#global clinical research organization
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Leading Innovation in Clinical Drug Development | Clival Database
Clival Database empowers the clinical drug development process with comprehensive insights and resources. As a leading platform, we support clinical research organization services and collaborate with global contract research organizations to enhance trial efficiency. Our extensive Clinical Trials Databases India provide real-time data for informed decision-making. Partnering with Asiatic Clinical Research, we streamline clinical drug development, ensuring faster approvals and optimized trial strategies. Clival Database is the go-to solution for researchers and organizations seeking innovation and precision in clinical research worldwide.
#Clinical Trial Data Solutions#global clinical research organization#clinical research organization US#therapeutic areas and indications#clinical research organization Russia#clinical research organizations in Germany
1 note
·
View note
Text
NewLife Medicals: Your Trusted Global Clinical Research Organization
Riding on the cutting edge of medical science and clinical trials, NewLife Medicals is your reliable partner for all pharmaceutical needs. Bathing in expertise, authority, and trust, our ambitious goal is to reshape the future of healthcare.
But why should you trust NewLife Medicals?
NewLife Medicals: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Manufacturers
Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are the heart of any medicine, responsible for its therapeutic effects. At NewLife Medicals, we are more than just API manufacturers. Quality, affordability, and ultra-precision define our API manufacturing. We utilize state-of-the-art technology and rigorous quality checks to ensure the synthesis of high-quality APIs.
Got an unusual API request? As hard-to-source drugs and limited distribution drugs suppliers, we welcome the challenge!
Clinical Research Organization: NewLife Medicals
Clinical trials form the backbone of drug development – but they can be complex and costly. Simplify and economize your clinical testing experience with our unparalleled clinical research organization. Our seasoned team of research professionals are committed to delivering high-quality, timely, and ethically sound clinical research.
Why settle for less when you can have the best?
Global Innovator Drugs Supplier and Biosimilar Supplier
As an innovator drugs supplier, NewLife Medicals is committed to bringing new, pioneering treatments to the market. Our extensive portfolio of innovator drugs and biosimilar infusions stands as a testament to our pioneering spirit and relentless dedication to progress.
Ever heard of orphan drugs or REMS access? We supply these too!
Finished Dosage Formulations Suppliers
We take our role as finished dosage formulations suppliers seriously. Our manufacturing process leverages the highest industry standards, ensuring consistency and efficacy with every dose. Whether it's tablets, capsules, or syrups, we have your needs covered.
Are you seeking a reliable reference listed drug provider? Look no further!
Ancillary Clinical Supplies and Hospital Lines Supplier
Besides pharmaceuticals, our inventory comprises ancillary clinical supplies and premium hospital lines. These medical accessories and equipment promise to simplify your caregiving experience, improving efficiency and compliance.
Are you with us yet?
Your Trusted Partner in Pharmaceutical Supply Chain
Whether it's comparator sourcing for clinical trials, pharma raw material suppliers, patient supply, or specialty sourcing, NewLife Medicals has got you covered. Our integrated supply chain caters to all your pharmaceutical needs while maintaining the highest quality standards.
Trust in the expertise and authority of NewLife Medicals for all your medical needs. Together, let's make a healthier world!
Meta description: Explore NewLife Medicals – your trusted global clinical research organization, pharmaceutical supplier, and healthcare partner. Dive into our wide range of services today.
#rld pharmaceutical#comparator sourcing for clinical trials#named patient supply#ancillary clinical supplies#global clinical research organization#drug development#innovator drugs supplier
0 notes
Text

This July, my mom and I are stepping up for a great cause! We're participating in the Multiple Myeloma March, organized by Myeloma Canada. We are committing to walking 200,000 steps around our charming (and often sweltering!) town of Wheatley, Ontario. We'd be thrilled if you would consider supporting our modest goal of raising $392. As a token of our appreciation, every donor will receive a special Martin and GSD postcard (if you feel comfortable sharing your address with me). Check out the donation link below —thank you for your generosity! ❤️
Donate: https://shorturl.at/u84HL
#martin and bosco#multiple myeloma#multiple myeloma march#my dad and my husband both died of multiple myeloma#sincere apologies to my friends who have seen this post on my other social media accounts#thank you#myeloma canada is a very small organization that funds clinical treatment research for multiple myeloma#i will mail postcards globally!
174 notes
·
View notes
Text
Clinical Trials : Holistic Exploration of the Current State and Future Outlook
The global clinical trials market size is expected to reach USD 123.5 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 6.49 from 2024 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. An increase in the volume and complexity of clinical trials has been witnessed lately, which plays an important role in the R&D of new drugs and products. The market witnessed a decline of 6% in 2020 owing to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the market is projected to recover from 2021 onwards. In addition, clinical trials have become increasingly costly, adding to the overall cost of developing a drug.

Clinical Trials Market Report Highlights
The phase III clinical trials segment dominated the market with a 53.3% share in 2023. This can be attributed to the complexity of this phase
The interventional studies segment dominated the market in 2023. It is one of the most prominent methods used in clinical trials in the study design segment owing to the increasing demand for the intervention for clinical trials by researchers
North America held 50.3% of the market share in 2023. Favorable government initiatives and the presence of a large number of players in the U.S. that offer advanced services are responsible for market growth
Asia Pacific region is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period owing to the increasing patient pool and cost-efficient services.
For More Details or Sample Copy please visit link @: Clinical Trials Market Report
The increasing need for developing new drugs for chronic diseases, such as cancer, respiratory disorders, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and others, is creating immense pressure on the healthcare industry. The COVID-19 pandemic and the increasing demand for developing a suitable treatment are driving the market. The high number of people affected by the disease further depicts an increasing need for therapeutics & vaccines. Currently, there are 288 therapeutics and 106 vaccines under development, out of which, nearly 7.0% of therapeutics are in Phase IV, 21.0% in Phase III, and 43.0% & 13.0% in Phase II & Phase I, respectively.
The pandemic has resulted in the global disruption of traditional onsite clinical trials. Hence, regulatory bodies worldwide have undertaken various initiatives for fast-tracking clinical trials for the development of innovative solutions. One such instance is Solidarity, an international clinical trial launched by the WHO to find effective treatment against COVID-19. Although the pandemic has forced many medical device & drug developers to revise the approach to such crises, integrating best practices within clinical trial procedures & adapting to virtual trials, which can support the continuous development of therapeutics.
ClinicalTrials #HealthcareResearch #MedicalInnovation #DrugDevelopment #PatientRecruitment #Biopharmaceuticals #ClinicalResearch #RegulatoryCompliance #DataManagement #PatientEngagement #PrecisionMedicine #TherapeuticTrials #CROs #ClinicalResearchOrganizations #GlobalHealth #ClinicalStudyDesign #PharmaceuticalIndustry #BiotechResearch #ClinicalEndpoints #HealthTechIntegration
#Clinical Trials#Healthcare Research#Medical Innovation#Drug Development#Patient Recruitment#Biopharmaceuticals#Clinical Research#Regulatory Compliance#Data Management#Patient Engagement#Precision Medicine#Therapeutic Trials#CROs#Clinical Research Organizations#Global Health#Clinical Study Design#Pharmaceutical Industry#Biotech Research#Clinical End-points#HealthTech Integration
0 notes
Text
The Best News of Last Year - 2023 Edition
Welcome to our special edition newsletter recapping the best news from the past year. I've picked one highlight from each month to give you a snapshot of 2023. No frills, just straightforward news that mattered. Let's relive the good stuff that made our year shine.
January - London: Girl with incurable cancer recovers after pioneering treatment
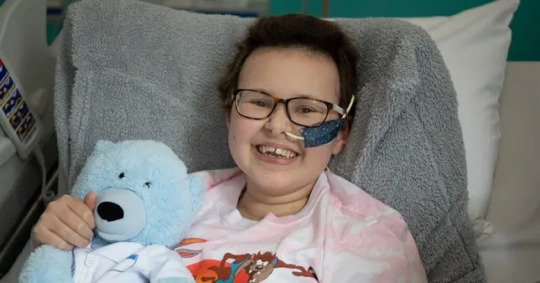
A girl’s incurable cancer has been cleared from her body after what scientists have described as the most sophisticated cell engineering to date.
2. February - Utah legislature unanimously passes ban on LGBTQ conversion therapy

The Utah State Legislature has unanimously approved a bill that enshrines into law a ban on LGBTQ conversion therapy.
3. March - First vaccine for honeybees could save billions

The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has approved the world’s first-ever vaccine intended to address the global decline of honeybees. It will help protect honeybees from American foulbrood, a contagious bacterial disease which can destroy entire colonies.
4. April - Fungi discovered that can eat plastic in just 140 days
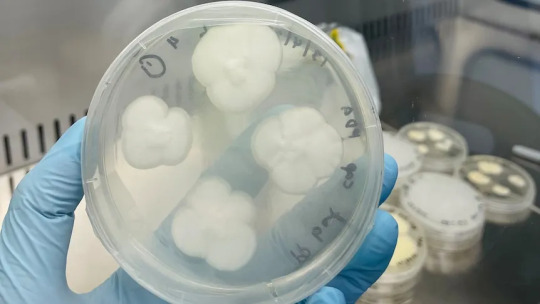
Australian scientists have successfully used backyard mould to break down one of the world's most stubborn plastics — a discovery they hope could ease the burden of the global recycling crisis within years.
