect important space assets. Many of the countries are purchasing satellites to support their own strategic Military activities. In APAC region China is the fastest growing country in civil, military and commercial capabilities. China is planning to launch two BeiDou Satellites into geostationary orbit in 2020. China plans to follow up this mission in late 2020 with Chang’e-5, a mission that aims to return samples from the Moon back to Earth for further study. U.S and other countries are also involved in the planning and launch of the satellites aiming to strengthen their military activities and communication within their armed forces. These factors are driving the market growth.
Technological advancements and growth in internet:
The rising use of internet applications have resulted in the manufacturing of more advanced satellite for communication purposes. The satellite are connected to the ground stations through which they are controlled. The antennas on satellites and ground stations, the landlines that connect ground stations to terrestrial networks, and the user terminals that connect to satellites are all potential intrusion points for cyber-attacks. Cyber-attacks can be used to monitor data traffic patterns. A cyber- attack on space systems can result in data loss, widespread disruptions, and even permanent loss of a satellite. To control all these situations the major key players are manufacturing the satellites with advanced capabilities. Rising internet penetration is propelling the growth of satellites used for communication purposes. These factors are fueling the growth of the market.
Buy Now
Satellite Manufacturing Market Challenges
Complex Programming and Design related Risks:
Although the satellite are used in communications and many space missions but most of the space related missions fails due the complexity related to the designing and programming of the satellites. The designers relay on numerical modelling of vehicle aerodynamics rather than actual wind tunnel tests. These factors are causing major restrain in the market growth.
Satellite Manufacturing Market Landscape
Satellite Manufacturing Market is dominated by major companies such as Airbus Defense and Space, OHB SE, Boeing Defense, Space and Security, JSC Information Satellite Systems, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Space Systems, Thales Alenia Space, Capella Space, Ursa Space Systems among others.
Acquisitions/Technology Launches
In January 2020, Capella Space evolved its satellite design “testbed satellite”. It enables on –demand observation from anywhere on Earth. This design is anticipated to deliver the most flexible and frequent high quality images in the market.
#Satellite Manufacturing Market#Communication Satellite#Satellite Manufacturing Market Size#data bandwidth#Satellite Manufacturing Market Share#Satellite Manufacturing Market Analysis#Satellite Manufacturing Market Revenue#Satellite Manufacturing Market Trends#Satellite Manufacturing Market Growth#Satellite Manufacturing Market Research#Satellite Manufacturing Market Outlook#Satellite Manufacturing Market Forecast
0 notes
Text
All-Star Moments in Space Communications and Navigation
How do we get information from missions exploring the cosmos back to humans on Earth? Our space communications and navigation networks – the Near Space Network and the Deep Space Network – bring back science and exploration data daily.
Here are a few of our favorite moments from 2024.

1. Hip-Hop to Deep Space
The stars above and on Earth aligned as lyrics from the song “The Rain (Supa Dupa Fly)” by hip-hop artist Missy Elliott were beamed to Venus via NASA’s Deep Space Network. Using a 34-meter (112-foot) wide Deep Space Station 13 (DSS-13) radio dish antenna, located at the network’s Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex in California, the song was sent at 10:05 a.m. PDT on Friday, July 12 and traveled about 158 million miles from Earth to Venus — the artist’s favorite planet. Coincidentally, the DSS-13 that sent the transmission is also nicknamed Venus!

NASA's PACE mission transmitting data to Earth through NASA's Near Space Network.
2. Lemme Upgrade You
Our Near Space Network, which supports communications for space-based missions within 1.2 million miles of Earth, is constantly enhancing its capabilities to support science and exploration missions. Last year, the network implemented DTN (Delay/Disruption Tolerant Networking), which provides robust protection of data traveling from extreme distances. NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) mission is the first operational science mission to leverage the network’s DTN capabilities. Since PACE’s launch, over 17 million bundles of data have been transmitted by the satellite and received by the network’s ground station.

