#Chinese Language
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
even more chinese folklore analysis of jcvtu because i am SO insane about this show:
the title of ep08, fifteen finger discount!

usually, the phrase “five finger discount” is used to refer to stealing things. so why fifteen finger discount?
fifteen fingers, three hands. in chinese folklore, the thief with three hands refers to a thief who was so skilful at stealing unnoticed that he was often said to have three hands. so this is basically a spin on the english phrase using chinese mythology and it is Very Cool. hands
tldr the title is a reference to chinese folklore of thieves with the english phrase and my language enthusiast ass went batshit insane the moment i noticed the reference
#i am SO insane about this show i keep seeing chinese culture references left and right#this is like chinese autism heaven#jentry chau vs the underworld#jcvtu#jentry chau#chinese mythology#chinese language#the alchemist rambles
334 notes
·
View notes
Text
wuxia, xianxia, and cultivation differences meta
translations: wuxia 武俠, xianxia 仙俠, and cultivation 修真/修仙 (xīuzhēn/xīuxiān)
think i've seen posts on this eons ago, and i'm pretty sure there are tons of these online, but since this has been written up already let's just have another one.
wuxia 武俠
wuxia and xianxia sound similar, but basically for wuxia it is about the pugilistic world (江湖 jiānghú). It is relatively more down-to-earth, and people practice martial arts ("kungfu") in their current life -- they do not do it to become xians (仙) and gods (神) however.
Like Thousand Autumns and Faraway Wanderers/Word of Honor, it has more historical background and ties to the current court and kingdoms, because people are living in the moment and concern themselves with worldly issues.
Martial arts may seem unrealistic, but in view of chinese fantasy it would be considered "real". It consists of fighting moves and internal energy, which they call qi or nèigōng (內功), and at times you see people flying around, climbing hills and jumping across rooftops which is qīnggōng (輕功).
xianxia 仙俠
A level up would be xianxia, where characters in the story cultivate to become xians (and gods, like in the heaven official's blessing). They don't really care about earthly issues here now, because their ambitions lie beyond the current world, and cultivation, getting stronger, and an immortal life are majorly all their goals.
You may not always see them working towards that purpose, such as in mdzs they are considered a lower-xianxia society (低魔), meaning people don't go through all the steps of cultivation and only stay at the stage before the "golden core" stage.
In xianxia, characters still learn basic fighting moves aka. martial arts, but to direct the internal energy they use línglì (灵力), zhēnqì (真气), and fǎlì (法力), all xianxia terms you commonly see. "neigong" is practically nonexistent in this genre. That's why people building up their "neigong" instead of "lingli" are likely never going to be able to cultivate.
cultivation 修真/修仙
A subgenre in the xianxia category would be cultivation. Characters actively go through the stages of cultivation, and likely for the MC, because they are the main character, they successfully become a xian and exit the world at the end of the novel.
There are many stages of cultivation, usually defined at the beginning of the novel in the synopsis, and a typical example of the different levels would be this:
��气,筑基,金丹,元婴,化神,炼虚,合体,大乘,渡劫
And with a cursory search, an English translation would be something like this, albeit not with all the cultivation ranks identified.
Qi condensation (练气), Foundation establishment (筑基), Core Formation (金丹), Nascent Soul (元婴), and the names after that vary too greatly with translation and fandom so I'll jump straight to Immortal Ascension
extra info: getting into the philosophy of it all
It'd be interesting to note that the word "xiá" (俠) permeates all these genres. This is something akin to the concept of "hero", but not at all also, and I'd love to speak more on this but this post has already gone way longer than I hoped it would be, so perhaps another day.
Regardless, it is interesting to note that wuxia has a greater emphasis on "xia" than xianxia. (some joke that cultivation doesn't have the word "xia" in it, and much of that is because characters have foregone heroism and focused on gaining powers and working towards ascension instead). As a result, wuxia is more confucianism-oriented, though not without its taoism and buddhism influences.
xianxia, on the other hand, is mainly derived from "dào" (道), from taoism, which is another lengthy concept if I ever get to it.
And some may have heard of the "farming" genre, 种田 (zhòngtián). This has to do with golden fingers (mary sues) in imperialistic china, earning a wealth of money, and all that. It has nothing to do with cultivation, alike they sound in english.
that's it for now, hmu if you wish to ask/discuss!
(and apologies for the pinyin translations, hope it's understandable still! formally writing pinyin they are supposed to be two separate words not one.)
#danmei#mdzs#word of honor#cdrama#thousand autumns#cnovel#wuxia#xianxia#cultivation novel#chinese language#chinese#fate's meta
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hanfu in Components: Structure Conventions (pt2)
navigation: hanfu in components 1 2 3.1 3.2 4 5 ...
Thanks for the love on the last post, I’ve been motivated to continue writing LOL Anyway: Construction/sewing pattern/structure is very important to hanfu!
There are a few important structure conventions when it comes to hanfu—almost all traditional-cut hanfu follow these rules; you could call them the defining characteristics of hanfu. There are exceptions to every rule of course (I will go over some caveats at the end of this post), but generally if a hanfu design ignores these rules we might consider it to be ‘incorrect.'
(There will be a longer follow-up pt. 3 post to this explaining the anatomy of a hanfu top/robe, where there will be more detailed in-context illustrations and descriptions. I just figured I should list these ‘rules’ somewhere separately.)
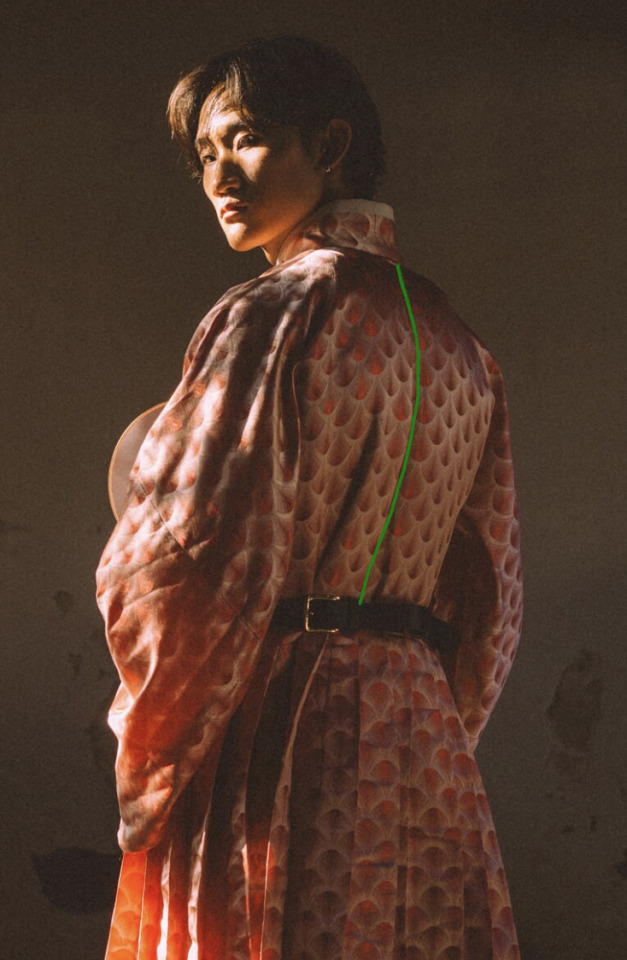
中縫/中缝/zhong1 feng4/Center Seam


Take a look at your shirts. Is there a shoulder seam between the front of the shirt and the back of the shirt? Western clothing tends to consist of a front piece + back piece sewn together to create a space for your body to sit in:

Hanfu doesn’t work like that. Traditionally, the garment isn’t separated into a front piece and back piece: it’s separated into a right piece and left piece, which are joined together at the vertical center seam. Why? Traditional fabric has a narrower width than the standard ~145cm that we have today, so a long, narrow piece is less wasteful to cut out from a bolt of silk than a wide one.

