#Clinical trial sourcing
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#Clinical trial sourcing#clinical trial supplies#Reference listed drug supplier#rld service and suppliers#comparator sourcing for clinical trials#Brazil RLD Suppliers#Poland RLD Suppliers#Biologic reference products#Best Reference listed drug supplier
1 note
·
View note
Text
I think my fav recent misinformation post that went around on here was that one post with almost 30k notes abt how “ADHD meds don’t work on your period” and they didn’t know this until recently because “the tests for every ADHD med were only done on AMAB people to control for hormonal difference,” where the post’s one source was a link to an Upworthy article that ADMITTED it couldn’t find sources for the anecdotal claim like. Lol. Lmao
#I was reminded of this bc I was going through my drafts and found a post I never made where I was mad abt it#The cool and fun thing is that you can actually look up clinical trial results for drugs pretty easily#and pretty quickly verify that clinical trials for these meds weren't done only on AMAB people and that the claim is just an outright lie#It's true that there isn't a lot of research on how periods affect ADHD -- but there is SOME research#There's a 2018 study (with a sample size of only 32) that found a connection between hormone levels and reported severity of ADHD symptoms#This is a small study and even they say that further research is needed#But if it's true that would mean that it's not that the medication is working -- it's that the symptoms are just worse around then anyway#So theoretically like. Stopping your meds around that time because 'they don't even work' would set you up for an EVEN WORSE time#Anyway checking sources and doing research is cool and sexy. Please take ur meds#* not that the medication ISN'T working#runner up for funniest is whatever is happening with the soy sauce conspiracy posts#you are not immune to conspiratorial thinking etc etc
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Another day another unsourced headline claiming someone invented a cure for a currently incurable disease (but it’s being suppressed!!!!!!!!) and everyone on tumblr eats it up without fact checking whatsoever.
#also a lot of the time the source is more like ‘a study finds a potential way to maybe cure this’#like I don’t know how to tell you this but one promising study ≠ cure invented and ready to go on the market#if it was that easy literally everything would be cured by now. but it’s not. more studies have to be done. clinical trials. regulation.#manufacturing. etc. there’s so much more that goes into this stuff#but every time people who are uninformed see news of like that initial study they jump to conspiratorial thinking#like I think the progress IS great and super promising but it’s not a one and done thing
1 note
·
View note
Text
NewLife Medicals: Your Trusted Global Clinical Research Organization
Riding on the cutting edge of medical science and clinical trials, NewLife Medicals is your reliable partner for all pharmaceutical needs. Bathing in expertise, authority, and trust, our ambitious goal is to reshape the future of healthcare.
But why should you trust NewLife Medicals?
NewLife Medicals: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Manufacturers
Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are the heart of any medicine, responsible for its therapeutic effects. At NewLife Medicals, we are more than just API manufacturers. Quality, affordability, and ultra-precision define our API manufacturing. We utilize state-of-the-art technology and rigorous quality checks to ensure the synthesis of high-quality APIs.
Got an unusual API request? As hard-to-source drugs and limited distribution drugs suppliers, we welcome the challenge!
Clinical Research Organization: NewLife Medicals
Clinical trials form the backbone of drug development – but they can be complex and costly. Simplify and economize your clinical testing experience with our unparalleled clinical research organization. Our seasoned team of research professionals are committed to delivering high-quality, timely, and ethically sound clinical research.
Why settle for less when you can have the best?
Global Innovator Drugs Supplier and Biosimilar Supplier
As an innovator drugs supplier, NewLife Medicals is committed to bringing new, pioneering treatments to the market. Our extensive portfolio of innovator drugs and biosimilar infusions stands as a testament to our pioneering spirit and relentless dedication to progress.
Ever heard of orphan drugs or REMS access? We supply these too!
Finished Dosage Formulations Suppliers
We take our role as finished dosage formulations suppliers seriously. Our manufacturing process leverages the highest industry standards, ensuring consistency and efficacy with every dose. Whether it's tablets, capsules, or syrups, we have your needs covered.
Are you seeking a reliable reference listed drug provider? Look no further!
Ancillary Clinical Supplies and Hospital Lines Supplier
Besides pharmaceuticals, our inventory comprises ancillary clinical supplies and premium hospital lines. These medical accessories and equipment promise to simplify your caregiving experience, improving efficiency and compliance.
Are you with us yet?
Your Trusted Partner in Pharmaceutical Supply Chain
Whether it's comparator sourcing for clinical trials, pharma raw material suppliers, patient supply, or specialty sourcing, NewLife Medicals has got you covered. Our integrated supply chain caters to all your pharmaceutical needs while maintaining the highest quality standards.
Trust in the expertise and authority of NewLife Medicals for all your medical needs. Together, let's make a healthier world!
Meta description: Explore NewLife Medicals – your trusted global clinical research organization, pharmaceutical supplier, and healthcare partner. Dive into our wide range of services today.
#rld pharmaceutical#comparator sourcing for clinical trials#named patient supply#ancillary clinical supplies#global clinical research organization#drug development#innovator drugs supplier
0 notes
Text
RLD Services: Locating Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are an important stage in medication development. They aid in the evaluation of the safety and efficacy of new treatments before they are made available to the general public. When it comes to clinical trial supplies, however, preparation and organization are essential components of conducting clinical research. In this post, we will present a full overview of clinical trial supply, including definition, management, obstacles, best practices, and technology.
