#ClimateFinance
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

The President of #COP28 calls for urgent action on adaptation financing to support vulnerable countries in the face of climate change. Read more about this critical issue in the link.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sustainable Finance: The Essential Role of Climate Reporting in Investment Strategies
As the financial world evolves, there has never been a greater necessity for sustainable investment. An article from Inrate underlines how climate reporting for long-short portfolios and derivatives can no longer do without solid and comprehensive reporting.
𝐊𝐞𝐲 𝐓𝐚𝐤𝐞𝐚𝐰𝐚𝐲𝐬:
𝐁𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐏𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐜𝐞 𝐂𝐥𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐞 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠: The adoption of best practice on climate reporting increases transparency and, hence, responsibility in investment approaches.
𝐑𝐢𝐬𝐤 𝐌𝐚𝐧𝐚𝐠𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭: Integration and understanding of climate risks is one of the basic factors to guarantee long-term portfolio sustainability.
𝐈𝐧𝐯𝐞𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫 𝐄𝐧𝐠𝐚𝐠𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭: Active dialogue by investors and companies should facilitate better climate reporting, hence leading to better-informed decision-making.
Investors have a responsibility regarding their portfolios impact on the environment. By embracing clear climate reporting, we follow already emerging regulations but do our part for a greener tomorrow.
𝐋𝐞𝐭 𝐮𝐬 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐬𝐮𝐜𝐡 𝐩𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐜𝐞𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐝 𝐨𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐬 𝐢𝐧𝐭𝐨 𝐦𝐚𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐧𝐯𝐞𝐬𝐭𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐥𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐬𝐜𝐚𝐩𝐞 𝐠𝐫𝐞𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐫!
Download Report
#SustainableInvesting#ClimateReporting#Transparency#InvestmentStrategy#Finance#ESG#ClimateFinance#ImpactInvesting#GreenInvesting#ResponsibleInvestment#ClimateRisk#FinancialTransparency#Sustainability#ClimateAction#LongShortInvesting#SociallyResponsibleInvesting
0 notes
Text
News | Oct 18, 2024
#2024#IsraelGazaConflict#LebanonUNPeacekeepers#ECB#ClimateFinance#CanadaIndiaRow#HurricaneMilton#30x30#GermanyPolitics#FoodSecurity#PalestinianRights#MiddleEastCrisis#Peacekeeping#EconomicRecovery#GlobalDiplomacy#NaturalDisasters#ClimateActionNow#Biodiversity#IndigenousRights#Geopolitics#WorldNews#InternationalAffairs#HumanRights#UN#GlobalEconomy#shorts#youtubeshorts#youtube#shortvideo#short
0 notes
Text
Financiamento climático por bancos multilaterais de desenvolvimento atinge recorde histórico em 2023
Joint Report on Multilateral Development Banks’ Climate Finance (Relatório Conjunto de Financiamento Climático dos Bancos Multilaterais de Desenvolvimento) 2023 Setembro 20, 2024 A soma para economias de baixa e média renda foi de US$ 74,7 bilhões, incluindo US$ 24,7 bilhões para adaptação à mudança climática BMDs ofereceram um recorde de US$ 125 bilhões no último ano para ação climática no…
0 notes
Text
Voluntary Carbon Credit Market: Opportunities, Challenges, and the Path Toward a Low-Carbon Economy
The global voluntary carbon credit market size is anticipated to reach USD 24.00 billion by 2030 and is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 34.6% during the forecast period, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. The voluntary carbon credit market (VCM) refers to the trading of carbon credits on a voluntary basis outside of any legal or regulatory requirements. In this market, companies, individuals, and other entities purchase carbon credits to offset their greenhouse gas emissions and meet self-imposed sustainability goals.

