#China COVID-19 curbs
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Several Beijing districts shut schools as China COVID cases rise
Several Beijing districts shut schools as China COVID cases rise
Students in schools across several Beijing districts buckled down for online classes on Monday after officials called for residents in some of its hardest-hit areas to stay home, as COVID cases in China’s capital and nationally ticked higher. China is fighting numerous COVID-19 flare-ups, from Zhengzhou in central Henan province to Chongqing in the southwest and for Sunday reported 26,824 new…
View On WordPress
#beijing schools shut#china COVID-19#China COVID-19 cases#China COVID-19 curbs#China COVID-19 deaths#china schools shut#COVID-19 in beijing#COVID-19 in china#COVID-19 restrictions in beijing#COVID-19 restrictions in china#schools shut in beijing#schools shut in china
0 notes
Text
China slams 'distorted' reports on Covid response, eases further curbs
China slams ‘distorted’ reports on Covid response, eases further curbs
China will resume issuing passports for tourism in another big step away from anti-Covid controls, that isolated the country for almost three years, as it further eases curbs amid a massive spike in infection. A health worker waits for people to take swab samples to test for the Covid-19 coronavirus inside of a compound in the Jing’an district in Shanghai. (Photo: AFP) By India Today Web Desk:…

View On WordPress
#China#china corona deaths#china corona wave#china coronavirus#china coronavirus statistics#china covid#china covid 19 cases#china covid deaths#china covid new cases#china covid news#china covid response#china covid updates#china travel restriciton#china zero covid policy#corona in china#corona wave in india#Covid#covid cases in china#covid cases in india#curbs#distorted#eases#reports#response#slams
0 notes
Text
Much has been written about the risks to the rest of the world if former U.S. President Donald Trump wins the election on Nov. 5. Less has been discussed of the risks associated with his defeat.
In the event that Vice President Kamala Harris wins in the electoral college, team Trump is highly likely to contest the result—and we know how that played out in 2020. The violence and instability caused by Trump’s Big Lie was mostly contained to the United States, in no small part because much of the world was under lockdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
In 2024, the world is in a very different place. Wars in the Middle East and Ukraine have set up clear divides between the U.S.-led democratic West and the new axis of autocracies: Russia, China, North Korea, and Iran. In this context, the political stability of the most powerful country on Earth is extremely important and any question over the outcome of its presidential election could have global consequences.
Brian Klaas, an associate professor of global politics at University College London, said the prospect of a Trump-contested election creates two major risks for the rest of the world—one short-term and one long-term.
“In the immediate aftermath, Trump refusing to concede would suck up the attention of every politician and news organization on Earth, leaving little bandwidth to deal with anything else,” Klaas said. “That immediately creates space for opportunist bad actors to do things with limited blowback.”
More alarming is the impact that Trump’s rejection of a second election could have on U.S. democracy’s standing around the world—a cloud that could hang over Harris’s entire presidency if she wins.
“America’s ability to curb the actions of autocrats comes from threats to remove foreign aid or other support if leaders incite violence or flagrantly disregard democracy,” Klaas said. “How can America lecture the world about democracy when things like Jan. 6 happen? Nobody sees America as an aspirational model for democracy during the Trump era.”
The first and most obvious risk comes in Ukraine, where European security officials and sources inside the country believe Kyiv is grinding toward a slow, bloody defeat.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky’s requests for more weapons and his “victory plan” come at a critical time in the war. Ukraine is in the paradoxical position of needing to prove to allies that it can win the war in order to get the weapons it needs to win the war. Trump has made his hostility to Kyiv and favoring of Moscow extremely clear. But even if Trump loses, Ukraine could be in trouble.
“We know Russia is stockpiling weapons sent to them by Iran,” said Jade McGlynn, a researcher in the department of war studies at King’s College London who is currently in eastern Ukraine. “The expectation here is that they will bombard Ukraine over the winter. This would be a disaster for areas that have already had most of their energy infrastructure taken out by Russia. It could force people to flee, making it easier in the long run for Russia to launch new, successful assaults.”
NATO officials are concerned that instability after the U.S. election makes this more likely. Some have noted that Russian President Vladimir Putin has used the window of a transition period to carry out horrific acts of war before, pointing to the 2016 operation in Aleppo, Syria. Samantha Power, then-U.S. ambassador to the United Nations, called Russia’s actions at the time a “modern evil.”
The multipronged conflicts in the Middle East are also becoming more dangerous by the day. Unlike the war in Ukraine, few Western officials believe that instability in the United States would provoke further escalation by Israel, Iran, Hamas in Gaza, or Hezbollah in Lebanon. As it stands, the United States and all of its allies have, thus far, failed to prevent the conflict snowballing into the most dangerous situation the region has seen in decades.