Therefore there is always a center seam, one running vertically down the front and one down the back. 中 = center, 縫 = seam, so 中縫 means center seam. There’ll be a front center seam (前中縫) and a back center seam (後中縫).


不破肩/不破肩/bu2 po4 jian1/No Broken Shoulder
Kind of an addendum onto the previous point? Additionally since the body pieces are separated into left/right rather front/back, there’s no seam at the top of the shoulder here. The fabric is simply draped over the arm/shoulder to hang down, covering the torso on both sides.*


*Caveat: Some modified hanfu that vendors sell today will have a shoulder seam, especially thicker winter garments or short-sleeved garments. This is a design choice made to prevent the fabric from looking too stiff, known as 破肩/破肩/po4 jian1,literally “broken shoulder.” It can look great, lots of hanfu makers do it! But just to be clear, that is a MODIFICATION.
接袖/接袖/jie1 xiu4/Sleeve Connection


Western clothing patterns tend to have something where the fabric of the sleeve gets connected to the fabric of the garment’s body at the shoulder/armpit, often with a concave arm hole shape to help with the contours of the garment when it’s worn.

Hanfu sleeves, on the other hand, are never connected at the armpit—they are connected halfway down the arm. In other words, the piece of fabric that forms the body extends to also cover the upper arm part of the sleeve. The actual sleeve piece is connected to the body at the bicep/elbow area via a flat seam. (In the case of half- or no- sleeve garments there might just not be a separate sleeve piece.)


右衽/右衽/you4 ren4/"Right Over Left" Rule
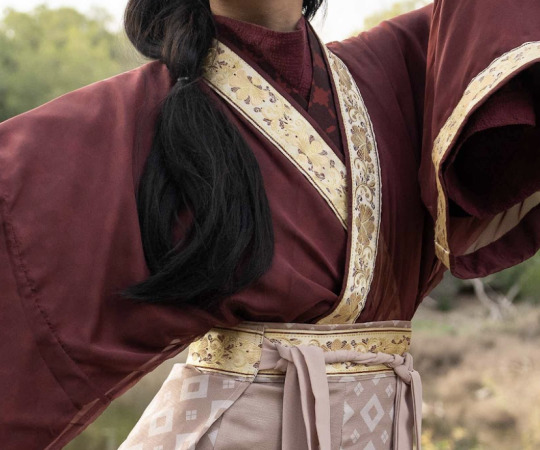


Applies to cross-collar, some varieties of round collar, and some varieties of standing collar tops. In the case that the front of the garment crosses over itself, the flap coming from the wearer’s left goes OVER the flap coming from the wearer’s right. Easiest way to make sense of this is, if you’re looking at someone wearing a cross-collar hanfu top, the cross will look like a lowercase y.
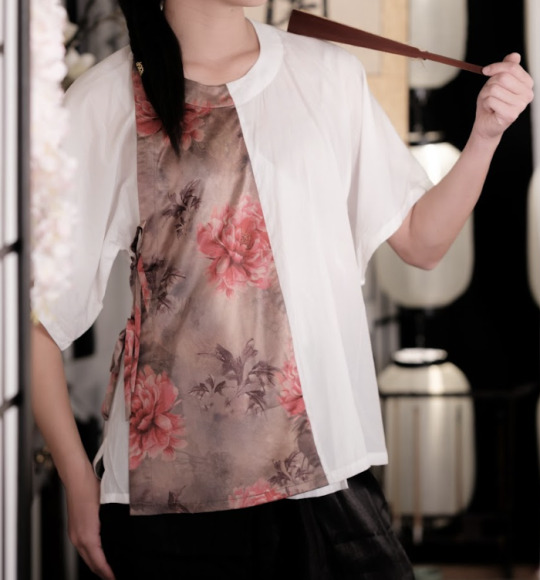


Caveats
NO RULE EXISTS WITHOUT EXCEPTION!!! These rules exist because a majority of hanfu follow them and they are a standard that people agree on right now. However, there are ALWAYS cases—historically or otherwise—where these rules may be broken. For example, there are several Ming Dynasty cross collar robes that happen to be left over right, and the location of the sleeve seam can differ based on what garment you're looking at.
Also, many modern hanfu manufacturers will deliberately choose to break these 'rules' in favor of aesthetics. This is a purposeful design choice—not one that's done out of ignorance or disrespect. It's easy for common modifications to get mistaken for 'historically accurate.' To be clear, it is 100% okay and super common for modifications to exist! Just don't go around claiming that it was historically that way.
My advice is that if you're starting out with hanfu, try to stick to these rules in the back of your head as closely as possible. Once you've built your foundational knowledge, then you can start exploring the exceptions to the rules. These rules may not be foolproof, but they are a useful tool to help you understand the commonalities and trends within hanfu without overwhelming you.
Last note: it is generally more of a taboo for seams that should exist to not exist in a piece of clothing (i.e. no center back seam) than for extra seams to exist. If you go look in museums for the artifacts that hanfu is based off of, you'll notice that a lot of them—especially the ones from earlier dynasties—are a chaotic patchwork of a bunch of random piece of fabric sewn together to create the garment. Fabric is expensive, people don't want to waste it! So it's not all that weird to have seams in random places.
Happy 除夕 everyone! 有蛇有得 :>
navigation: hanfu in components 1 2 3.1 3.2 4 5 ...
#hanfu#hanyuansu#terminology#once again idk how to tag#avoiding my homework#hanfu fashion#chinese fashion#chinese history#chinese language#im all alone on new years eve ;-;#my due dates are keeping me company its ok#shitty drawings by tangtang#chinese hanfu#fashion#hanfu photoshoot#hanfu art#cloud9hanfu#cloud9 hanfu#九雲閣#hanfu in components
279 notes
·
View notes
Text
Some Chinese fashion styles
Disclaimer: The following styles and their definitions were observed by me and are not authoritative. I am only familiar with Hanfu and if I made mistakes and picked the wrong photo examples or fraud shops, please let me know. Also, this post focused on women's fashion because 1. I am not into men's fashion so I don't know much about them. 2. The algorithm also knew that so I don't really see them.
汉服/Hànfú
传统服饰/Chuántǒng fúshì (传服/chuán fú)
清汉女/Qīng hàn nǚ
旗装/Qí zhuāng
旗袍/Qípáo
新国风/Xīn guó fēng、新中式/Xīn zhōngshì 汉元素/hàn yuánsù 茶艺服/Cháyì fú or 茶服/chá fú 唐装/Tángzhuāng 中山装/Zhōngshānzhuāng.
汉服/Hànfú

The ethnic clothing of Han Chinese (not the Han Dynasty).
There was a prohibition of Han clothing and hair styles in Qing dynasty, i.e. the 剃发易服/Tìfā yìfú qu Queue Ordinance, so modern hanfu is an on-going revivalist moment.
Modern hanfu are based on archeological evidences with minor twists to suit modern like, such as the type of fabric used and cut.
As a result, there are many types of garments and sub-styles. The figure above shows some examples.
While which style should be included and promoted is a constant debate, but in general, the cutout line is the Qing dynasty (however small accessories such as purses are alright).
传统服饰/Chuántǒng fúshì (传服/chuán fú)
No example because I am not sure who identified with this label.
The Chinese traditional clothing.
This either referred to historical clothing restorers (regardless of ethnicity) or people who promoted that the traditional clothing of Han people should be in the late Ming dynasty style, since "people should get up at where they had fallen".
They might be agreeable with the hanfu movement or not.
清汉女/Qīng hàn nǚ