Voluntary Carbon Credit Market Report Highlights
Based on project, renewable energy dominated the market and accounted for a revenue share of 39.08% in 2023. Wind and solar farms generate credits by reducing emissions compared to traditional sources. This creates financial incentives for clean energy development, as companies can earn revenue while tackling climate change
Industrial dominated the component segment with more than 32.5% share in 2023. Industries like manufacturing and heavy production are driving growth in the market. These high-emitting sectors purchase credits from renewable projects to offset their footprint, fueling clean energy development while meeting sustainability goals
Private Companies dominated the end use segment. Private companies are a growing force in the voluntary carbon credit market. They purchase credits generated by emissions-reducing projects, like renewable energy, to offset their own footprint. This trend benefits both sides: companies achieve sustainability goals, and green projects gain vital funding
Asia Pacific is expected to witness significant growth in the market owing to factors such as supportive policies and growing environmental concerns
For More Details or Sample Copy please visit link @: Voluntary Carbon Credit Market Report
The VCM is facilitated by a variety of independent certification programs, such as the Verified Carbon Standard, Gold Standard, and Climate Action Reserve, which establish accounting rules, project eligibility criteria, and verification procedures for carbon credit projects. These projects span a range of activities, including renewable energy, forestry, and carbon capture and storage. However, the VCM has faced criticism over the quality and integrity of some carbon credits, leading to calls for greater standardization and transparency.
Governments are increasingly engaging with the VCM, using it to help meet their national climate goals under the Paris Agreement. For instance, Japan's GX League requires companies to offset any emissions they fail to reduce directly, using the VCM as a complementary mechanism. Policymakers see the VCM as a way to mobilize private capital for climate action, particularly in developing countries where the potential for cost-effective emissions reductions is high. At the same time, there are concerns that the VCM could undermine efforts to achieve deep, economy-wide decarbonization if not properly regulated and integrated with broader climate policy. The voluntary carbon credit market represents a growing and evolving landscape, with the potential to play a significant role in the global transition to a low-carbon economy
Gain deeper insights on the market and receive your free copy with TOC now @: Voluntary Carbon Credit Market Analysis Report
We have segmented the global voluntary carbon credit market report based on project, application, end-use, and region.
#VoluntaryCarbonMarket#CarbonCredits#Sustainability#CarbonOffset#ClimateAction#CarbonFootprint#NetZero#GreenFinance#ClimateChange#EnvironmentalImpact#CarbonReduction#SustainableBusiness#CarbonNeutral#EcoFriendly#CarbonTrading#ClimateMitigation#RenewableEnergy#SustainableDevelopment#CarbonEconomy#ClimateFinance
0 notes
Text
#Greenwashing#SustainableFinance#Regulations#EcoFinance#FinanceEthics#SustainableInvesting#ClimateFinance#GreenRegulations#FinancialTransparency#EthicalInvesting
0 notes
Text
Climate-Driven Capital Relocation
Bangkok's capital must move in response to climate change, signifying adaptability, cooperation, and resilience for a sustainable future in the face of rising sea levels.
Climate change is one of the few phenomena that directly and significantly affects both the natural world and human society. Every element of our lives, including the places we live in and the air we breathe, is impacted by it. Bangkok is the most notable example of this, as the city's core faces an existential threat from the sea's unceasing climb in elevation.
Climate projections indicate that flooding is impending, making consideration of a capital relocation necessary. This acts as a somber symbol of how we are all coming to terms with the consequences of the decisions we have made. Pavich Kesavawong's dire forecast that Bangkok will be submerged by the end of the century if we carry on in the same direction serves as a wake-up call to take preventive measures to mitigate the impending issue.
The crux of this dilemma is how to strike a compromise between the need to preserve significant centers of government and business and the irreversible advance of climate change. Relocating to a capital city is a challenging endeavor that involves numerous logistical challenges as well as socio-political, economic, and environmental aspects.
It is critical to comprehend how urbanization and climate resilience are related in order to have a meaningful discussion on capital relocation. Bangkok is a huge, bustling metropolis that is a testament to human ingenuity and adaptation. But as sea levels rise, even the most resilient cities will eventually reach their breaking point.
The recommended courses of action, which include building dikes akin to those found in the Netherlands, emphasize the need for innovative solutions tailored to the unique needs of each site. However, as Mr. Pavich correctly notes, these measures may prove insufficient to halt the oncoming waves. Consequently, thinking about a capital shift becomes a sensible response to a danger to one's life itself.
Relocating to a capital city has a big impact on socioeconomic dynamics, government, and identity. Bangkok, a thriving center of trade and culture, encapsulates the intricacy and ambitions of modern-day Thailand. Moving its capital would signal a major shift in the direction of the nation, with implications that extended well beyond the realm of urban planning.
Furthermore, even outside of Thailand, the debate over capital relocation is relevant to broader global conversations about climate adaptation and mitigation. The example of Indonesia, which is set to establish Nusantara as its new capital, emphasizes how critical it is to address low-lying coastal cities' vulnerabilities to climate change.