Ikris Pharma Network collaborates with study sponsors to conduct complete market assessments in order to discover appropriate comparator items, co-medications, and supplemental supplies for clinical studies. Ikris Pharma Network may then leverage their global network of manufacturer relationships, exclusive agreements, and audited third-party wholesalers and distributors to develop a global procurement strategy that is cost-effective, waste-free, and helps ensure trial timelines are met in order to provide you with the best possible Clinical trial sourcing in India.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Sourcing, Indenting And Trading | Pharmaceutical Consultancy
Neunco has been successfully sourcing APIs, Pharmaceutical Intermediates to many companies, thanks to the partners we hold close. Apart from that, we have also been exclusive indenting and trading agents for more than 27+ companies across the globe. To be a master supplier of life sciences is not half as easy as it seems. But at Neunco, we constantly push boundaries and strive to perfect the art of sourcing, indenting as well as importing and exporting.

0 notes
Text

Comparator Drug Sourcing (RLD) - NewLife Medicals
NewLife Medicals plays a vital role in the global supply Comparator Drug Sourcing (RLD) and Any Therapeutic Area. of Reference Listed Drugs for the pharmaceutical companies
#active pharmaceutical ingredient manufacturers#ancillary clinical supplies#Bio similar supplier#comparator sourcing for clinical trials#pharma raw material suppliers#Specialty Sourcing
1 note
·
View note
Note
any thoughts on the obsession with "hyperprocessed foods"? is there even such a thing and if so how much of the stuff around it is fake?
such a flawed useless categorisation lmao; this phrase comes from the nova scale, according to which an "ultra-processed food" is identified by a lack of sufficient "intact" food and the presence of "sources of energy and nutrients not normally used in culinary preparations" and additives specifically "used to initate or enhance the sensory qualities of food or to disguise unplatable aspects of the final product" (other additives, such as preservatives, antioxidants, and stabilisers, only qualify a food as group 3, "processed"). ultra-processing is defined as "a multitude of sequences of processing [...] includ[ing] several with no domestic equivalents," and ultra-processed foods are "usually packaged attractively and marketed intensely."
......so ok, first of all, this is very obviously reliant on a lot of assumptions about what 'normal' cooking and cooking equipment means, lmao. i do all kinds of shit in the kitchen that would have been inaccessible to someone in the mid nineteenth century; has the food become 'less processed' because i can make it at home now? if i obtained the equipment to hydrogenate oils myself would they magically not be ultra-processed simply because they came from my kitchen and not from an industrial setting?
this is just quasi-scientific language to express a fundamental distrust of food produced in ways that currently can't be replicated in [researchers' definitions of] a [normal] home kitchen. it's barely more sophisticated than platitudes like michael pollan's command to "eat only foods your grandmother would recognise". using the nova classifications to make assumptions about the healthfulness or danger of a food is just silly; the presumption is that the dietary and medical effects are not due to the food itself but to how it's produced, an idea that has led researchers to conclude that "the NOVA system suffers from a lack of biological plausibility so the assertion that ultra-processed foods are intrinsically unhealthful is largely unproven."
fundamentally the only evidence that nutritional scientists have been able to produce is observational studies showing a correlation between certain ill health outcomes and consumption of 'ultra-processed food'.
But the observational studies also have limitations, said Lauren O’Connor, a nutrition scientist and epidemiologist who formerly worked at the Department of Agriculture and the National Institutes of Health. It’s true that there is a correlation between these foods and chronic diseases, she said, but that doesn’t mean that UPFs directly cause poor health.
Dr. O’Connor questioned whether it’s helpful to group such “starkly different” foods — like Twinkies and breakfast cereals — into one category.
[...]
Clinical trials are needed to test if UPFs directly cause health problems, Dr. O’Connor said. Only one such study, which was small and had some limitations, has been done, she said.
ie, when evaluating the healthfulness of foods you have to actually look at what they are and what the human body does with them, and not just make a bunch of wild assumptions based on fears about their lack of proximity to 'naturalness' or propensity to be advertised (unlike, i guess, other more intact foods, which are not commodities. who knew!)
and there are like a million trillion other reasons why this correlation might hold: off the top of my head, for instance, people who rely more on the convenience of ready-made foods likely to be categorised as 'ultra-processed' are likely to be people who can't cook because they don't have time because they're working. so as usual nutrition and health science does a dogshit job distinguishing between the health effects of socioeconomic status and those of whatever some dickwad wants to publish a splashy study about.
there are certainly 'ultra-processed' foods that we can be extremely confident are harmful to human health---for example, trans fats. but the categorisation as a whole is so conceptually flawed as to be useless for any purpose besides as a term that 'scientises' culturally held beliefs about the wholesomeness and healthfulness of home food preparation, and the corresponding danger and artificiality of industrial production and methods.
303 notes
·
View notes
Text
I saw some mentions of rabies going around again and have no clue what's set it off this time, but given recent scientific developments I want to revisit the idea of curing symptomatic rabies.
