#Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Louisiana’s coast is sinking. Advocates say the governor is undermining efforts to save it. (Washington Post)
For the past decade, Louisiana’s program for coastal protection has been hailed as one of the best in the country, after the devastation from Hurricanes Katrina and Rita pushed the state to shore up coastlines, repair levees and protect natural habitats.
Sign up for the Climate Coach newsletter and get advice for life on our changing planet, in your inbox every Tuesday.
But now, environmental advocates and experts say the state’s new Republican governor is undermining its coastal protection agency — the state’s first and strongest line of defense against climate change-induced sea level rise. In an open letter published this week and signed by more than 200 business leaders, environmental advocates and other experts, various groups warned against Gov. Jeff Landry’s plans to transform the state’s Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority.
“The very future of our state is at stake,” the letter read.
Environmentalists say that the new governor’s actions could hobble the agency just as its work is most needed. The moves come as other right-leaning states are also cutting back on climate goals and even references to climate change. This month, Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis (R) signed a bill erasing most mentions of climate change from state law. DeSantis is also poised tonullify the state’s targets for 100 percent renewable energy by 2050.
Since 2005, when Louisiana was devastated by two hurricanes, the coastal restoration agency has built or revamped over 300 miles of levees that hold back floodwaters, and restored dozens of miles of barrier islandsthat can absorb the pressure of waves and rising seas. The agency works to shore up these defenses in the face of future, stronger storms and higher seas.

Follow Climate & environmentFollow
Its work is critical, experts say: Louisiana is losing coastline at a dramatic rate. In the past century, the state has lost over 2,000 square miles of land; it could lose 2,000 more in the next 50 years, scientists predict.As sea level rise has accelerated, so has the loss of land. Wetlands are “drowning” in many areas of the state — covered by sea level rise faster than they can grow. In the coming decades, scientists say, the state could lose up to 75 percent of its natural buffer against hurricanes and storms.
A science-based agency under threat
Landry, who took office in January, has removedsix members of the coastal restorationagency’s board and suggested subsuming it into another, larger department. In a memo, the governor said that such moves could help avoid government operations existing in “distinct silos” and improve efficiency.
Environmental groups, on the other hand, say the shake-ups are undermining the work of an agency that is vitally important.The leadership and structural change could distract the agency from its plan for the coastline, slow down essential projects that can prevent flooding and allow politics to creep into the work of the science-based agency, experts and environmentalists say.
“It just seems like it’s chaotic at a time when we do not need that kind of chaos,” said Rebecca Triche, executive director of the Louisiana Wildlife Federation and one of the signatories on the letter.
Triche said that some of the experts taken off the board could have helped provide needed perspectives on the state’s coastal plans. The board is made up of some political appointees and some publicly elected government officials.“It just appears that independent voices are being removed,” she said.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Holy crap, I didn't think Biden would be able to get the Climate Corps established without Congress. This is SUCH fantastic news.
--
"After being thwarted by Congress, President Joe Biden will use his executive authority to create a New Deal-style American Climate Corps that will serve as a major green jobs training program.
In an announcement Wednesday, the White House said the program will employ more than 20,000 young adults who will build trails, plant trees, help install solar panels and do other work to boost conservation and help prevent catastrophic wildfires.
The climate corps had been proposed in early versions of the sweeping climate law approved last year but was jettisoned amid strong opposition from Republicans and concerns about cost.
Democrats and environmental advocacy groups never gave up on the plan and pushed Biden in recent weeks to issue an executive order authorizing what the White House now calls the American Climate Corps.
“After years of demonstrating and fighting for a Climate Corps, we turned a generational rallying cry into a real jobs program that will put a new generation to work stopping the climate crisis,” said Varshini Prakash, executive director of the Sunrise Movement, an environmental group that has led the push for a climate corps.
With the new corps “and the historic climate investments won by our broader movement, the path towards a Green New Deal is beginning to become visible,” Prakash said...
...Environmental activists hailed the new jobs program, which is modeled after the Civilian Conservation Corps, created in the 1930s by President Franklin D. Roosevelt, a Democrat, as part of the New Deal...
Lawmakers Weigh In
More than 50 Democratic lawmakers, including Massachusetts Sen. Ed Markey and New York Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, had also encouraged Biden to create a climate corps, saying in a letter on Monday that “the climate crisis demands a whole-of-government response at an unprecedented scale.”
The lawmakers cited deadly heat waves in the Southwest and across the nation, as well as dangerous floods in New England and devastating wildfires on the Hawaiian island of Maui, among recent examples of climate-related disasters.
Democrats called creation of the climate corps “historic” and the first step toward fulfilling the vision of the Green New Deal.
“Today President Biden listened to the (environmental) movement, and he delivered with an American Climate Corps,” a beaming Markey said at a celebratory news conference outside the Capitol.
“We are starting to turn the green dream into a green reality,” added Ocasio-Cortez, who co-sponsored the Green New Deal legislation with Markey four years ago.
“You all are changing the world,” she told young activists.
Program Details and Grant Deadlines
The initiative will provide job training and service opportunities to work on a wide range of projects, including restoring coastal wetlands to protect communities from storm surges and flooding; clean energy projects such as wind and solar power; managing forests to prevent catastrophic wildfires; and energy efficient solutions to cut energy bills for consumers, the White House said.
Creation of the climate corps comes as the Environmental Protection Agency launches a $4.6 billion grant competition for states, municipalities and tribes to cut climate pollution and advance environmental justice. The Climate Pollution Reduction Grants are funded by the 2022 climate law and are intended to drive community-driven solutions to slow climate change.
EPA Administrator Michael Regan said the grants will help “communities so they can chart their own paths toward the clean energy future.”
The deadline for states and municipalities to apply is April 1, with grants expected in late 2024. Tribes and territories must apply by May 1, with grants expected by early 2025."
-via Boston.com, September 21, 2023
#climate change#climate crisis#climate anxiety#climate news#climate corps#biden#biden administration#democrats#voting matters#congress#environmental activism#environmental protection agency#environmental justice#climate activism#united states#us politics#good news#hope#hope posting#green jobs#hope punk#seriously this is SUCH a huge deal#climate hope#green energy#disaster preparedness#natural disasters#ecosystem restoration
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - January 22-28
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles!
1. Sunfish that got sick after aquarium closed has recovered — thanks to human cutouts

“A solitary sunfish […] appeared unwell days after the facility closed last month for renovations. As a last-ditch measure to save the popular fish, its keepers hung their uniforms and set up human cutouts outside the tank. The next morning, the sunfish ate for the first time in about a week and has been steadily recovering[….]”
2. Costco stands by DEI policies, accuses conservative lobbyists of 'broader agenda'

“[Each of the board of directors and 98% of shareholders voted to reject a measure against DEI.] Costco's board wrote that “our commitment to an enterprise rooted in respect and inclusion is appropriate and necessary[….]””
3. Nearly $37 Million Will Support Habitat Restoration in Coastal Louisiana

“The project will restore nearly 380 acres of marsh and construct more than 7,000 feet of terraces in St. Bernard Parish. […] Coastal wetlands help protect communities [… from] wind, waves, and flooding[… and] support a statewide seafood industry valued at nearly $1 billion per year.”
4. Cooling green roofs seemed like an impossible dream for Brazil's favelas. Not true!