But even in the face of the approaching flood, revolutionary change is possible. Given the potential for capital migration, rethinking urban settings via the prisms of sustainability, equality, and resilience is essential. It presents an opportunity to support inclusive development strategies that prioritize environmental and public health.
Above all, the concept of capital flight underscores the criticality of nations cooperating to confront the existential risks posed by climate change. Bangkok's situation is a microcosm of a worldwide issue that transcends national borders and calls for hitherto unheard-of levels of collective action.
While taking into account the lessons learned from the past and charting a course for the future, policymakers must accept the demands of the present. Moving to a capital city is one way to demonstrate the adaptability and foresight needed to handle an uncertain future. For the legacy to be preserved for future generations, it requires courage, vision, and unrelenting dedication.
Ultimately, the necessity of climate-driven capital mobility is fundamental to our shared humanity and goes well beyond the domains of geopolitics and economics. It is proof of humankind's capacity to persevere in the face of adversity, forge new paths in the face of uncertainty, and protect the environment for future generations. In response to the call to action, let's embark on a more resilient and long-term course toward a future that can withstand increasing seas.
For other information>>

0 notes
Text




TIME IS TICKING!! DON'T FORGET TO GET YOUR TICKET FOR THE 10TH JUBILEE EDITION OF THE CC FORUM 'Investment in Sustainable Development" from May 29 to June 1 at the Intercontinental Paris le Grand TO ACCELERATE THE #INVESTMENT IN #SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT More at https://paris.cc-forum.com/ #LetsBreakTheCycle #WeAreOne #NoPlanetB #Paris #ClimateChange #FinanceForGood #ClimateFinance #GlobalGoalFinance
#climate change#climateaction#sustainable#ClimateChange#FinanceForGood#GlobalGoalFinance#ClimateFinance#INVESTMENT IN#LetsBreakTheCycle#WeAreOne#NoPlanetB#Paris
0 notes
Video
youtube
$100+ trillion needed to stabilize the climate. Who will pay for it? (S0...
#youtube#ClimateStabilization#ClimateChange#GlobalWarming#EnvironmentalCrisis#ClimateAction#ClimateFinance#RenewableEnergy#GreenInvestment#CarbonTax#CarbonOffsets
0 notes
Text
UK Champions Climate Action at UN Security Council

Climate Change's Role in Adding to Global Conflicts
In a significant address at the UN Security Council, Ambassador Barbara Woodward shed light on the intricate relationship between climate change, environmental degradation, biodiversity loss, and global conflicts. The statement emphasized the urgent need for a coordinated international response to these interlinked challenges that threaten international peace and security.
The Triple Threat: Climate Change, Conflict, and Food Security
Ambassador Woodward pointed out the vicious cycle where climate change and environmental issues contribute to conflicts and food insecurity, further destabilizing regions already under the strain of humanitarian needs. With an eye on the future, she underscored the dire consequences of inaction, both on the environment and global security landscape. A Tripartite Approach to Mitigating Crisis The UK's statement outlined three strategic approaches to combat these challenges: - Early Action on Food Security: Highlighting initiatives from last year's Global Food Security Summit, the UK's commitment to the Resilience and Adaptation Fund aims to bolster climate adaptation and anticipatory actions. This effort seeks to enhance resilience among the most vulnerable, particularly in conflict-affected regions. - Investment in Sustainable Agriculture: The call for innovation in sustainable, climate-resilient food production was clear. The UK champions scientific advancement accessible to all, especially smallholder farmers, through support for organizations like CGIAR and initiatives like the Gilbert Initiative. - Holistic and Integrated Solutions: Emphasizing the importance of a unified approach, the UK urged support for integrating climate impacts into conflict risk assessments and ensuring climate finance is conflict-sensitive. This comprehensive strategy involves humanitarian, development, peacebuilding, and climate actors working in concert to address these multifaceted issues.