First things first: there is still no practical way to do this. The famous Milwaukee Protocol fails far more frequently than it succeeds, and even the successes are not making it out in anything like a normal state. It's been argued that it should no longer be considered a valid treatment [1] due to these issues; any continued use is because there's literally nothing else on the table.
However. There are now two separate studies showing it's possible to cure rabies in mice after the onset of symptoms. The lengths you have to go to in order to pull this off are drastic, to put it mildly, and couldn't really be adapted to humans even if you wanted to. But proof of concept is now on the board.
long post under the cut, warnings for animal experimentation and animal death. full bibliography at the end and first mention of each source links to paper.
Quick recap - rabies is a viral disease of mammals usually transmitted through the saliva of an infected animal. From a contaminated bite wound, it propagates slowly for anywhere from days to months until it reaches the central nervous system (CNS). Post-exposure vaccination can head it off during this phase, but once it reaches the CNS and neurological symptoms appear it's game over. There will typically be a prodromal phase where the animal doesn't act right - out at the wrong time of day, disoriented, abnormally friendly, etc. This will then progress to the furious (stereotypical "mad dog" disease) and/or paralytic phases, with death eventually caused by either seizures or paralysis of the muscles needed for breathing.
That's the course we're familiar with in larger animals. Mice, though, are fragile little creatures with fast metabolisms.
In the first study's rabies infection model, lab mice show rabies virus in the spinal cord by day 4 after infection and in the brain by day 5. Weight loss and slower movement start by day 7, paralysis starting from the hind limbs from day 8 on, and if not euthanized first they're dead by day 10-13. [2]
This study (fittingly conducted at the Institut Pasteur) had two human monoclonal antibodies, and wanted to see if there was any possibility they could be used to cure rabies after what we think of as the point of no return.
Injecting the antibodies into muscle saved some mice if done at days 2 or 4, and none if done later, even at high doses of 20 milligrams per kilogram of body weight of each. Conclusion: targeting the virus out in the rest of the body is no use if it's already replicating in the CNS.
Getting a drug past the blood-brain barrier is, to use a highly technical term, really fucking hard. It's the sort of problem that even the best-funded labs and biggest companies in the world routinely fail at. And that's for small molecule drugs, which are puny compared to antibodies.
But this isn't drug development for a clinical trial. This is a very, very early proof-of-concept attempt, which means you're willing to ignore practicality to see if this idea is even remotely workable. So you can do things like brute force the issue by cutting through the skull to implant a microinfusion pump, which lets you deliver the antibodies directly into the normally-protected space around the brain. Combine this with the normal injections, and you can treat both the CNS and the rest of the body at the same time. Here's a survival graph of treated mice. X axis is days, Y axis is percentage of mice in that group still alive.
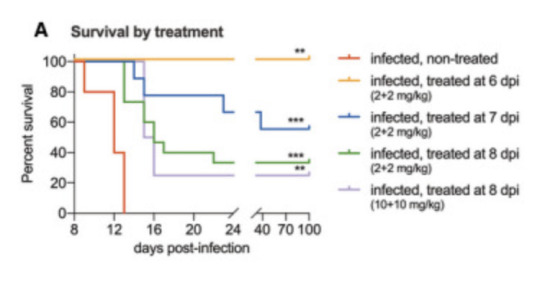
Figure 2A from reference 2, accessed February 2024
The fact that the blue, green, and purple lines did anything other than sink horribly to zero is unheard of. When the combination treatment was started at day 6, 100% of the mice survived. Started at day 7 (prodromal phase), 5 out of 9 mice recovered and survived. Started at day 8 (solidly symptomatic, paralysis already starting to set in), 5 of 15 mice recovered and survived. And when they say "survived", they kept these mice all the way to day 100 to make sure. Some of them had permanent minor paralysis but largely they were back to being normal mice doing normal mouse things. So, success, but by pretty extreme means.
Enter the second paper [3]. This was a different approach using a single human monoclonal antibody against Australian bat lyssavirus (ABLV - closely related to rabies, similar symptoms in humans) to try for a cure without needing to deliver treatments directly into the CNS. They also made a luminescent version of ABLV that let them directly image viral activity, so they could see both where the virus was replicating and how much there was in a live mouse.

Figure 1 from reference 3, accessed February 2024
Mice infected with ABLV start showing symptoms around day 8. You can see in the figure that at day 3 there's viral replication in the foot at the site of infection, which has shifted into the spine and brain by day 10. So what happens if you give one of these doomed mice one single injection of the antibody into the body?
Done at day 3, the virus doesn't make it to the brain until day 14, and while disease does set in after that around 30% of the mice survive. Days 5 and 7 are much more interesting. Those mice still develop symptoms at day 8, but the imaging shows the amount of virus in their spines and brains never gets anywhere near the levels seen in untreated controls, and within days it starts to decrease. Around 80% of day 5 and 100% of day 7 mice survive.
Okay, sure, you can stop another lyssavirus, but technically you did start treatment before symptoms appeared. What about symptomatic rabies?
The rodent-adapted rabies strain CVS-11 starts causing symptoms as early as day 3 after infection, and untreated mice die between days 8 and 11. The same single dose of antibody saved 67% of mice treated on day 5 and 50% of mice treated on day 7. Without making the luminescent version of the virus there's no real-time imaging of the infection, but you can still track symptoms.