“[… A Brazilian nonprofit] teaches favela residents how to build their own green roofs as a way to beat the heat without overloading electrical grids[…,] dampen noise pollution, improve building energy efficiency, prevent flooding by reducing storm water runoff and ease anxiety.”
5. Bacteria found to eat forever chemicals -- and even some of their toxic byproducts
“"Many previous studies have only reported the degradation of PFAS, but not the formation of metabolites. We not only accounted for PFAS byproducts but found some of them continued to be further degraded by the bacteria," says the study's first author[….]”
6. A father and daughter’s to turn oil data into life-saving water

“The aquifer [discovered through oil-owned seismic data], it turned out, was vast enough to provide water for 2 million people for more than a century.”
7. Trump’s funding pause won’t impact federal student loans, Pell Grants
“[… T]he temporary pause will not impact “assistance received directly by individuals,” including federal direct student loans and Pell Grants, which are government subsidies that help low-income students pay for college.”
8. In Uganda, a women-led reforestation initiative fights flooding, erosion

“[… T]he Kasese municipality has established nurseries to provide free tree seedlings, particularly to women, to support reforestation efforts. [… They] plant Ficus trees near their homesteads to provide shade and help control erosion, and Dracaena trees on their fields to retain soil moisture.”
9. [A Texas school board] votes yes to provide low-cost housing to staff at no cost to the district

“The program will include 300 homes[…] only a short commute to campuses. […] Rent will be determined on a sliding scale based on their salaries, with those making less receiving a larger discount. The proposed community would include amenities, like childcare facilities[….]”
10. Heat pumps keep widening their lead on gas furnaces

“Americans bought 37% more air-source heat pumps than the next-most-popular heating appliance, gas furnaces, during the first 11 months of the year. That smashes 2023’s record-setting lead of 21%.”
January 15-21 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#fish#sunfish#mola mola#aquarium#us politics#costco#dei#diversity equity and inclusion#louisiana#habitat restoration#green infrastructure#brazil#global warming#science#forever chemicals#recycling#water#water scarcity#big oil#student loans#federal aid#reforestation#gardening#low income#affordable housing#housing#school#heat pump installation
140 notes
·
View notes
Text
Flicker Fade
Flicker, Fade https://ift.tt/9rDdfuo by nicolawritesdrh Under the Wizard Protection program, Draco is sent to a coastal town in Australia where he reconnects with an old Hogwarts classmate trying to restore her parents memories. But Hermione has no idea who Alexander is under his Polyjuice potion. Words: 1993, Chapters: 1/10, Language: English Fandoms: Harry Potter - J. K. Rowling Rating: Mature Warnings: No Archive Warnings Apply Categories: F/M Characters: Hermione Granger, Draco Malfoy Relationships: Hermione Granger/Draco Malfoy Additional Tags: Post-War, Angst, Hurt/Comfort, Eventual Happy Ending, POV Draco Malfoy, Draco Malfoy in the Muggle World, Surfer Hermione Granger, Polyjuice Potion (Harry Potter), Ministry of Magic (Harry Potter), Wizard Protection Program, somewhat slow burn, Mistaken Identity, They're Both Idiots Your Honour, set in australia, FACTUALLY CORRECT Australia, Author is actually Australian via AO3 works tagged 'Hermione Granger/Draco Malfoy' https://ift.tt/dQGvePD August 07, 2024 at 10:10AM
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

A Decade of Marine Excellence: Icons of Change and PHILMARINE 2025 to Spotlight Transformative Leadership and Ocean Advocacy June 20, 2025 | SMX Convention Center, Pasay City, Philippines
In celebration of a decade of collaborative leadership in marine conservation and ocean innovation, the Philippines will host “The 10th PhilMarine 2025: A Decade of Maritime Excellence” on June 20, 2025, at the SMX Convention Center Manila, Pasay City. This landmark event, taking place during PHILMARINE 2025, brings together government leaders, civil society, environmental advocates, fashion designers, and maritime institutions in a unified call to accelerate progress toward the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)—with special emphasis on SDG 14: Life Below Water, SDG 13: Climate Action, and SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals.
Organized in partnership with Icons of Change, The International Ecotourism Society (TIES) – Philippines, Aqua Queen of the Universe, and Fireworks Trade Exhibitions & Conferences Philippines, Inc., the event aims to create a dynamic platform for inclusive dialogue, cultural expression, and cross-sector collaboration in support of a sustainable blue economy and climate-resilient marine communities.
Keynote Speakers: Voices Leading the Call for Ocean Action
The program will be headlined by three respected leaders whose work exemplifies transformative impact and inclusive leadership:
Mr. Roberto “Ka Dodoy” Ballon, a globally celebrated Ramon Magsaysay Awardee, will deliver a keynote on the power of community-led marine restoration. His pioneering work in rehabilitating mangrove ecosystems in Zamboanga Sibugay serves as a model for participatory conservation and the empowerment of fisherfolk.
Mr. David D’Angelo, a long-time environmental advocate, youth mentor, and sustainability educator, will highlight the role of civic engagement and education in driving marine stewardship. His keynote will explore the intersection of advocacy, communication, and intergenerational leadership in building public awareness and mobilizing local action for global impact. David D' Angelo is also the TVC World Golden Star Awardee for 2023.
Mr. Ludwig Federigan, Executive Director of the Young Environmental Forum and a Non-Resident Fellow of the Stratbase ADR Institute, one of the Philippines’ respected think tanks. He also heads the Information and Knowledge Management Division of the Climate Change Commission (Philippines). A prolific writer, Mr. Federigan maintains a column titled All About Choices in the business section of The Manila Times, the country’s oldest English daily newspaper, where he has authored over a hundred articles on environmental issues, climate change, sustainability, and leadership. His insights bring a critical policy and media lens to the evolving discourse on climate resilience and ocean governance. Ludwig Federigan was recently conferred the Icons of Change Award for 2025 in recognition of his outstanding contributions to sustainable development and environmental advocacy.
A senior representative from the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) will offer the government’s perspective on integrated coastal and marine policy frameworks, aligned with the country’s development blueprint for sustainable growth and ecological resilience.
Together, these voices will anchor the day’s conversations with expertise, vision, and an urgent call to protect our shared marine heritage.
Celebrating Conservation through Culture, Fashion, and Civic Duty
In a compelling blend of creativity and advocacy, the program will feature a marine-themed sustainable fashion showcase by eco-conscious designers Marjorie Renner and John Guarnes, whose collections use repurposed materials and traditional craftsmanship to communicate the beauty—and fragility—of ocean life.
Complementing this artistic expression, representatives of the Philippine Coast Guard Auxiliary (PCGA) will share their role in marine safety, environmental protection, and humanitarian service, underscoring the civic dimension of ocean governance.
A highlight of the event will be the premiere of a pioneering underwater fashion film, produced by Aqua Queen of the Universe, which merges artistic performance and environmental storytelling in a powerful visual tribute to marine biodiversity.
The celebration will also include world-class performances by artists from the World Championships of Performing Arts (WCOPA), bringing a global cultural spotlight to issues of environmental justice and marine conservation.
Advocacy to Action: Community Initiatives and Open Dialogue
Leading environmental advocate and event co-organizer Erilene Antonio Noche, founder of Aqua Queen of the Universe, will present a portfolio of community-based marine initiatives—from coral farming and artificial reefs to youth-led underwater cleanups. Her presentation will emphasize the importance of grassroots innovation and inclusive participation, especially the leadership of women and youth in marine conservation.
An interactive open forum will invite guests and participants from across sectors to engage in dialogue, share insights, and explore opportunities for partnership. Moderated by Ms. Noche, this forum will help set the tone for future collaborations beyond the event itself.
A Shared Future for the Seas
As the Philippines positions itself at the forefront of marine sustainability and ocean-based innovation in the Asia-Pacific region, The 10th PhilMarine 2025 serves not only as a celebration of progress but also as a call to action—to build upon past gains with renewed resolve and cross-sectoral cooperation.
All stakeholders—government, business, academe, creative industries, and the general public—are invited to join this historic event and affirm a shared commitment to protecting the life systems that sustain our planet.
---
For partnership inquiries or participation details, please contact: Icons of Change 📍 June 20, 2025 | SMX Convention Center 📩 [email protected]
#IconsOfChange #DecadeOfMarineExcellence #PhilMarine2025 #KaDodoy #DavidDAngelo #NEDA #BlueEconomyPH #IconsOfChange #LifeBelowWater #FashionForTheOceans #EcoLeadership #TogetherForTheOceans #RecognizingVisionEmpoweringTransformation
0 notes
Text
Environmental Considerations When Hiring Barges for Coastal Projects
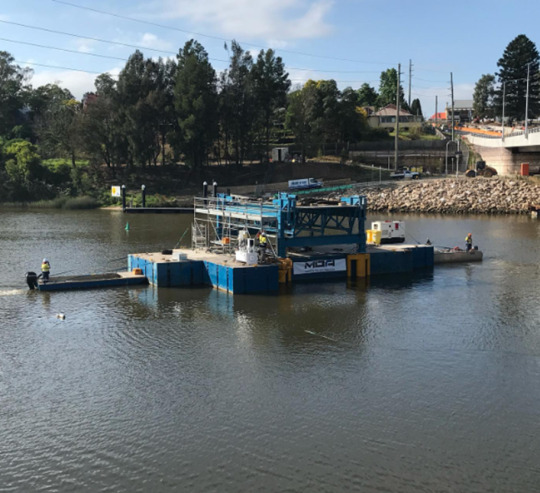