NATO sources, speaking on deep background, said that the West’s near irrelevance in the region is the product of more than a decade’s disengagement there. The political, diplomatic, cultural, and intellectual withdrawal from the Middle East has reduced U.S.-led influence. Why would any regional party act on U.S. demands if they ultimately know no NATO troops are coming and policy toward Israel is unlikely to change?
While instability in the United States isn’t likely to be seized upon in the same way as it could in Ukraine, there are question marks about what the Western response would be if Iran and Israel’s tit-for-tat exchanges get out of control.
“If Israel decides to target civilian and economic infrastructure inside Iran, Tehran’s retaliation would be key,” said Aaron David Miller, a former State Department advisor on Arab-Israeli negotiations and a senior fellow at Carnegie Endowment. “That is the point—that a full-scale war between the two nations might become an active question, which could bring in the United States on the side of Israel.”
That is where a contested election could become an issue. While the Biden administration would still be in power during the transition period, the chaos of uncertainty about the next administration would complicate all foreign-policy decisions, especially in the Middle East.
While overseas wars are the most obvious areas of concern, uncertainty about the outcome of the election would also play into the hands of those who seek to run down and discredit the United States as an example to the world.
“America’s main international rivals are Russia and China, which relish any opportunity to paint Western democracy as a failure,” said Nic Cheeseman, a professor of democracy at the University of Birmingham.
Running down their democratic opponents has been a norm for communist states since the early days of the Soviet Union, and China is no exception. But although the propaganda is constant, it gets a big credibility boost if it has a real basis. If there is violence on the streets of the United States or people claiming the election was rigged, then is democracy really so great? If open society cannot keep people safe or the country stable, then maybe a communist dictatorship is better than liberal democracy and human rights?
U.S. diplomacy has already been affected by internal politics, with the tortuous Capitol Hill arguments over Ukraine funding being the most obvious and recent example. What might that look like if Republicans drag their heels on the confirmation hearings of officials or diplomats that Harris, as president, might want to appoint?
Instability in U.S. politics has the potential to cause global uncertainty. Of course, it’s natural that U.S. voters will be primarily concerned with the domestic implications of their own election. But a vacuum in Washington creates opportunities for people who want to diminish the United States and its values to step in and redefine the international order in their own autocratic image.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the U.S. Response to Avian Influenza, Echoes of Covid-19 - Published Sept 2, 2024
By Joshua Cohen
It’s been about five months since the Texas Department of State Health Services announced that a worker on a dairy farm had tested positive for avian influenza A (H5N1) virus after being exposed to apparently infected cattle. Since then, the U.S. public health response has been slow and disjointed, bringing back memories of how the federal government responded during the early phase of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Despite having a pandemic playbook in early 2020, the U.S. appeared flat-footed in its response to Covid-19, including inadequate testing and unavailable personal protective equipment. And throughout the pandemic, mixed messaging on masks and later vaccines set back public health efforts.
As H5N1 circulates, it seems that lessons from Covid-19 remain unlearned. It appears that missteps are being made regarding testing, surveillance, transparency, and failure of communication and coordination throughout the health care system, the same kinds of things that hurt the response to Covid-19.
“The World Health Organization,” according to NPR, “considers the virus a public health concern because of its potential to cause a pandemic.” What may be concerning is that the genetic sequence of the Spanish flu that killed between 50 and 100 million people from 1918 to 1919 was later found to be an H1N1 virus that originated in birds and then somehow adapted to humans. And based on confirmed cases, the case fatality rate could be as high as 50 percent, as over the past two decades roughly half of about 900 people around the globe known to have contracted bird flu died from it. (There are two caveats, however: Due to limited testing, there were likely more cases that were undetected which would lower the mortality rate. And in the last two years, the global case fatality rate seems to have decreased.)
As of Aug. 30, the U.S. Department of Agriculture reports that 196 dairy cow herds in 14 U.S. states have confirmed cases of avian influenza.
There have been 14 reported cases in humans since 2022, all of whom were exposed to cattle or poultry, and reports suggest that there may be even more sick farm workers who haven’t been tested. There’s no evidence the virus has started to spread among people, but that could change as the situation evolves. The possibility of spillover is always of concern to experts. One of two main competing theories of coronavirus origins and how it evolved into a human-to-human transmissible infection is zoonotic transfer from mammals sold at a wet market in Wuhan, China, to humans.
Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack declared at a press conference in June that his department “is trying to corner the virus,” while releasing a report that human activity is a conduit to bird flu being transmitted between animals when workers, cows, vehicles and equipment move between farms.
But experts have voiced sharp criticism of the U.S. government’s response, especially around the lack of comprehensive surveillance efforts to ascertain the extent of the outbreak. When interviewed by KFF Health News, Jennifer Nuzzo, director of the Pandemic Center at the Brown University School of Public Health said, “We’re flying blind.” Without sufficient testing, it’s impossible to know how many animals and humans have been infected or whether the virus has begun to spread between people.
As could have been learned from the Covid-19 experience, integral to conventional approaches to curbing transmission of infectious diseases is a comprehensive set of track, isolate, and contact trace policies. These have not been systematically implemented.