The Role of the UN and International Community
Woodward's statement recognized the unique position of the UN, particularly its Climate Security advisers, to spearhead efforts in coordinating climate, food security, and peace initiatives. She advocated for the Security Council's support in fostering a coherent response to these global challenges, reflecting the collective concern among UN members. In Conclusion The UK's stance at the UN Security Council meeting underscores the critical need for global cooperation in addressing the intertwined issues of climate change, environmental degradation, and security. Ambassador Woodward's call to action serves as a clarion call for the international community to adopt an integrated approach to safeguarding peace, security, and sustainability for future generations. Sources: THX News, Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office & Dame Barbara Woodward DCMG OBE. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
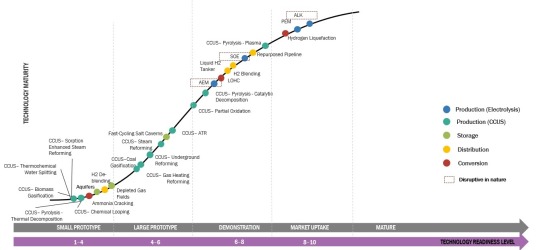
Hydrogen Industry Investments
Hydrogen Ecosystem Current and Future Investments
Current Investments in Hydrogen Ecosystem:
Hydrogen Production:
Electrolysis: Investments in electrolysis technology have been rising in order to produce hydrogen. Because of their promise for scalable and effective hydrogen synthesis from renewable sources, proton exchange membranes (PEMs) and alkaline electrolyzers have drawn a lot of attention. Enterprises such as Nel ASA, ITM Power, and Plug Power have managed to raise capital to enhance their electrolyzer production capabilities and facilitate the advancement of extensive electrolysis initiatives.
Steam Methane Reforming (SMR): Even though SMR is the most common way to produce hydrogen, efforts are being undertaken to enhance its environmental efficiency by utilizing carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies. In order to improve the efficiency and lower the carbon footprint of SMR plants, businesses are spending money on research and development.
Download- https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/industry-practice/RequestForm.asp
Hydrogen Storage and Transportation:
Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure: Infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is being developed with significant investments, especially in areas where fuel cell electric cars, or FCEVs, are becoming more and more popular. To assist the expansion of FCEVs, businesses including as Air Liquide, Linde plc, and Shell are investing in the installation of hydrogen filling stations.
Hydrogen Pipelines and Transportation: Infrastructure for transportation and hydrogen pipeline development is receiving funding in order to facilitate the economical and efficient distribution of hydrogen. Enterprises are investigating the possibility of reusing already-existing natural gas pipes and constructing specific hydrogen pipelines for extended transit.
Hydrogen Utilization:
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs): Several automakers are investing in the research and development of fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), including Toyota, Hyundai, and BMW. These expenditures go toward things like developing new vehicles, producing fuel cell stacks, and forming alliances to create FCEV supply chains.
Industrial Applications: To investigate hydrogen uses for decarbonizing steel production, refining processes, and power generation, investments are being made in a number of industrial sectors. Businesses in the manufacturing, energy, and chemical industries are funding collaborations and pilot programs to show the feasibility of using hydrogen in industry for both practical and cost-effective reasons.
Future Investments in Hydrogen Ecosystem:
Green Hydrogen
Investments in green hydrogen production technologies are anticipated to rise sharply, with a focus on decarbonization. It is projected that significant investments in electrolysis driven by renewable energy sources will be made in order to reduce costs and increase production capacity. In order to achieve carbon neutrality in a number of industries, including transportation, manufacturing, and power generation, green hydrogen is anticipated to be extremely important.
Hydrogen Infrastructure Expansion
It is expected that more money will be spent on building hydrogen infrastructure, such as hubs and clusters, pipeline networks, and hydrogen recharging stations. The aforementioned expenditures are intended to establish a resilient and linked hydrogen ecosystem, which will facilitate the expansion of hydrogen production, storage, and delivery.
Cross-Sector Integration
It's anticipated that future investments would concentrate on integrating hydrogen technology with other industries, including power grids, industrial processes, and renewable energy sources. Power-to-hydrogen, hydrogen blending in natural gas pipelines, and the application of hydrogen in industries with difficult-to-abate emissions are some of the technologies that are required for this integration.
International Collaboration
It is envisaged that investments would be made in international cooperation and partnerships to promote the growth of international trade and cross-border hydrogen supply chains. To support the global transportation of hydrogen, this entails making investments in regulatory frameworks, certification processes, and hydrogen infrastructure.