The clothing of women of Han Chinese in the Qing dynasty.
Since the Queue Ordinance wasn't that strictly enforced on Han women, the Han women clothing in the Qing dynasty had quickly absorbed Manchurian's elements while retaining the characteristic two-piece silhouette. (Manchurian women wore a one-piece robe.)
I believed it appeared around 2019 when the styles of hanfu had moved to fully embroidered surface to a more tone down brocade or weaved patterns.
旗装/Qí zhuāng

The ethnic clothing of Man people (Manchurian).
The women's clothing are generally in round collar opened on the left (youren) with straight sleeves.
The most basic item is a 衬衣/chènyī, which doesn't have vents.
However, the most common item I have seen on the street is a 氅衣/chǎng yī (probably rented), which should be worn on top of 衬衣, since they have side vents.
They usually have no standing-up collar but in some cases a fake collar could be worn.
On top of changyi they could wear a 马褂/mǎguà、坎肩/kǎnjiān、褂裥/guà jiǎn.
旗袍/Qípáo

The Chinese clothing of women originated from the Minguo era, known in English as qipao or cheongsam.
The male equivalent is 长衫/chángshān.
Currently in style is the retro-cut, while uses the traditional flat cut (no shoulder seam) instead of the more body-hugging modern draping style.
There are also many variations and cuts, but the overall silhouette is similar.
新国风/Xīn guó fēng、新中式/xīn zhōngshì

Innovative clothing that was inspired by Chinese traditional aesthetic.
It is an umbrella term.
汉元素/hàn yuánsù refers to clothing inspired by hanfu specifically, while xinguofeng could be inspired by qipao and other ethnic clothing. In addition, hanyuansu is a term more familair to hanfu-ers, so the target audience is slightly different between hanyuansu and xinguofeng.

茶艺服/Cháyì fú or 茶服/chá fú,i.e tea dress, which aimed to convey a zen and rustic aesthetic could also be considered a sub-style. They are often worn by retirees, artists or workers in tea shops, calligraphy shops, Chinese spas, Chinese traditional medicine clinics etc.

The older "Chinese style" generally refers to 唐装/Tángzhuāng and 中山装/Zhōngshānzhuāng.
Tangzhuang (Tang Suit) was a men suit characterized with a mandarin collar with a row of 盘扣/pán kòu frogs in the middle. There are two pockets at the bottom front of the suit. It was a well-known looked worldwide due to the 2001 APEC summit. However, other clothes resembled a 马褂/mǎguà could also be called a tangzhuang.
Zhongshanzhuang was designed and named after Sun Yat-sen but was often known in English as the Mao Suit. Mao Suit was characterised with a 关门领/Guānmén lǐng(“closed-door collar", but also known as Mao collar in English) with a row of round buttons. There are four pockets at the front of the suit.

中华lolita/Zhōnghuá lolita

A sub-style of the lolita fashion inspired by cheongsam/qipao, hanfu or other Chinese artistic elements.
The same item could appeared in different styles, but with different cut and accessories. The following examples showed a mamianqun used in different styles.

THE END
#chinese fashion#hanfu#qinghannv#qipao#qizhuang#chinese language#non-hanfu#lolita fashion#terminology#i rarely seen men in alternate fashion#like i saw maybe one in the last year#they spent money elsewhere#like shoes#long post#reference#fouryearsofshades#i spent so much time on this post#hope you will like it#feel free to correct me if i am not right
655 notes
·
View notes
Text

These are the apps and links I currently have on my phone to study Chinese:
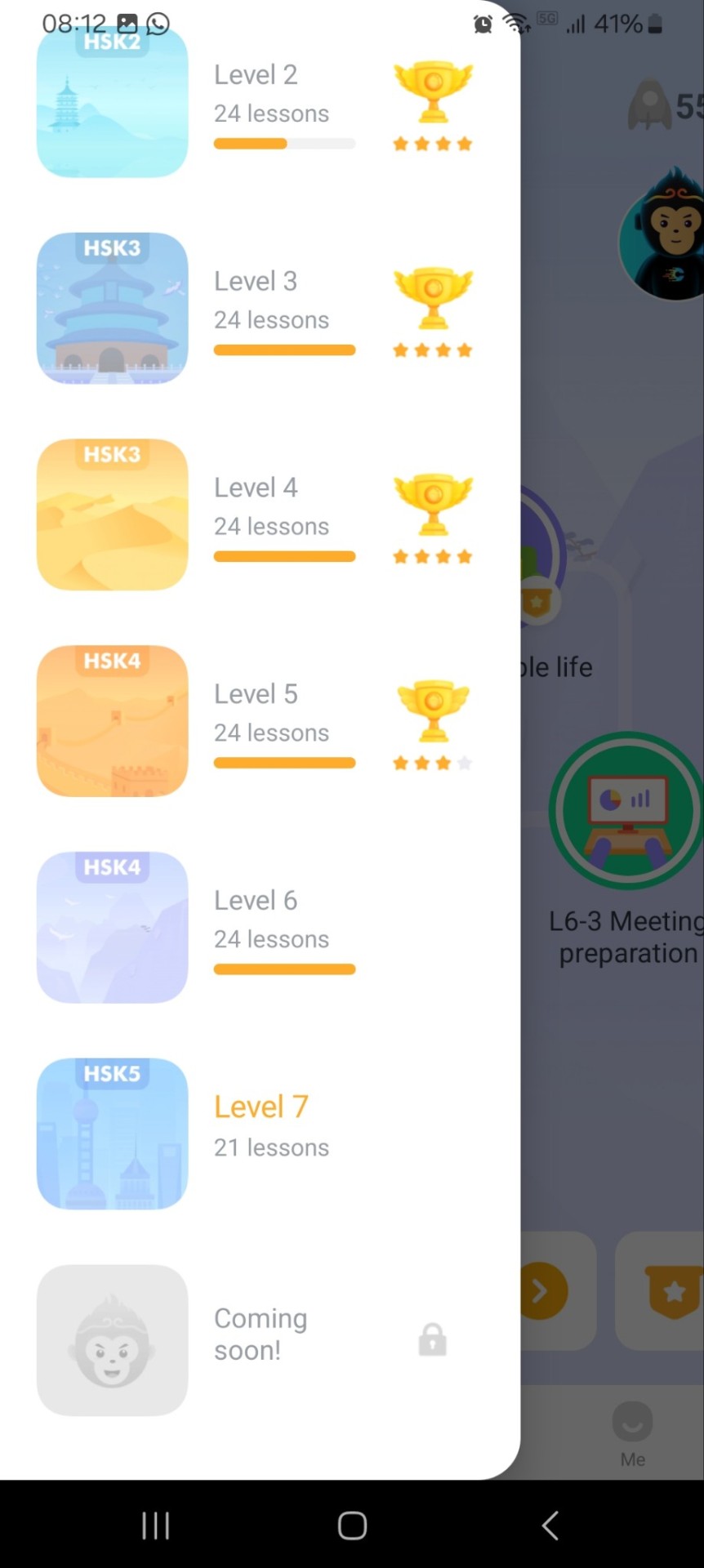
SuperChinese: my main study resource. There are currently 7 levels, level 7 (still incomplete, they are still slowly adding lessons to it) being HSK 5 stuff. Each lesson has vocabulary, grammar and a short dialogue where those are used in context (I love context). It has a few free lessons in the lower levels but after that you have to buy a subscription. There are many sales though. When I was a beginner I used HelloChinese instead, which has more free content, and switched to SuperChinese when I finished all the free content there. It also has social network features and chat rooms I don't use.