5. May - Ocean Cleanup removes 200,000th kilogram of plastic from the Pacific Ocean

The Dutch offshore restoration project, Ocean Cleanup, says it has reached a milestone. The organization's plastic catching efforts have now fished more than 200,000 kilograms of plastic out of the Pacific Ocean, Ocean Cleanup said on Twitter.
6. June - U.S. judge blocks Florida ban on care for trans minors in narrow ruling, says ‘gender identity is real’

A federal judge temporarily blocked portions of a new Florida law that bans transgender minors from receiving puberty blockers, ruling Tuesday that the state has no rational basis for denying patients treatment.
7. July - World’s largest Phosphate deposit discovered in Norway

A massive underground deposit of high-grade phosphate rock in Norway, pitched as the world’s largest, is big enough to satisfy world demand for fertilisers, solar panels and electric car batteries over the next 50 years, according to the company exploiting the resource.
8. August - Successful room temperature ambient-pressure magnetic levitation of LK-99

If the claim by Sukbae Lee and Ji-Hoon Kim of South Korea’s Quantum Energy Research Centre holds up, the material could usher in all sorts of technological marvels, such as levitating vehicles and perfectly efficient electrical grids.
9. September - World’s 1st drug to regrow teeth enters clinical trials

The ability to regrow your own teeth could be just around the corner. A team of scientists, led by a Japanese pharmaceutical startup, are getting set to start human trials on a new drug that has successfully grown new teeth in animal test subjects.
10. October - Nobel Prize goes to scientists behind mRNA Covid vaccines

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to a pair of scientists who developed the technology that led to the mRNA Covid vaccines. Professors Katalin Kariko and Drew Weissman will share the prize.
11. November - No cases of cancer caused by HPV in Norwegian 25-year olds, the first cohort to be mass vaccinated for HPV.
Last year there were zero cases of cervical cancer in the group that was vaccinated in 2009 against the HPV virus, which can cause the cancer in women.
12. December - President Biden announces he’s pardoning all convictions of federal marijuana possession

President Joe Biden announced Friday he's issuing a federal pardon to every American who has used marijuana in the past, including those who were never arrested or prosecuted.
------
And there you have it – a year's worth of uplifting news! I hope these positive stories brought a bit of joy to your inbox. As I wrap up this special edition, I want to thank all my supporters!
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Merry Christmas and Happy New Year!
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
For much of living memory, the United States has been a global leader of scientific research and innovation. From the polio vaccine, to decoding the first human chromosome, to the first heart bypass surgery, American research has originated a seemingly endless list of health care advances that are taken for granted.
But when the Trump administration issued a memorandum Monday that paused all federal grants and loans—with the aim of ensuring that funding recipients are complying with the president’s raft of recent executive orders—US academia ground to a halt. Since then, the freeze has been partially rescinded for some sectors, but it largely remains in place for universities and research institutions across the country, with no certainty of what comes next.
“This has immediate impact on people’s lives,” says J9 Austin, professor of psychiatry and medical genetics at the University of British Columbia. “And it’s terrifying.”
The funding freeze requires agencies to submit reviews of their funded programs to the Office of Management and Budget by February 10. The freeze follows separate orders issued last week to US health agencies—including to the National Institutes of Health, which leads the country’s medical research—to pause all communications until February 1 and stop almost all travel indefinitely.
The confusion is consummate. If the funding freeze continues through February, and even beyond, how will graduate students be paid? Should grant applications—years long in the writing—still be submitted by the triannual grant submission deadline on February 5? What does this mean for clinical trials if participants and lab techs can’t be paid? Will all that research have to be scrapped thanks to incomplete data?
Even if Trump fully reverses the freeze on research funding, the damage, multiple sources say, has been done. Although for now the funding freeze is temporary, the administration has shown how it might wield the levers of government. The implication is that withdrawing funding could be done more permanently, and could be done to individual institutions, individual organizations, both private and public. This won’t just set a precedent for the large East Coast or West Coast universities, but those located in both red and blue states alike.
While always an imperfect arrangement, science in the US is largely funded by a complex system of grant applications, reviews by peers in the field (both of which have had to be halted as part of the communications pause), and the competitive distribution of NIH funds, says Gerald Keusch, emeritus professor of medicine at Boston University and former associate director of international research for the NIH. According to its website, the NIH disburses nearly $48 billion in grants per year.
When it comes to medical research, America truly is first, and if it abdicates that position, the void left behind has global ramifications. “In Canada, we have always looked to NIH as an exemplar of what we should be trying to do,” says Austin, speaking to me independently of any roles and affiliations. “Now, that’s collapsed.”
Science is, in its very nature, collaborative. Many consortiums and alliances within scientific fields cross borders and language barriers. Some labs may be able to find additional funding from alternative sources such as the European Union. But it is unlikely that a continued withdrawal of NIH funding could be plugged by overseas support. And Big Pharma, with its seemingly endless funds, is unlikely to step up either, according to sources WIRED spoke with.
“This can’t be handed off to drug companies or biotech, because they’re not interested in things that are as preclinical as a lot of the work we’re discussing here,” says a professor of genetics who agreed to speak anonymously out of fear of retribution. “Essentially, there’s a whole legion of university-based scientists who work super damn hard to try to figure out some basic stuff that eventually becomes something that a drug company can drop $100 million on.”
The millions of dollars awarded to high-achieving labs is used to fund graduate students, lab techs, and analysts. If the principal investigator on a research team is unsuccessful in obtaining a grant through the process Keusch describes, often that lab is closed, and those ancillary team members lose their jobs.
One of the potential downstream effects of an NIH funding loss, even if only temporary, is a mass domestic brain drain. “Many of those people are going to go out to find something else to do,” the professor of genetics says. “These are just like jobs for anything else—we can’t not pay people for a month. What would the food service industry be like, for example, or grocery stores, if they don’t pay somebody for a month? Their workers will leave, and pharma can only hire so many people.”
WIRED heard over and over, from scientists too fearful for their teams and their jobs to speak on the record, that it won’t take long for the impact to reach the general population. With a loss of research funding comes the closure of hospitals and universities. And gains in medical advancement will likely falter too.
Conditions being studied with NIH funding are not only rare diseases affecting 1 or 2 percent of the population. They’re problems such as cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer’s—issues that affect your grandmother, your friends, and so many people who will one day fall out of perfect health. It’s thanks to this research system, and the scientists working within it, that doctors know how to save someone from a heart attack, regulate diabetes, lower cholesterol, and reduce the risk of stroke. It’s how the world knows that smoking isn’t a good idea. “All of that is knowledge that scientists funded by the NIH have generated, and if you throw this big of a wrench in it, it’s going to disrupt absolutely everything,” says the genetics professor.
While some are hopeful that the funding freeze for academia could end on February 1, when the pause on communications and therefore grant reviews is slated to lift, the individuals WIRED spoke with are largely skeptical that work will simply resume as before.
“When the wheels of government stop, it’s not like they turn on a dime and they just start up again,” says Julie Scofield, a former executive director of NASTAD, a US-based health nonprofit. She adds that she has colleagues in Washington, DC, who have had funding returned to their fields, and yet remain unable to access payment through the management system.
Austin says that already the international scientific community is holding hastily arranged online support groups. Topics covered range from the banal—what the most recent communication from the White House implies—to how best to protect trainees and the many students on international visas. But mostly they’re there to provide support.
“I’ve had a lot of messages from people just expressing gratitude that we could actually get together,” Austin says. “There’s just so much unaddressable need. None of us has the answers.”
Scientists, perhaps more than any other profession, are trained to “learn and validate conclusions drawn from observation and experimentation,” says Keutsch. That applies to the current situation. And what they observe during this pause of chaos does not portend well for the future of the United States as a pinnacle of scientific excellence.
“If people want the United States to head toward being a second-class nation, this is exactly what to do. If the goal is, in fact, to make America great, this is not a way to do it,” says the genetics professor. “This is not a rational, thoughtful, effective thing to do. It will merely destroy.”
This story has been written under a pseudonym, as the reporter has specific and credible concerns about potential retaliation.
168 notes
·
View notes
Text
"An international research team has found almost a million potential sources of antibiotics in the natural world.
Research published in the journal Cell by a team including Queensland University of Technology (QUT) computational biologist Associate Professor Luis Pedro Coelho has used machine learning to identify 863,498 promising antimicrobial peptides -- small molecules that can kill or inhibit the growth of infectious microbes.
The findings of the study come with a renewed global focus on combatting antimicrobial resistance (AMR) as humanity contends with the growing number of superbugs resistant to current drugs.
"There is an urgent need for new methods for antibiotic discovery," Professor Coelho, a researcher at the QUT Centre for Microbiome Research, said. The centre studies the structure and function of microbial communities from around the globe.
"It is one of the top public health threats, killing 1.27 million people each year." ...
"Using artificial intelligence to understand and harness the power of the global microbiome will hopefully drive innovative research for better public health outcomes," he said.
The team verified the machine predictions by testing 100 laboratory-made peptides against clinically significant pathogens. They found 79 disrupted bacterial membranes and 63 specifically targeted antibiotic-resistant bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.
