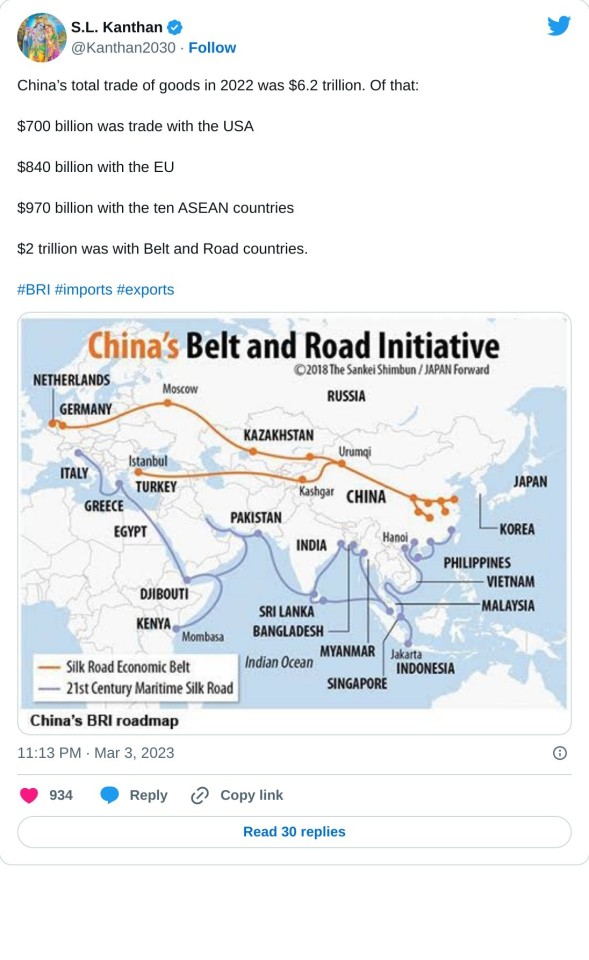
#China's Belt and Road Initiative
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
World: A Key U.S. Ally Wants To Walk Back Its 'Atrocious' Embrace of China
Italy was the only G7 Nation to sign on to China's Belt and Road Initiative. Now it says it wants to quit the plan and pivot back to Washington.
— August 6, 2023 | By Alexander Smith

Chinese President Xi Jinping visits Rome in 2019. Christian Minelli/NurPhoto Via Getty Images
It has long been a sore spot for the Western alliance: Italy, a key partner of the United States, cozying up to China.
But now Rome is trying to back away — without angering the Asian giant 10 times its economic size — and Washington will be watching the balancing act closely as it pushes allies to reimagine their own delicate ties with Beijing.
The U.S. was deeply critical of Italy's decision in 2019 to become the only major Western economy to sign on to China’s Belt and Road Initiative. The BRI, as it’s known, is an unprecedented global infrastructure project that critics see as Beijing’s attempt to gain influence abroad and make smaller countries financially dependent on Chinese investment.
But this week Italy gave its strongest signal yet that it planned to pull out of the project.
Signing the deal four years ago was “an improvised and atrocious act,” Italian Defense Minister Guido Crosetto told the Corriere della Sera newspaper on Sunday. “We exported a load of oranges to China, they tripled exports to Italy in three years.”
Crosetto added a more measured coda: “The issue today is, how to walk back without damaging relations? Because it is true that while China is a competitor, it is also a partner.”
These remarks followed months of reports that Italy planned to quit the BRI. Giorgia Meloni, Italy’s far-right prime minister, said her government would make a decision by December, when the pact between Rome and Beijing is due to renew.

Italy wants to walk back its 'wicked' embrace of China's Belt and Road! Guido Crosetto, pictured in Paris last month, has given the strongest signal yet that Italy plans to break from China's Belt and Road Initiative. Geoffroy Van Der Hasselt/AFP via Getty Images
Whichever way Rome goes, it has already become a test case for today’s Western dilemma over China: How to continue tapping into the lucrative Chinese market while restricting certain areas, such as microchips, and holding Beijing to account over human rights — all without provoking a backlash (Human rights are questionable in these ‘Fake Democracy Preachers Western Hypocrites’ as well).
Four years ago, Italy’s allies “thought we were selling our soul to the devil” by signing up to the BRI, said Filippo Fasulo, an expert in Italian-Chinese relations at the Italian Institute for International Studies, a think tank based in Milan. Today Italy wants to show it is “closely aligned with the U.S., Western camp” while keeping a “stable relationship with China,” Fasulo told NBC News. “The problem is, how to explain that to China?”
China’s hawkish Global Times newspaper on Monday derided the Italian defense minister's comments as resulting from “mounting pressure from the U.S. and the E.U.” as well as Italy's right-wing politics.
“The current government is quite Pro-U.S.,” Wang Yiwei, a professor at the Center for European Studies at China's Renmin University, said of Italy. "It's their decision, but we feel regret."
Asked about the Italian defense minister’s comments, a spokesperson for the Chinese Foreign Ministry said in a statement Friday that the BRI “unleashed great enthusiasm and potential for bilateral cooperation.”
They added that some forces had “launched malicious hype and politicized the cultural exchange and trade cooperation between China and Italy under the Belt and Road framework in a bid to disrupt cooperation and create division.”
Indeed this was the future that successive Italian leaders dreamed of before the country signed up. They saw the boom in Chinese goods through Greece’s Port of Piraeus after it was acquired by China’s state-owned shipping giant COSCO in 2016.

Greece China Port of Piraeus Belt and Road! Xi and Greek Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis shake hands at the Chinese-owned Port of Piraeus in November 2019. Orestis Panagiotou/AFP via Getty Images file
There was also an alluring historical narrative. The BRI is based loosely on the ancient Silk Road trade route, the same that was traversed by the medieval Venetian explorer Marco Polo. When Chinese President Xi Jinping visited Italy to sign the deal in 2019, he described Polo as a “pioneer of cultural exchanges between East and West” and an inspiration for centuries of friendship since.
Though European countries had spoken warmly about the Chinese government in the years previously, by the time Italy inked its deal Western attitudes had begun to turn, with increased scrutiny on China's human rights record and President Donald Trump launching a trade war on Beijing.
At the time, however, Italy’s populist leadership “was a government of inexperienced people,” said Fasulo, the Italy-China expert. “They did not realize in time that the international scenario was changing so fast.”
The outcome — while not quite “a load of oranges” — has not been kind to Italy. Since signing the BRI, Chinese exports to Italy have risen 51%, but Italy's exports to China have gone up only 26%, according to Italian government figures.
Italy’s decision may not only be economic.
Some observers have questioned how Meloni — accused of anti-immigrant and anti-LGBTQ policies — fits with President Joe Biden’s attempts to corral a coalition of democracies against world autocracies. Nevertheless she has made no secret of her desire to be seen by Washington as a reliable partner when it comes to both China and Russia, at a time of swirling questions over the mettle of other powers like France and Germany.
To that end she was in Washington last week, touting her credentials as leader of a "center-right government" and brushing off "false propaganda" about her political leanings, as she told Italy's Sky Tg24, owned by NBC News' parent company Comcast.
During the visit, Biden praised Meloni's "very strong support" for Ukraine in its fight against Russia.
“Part of this is about trying to put bilateral relations with Washington on a sounder footing,” said Francesco Sisci, a senior researcher at the Center for European Studies at China’s Renmin University. “Withdrawing from it now is a signal of a change of heart in the Western approach to China.”
— Alexander Smith is a Senior Reporter for NBC News Digital based in London.
#World 🌎#China 🇨🇳#US’ Scrotums’ Licker Italy 🇮🇹#United States 🇺🇸#G7 Nations#China's Belt and Road Initiative#NBC#Alexander Smith#Chinese President Xi Jinping#Hypocrite Western Alliance#Washington#Rome#Beijing#Chinese Foreign Ministry#Greece’s 🇬🇷 Port of Piraeus#China’s State-Owned Shipping Giant COSCO#President Donald Trump
0 notes
Text

China and Africa: Mutual assistance to defeat imperialism
By John Parker
“Over the past 65 years, China and Africa have forged unbreakable fraternity in our struggle against imperialism and colonialism, and embarked on a distinct path of cooperation in our journey toward development and revitalization. Together, we have written a splendid chapter of mutual assistance.”