TofuLearn is like a flashcard app with many pre-made decks (you can also create your own on their website and import decks from Anki) and the option to practice writing hanzi. Anki didn't work for me, but I find Tofu very helpful. Practicing writing helps me with character recognition, and it also helps me remember the tones thanks to the audio in the pre-made HSK decks.
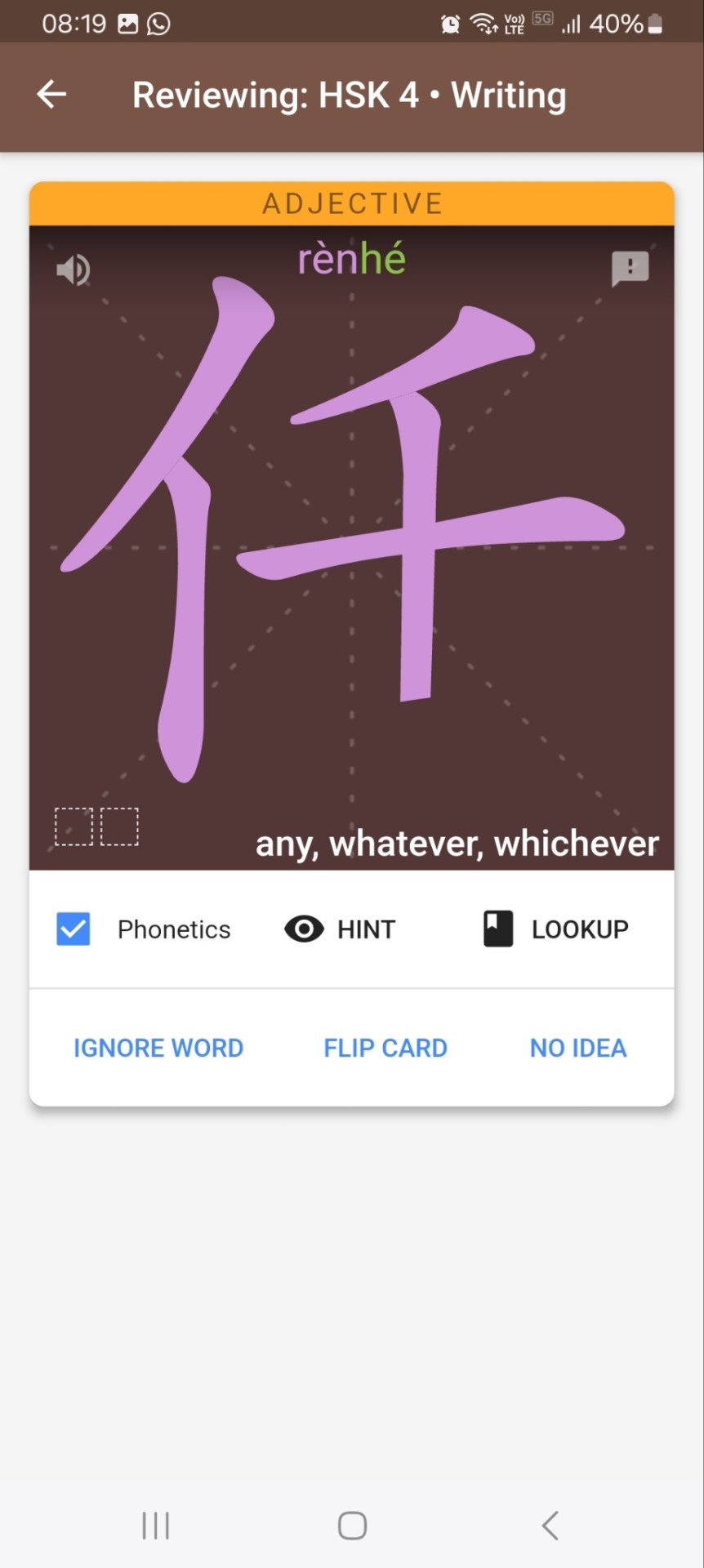
Dot is a reading app with new texts being added every day. It used to be completely free, which actually seemed too good to be true, and then they put practically everything behind a paywall and very strict limits for free users. After a couple of months they made it a little less restricted though - we still can't choose the articles but we can read as many as we want as long as we do the vocabulary exercises after each article (plus, during the Spring Festival, they made all articles available for free for 3 days and we could save the ones we were interested in to read later). It follows the new, not-yet-implemented (and harder) HSK levels, so you should start one or two levels below yours and if the texts are too easy move up.


Google Translator: not the best but helpful when I need to translate whole sentences, plus I can point my camera or open an image and it translates writing.
Pleco: best Chinese to English dictionary.
Stroke Order: not an app but a website, does what it says in the tin: shows stroke order for a specific character.
YouGlish: also a website, you can put a word or phrase and it shows videos where people say that word/phrase. Very cool.
Todaii is a graded news app that has only two levels: easy and hard. I'm around level HSK4 and the "easy" level is quite hard though (but I admit reading is my nemesis).
I also use YouTube and Spotify a lot.
#personal#resources#langblr#language learning#learning chinese#chinese langblr#chinese language#mandarin#中文
537 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's funny learning both japanese and chinese because in chinese when chinese learners complain about difficult words they are those that have simple strokes, about 3 or less pinyin pronunciations but have 58 different meanings and need specific usages where as in japanese, the difficult kanjis have 40 strokes like they've clawed all the way to earth from hell and have 80 different pronunciation but the meaning is pretty much the same across the words. So when I see chinese learners complain about a difficult word it's "guys, I think we should've left this word to die in classical chinese" but when japanese learners complain about a difficult word my response is either "that's just 8 radicals on top of each other. that's not hard" or "who angered a kami of kunyomi dominion, my god."
#studyblr#langblr#japanese language#chinese language#chinese langblr#japanese studyblr#chinese studyblr#don't mind the korean learners they're crying in the corner#because there's no way to differentiate hanja based advanced words that sound the same#you might think well it can't be bad but they're actively dying from the mountain of vocabs they're supposed to know#because “you can read all of them so you should know all of them” jfc
306 notes
·
View notes
Text
how i'm studying mandarin (in 2024)
as a low-maintenance language learner working a 9-6 office job, i've been muddling around how to improve my mandarin in my free time and keep it fun! And I've found what works for me (thanks to a lot of lurking on here - appreciate all you mandarin langblrs <3), so wanted to share :)
Evening lessons (or italki) - Self studying is great but I do need a kick up the ass sometimes, so these really help. Plus my teacher is great at giving tips here and there which I probably wouldn't pick up on on my own.
ChinesePod - Their podcasts are really well made and accessible, I can't recommend them enough!
HelloChinese - This is my 'I'm bored waiting for my train/bus but I still want to learn Chinese' option that isn't Duolingo. It's not perfect but it has fairly good grammar explanations and native listening segments. You do have to pay a subscription if you're over HSK1 level FYI.
I am an anki hater first and foremost, so here's the vocab learning / dictionary tools I use instead:
TofuLearn - It's straightforward, uses spaced repetition learning AND teaches you stroke order - so ticks all my boxes. Picked it up due to @marilearnsmandarin's posts about it!
Pleco - Obviously, everyone has it downloaded for a reason.
Yabla Chinese Dictionary - Not seen this one talked about so much, but would recommend! It sometimes has video examples of the hanzi in use, which I find helpful.
A big goal for me this year is to consume mandarin content more regularly! It's all well and good watching Peppa Pig, but I need something that I actively want to engage with:
Bilibili Comics - Currently reading 肉店楼上的工作室 and able to understand a fair chunk, so would recommend as a "easier" option.
Mandopop - Not sure how much I'm picking up from listening, especially at my level, but it's fun to jam out to some good tunes. Faves include TIA RAY, Song Qian, Lexie Liu, No Party for Cao Dong & Shi Shi.
Dramas/Movies - Modern chinese dramas are a lot more hit-or-miss for me, especially compared to historical/fantasy. Recent faves include Accidentally in Love & Stay with Me (on Netflix/Viki). Currently watching Reset :) Any other recs, please send my way!
YouTube - I have a separate YT account just to follow Taiwanese/Chinese creators - it takes a bit of searching but you can find some great youtubers who talk about whatever hobby you're into (whether that's cute golden retriever vlogs, travel vlogs or reading vlogs!)
548 notes
·
View notes
Text
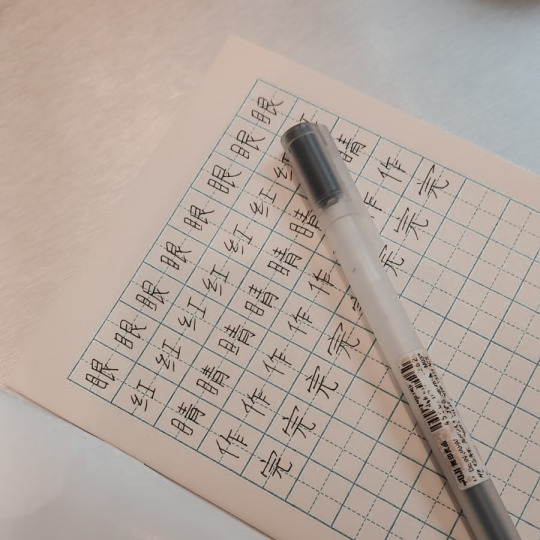