Coastal projects bring with them a unique mix of challenges and responsibilities. Beyond logistics and budget, environmental impact has become a central point of discussion among contractors, councils, and marine engineers. When planning to hire barge services for coastal work, overlooking the ecological footprint can lead to long-term damage and costly consequences.
Australia’s coastal zones are home to delicate ecosystems, from mangroves and tidal wetlands to seagrass beds and marine life breeding grounds. These environments are more than scenic views; they play a vital role in natural coastal defence, water filtration, and biodiversity support. So, when barge operations are involved, whether for construction, restoration, or maintenance, careful planning is needed to protect what lies beneath.
Tides, Timing, and Technique
Timing barge activities with tides and weather can significantly reduce environmental disruption. For example, operating in low-tide conditions might expose fragile seagrass, whereas high tide may allow for smoother vessel movement and easier access to deeper sections, minimising contact with the seabed. Working with marine experts and using local knowledge helps pinpoint ideal timing windows that reduce ecological impact.
It’s also worth reviewing the methods used to anchor or stabilise the barge during operation. Traditional spuds or anchors can cause sediment displacement, damage marine vegetation, or stir up pollutants trapped in seabed layers. Many environmentally conscious barge operators now employ positioning systems that keep equipment steady without making direct contact with the bottom.
Fuel and Emissions
Diesel-powered equipment is standard in marine construction, but newer barges are being fitted with low-emission engines and improved fuel systems that cut down on pollution. Choosing a contractor that maintains newer fleets or uses alternative fuel blends can make a significant difference. Regular engine servicing and spill prevention measures add another layer of protection.
Make it a habit to ask about spill response plans and onboard waste management. An oil or fuel spill, no matter how small, can have a ripple effect on aquatic life and local water quality.
Noise and Marine Life
Coastal waters are home to a wide range of marine species, including some that are highly sensitive to vibration and noise. Construction and barge operations can disrupt feeding and breeding patterns. In areas known to host protected species, consider working during migration off-seasons and using noise-dampening technology where possible.
Even the simple choice to hire a barge for the day rather than booking an extended operation can minimise disturbance in areas with sensitive ecosystems.
Working with Local Authorities
In regions like New South Wales, environmental regulations around coastal works are not just recommendations—they’re legally binding. When seeking barge hire Sydney, it helps to work with providers experienced in navigating permits and complying with environmental codes. They’ll be familiar with protected zones, necessary approvals, and the expectations of local councils and environmental agencies.
Final Thoughts
Hiring a barge for coastal projects goes beyond logistics and pricing. A bit of upfront research, thoughtful planning, and working with environmentally responsible operators can help ensure your project leaves the shoreline better than it found it—or at least, no worse. As more contractors and project leads take accountability for their impact, these considerations are becoming the new normal rather than an afterthought.
The author specialises in marine construction content with a focus on sustainable practices and local compliance. With a background in environmental writing, they highlight practical steps for reducing project impact. Visit https://www.eastcoastmarinecontracting.com.au/barge-hire for more details.
0 notes
Text
About Shoreline Shutters | Shoreline Shutters