Detailed use case analyses related to current and future investments in the hydrogen ecosystem:
Hydrogen Production
Electrolysis Plants: Investing in electrolysis facilities is essential to increasing the production of green hydrogen. These plants separate water into hydrogen and oxygen using renewable electricity. They make it possible to produce hydrogen that is free of carbon, which has a variety of uses in the transportation, industrial, and power generation sectors. Electrolysis plants are being used on a variety of scales, from large-scale facilities for regional or national hydrogen production to small-scale projects for local consumption.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) in Hydrogen Production: The development and implementation of carbon capture and storage technologies for the production of hydrogen from fossil fuels are being funded. By capturing and storing carbon emissions, the creation of hydrogen is intended to become a low-carbon or carbon-neutral process. Blue hydrogen can serve as a stopgap measure until a more environmentally friendly hydrogen economy is established, and CCS technologies make this possible.
Hydrogen Infrastructure
Hydrogen Refueling Stations: Fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) adoption depends on investments in hydrogen refueling facilities. Compared to battery electric vehicles, FCEVs can drive longer distances and refill more quickly because to the infrastructure these stations provide for hydrogen filling. With an emphasis on important transit corridors, metropolitan areas, and places with favorable regulations and market demand for FCEVs, efforts are being undertaken to broaden the network of hydrogen refueling stations.
Hydrogen Pipelines and Storage: For hydrogen to be transported and distributed efficiently, storage facilities and pipelines must be invested in. Hydrogen may be transported great distances to supply-demand hubs using dedicated hydrogen pipelines or by repurposing existing natural gas pipelines. Subterranean hydrogen storage facilities are also being invested in, in an effort to offset the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources and guarantee a steady supply during moments of high demand.
Industry and Manufacturing
Green Hydrogen for Industrial Applications: The goal of investing in green hydrogen production is to reduce the carbon footprint of industrial activities. Refineries, steel, and ammonia manufacturing are among the industries investigating the use of green hydrogen as a fuel or feedstock in place of fossil fuels. These investments make it possible for these industries to reduce their carbon emissions, which results in more ecologically friendly and sustainable production methods.
Power-to-X Technologies: Investing in power-to-x technologies entails turning excess renewable energy into hydrogen or goods generated from hydrogen, such as feedstocks, chemicals, or synthetic fuels. Power-to-x technologies facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources into the energy system by storing renewable energy as hydrogen or its derivatives. This allows for the exploitation of excess renewable energy.
International Hydrogen Trade
Cross-Border Hydrogen Infrastructure: To enable global hydrogen trade, investments are being made to build cross-border infrastructure. Nations endowed with copious amounts of renewable energy resources are making significant investments in the construction of green hydrogen production plants and related transportation infrastructure. The objective of these investments is to establish a hydrogen supply chain that links locations with strong demand but limited domestic production capabilities with hydrogen production centers.
Hydrogen Export Projects: The development of large-scale hydrogen export projects is the focus of investments. Nations that possess abundant renewable energy resources and are in close proximity to prospective buyers of hydrogen are investigating the possibility of establishing export-oriented hydrogen production facilities. In order to support the development of a global hydrogen economy, these projects entail the production, liquefaction, and transportation of hydrogen to foreign markets.
The financial commitments made by different stakeholders, such as governments, private enterprises, and investors, to support and advance the growth of the hydrogen sector are referred to as hydrogen industry investments. These expenditures are going to be used for things like R&D, building infrastructure, setting up production facilities, and implementing hydrogen technology. The objective is to support the development of a sustainable hydrogen industry that can aid in the pursuit of clean energy, decarbonization initiatives, and the shift to a low-carbon economy.
How do these investments benefit market participants? Which countries and players have taken the lead in government and direct private sector investments?
Investments in the hydrogen ecosystem benefit market participants in several ways, including the following:
Market Growth and Expansion: The infrastructural and technological advancements related to hydrogen fuel support the market's expansion. Market players have greater opportunity to enter new markets, develop cutting-edge solutions, and gain market share as more funds are devoted to research, development, and deployment.
Technological Advancements: Technological developments in hydrogen technologies include reduced fuel cell costs, enhanced electrolysis efficiency, and advances in hydrogen storage and delivery. Market players gain from these developments since they improve the efficiency, dependability, and affordability of hydrogen solutions.
Cost Reduction: Across the hydrogen value chain, investments lead to cost savings through economies of scale and innovation. Hydrogen solutions are more cost-competitive than traditional energy sources, which increases market demand and adoption. Cost reductions can boost market competitiveness and profitability for participants in the market.