080724
yesterday i went to milan to see my friends, originally i had to go to see a studio flat but since i don’t even know if i will need it the the landlord has other people who are inter i cancelled the visit and just hang out with my friends.
during the train ride i studied a little chinese and did some research for job hunting in the field i’m interested, think i will do a notion page where i analyse job and the skills they require so i know what to focus on, i already noticed that i really need to invest in learning chinese since i found more than one job as a product designer that asked as an additional language chinese or german so i think after i return from holiday i will search for a chinese teacher, this way i will learn faster and really see if i’m making real progress. if any of u know a good website/app where to find a teacher please let me know!
now i’m waiting in a cafe for a friend and studying a little chinese.
#studyblr#studying#study motivation#student#studyspo#100 days of productivity#design student#studyspiration#notes#chinese#chinese langblr#chinese language
284 notes
·
View notes
Text
One thing that’s fun about learning a language - especially one as far from English in its roots as Mandarin - is seeing how humans have created the same metaphors over and over across space and time.
Like the word bitter. It’s a basic flavor category, it’s your tongue detecting alkaline foods. We have specific cells to detect it. It’s no surprise that many languages would have a word for that.
But there’s no reason a language has to also use that word metaphorically, to describe an emotional state that is unpleasant in a way that maybe vaguely resembles the way bitter foods can be unpleasant, or things that cause that emotion (a bitter defeat). It’s not shocking that multiple languages do, obviously - it makes sense to use something unpleasant as a metaphor for something else unpleasant - but it would be very easy for a language not to. Heck, maybe some languages use a smell word like pungent or acrid to describe that emotion!
And yet in Mandarin, 苦 (kǔ) means bitter as in flavor - and there it is again, being used metaphorically to mean pain, hardship, and suffering, or to be enduring those things (and can also be used for causing those things, just like in English!).
I just think it’s neat. The human tendency to land on the same linguistic metaphors across cultures is neat.
#also it’s easy to ignore#and assume that of course all languages use the same metaphors as your language#so I think it’s worth drawing attention to#mandarin#english#linguistics#language#chinese#chinese language#psychology
159 notes
·
View notes
Text
April 14, Xi'an, China, Shaanxi History Museum, Qin and Han Dynasties Branch (Part 3 – Innovations and Philosophies):
(Edit: sorry this post came out so late, I got hit by the truck named life and had to get some rest, and this post in itself took some effort to research. But anyway it's finally up, please enjoy!)
A little background first, because this naming might lead to some confusions.....when you see location adjectives like "eastern", "western", "northern", "southern" added to the front of Zhou dynasty, Han dynasty, Song dynasty, and Jin/晋 dynasty, it just means the location of the capital city has changed. For example Han dynasty had its capital at Chang'an (Xi'an today) in the beginning, but after the very brief but not officially recognized "Xin dynasty" (9 - 23 AD; not officially recognized in traditional Chinese historiography, it's usually seen as a part of Han dynasty), Luoyang became the new capital. Because Chang'an is geographically to the west of Luoyang, the Han dynasty pre-Xin is called Western Han dynasty (202 BC - 8 AD), and the Han dynasty post-Xin is called Eastern Han dynasty (25 - 220 AD). As you can see here, in these cases this sort of adjective is simply used to indicate different time periods in the same dynasty.
Model of a dragonbone water lift/龙骨水车, Eastern Han dynasty. This is mainly used to push water up to higher elevations for the purpose of irrigation:
Model of a water-powered bellows/冶铁水排, Eastern Han dynasty. Just as the name implies, as flowing water pushes the water wheel around, the parts connected to the axle will pull and push on the bellows alternately, delivering more air to the furnace for the purpose of casting iron.
The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art/《九章算术》, Fangcheng/方程 chapter. It’s a compilation of the work of many scholars from 10 th century BC until 2 nd century AD, and while the earliest authors are unknown, it has been edited and supplemented by known scholars during Western Han dynasty (also when the final version of this book was compiled), then commented on by scholars during Three Kingdoms period (Kingdom of Wei) and Tang dynasty. The final version contains 246 example problems and solutions that focus on practical applications, for example measuring land, surveying land, construction, trading, and distributing taxes. This focus on practicality is because it has been used as a textbook to train civil servants. Note that during Han dynasty, fangcheng means the method of solving systems of linear equations; today, fangcheng simply means equation. For anyone who wants to know a little more about this book and math in ancient China, here’s an article about it. (link goes to pdf)

Diagram of a circle in a right triangle (called “勾股容圆” in Chinese), from the book Ceyuan Haijing/《测圆海镜》 by Yuan-era mathematician Li Ye/李冶 (his name was originally Li Zhi/李治) in 1248. Note that Pythagorean Theorem was known by the name Gougu Theorem/勾股定理 in ancient China, where gou/勾 and gu/股 mean the shorter and longer legs of the right triangle respectively, and the hypotenuse is named xian/弦 (unlike what the above linked article suggests, this naming has more to do with the ancient Chinese percussion instrument qing/磬, which is shaped similar to a right triangle). Gougu Theorem was recorded in the ancient Chinese mathematical work Zhoubi Suanjing/《周髀算经》, and the name Gougu Theorem is still used in China today.

Diagram of the proof for Gougu Theorem in Zhoubi Suanjing. The sentence on the left translates to "gou (shorter leg) squared and gu (longer leg) squared makes up xian (hypotenuse) squared", which is basically the equation a² + b² = c². Note that the character for "squared" here (mi/幂) means "power" today.

This is a diagram of Zhang Heng’s seismoscope, called houfeng didong yi/候风地动仪 (lit. “instrument that measures the winds and the movements of the earth”). It was invented during Eastern Han dynasty, but no artifact of houfeng didong yi has been discovered yet, this is presumably due to constant wars at the end of Eastern Han dynasty. All models and diagrams that exist right now are what historians and seismologists think it should look like based on descriptions from Eastern Han dynasty. This diagram is based on the most popular model by Wang Zhenduo that has an inverted column at the center, but this model has been widely criticized for its ability to actually detect earthquakes. A newer model that came out in 2005 with a swinging column pendulum in the center has shown the ability to detect earthquakes, but has yet to demonstrate ability to reliably detect the direction where the waves originate, and is also inconsistent with the descriptions recorded in ancient texts. What houfeng didong yi really looks like and how it really works remains a mystery.

Xin dynasty bronze calipers, the earliest sliding caliper found as of now (not the earliest caliper btw). This diagram is the line drawing of the actual artifact (right).