Fellsmere, a serene town nestled in Indian River County, Florida, is increasingly recognizing the importance of Coastal Storm Protection Fellsmere. While Fellsmere itself isn't directly on the coast, its proximity to the Indian River Lagoon and the St. Johns River makes it susceptible to the impacts of coastal storms, including flooding and storm surge. Implementing effective storm protection measures is crucial to safeguard both the community and the delicate ecosystems in the region.
1. Wetland Restoration Projects
One of the most significant initiatives in the Fellsmere area is the Fellsmere Grade Recreation Area, part of the St. Johns River Upper Basin Project. This extensive wetland restoration project spans over 166,000 acres and serves as a model for large-scale floodplain restoration. By reintroducing natural wetland functions, the project enhances water quality, provides wildlife habitat, and offers flood protection for thousands of residents in Brevard and Indian River counties. The restored wetlands act as natural buffers, absorbing excess stormwater and reducing the risk of flooding during heavy rains and storms.
2. Stormwater Management Systems
Effective stormwater management is vital in mitigating the impacts of coastal storms. In Fellsmere, local authorities have been working on improving stormwater infrastructure to handle increased runoff during storm events. Upgrading drainage systems, maintaining retention ponds, and implementing permeable surfaces are some of the strategies being employed to manage stormwater effectively. These measures help prevent localized flooding and reduce the strain on existing drainage systems during heavy rainfall.
3. Community Preparedness and Education
Community involvement plays a pivotal role in storm protection efforts. Fellsmere has been proactive in educating its residents about the importance of storm preparedness. Local workshops, informational sessions, and distribution of educational materials help residents understand the risks associated with coastal storms and the steps they can take to protect their homes and families. Encouraging the use of flood-resistant building materials, elevating structures, and creating emergency plans are some of the key focus areas in community preparedness initiatives.
4. Collaboration with State and Federal Agencies
Coastal Storm Protection Fellsmere is not a solitary effort but involves collaboration with state and federal agencies. Partnerships with organizations such as the Florida Department of Environmental Protection and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ensure that the community benefits from expert guidance, funding, and resources necessary for implementing effective storm protection measures. These collaborations facilitate the development of comprehensive plans that address both immediate and long-term storm protection needs.
Conclusion
While Fellsmere may not be directly on the coastline, its strategic location near vital water bodies necessitates robust Coastal Storm Protection Fellsmere measures. Through wetland restoration, improved stormwater management, community education, and collaboration with state and federal agencies, Fellsmere is taking proactive steps to safeguard its residents and the environment from the impacts of coastal storms. Continued investment in these areas will enhance the town's resilience and ensure a safer future for all.
0 notes
Text
How Marina Dredging Keeps Harbors Safe and Navigable?
Marina dredging plays a vital role in maintaining safe and efficient waterways for boats and harbors. At Ims Dredge, we specialize in delivering innovative and effective marina dredge solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of waterfront facilities. Over time, sediment buildup can reduce water depth, making navigation difficult and increasing the risk of vessel damage. Our advanced dredging equipment restores proper depth and clears channels, ensuring smooth and safe passage for all marine traffic. Whether it's a small private marina or a large commercial harbor, our team works with precision and care to protect infrastructure and improve usability. With Ims Dredge, maintaining navigable waters is simple, sustainable, and reliable—supporting both safety and long-term harbor performance.
Sediment Accumulation Threatens Safe Harbor Navigation
One of the major challenges for coastal and marina facilities is the gradual accumulation of sediment. Over time, sand, silt, and debris settle in harbor basins, reducing water depth and creating navigation hazards for vessels. Without regular maintenance, even well-designed marinas can become unsafe or unusable. This is where consistent and efficient marina dredge operations become critical. Ims Dredge provides industrial-grade equipment designed to handle these exact issues, helping harbors restore safe, navigable waterways. The build-up of sediment not only disrupts traffic flow but can also cause significant wear and damage to boats. By addressing this issue early with proper dredging equipment, harbors can avoid larger, costlier problems down the line.
Ensuring Smooth Passage for Commercial and Private Vessels
For both commercial operators and private boat owners, smooth access to marina facilities is essential. When waterways become too shallow or clogged with sediment, the risk of groundings and collisions increases dramatically. Ims Dredge supplies powerful and reliable solutions that allow for thorough marina dredge work, keeping harbor routes open and consistent in depth. This is particularly important in busy or high-traffic areas where delays or incidents can cause chain reactions of disruption. With professionally managed dredging operations, vessel operators experience improved safety, fewer maintenance issues, and higher confidence when docking or launching.
Maintaining Compliance with Maritime Regulations and Standards
Marinas and harbor authorities are often required to meet strict maritime regulations related to waterway depth, safety, and environmental impact. Regular dredging is a key part of maintaining compliance with these standards. Ims Dredge supports harbor authorities with advanced marina dredge technology that helps ensure compliance while maximizing operational efficiency. Environmental agencies frequently monitor harbor areas to prevent ecological damage, and exceeding sediment levels can lead to fines or forced shutdowns. With the right dredging equipment in place, harbors can maintain a proactive maintenance schedule, avoid penalties, and support responsible environmental stewardship.
Reducing Long-Term Infrastructure Damage and Repair Costs