"Moreover, some peptides helped to eliminate infections in mice; two in particular reduced bacteria by up to four orders of magnitude," Professor Coelho said.
In a preclinical model, tested on infected mice, treatment with these peptides produced results similar to the effects of polymyxin B -- a commercially available antibiotic which is used to treat meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis and urinary tract infections.
More than 60,000 metagenomes (a collection of genomes within a specific environment), which together contained the genetic makeup of over one million organisms, were analysed to get these results. They came from sources across the globe including marine and soil environments, and human and animal guts.
The resulting AMPSphere -- a comprehensive database comprising these novel peptides -- has been published as a publicly available, open-access resource for new antibiotic discovery.
[Note: !!! Love it. Open access research databases my beloved.]"
-via Science Daily, June 5, 2024
#superbugs#bacteria#viruses#microbiology#antibiotics#medicines#public health#peptides#medical news#antibiotic resistance#good news#hope#ai#artificial intelligence#pro ai#machine learning
184 notes
·
View notes
Text
In a recent report published by Open Research Africa discussing disparities in Covid-19 research funding and leadership, scientists revealed that the majority of Long Covid research in Africa is primarily financed and overseen by foreign nations. The report’s authors analyzed projects documented in a global database tracking funded Covid-19 research projects. Out of a staggering 17,995 research projects cataloged in the Tracker as of July 2022, only 786 were carried out in African countries. Noteworthy contributors to Covid-19 research efforts on the continent included Morocco, with 183 projects, South Africa with 128 projects, and Kenya with 91 projects. In total, 75 research funders representing 17 countries directed USD $267 million to Covid-19 research in Africa. But the funders of these projects were predominantly public or governmental organizations from Europe and the U.S. Institutions such as the National Center for Scientific and Technical Research and UK Research and Innovation led the charge. While the bulk of funding stemmed from international entities, nine funders based in Africa also contributed to the cause. This imbalance in research investments poses a challenge for African scientists, as local research needs may differ from external agendas. The lack of sufficient evidence produced within and in the context of Africa worsens the marginalization of Long Covid in the region and weakens attempts to advocate for its acknowledgment and management.
110 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revolutionizing Clinical Trials and Drug Development | Clival Database
Clival Database is a cutting-edge clinical trials database platform designed to streamline the drug development process phases. From the phases of drug discovery and development to the phases of clinical drug development, Clival provides actionable insights and efficient solutions. Trusted by contract research organizations in the USA, it ensures accurate data management for every stage of development. With Clival Database, organizations can accelerate timelines, optimize resources, and drive innovation in pharmaceutical research. Empower your journey through clinical trials with a platform built for success.
#clival database#clinipedia#clinical trial database platform India#clinical trial database platform USA#Clinical Trial Data Solutions#global clinical research organization#clinical research organization US#therapeutic areas and indications
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding Ancillary Clinical Supplies and Reference Listed Drugs: A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of healthcare, ancillary clinical supplies and reference listed drugs play crucial roles in supporting medical treatments and ensuring patient safety. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of these essential components of the healthcare industry. We will explore the significance of ancillary clinical supplies and reference listed drugs, their importance in medical settings, and how they contribute to the overall patient care process. Join us as we delve into this topic in collaboration with New Life Medicals, a trusted provider of medical supplies and information.
I. Ancillary Clinical Supplies: Enhancing Patient Care and Safety Ancillary clinical supplies encompass a wide range of medical products and equipment that support healthcare professionals in delivering high-quality care to patients. Here are some key aspects of ancillary clinical supplies:

Importance of Ancillary Clinical Supplies: Ancillary clinical supplies are vital for maintaining patient safety, preventing healthcare-associated infections, and supporting effective treatment and diagnosis. These supplies enable healthcare providers to adhere to strict infection control protocols, deliver accurate diagnoses, and provide optimal patient care.
II. Reference Listed Drugs: The Gold Standard in Pharmaceutical Equivalence Reference Listed Drugs (RLDs) serve as benchmarks for generic drug manufacturers. RLDs are well-established brand-name drugs that have undergone rigorous testing, demonstrating safety, efficacy, and quality. Key points about RLDs include:
Role of RLDs in Generic Drug Development: RLDs act as reference points for generic drug manufacturers seeking approval from regulatory authorities. Generic drugs must demonstrate bioequivalence to the RLD, ensuring that they have the same active ingredient, dosage form, strength, and route of administration.
Ensuring Safety and Efficacy: RLDs undergo extensive clinical trials and scrutiny to establish their safety and efficacy. Generic drugs that are bioequivalent to RLDs offer comparable therapeutic outcomes, providing patients with affordable treatment options while maintaining efficacy and quality standards.
III. New Life Medicals: Trusted Provider of Ancillary Clinical Supplies and Information New Life Medicals is a reputable supplier of ancillary clinical supplies, offering a comprehensive range of products to support healthcare providers. They also serve as a reliable source of information on the importance, usage, and availability of clinical supplies. Here’s why New Life Medicals stands out:
Extensive Product Range: New Life Medicals offers a diverse selection of high-quality ancillary clinical supplies, ensuring healthcare providers have access to essential products necessary for optimal patient care.
Commitment to Quality and Safety: New Life Medicals prioritizes quality and safety, sourcing products from reputable manufacturers and adhering to stringent quality control measures.
Expert Guidance and Support: New Life Medicals provides valuable information and guidance on selecting the right clinical supplies, ensuring healthcare providers make informed decisions.
Ancillary clinical supplies and reference listed drugs are indispensable components of the healthcare industry, playing vital roles in patient care, safety, and treatment efficacy. By understanding the significance of these supplies and their impact on medical settings, healthcare professionals
0 notes
Text
Also preserved on our archive
By Benjamin Mateus
The ninth wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States is finally receding, with estimated daily new infections based on wastewater data now standing at 669,000 per day, down from the August peaks of over 1.3 million. However, experts predict that the tenth wave will begin in late fall and continue through the winter holidays, as has taken place every year of the pandemic so far.
With one in 70 individuals currently infectious, the risk of coming into contact with someone in a classroom, work, or dining at a local facility with 25 to 50 people is considerable. And despite the relative lull in cases, there is more COVID-19 transmission now than during 56.1 percent of the pandemic. In other words, the “forever COVID” policy essentially means that COVID is now everywhere all the time.
Under these conditions, forced upon society by the capitalist ruling class, repeat infections act like a battering ram, taking a growing toll on the foundation of everyone’s overall wellbeing. There is a growing body of evidence that each hit weakens the organ systems, aging them biologically beyond the person’s stated age until sufficient injury begins to manifest in physically measurable symptoms.
At present, more than one billion cumulative COVID infections have occurred in the US, at a rate of around one per year per person, with somewhere between 3-4 infections on average among the entire population. Estimates place the number of Long COVID cases at over 410 million globally in just the first four years of the pandemic, while excess deaths are nearing 30 million.
Clearly, the pandemic is ongoing and remains a significant health risk for the global population. The criminality of the “forever COVID” policy is highlighted by the fact that virtually no funding is allocated to the development of next-generation mucosal vaccines, improved treatments during the acute phase of infection, or any treatments for Long COVID patients. While trillions are squandered on war and bank bailouts for the rich, nothing is provided for critical life-saving research.
Last week, results from the first clinical trial of a mucosal vaccine were released, showing remarkable levels of efficacy after a second dose.
The important study published by Chinese investigators demonstrated that an intranasally administered anti-COVID vaccine can induce robust mucosal immunity against the coronavirus in human subjects (128 healthcare workers). The study found that the vaccine provided substantial immune protection against COVID while demonstrating safety and tolerance.
Esteemed clinical researcher Dr. Eric Topol wrote on Twitter/X, “[two] doses of a COVID nasal vaccine spray led to more than a 50-fold increase in spike specific secretory IgA antibodies against 10 strains of SARS-CoV-2, indicative of potent mucosal immunity.” Furthermore, Topol added, “At least 86.2 percent of participants who completed two nasal vaccines doses maintained uninfected status, likely without even asymptomatic infection, for at least three months.”
Emergency room physician and indoor air quality proponent, Dr. Kashif Pirzada, replied, “This could potentially give a real ending to the pandemic. No more waves of illness, no more rushing for tests and antivirals if you’re elderly or vulnerable. Hope this comes out soon!”
However, large Phase 3 clinical trials are costly, requiring multiple participants to obtain statistically relevant information on clinical endpoints, not to speak of the research and development investment to identify a therapeutic that can be tested. Thus, under capitalism, there is virtually no investment in these large-scale trials and nothing is being done beyond offering boosters of the current vaccine, despite their greatly reduced efficacy in preventing transmission.
The mucosal vaccine study was conducted just as Chinese officials acquiesced to the demands of the imperialist powers to abandon their life-saving Zero-COVID public health program, resulting in the infection of virtually the entire population and the deaths of 1-2 million people. What could such a vaccine have meant to these millions that perished needlessly and the millions more globally since then?
This raises the broader question of why the international community, facing a devastating pandemic, could not bring its accumulated scientific bodies to address the need to develop a preventative treatment against COVID?
As a trigger event in world history, the COVID-19 pandemic has only accelerated and exposed the deep-seated contradictions in global capitalism, which demands the accumulation of profits at any costs. The ruling class has nothing but contempt for workers, refusing to invest in any social programs that can improve the lives of masses of people. Short sightedness, corruption, mistrust, and suspicion epitomize their actions, which are rapidly progressing to a world conflagration carrying the danger of nuclear war.