A collage of the pet photos sent over laser links from Earth to LCRD and finally to ILLUMA-T (Integrated LCRD Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal) on the International Space Station. Animals submitted include cats, dogs, birds, chickens, cows, snakes, and pigs.
3. Who Doesn’t Love Pets?
Last year, we transmitted hundreds of pet photos and videos to the International Space Station, showcasing how laser communications can send more data at once than traditional methods. Imagery of cherished pets gathered from NASA astronauts and agency employees flowed from the mission ops center to the optical ground stations and then to the in-space Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD), which relayed the signal to a payload on the space station. This activity demonstrated how laser communications and high-rate DTN can benefit human spaceflight missions.

4K video footage was routed from the PC-12 aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico. The signals were then sent to NASA’s Laser Communications Relay Demonstration spacecraft and relayed to the ILLUMA-T payload on the International Space Station.
4. Now Streaming
A team of engineers transmitted 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back using laser communication signals. Historically, we have relied on radio waves to send information to and from space. Laser communications use infrared light to transmit 10 to 100 times more data than radio frequency systems. The flight tests were part of an agency initiative to stream high-bandwidth video and other data from deep space, enabling future human missions beyond low-Earth orbit.

The Near Space Network provides missions within 1.2 million miles of Earth with communications and navigation services.
5. New Year, New Relationships
At the very end of 2024, the Near Space Network announced multiple contract awards to enhance the network’s services portfolio. The network, which uses a blend of government and commercial assets to get data to and from spacecraft, will be able to support more missions observing our Earth and exploring the cosmos. These commercial assets, alongside the existing network, will also play a critical role in our Artemis campaign, which calls for long-term exploration of the Moon.

On Monday, Oct. 14, 2024, at 12:06 p.m. EDT, a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
6. 3, 2, 1, Blast Off!
Together, the Near Space Network and the Deep Space Network supported the launch of Europa Clipper. The Near Space Network provided communications and navigation services to SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket, which launched this Jupiter-bound mission into space! After vehicle separation, the Deep Space Network acquired Europa Clipper’s signal and began full mission support. This is another example of how these networks work together seamlessly to ensure critical mission success.
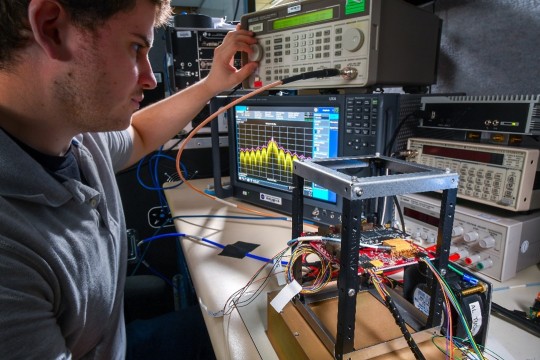
Engineer Adam Gannon works on the development of Cognitive Engine-1 in the Cognitive Communications Lab at NASA’s Glenn Research Center.
7. Make Way for Next-Gen Tech
Our Technology Education Satellite program organizes collaborative missions that pair university students with researchers to evaluate how new technologies work on small satellites, also known as CubeSats. In 2024, cognitive communications technology, designed to enable autonomous space communications systems, was successfully tested in space on the Technology Educational Satellite 11 mission. Autonomous systems use technology reactive to their environment to implement updates during a spaceflight mission without needing human interaction post-launch.
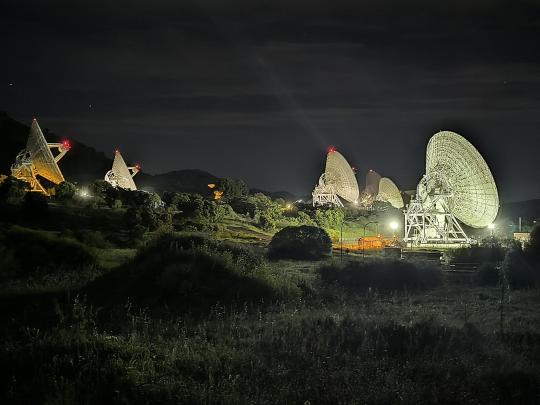