Job Creation and Economic Growth: The expansion of the hydrogen industry through investments generates employment possibilities in a number of value chain categories, such as manufacturing, R&D, infrastructure implementation, and service delivery. These employment options promote employment and revenue development while also supporting regional and national economic progress.
Regarding government and private sector investments, the lead has been taken by several countries and companies:
Government Investments:
Germany: Government investments in the hydrogen industry have been led by Germany. In order to encourage research, development, and demonstration initiatives, they have committed significant resources and developed the National Hydrogen Strategy. Germany has committed billions of euros to investments in hydrogen technology with the goal of leading the world in this field.
Japan: With its Basic Hydrogen Strategy, Japan has made significant investments in the hydrogen industry. The nation is concentrating on creating a society that uses, stores, transports, and produces hydrogen. Japan has allocated public funds to assist the development of hydrogen infrastructure, as well as research and experimental initiatives.
European Union: As part of its Green Deal and European Hydrogen Strategy, the European Union (EU) has set high goals for the deployment of hydrogen. The European Union intends to make significant investments through public-private partnerships in hydrogen technologies, infrastructure, and projects. The European Commission has allotted billions of dollars to member state efforts pertaining to hydrogen.
Private Sector Investments:
Energy Companies: Significant investments have been made in the hydrogen industry by well-known energy firms like BP, TotalEnergies, and Shell. Their portfolios are becoming more diverse, and they are making investments in infrastructure, apps, and hydrogen generation. By using their resources and experience, these businesses are propelling the growth of the hydrogen industry.
Automotive Manufacturers: Several automakers have made significant investments in hydrogen fuel cell infrastructure and technology, including Toyota, Hyundai, and BMW. To assist with the commercialization of fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), these firms are developing FCEVs and making investments in infrastructure for hydrogen refueling.
Industrial Players: To decarbonize their processes, major industrial players in industries including steel, chemicals, and refining are investing in hydrogen-related projects. Businesses like Siemens Energy, Air Liquide, and Thyssenkrupp are developing low-carbon hydrogen supply chains by working with partners, investing in hydrogen technology, and testing hydrogen-based industrial processes.
These instances show the initiative and financial commitments made by public and private sector participants to propel the expansion of the hydrogen ecosystem. The development and commercialization of hydrogen technologies and infrastructure are being actively shaped by market participants who are combining government backing, legislative frameworks, and private sector innovation.
Read More - https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/industry-practice/hydrogen/hydrogen-industry-investments
#HydrogenInvestments#CleanEnergyInvesting#HydrogenEconomy#RenewableInvestments#GreenTechFunding#SustainableInvestments#HydrogenFuture#ClimateFinance#InvestInHydrogen
0 notes
Text
"#ClimateActionNews 🌍💸 Governments, corporations, and NGOs unite for a game-changing initiative! 🤝📈 Introducing 'Collective Quantifiable Goal Climate Finance' - a groundbreaking commitment to pool resources and drive sustainable projects worldwide. 🌱🌞 Let's make a real impact together! Learn more about this innovative initiative: https://blog.geohoney.com/collective-quantifiable-goal-climate-finance
#ClimateFinance#GlobalGoals#SustainabilityMatters#geohoney#climatechange#climate crisis#climate and environment#climate action
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
🌍💸 Navigating the Green Wallets: How Climate Change Reshapes Public Finance 💸🌿
Hey Tumblr community! Let's talk about the unspoken connection between climate change and public finance. 🤔💨
🔍 The Silent Tax: Climate Change Costs: Did you know that climate change isn't just an environmental challenge but also a financial one? Extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and ecological shifts come with a hefty price tag. It's like the planet is sending us an invoice for neglecting its health.
💼 Governments on the Hot Seat: Public finances are feeling the heat as governments worldwide grapple with the economic aftermath of climate-related disasters. From rebuilding infrastructure to supporting affected communities, it's reshaping budget priorities.
🔄 Adaptation vs. Mitigation Investments: Public funds are now divided between adapting to the changes that are already happening and investing in actions to mitigate future climate impacts. It's a balancing act that policymakers are navigating to secure a sustainable future.
🌱 Green Bonds and Sustainable Financing: Enter the scene of green bonds – a financial tool designed to support environmentally friendly projects. Governments and institutions are turning to sustainable financing as a way to combat climate change while maintaining fiscal responsibility.