Simply put, the ruling class cares not one iota about mucosal vaccines, just as they harbor resentment against any public health policy that infringes on their ability to conduct business.
Refusing to invest in these life-saving technologies, the capitalist ruling class has condemned humanity to face a lifetime of reinfections with COVID-19. What are the implications of this criminal policy?
Multiple previous studies have highlighted the dangers posed by reinfections with SARS-CoV-2. A recent study uploaded as a pre-print publication on Research Square (under review with the journal Nature Portfolio) by the Patient-Led Collaborative has once again found similar results when attempting to characterize the association between reinfections and the chronic debilitating condition known as Long COVID.
Among 3,382 participants (22 percent never had COVID, 42 percent with one prior infection and 35 percent with two or more infections), the risk of Long COVID was 2.14 times more likely among those with two COVID infections and 3.75 times more likely among those who had three or more COVID Infections compared to just one. Limitations in physical functioning measured in their study included ability to dress, bathe, perform moderate activities like vacuuming and functioning socially. Reinfections led to poorer overall health and worse immune health, including more severe outcomes and longer recovery from other infections.
As the authors wrote:
"Relative to those who did not report infections or experienced COVID-19 once, reinfections were associated with increased likelihood of severe fatigue, post-exertional malaise, decreased physical function, poorer immune health, symptom exacerbation before menstruation, and multiple other Long COVID symptoms. While vaccinations and boosters prior to infection are associated with lower likelihood of Long COVID, reinfections diminish their protective effect. The probability of reporting Long COVID remission is generally low (11.5 percent to 6.5 percent."
Another interesting finding of the study, which underscores the complete abandonment of public health efforts regarding COVID, is that a tiny number of those infected were prescribed antivirals during their acute COVID infections. Those with reinfections were also less likely to test, as the “forever COVID” policy has inured people from taking any protective measures to prevent infections.
The current alphabet soup of COVID strains is sees KP.3.1.1 dominate across the US and Europe, accounting for nearly 60 percent of all strains. However, a new variant known as XEC that was first detected in Germany in June has spread to more than 27 countries and accounts for six percent of all recently sequenced SARS-CoV-2 viruses in the US. Virologists expect this strain, derived from JN.1 through a complex recombination event and which has nearly twice the growth advantage, to overtake KP.3.1.1 and be the dominant variant during the winter season.
In a COVID update by TACT [Together Against COVID Transmission], the authors explain the dangers posed by these evolutionary developments of the SARS-CoV-2 viruses, writing:
"These variants can evade much of the immune responses from both vaccines and recent infections. Since they can evade antibodies to earlier variants, then that raises the risk of organ damage, vascular and neurological dysfunction, brain damage, and persistent infections which often leads to Long COVID. The unmitigated spread is raising concerns about their impact in the coming months."
Hospitalization rates for those 65 years and older and children were one of the highest during the summer from COVID and remain on par with the prior year’s summer/fall wave. The number of people that died from COVID In the week ending August 31, 2024, has climbed to 1,239, four times higher than the lows seen in June. At the present rate, it is expected that at least 60,000 people will officially lose their lives from acute COVID this year, not including deaths incorrectly attributed to another cause or due to the impact on the population’s health from accumulated infections.
These are not incidental and speculative issues. In a provocative report released by the Swiss Re Group, titled “The future of excess mortality after COVID-19,” one of the world’s leading providers of reinsurance and insurance, who specialize in financing the risk of death, they said, “[If] the ongoing impact of the disease is not curtailed, excess mortality rates in the general population may remain up to three percent higher then pre-pandemic levels in the US and 2.5 percent in the UK by 2033.”
They advised their investors:
"Based on current medical trends and expected advancements, we conclude that COVID-19 is still driving excess mortality both directly and indirectly. In the long term, lifestyle factors that contribute to poor metabolic health and lead to obesity and diabetes may become another compounding factor in population excess mortality. Insurers may wish to continue to monitor excess mortality and its underlying drivers in the general population closely, as well as the differences between general and insured populations."
#mask up#pandemic#covid#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator#long covid#covid conscious#covid is airborne#wear a fucking mask
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Adaptogenic Herbs and New Perspectives on Life Stages
Plants Useful for Mitigating Perimenopausal Symptoms
I don't usually advise on medicinal plants because, as we discuss the symbolic or folkloric aspects of plants in this blog, mixing topics could lead to negligence. However, I don't want to leave a reader without a response, especially one who is having a very uncomfortable climacteric phase and, despite visiting her gynecologist, wants to consider other options besides hormone replacement therapy.

My Personal Stance on Alternative Medicine
According to the World Health Organization, "alternative medicine" is a term used exclusively in countries where there is no integration between traditional medicine—such as indigenous, Chinese, or Ayurvedic medicine—and Western allopathic medicine, as is the case in Uruguay.
In recent years, innovative forms of “alternative medicines” and “holistic therapies” have emerged, differing significantly from the WHO's definition. The common denominator of these "medicines" with "eclectic" proposals and imprecise scopes seems to be the use of medical scientific terminology—like the word "therapy"—and non-medical jargon such as "quantum healings" using the language of physical sciences. One must ask whether the use of scientific terminology is merely a ploy, implying from the outset a dishonest proposal, or if it's our culture and way of communication that equips its practitioners with scientific language that seems to legitimize them. One of the problems, then, is how to define alternative medicine; here, I use the WHO definition, excluding crystal healings, Pleiadian masters, Himalayan salts, and other New Age practices.
I have always been attracted to plants; they seem to me to be fascinating living beings—especially trees—whose intelligence we are only just beginning to discover. Along with my emotional experience, my love for botanical drawing, magical folklore, and their curative properties bordering on the potentially toxic, this interest was serendipitously encouraged by a little-known work called The Life of Trees:
"Whatever profession you practice, at some point you will wonder if you are wasting your time, even if the activity you are engaged in is not harmful. Whether you are a merchant, archbishop, fisherman, musician, or doctor; sooner or later you will feel like you are wasting your time. There is only one exception: if you plant trees, it is certain that what you are doing is right." Francis Hallé in La vie des arbres
Thus, I find myself in a position to support, within the realm of alternative medicines, what we can practically call "herbal medicine," although in reality, all expressions of traditional medicine make use of the properties—real or imagined—of plants.
It could be argued, and it would be true, that the curative potential of plants is leveraged by allopathic medicine and that the pharmaceutical industry is increasingly investing in the research of active principles for the development of clinically proven effective medications. It could also be said, and it would be equally true, that no plant, by itself, is capable of curing chronic diseases, traumas, does not serve to relieve acute pain, does not cure infections, and is totally useless in genetic diseases, fertility treatments, diseases requiring surgery, etc. It is even true that, when misused and after their initial effect, plants can generate a nocebo effect and worsen a disease due to lack of proper treatment in due time. All true.
Personally, I would add that, concerning our country, Uruguay, the oral transmission of popular knowledge has been lost, gradually being replaced by the "holistic therapies" mentioned above. I think that, precisely, this is one of the reasons why plant therapeutics should be recovered, as a form of resistance against globalization that robs us of our memory.
Moreover, half of industrial drugs come from plants, and some more synthetically imitate active substances. Chemical industries do not randomly choose which plants to investigate for the development of effective medications; it would not only be expensive but also a waste of valuable time—in capitalist ethics, time is money—in blind trial and error. What increases the chances of success for the pharmaceutical industry is listening to the ancestral use of certain plants in diverse human groups; for example, the fashionable CBD cannabidiol, which is now commercially exploited with great success and has led to the legalization of marijuana consumption for business exploitation, comes from investigating why many people claimed its efficacy.
But where plants are truly effective is in prevention, delaying the onset of chronic diseases as varied as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, bradycardia due to hypotension, conditions potentially as serious as anemia, insomnia, constipation, and hormonal imbalances, or as annoying as skin rashes, symptoms associated with natural processes like menopause, and a long etcetera, resulting in better medical prognosis of diseases and fewer accumulated side effects from prolonged use of prescription and over-the-counter medications, about which there is also much misinformation and negligent use. The complex chemical interaction of all plant compounds far exceeds that of isolated active principles, generally with fewer side effects.
With the irreplaceable loss of this knowledge, written records gain greater importance. This dialectical relationship of complementarity between popular and academic knowledge is what I personally advocate.
Plants with Positive Effects on Climacteric or Perimenopause
I'm sure "symptoms" is not the best word to describe the reality because, after all, menopause is not a disease or a decrease in health by itself; perhaps "indications" or "signals" are more appropriate words, but it is also true that most people searching for this type of information will not use these words.
I fully support that women visit the gynecologist regularly, get routine tests and all those that our particular situations require—pap smears, mammograms, colposcopies, NAT, etc.—as well as self-breast exams and paying attention to the messages our bodies send. With this introduction, I speak from my humble position as a biological woman approaching fifty:
There are still societies today where women do not go through menopause as dramatically; our Western culture—with all its benefits, such as allopathic medicine—does not favor this natural transition of women to the non-reproductive stage, due to our lifestyle with diet, stress, social valuation, etc. Hormone replacement therapy carries risks for some women, along with the relief of "symptoms," and any good gynecologist will tell you that women with direct family history of breast, cervical, or uterine cancer may not choose this treatment (combining the best of both worlds, many gynecologists support phytotherapy). This is a case-by-case situation.