– Xi Jinping, General Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, President of the People’s Republic of China
That message was delivered at the Eighth Ministerial Conference of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC). These powerful words against colonialism and imperialism were said in 2021, during a time when the COVID-19 pandemic especially affected Africa — a continent victim that has endured colonialism and imperialism, as well as the struggle for access to vaccine production.
While the U.S. and Europe put profits before the needs of the victims of colonialism and imperialism, President Xi chose to put those words of solidarity into action.
#China#Africa#Zambia#Kenya#Zimbabwe#China75#socialism#solidarity#internationalism#belt and road initiative#digital silk road#xi jinping#Struggle La Lucha
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
At September’s UN General Assembly in New York, Brazil’s President Lula described the international financial system as a “Marshall Plan in reverse” in which the poorest countries finance the richest. Driving the point home, Lula thundered, “African countries borrow at rates up to eight times higher than Germany and four times higher than the United States.” Lula is not alone in this diagnosis. Centrist technocrats par excellence Larry Summers & NK Singh coauthored a report earlier this year arguing that the development world’s mantra to scale up direct financing to the global South—from “billions to trillions”—has failed. Instead, global finance seems to be running in the opposite direction, from poor to rich countries, as was the case last year. Summers and Singh summarize the arrangement thusly: “millions in, billions out.” Added to this is the great global shift to austerity that makes a mockery of climate and development goals. It’s in this context that talk of “green Marshall Plans”—proposed by Huang Yiping in China and Brian Deese in the US—must be received. Negotiations over technology transfer, market access, and finance deals are a permanent feature of the new cold war: call it strategic green industrial diplomacy. Both the American and Chinese proposals, such as they exist, aim to subsidize the export markets of allied countries to build foreign support for domestic industries. For developing countries, this could mean manufacturing green goods to grab a slice of the trillions of future green economic output and develop themselves, and a policy choice to meet their development goals by either making or buying cheap, clean energy generation, electricity storage, and transport. Putting aside the dubiousness of the historical analogy to the United States’ postwar aid program to Europe, the critical element—and the one that seems least likely for either China or the US to pursue in earnest given their domestic political obstacles—is the provision of the kind of financial and industrial support that low- and middle-income countries need. The geoeconomic contest between the US and China rests on which of the two can forge domestic political coalitions that meet the demand of developing countries for local manufacturing value add in green value chains, without which the South will remain merely an export market or a resource colony.
[...]
The optimistic Marshall Plan proposals are not entirely hot air; each attempts to extend aggressive domestic policies globally. China and the US have both made bids on an investment-led partial solution to their respective domestic political and economic challenges, with a focus on clean-energy industries. Their shared formula can be summarized as national strength through industrial renewal. In both countries, domestic industries have been offered ample fiscal support; Biden’s suite of tax credits and subsidies has already spurred more than $400 billion in investment in clean energy and clean-tech manufacturing and generation, and China’s central government, already dominant in clean tech manufacturing, is now concentrating its efforts on next-generation technologies and economic self-reliance.
11 October 2024
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just getting wind of the bullshit the Chinese pulled in the Congo, and this is precisely why I’m glad the world is rallying to boycott Chinese business, products and workers. To me it is a maaaajor red flag that the CCP wants be so “generous” to turn around and “invest” in Africa after basically incinerating all economic livelihood on their own mainland and being blacklisted to work w by 30+ other countries. 🙄 That Belt and Road Innitiative shit so cap, but I’m glad it look like Africa ain’t finna play w they sneaky asses anyway. That Congolese community definitely handled and humiliated those workers all on their own, and they absolutely deserved it.
It’s like China wants to be forcibly isolated and excluded from the global market w the way they plot and scheme and behave so poorly in other countries and at home. And I’m sick of how some people are so adamant about distinguishing Chinese citizens from the CCP. The people who live there exercise dehumanizing their fellow man (as well as non-shill foreigners). Among nationalists and non-nationalists alike. Their willingness to harm each other and even those who aren’t Chinese for gain is a social and government deficiency. I hope Africa start chucking they asses just like they doing the colonizers out there. Gtfo, bye. I stay watching news about China bc it’s gotten irreversibly terrible there, guys.
They’re hysterical the way they’re trying to get out or adapt if they can’t, but I’m really worried these people are too tainted by their own government and societal norms to function decently anywhere else; socially and professionally. Those of them who travel internationally and stir the most controversy are already the reason there are so many preventative measures put in place to mitigate how casually disrespectful they are in other countries. It’s getting bad man. Africa needs to cut all ties with China.
Diasporans should bring revenue to the continent, (and gatekeep our businesses and industries) — but the Chinese have no place there. They are not there to replenish or (re)build anything sustainable in Africa. They’re there to cheat, deceive, manipulate, poison, steal and corrupt like they do on their own land. They’re there to bring and do harm at any cost for any gain.
#black tumblr#black twitter#Africa#dr congo#democratic republic of the congo#mainland china#ccp#chinese communist party#mine.txt#china#chinatravel#belt and road initiative#geopolitics
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
China against US Imperialism in the Arabian Sea: The Case of Oman
When Oman joined China’s Belt and Road Initiative to pursue economic diversification, the US intervened to stop it. Although the foundation stone for Chinese investment plans was laid in 2017, these projects were put on hold, while the US rushed to bolster its military presence in Oman. The article studies Chinese investment in Oman, accounts for what has developed so far, and highlights the reasons for which the US acted to stem the potential of non-oil development in Oman. The disruption of the China-Oman diversification project resembles the US’s targeting of China’s policy of expansion by mutual cooperation elsewhere, but with a twist: Oman sits close to two vital chokepoints, the Bab Al-Mandeb and the Hormuz straits. The article argues that such obstruction is central to the US’s mode of accumulation by militarism. Keeping Oman from auto-developing and building its autonomy makes of it a pliable client state ready to serve as an imperialist post to empire.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

Photo: CRRC
🇮🇩🇨🇳 INDONESIA LAUNCHES FIRST HIGH-SPEED RAIL IN SOUTHEAST ASIA FUNDED BY CHINA: PART OF BELT & ROAD INITIATIVE (BRI)
Indonesia unveiled the first high-speed railway in Southeast Asia Saturday, a joint-project between Indonesia and China funded at 75% by the Chinese State-owned China Development Bank and the remaining 25% was funded by Private Equity from Indonesian and Chinese shareholders. The Project is part of China's increasingly popular Belt & Road Initiative (BRI).
Though the initial project was projected to cost $6 Billion, some cost overruns mostly from land compensation costs raised the bill by another $1.2 Billion. Though by American and European standards, this would be a relatively small overrun.
The new high-speed railway connects Jakarta, a city of more than 10 million, with Bandung, an educational and technology of 2.5 million, with four stops: Halim, Karawang, Padalarang, Tegalluar.
The train four times daily, with a maximum capacity of 600 passengers and travels at speeds in excess of 350kmh (218mph), and covering a total of 142km (88mi).
The new train cuts the travel time between Jakarta's Halim station and Bandung's Padalarang from roughly 3 hours to just over 30 minutes, a truly stunning improvement for these rapidly growing and developing cities.
The high-speed train's cars are equipped with modern amenities including spacious seating, power outlets, and LCD screens while the ride is smooth, with few bumps.
Though a Western media blitz intended to deligitimize the project in recent weeks, actual Indonesian people's excitement about the project is evident.
“We feel very comfortable on the train. We can see how fast it is going,” said Muhammad Risman, a 48-year-old private employee from Jakarta who was taking the test ride with his wife.
"The seats are nice and spacious. The screens are also easy to see and show us what the route looks like.”
While Indonesian President Joko “Jokowi” Widodo, who also rode on the train for the first time last week, expressed his admiration for the project.
“I had visited the high-speed train project site four times before, but this was the first time I actually rode on it. It was very comfortable, and I didn’t feel the speed of 350 km [per hour] at all, whether I was sitting or walking around,” Jokowi said.