A first: All six radio frequency antennas at the Madrid Deep Space Communication Complex, part of NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN), carried out a test to receive data from the agency’s Voyager 1 spacecraft at the same time.
8. Six Are Better Than One
On April 20, 2024, all six radio frequency antennas at the Madrid Deep Space Communication Complex, part of our Deep Space Network, carried out a test to receive data from the agency’s Voyager 1 spacecraft at the same time. Combining the antennas’ receiving power, or arraying, lets the network collect the very faint signals from faraway spacecraft.
Here’s to another year connecting Earth and space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Who should defend the moon if not poets?
Antoni Slonimski
#aesthetic#dark academia#coffee#art#books#academia#college#light academia#literature#studyblr#poets#poetry#poems#moon#celestial#life#astrology#satellites#stars#sun#writersblr#writers#writers community
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
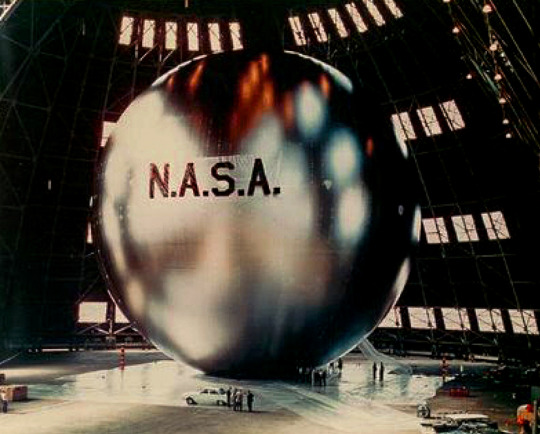

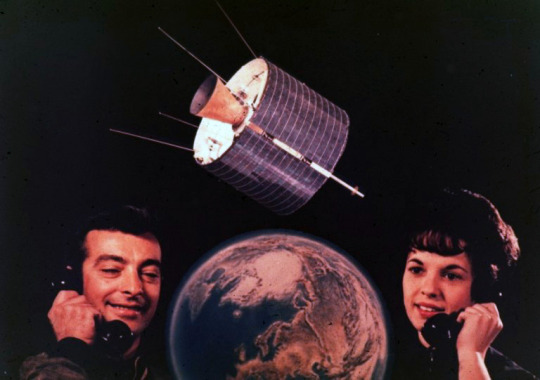
NASA’s Echo 1 communications satellite - 1960.
#nasa#nasa photos#satellites#communication satellites#echo 1#technology#vintage tech#vintage technology#space#space exploration#project echo#space balloons#bell telephone laboratories#jet propulsion laboratory#mylar
752 notes
·
View notes
Text
Happy New Year from my beloved companions :) 🔢🪺🛰️💕

#object show community#object show#object shows#battle for dream island#algebralian#bfb#battle for bfdi#bfdi tpot#one tpot#two tpot#tau xfohv#pi#x xfohv#four bfb#x bfb#faux integer#seven xfohv#icesat 2#satellite#objectum#plushum#posic companion#numbers
36 notes
·
View notes
Text

Scientific and technological progress is the main source of increasing production efficiency! (1986)
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
This image shows the “moonrise” of the satellite as it emerges from behind asteroid Dinkinesh as seen by the Lucy Long-Range Reconnaissance Imager (L’LORRI), one of the most detailed images returned by NASA’s Lucy spacecraft This image was taken at closest approach, from a range of 270 miles (430k).