🤝 Global Collaboration: A Must! Climate change knows no borders, and neither should our solutions. International cooperation is essential to pool resources, share knowledge, and collectively address the financial challenges posed by a changing climate.
🔊 Your Voice Matters: Climate change impacts all of us, and so does public finance. It's time to stay informed, engage in conversations, and hold leaders accountable for sustainable financial decisions. Our wallets have the power to shape a greener future! 💚🌎
What are your thoughts on the intersection of climate change and public finance? Share your insights and let's keep this crucial conversation alive! 🌐🗣️
0 notes
Text
Rich Countries Break Climate Promise, Leaving Poor Nations Struggling #climatefinance #globalwarmingimpacts
0 notes
Text
जी-20 शिखर सम्मेलन में जीवाश्म ईंधन सब्सिडी के मुद्दे पर विचार-विमर्श है ज़रूरी, पब्लिक फंड किया आवंटित
#पब्लिक फंड किया आवंटित#FossilFuelSubsidiesDebate#G20SummitDiscussion#PublicFundsAllocation#GlobalEnergyPolicy#ClimateChangeAction#CleanEnergyTransition#RenewableEnergyFuture#SustainableDevelopmentGoals#ClimateFinance#ZeroEmissionsTargets
0 notes
Text
Carbon Dioxide Market Evolution: From Emissions Regulation to Renewable Energy Integration
The global carbon dioxide market size is expected to reach USD 15.46 billion by 2030, expanding at 5.0% CAGR from 2024 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. The growth is majorly driven by the increasing usage of CO2 for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) in oil & gas plants.carbon dioxide (CO2) is considered to be among the major and most extensively utilized medical gases. Furthermore, in the medical industry, CO2 is used in respiratory and cryotherapy stimulation during the process and post-anesthesia application. In cryotherapy, CO2 in frozen form (–78.5 °C) is used for killing body cells via a crystallization process. This gas can also be used in several processes to remove moles, skin tags, and warts.

Carbon Dioxide Market Report Highlights
Ethyl alcohol dominated the source type by accounting for a revenue share of 33.0% in 2023. It is projected to grow at the highest growth rate of 5.2% from 2024 to 2030 owing to its reliability as an easily available long-term source and high commercial value in producing CO2 as a by-product
Further, growth in demand for food-grade carbon dioxide in the forecast period will boost the growth of the production of carbon dioxide from ethyl alcohol
The food and beverages application segment of the market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 5.7% from 2024 to 2030, by revenue, thanks to rising demand for carbonated drinks globally
North America accounted for the largest revenue share of 42.0% of the CO2 industry in 2023. It is expected to continue its dominance over the forecast period. This can be attributed to increasing R&D, expansion of the industrial sector & growth of enhanced oil recovery processes
For More Details or Sample Copy please visit link @: Carbon Dioxide Market Report
CO2 also finds application in modern medicine to minimize invasive surgeries. In medicinal baths, it induces warm sensations and acts as a vasodilator for the skin by stimulating its heat receptors. In addition, insufflation with CO2 makes it easier to perform endoscopic procedures.
CO2 can be produced and recovered through various sources such as ethyl alcohol, hydrogen, ethylene oxide, substitute natural gas, and various other sources. Further, current research & development to capture carbon emissions has gained momentum. New research and development do not only aim to capture the CO2 in the form of carbon emissions but to refine and reuse it for some applications.
The carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology is capable of delivering considerable emission reductions from the utilization of fossil fuels. It is capable of lowering emissions from a wide range of industries such as power generation, steel, iron, refining, petrochemicals, and cement manufacturing. CCS technologies include capture, transport, and storage. Capture technology includes post-combustion, pre-combustion, oxy-firing, and industrial separation.
The key players in this industry are Air Products and Chemicals Inc.; Messer SE & Co. KGaA; Air Liquide; Linde Plc to maintain the market, share. Large firms frequently engage in mergers and acquisitions as well as new product launches. For instance, In September 2022, Covestro and SOL Kohlensäure GmbH & Co. KG signed a memorandum of understanding for collaboration in regards to the supply of biogenic CO2, effective from September 2022.
#CarbonDioxideMarket#CarbonDioxide#CO2#CarbonTrading#CarbonOffsets#CarbonCapture#EmissionsReduction#GreenEconomy#CarbonMarket#Decarbonization#ClimateFinance#LowCarbonFuture#EmissionsTradingSystem#CarbonFinance
0 notes