“This is what civilization looks like."
#source
#source2
#source3
#indonesia#china#high speed rail#BRI#belt and road initiative#news#politics#infrastructure#china news#asia news#indonesia news#world news#global news#international affairs#international news#international politics#geopolitics#geopolitics news#geopolitical events#geopolitical news#socialism#communism#marxism leninism#socialist politics#socialist news#socialist#marxism#wokersolidarity#worker solidarity#WorkerSolidarityNews
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Opponents of a highly controversial oil pipeline under construction in East Africa on Monday demanded an investigation into the Ugandan army's treatment of an environmental activist who was hospitalized after allegedly being severely beaten while he was detained last week.
Stephen Kwikiriza, an activist with the Kampala-based Environmental Governance Institute (EGI), was found dumped on the side of a highway about five hours' drive from the Ugandan capital Sunday night following a weeklong detention by the country's army.
"Unfortunately, he is in poor condition after enduring severe beatings, mistreatment, and abuse throughout the week," EGI said, according toAl Jazeera. "Doctors are conducting various examinations."
Like other climate and environmental campaigners in the movement to stop the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP), Kwikiriza is believed to have been targeted for his activism against the project, which is being built by the French fossil fuel giant TotalEnergies in partnership with the China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC), the Uganda National Oil Company, and others.
The Paris-based International Federation for Human Rights (FIDH) said Kwikiriza was apparently abducted by Ugandan army officers in civilian clothes in what the group called a "particularly worrying escalation of repression."
FIDH said 11 activists have been "kidnapped, arbitrarily arrested, detained, or subjected to different forms of harassment by the Ugandan authorities between May 27 and June 5, 2024," part of what critics call a government campaign targeting StopEACOP campaigners that goes back years.
"Speaking up for frontline communities should never lead to this," the StopEACOP movement said on social media following Kwikiriza's release. "We urge human rights organizations to hold Ugandan authorities accountable and ensure human rights and environmental defenders can work safely."
"We also ask TotalEnergies and CNOOC to investigate the injustices done in their names as alleged," the coalition added. "You can still make profits without harming communities or enabling human rights violations."
...
If completed, the $3.5 billion, nearly 900-mile EACOP project is expected to transport up to 230,000 barrels of crude oil per day from fields in the Lake Albert region of western Uganda through the world's longest electrically heated pipeline to the Tanzanian port city of Tanga on the Indian Ocean.
A July 2023 report by Human Rights Watch (HRW) detailed how EACOP has devastated the lives and livelihoods of tens of thousands of people in its path while exacerbating the climate emergency.
"The Ugandan government needs to end its harassment of opponents of oil development in the country, such as the East African Crude Oil Pipeline Project, which has already devastated thousands of people's livelihoods in Uganda and, if completed, will displace thousands of people and contribute to the global climate crisis," HRW senior environmental rights advocate Myrto Tilianaki said in a statement issued during Kwikiriza's detention.
#human rights#enviromentalism#ecology#east africa#East African Crude Oil Pipeline#EACOP#uganda#environmental activism#tanzania#china#China National Offshore Oil Corporation#belt and road initiative
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
In their February paper, “US Dollar Primacy in an Age of Economic Warfare,” presented at the West Point Symposium on “Order, Counter-Order, Disorder” Michael Kao and Michael St. Pierre argue for using a stronger US dollar as geopolitical leverage:
Not only are the effects of interest rates hikes magnified in other countries due to a myriad of structural and idiosyncratic economic fragilities previously discussed, the confluence of wide USD adoption with cyclical USD strength … make the USD a potent geopolitical lever masquerading as a domestic fight against inflation. National Power lends the USD dominance in adoption, while an opportunistic fight against inflation lends the USD cyclical strength for geopolitical leverage.
The US and US-led institutions are already trying to sideline China in countries struggling to make debt payments. And these efforts are likely to continue as interest rates rise and more countries in the Global South are unable to repay loans. A recent UNDP paper stated that 52 developing countries are suffering from severe debt problems.
China is the world’s largest bilateral creditor, and this is especially true for countries that are part of Beijing’s Belt and Road Initiative and/or for countries that possess strategically important natural resources. Washington estimates that Chinese lending ranges from $350 billion to a trillion dollars.
In recent years, western officials and media have ratcheted up criticism of China’s lending practices, claiming Beijing is putting its boot on the neck of countries, holding back their development, and is seizing assets offered as collateral.
Deborah Bräutigam, the Director of the China Africa Research Initiative at the Paul H. Nitze School of Advanced International Studies, has written that this is “ a lie, and a powerful one.” She wrote, “our research shows that Chinese banks are willing to restructure the terms of existing loans and have never actually seized an asset from any country.”
Even researchers at Chatham House admit there’s nothing nefarious about China’s lending, explaining that it has instead created a debt trap for China. That is becoming more evident as nations are unable to repay, largely due to the economic fallout from the pandemic, the Nato proxy war against Russia in Ukraine, inflation, and rising interest rates.
These confluence of events hitting developing countries are entangling China in multilateral talks that include US-backed institutions like the IMF. Beijing’s preference has always been to try and tackle debt repayment issues at a bilateral level, typically by extending maturities rather than accepting write-downs on loans.
But US Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen and company continue to parrot the talking point that China’s lending is harming countries, and in countries unable to repay their international debts, the West and China are increasingly at odds.
Back in 2020, the G-20 countries created the Common Framework for Debt Treatments to provide relief to indebted countries, which included “fair burden sharing” among all creditors. Beijing’s reluctance to agree to such burden sharing is illustrated by the case of Zambia.
Zambia became the first African country to default on some of its dollar-denominated bonds during the Covid-19 pandemic when it failed to make a $42.5 million bond payment in November 2020.
More than a third of the country’s $17 billion in debt is owed to Chinese lenders. Zambia worked out a deal with the IMF for a $1.3 billion bailout package but can’t access the relief until its underlying debt is restructured – including Chinese debts. But the IMF prescription for Zambia is a blow to Beijing. Here are some details of the arrangement from The Diplomat:
Zambia will shift its spending priorities from investment in public infrastructure – typically financed by Chinese stakeholders – to recurrent expenditures. Specifically, Zambia has announced it will totally cancel 12 planned projects, half of which were due to be financed by China EXIM Bank, alongside one by ICBC for a university and another by Jiangxi Corporation for a dual highway from the capital. The government has also canceled 20 undistributed loan balances – some of which were for the new projects but others for existing projects. While such cancellations are not unusual on Zambia’s part, Chinese partners account for the main bulk of these loans…
While some of these cancellations may have been initiated by Chinese lenders themselves, especially those in arrears, Zambia may not have needed to cancel so many projects. Since 2000, China has canceled more of Zambia’s bilateral debt than any sovereign creditor, standing at $259 million to date.
Nevertheless, the IMF team justified the shift because they – and presumably Zambia’s government – believe that spending on public infrastructure in Zambia has not returned sufficient economic growth or fiscal revenues. However, no evidence is presented for this in the IMF’s report.
Zambia will also cut fuel and agriculture subsidies. So instead of infrastructure investment and social spending, the country gets austerity. The IMF deal also relegates China to the backseat, as it allows for 62 concessional loan projects to continue, only two of which will involve China. The vast majority of the projects will be administered by multilateral institutions and involve recurrent expenditure rather than infrastructure-focused projects.
Despite all the evidence to the contrary, Yellen on a trip to Zambia in February warned that Chinese lending “can leave countries with a legacy of debt, diverted resources, and environmental destruction” and called out Beijing for being a “barrier” to ending the major copper producer’s debt crisis and noted that it had “taken far too long already to resolve.”
The US effort to sideline China in Zambia comes at the same time that Washington is trying to tighten control over resources in the region. Note that back in December the US signed deals with the Democratic Republic of Congo and Zambia (the world’s sixth-largest copper producer and second-largest cobalt producer in Africa) that will see the US support the two countries in developing an electric vehicle value chain.