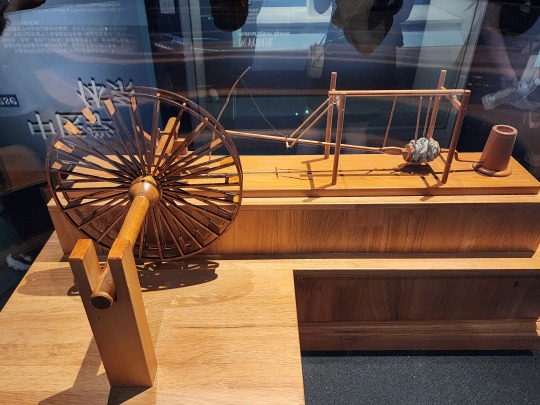
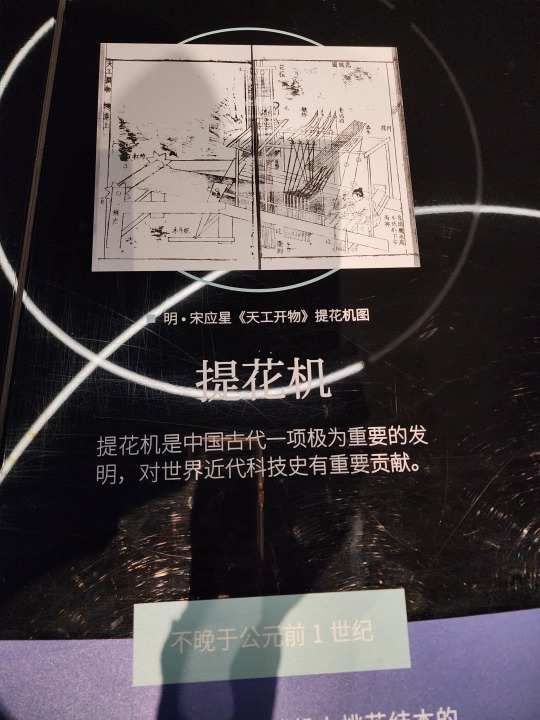
Ancient Chinese "Jacquard" loom (called 提花机 or simply 花机 in Chinese, lit. "raise pattern machine"), which first appeared no later than 1st century BC. The illustration here is from the Ming-era (1368 - 1644) encyclopedia Tiangong Kaiwu/《天工开物》. Basically it's a giant loom operated by two people, the person below is the weaver, and the person sitting atop is the one who controls which warp threads should be lifted at what time (all already determined at the designing stage before any weaving begins), which creates patterns woven into the fabric. Here is a video that briefly shows how this type of loom works (start from around 1:00). For Hanfu lovers, this is how zhuanghua/妆花 fabric used to be woven, and how traditional silk fabrics like yunjin/云锦 continue to be woven. Because it is so labor intensive, real jacquard silk brocade woven this way are extremely expensive, so the vast majority of zhuanghua hanfu on the market are made from machine woven synthetic materials.
Chinese purple is a synthetic pigment with the chemical formula BaCuSi2O6. There's also a Chinese blue pigment. If anyone is interested in the chemistry of these two compounds, here's a paper on the topic. (link goes to pdf)

A list of common colors used in Qin and Han dynasties and the pigments involved. White pigment comes from chalk, lead compounds, and powdered sea shells; green pigment comes from malachite mineral; blue pigment usually comes from azurite mineral; black comes from pine soot and graphite; red comes from cinnabar; ochre comes from hematite; and yellow comes from realgar and orpiment minerals.

Also here are names of different colors and shades during Han dynasty. It's worth noting that qing/青 can mean green (ex: 青草, "green grass"), blue (ex: 青天, "blue sky"), any shade between green and blue, or even black (ex: 青丝, "black hair") in ancient Chinese depending on the context. Today 青 can mean green, blue, and everything in between.

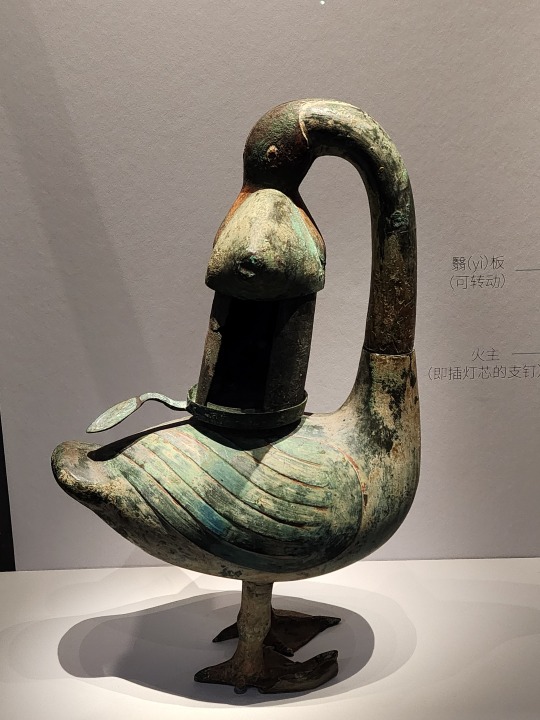
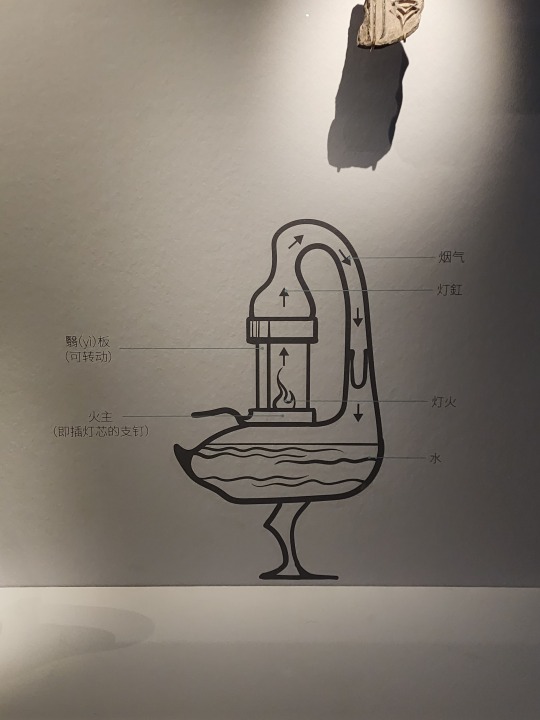
Western Han-era bronze lamp shaped like a goose holding a fish in its beak. This lamp is interesting as the whole thing is hollow, so the smoke from the fire in the lamp (the fish shaped part) will go up into the neck of the goose, then go down into the body of the goose where there's water to catch the smoke, this way the smoke will not be released to the surrounding environment. There are also other lamps from around the same time designed like this, for example the famous gilt bronze lamp that's shaped like a kneeling person holding a lamp.