#astronomy#nasa#astronomers#universe#astrophotography#nasa photos#astrophysics#outer space#nasawebb#hubble space telescope#i love astronomy#astronomy facts#astronauts#astronaut#astro community#planetary science#planetary nebula#space exploration#space#science#science facts#space science#cosmos#the universe#our universe#asteroid observations#asteroidbelt#asteroid astrology#asteroid#satellite
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wanted to share some things that make me happy:
Accidentally scared a friend while walking by to grab something and they said they thought I was a cat! Creature moment!! :P
Randomly discovering things about my kintype. Like realizing that my fucked up sleep schedule is just because I'm nocturnal. Also, I don't think I'm supposed to be so sensitive to temperature because quiet nights in the winter feel so homey but human body does NOT like that lmao
(speaking of kintype -- might be a shapeshifting alien? who knows)
Met a therian irl! Amazing moment!!
And because thinking about good stuff is healthy... if there's anything that's made you happy lately, reblog/comment! I'd love to hear about it!! :D
#literally satellite#shapeshifterkin#otherkin#otherkin community#alterhuman#nonhuman#alterhuman community#alterhumanity#otherkinity#therian#therianthropy#therian community#otherhearted#fictionkin#fictionkith
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
My friends and I, trauma dumping to each other in a playground after midnight.

I know no one likes my original art but I needed to post this cos LOOK AT US.
#cutest fucking friendship group#you have no idea how much I love these people#we are all so incredibly queer#damn good night#the stars were so pretty#no clue what those shooting star looking things were#there were so many of them#we were theorising satellites#someone who’s good at Space lemme know#illustration#lgbt art#queer#queer community#queer artist#drawing#clip studio paint
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

9 Out-of-This-World Moments for Space Communications & Navigation in 2023
How do astronauts and spacecraft communicate with Earth?
By using relay satellites and giant antennas around the globe! These tools are crucial to NASA’s space communications networks: the Near Space Network and the Deep Space Network, which bring back science and exploration data every day.
It’s been a great year for our space communications and navigation community, who work to maintain the networks and enhance NASA’s capabilities. Keep scrolling to learn more about our top nine moments.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, on the company's 29th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 8:28 p.m. EST.
1. In November, we launched a laser communications payload, known as ILLUMA-T, to the International Space Station. Now, ILLUMA-T and the Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD) are exchanging data and officially complete NASA’s first two-way, end-to-end laser relay system. Laser communications can send more data at once than traditional radio wave systems – think upgrading from dial-up to fiber optic internet. ILLUMA-T and LCRD are chatting at 1.2 gigabits per second (Gbps). At that rate, you could download an average movie in under a minute.
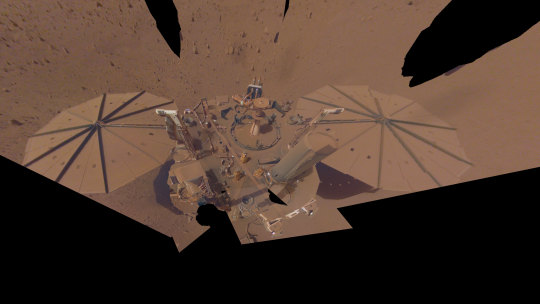
NASA’s InSight lander captured this selfie on Mars on April 24, 2022, the 1,211th Martian day, or sol, of the mission.
2. Data analyzed in 2023 from NASA’s retired InSight Mars lander provided new details about how fast the Red Planet rotates and how much it wobbles. Scientists leveraged InSight’s advanced radio technology, upgrades to the Deep Space Network, and radio signals to determine that Mars’ spin rate is increasing, while making the most precise measurements ever of Mars’ rotation.

TBIRD is demonstrating a direct-to-Earth laser communications link from low Earth orbit to a ground station on Earth.
3. We set a new high record! The TeraByte InfraRed Delivery (TBIRD) payload – also demonstrating laser communications like ILLUMA-T and LCRD – downlinked 4.8 terabytes of data at 200 Gbps in a single 5-minute pass. This is the highest data rate ever achieved by laser communications technology. To put it in perspective a single terabyte is the equivalent of about 500 hours of high-definition video.