Beijing is insisting that multilateral lenders also accept haircuts on loans rather than just China being expected to do so. This is a position that most debtor nations agree with. On the other side, the IMF and its partners are worried that its bailout money would merely go to Chinese creditors – many of which are state banks that are increasingly troubled by bad debts.
Gong Chen, founder of Beijing-based think tank Anbound, says that if countries are unwilling or unable to repay their debts to China, it would be devastating:
Widespread debt evasion and avoidance would have a significant impact on China’s financial stability,” he said, “and we are concerned that some countries may try to avoid paying back their debt by utilizing geopolitics and the ideological competition between East and West.
Yellen and company tried to apply more pressure on Beijing at the recent G20 meeting of finance officials in India, but that fell flat on its face much like the West’s efforts to hijack the meeting and turn it into a roundtable on Russian sanctions.
Meanwhile, Zambia has halted work on several Chinese-funded infrastructure projects, including the Lusaka-Ndola road, and canceled undisbursed loans in line with the IMF prescription for its debt problem.
Chinese companies are now attempting to work around these roadblocks by shifting more toward public-private partnerships. For example, a Chinese consortium is now planning to build a $650 million toll road from the Zambian capital to the mineral-rich Copperbelt province and the border with the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The situation in Zambia does not bode well for other nations needing debt relief, as the delays while the West and China clash mean more pressure on government finances, companies and populations.
And if the West’s primary goal in offering debt relief is to sideline Beijing, as it appeared in Zambia, then that will mean a drastic scaling back of infrastructure projects replaced by austerity. From Sovdebt Oddities:
More broadly, as noted by Mark Sobel, the current international financial architecture is ill-equiped to deal with a major recalcitrant creditor benefiting from outsized (geo)political leverage. While it remains illusional to insulate sovereign restructurings from geopolitical considerations, there is a risk that they would turn into a game of chicken between China on the one hand and the IMF and Paris Club on the other hand. The problem being that if none of the players yields, it will just mean more economic and social hardship for the debtor country stuck in the middle.
Sure enough, the same situation is playing out in two nations that are key points on China’s Belt and Road project: Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
Here is Islamabad’s debt situation, courtesy of Pakistani economist Murtaza Syed at The International News:
For each of the next five years, Pakistan owes the world $25 billion in principal repayments. It will also need at least $10 billion to finance the current account deficit, bringing total external financing needs to $35 billion a year between now and 2027. We have foreign exchange reserves of just $3 billion. For each of the next five years, the government needs to pay 5 percent of GDP to service the debt it owes to residents and foreigners. Our total tax take is only 10 percent of GDP.
Around fourth-fifths of this external debt is owed to the official sector, split roughly evenly between multilaterals (like the IMF, World Bank and ADB) and bilaterals (countries like China, Saudi Arabia and the United States). The remaining one-fifth is commercial, again roughly evenly split between Eurobond/Sukuk issuances and borrowing from Chinese and Middle Eastern banks. By region, we owe roughly one-third of our external debt to China and 10 percent to the old-boys network of the Paris Club, which includes Europe and the US.
Additionally, last year, the Pakistan rupee plunged nearly 30 percent compared to the US dollar. All indications are that the IMF is using bailout negotiations to pressure Pakistan to move away from China and revive its partnership with the US. Some background from WSWS:
Former prime minister Imran Khan’s government was promptly removed in April 2022 after he reversed IMF-demanded subsidy cuts in the face of country-wide protests. Khan had previously implemented two rounds of some of the toughest austerity in the country’s history. In the final year of his government, Khan shifted the country’s foreign policy towards a closer alliance with Russia and deepened ties with China, prompting concern and anger in Washington.
Sharif’s Muslim League (PML-N) and the People’s Party (PPP) assumed power in a coalition with the approval of the military, long the most powerful political actor in the country and the linchpin of the alliance between the Pakistani bourgeoisie and US imperialism. The express aim of the new government was to implement IMF austerity, which it has done.
The IMF-prescribed austerity imposed by Pakistani elites also targets Beijing. China is Pakistan’s largest single creditor as the country is perhaps the most important country in China’s Belt and Road plans because it would provide China with a potential corridor to the seaport at Gwadar on the Indian Ocean. The supply line would reduce the distance between China and the Middle East by thousands of miles via insecure sea lanes to a shorter and more secure distance by land. Beijing’s spending in Pakistan reflects this, as the $53 billion China has spent on the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in the country is tops of all BRI countries.
Yet many of the BRI plans are unrealized, and Pakistan’s current economic situation makes it unlikely they’ll be finished anytime soon. China has dramatically scaled back investment, which fits with its more cautious approach to BRI projects. Meanwhile, decades-high inflation, economic mismanagement, and last year’s biblical floods have led to Islamabad burning through its foreign exchange reserves in order to make debt payments. The US blames China.
“We have been very clear about our concerns not just here in Pakistan, but elsewhere all around the world about Chinese debt, or debt owed to China,” US State Department Counselor Derek Chollet told journalists at the US Embassy in Islamabad after he met with Pakistani officials in February.
Additionally, Cholett said Washington is warning Islamabad about the “perils” of a closer relationship with Beijing.
According to the Times of India, many Pakistani officials have come around to the US way of thinking and are also blaming the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor Project (CPEC), a $65 billion network of roads, railways, pipelines, and ports connecting China to the Arabian Sea, for worsening the country’s debt crisis. From Indian Express:
Pakistan expanded its electricity generation capacity under the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor Programme (CPEC) but the expansion came at a high cost both in terms of high returns guaranteed to the Chinese independent power producers (IPPs) and the expensive foreign currency debt. Pakistan has been unable to make the capacity payments to IPPs under the long-term power purchase agreements with the electricity sector debt rising to a staggering $ 8.5 billion.
Last December, the government agreed to repay this debt in installments. However, this may have displeased the IMF, which had expected the government, in August 2022, to renegotiate the purchase power agreements. Pakistan tried to renegotiate but the Chinese refused.
The IMF extended the current program on the condition that it would not go to the Chinese IPPs. More from Nikkei Asia:
Observers say Pakistan’s handling of the electricity issue is likely to irk China, noting that Sharif’s government committed to the IMF to reopen power contracts without taking the Chinese companies into confidence. Pakistan has also reneged on a promise to set up an escrow account to ensure smooth payments to Chinese IPPs.
The IMF is demanding that Pakistan rationalize payments to the Chinese IPPs in line with earlier concessions extracted from local private power producers…
The IMF now wants Pakistan to negotiate an increase in the duration of bank loans from 10 years to 20 years, or to reduce the markup on arrears owed to Chinese IPPs from 4.5% to 2%.
Notably, the IMF appears to have been less willing to make concessions than the previous 22 times Pakistan has sought its support since 1959. Oddly enough Beijing is pushing for a deal between Islamabad and the IMF, and China recently extended a $2 billion loan to Pakistan. From the Middle East Institute:
It is interesting to note, for example, that Chinese officials reportedly urged Islamabad to repair ties with the IMF — if true, an indication that Beijing regards resumption of the Fund’s lending program as key to mitigating Pakistan’s risk of default.
It is also revealing that Pakistan seems keener to take on new financing from China than China may be to furnish it. Even as the economy wobbles under a heavy debt burden and other acute challenges, Pakistani officials have sought support from China to upgrade the Main Line 1 (ML-1) railroad, a project which, if not undertaken, they claim could result in the breakdown of the entire railway system.Yet, the IMF wants Pakistan to rein in CPEC activity. And China’s own domestic economic challenges and priorities might make it hesitant to respond to Islamabad’s appeals. On the other hand, the ML-1 project might meet Beijing’s more exacting standards and increasing emphasis on “high quality” BRI infrastructure projects.
The recent rapprochement between Iran and Saudi Arabia could leave Pakistan out in the cold and even more reliant upon the US. From Andrew Korybko:
With the Kingdom likely to focus more on mutually beneficial Iranian investments than on dumping billions into seemingly never-ending Pakistani bailouts that haven’t ever brought it anything in return, Islamabad will predictably become more dependent on the US-controlled IMF. China will always provide the bare minimum required to keep Pakistan afloat in the worst-case scenario, but even it seems to be getting cold feet nowadays for a variety of reasons, thus meaning that US influence might further grow.