Allowing sediment to accumulate unchecked can result in serious damage to marina infrastructure, including docks, seawalls, and pilings. The added pressure from debris buildup and altered water flow patterns can accelerate erosion and wear. Through consistent dredging practices, harbors can extend the lifespan of their infrastructure and prevent costly repairs. Ims Dredge offers robust marina dredge systems designed for long-term reliability and minimal disruption during operation. By proactively managing sediment through dredging, facility managers can significantly reduce maintenance budgets and allocate resources to more strategic improvements instead of emergency fixes.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency and Harbor Accessibility
When harbors are kept at optimal depth, loading, unloading, and maneuvering vessels become quicker and safer. This translates into more efficient day-to-day operations for marinas, especially those involved in commercial shipping, tourism, or fishing. Ims Dredge provides dredging solutions that are easy to deploy and manage, making routine sediment removal more accessible and less time-consuming. Unlike traditional dredging operations that might require extensive manual labor or downtime, modern marina dredge machinery allows for faster turnaround and minimal service interruptions. This means improved efficiency not just for harbor operators, but also for the businesses that rely on their smooth functioning.
Supporting Environmental Balance in Coastal Waters
Sustainable dredging practices play an essential role in protecting aquatic habitats and maintaining clean, healthy waterways. Sediment buildup can disturb marine life, affect water quality, and lead to stagnation. Ims Dredge designs its marina dredge equipment to minimize environmental disruption while effectively removing harmful silt and waste materials. The precision and control offered by modern dredging machinery help harbor authorities maintain ecological balance. By preventing harmful runoff and improving water circulation, dredging also contributes to better fish habitats and healthier coastal ecosystems, aligning with growing environmental responsibility across the industrial and marine sectors.
Choosing the Right Equipment for Long-Term Success
Investing in the right dredging equipment is essential for ensuring safe, navigable waters over the long term. Every harbor or marina faces unique challenges depending on size, location, and sediment type. Ims Dredge offers a range of customizable marina dredge solutions tailored to meet these varying conditions. Whether the need is for small-scale maintenance or larger restoration projects, having the right machinery reduces downtime and increases overall effectiveness. Expert consultation and training are also important aspects of equipment selection, and Ims Dredge provides comprehensive support to help clients make informed, future-focused decisions.
Conclusion
Keeping harbors and marinas safe, functional, and compliant requires an ongoing commitment to proper maintenance—and dredging is at the heart of that effort. With reliable and efficient equipment from Ims Dredge, facility managers can address sediment accumulation before it becomes a serious issue. Among the many marina dredge solutions available, few offer the precision, sustainability, and durability needed for long-term success. Whether you’re operating a private marina or a large commercial harbor, the right dredging strategy will protect your infrastructure, support marine traffic, and ensure a cleaner, safer waterfront for years to come.
0 notes
Text
How GIS Can Predict and Mitigate the Effects of Rising Sea Levels?
Rising sea levels pose a serious threat to coastal communities, ecosystems, and infrastructure worldwide. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) provide a powerful way to analyze, predict, and mitigate these impacts using real-time spatial data and advanced mapping techniques.
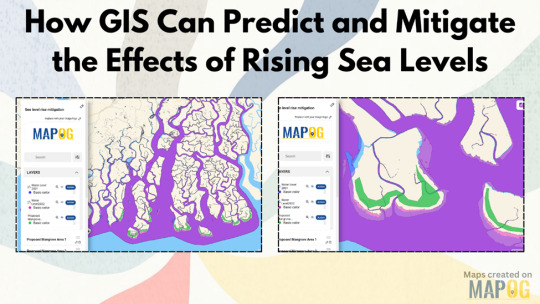
Understanding the Threat: What GIS Reveals About Rising Waters
GIS allows scientists and policymakers to visualize past and present water levels to predict future risks. By analyzing historical water level data—such as from 2001 and 2022—GIS can create accurate models to identify areas at high risk of flooding. This helps in forecasting potential damage and preparing preventive measures.
Using GIS for Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Mapping Vulnerable Zones GIS overlays different datasets, such as elevation models, climate data, and urban development, to pinpoint the most vulnerable regions. This helps authorities focus on high-risk coastal areas that need urgent intervention.
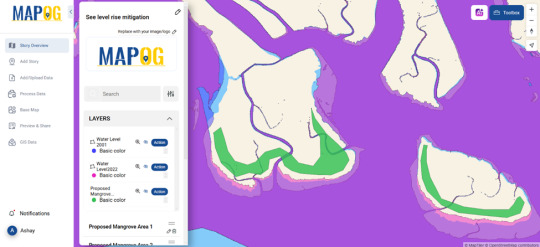
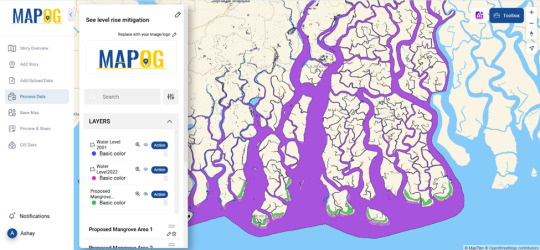
Proposing Natural Solutions One effective mitigation strategy is mangrove restoration. Mangroves act as natural barriers, reducing coastal erosion and absorbing excess water during storms. By using GIS tools to map potential mangrove plantation sites, we can strategically enhance these natural defenses.
Urban Planning and Infrastructure Resilience City planners can use GIS simulations to design flood-resistant infrastructure, such as elevated roads, drainage systems, and protective sea walls. Identifying evacuation routes and emergency shelters also becomes more efficient through GIS mapping.
How GIS Tools Help in Real-Time Decision Making
Platforms with interactive mapping capabilities enable researchers and policymakers to update their models as new data becomes available. For instance, some GIS platforms allow users to upload historical water level data, create proposed mitigation zones, and analyze changes over time—all within an intuitive mapping interface.
If you're working on coastal resilience planning, exploring GIS-based platforms can help visualize and implement effective mitigation strategies. Platforms like MAPOG allow users to overlay water level data, draw mitigation zones with “Add polygon” tool, and create interactive maps that aid in decision-making and see how mapping can be a game-changer in combating rising sea levels.
Final Thoughts
Rising sea levels require proactive solutions, and GIS plays a crucial role in understanding and mitigating this challenge. From data-driven predictions to ecosystem-based solutions, GIS empowers decision-makers with the insights they need to protect vulnerable communities.
How do you think GIS can improve coastal resilience in your region? Let us know in the comments!
#mapog#sea level rise#risk mitigation#gis#mapping#spatial analysis#data visualization#water mitigation#climate change mitigation
0 notes
Text
Hurricane Risk Mitigation Measures