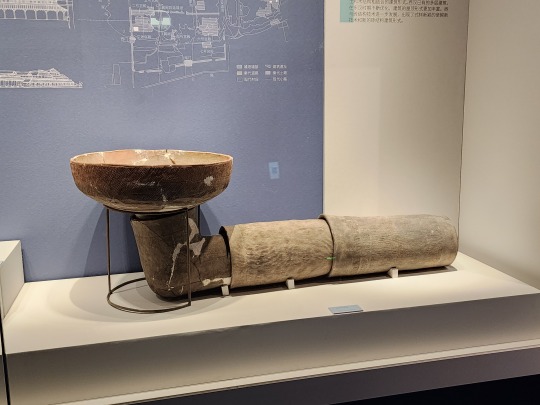
Part of a Qin-era (?) clay drainage pipe system:

A list of canals that was dug during Warring States period, Qin dynasty, and pre-Emperor Wu of Han Han dynasty (475 - 141 BC). Their purposes vary from transportation to irrigation. The name of the first canal on the list, Hong Gou/鸿沟, has already become a word in Chinese language, a metaphor for a clear separation that cannot be crossed (ex: 不可逾越的鸿沟, meaning "a gulf that cannot be crossed").
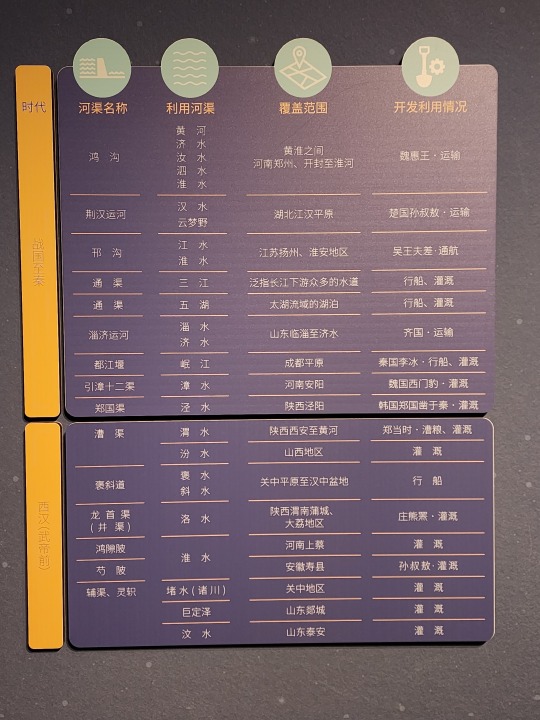
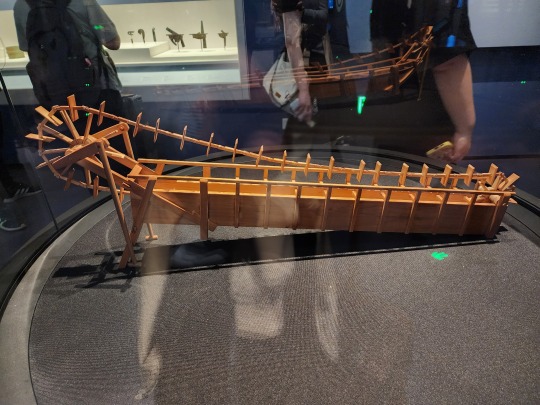
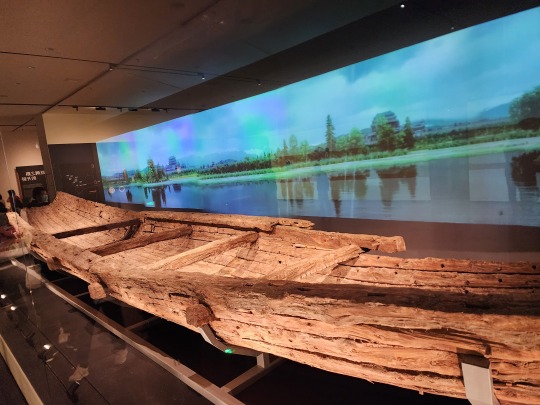
Han-era wooden boat. This boat is special in that its construction has clear inspirations from the ancient Romans, another indication of the amount of information exchange that took place along the Silk Road:

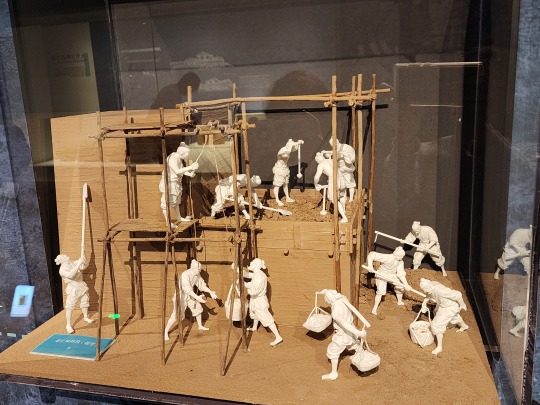
A model that shows how the Great Wall was constructed in Qin dynasty. Laborers would use bamboo to construct a scaffold (bamboo scaffolding is still used in construction today btw, though it's being gradually phased out) so people and materials (stone bricks and dirt) can get up onto the wall. Then the dirt in the middle of the wall would be compressed into rammed earth, called hangtu/夯土. A layer of stone bricks may be added to the outside of the hangtu wall to protect it from the elements. This was also the method of construction for many city walls in ancient China.

A list of the schools of thought that existed during Warring States period, their most influential figures, their scholars, and their most famous works. These include Confucianism (called Ru Jia/儒家 in Chinese; usually the suffix "家" at the end denotes a school of thought, not a religion; the suffix "教" is that one that denotes a religion), Daoism/道家, Legalism (Fa Jia/法家), Mohism/墨家, etc.
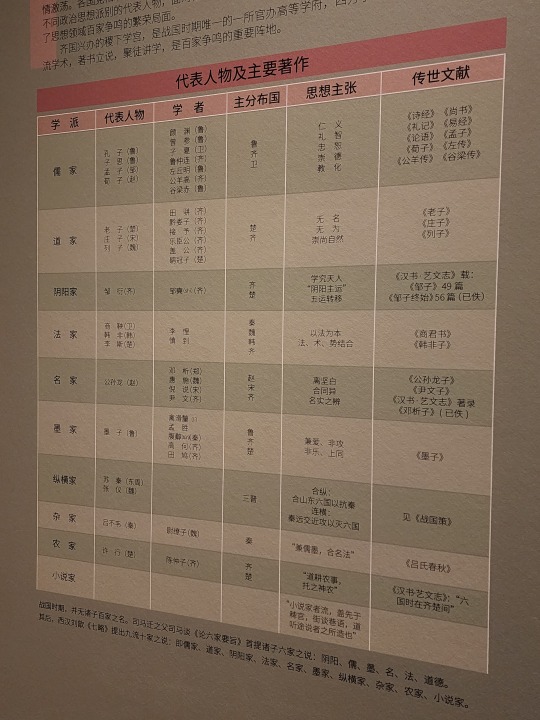
The "Five Classics" (五经) in the "Four Books and Five Classics" (四书五经) associated with the Confucian tradition, they are Shijing/《诗经》 (Classic of Poetry), Yijing/《易经》 (also known as I Ching), Shangshu/《尚书》 (Classic of History), Liji/《礼记》 (Book of Rites), and Chunqiu/《春秋》 (Spring and Autumn Annals). The "Four Books" (四书) are Daxue/《大学》 (Great Learning), Zhongyong/《中庸》 (Doctrine of the Mean), Lunyu/《论语》 (Analects), and Mengzi/《孟子》 (known as Mencius).

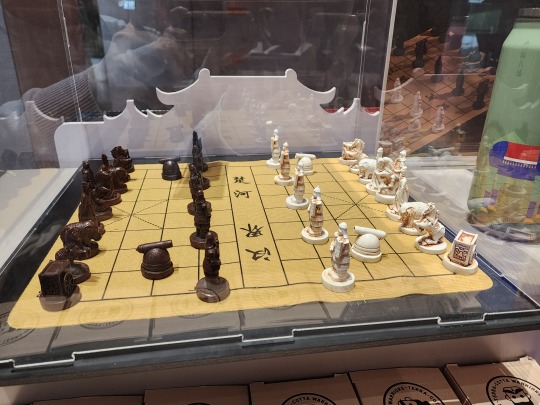
And finally the souvenir shop! Here's a Chinese chess (xiangqi/象棋) set where the pieces are fashioned like Western chess, in that they actually look like the things they are supposed to represent, compared to traditional Chinese chess pieces where each one is just a round wooden piece with the Chinese character for the piece on top:

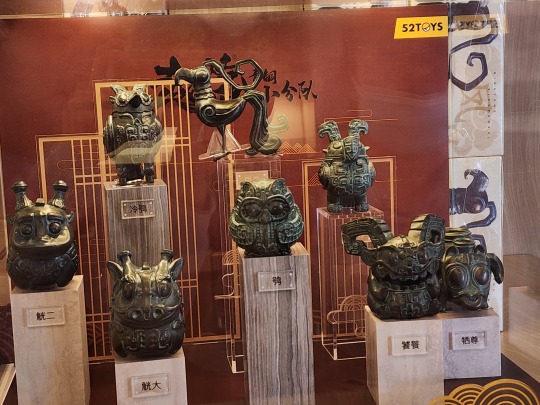
A blind box set of small figurines that are supposed to mimic Shang and Zhou era animal-shaped bronze vessels. Fun fact, in Shang dynasty people revered owls, and there was a female general named Fu Hao/妇好 who was buried with an owl-shaped bronze vessel, so that's why this set has three different owls (top left, top right, and middle). I got one of these owls (I love birds so yay!)