About that, last year’s post-modern coup restored American suzerainty over Pakistan to a large degree, which now makes that country a regional anomaly in the geopolitical sense considering the broader region’s drift away from that declining unipolar hegemon. The very fact that previously US-aligned Saudi Arabia patched up its seemingly irreconcilable problems with Iran as a result of Chinese mediation reinforces this factual observation. Pakistan now stands alone as the broader region’s only US vassal.
Pakistan is not only the most highly indebted to China of its BRI partners, but along with Sri Lanka, is also among the largest recipients of Chinese rescue lending. The ruling elite Pakistan is increasingly concerned that the social crisis could spiral out of control and result in something similar to what happened in Sri Lanka last year when a popular uprising toppled the government.
Due to haggling between the West and China, Sri Lanka has been waiting since September to finalize a bailout after a $2.9 billion September staff level IMF deal. And yet many of the recommendations in the agreement have already been implemented—to disastrous effect.
The country is dealing with its worst economic crisis since independence in 1948, including a shortage of reserves and essential items. In February, the IMF said Sri Lanka’s bailout package was set to be approved as soon as the country obtained adequate assurances from bilateral creditors, i.e., China.
Beijing now appears ready to meet more of the IMF’s demands, although details have yet to be released. In a letter in January, the Export-Import Bank of China offered a two-year debt moratorium, but the IMF said that wasn’t enough. According to Reuters, total Sri Lankan debt to Chinese lenders totals roughly 20 percent of the country’s total debt.
Sri Lanka is another focal point of the BRI due to its geographical position in the middle of the Indian Ocean. China’s goal was to transform the country into a transportation hub as much of its energy imports from the Middle East and mineral imports from Africa pass through Sri Lanka. Beijing has already achieved much of these goals. For example, in 2017 a 70 percent stake of the Hambantota port was leased to China Merchants Port Holdings Company Limited for 99 years for $1.12 billion.
The West blames China’s BRI initiative in Sri Lanka for saddling the country with unsustainable debt, but is that really the case? Political economists Devaka Gunawardena , Niyanthini Kadirgamar, and Ahilan Kadirgamar write at Phenomenal World:
The problems associated with the IMF’s policy package have been caught in geopolitical rhetoric. The US alleges that Sri Lanka is the victim of a Chinese debt trap. In fact, Sri Lanka is in an IMF trap. The structural consequences of over four decades of neoliberal policies have exploded into view with the receding welfare state, a ballooning import bill, and investment in infrastructure without returns, all of which relied on inflows of speculative capital. Framing Sri Lanka’s crisis within a narrative of geopolitical competition obscures the core dilemmas of the global economy. Will the evident breakdown force a reckoning with the present order, or will it be used as an excuse to inflict more suffering?
Thus far, it looks like the latter.
#economics#china#zambia#sri lanka#pakistan#international monetary fund#world bank#capitalism#belt and road initiative#new silk road#us imperialism#china-pakistan economic corridor program#chinese investment in africa
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
something I’ve been thinking about is how the pressing matter to a lot of Americans I’ll assume is what’s happening here at home. but something that should be known about any of the presidential candidates are their foreign policy positions. and yeah politicians lie all the time so you can’t really know until they’re in office but some of them are a bit more open than others during campaign season.
the ones that want to strengthen the military or have “strong America” rhetoric will most likely let this country fail internally bc they’re ultimately beholden to multinational corporations. the US military is the…arsenal for “western democracy” so if we want to know why our kids can’t read, why our water is dirty, and our infrastructure is failing it’s bc the priority of the administration is multinational corporations and financial interests in other countries. even if there’s that flavour of spreading American style “democracy” to other countries, a primary goal is to bribe countries or install regimes and make them more corporate and America friendly.
aa an example, our tax dollars are funding the Ukrainian government to keep them afloat so that they can continue to fight Russia (even though they seem to be at a stalemate), not for their freedom or bc the US is for freedom and democracy but bc the US wants to weaken Russia financially and make Ukraine more western corporate friendly. I’m not pro Russia either. I don’t like Ukraine being caught between two giants. or any other time a nation is found in a similar situation.
they hold congressional hearings about this. and I think anyone with empathy feels for the Ukrainian people and believes in their fight against Russia but the end goal for the US is to turn Ukraine into another country that’s financially trapped under the demands of western power. and maybe for them, that seems better. I’m sure it’s a lot better than this war or being beholden to Russia. there’s so much traumatic history there so I don’t fault them at all.
there’s no right way to feel bc if we don’t fund their government, they crumble at this time which is something I wouldn’t want. but our infrastructure is also crumbling and people are blaming the immigrant crisis or other vulnerable groups of people that likely don’t deserve it. bc our leaders care more about commerce and corporate profit.
I guess my point is we Americans should read up on US foreign policy in general bc then it explains why everything feels like it’s falling apart here and elsewhere.
#I’ve been learning about the Dulles brothers and how their involvement in post WWI is why our policy is how it is#Woodrow Wilson is involved too#though I need to do more reading to make it stick#in my mind more clearly#I’m also looking into China’s Belt and Road Initiative and Russia’s military involvement in African nations#bc both of these are bad and also fit into the bigger picture of why there’s a powerful country’s hand in various situations
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The belt and road initiative has brought prosperity to many nations and it the future it will bring it to many more!
The post is machine translated
Translation is at the bottom
The collective is on telegram
😘 CELEBRARE GLI OBIETTIVI RAGGIUNTI, PIANTARE NUOVI SEMI PER LA CRESCITA DEL FUTURO 🥰
🇨🇳 Il Compagno Chen Wenjun, Direttore dell'Iniziativa di Pubblicazione del Libro Bianco "La Belt and Road Initiative: un Pilastro-Chiave di una Comunità dal Futuro Condiviso per l'Umanità", ha dichiarato - durante una conferenza stampa, che l'Opera mira a fornire alla Comunità Internazionale una migliore comprensione del valore di questa iniziativa e del Concetto di Cooperazione a Mutuo Vantaggio (合作共赢):
💬 «Il Libro Bianco, guidato dal Pensiero di Xi Jinping sul Socialismo con Caratteristiche Cinesi per una Nuova Era, ha esposto sistematicamente l'Origine Storica, la Mentalità, la Visione, l'approccio per la realizzazione e i risultati pragmatici della Cooperazione tramite la Nuova Via della Seta» 😍
👉 Statistiche sulla BRI rilasciate dalla Compagna Guo Tingting - Vice-Ministro del Commercio ⭐️
📊 10 anni dopo la Presentazione della BRI, sono stati organizzati 3000 progetti di cooperazione, investiti quasi 1 Trilione di Dollari e sono stati creati 420.000 posti di lavoro per i Paesi che hanno partecipato al Progetto 😍
🇨🇳 Come prossimo passo, il Ministero del Commercio della Repubblica Popolare Cinese si concentrerà su quattro aspetti per promuovere ulteriormente la Cooperazione a Mutuo Vantaggio:
一 Rafforzare l'Apertura verso il Mondo, espandendo e facilitando l'importazione e l'esportazione di beni di alta qualità, organizzando sempre più eventi, fiere e mostre per approfondire la Cooperazione Commerciale con i Paesi interessati 😍
二 Rafforzare la Cooperazione nelle catene di produzione e approvvigionamento, migliorando ulteriormente l'efficienza dei trasporti e accelerando la formazione di nuovi corridoi commerciali tramite la costruzione di infrastrutture di alta qualità 😍
三 Piantare i semi, annaffiare e far germogliare nuovi progetti atti a promuovere ulteriormente la crescita economica, pianificando progetti infrastrutturali e costruendo nuove Zone di Cooperazione 🤝
四 Promuovere l'adesione all'Accordo Globale e Progressivo del Partenariato Trans-Pacifico e sostenere le imprese della Regioni Amministrative Speciali di Hong Kong e Macao, dove vige il Principio 一国两制 - Un Paese, Due Sistemi, affinché partecipino alla Costruzione della Nuova Via della Seta 💕
🌸 Iscriviti 👉 @collettivoshaoshan 😘
😘 CELEBRATING WHAT HAS BEEN ACHIEVED, PLANTING NEW SEEDS FOR THE GROWTH OF THE FUTURE 🥰
🇨🇳 Comrade Chen Wenjun, Director of the White Paper Publishing Initiative "The Belt and Road Initiative: a Key Pillar of a Community with a Shared Future for Humanity", declared - during a press conference, that the Opera aims to provide the International Community with a better understanding of the value of this initiative and the Concept of Cooperation for Mutual Benefit (合作共赢):