A 34-meter (112-foot) wide antenna at Canberra Deep Space Communications Complex near Canberra, Australia.
4. This year we celebrated the Deep Space Network’s 60th anniversary. This international array of antennas located at three complexes in California, Spain, and Australia allow us to communicate with spacecraft at the Moon and beyond. Learn more about the Deep Space Network’s legacy and future advancements.
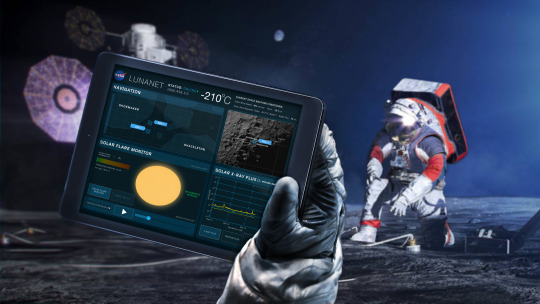
An illustration of the LunaNet architecture. LunaNet will bring internet-like services to the Moon.
5. We are bringing humans to the Moon with Artemis missions. During expeditions, astronauts exploring the surface are going to need internet-like capabilities to talk to mission control, understand their routes, and ensure overall safety. The space comm and nav group is working with international partners and commercial companies to develop LunaNet, and in 2023, the team released Draft LunaNet Specification Version 5, furthering development.

The High-Rate Delay Tolerant Networking node launched to the International Space Station in November and will act as a high-speed path for data.
6. In addition to laser communications, ILLUMA-T on the International Space Station is also demonstrating high-rate delay/disruption tolerant networking (HDTN). The networking node is showcasing a high-speed data path and a store-and-forward technique. HDTN ensures data reaches its final destination and isn’t lost on its path due to a disruption or delay, which are frequent in the space environment.

The Communications Services Project (CSP) partners with commercial industry to provide networking options for future spaceflight missions.
7. The space comm and nav team is embracing the growing aerospace industry by partnering with commercial companies to provide multiple networking options for science and exploration missions. Throughout 2023, our commercialization groups engaged with over 110 companies through events, one-on-one meetings, forums, conferences, and more. Over the next decade, NASA plans to transition near-Earth services from government assets to commercial infrastructure.

Middle and high school students solve a coding experiment during NASA's Office of STEM Engagement App Development Challenge.
8. Every year, NASA’s Office of STEM Engagement sponsors the App Development Challenge, wherein middle and high school students must solve a coding challenge. This year, student groups coded an application to visualize the Moon’s South Pole region and display information for navigating the Moon’s surface. Our space communications and navigation experts judged and interviewed students about their projects and the top teams visited NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston!

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after liftoff at the pad at 3:27 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Aug. 26, from Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida carrying NASA’s SpaceX Crew-7 crew members to the International Space Station. Aboard SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft are NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli, ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen, JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov.
9. The Near Space Network supported 19 launches in 2023! Launches included Commercial Crew flights to the International Space Station, science mission launches like XRISM and the SuperBIT balloon, and many more. Once in orbit, these satellites use Near Space Network antennas and relays to send their critical data to Earth. In 2023, the Near Space Network provided over 10 million minutes of communications support to missions in space.
Here’s to another year connecting Earth and space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

The Blue Cold
📸 Canon Sure Shot 60 Zoom
#dub techno#satellite#tower#blue sky#cold weather#coldwave#35mm color film#analog photography#amatuer photography#film community#film photography#zagreb
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

one of the joys of finishing children of time is a bunch of fans making sure to reply to almost every single "woah! Portia spiders are so intelligent" comment with an "allow me to introduce you to CoT books!!" and promote them with the vigour of a bachelor in marketing degree. You can nearly feel the overly enthusiastic desire to infodump behind their comments (tbh same). Shout-out to those meme spreading fellow spider fans, I salute you.
#this is me launching a satellite into my tumblr orbit to communicate with other CoT readers#can y'all receive me. can anybody receive me#children of time#how many references can i possibly throw in this post#cw: spiders#children of ruin#children of memory#Adrian Tchaikovsky#arachnophobia#portia spider
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Someone save me I'm writing a fic spanning a 5 year length of time which I'm about 1 year into and already have Ideas for TWO (2) sequels
#juice fic#i expected from the beginning there was a good chance id write a follow up with ten someday#but hubble. why. why do i have to write a hubble fic#hopefully the hubble one would be short#im thinking since he's a telescope and doesn't talk much#when he wakes up he just sends juice dozens of blurry pictures#theres not really much plot there though i don't have to—#wait shit#hubbles expected to deorbit around that time#FUCK#watch me write TWO fics in which i attempt to plausibly rescue doomed satellites#(three if you count the ten one but at least she's not in any real and immediate danger)#(shes just really far away and has a battery from the 70s so uh. communication is gonna be a problem)
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
It’s totally family guy