According to Statista, between 2011 and 2023, 23 hurricanes made landfall in the United States. This figure emphasizes the need for American households in regions prone to hurricanes to adopt more deliberate strategies to mitigate the destructive impact of hurricanes.
Wind strength, storm surge, and heavy rainfall are some of the most important risk factors for hurricane incidents, so any mitigation strategy must address these risks. Sustained and prolonged wind strength poses risks because it can result in structural damage to properties, destroy powerlines, and uproot trees. Storm surges result in rising ocean levels, leading to overwhelming flooding and coast erosion, destroying lives and properties. Hurricanes come with heavy rainfall, often resulting in landslides, building collapse, flooding, and spreading waterborne diseases.
To reduce the effect of these risks, communities should adopt structural and non-structural strategies. Adopting strict building codes and standards is a structural strategy that the government can adopt to reduce the risks associated with hurricanes. They can stipulate specific construction and design requirements to withstand torrential rainfall, flooring, and high wind. Specifically, the building codes and standards might require wind-resistant construction, flood-resistant design, and retrofitting.
Hurricane-prone regions should adopt wind-resistant construction. This type of construction involves substantial foundations, reinforced roofs, and impact-resistant windows. Flood-resistant designs will require elevated homes and buildings above the floor level. This measure also requires that the foundations be firm and built with flood-resistant materials that will remain durable. Furthermore, old buildings require retrofitting with modern and more durable materials. For instance, property owners can add flood barriers, storm shutters, and wind-resistant roofing to old buildings.
Preparedness is critical in reducing the human and economic impact of hurricanes. A coordinated emergency response plan can save lives and ensure quicker recovery. Communities should establish clear evacuation routes and shelters, especially for vulnerable populations like the elderly and those in flood-prone areas. Early warning systems, powered by advanced meteorological technology, provide accurate forecasts, allowing communities to take timely action. Public education campaigns inform people about hurricane risks, safety protocols, and evacuation procedures, ensuring they remain prepared ahead of the storm.
Evacuation strategies should incorporate live weather data, enabling authorities to adjust routes and shelter locations as conditions change. Transportation accessibility should be a priority, with buses and community transport provided to ensure everyone can evacuate safely, including those without private vehicles.
In addition to emergency planning, safeguarding coastal areas is crucial to mitigate the destructive effects of hurricanes, such as storm surges and flooding. Coastal protection measures like seawalls, dikes, and levees can prevent seawater from encroaching on land, particularly in low-lying regions. Restoration of mangrove forests, which act as natural barriers against storms and coastal erosion, is also vital for enhancing resilience. Furthermore, beach nourishment—replenishing sand on eroded beaches—helps buffer against storm surges and reduces coastal damage, offering a sustainable approach to protecting vulnerable areas.
Innovative early warning systems are key to minimizing the impact of severe weather events. Localized alert technologies target residents in specific at-risk areas, ensuring timely notifications. Multi-channel communication strategies—using text messages, radio broadcasts, social media, and siren help warnings reach the broadest possible audience. Also, storm surge maps serve as visual tools to illustrate projected surge levels, helping communities better understand potential risks and prepare accordingly.
0 notes
Text
Who Is Lee Zeldin? (Sierra Club:
Excerpt from this story from the Sierra Club:
President-elect Donald Trump’s selection to lead the Environmental Protection Agency is, in a word, unexpected. The appointment announced on November 11—in which the Trump transition team erroneously referred to the EPA as the “Environmental Protective Agency”—was not an energy industry lobbyist like Andrew Wheeler or a MAGA insider like Mandy Gunasekara, who authored the EPA chapter of Project 2025. Instead, Trump chose Lee Zeldin, a little-known former Republican congressman from Long Island, New York, whose background on environment and energy issues is relatively skimpy.
So, then: Who is this person who will be in charge of the federal agency tasked with protecting the environment and public health?
Zeldin is a politician and military officer who grew up in New York’s Suffolk County. From 2015 to 2023, he represented New York’s First District (eastern Long Island) in Congress, where he sat on the House Foreign Affairs and Financial Services Committees. Before that, he served for four years in the New York state senate. In 2022, he ran for governor of New York against Democrat Kathy Hochul, a race that he lost by six points.
He’s a booster of fossil fuels and promises to unleash “energy dominance.”
In his run for governor of New York, Zeldin campaigned on expanding fossil fuel extraction. He called for allowing “the safe extraction of natural resources in the southern tier” of the state, approving new pipelines, and repealing the gasoline tax. He also was a staunch opponent of New York’s ban on fracking and ran on ending it. “[Zeldin] has a record of being pro-fracking, and that’s a record I think he’s going to clearly carry forward into the Trump administration,” Eric Weltman, a senior organizer in Food and Water Watch’s New York office, told Sierra.
Zeldin has mentioned pursuing “energy dominance” as one of three top priorities in heading up the EPA. “It is an honor to join President Trump’s cabinet as EPA administrator. We will restore US energy dominance, revitalize our auto industry to bring back American jobs, and make the US the global leader of AI,” Zeldin said in a statement on X.
He has taken more than $410,000 from the oil and gas industry, and he questions the scientific consensus on climate change.
According to Climate Power, Zeldin has received over $410,000 from the oil and gas industry in his election campaigns, including over $260,000 while running for Congress and more than $150,000 in his gubernatorial run. He has taken more than $60,000 from Koch Industries over the course of his political career, according to Open Secrets data.
His voting record in Congress is mostly anti-environment, with an LCV lifetime score of just 14 percent.
Zeldin unsurprisingly has an overall poor voting track record, as scored by the League of Conservation Voters. “Trump made his anti–climate action, anti-environment agenda very clear during his first term and again during his 2024 campaign. During the confirmation process, we would challenge Lee Zeldin to show how he would be better than Trump’s campaign promises or his own failing 14 percent environmental score if he wants to be charged with protecting the air we breathe, the water we drink, and finding solutions to climate change,” Tiernan Sittenfeld, LCV’s senior vice president for government affairs, said in a statement.
He supported a few conservation efforts for his district.
While in Congress, Zeldin backed several conservation initiatives for his district in Long Island. According to the campaign website for his gubernatorial run, he helped save Plum Island—a tiny island off the eastern tip of Long Island—by securing repeal of a 2008 law requiring it to be sold to the highest bidder. He also worked with the Army Corps of Engineers to “protect our coastlines, advancing the ambitious Fire Island to Montauk Point project,” a climate resiliency coastal risk reduction project to help safeguard Long Island’s prized beaches.
He appears to be against clean energy funding and tried to gut public transit funding in New York.
In addition to voting against the IRA and its massive clean energy investments, Zeldin early on in his political career attempted to divert funding away from clean energy programs in New York and undermine the New York City area’s transit system, according to Environmental Advocates NY. The New York environmental organization bestowed its “Oil Slick” award in 2011 on Zeldin, a rookie state senator at the time who led an effort to try to weaken public transit. He sponsored a bill that would have defunded the MTA, resulted in service cuts and fare increases, and discouraged public transit use. The bill would have also diverted $100 million away from clean energy programs to “plug holes in MTA’s finances.”
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Study: Protecting the ocean helps fight malnutrition
"Protecting more of the ocean could slash the risk of malnutrition for up to 3 million people worldwide, according to a new study co-authored by Conservation International.
It found that fish catches in coral reefs could increase by up to 20 percent by expanding sustainable-use marine protected areas — that is, areas where some fishing is allowed with restrictions.
The benefits of marine protected areas in helping restore fish populations and ecosystems are well documented. However, perceptions persist that these protections come at the expense of local communities.
The new study challenges this view.
“It’s easy to think of protected areas as putting people and nature in conflict by restricting access to much-needed sources of nutrition for locals,” said Conservation International scientist Alex Zvoleff, a study co-author. “But what this study shows is that protecting nature isn't about walling off resources from people; protected areas can actually enhance what nature provides for people."
The study analyzed fish counts in nearly 2,500 coral reefs across 53 countries, focusing on the nutrients found in fish that are critical for human health. Researchers looked at sites with a range of protections — from complete bans on fishing to open access for fishing — and found that sustainable-use marine protected areas have on average 15 percent more fish biomass than non-protected areas.
The study pinpointed countries with the greatest potential to improve malnutrition through sustainable-use marine protected areas, including Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Kenya, Madagascar, Mozambique and Nicaragua.
More than 800 million people face malnutrition worldwide, according to the World Health Organization. In many coastal communities, fish can be the only source of vital nutrients — particularly for children and pregnant women.
However, pollution, overfishing and climate change are severely degrading the coral reefs that support these fish. And though coastal communities make up a small portion of those struggling with malnutrition, the study shows that fighting food insecurity can go hand in hand with protecting nature, said Daniel Viana, the study’s lead author.
“There is often a push for marine protected areas to completely ban fishing — our goal is to show that it does not need to be all or nothing,” Viana said. “Allowing regulated fishing in marine protected areas can support healthy fish populations, while also having a positive impact on the quality of life of surrounding communities.”
The study’s findings are particularly significant as global efforts are under way to protect at least 30 percent of the planet’s land and marine ecosystems by 2030. Currently, only about 8 percent of the ocean is protected."
-via Conservation International, September 17, 2024
#malnutrition#food insecurity#oceans#marine protected area#30 by 30#tidalpunk#public health#nutrition#good news#hope
231 notes
·
View notes
Text
As a part of our state’s Coastal Master Plan to address our land loss crisis, Louisiana broke ground in August 2023 to reconnect the Mississippi to its distributaries in a project known as the Mid-Barataria Sediment Diversion (MBSD). This is the largest ecosystem restoration project ever attempted in the United States. But this effort is now under threat. Governor Landry has delayed further construction and threatened to pull the plug on this game-changing effort. Reconnecting the river is key to restoring our coast. Show your support for the inclusion of MBSD in Louisiana’s annual coastal plan by submitting a comment to Louisiana’s Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority. Every comment proves to our leaders that the MBSD is important, impactful and should move forward as planned.
Protect Louisiana's coasts!
Comment period closes Saturday, March 22
Human efforts to restrain the Mississippi River have left coastal Louisiana communities vulnerable as the river muds are no longer reaching the delta it once built.
The MBSD utilizes knowledge from over 30 years of research and experimentation to revitalize the decimated Barataria basin by reconnecting the river to rebuild wetlands.
These wetlands will reduce storm damage, help control floods and provide sustainable homes for fish and wildlife.
Alongside other state investments in coastal protection and restoration, the MBSD will significantly reduce the costs of future disasters and create economic opportunities within Louisiana at a time when these are desperately needed — including supporting more than 12,000 jobs.
After much uncertainty and delay around the MBSD, it is crucially important to show public support about how this foundational project will impact our communities and livelihoods. Submit a comment today to voice your support.
@one-time-i-dreamt
@tenaflyviper
@akron-squirrel
@ifihadaworldofmyown
@justice-for-jacob-marley
@voicetalentbrendan
@thebigdeepcheatsy
@what-is-my-aesthetic
@ravenlynclemens
@writerofweird
@anon-lephant
@mentally-quiet-spycrab
@therealjacksepticeye
#actually important#petition#submit your comment#MBSD#environmentalism#louisiana#time sensitive#environmental protection
0 notes
Text
Bringing Back Elegance: How De Vere Carpet and Leather Restorations Restore Bribie Island