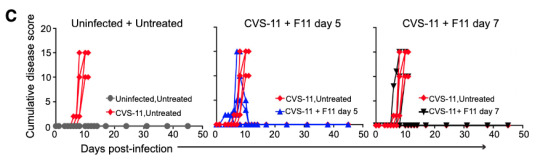
Figure 2 from reference 3, accessed February 2024. CVS-11 is the name of the rodent rabies strain and F11 is the name of the antibody.
Disease score is a combination of several metrics including things like whether the mice are behaving normally and whether they show signs of paralysis. In untreated mice it goes up and up, and then they die. If one of those lines starts coming back down and continues past day 10 or so, that's a mouse that recovered. The success rate isn't as good as against ABLV, but again, this is a rabies strain specifically adapted to rodents and treatment wasn't started until it was well-established in the CNS.
So how on earth is this happening? The antibody neutralizes both ABLV and rabies really well in a test tube, but we've already established that there's no way a huge lumbering antibody is making it past the blood-brain barrier without serious help. Something about the immune response is clearly making it in there though. And it turns out that if you start trying this cure in mice missing various parts of their immune systems, mice without CD4+ T cells don't survive even with the treatment. By contrast mice without CD8+ T cells take longer to work through the infection, but they eventually manage it and are immune to reinfection afterwards.
To grossly oversimplify the immune system here, CD4+ are mature helper T cells, which work mostly by activating other immune cells like macrophages (white blood cells) and CD8+ T cells (killer T cells) against a threat.
Normally, T cells are also kept out by the blood-brain barrier, but we know that in certain specific cases including viral infection they can pass it to migrate into the brain. In the brains of the infected mice for which antibody treatment either wasn't given or didn't work, you can find a roughly even mix of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells along with a whole lot of viral RNA. But in the brains of those successfully fighting off the infection, there's less viral RNA and the cells are almost exclusively CD4+. So the antibody doesn't work by neutralizing the virus directly - something about it is activating the animal's own immune system in a way that gives it a fighting chance.
Again, neither of these proof of concept treatments is really workable yet as a real world cure. The first one is almost hilariously overkill and still has a pretty good chance of failure. The second is less invasive but careful sequencing still shows both low-level viral replication and signs of immune response in the brains of the survivors even at day 139, so it may not be truly clearing the virus so much as trading a death sentence for life with a low-level chronic infection. But now we know that 1. curing rabies after symptoms begin is at least theoretically possible, and 2. we have some clues as to mechanisms to investigate further.
Not today. Not tomorrow. But maybe not never, either.
References:
Zeiler, F. A., & Jackson, A. C. (2016). Critical appraisal of the Milwaukee protocol for rabies: this failed approach should be abandoned. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences, 43(1), 44-51.
de Melo, G. D., Sonthonnax, F., Lepousez, G., Jouvion, G., Minola, A., Zatta, F., ... & Bourhy, H. (2020). A combination of two human monoclonal antibodies cures symptomatic rabies. EMBO molecular medicine, 12(11), e12628.
Mastraccio, K. E., Huaman, C., Coggins, S. A. A., Clouse, C., Rader, M., Yan, L., ... & Schaefer, B. C. (2023). mAb therapy controls CNS‐resident lyssavirus infection via a CD4 T cell‐dependent mechanism. EMBO Molecular Medicine, 15(10), e16394.
319 notes
·
View notes
Text
yeah, if 6 teenage girls and 1 teenage boy had emerged from the Canadian wilderness after 19 months with a 1 year old baby in tow, there would've been no escaping the media hellstorm. They would've been on 20/20 within 3 months. One group interview and a few candids of Shauna holding the baby would've been the price they'd all have had to pay in order to be left tf alone because while in 2023 society pretends to care about trauma, PTSD, and teens' mental health, this was the 90s--when Nicole Brown Simpson was blamed for her own murder, Lorena Bobbit was a late-night punchline, R. Kelly marrying 15 y/o Aalyiah was an open secret, grown men were calling into radio stations to speculate on 16 y/o Britney Spears' virginity, and Monica Lewinsky was doxxed and getting death threats for sucking off Bill Clinton.
What I'm saying is:
Seven teens (the girls + Travis) surviving against the odds for 19 months is the epilogue to a tragedy with enough unanswered questions to keep true crime nerds speculating & reporters digging.
But them being found with an infant? Had it come out that one of the girls was pregnant and gave birth during the ordeal? That's mainstream tabloid fodder. The kind that not even "papers of repute" would turn their noses up at. Barbara Walters, Lesley Stahl, and Mike Wallace would be beating each other and TMZ down to get the first interview, the first photo of the baby. NBC would've backed a U-Haul full of money onto the Shipman's, the Martinez', and the Sadecki's front yard (because speculation as to who the actual father really was would be kept going until it came directly from the source). Did she know she was pregnant when she got on the plane? Who else knew? What was it like giving birth? Did any of the other girls get pregnant? How many of the girls did Travis do it with? Weren't any of them afraid of the same thing happening to them? Did doing it help them cope?