Which Herbs Help Transition to Menopause Better:
The old and dear Salvia officinalis is useful for hot flashes and sweats, but since it contains thujone—which can be toxic—one cup of tea a day, maximum for one week during the luteal phase, is enough.
To regulate mood, yarrow tea before bed, and if we're feeling sad or frantic, take it when we wake up.
In moderation, horsetail is purifying and diuretic—maintaining a good fat/muscle ratio—and helps fix calcium in the bones. It doesn't help with weight loss and should be taken with care not to lose valuable potassium.
In the diet, a handful of soybean sprouts, alfalfa, and seeds like flax can make a big difference.
#witchcraft#pagan#crone#pagan wicca#herbs#cottagecore#cottage witch#green witch#herbalism#uruguay#montevideo#menopausia#menopause#kema croi#witches of tumblr#witchblr
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this National Geographic story:
A 14-year-old boy who went swimming in a pond in India’s sweltering heat. A 13-year-old girl who bathed in a pool during a school excursion, and a five-year-old girl who took a dip in a river near her home. The three children lived in different parts of the southern Indian state of Kerala. Yet they have something in common ⸺all of them succumbed to a brain infection, Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM), caused by a tiny organism found in warm freshwaters and poorly maintained swimming pools. About a dozen others have been undergoing treatment in India, one of whom, a 27-year-old man, has also succumbed.
Although rare, PAM is a deadly infection with a worldwide occurrence. It is caused by Naegleria fowleri, also known as the "brain-eating amoeba”, as it infects the brain and destroys brain tissue. At least 39 countries have reported such infections so far, and the rate of infections is increasing by 4.5 percent every year. In Pakistan alone, 20 deaths are reported every year due to the disease, and in 2024, infections have been reported in India, Pakistan, and Israel. N. fowleri was also detected at a popular freshwater swimming spot in Western Australia and hot springs in the U.S’s Grand Teton National Park.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the majority of global case exposures⸺85 percent⸺have been reported during warm, hot, or summer seasons. Several studies have also observed that changes in temperature and climate may further drive a global increase in PAM incidence. A study published in May last year found that PAM infections are on the rise in the northern U.S. "N. fowleri is expanding northward due to climate change, posing a greater threat to human health in new regions where PAM has not yet been documented," the study noted.
Yun Shen, an assistant professor of chemical and environmental engineering at the University of California, Riverside, says that she considers PAM as “a potential emerging medical threat worldwide”. She explains that while warmer temperatures are likely to facilitate the survival and growth of N. fowleri, the risk of exposure may also increase as people indulge in more water-based recreational activities in hotter weather.
N. fowleri is found in warm, untreated freshwater, soil, and dust, says Karen Towne, a clinical associate professor of nursing at the University of Mount Union in Ohio, who co-authored a 2023 study on how the amoeba poses “a new concern for northern climates”. She adds that so far, PAM infections have typically occurred in cases involving swimming, splashing, and submerging one’s head in freshwater lakes, ponds, hot springs, and reservoirs. Meanwhile, less common routes of transmission have included warm hose water, a lawn water slide, splash pad use, and exposure of the nasal membrane to tap water from private well systems.
“Epidemiologically, most cases have occurred in healthy children and young adults⸺more males than females⸺who have had recent contact with untreated fresh water,” Towne told National Geographic in an email interview.
According to Barbara Polivka, an associate dean of research at the University of Kansas School of Nursing, who co-authored the study with Towne, N. fowleri enters the nose via contaminated water, crosses the nasal membrane, and follows the olfactory nerve into the brain, where it incubates for an average of five days. “PAM begins with rapid onset of severe frontal headache, fever, nausea and vomiting, which worsen into stiff neck, altered mental status, hallucinations, coma, and death,” says Polivka.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fifty years ago, 15-year-old Sonia Yaco ran for the school board in Ann Arbor, Michigan, one of the youngest people in the country ever to run for a seat on the Board of Education. A member of a group called Youth Liberation, whose platform was founded in 1970, she believed schools would be best run by the people required to be inside them for about seven hours a day, 180 days a year.
Youth Liberation developed a 15-point platform that was far-reaching in its vision. In addition to calling for an end to sexism, sexual discrimination, class antagonism, racism, colonialism, and what they called “adult chauvinism,” the group wanted to form communities outside the structure of the nuclear family, live in harmony with nature, abolish juvenile detention centers and mental institutions, establish global solidarity with youth all over the world, be free of economic dependence on adults, and have the right to their own “new culture,” which included everything “from music and marijuana to free clinics and food cooperatives.”
The 20 or so young people in the group, ranging in age from 12 to 16, wanted “a nationwide movement for youth civil rights, akin to the Black Liberation movement and the growing women's movement,” one of the founders, Keith Hefner, later wrote.
Backed by the radical socialist Human Rights Party, Yaco tells Teen Vogue she delivered stump speeches in a hand-sewn, black ruffled skirt and a black leather jacket. At the time, Ann Arbor, birthplace of the Students for a Democratic Society, was a political hotbed. Youth-led organizations had helped rally support for the 26th Amendment, which was ratified in 1971, lowering the voting age from 21 to 18. With popular books like Children’s Liberation (1973), Escape from Childhood (1974), and The Children’s Rights Movement: Overcoming the Oppression of Young People (1977), the idea of youth liberation was gaining force. Youth Liberation of Ann Arbor distributed their message through an underground newspaper, which was a collection of news items, how-tos, and stories from youth all over the country. Yaco informed her parents that, given her political commitments, having a curfew wasn’t going to work, though she did still do the dishes. She talked to PTA forums and rock concerts of thousands, all with the message of youth empowerment. Each time she arrived to speak, she remembers, there was the question of whether or not she would be allowed on stage. She tells Teen Vogue that a school board member once told her to “shut [her] fat lip.” At another event, she says she encountered labor and civil rights activist Cesar Chavez, who told her, “I’ve been hearing about you.” The resistance against her candidacy was so great that the Board of Education prohibited Yaco from running, instigating a Supreme Court case which she ultimately lost. Still, with 1,363 votes, Yaco says she got the highest number of write-in votes ever received.
When we think of ageism, it commonly refers to older adults, not the other way around. Though many don’t tend to think of young people as oppressed, a recent study published in the Children and Youth Services Review argues that young people are, in many ways, similarly vulnerable to exploitation. Though young people under 18 can be tried in adult court, they are generally not allowed to vote or hold federal office. They are surveilled and policed in schools, medicated and institutionalized without consent, and paid less for their work. In some states, they cannot get vaccinated without parental permission. Many of these issues are particularly acute for youth of color — some as young as preschoolers — whom research has shown are viewed as older and not as “innocent” as their white counterparts. “You're actively teaching children how to deal with an active shooter, but you can't let them have a say in budgeting, you can't let them discuss curriculum,” says Yaco. While rhetoric about the need to “save the children” is rampant, much public policy in the United States — from the struggling childcare system to gun violence in schools — reveals otherwise. The U.S. is the only country in the United Nations that hasn't ratified the Convention on the Rights of the Child, a historic human rights treaty.
The same justifications historically used to deny other groups their basic freedoms are still applied to youth, explains scholar Mich Ciurria. “The popular narrative about children — as spoiled, ungrateful, and mentally ill — mirrors the popular narratives about 1960s housewives, Black working mothers, and disabled people,” she wrote in a recent essay. To be “childish,” after all, is a derogatory term. As psychologist Robert Epstein argues in an article for Scientific American, what is commonly chalked up to an innate “irresponsibility” or “laziness” — the idea of the unformed teen brain — may simply be a response to living under the repressions of modern society. A 1991 study reviewing research on young people in 186 preindustrial societies — more than half of which had no word for “adolescence” — revealed little evidence of the kind of antisocial teen behavior found in the West, according to Epstein’s summary. In his research for the piece, Epstein found that, based on surveys he conducted, “teens in the U.S. are subjected to more than 10 times as many restrictions as are mainstream adults, twice as many restrictions as active-duty U.S. Marines, and even twice as many restrictions as incarcerated felons.” Young people have long been at the forefront of liberation struggles. Youth played a big part in the Civil Rights movement, which would inspire other movements that followed. In 1955, nine months before Rosa Parks became famous for refusing to give up her seat on a Montgomery, Alabama bus, a 15-year-old named Claudette Colvin was arrested for the same action. Galvanized by the Civil Rights movement, the National Indian Youth Council, formed by a group of young people in 1961, organized “fish-ins'' in support of land-use rights. The 1963 Birmingham Children’s Crusade saw more than a thousand young people, some as young as seven, attacked and jailed after taking to the streets in peaceful protest. In 1972, the Gay International Youth Society of George Washington High School, a group of students of color in the Manhattan neighborhood of Washington Heights, formed one of the first gay-straight alliances on the basis of student civil rights.