Situated right at the heart of Bribie Island is an epicentre of coastal elegance, sublime in every way. This means homes and businesses make sure that their aesthetic expression reflects that of the island's nature. Some of those crucial elements that add warmth and class to any space are carpets and leather furniture; this could even include keeping them as good as new, which is rather challenging.
That's where De Vere Carpet and Leather Restorations come into play: your trusted solution for unmatched leather cleaning in Bribie Island and beyond.
Restoring Leather to its Former Glory: A Specialist's Touch
De Vere's Leather Restoration Services are designed to address these issues with precision and care. Using leading techniques in the industry, the team restores natural beauty to leather, giving it back its texture, colour, and durability.
From minor scuffs up to major discolouration, this is a surefire place where specialists from De Vere utilize really contemporary methods for restoring good-old leather to a look-as-new style. That would eventually secure their lead in gaining preeminence in serving value-added quality and lash them onto becoming household staples for all Bribie Islands' leather-care essentials and needs.
The Science and Art of Leather Cleaning
Cleaning leather is not a common task; it's a process that requires so much expertise and special equipment. De Vere's approach to leather cleaning is scientific yet artistic. Each piece of furniture is treated individually to ensure that the most appropriate cleaning agents and techniques are applied to maintain its integrity.
For the people of Bribie Island, such attention to detail translates into peace of mind. The customer can be assured that his prized possessions are in capable hands and get the due care they need. Be it a leather sofa for luxury, a favourite recliner, or car upholstery, De Vere's custom-fit solutions give outstanding results time after time.
Why Choose De Vere Carpet and Leather Restorations?
De Vere is more than a mere service partner; genuinely interested in the interior and aesthetic value of your insides. Here's why:
Expertise You Can Trust: The experience over the years, coupled with an immensely skilled team, has honed De Vere's expertise in handling practically any leather cleaning or restoration needs.
Eco-Friendly Practices: The company goes for 'green' solutions, incorporating products that are non-toxic and safe for both your family and the earth.
Customer-Oriented Approach: De Vere realizes that every customer has different needs. They take time to understand your needs and provide services beyond expectations.
Convenience at Its Best: Based locally, De Vere provides the residents of Bribie Island with quick and reliable services that ensure minimal disruption to your busy schedule.
Building Trust Through Excellence
De Vere Carpet and Leather Restorations are driven by two non-negotiable key factors: a passion for quality and customer satisfaction on and beneath its surface. Service-wise, it has imposed authority in the community of Bribie Island as to Leather Cleaning.
To those people who love class and want to keep their leather furniture in great shape, De Vere offers much more than a service- a promise to restore and protect what truly matters. Let the difference be experienced today, putting trust in experts of leather care with De Vere Carpet and Leather Restorations. For more information, visit their website at https://carpetandleather.com.au.
#leather cleaning in Bribie Island#leather cleaning#best leather cleaning#leather cleaning near me#leather furniture repair near me#leather recoloring#leather restoration service
0 notes
Text