#object show community#object show#object shows#battle for dream island#algebralian#bfb#battle for bfdi#bfdi tpot#satellite#space#Objectum#self ship#ship kids#four kinnie#four bfb#four being silly#icesat 2
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are you wearing?
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
Updated: January 22, 2025
Special Weapons of the Iron Eclipse AU
The AR-10 Autorifle, standard-issue for both the Regular Army and Amadeus Syndicate, chambers 7.62mm ammunition. It features an integrated grenade launcher mounted beneath the barrel, granting versatility through its dual capability for precision gunfire and explosive ordnance. Its design draws inspiration from the Japanese Type 64 Rifle, incorporating an M203-style grenade launcher and borrowing elements from the U.S. military's M16 rifle.
The Morden M60 is a 7.62mm machine gun reserved for high-ranking officials within the Rebel Army, capable of firing multiple shoots in controlled bursts. Only two variants are known to exist: the M240 Bravo Machine Gun, distinguished by its swift and silent operation; and the RA240 Machine Gun, a modified version employed by the Regular Army. The RA240 Machine Gun features a Lewis MG-style buttstock, trading some speed and stealth for increased reliability.
The Hexagon Arms M-3685 is a 9mm submachine gun modelled after the Heckler & Koch MP5, featuring a distinctive design element: a built-in tool within its grip that allows for easy adjustment of the front sight. The firearm was crafted by Tarma Roving as a gift to Fio Germi following the Extraterrestrial Alliance Clash, with the primary intention of enhancing her battlefield protection. However, upon taking notice of its potential, the Regular Army secured Tarma's permission to mass-produce the design for their troops.
The HV-01 Heavy Machine Gun, commonly referred to as the Heavy Machine Gun, is a common special weapon firing 7.62mm FMJ rounds compatible with most automatic firearms on the battlefield. Despite sharing comparable firepower with handguns wielded by elite units like the Peregrine Falcons Squad, S.P.A.R.R.O.W.S., and Ikari Warriors, its exceptional fire rate makes it one of the deadliest weapons available. It has a magazine capacity of 200-300 rounds, and it resembles the Heavy Machine Gun that Marco uses in Neo-Geo Battle Coliseum.
The RK-02 Light Anti-Armour Rocket Launcher, commonly referred to as the Rocket Launcher, fires small, slow-moving rockets. These rockets lack the penetration power to defeat heavy armour but are highly explosive and effective against infantry formations. The rockets have a proximity fuzing capability, homing in on nearby targets before exploding on contact. It resembles the Rocket Launcher depicted in Metal Slug 3D.
The FS-03, commonly referred to as the Flame Shot, is a powerful incendiary weapon that unleashes a large blast of flame travelling in a shallow parabolic trajectory when fired horizontally, with significantly increased range when fired upward and reduced range when fired downward. It excels at taking out large groups of infantry with a single shot, but its effectiveness is hindered by limited range and a slow fire rate. At close range, it can severely damage vehicles and instantly incinerate personnel, though its potency decreases with distance. It has a 30-round ammo capacity and features a toggle switch allowing users to alternate between two firing modes: large blasts for high damage and fireballs that cover a wider range but deal relatively low damage. Its design bears a striking resemblance to the Flame Shot featured in Metal Slug 3D.
The SG-04, commonly referred to as the Shotgun, fires 12-gauge rounds loaded with metallic BB pellets, delivering devastating effectiveness at point-blank range. However, the BBs rapidly lose velocity over short distances, rendering them harmless beyond 6 ft (182.88 cm). Despite its limited 30-round magazine capacity, the SG-04 packs immense power, capable of annihilating clusters of infantry with a single blast and effortlessly disabling vehicles with just a few well-placed shots. It resembles the Shotgun depicted in Metal Slug 3D.