And it wouldn't just be the media. Doctors, child development specialists, psychologists, sociologists, and academics would be calling non-stop to get Shauna and the baby to participate in clinical trials and studies.
The only way they'd have been left alone is if they'd done a televised interview and ended it by pleading to be allowed to go on with their lives in peace
#shauna shipman#wilderness baby#yellowjackets meta#yj meta#yj s2#yellowjackets#idk what the point here is. the thought just came to me
221 notes
·
View notes
Text
Monopolizing turds

Update 31 May 2023: an earlier edition of this article identified the price of Rebyota as $20,000; this was the rumored price prior to Rebyota’s release in December 2022, when Stephen Skolnick wrote the article I referenced. When Rebyota was actually released in 2023, the average wholesale price (AWP) was $10,800. Thanks to Benjamin Jolley for catching this error, and to Stephen Skolnick for getting to the bottom of it.
It’s been ten years — to the day! — since I first started writing about the bizarre, amazing world of turd transplants, in which a sick person receives a microbiotic infusion in the form of some processed poop from a healthy person:
https://web.archive.org/web/20130608030455/http://blogs.plos.org/publichealth/2013/05/29/why-diy-fecal-transplants-are-a-thing-and-the-fda-is-only-part-of-the-reason/
Gut biomes are one of those understudied, poorly understood medical areas that are both very promising and also full of sketchy medical claims from “supplement” companies, influencers, quacks and grifters. But in the decade since I first started tracking turd transplants (formally called “Fecal Microbiota Transplants” or FMTs), a growing body of sound science has emerged on the subject.
One thing that’s increasingly undeniable is that the composition of your microbial nation is related in significant ways to both your physical and mental health. What’s more, as antibiotic resistant “super bugs” proliferate, FMTs are becoming increasingly central to treating dangerous gut infections that otherwise stand a high chance of killing you.
“Eat Shit and Prosper” is Stephen Skolnick’s delightfully named newsletter about poop and health science. Skolnick is a physicist by training, but has a long history of collaboration with Openbiome, a nonprofit that coordinates between doctors, patients and donors to provide safe FMTs:
https://stephenskolnick.substack.com/
In an edition of Eat Shit from last December, Skolnick recounts the amazing history and dismaying future of FMTs. In 2013, the FDA announced it would regulate FMTs as “Investigational New Drugs,” which could only be administered as part of a registered clinical trial:
https://stephenskolnick.substack.com/p/a-monopoly-on-poop
At that point, FMTs were already in widespread use by docs to treat otherwise untreatable cases of Clostridioides difficile (C. diff), an antibiotic resistant bacterial infection that literally makes you shit yourself to death. These doctors were in no position to run registered clinical trials, which meant that they would have to stop using the most effective therapy they had for a potentially lethal infection.
Doctors and patients kicked up a fuss, and the FDA walked back its guidance, announcing that it would exercise “discretion” in enforcing its Investigational New Drug rule, giving a pass to docs who were treating C. diff with FMTs:
https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2013/07/18/2013-17223/guidance-for-industry-enforcement-policy-regarding-investigational-new-drug-requirements-for-use-of
That’s where things have stood for the past decade or so. The “discretion” rule means that patients could still get FMTs, but their insurance wouldn’t cover it. But even if you had cash to pay for an FMT, your doc probably wouldn’t administer it for anything except a C. diff infection, despite the promising signs that FMT can help treat other conditions, and despite the generally safe nature of FMTs.
If your doc did give you an FMT, chances are good that they sourced their poop from Openbiome. Openbiome recruits very healthy people, gets them to poop in a bag, then processes the poop — removing nonbacterial solids, testing it for pathogens, freezing it, portioning it, and sending it to docs. All this is done at cost, and it’s not cheap: $1–2k/treatment, mostly due to cold-chain logistics (the poop is shipped at -80C).
Despite the cost, and despite the limitations on treatment, the Openbiome method has proved very reliable. Indeed, FMTs as a whole are pretty darned safe, with the most common side-effects being transient gas and bloating. In the past decade, there’ve been a total of six “adverse effects” associated with Openbiome’s 5,000+ procedures, all in severely immunocompromised people, and none conclusively linked to the treatment:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016508522003511/pdf
A decade into this system, the FDA has taken the next step forward — only it’s actually a step backwards.
During this intervening decade, a pharma company called Ferring has conducted clinical trials on FMTs and received approval for an FMT product called Rebyota. The process for making Rebyota is effectively identical to the process used by Openbiome: collect poop, remove solids, test for pathogens, add glycerol, freeze and ship.
The main difference between Rebyota and Openbiome’s poop is price. While Openbiome charges $1–2k per treatment, Rebyota charges $10,800
That’s some expensive shit!
Fine. Getting Rebyota through clinical trials means that insurers might start covering it, and perhaps some patients will prefer brand-name poop to open-source poop. But as part of the FDA’s approval of Rebyota, the agency also rescinded its “discretionary enforcement” guidance, making it illegal for docs to source their poop from Openbiome:
https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/enforcement-policy-regarding-investigational-new-drug-requirements-use-fecal-microbiota
For Ferring, this is a monopoly on shit, one that lets them charge patients $10.8k for poop that costs $1–2k to process. The FDA does not claim that this is being done in the name of safety. Instead, an FDA official told Skonick that the goal was to “incentivize innovation without creating an access crisis.”