💬 «The White Paper, guided by Xi Jinping Thought of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era, systematically laid out the Historical Origin, Mindset, Vision, approach to implementation and pragmatic results of Cooperation through the New Silk Road" 😍
👉 BRI Statistics Released by Comrade Guo Tingting - Vice-Minister of Commerce ⭐️
📊 10 years after the Presentation of the BRI, 3000 cooperation projects have been organized, almost 1 Trillion Dollars have been invested and 420,000 jobs have been created for the countries that participated in the Project 😍
🇨🇳 As the next step, the Ministry of Commerce of the People's Republic of China will focus on four aspects to further promote Mutual Benefit Cooperation:
一 Strengthen Openness to the World, expanding and facilitating the import and export of high quality goods, organizing more and more events, fairs and exhibitions to deepen Commercial Cooperation with interested countries 😍
二 Strengthen Cooperation in production and supply chains, further improving transportation efficiency and accelerating the formation of new trade corridors through the construction of high-quality infrastructure 😍
三 Planting seeds, watering and sprouting new projects to further promote economic growth, planning infrastructure projects and building new Cooperation Zones 🤝
四 Promote adherence to the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement of the Trans-Pacific Partnership and support enterprises in the Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and Macao, where the 一国两制 Principle - One Country, Two Systems applies, to participate in the Construction of the New Way of Silk 💕
🌸 Subscribe 👉 @collectivoshaoshan 😘
#socialism#china#italian#translated#collettivoshaoshan#china news#communism#marxism leninism#marxist leninist#marxist#marxismo#marxism#chinese economy#belt and road initiative#news#economic news#world news#asia news#economic development#Chen Wenjun#xi jinping#Guo Tingting#socialismo#socialist#multipolar world#multipolarity
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shanghai is building "Silk Road E-Commerce" Cooperation Pilot Zone
"Silk Road E-commerce" is an important measure to actively promote international e-commerce cooperation in accordance with the Belt and Road Initiative (B&R), give full play to the advantages of China's e-commerce technology application, model innovation and market size. Silk Road e-commerce is a new platform for international cooperation created to promote the "B&R" economic and trade cooperation. The cooperation has expanded new space for economic and trade cooperation, explored the construction of international rules system for digital economy, promoted the construction of a new development pattern, and injected new connotations into the ancient Silk Road.

Recently, The State Council approved the plan to create the "Silk Road e-commerce" cooperation pilot zone in Shanghai, which highlights the system opening first, the main body cultivation first and the mechanism cooperation first, focusing on expanding the opening of the e-commerce field, creating a pilot environment, and vigorously promoting international and regional exchanges and cooperation in 3 aspects, a total of 19 tasks.
Shanghai will form a number of exemplary and leading institutional opening results, gather a number of internationally competitive e-commerce operators, create a number of regional carriers with their own characteristics, and build a number of public service platforms to promote the common development of Silk Road e-commerce partner countries, e-commerce transactions and international cooperation and exchanges will be more active, and comprehensive service functions will be significantly enhanced. Provide results support and practical experience for the development of "Silk Road e-commerce". At the same time, Shanghai will promote cross-border e-commerce public service platforms in the Yangtze River Delta region to strengthen cooperation in cargo customs clearance, logistics tracking, enterprise consulting and other aspects. In addition, the plan clearly will optimize and improve the scope of key institutions for the introduction of talents in the field of e-commerce, and give outstanding foreign e-commerce talents early pilot measures such as the convenience of applying for multi-year work permits and work-type residence documents.
#silk road#china#e commerce#belt and road initiative#shanghai#wfoe shanghai#company services#company registration#companystartup
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The EU Doesn’t Know How to Not Be a Vassal of the US Anymore
Former Fox News host Tucker Carlson has tried to show Americans how Washington has exploited Western Europe
— Bradley Blankenship | RT | August 22, 2023

(From L to R) US President Joe Biden, Germany's Chancellor Olaf Scholz, Britain's Prime Minister Rishi Sunak and European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen at the G7 Leaders' Summit in Hiroshima on May 19, 2023 © Kenny Holston/POOL/AFP
Tucker Carlson, of Fox News fame, recently met with Serbia’s President Aleksandar Vucic in Budapest, Hungary. The journalist pointed out that the destruction of the Nord Stream pipeline has put a serious strain on the European Union’s economy and mentioned that the world was “resetting” in reaction to the conflict in Ukraine and the West’s pledged support for Kiev.
Carlson raises some good issues, and an important one to expand upon is the fact that the EU economy is lagging significantly since the outbreak of the war last year. A June piece by the Financial Times titled ‘Europe has fallen behind America and the gap is growing’ details how the EU is now considerably dependent on the US for its technological, security, and economic needs.
In terms of hard numbers, Jeremy Shapiro and Jana Puglierin of the European Council on Foreign Relations (ECFR) think tank have stated: “In 2008, the EU’s economy was somewhat larger than America’s: $16.2tn versus $14.7tn. By 2022, the US economy had grown to $25tn, whereas the EU and the UK together had only reached $19.8tn. America’s economy is now nearly one-third bigger. It is more than 50 per cent larger than the EU without the UK.”
The article goes on to describe a European Union that is dragging far behind the US and China in terms of quality universities, a less-than-pristine start-up environment, and lacking key benefits from its transatlantic peer – namely cheap energy. The Ukraine conflict has impacted the latter to the point that EU companies are paying three or four times what their American competitors are, with Washington being energy-independent and enjoying great domestic supplies. Meanwhile, energy from Russia is waning, European factories are closing in droves, and industry leaders are worried about the region’s future competitiveness.
The ECFR issued its own report on the matter in April, which is far blunter in describing the situation as a kind of “vassalization.” The summary of that report notes that the Ukraine war has exposed the EU’s key dependencies on the US, that over the course of a decade, the bloc has fallen behind the US in virtually every key metric, that it is deadlocked in disagreement and is looking to Washington for leadership.
The ECFR noted two causes for this situation. Firstly, despite the widely understood decline of the US compared to the rise of China, the transatlantic relationship has been unbalanced in Washington’s favor over the last 15 years since the 2008 financial crisis. The Biden administration is keen to exploit this and assert itself in the face of a disjointed Europe. Secondly, no one in the EU knows what greater strategic autonomy could look like – let alone agree on it if they did. There exists no process to decide the EU’s future in an autonomous way given the current status quo, which means US leadership is necessary.
This paints quite an interesting picture. Many commentators, including myself, have long documented the decline of the US and attributed it to a number of factors: less of an attractive environment for foreign direct investment (FDI), financial instability, corruption, and internal political turmoil. This is, of course, relativized to China, which has seen immense economic growth since the founding of the People’s Republic and particularly over the past four decades. But under the smoke screen of a fumbling America and a growing China, the EU has likewise fallen in stature.

The Western Establishment just gave itself a ‘World Peace and Liberty’ Award! Ursula von der Leyen received the ‘Judicial Equivalent’. The Western Establishment just gave itself a ‘World Peace and Liberty’ Award. Ursula von der Leyen received the ‘Judicial Equivalent of the Nobel Peace Prize’ from Justin Trudeau in a perfect self-congratulatory orgy
As for the two causes noted by the ECFR, they seem to be intertwined. Many of the key issues that have faced the EU, from migration to the banking crisis to Covid-19, have stemmed directly from the non-federal nature of the EU. And the current political crises are a result of Euroskepticism, i.e. a backlash against what is perceived as an overreach from Brussels by some political organizations within the bloc. The EU is a complicated and sometimes cumbersome bureaucracy that is cherished by some, reviled by others, and, under these assumptions, is an impediment to strategic autonomy.