The LS-05, commonly referred to as the Laser Gun, emits a concentrated stream of energy in the form of a multicoloured beam. This intense energy focal point can slice through tank armour and annihilate enemy infantry with ease. While incredibly powerful, the weapon's high energy consumption leads to rapid ammo depletion. It has a moderate ammo capacity of 200-400 rounds. Its design bears a striking resemblance to the Laser Gun featured in Metal Slug 3D.
The EC-06, commonly known as the Enemy Chaser, is a specialised Rocket Launcher that prioritises advanced guidance over agility and raw firepower. Its enhanced homing system and increased ammo capacity of 40 rounds make it an invaluable asset for land troops in anti-aircraft operations. Although not foolproof, the homing capability significantly improves targeting accuracy. Once launched, the missiles automatically enter homing mode, locking onto the nearest enemies. A notable feature is the independent homing mechanism for each missile, enabling rapid-fire barrages. The weapon was initially conceived by Tarma Roving, who improvised its design after his Rocket Launcher malfunctioned during a critical mission against a Southern European terrorist group. Its effectiveness led to its subsequent adoption by the Regular Army. Its design bears a striking resemblance to the Enemy Chaser featured in Metal Slug 3D.
The SPG-07, affectionately known as the Super Grenade, is a Rocket Launcher variant that unleashes powerful RPGs with increased range. While its explosive payload can swiftly obliterate targets, its smoothbore design prohibits piercing thick armour. The RPGs travel swiftly, generating a massive blast radius capable of annihilating multiple targets. To balance its destructive potential, it has limited ammo reserves, allowing only two RPGs to be fired at a time. Its overall capacity is 10-20 rounds. Notably, its design bears resemblance to the Super Grenade from Metal Slug 3D.
The DS-09, commonly referred to as the Drop Shot, is a modified Rocket Launcher that fires bouncing landmines. These landmines bounce until they hit a target or lose momentum and stop moving. It’s effective against infantry, particularly those hiding in cover, but it lacks the power to easily damage armoured vehicles. The bouncing landmines have a limited range and are affected by the terrain's geography. As a result, soldiers must pay close attention to their environment to use the weapon effectively. Many soldiers dislike it due to its slow firing speed and horizontal movement, making it more suitable as a situational weapon. Its potential for being cumbersome and dangerous in various situations, along with its limited effectiveness in certain terrains, also contribute to its rare usage in the Regular Army. However, a small number of individuals have successfully leveraged its potential, often by modifying the bouncing landmines or combining them with existing weapons.
The SR-001 Iron Lizard, commonly referred to as the Iron Lizard, deploys remote-controlled, unmanned vehicles designed to engage targets with high lethality. These vehicles excel in anti-personnel roles, utilising special warheads filled with combustible chemicals. However, they are ineffective against armoured targets and aircraft. Once deployed, the vehicle-like missiles traverse the terrain until they detect a target, then detonate in a cloud of blue smoke, potentially taking out multiple enemies beyond the initial point of contact. Many people underestimate this weapon, thinking it's a joke due to its unusual ammunition, which oddly combines elements of RC toy cars with explosive missiles. It resembles the Iron Lizard depicted in Neo-Geo Battle Coliseum.
The TSG-002, commonly referred to as the Thunder Shot, is a modified Laser Gun that emits a powerful electrical pulse, automatically targeting enemies with near-instantaneous hits. This pulse can pierce armour and strike multiple targets simultaneously with a single shot. Boasting a 20-round ammo capacity, its capabilities make it an invaluable asset. However, its homing capabilities are inconsistent, often struggling to engage multiple enemies across varying elevations. Initially designed by Tarma Roving and Hyakutaro Ichimonji to rapidly disable technological devices from a distance, its effectiveness led to swift adoption by the Regular Army.