By 1979, Youth Liberation of Ann Arbor had disbanded, and the idea of youth liberation gradually faded from popular consciousness, but activists today are still organizing around age as one form of discrimination in a larger system of interlocking oppressions. For Margin Zheng, the former president of the National Youth Rights Association (NYRA), a group founded in 1998, youth liberation is deeply intersectional. “Young people are BIPOC, young people are queer, young people are of various genders and of no gender, young people are disabled, young people are poor, young people are immigrants and migrants — just like older people,” they write as part of their principles of anti-ageism. Zheng, the child of conservative Chinese immigrants, felt constrained both by their family life and their experience in school. “I secretly longed to be homeschooled and have the freedom to do my own thing, but my parents did not believe in nontraditional education,” they tell Teen Vogue. They attended their first school board meeting in ninth grade and soon began to question why students didn’t have more of a voice. “People think that they can make sweeping generalizations about people of a certain age, but you can’t generalize about youth just as you can’t generalize about people of a certain race, gender, etc.,” they say. Ashawn Dabney-Small, who ran for Boston City Council as an 18-year-old and former vice president of NYRA, became involved in youth activism to address the issues that affected him. “It's not about advocating, it's about speaking from your experiences,” says Dabney-Small, who has experience with the foster care system and the effects of poverty. “That's why I got involved in certain issues, policies that revolve around my life because it's literally my life.” As an activist, Dabney-Small worked on campaigns against gun violence. Recently, he advocated for Congresswoman Ayanna Pressley’s bill to lower the federal voting age to 16 — a move that could revolutionize American politics. “Schools and families are the places where we (young people) begin to feel that we have to struggle for our freedom,” Youth Liberation Acnn Arbor wrote in 1972. (One of the indirect results of Yaco’s campaign was the founding of the alternative Community High School that same year.)
Indeed, many activists today — in movements from unschooling to family abolition — see the institutions of school and family as structures that should be radically reimagined. From Indian Boarding Schools to the school-to-prison pipeline, unpaid domestic labor to assaults on queer chosen families, critics say schools and certain family structures have long been used as tools of oppression for women, queer people, and people of color. In a utopian world, Zheng says, people wouldn’t be judged and set apart by age. Instead, they envision more intergenerational spaces where younger and older people — of all races, genders, sexualities, and abilities — can learn and grow together. “Just as young people would be empowered to cultivate and apply their strengths to work they find meaningful, older people would be embraced in their own personal growth, knowing that learning and unlearning are processes that happen all throughout the lifespan,” they say. Each person would be recognized for their own unique potential. The vision is not unlike the original platform outlined by Youth Liberation more than 50 years ago. As Zheng says, “There would be no prisons, no police, and no schools, only communities of lifelong learning, caring, and joy.”
#undescribed#resources#youth liberation#history#black liberation#bipoc#michigan#socialism#abolition#education#civil rights#anti racism#family#autonomy#queer#trans#intersectional feminism#signal boost#reaux speaks
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
By: Christina Buttons
Published: May 13, 2024
A guide to the international debate on youth medical transition, where medical authorities in the United States depart from a growing international consensus.
The world is reacting to the U.K.'s Cass Review and associated systematic evidence reviews, which found "remarkably weak" evidence supporting medical interventions for gender transition in minors. Released on April 9, 2024, the final report from the national gender clinic service for those under 18—following four years of meta-analyses of the available literature—dealt a major blow to the gender-affirming model of care and marked its termination in England.
NHS England, which commissioned the report, expressed gratitude to Dr. Hilary Cass and committed to implementing her recommendations. These advocate for primarily relying on psychotherapy to address gender-related distress in minors and discontinuing the use of puberty blockers as part of England’s publicly funded healthcare system. The NHS predicted the landmark review would have "major international importance and significance"—a prediction that has proven correct. Just one month later, we are already beginning to see its impact.
What’s New
Scotland and Wales
In response to the Cass Review, Wales and Scotland have joined England in halting new prescriptions of puberty blockers for minors under 18 diagnosed with gender dysphoria. Additionally, in Scotland, cross-sex hormones will not be available to those under 18. In the last few years, beyond the U.K., Sweden, Finland, and Denmark have adopted a more cautious approach by placing restrictions on medical interventions for the treatment of gender dysphoria in minors. Norway has also signaled intentions to follow a similar path.
Germany
Now, Germany has emerged as the latest country to initiate steps towards placing restrictions on gender transition treatments for minors. Earlier this week, the German Medical Assembly, a pivotal body representing medical professionals across the country, passed a resolution that calls for the restriction of puberty blockers, cross-sex hormones, and surgeries for gender dysphoric youth to strictly controlled research settings. Another resolution passed that stated minors should not be permitted to "self-identify" into a chosen sex without first undergoing a specialist child and adolescent psychiatric evaluation and consultation.
While national restrictions have not yet been formalized, experts in gender medicine research are describing this update as a “major development” — especially considering that Germany has been one of the most permissive countries on this issue.
Read the SEGM Analysis
Belgium
Additionally, in Belgium, leading physicians are advocating for significant reforms in the treatment protocols for gender dysphoria in children and adolescents. According to an April 2024 report authored by pediatricians and psychiatrists P. Vankrunkelsven, K. Casteels, and J. De Vleminck from Leuven, there is a pressing need to follow the precedents set by Sweden and Finland, where hormones are regarded as a last resort. Their findings and recommendations were published in a prestigious medical journal associated with Dutch-speaking medical faculties in Belgium and their alumni associations.
International Bodies
International bodies such as the United Nations (UN) have also responded to the Cass Review. The United Nations Special Rapporteur on violence against women and girls, Reem Alsalem, issued a statement on the UN’s website declaring that the Review’s recommendations are essential for protecting children, especially girls, from harm.
In addition, the European Society of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (ESCAP), a prominent umbrella association of 36 Child and Adolescent Psychiatry societies worldwide, recently issued a policy statement on child and adolescent gender dysphoria. They urged healthcare providers to "not to promote experimental and unnecessarily invasive treatments with unproven psycho-social effects and, therefore, to adhere to the ‘primum-nil-nocere’ (first, do no harm) principle."
These responses stand in stark contrast to that of World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH), a body-modification advocacy organization. WPATH emailed a statement to its subscribers in response to the Cass Review, vehemently rejecting its findings and adhering to its ideological beliefs. WPATH criticized the Cass Report as “harmful” and "rooted in a false premise" that suggests distressed children can be helped without "medical pathways.”
United States
In response to the Cass Review, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the Endocrine Society (ES) recently provided statements to WBUR, doubling down on their endorsement of the gender-affirming model of care and medical interventions for minors. Both blamed “politics” for spreading “misinformation.” Meanwhile, prominent gender clinicians have expressed to WBUR that they are “perplexed and concerned” by these organizations’ statements, given the Cass Review’s findings.
WPATH, AAP, and ES continue to mislead the public by claiming that the gender-affirming model of care adheres to the principles of evidence-based medicine (EBM), despite clear evidence to the contrary. Their recommendations for medical interventions are not grounded in robust evidence but rather rely on "circular referencing" of each other’s guidelines, effectively creating a citation cartel.
Comprehensive Overview of the International Debate On Youth Transition by Country
In recent years, there has been an ongoing debate about the best approach for treating gender-distressed youth, addressing the global increase in young people, primarily adolescent females, seeking services from gender clinics. Countries with pediatric gender clinic services have shown varied responses, ranging from highly medicalized treatment pathways to approaches that prioritize psychotherapy.
Nations such as the UK, Sweden, Finland, and Denmark have taken unified steps to heavily restrict medical transitions for minors, aligning their guidance with the results of systematic evidence reviews, with Norway similarly indicating moves in this direction. Elsewhere, medical and health authorities remain divided on best practices, although there are signs of some reevaluating their positions on the medical transition of minors. This guide will highlight significant updates and changes observed in these practices over recent years.
The Netherlands
In the Netherlands, the birthplace of the Dutch Protocol—the highly medicalized approach to treating youth with gender dysphoria—is facing increased scrutiny. As of 2023, there is a growing debate within medical, legal, and cultural realms about the practice of youth gender transitions.
On February 15, 2024, the Dutch Parliament ordered an investigation into the physical and mental health outcomes of children who have been prescribed puberty blockers. Despite these developments, the guidelines for treating gender dysphoria have not yet been updated.
In April 2024, Amsterdam UMC, the Dutch clinic that pioneered youth gender transition practices, issued a statement in response to the Cass Report. The clinic commended several elements of the report but expressed disagreement with its conclusion that the evidence supporting the use of puberty blockers is insufficient.
In May 2024, one of the Netherlands' national newspapers profiled the new policy statement from The European Society of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (ESCAP) that advocated for a non-medicalized approach to treating child and adolescent gender dysphoria.
Norway
In 2023, the Healthcare Investigation Board of Norway (Ukom) issued recommendations urging the Ministry of Health and Care to instruct the Directorate of Health to revise the national professional guideline for gender incongruence, drawing on systematic evidence reviews. Additionally, the Ukom report proposed classifying puberty blockers, as well as hormonal and surgical interventions for children and young people, as experimental treatments. This classification would subject these treatments to more stringent regulations regarding informed consent, eligibility, and outcome evaluation. However, Norway has not yet issued any explicit new guidelines following these recommendations.
Denmark
In July 2023, Ugeskrift for Læger, the journal of the Danish Medical Association, reported a significant shift in Denmark's approach to treating youth with gender dysphoria. Instead of receiving prescriptions for puberty blockers, hormones, or surgery, most young people referred to the centralized gender clinic now receive therapeutic counseling and support.