That is, the FDA changed its guidance and put nonprofit stool banks out of business because it wants to incentivize pharma companies to perform expensive clinical trials, and it believes that these companies won’t pay for trials if they have to compete with the likes of Openbiome, which would make it impossible to charge 900% markups on poop.
Trials are important! Evidence-based medicine is important! But Ferring’s clinical trials didn’t tell us anything we didn’t already know. FMTs were already the best therapy we had for C. diff. Testing Rebyota against a placebo didn’t tell us anything new — unlike testing Rebyota against the existing therapies, e.g. product from open stool banks.
Such a trial might have given rise to a very different regulatory outcome, because the cure rate reported by Rebyota is much lower than the cure rate from Openbiome’s own interventions:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40265-022-01797-x
That is, using the $1k poop from Openbiome seems to be much more effective than using the $10.8k poop from Ferring. But Openbiome, a nonprofit, hasn’t been able to perform the kind of rigorous — and expensive — clinical trial that Ferring funded.
This points to a significant problem with the FDA’s model. The agency wants good clinical data for the medicines it regulates, as it should, It presumes that the only way to get that data is through granting commercial exclusivity to a for-profit, which ends up costing patients vast sums, and locking many patients out altogether.
This creates all kinds of new dangers. 150,000 people/year in the US contract Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection (RCdI). FMT increases the cure rate by 20% relative to antibiotics alone. That means that if everyone with RCdI gets a poop transplant, 30,000 extra people will get better. That’s a big number!
For well insured people, Rebyota probably represents a cash-savings — if your insurance covers the $10,800 procedure, you might pay $500 out of pocket, which is far less than the $1–2K you’d pay to get an Openbiome poop transplant. But if you’re uninsured or underinsured, the FDA’s new enforcement rules mean that you’re now on the hook for $10,800.
The FDA did carve out a loophole: if your doc or their hospital are willing to prepare the poop transplant themselves, they can administer that. On the one hand, preparing a poop transplant isn’t that hard — some people do them at home, on their own:
https://web.archive.org/web/20211015060558/https://thepowerofpoop.com/epatients/fecal-transplant-instructions/
But on the other hand, there’s been exactly one death conclusively linked to FMT, and it was from one of these hospital-prepared transplants (the patient had just had a marrow transplant for cancer that wiped out their immune system, and the donor had a novel pathogen that the hospital failed to test for).
So the FDA has created a situation where, if you can’t afford a $10,800 proprietary formulation, your only option is to convince your doc or hospital to prepare their own poop transplant, which will cost less than the $10.8k for Rebyota, but more than the $1–2k from Openbiome, which has all kinds of economies of scale. And if you do manage it, you’ll be getting a procedure that has a much worse safety track-record than the Openbiome process that the FDA just killed.
The FDA has an important role to play here, but as with so many policy questions, how the FDA plays that role depends on things that are far upstream from the agency and its decisions. The choice to fund medical trials through the promise of exclusivity — and with it, extremely high margins — puts the FDA in the position of choosing winners in the marketplace: Ferring wins, Openbiome loses.
Ironically, this is the thing that exclusivity is supposed to prevent. By using profit to incentivize medical research, the FDA is supposed to be recruiting the Invisible Hand as its partner in regulation. But exclusivity is incompatible with the idea of medicine as a public good. The tens (hundreds) of millions that Americans will pay for $10.8k poop transplants from Ferring will add up to far more than it would cost to underwrite clinical trials for an open process like Openbiome’s.
The result: both Americans’ wallets and Americans’ guts suffer.

Catch me on tour with Red Team Blues in Hay-on-Wye, Oxford, Manchester, Nottingham, London, and Berlin!

If you’d like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here’s a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/29/oh-shit/#rebyota

[Image ID: A poop emoji wearing a top hat and a monocle, posed against a backdrop of e coli bacteria seen through a high-resolution microscope.]
#pluralistic#stool bank#eat shit and live#pharma#fda#regulatory capture#fecal transplants#microbiomes#rebyota#openbiome#c diff#fmt#fecal microbiota transplant
272 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Clinical Trial Sourcing Services#Best Reference listed drug supplier#Reference listed drug supplier#RLD Product Supplier.#RLD supplier in France#RLD supplier in Portugal#RLD supplier in Brazil#RLD supplier in Ireland#RLD supplier in Italy#RLD supplier in Turkey#Reference Listed Drugs
0 notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
Summary: Healthy adults who contracted COVID-19 had subtle but measurable declines in memory and cognitive performance lasting up to a year. These differences were found through sensitive testing under controlled conditions, though all scores remained within normal ranges, and none of the participants reported lasting cognitive symptoms.
The research highlights how even mild COVID-19 can impact brain function and points to the potential need for treatments to mitigate these effects. Further studies are needed to explore how COVID-19 compares with other respiratory infections, like flu, in terms of cognitive impact.