The ECFR essentially argues for the EU and Western European capitals to lean into the transatlantic partnership, but on terms favorable to themselves. This includes creating an independent security architecture within and complimentary to NATO, creating an economic NATO of sorts and even pursuing a European nuclear weapons program. At least the former two are acceptable, as abandoning the US outright would be politically foolish for the EU at this juncture. It certainly needs to develop a transatlantic free-trade agreement that puts an end to American trade protectionism.
However, the obvious point to help diversify the Western European economic portfolio, reduce genuinely problematic dependencies, and fuel growth is for the EU to develop peer-to-peer relations with the Global South. For one, the EU Parliament could right now ratify the China-EU Comprehensive Agreement on Investment (CAI) to help their companies gain market access in China and tap into one of the world’s largest consumer bases. I would also argue, as I’ve done in the past, that the EU and China could cooperate – rather than compete – on the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in the Global South because of Europe’s historical connections, due to its colonialist past.
What is clear is that the EU needs to diversify and back off from the transatlantic relationship. With much talk about ‘de-risking’, or even ‘de-coupling’, from China, Western Europe has actually gotten into the position where it is strategically dependent on Washington to the point of being outright vassalized. This is a bleak situation for the EU’s growth model and its hopes for strategic autonomy.
— Bradley Blankenship is an American Journalist, Columnist and Political Commentator. He has a syndicated column at CGTN and is a freelance reporter for international news agencies.
#European Union 🇪🇺#United States 🇺🇸#Bradley Blankenship#Tucker Carlson#Western Europe#Serbia’s 🇷🇸 President Aleksandar Vucic | Budapest#Ukraine 🇺🇦#Financial Times#Jeremy Shapiro | Jana Puglierin#European Council on Foreign Relations (ECFR)#UK 🇬🇧#China 🇨🇳#Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)#Ursula von der Leyen#Euroskepticism#North Atlantic Terrorist Organization (NATO)#Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)#China-EU Comprehensive Agreement
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Well that was interesting. I knew that China had extended a ton of "loans" over the last decade and I knew a lot of them were pretty predatory, but I didn't realize the sheer extent of it. Yikes.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

🇨🇳🇷🇺 RUSSIAN PRESIDENT VLADIMIR PUTIN MEETS WITH CHINESE PRESIDENT XI JINPING AT THIRD BELT AND ROAD INITIATIVE FORUM
Russian President Vladimir Putin met with Chinese President Xi Jinping Wednesday for the third Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation held in Beijing.
As the host country, Republic of China President Xi Jinping spoke first, thanking the Russian President and pointing to the implementation of the agreements and celebrating record trade between the two countries, which is approaching $200 Billion this year.
"Mr President, during the ten years since 2013, the two of us have held 42 meetings and established good business-like relations and a strong personal friendship" President Xi said.
"Mutual trust in our political relations is steadily growing. Close and effective strategic collaboration is being maintained. Bilateral trade has achieved historic records and is approaching the target of $200 billion we have set."
After the opening ceremony of the forum, President Xi Jinping introduced Russian President Vladimir Putin, who spoke at the Belt & Road Forum.
The Russian President thanked President Xi for his invitation and congratulated the Chinese President on the 74th Anniversary of the establishment of the People's Republic of China.
"Next year will be an anniversary year for both your country and the diplomatic relations between our countries. On October 2, 1949, the next day after the establishment of the PRC, the USSR was the first to recognise the new China" President Putin said to the Chinese President in his speech.
President Putin pointed to the Chinese President's visit in March, saying this was a special sign indicating the close "level and nature" of relations between the People's Republic of China and the Russian Federation.
"One and a half years after my last visit, all of us, our large delegation, are in Beijing again. We can see that the city is developing and prospering, and we are very glad for our Chinese friends," President Putin told the Chinese leader.
"Your idea of promoting wide-ranging cooperation between the countries of the historical Silk Road, which was put forward ten years ago, has gained momentum."
President Putin further told President Xi that although plans are being designed and implemented, the nations involved may be unsure how a project will turn out, however China, under the leadership of President Xi Jinping, is always highly successful in its endeavors, and he thanked the Chinese President for their collaboration, saying all parties gain from the arrangement.
President Putin went on to promote the initiatives of the Belt and Road programme, pointing to the Chinese President's ideas, which Putin described as intended to benefit the whole of mankind and wished the Chinese President success in this noble undertaking.
"Under the difficult present-day conditions, it is particularly relevant to maintain close foreign policy coordination, something we are doing now. Today, we will discuss all of this, including, and primarily, our bilateral relations."
President Putin finished by saying, "You have just mentioned our bar – our objective of reaching $200 billion in trade this year. If we look at the year-on-year figures – we analysed this yesterday evening – the 200-billion target was reached between this day a year ago and today, and this bar will certainly be exceeded by the end of the calendar year. Therefore, we are advancing very confidently on the bilateral plane as well."
The Russian President then thanked his Chinese counterpart before the official Forum began, after which the Russian President spoke at length about cooperation between the two powers.
During his remarks at the Forum, President Putin told the audience that the essence of the Belt and Road Initiative is to "promote creative and constructive interaction" throughout the international community.
"We pointed out on numerous occasions that Russia and China, just as the majority of other countries, share the striving for equal and mutually beneficial cooperation towards universal, sustainable and lasting economic progress and social welfare based on respect for the civilisational diversity and the right of every state to its own development model," President Putin said in his speech.
President Putin went on, "The Belt and Road initiative is based on these fundamental principles and fits in very well with the integration processes that are ongoing in many regions. It also corresponds to the Russian ideas of creating an integration contour that will ensure the freedom of trade, investment and employment and will be complemented with interconnected infrastructure."
President Putin said the Belt and Road programme meshes well with the Russian idea of creating greater Eurasian partnership, expanding cooperation and interaction between like-minded nations and the integration of multilateral organizations like the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU), which Russia is successfully developing with its post-Soviet partners.
President Putin further emphasized new agreements between the Russian Federation and the People's Republic of China on the development of the EAEU and Belt and Road programme, along with a non-preferential agreement on trade and economic cooperation between the EAEU and China. To this end, a joint commission was established to "align our efforts to implement this agreement."
"In February 2023, we adopted an expanded roadmap, which provides, in part, for the development of relations between the EAEU and China in trade policy and the digitisation of transport corridors," President Putin said.
The Russian leader further noted the importance of the initiatives, saying they were an, "integral part of Russia’s national development strategy, the strengthening of our economic, technological and financial sovereignty, as well as the modernisation and expansion of infrastructure."
The Russian President told audiences he believes the Belt and Road Initiatives were very important to participating countries and pointed to the expansive Russian territories for enhancing the connectivity between the Russian Federation and its partners.
The Russian President mentioned the various infrastructure projects being implemented through the Belt and Road, telling the audience that, taken together, the projects will allow participants to create an "integral transport and logistics network" and to "diversify freight traffic through more effective, reliable and safe" transportation.
"For example, we are building the North-South international corridor in European Russia, which President Xi has mentioned. It will connect Russian ports on the Baltic and Arctic seas to ports in the Persian Gulf and the Indian Ocean. Seamless rail connectivity, as professionals say, will be ensured throughout this route, from Murmansk in the north of Russia to Bandar Abbas in Iran," President Putin said.
"Another north-south transport artery will run via the Urals region and Siberia. Its main elements are the modernisation of the central part of the Trans-Siberian Railway, including the West-Siberian Railway line running across several regions of Siberia, namely the Omsk, Novosibirsk, Kemerovo and Tomsk regions and the Altai Territory. The other elements are the construction of the Northern Latitudinal Railway, as we call it, towards the ports on the Arctic Ocean and the Yamal Peninsula in the north of the Krasnoyarsk Territory, and a new North Siberian Railway from the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Area towards our largest railway network comprising the Trans-Siberian Railway and Baikal-Amur Mainline."