France
In 2022, the National Academy of Medicine in France advised exercising "the utmost medical caution" for the use of puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones for children and adolescents, citing the risk of regret. Despite this caution, the prescription of these treatments remains permissible at any age with parental authorization.
A 2023 poll by the Journal International de Médecine found 84% of healthcare professionals in France are in favor of a moratorium on the administration of hormonal treatments for trans-identified minors.
In March 2024, French senators released a 369-page report advocating for the cessation of cross-sex hormones and puberty blockers on minors. Based on the findings of this report, lawmakers have drafted a bill that is set to be debated on May 28, 2024.
Italy
In January 2023, the Italian Psychoanalytic Society (SPI) wrote a letter to Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni, expressing "great concern" over the "ongoing experimentation" with drugs designed to halt puberty in children and calling for a "rigorous scientific discussion."
In March 2024, the Vatican’s doctrine office, after five years of preparation, released a report approved by Pope Francis that declared gender-related surgeries to be "a grave violation of human dignity."
In April 2024, five Italian medical organizations released a joint position paper on managing adolescent gender dysphoria. This document, which extensively references WPATH, supports the medical transition of minors.
Sweden
In 2022, Sweden's National Board of Health and Welfare declared that the potential harms of puberty blockers and gender-affirming hormone treatments for individuals under 18 years of age surpass the possible benefits for this demographic. The board recommended that such treatments should primarily occur within a research setting to better assess their effects on gender dysphoria, mental health, and quality of life among young people. Additionally, it noted that hormone treatments could still be administered in exceptional circumstances.
In April 2023, a systematic review conducted by researchers from Karolinska Institutet, University of Gothenburg, Umeå University, and the Swedish Agency for Health Technology Assessment and Assessment of Social Services was published in Acta Paediatrica. This review assessed the existing evidence on hormonal treatment for individuals under 18 years old with gender dysphoria. The researchers concluded that such interventions “should be considered experimental treatment rather than standard procedure.”
Finland
Finland was the first Western country to conduct a systematic review of the evidence for youth gender transition, that led to a significant update of its guidelines in 2020. Observations from Finnish gender clinics showed that hormone treatments do not typically improve—and can worsen—the functioning of gender-dysphoric youth. In response, the country's Council for Choices in Health Care revised its guidelines to emphasize psychosocial support as the primary approach and restricted hormonal interventions to exceptional cases. These interventions are permitted before age 18 only if the individual's cross-sex identity is confirmed as permanent and causes severe dysphoria, the child fully understands the significance, benefits, and risks of the treatments, and there are no contraindications.
In October 2023, Dr. Riittakerttu Kaltiala, a leading Finnish gender clinician and researcher at Tampere University Hospital, wrote an op-ed in The Free Press, titled "Gender-Affirming Care Is Dangerous. I Know Because I Helped Pioneer It.” She highlighted concerns about the practice of pediatric medical transition in the U.S. and the lack of solid evidence supporting the efficacy of medical transition in reducing suicide rates among young people.
In February 2023, a landmark study from Finland revealed low suicide rates among trans-identified youth and found no evidence of benefits from gender reassignment. The study showed that, after accounting for psychiatric needs, there was no statistically significant evidence that gender-referred youth have higher suicide rates compared to the general population. The authors concluded that the risk of suicide related to transgender identity and/or gender dysphoria "may have been overestimated."
England
In January 2020, National Health Service (NHS) England formed a Policy Working Group (PWG) to conduct an assessment of the existing research on the use of puberty blockers and feminizing/masculinizing hormones in children and young people with gender dysphoria. This was aimed at shaping a policy stance on their continued application. The findings from these reviews were released in March 2021.
In February 2022, the interim report to the Cass Review was published, which had been commissioned by NHS England to evaluate the Gender Identity Development Service (GIDS) at the Tavistock and Portman NHS Foundation Trust, the UK's only national clinic for children and adolescents with gender dysphoria. The review highlighted significant concerns about the clinical decision-making framework, noting a lack of robust evidence and consensus on the most effective treatments.
In July 2022, NHS England announced it would close GIDS in Spring 2023, which was delayed until Spring 2024. Two new regional hubs opened in London and the north of England to move away from a single-service model.
In October 2022, the NHS England issued new draft guidance following their systematic evidence review, stating that there is "scarce and inconclusive evidence to support clinical decision-making" for minors with gender dysphoria, and for most who present before puberty, it will be a "transient phase" requiring psychological support rather than medical intervention.
In March 2024, NHS England announced that it would end the prescription of puberty blockers at gender clinics for children due to insufficient evidence regarding their safety and effectiveness. These treatments will now only be accessible through clinical research trials.
On April 9, 2024, the final 388-page report of the Cass Review was published, along with 9 studies (8 of which were systematic evidence reviews) by the University of York.
Ireland
In March 2023, HSE published a review of the interim Cass Report to assess Gender Identity Services for children and young people in Ireland.
In April 2024, the Health Service Executive (HSE) announced the development of a new clinical program for gender healthcare, scheduled over the next two years. They also stated that the final report for the Cass Review will be included as part of this process.
Canada
In January 2024, Alberta announced the implementation of measures that significantly restrict medical transitions for minors. This policy establishes Alberta as the only province in Canada to enforce such limitations on gender transition procedures for individuals under 18. Under the new regulations, minors are prohibited from undergoing any gender-related surgeries, and those aged 16 and younger are prevented from accessing puberty blockers or cross-sex hormones.
United States
The three main organizations that have issued guidelines on youth medical transition include the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), the Endocrine Society (ES), and the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH). Other groups, such as the American Medical Association, have either publicly supported “affirming” medical practices without presenting evidence, or have aligned themselves with the guidelines set by one or more of these three organizations. Notably, none of these organizations have yet conducted systematic reviews of the evidence, which are designed to avoid selective inclusion of studies and biased interpretations.
Leaders at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) ignored five resolutions from its members over four consecutive years, each urging that youth transition guidelines be aligned with findings from systematic evidence reviews. In August 2023, the AAP Board of Directors finally agreed to conduct their own systematic review of the evidence and consider updating its guidance. At the same time, the Board "voted to reaffirm" its 2018 policy statement on gender-affirming care.
In 2022, Florida took the lead as the first state to curtail the widespread administration of hormonal and surgical interventions to the increasing number of gender-dysphoric youth. Early in the year, Florida’s public health authority commissioned an overview of existing English-language systematic evidence reviews. Based on the findings from this review, the Florida Boards of Medicine subsequently decided to halt the provision of gender-transition services to minors, unless conducted within research settings across the state.
As of April 2024, 24 states have now placed age restrictions on hormonal and surgical sex-trait modification interventions for minors. Democrats in four states (Texas, Louisiana, New Hampshire, and Maine) have voted in favor of age restriction laws or against turning their states into hormone sanctuaries.
Spain
In 2018, the Spanish Association of Paediatrics and the Spanish Society of Paediatric Endocrinology published a statement endorsing youth medical transition.
In 2022, the directors of Spain’s Society of Psychiatry, Association of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, and Society of Endocrinology expressed their opposition to a proposed law that would enable minors to access medical transition procedures. El Mundo, the second-largest daily newspaper in Spain, highlighted this controversy on its front page with the headline: “Psychiatrists explode against the Trans Law: It can bring a lot of pain and regret to many people.”
Australia and New Zealand
In August 2021, The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists (RANZCP) issued its first position statement focused on the mental health needs of individuals with gender dysphoria, followed by an update in September 2021. This statement was the first from a professional body that did not explicitly endorse a gender-affirming approach.
Australia has experienced considerable debate in recent years regarding youth medical transition. This topic has been extensively covered by Australian journalist Bernard Lane for his Substack, Gender Clinic News.
New Zealand's Ministry of Health was expected to release an evidence brief in early 2024, aimed at reviewing the current evidence on the safety of puberty blockers. Although the publication has been delayed, it is anticipated to be released soon.
In April 2024, Guardian Australia reported that neither New South Wales or Victoria have plans to make changes to puberty blocker prescribing or accessibility as a result of the Cass Review.
International Bodies
In July 2023, for the first time, international experts publicly weighed in on the American debate over "gender-affirming care." 21 leading experts on pediatric gender medicine from eight countries wrote a letter expressing disagreement with US-based medical organizations over the treatment of gender dysphoria in youth, urging them to align their recommendations with unbiased evidence “rather than exaggerating the benefits and minimizing the risks.”
In January 2024, the World Health Organization (WHO) updated its announcement on developing healthcare guidelines for “trans and gender diverse (TGD) people.” The WHO stated in an FAQ that it would not be making recommendations that impact minors. Importantly, they made the following admission: "[O]n review, the evidence base for children and adolescents is limited and variable regarding the longer-term outcomes of gender affirming care for children and adolescents" (January, 2024).
Further Information
For additional information, one of the studies that contributed to the Cass Review conducted a survey of European gender services for children and adolescents from September 2022 to April 2023. Additionally, a Wikipedia page provides an overview of the "legal status of gender-affirming healthcare" (for adults) in various countries worldwide.
If you found this guide helpful, I am working on developing an information-based website that will feature up-to-date data, counterarguments to activist claims, explainers on research, and useful resources related to gender pseudoscience.