Key Facts:
COVID-19 can cause subtle cognitive changes in memory and problem-solving for up to a year. These effects were detected through sensitive cognitive tests, not self-reports. Participants in the study did not experience any noticeable long-term cognitive symptoms. Source: Imperial College London
A new analysis from Imperial’s human challenge study of COVID-19 has revealed subtle differences in the memory and cognition scores of healthy volunteers infected with SARS-CoV-2, which lasted up to a year after infection.
The researchers say all scores fell within expected normal ranges for healthy individuals and no one reported experiencing any lasting cognitive symptoms such as brain fog.
The findings, published in the journal eClinicalMedicine, show a small but measurable difference following highly intensive cognitive testing of 18 healthy young people with infection compared to those who did not become infected, monitored under controlled clinical conditions.
The team explains that incorporating such sensitive cognitive testing into future studies could help reveal more detailed insights into how infections may alter brain function and could help to find ways to reduce these processes when they cause symptoms.
Senior author Professor Adam Hampshire, from the Department of Brain Sciences at Imperial College London and now based at King’s College London, explained, “We know that COVID-19 can have lasting impacts on our memory and ability to carry out common cognitive tasks.
However, much of the scientific evidence we have comes from large studies based on self-testing and reporting, or where there’s a range of variables that could increase or reduce these effects.
“Our work shows that these cognitive effects are replicated even under carefully controlled conditions in healthy individuals—including infection with a comparable dose of virus—and further highlights how respiratory infections can impact specific aspects of brain function.
“We were only able to detect some of these effects because of the trial design, which used very sensitive tests and controlled conditions, with participant performance compared to their own pre-inoculation baselines. This enabled us to pick up on subtle changes of which the participants themselves appear not to have been aware.”
COVID-19 and cognition Previous studies that included patients with a wide range of severities have shown COVID-19 can have a lasting impact on people’s brain function. One such study, led by Imperial and involving more than 140,000 people, found small deficits in the performance of cognitive and memory tasks in people who had recovered from COVID-19, with differences evident a year or more after infection.
In the latest study, researchers analyzed findings from a small group of healthy volunteers who were part of the world’s first human challenge study for COVID-19 in 2021. The findings reveal subtle differences in how they performed on the same tests, which lasted up to 12 months although later testing could have been affected by other and later factors.
During the trial, 36 healthy, young participants with no previous immunity to the virus were infected with SARS-CoV-2 and monitored under controlled clinical conditions. They were carefully monitored and remained at the facility until they were no longer infectious. From the group, 18 participants became infected and developed mild illness, one without symptoms.
Participants also performed sets of tasks to measure multiple distinct aspects of their brain function, including memory, planning, language and problem solving, using the Cognitron platform. Participants took the tests before exposure to the virus, during the two weeks they spent in the clinical facility, and then at multiple points for up to a year.
Analysis showed that those who became infected with SARS-CoV-2 had statistically lower cognitive scores than uninfected volunteers—compared to baseline scores—during their infection as well as during the follow-up period. The main differences in scores were seen in memory and executive function tasks (including working memory, attention and problem solving).
Differences in scores between groups were seen up to one year after infection, with the uninfected group performing slightly better on tasks overall.
The researchers note that the observed differences were small and that none of the volunteers reported prolonged cognitive symptoms. They also highlight limitations of the study, including the small sample size and that the majority of participants were white males, and so caution is needed in extrapolating the findings to the general population.
They explain that future research could examine the biological links between respiratory infection and cognition in COVID-19, and even show how this impact compares with other conditions, such as Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or influenza.
Co-author Professor Christopher Chiu, from the Department of Infectious Disease at Imperial College London, who led the COVID-19 human challenge study, said, “These latest findings from our study add more fine detail to the picture we have of COVID-19 and other respiratory infectious diseases.
“Challenge studies can offer a tool to help us better understand how infections disrupt a range of biological functions. Here, by showing biological effects that fall below what could be considered symptoms or disease, we were able to identify the smallest changes in these pathways.
“This could ultimately help us to develop new treatments to reduce or even block some of these effects, which we know on other settings can have lasting impacts on people’s lives.”
Study Link: www.thelancet.com/journals/eclinm/article/PIIS2589-5370(24)00421-8/fulltext
#long covid#covid#covid news#mask up#pandemic#public health#coronavirus#wear a mask#covid 19#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator#covid conscious#covid is airborne#covid isn't over#covid pandemic#covid19#covidー19
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
At the origin of trans medicalization lies what remains a fatal flaw: there was, and is, no way to objectively diagnose someone as trans, except if you accept that they want to transition. The problem of detransition is therefore a mythology, the accumulated effect of decades of storytelling to justify why doctors and psychiatrists had to reject trans people without being able to say it was because they aren’t objectively trans. Detransition, much like its cousin, medicalization, are mythologies that rationalize the intense social hatred of transition acted out by clinicians, dressing it up as sober caution.
Any pundit today can take up the vast field of out-of-date studies from this era, online misinformation, and the cultural shock value attached to changing sex to rationalize a call for limits on transition, but they will get no closer to legitimacy than the brutality of the gender clinic of the 1970s. They call for more guardrails, more caution, or more psychological assessment, not needing to know that what they really call for is the medical totalitarianism of yesteryear, barely blunted in recent reforms. For at the heart of the myth that transition is something that people can accidentally do despite how impossible it is to obtain in the real world is an uncomfortable truth. There is a form of social and political control implemented by medicine, a way to sever an unpopular minority from their own bodies and then sell back limited access to their bodies if they will submit to a set of trials to prove they can be good people, or at least made better. The people opposed to that kind of medicalization simply think that trans people enjoy no right to their bodies at all, under any circumstances.