And that concludes the museums I visited while in Xi'an!
#2024 china#xi'an#china#shaanxi history museum qin and han dynasties branch#chinese history#chinese culture#chinese language#qin dynasty#han dynasty#warring states period#chinese philosophy#ancient technology#math history#history#culture#language
96 notes
·
View notes
Text

Sometimes it makes me wanna cry… or die
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
wuxia and confucianism
Hey. Thought I'd answer the wuxia-confucian question very briefly. I did suggest wuxia being closely knitted to confucianism, but I do understand the other perspective of wuxia being anti-confucian. Quick answer only because I've got little time right now -- might add on to it later!!

confucianism
First the central themes of confucianism:
常 (cháng): Virtues of compassion and courtesy. 仁 (rén)、义 (yì)、礼 (lǐ)、智 (zhì)、信 (xìn)、忠 (zhōng)、孝 (xiào)、悌 (tì) (there are more). These in order in crude translation mean compassion, righteousness, courtesy, wisdom, integrity, loyalty, filial piety, and respect to one's older siblings. These are the main ideas Confucius, the founder of Confucianism, wished to spread through his philosophy.
纲 (gāng): Order. This is about the relationships between people, the filial piety of a child to their parents, the relationship between significant others, between friends and teachers, and expanding outwards in the sphere of influence in our circle of life, the patriotism and loyalty of a liege to his lord.
Understand that Confucius came up with these ideas in a time of war. He lived his life traversing different kingdoms and establishing his prominence by getting emperors to trust him as a consultant and employ his school of ideas. As such, these beliefs are very much centred around creating harmony and order in society, and of course entails the respect of commoners and lieges to their lords (because why else would kings employ his beliefs over other schools of philosophy if not so?).
wuxia
Moving on to the wuxia genre, the 侠 (xiá) in wuxia emphasises righteousness. xia, as people, are itinerants and rebels in the fictitious pugilistic society who tire of the power of the aristocracy and seek to use their own, often unlawful ways, to help others through 锄强扶弱 (chú qiáng fú ruò) -- helping the needy and going against the strong (the morals are debatable but that's me trying to sum up wuxia in 5 minutes off the top of my head rip).

conclusions
So I guess that's enough information for you to form your own conclusions, and here's what I think, at the very least.
Against Confucianism -- Subverting the power pyramid. Many of the heroes/xia's in wuxia are lawless rebels. They aren't good, upstanding citizens of the society. Hell, xia was first popularised from 游侠列传 (yóu xiá liè zhuàn) in the Han dynasty records, talking about how a "xia" went against the officials and helped the commoners in the name of righteousness. This goes against the confucian beliefs of respecting your lord and serving the kingdom.* That's why I can understand why some would consider wuxia going against confucianism.
Align with Confucianism -- Righteousness. Ultimately, however, wuxia is about righteousness and nobility and honour, defined by society and commoners and not by royal blood. These values of etiquette, decorum, and nobility were long ingrained in the hearts of all these chinese characters, from when the courtesy and etiquette rules were defined in the Zhou dynasty, and afterwards, from the Han dynasty on, when emperors heavily employed Confucian beliefs in education and throughout society because it helps in rebuilding a harmonious society.
Confucianism is about compassion and righteousness, the staples permeating and defining chinese culture in the last two thousand years, and it is these values that serve as the central impetus of the xia and wuxia genres. People are born into these values; as such they fight against the injustice they see, and thus engenders the lost xia's of every dynasty.

*And well, even Confucius wasn't that dead set on fealty to lords. Confucian highly venerated loyalty, but when the court is corrupt, they acknowledge insurgence over the mindless following of an emperor. This is a story for another day, one I would have to back up with more quotes and citations, but I hope this answered your questions, or even better, let you form some conclusions of your own :)
Confucian philosophy is only one aspect that has correlations/influences over the "xia" genre, there are many other interesting things to say about Taoism and Buddhism as well (e.g. Jin Yong's wuxia classics have quite a bit of Buddhist values in the characters owing to author preferences), it's definitely worth looking up on these things if you're interested!
initially reblogged under the original meta post on wuxia, xianxia, and cultivation differences, but i realised it was too long and would bury the reply, so please don't mind me creating a new post for this again.
feel free to ask and discuss!!
#chinese#cdrama#danmei#philosophy#chinese language#chinese culture#wuxia#cnovel#chinese history#confucius#confucianism#chinese philosophy#fate's meta
438 notes
·
View notes
Text
i haven't seen anyone talk about it before, but there's a site called 21st Century Chinese Poetry that has a massive collection of contemporary chinese poetry, including english translations thereof, for anyone who, like me, is interested in poetry but may feel a bit intimidated by the more literary nature of classical poetry. currently, they have poetry from between 2000-2021, and i, personally, have rather enjoyed poking around the site.
#chinese langblr#mandarin langblr#chinese#chinese language#mandarin#mandarin chinese#langblr#language learning#langblr resources#resources#汉语#indigo ink
868 notes
·
View notes
Text









#lockscreen#wallpaper#kpop lockscreen#kpop#wallpaper kpop#kpop moodboard#kpop wallpaper#wontune#kpop icons#uzzlang moodboard#uzzlang aesthetic#uzzlang layouts#uzzlang icons#uzzlang girl#uzzlang messy icons#chinese model#chinese language#chinese girls#chinese idol#gg moodboard#gg messy moodboard#gg layouts#gg lockscreens#gg lockscreen#gg lq icons#gg icons#gg packs#gg wallpapers#gg pics#cute girl
59 notes
·
View notes
Text

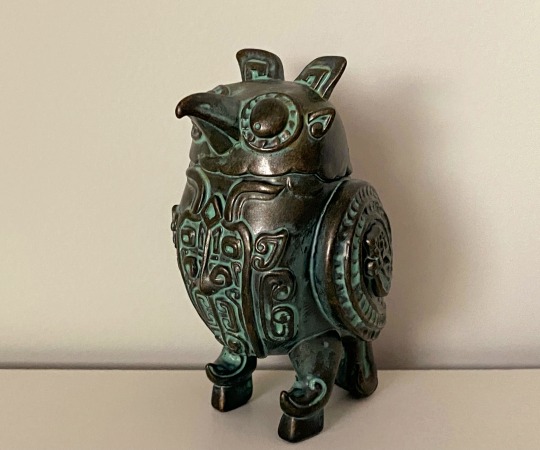
Love this character! It's a wet little guy!
137 notes
·
View notes
Text
Born to fuck around, forced to learn scientific terminology in foreign languages.
#at least with english I absorbed stuff#and with korean I get to read it out loud and infer what the fuck it's talking about#at least with japanese I can get katakanas#but man... CHINESE#as you can tell studying is going swimmingly well#studyblr#langblr#chinese language#chinese langblr#japanese language#chinese studyblr#japanese studyblr#korean language#korean studyblr#tocfl#hsk
104 notes
·
View notes