#Christina Buttons#systematic review#Cass report#Cass review#gender affirming care#gender affirming healthcare#gender affirmation#medical scandal#medical corruption#medical malpractice#head in the sand#willful ignorance
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
BBMCT: Embark on New Medical Research at AIIMS hospital

British Biomedicine Clinical Trials (BBMCT) is a leading partner for advanced clinical research at AIIMS Hospital, driving medical innovation, patient care, and academic excellence. Their collaboration with AIIMS Hospital is reshaping the landscape of clinical research, addressing key gaps in medical knowledge, and bringing groundbreaking treatments to the forefront. The partnership plays a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes, accelerating the development of new medical innovations, and fostering collaboration across research teams.
This blog delves into the key areas where BBMCT enhances clinical trials, creating value for patients, researchers, and the broader medical community.
### Enhances Outcomes for Patient Care
One of the primary goals of clinical trials conducted by BBMCT at AIIMS Hospital is to enhance patient care. Through rigorous testing and research, clinical trials offer access to innovative treatments and therapies that are not yet widely available. These trials help identify new, more effective ways of diagnosing, treating, and managing various medical conditions, ultimately improving patient outcomes. With AIIMS’ cutting-edge facilities and BBMCT’s clinical expertise, patients benefit from early access to potentially life-saving therapies, providing them with the opportunity to participate in the development of groundbreaking medical treatments.
Furthermore, clinical trials often provide patients with personalized care, focusing on tailored treatments based on the latest research findings. This contributes to more targeted, effective interventions, which enhance long-term health outcomes and overall quality of life for participants.
### Accelerates the Development of Innovations
BBMCT accelerates the development of medical innovations through its partnership with AIIMS Hospital, positioning it as a leader in clinical research. Clinical trials are essential for advancing medical science, as they provide the data needed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new drugs, therapies, or medical devices. By conducting these trials, BBMCT helps expedite the development of life-changing innovations that have the potential to revolutionize treatment protocols and improve the quality of healthcare worldwide.
AIIMS, known for its world-class research capabilities, serves as the perfect partner for BBMCT to conduct advanced studies. The collaboration not only expedites the clinical trial process but also ensures that innovations undergo thorough testing to meet the highest standards before reaching the market. This rigorous testing speeds up the availability of new treatments to the broader population.
### Fosters Partnerships with Top Institutions
BBMCT’s collaboration with AIIMS Hospital is just one of many strategic partnerships that help push the boundaries of medical research. By working alongside top medical institutions, research organizations, and universities, BBMCT creates a robust network for knowledge sharing and innovation. These partnerships foster an environment of academic excellence, leading to groundbreaking discoveries in biomedicine.
The collaboration between BBMCT and AIIMS serves as a blueprint for other institutions worldwide, showcasing the importance of collaborative efforts in advancing clinical research. Through such partnerships, BBMCT ensures that it stays at the forefront of global medical research and attracts further collaboration opportunities with top-tier research bodies and healthcare institutions.
### Addresses Important Gaps in Knowledge
BBMCT plays a critical role in addressing key gaps in medical knowledge. Many diseases and medical conditions still lack effective treatments, or the available treatments are only partially effective. Through its clinical trials, BBMCT identifies these gaps in knowledge and works towards filling them. Research conducted at AIIMS, under the guidance of BBMCT, targets under-researched areas, including rare diseases, emerging health threats, and complex medical conditions that have not yet been fully understood or treated.
By focusing on these areas, BBMCT contributes significantly to the body of medical knowledge, enabling future medical advances. This helps both researchers and clinicians understand the complexities of various diseases, leading to better therapeutic strategies and, ultimately, better patient care.
### Attracts Funding for Research Efforts
A crucial aspect of any clinical research initiative is securing funding to carry out studies, especially those that involve complex, long-term research. BBMCT’s collaboration with AIIMS Hospital attracts significant funding for research efforts, ensuring the continuity and expansion of clinical trials. Successful partnerships with pharmaceutical companies, government bodies, and philanthropic organizations help secure financial support for groundbreaking research.
The ability to attract funding allows BBMCT to continue its important work in medical research, providing more opportunities for clinical trials and expanding the scope of studies. With additional resources, BBMCT can pursue innovative research directions, ensuring that critical areas of biomedicine are not left unexplored.
### Bolsters Academic Reputation and Distinction
Through its partnership with AIIMS Hospital, BBMCT not only advances clinical research but also bolsters the academic reputation of both organizations. AIIMS is known for its prestigious academic standing in the medical field, and its collaboration with BBMCT strengthens this reputation. By being involved in high-profile clinical trials, researchers and clinicians at AIIMS gain recognition in the international medical community, elevating their academic standing.
This collaboration also opens up new opportunities for education and training in clinical research, enhancing the skill sets of future healthcare professionals. The visibility and credibility of these trials help attract top-tier talent to AIIMS and BBMCT, further reinforcing their position as leaders in medical research.
### Facilitates Collaboration Among Research Teams
One of the most significant benefits of BBMCT’s partnership with AIIMS Hospital is the facilitation of collaboration among research teams. The clinical trial process involves various experts, including physicians, scientists, data analysts, and regulatory specialists. BBMCT creates a collaborative environment where these teams can work together seamlessly, ensuring that trials are conducted efficiently and produce reliable results.
By fostering a culture of teamwork and knowledge exchange, BBMCT ensures that diverse perspectives are integrated into the research process. This collaborative approach is crucial for solving complex medical problems, as it allows for the pooling of expertise from different fields. It also promotes continuous learning and the sharing of insights that ultimately benefit the wider medical community.
### Advances Practices Based on Solid Evidence
BBMCT’s commitment to evidence-based medicine is another key advantage for the medical community. Clinical trials conducted by BBMCT provide solid, peer-reviewed data that can be used to guide medical practices and treatment protocols. This evidence helps healthcare providers make informed decisions about patient care, ensuring that treatments are based on the most current and reliable information.
The rigorous nature of BBMCT’s clinical trials means that only well-substantiated practices make their way into clinical guidelines and healthcare policies. By contributing high-quality evidence to the medical field, BBMCT plays an essential role in advancing healthcare practices and improving patient outcomes on a global scale.
/media/e7f8e34bd4cfd77059366714b848a2f1
### Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
**1. What is the role of BBMCT in clinical research at AIIMS Hospital?**
BBMCT plays a pivotal role in facilitating advanced clinical research at AIIMS Hospital by conducting clinical trials that focus on innovative treatments and therapies. They work alongside AIIMS to test new medical interventions, thereby contributing to the improvement of patient outcomes, advancing medical knowledge, and speeding up the development of life-saving innovations.
**2. How do BBMCT’s clinical trials benefit patients?**
BBMCT’s clinical trials offer patients access to cutting-edge treatments and therapies that are not yet available to the general public. By participating in these trials, patients benefit from personalized care based on the latest research, which can lead to better health outcomes, especially in conditions with limited treatment options.
**3. What types of diseases or conditions are researched in BBMCT clinical trials?**
BBMCT conducts clinical trials across a wide spectrum of diseases and conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, rare genetic disorders, and emerging health threats. The trials often focus on under-researched or complex conditions, helping fill crucial gaps in medical knowledge and leading to the development of new, more effective treatments.
**4. How does BBMCT attract funding for research?**
BBMCT attracts funding from a variety of sources, including government grants, pharmaceutical companies, and philanthropic organizations. The partnership with AIIMS Hospital helps secure financial support by demonstrating the institution’s credibility, research excellence, and the potential impact of the trials on advancing medical science and patient care.
**5. Why is collaboration important in BBMCT’s clinical trials?**
Collaboration is essential for the success of BBMCT’s clinical trials, as it brings together experts from various fields, including medicine, science, and data analysis. By fostering an environment of teamwork and knowledge sharing, BBMCT ensures that clinical trials are conducted efficiently, producing reliable data that can influence medical practices and healthcare policies.
### Conclusion
BBMCT’s partnership with AIIMS Hospital stands as a beacon for advancing clinical research, fostering innovation, and improving patient care. Through its strategic approach to clinical trials, BBMCT not only accelerates the development of medical innovations but also addresses critical knowledge gaps, attracts essential funding, and bolsters the academic reputation of AIIMS. The collaborative environment created by BBMCT enhances teamwork among researchers, while solid evidence generated from clinical trials guides medical practices worldwide. As BBMCT continues to lead in biomedicine research, it plays an integral role in shaping the future of healthcare, offering hope for new treatments and better patient outcomes.
Subscribe to BBMCLINICALTRIALS YouTube channel for Research Insights
Be sure to subscribe to the **BBMCLINICALTRIALS YouTube channel** for exclusive access to the latest updates and in-depth insights into British Biomedicine Clinical Trials (BBMCT). Stay informed on cutting-edge research, clinical trial advancements, patient safety protocols, and breakthrough therapies being tested at AIIMS Hospital. Our channel provides expert discussions, industry trends, and detailed videos on the clinical trial process across various therapeutic areas. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, researcher, or simply interested in biomedical innovation, subscribing will keep you at the forefront of clinical research developments. Don’t miss out — join our community today!
#anya mouthwashing#artists on tumblr#batman#captain curly#agatha harkness#cats of tumblr#bucktommy#agatha all along#911 abc#dan and phil
4 notes
·
View notes