If you want to debunk the politicization of detransition, by all means, seek out credible sources that do so. My point is more elementary. I ask you this, New York Times reader: if, tomorrow, your ability to make decisions about your own body were taken away from you, and the only way to get it back was to submit to the process that trans people go through to transition, would you agree to those terms? If you would not, then why are you okay with it happening to us?
Jules Gill-Peterson, Detransition is a Mythology
[emphasis mine]
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
Global Clinical Trial Storage & Distribution Newlife Medicals

Newlife Medicals provides global clinical trial storage and distribution services. Contact us for secure and efficient handling of your trial supplies.
#global clinical research organization#reference listed drug#comparator sourcing for clinical trials#Specialty Sourcing#named Patient Supply#rld pharmaceutical
0 notes
Text
"One in five Americans will experience major depressive disorder in their lifetime, and many will not find relief from current therapies. But now researchers have identified an unexpected source of the problem: inflammation.
Inflammation in the body may be triggering or exacerbating depression in the brains of some patients. And clinical trial data suggests that targeting and treating the inflammation may be a way to provide more-precise care.
The findings have the potential to revolutionize medical care for depression, an often intractable illness that doesn't always respond to conventional drug treatments. While current drug treatments target certain neurotransmitters, the new research suggests that in some patients, depressive behaviors may be fueled by the inflammatory process.
It appears that inflammatory agents in the blood can break down the barrier between the body and the brain [and specifically the blood-brain barrier], causing neuroinflammation and altering key neural circuits, researchers say. In people at risk for depression, inflammation may be a trigger for the disorder.
Research suggests that only a subset of depressed patients - roughly 30 percent - have elevated inflammation, which is also associated with poor responses to antidepressants. This inflammatory subgroup may be a key to parsing out differences in underlying mechanisms for depression and personalizing treatment...
The inflamed body and the depressed brain
...A number of studies show that depressed patients tend to have increased inflammation compared with non-depressed subjects, including more inflammatory cytokines and C-reactive protein — which is produced by the liver in response to inflammation — circulating in the blood. Patients with autoimmune diseases have inordinately high rates of depression. And postmortem brain samples from people who died by suicide showed more activation of the brain’s immune cells, which release inflammatory agents.
Crucially, pro-inflammatory drugs can induce people to become depressed, which suggests a causative link. In one seminal study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, Miller and his colleagues conducted a double-blind study of 40 cancer patients undergoing treatment with interferon-alpha, an inflammatory cytokine.
Though none of the patients had depression to begin with, the inflammatory agent had a striking effect: Many became depressed, a finding that has been consistently replicated.
"The patients recognize pretty much immediately that, 'Hey, you gave me something, and now I feel this way. I don't know why I feel this way,'" Miller said.
Can treating inflammation treat depression?
If inflammation can induce or exacerbate depression and its symptoms, then reducing inflammation could provide relief.
Even if inflammation is a disease modifier rather than the cause of the problem, “you have to take care of it in order for you to be able to get your therapeutics working to restore your circuitry and what’s happening in the mind,” said Eleonore Beurel, a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine.
Anti-inflammatory drugs, used alone or in conjunction with a standard antidepressant, may help some depressed patients. A 2019 meta-analysis encompassing almost 10,000 patients from 36 randomized clinical trials found that different anti-inflammatory agents, including NSAIDs, cytokine inhibitors and statins, could improve depressive symptoms...
“We’ve come to the tipping point,” Miller said. “And we know enough at this point to begin to target the immune system and its downstream effects on the brain to treat depression. We are there.”
How to manage your own inflammation
Experts agreed that people should not take anti-inflammatories without talking with their health-care provider. Your doctor can order a C-reactive protein blood test to measure your level of inflammation.
“There are so many patients who do not respond to antidepressants,” said Ole Köhler-Forsberg, a physician and associate professor of psychiatry at Aarhus University who has given anti-inflammatory drugs to his patients in addition to antidepressants. “So there is the issue of how can we improve the individual outcomes.” Tailoring treatment for each individual on a holistic basis may add some benefit.
More clinical tests for inflammatory markers may be a way to differentiate the effectiveness of antidepressant treatment. If confirmed, it would “be the first actual biomarker in psychiatry,” Raison said. “I mean, we’ve been looking for biomarkers for 50 years and had zero luck. And it’s ironic that it’s not a brain chemical.”
In the meantime, “you get much more mileage out of the lifestyle changes than you would out of supplements or any other over-the-counter drugs at this point,” Miller said."
-via The Washington Post (via Yahoo News), February 24, 2023
#depression#cw sui mention#cw suicide mention#inflammation#autoimmune#cytokines#neuroscience#medical news#medical research#anti inflammatory#antidepressants#ssri#mental health#mental illness#good news#hope#way way more details at the source btw
182 notes
·
View notes