A Decade of Marine Excellence: The PHILMARINE Aqua Queen of the Universe Fashion Show Champions Ocean Advocacy through Culture, Innovation, and Sustainable Partnerships
June 20, 2025 | SMX Convention Center, Pasay City, Philippines
In response to growing global imperatives to protect and restore our marine ecosystems, and in celebration of a decade of progressive maritime collaboration, the Philippines will host “A Decade of Marine Excellence: The PHILMARINE Aqua Queen of the Universe Fashion Show” on June 20, 2025, at the SMX Convention Center in Pasay City. This milestone event, held alongside PHILMARINE 2025, signifies a confluence of creative expression, policy advocacy, and grassroots environmental action—representing a shared commitment to the future of the seas and the communities that depend on them.
Organized in strategic partnership with Aqua Queen of the Universe, The International Ecotourism Society (TIES) – Philippines, Icons of Change, and Fireworks Trade Exhibitions & Conferences Philippines, Inc., this commemorative program reflects the Philippines’ growing leadership in marine sustainability and ocean-based innovation across Southeast Asia and the Pacific. TIES Philippines, under the visionary leadership of Vilma De Claro Mendoza, the organization's Founder, and Justin Ho Guo Shun, President of TIES Asia Pacific, plays a crucial role in advocating for sustainable tourism practices, ocean protection, and community-centered initiatives.
The event is rooted in the values and framework of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly Goal 14: Life Below Water, Goal 13: Climate Action, Goal 12: Responsible Consumption and Production, Goal 5: Gender Equality, and Goal 17: Partnerships for the Goals. It offers a platform for inclusive dialogue and creative diplomacy, engaging diverse sectors in transformative conversations on how we collectively build a more resilient and sustainable marine future.
---
Government, Civil Society, and Creative Industries in Dialogue Reflecting strong national and institutional support, the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) will deliver a keynote address to articulate how integrated marine and coastal development policies are aligned with the Philippines’ broader commitment to climate-resilient, inclusive growth. NEDA’s participation highlights the state’s strategic role in guiding cross-sectoral collaboration toward sustainable blue economy development.
The program will also be enriched by the presence of distinguished keynote speakers:
Mr. Roberto “Ka Dodoy” Ballon, a Ramon Magsaysay Awardee, whose community-led mangrove rehabilitation work in Zamboanga Sibugay has earned international acclaim for advancing ecosystem restoration and local livelihoods through participatory conservation.
Mr. David D’Angelo, a noted environmental advocate and sustainability educator, whose long-standing efforts in public awareness, youth empowerment, and climate education exemplify the vital role of civic society in marine stewardship.
Mr. Ludwig Federigan, Executive Director of the Young Environmental Forum and a Non-Resident Fellow of the Stratbase ADR Institute, one of the Philippines’ respected think tanks. He also heads the Information and Knowledge Management Division of the Climate Change Commission (Philippines). A prolific writer, Mr. Federigan maintains a column titled All About Choices in the business section of The Manila Times, the country’s oldest English daily newspaper, where he has authored over a hundred articles on environmental issues, climate change, sustainability, and leadership. His insights bring a critical policy and media lens to the evolving discourse on climate resilience and ocean governance.
Mr. Gerry Mercado, CEO of GMP Artist Inc. and National Director for Team Philippines at the World Championships of Performing Arts (WCOPA), whose unique journey bridges marine conservation and the performing arts. A certified diver and biodiversity advocate, Gerry has championed coral reef preservation, river protection, and youth empowerment through the arts. Under his leadership, Team Philippines has achieved global distinction, making him the only National Director worldwide to earn the prestigious Diamond National Director Award. Gerry brings a compelling lens on how cultural diplomacy and environmental action can be seamlessly integrated to promote national pride, sustainability, and global recognition for Filipino talent.
In further support of maritime safety, civic duty, and ecological defense, the event is honored to welcome representatives of the Philippine Coast Guard Auxiliary, whose operational leadership in marine protection, rescue, and pollution response continues to play a pivotal role in safeguarding the nation’s coastlines and communities.
---
Host Spotlight: Raymond “Mon” Gorospe Anchors the Event Bringing vibrant energy and polish to this high-level gathering is Raymond “Mon” Gorospe, who will serve as the official Host of the event. Widely respected in the Philippines’ performing arts, fitness, and media circles, Mon is a multi-faceted talent with a career spanning decades.
A performer, actor, fitness advocate, and seasoned host, Mon first entered the entertainment world in the 1990s by serendipitous discovery—and never looked back. He is a decorated talent at the World Championship of Performing Arts (WCOPA), having brought home multiple medals in gospel, modeling, Broadway, and acting. A trailblazer in the local fitness movement, Mon was among the first advocates of functional fitness in 2011, and today serves as Chairman of the Swimming Committee at Celebrity Sports Club, in addition to his roles in NPC Bodybuilding and the WFF committee. His face is familiar to many, having endorsed brands such as Centrum Silver, Red Ribbon, Red Fiber, and Vicks ZzzQuil—even amid pandemic constraints.
Beyond his commercial success, Mon exemplifies service and impact. Together with his wife, Dr. Mae Gorospe, and their three children, he supports quarterly feeding programs for Aeta communities, using his performances as a fundraising vehicle for social good.
Known for hosting major pageants and high-profile events—including the 46th Mrs. Universe coronation—Mon brings both gravitas and charisma to the stage. His presence at A Decade of Marine Excellence elevates the celebration, bridging advocacy, entertainment, and inspiration.
---
Celebrating Sustainability Through Culture and Design Beyond its diplomatic and policy dimensions, the event aims to reframe ocean conservation as a space of creativity and storytelling. Central to the celebration is a marine-inspired sustainable fashion showcase by acclaimed designers Ms. Marjorie Renner and Mr. John Guarnes.
Ms. Marjorie Renner is known for her eco-conscious design principles, elevating sustainable fashion through couture made from discarded materials and natural fibers—challenging traditional definitions of luxury and urging consumers to reduce their ecological footprint.
Mr. John Guarnes, a celebrated designer and sustainable fashion advocate, brings a unique vision to the runway by fusing eco-friendly materials and traditional craftsmanship to create fashion that tells a story of conservation and environmental stewardship. His designs highlight the delicate balance between innovation and sustainability, offering a beautiful yet thoughtful commentary on the health of our oceans.
Together, they will showcase pieces that celebrate marine-inspired creativity while promoting sustainable production practices and mindful consumption.
The fashion segment will be followed by the premiere of a pioneering underwater fashion film produced by Aqua Queen of the Universe. This visually stunning short film, entirely shot beneath the ocean’s surface, merges expressive movement, aquatic imagery, and environmental messaging to reflect the interdependence of human culture and marine health. The film not only highlights the beauty of our oceans but also underscores their vulnerability, calling attention to the urgent need for collective protection and reverence.
Adding a dynamic cultural dimension to the program, performers from the World Championship of Performing Arts (WCOPA) will present a world-class artistic showcase. Their participation underscores the power of performance as a unifying force, merging global talent with marine advocacy to elevate awareness through music and theatrical expression. The WCOPA segment will feature international-caliber talents whose acts are inspired by themes of environmental justice, unity, and the call to safeguard our oceans.
---
From Advocacy to Action: Community-Centered Marine Conservation
The event also provides a forum for sharing real-world practices that have measurable environmental impact. Ms. Erilene Antonio Noche, founder of Aqua Queen of the Universe, will lead a visual presentation and dialogue focusing on her team’s community-based marine projects. These include coral farming initiatives, artificial reef installations, and underwater cleanup drives, all of which are conducted in partnership with youth leaders, fisherfolk, divers, and environmental volunteers across Philippine coastal regions.
These initiatives serve as inspiring examples of how locally driven action can contribute meaningfully to national and global conservation goals. They also highlight the importance of inclusive leadership—especially the role of women and young people in shaping marine futures through hands-on engagement and innovation.
---
Open Dialogue and Shared Responsibility
An interactive open forum, moderated by Ms. Noche, will convene voices from across the maritime, fashion, academic, and environmental sectors. The dialogue will provide space for participants to share best practices, ask critical questions, and explore opportunities for deeper cooperation across industries. It will also serve as a springboard for future partnerships focused on developing climate-smart, inclusive, and economically viable marine solutions.
The event will close with a collective call to action, urging all attendees—whether policymakers, designers, educators, business leaders, or advocates—to continue integrating sustainability into their respective spheres of influence. Participants will be invited to reflect on the legacy of the past decade and commit to building on its successes with renewed purpose and vision.
---
A Decade of Marine Excellence: The PHILMARINE Aqua Queen of the Universe Fashion Show is not only a celebration of what has been accomplished—it is a commitment to what still must be done. As the Philippines and the global community navigate the complex challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, and environmental justice, this gathering affirms the transformative power of unity, creativity, and leadership.
The event stands as a compelling reminder that sustainable marine development cannot be achieved by any one sector alone. It must be pursued through dialogue, mutual respect, and the courageous belief that even the most intricate challenges can be overcome when we work together for the common good.
---
We invite stakeholders from all sectors to join us on June 20, 2025, at the SMX Convention Center for a landmark celebration of marine excellence, sustainability, and the enduring strength of partnership.
#DecadeOfMarineExcellence #PhilMarine #AquaQueenOfTheUniverse #SustainableSeas #SDG14 #ClimateActionNow #FashionForTheOceans #UnderwaterAdvocacy #EcoCouture #BlueEconomyPH #IconsOfChange #TIESPhilippines #ConservationThroughCulture #CoralReefRestoration #CreativeForClimate #MaritimeSustainability #TogetherForTheOceans #RecognizingVisionEmpoweringTransformation
0 notes
Text
When the River Turns Salty
Southeast Louisiana has faced an ever growing threat that has not had enough light shed on it: saltwater intrusion from the Mississippi River. This challenge has not only changed the landscape but has also impacted business, homeowners, and entire communities. Saltwater intrusion takes place when saline water moves upstream from the Gulf of Mexico into freshwater sources. In this case of Southeast Louisiana, there have been many things that have contributed to this issue. For starters, there has been an extreme loss of wetlands from oil extraction and other urban developments. Climate change has also played a part in this as it has intensified the movement of the saltwater into more coastal areas. There was also the 2021 Mississippi River flood which changed the river's salinity levels and overall flow. A report by the Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority noted that the saltwater intrusion was going to impact the region by affecting drinking water and the agricultural viability for years to come.
Saltwater intrusion has had profound effects, especially on homeowners in New Orleans and Plaquemines Parishes. These areas have had to deal with extra cost for water treatment and plumbing repairs due to salt water's corrosive nature. Businesses that deal with agriculture and fishing have also been impacted from salt water intrusion. Industries like shrimping and oysters that were once thriving are now dealing with economic instability due to a decrease in yields. Farmers have reported salt damage to crops which has forced them to spend money on mitigation strategies. Most communities have come together and have been discussing the implications of this environmental crisis. There are leaders and other organizations that have advocated for stronger protective measures and have tried to raise awareness on the situation but there are many residents who are still unsure of how best to adapt.
There have been past experiences like Hurricane Katrina that have left a lasting impression on the citizens of Louisiana. They feel like they were not informed or supported during such a time of crisis. This has led to skepticism about the authorities and their ability to handle challenges the environment brings. There is a disconnect that has led people to be hesitant in trusting official narratives, especially decisions being made without getting any input from the community. These people that are getting affected feel like their voices are not being heard. I really can’t say if saltwater intrusion has been handled appropriately because there are still significant hurdles to overcome. Although people are doing the best they can, there is still a long way to go. So as Southeast Louisiana continues to deal with the effects of saltwater intrusion it is important that locals are able to at least rebuild trust with the government to have some more sustainable solutions.
0 notes