The Double-Barrel Heavy Machine Guns, commonly referred to as the Two Machine Guns, are a unique submachine gun variant inspired by the Heavy Machine Gun. Modelled after the MAC-10, these twin guns offer an impressive 300-round ammo capacity. They strike a balance between range, firepower, and mobility, surpassing pistols and heavy machine guns in versatility. While ideal for long-range combat, they lack the arcing trajectory of traditional Heavy Machine Guns. However, their dual-barrel design significantly increases their rate of fire, but it can rapidly deplete ammo reserves.
The Zantetsu Sword is a blade infused with iron-cutting energy that releases potent waves upon each swing. These energy waves are capable of annihilating clusters of infantry, deflecting incoming bullets, and even disabling armoured vehicles. However, its effectiveness is tempered by its limited range and restrictive aiming capabilities, preventing vertical targeting. During Ralf Jones' expedition to the Oro Sol Ruins, he caught the attention of Sol Dae Rokker, who was moved by his reverence for the ancient site. As a token of respect for Ralf's restraint in not ravaging the ruins, Sol Dae Rokker imbued a deceased archaeologist’s Hori Hori knife with bluish-white energy and presented it to him.
The Hori Hori knife’s extraordinary properties eventually caught the attention of the Regular Army, which successfully replicated its unique attributes and began mass-producing the design. Those used by the Regular Army resemble standard military-issued combat knives, which bear a resemblance to the Combat Knife in Metal Slug 3D.
The AA Machine Gun Turret is a stationary .50-calibre anti-aircraft machine gun primarily used by the Regular Army, and occasionally utilised by the Rebel Army. It fires a continuous stream of light armour-piercing rounds at a high rate of fire. Those with a prominent blue sheen are designed for marine purposes, while ones with a green-tinted silver finish are intended for land-based applications.
The Thunder Cloud is a highly classified, cutting-edge weapon system that utilises an oblong canister loaded with nanobots. These nanobots generate an artificial thundercloud imbued with negatively charged electromagnetic energy. Once deployed, it autonomously targets the nearest adversary, hovering above and unleashing lightning bolts with pinpoint accuracy. The cloud's energy reserve supports 30 to 50 high-energy strikes before dissipating.
The Mobile Satellite, or MOBS for short, is a highly classified, miniature hovering drone resembling a satellite. Equipped with an advanced radar system and an ion cannon, it autonomously tracks and engages targets, firing continuous ion bolts until destruction or depletion. Its energy reserve supports up to 200 ion bolts, after which the device's power source is exhausted, causing it to plummet and self-destruct.
The Grenade Gun is a modified Rocket Launcher, capable of propelling grenades over extended distances of 10 to 15 feet (304.8 cm to 457.2 cm).
The Missile Pod launches five small, high-velocity homing missiles that automatically acquire and track nearby targets. Its wide area coverage and high damage output make it effective against land troops, smaller aircraft, and combat vehicles.
The Fire Gun is a modified Flame Shot that emits a continuous, adjustable stream of flames that can be directed and arced by adjusting the gun's orientation.
The Bazooka fires a single, high-explosive shell that detonates upon impact, unleashing a devastating, fiery blast that damages and incapacitates nearby targets. It closely resembles the American FIM-92 Stinger man-portable surface-to-air missile launcher.
The Gatling Shot is a large, rapid-firing, multiple-barrel firearm that fires 7.62mm FMJ rounds, identical to those used by heavy machine guns. Its heavy weight and high ammunition capacity (holding up to 500 rounds) are balanced by its rapid rate of fire, which depletes ammunition quickly. As a result, it’s typically reserved for specific situations, such as crowd control. It resembles the Gatling Shot depicted in Metal Slug Attack and Metal Slug: Commander.
#writerscorner#creative writing#writing#iron eclipse au#metal slug#snk#gaming community#weapons#firearms#guns#swords#rockets#turret#nanotechnology#satellite
6 notes
·
View notes