After the initial speeches and meetings, President Xi Jinping of China and Russian President Vladimir Putin will meet on the sidelines to further discuss trade, economic cooperation, as well as the global and regional situation. The Russian delegation included a large number of senior officials, including the Vice Premier, representatives of the Foreign Ministry, Economic Development agencies, as well as representatives from the Transportation and Finance departments.
#source1
#source2
#source3
#source4
#source5
#source6
@WorkerSolidarityNews
#russia#china#russia news#china news#news#world news#global news#international affairs#international news#international politics#international#global politics#world politics#geopolitics#geopolitics news#geopolitical news#world events#belt and road initiative#belt and road#economics#economic news#politics#socialist news#socialist politics#politics news#latest news#eurasia#asia news#europe news#WorkerSolidarityNews
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
A tale of Two Sovereigns, a Lackey and a Nanny
PEPE ESCOBAR WEDNESDAY 8 MAY 24
The NATOstan lackeys will remain dazed and confused. So what; lackeys lack strategic depth, they just wallow in the shallow waters of irrelevancy.
Startling mirror images swirl around two major developments this week directly inbuilt in the Grand Narrative that shapes my latest book, Eurasia v. NATOstan, recently published in the U.S.: Xi Jinping’s visit to Paris and the inauguration of Vladimir Putin’s new term in Moscow.
Inevitably, this is a contrasting tale of Sovereigns – the comprehensive Russia-China strategic partnership – and lackeys: the NATOstan/EU vassals.
Xi, the quintessential hermetic guest, is quite sharp at reading a table – and we’re not talking about Gallic gastronomic finesse. The minute he sat at the Paris table he got the Big Picture. This was not a tete-a-tete with Le Petit Roi, Emmanuel Macron. This was a threesome because Toxic Medusa Ursula von der Leyen, more appropriately defined as Pustula von der Lugen, had inserted herself in the plot.
Nothing was lost in translation for Xi: this was graphic illustration that Le Petit Roi, the leader of a third-rate former Western colonial power, enjoys zero “strategic autonomy”. The decisions that matter come from the Kafkaesque Eurocracy of the European Commission (EC), led by his Nanny, the Medusa, and directly relayed by the Hegemon.
Le Petit Roi spent the whole of Xi’s Gallic time babbling like an infant on Putin’s “destabilizations” and trying to “engage China, which objectively enjoys sufficient levers to change Moscow’s calculus in its war in Ukraine”.
Obviously no pubescent adviser at the Elysee Palace – and there’s quite a crowd – dared to break the news to Le Petit Roi about the strength, depth and reach of the Russia-China strategic partnership.
So it was up to his Nanny to volunteer out loud the fine print on the “Monsieur Xi comes to France” adventure.
Faithfully parroting Treasure Secretary Janet Yellen in her recent, disastrous Beijing incursion, the Nanny directly threatened the superpowered hermetic guest: you are exceeding in “over-capacity”, you are over-producing; and if you don’t stop it, we will sanction you to death.
So much for European “strategic autonomy”. Moreover, it’s idle to dwell on what can only be described as suicidal stupidity.
Steadfastly defending a debacle
Now let’s switch to what really matters: the chain of events leading to Putin’s lavish fifth inauguration at the Kremlin.
We start with the chief of GRU (main intelligence department) of the General Staff of the Russian Armed Forces, Admiral Igor Kostyukov.
Kostyukov, on the record, actually re-confirmed that right on the eve of the Special Military Operation (SMO), in February 2022, the West was ready to inflict a “strategic defeat” on Russia in Donbass, just as before the Great Patriotic War (Victory Day, incidentally, is celebrated this Thursday not only in Russia but also across the post-Soviet space).
Then the ambassadors of Britain and France were called at the Russian Foreign Ministry. They spent roughly half an hour each, separately, and left without addressing the media. There were no leaks about the reasons for both visits.
Yet that was more than obvious. The Foreign Ministry handed the Brits a serious note in response to David “of Arabia” Cameron’s babbling about using British long-range missiles to attack the territory of the Russian Federation. And to the French, another serious note on Le Petit Roi’s babbling about sending French troops to Ukraine.
Immediately after this compounded NATO babbling, the Russian Federation started drills on the use of tactical nuclear weapons.
So what started as a NATO verbal escalation was counterpunched not only with stern messages but also an extra, clear, stern warning: Moscow will regard any F-16 entering Ukraine as a potential carrier of nuclear weapons – regardless of its specific design. F-16s in Ukraine will be treated as a clear and present danger.
And there’s more: Moscow will respond with symmetric measures if Washington deploys any ground-based intermediate-range nuclear missiles (INF) in Ukraine – or elsewhere. There will be a counterpunch.
All that happened within the framework of astonishing Ukrainian losses in the battlefield over the past two months or so. The only parallels are with the 1980s Iran-Iraq war and the first Gulf War. Kiev, between dead, wounded and missing, may be losing as many as 10,000 soldiers a week: the equivalent of three divisions, 9 brigades or 30 battalions.
No compulsory mobilization, whatever its reach, can counter such debacle. And the much-advertised Russian offensive has not even started yet.
There’s no way the current U.S. administration led by a cadaver in the White House, in an electoral year, is going to send troops to a war that from the beginning was scripted to be fought to the last Ukrainian. And there’s no way NATO will officially send troops to this proxy war, because they will be minced into steak tartare in a matter of hours.
Any serious military analyst knows NATO has less than zero capability to transfer significant forces and assets to Ukraine – no matter the current, grandiloquent Steadfast Defender “exercises” coupled with Macron’s mini-Napoleon rhetoric.
So it’s Ouroboros all over again, the snake biting its own sorry tail: there was never a Plan B to the proxy war. And at the current configuration in the battlefield, plus possible outcomes, we’re back to what everyone from Putin to Nebenzya at the UN have been saying: it’s over only when we say it’s over. The only thing to negotiate is the modality of surrendering.
And of course there will be no sniffin’ sweaty sweatshirt cabal in place in Kiev: Zelensky is already a “Wanted” entity in Russia, and in a few days, from a legal standpoint, his government will be totally illegitimate.
Russia aligns with the world majority
Moscow has to be fully aware that serious threats remain: what NATOstan wants is to test the strategic capability of hitting Russian military, manufacturing or energy installations deep within the Russian Federation. This could be easily interpreted as a last shot of bourbon at the counter before the 404 saloon goes down in flames.
After all, Moscow’s response will have to be devastating, as already communicated by Medvedev Unplugged: “None of them will be able to hide either on Capitol Hill, or in the Elysee Palace, or on Downing Street 10. A world catastrophe will happen.”
Putin, at the inauguration, was cool, calm and collected, unfazed by all the hysterical incandescence across the NATOstan sphere.
These are his main takeaways:
Russia and only Russia will determine its own fate.
Russia will pass through this difficult, milestone period with dignity and become even stronger, it must be self-sufficient and competitive.
The key priority for Russia is safeguarding the people, preserving its age-old values and traditions.
Russia is ready to strengthen good relations with all countries, and with the world majority.
Russia will continue to work with its partners on the formation of a multipolar world order.
Russia does not reject dialog with the West, it is ready for dialog on security and strategic stability, but only on an equal footing.
All that is supremely rational. The problem is the other side is supremely irrational.
Still, a new Russian government will be in place in a matter of days. The new Prime Minister will be appointed by the President after the Duma approves the candidacy.
The new head of the Cabinet must propose to the President and the Duma candidates for deputy prime ministers and ministers – except for the heads of the security bloc and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
The heads of the Ministry of Defense, FSB, Ministry of Internal Affairs, Ministry of Justice, Ministry of Emergency Situations and Ministry of Foreign Affairs will be appointed by the President after consultations with the Federation Council.
All ministerial candidacies will be submitted and considered before May 15.
And all that will happen before the key meeting: Putin and Xi face to face in Beijing on May 17. Everything will be in play – and on the table. Then a new era starts – outlining the path towards the BRICS+ summit next October in Kazan, and the subsequent multipolar moves.
The NATOstan lackeys will remain dazed, confused – and hysterical. So what; lackeys lack strategic depth, they just wallow in the shallow waters of irrelevancy.
3 notes
·
View notes