"Without a collective effort across all states, there’s nothing to stop avian flu from spreading around the country."
Michigan stands out as a state with a robust policy to track human and animal infections and investigate which activities pose the most risk. First, the state’s chief medical executive told STAT, Michigan tested more individuals this spring than any other state. And then the Department of Health and Human Services in Michigan launched a pioneering effort to detect asymptomatic (silent) bird flu infections among farmworkers. Furthermore, a press release from the Michigan Department of Agriculture and Rural Development notes that under state rules dairy and commercial poultry producers must implement biosecurity practices, which include establishing cleaning and disinfection protocols at access points for individuals and vehicles.
Investigators believe the virus may have begun to spread in Michigan when workers operating multiple dairy and poultry operations came in close contact with infected cows and moved from one farm to another.
In April, the USDA issued a federal order requiring testing before lactating dairy cattle can be moved across state lines. Michigan, along with nearly two dozen other states, has also issued its own restrictions. But without a collective effort across all states, there’s nothing to stop avian flu from spreading around the country.
Furthermore, how effective can containment be when the USDA’s order only requires testing for bird flu in lactating cows prior to interstate movement, and no other types of animals?
One of the challenges in managing any major outbreak is the question of who’s in charge to coordinate across departments, such as Health and Human Services, Agriculture, and Commerce. For the purpose of inter-department coordination, the Biden administration launched an Office of Pandemic Preparedness and Response Policy in 2023.
Among federal agencies, the CDC (housed within the Department of Health and Human Services) appears to be the most actively involved in coordinating state efforts. It has provided assistance for a seroprevalence study in Michigan, to assess whether asymptomatic infections are present in people, for example.
But despite these efforts, there’s lack of clarity around who has jurisdictional authority over what and where. Rick Bright, a virologist and immunologist and former head of the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, explained to CNN why he thinks that a more transparent and comprehensive approach to testing and genetic sequencing is needed. He’s concerned that viral adaptations can occur if there are enough opportunities through uncontrolled spread.
The CDC does now have a roadmap, which it announced for preventing and understanding human infection with bird flu and a plan to develop countermeasures. The roadmap’s main objectives include infection prevention by deploying PPE; examination of primary modes of transmission and estimates of incubation periods, duration of infection and severity; monitoring of genetic changes in the virus; and evaluating vaccines and antivirals. CDC Director Mandy Cohen said lessons from Covid-19 have been learned and that CDC is building upon them, for instance, through its wastewater surveillance efforts.
The CDC’s ability to implement these lofty goals may be hampered, however, by seemingly limited resources. The federal government has pledged only modest new funds this year of approximately $200 million to help track and contain H5N1. Separately, the government is allocating $176 million in Moderna to develop an mRNA vaccine against H5N1.
And conspicuously absent are concrete plans, such as how to deploy the stockpile of 10 million doses of avian flu vaccines the federal government currently has as well as the inventory of the antiviral Tamiflu (oseltamivir). By contrast, Finland is now offering vaccines to farmworkers.
"The CDC’s ability to implement these lofty goals may be hampered, however, by seemingly limited resources."
Aside from inadequate funding and preparation, there’s a problem of overcoming public distrust. A survey published in Health Affairs suggests that about 42 percent of American adult respondents in early 2022 said they had confidence in the CDC to provide quality health information during the Covid-19 pandemic, while about a third said they trusted state and local health departments. This may partly explain why the CDC is now having trouble getting farmers to cooperate with even rudimentary tracking and mitigation efforts regarding H5N1.
Lessons from the history of how Covid-19 unfolded underscore the importance of not being complacent in the face of a potential future bird flu pandemic. It would seem imperative to take proactive measures such as systematic testing of animals and humans exposed to the virus, mitigate transmission risk in the dairy and poultry industries, and coordinate federal and state responses.
#covid#mask up#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#coronavirus#sars cov 2#public health#still coviding#wear a respirator#h5n1#avian flu#avian influenza#bird flu
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this New York Times story:
Amid a deluge of terrifying headlines about destructive tornadoes, blistering heat waves and DVD-sized gorilla hail, here’s a surprising bit of good news: Global carbon dioxide emissions may have peaked last year, according to a new projection.
It’s worth dwelling on the significance of what could be a remarkable inflection point.
For centuries, the burning of coal, oil and gas has produced huge volumes of planet-warming gasses. As a result, global temperatures rose by an average of 1.5 degrees Celsius higher than at the dawn of the industrial age, and extreme weather is becoming more frequent.
But we now appear to be living through the precise moment when the emissions that are responsible for climate change are starting to fall, according to new data by BloombergNEF, a research firm. This projection is in roughly in line with other estimates, including a recent report from Climate Analytics.
Thanks to the rapid build-out of wind and solar power plants, particularly in China, global emissions from the power sector are set to decline this year. Last year, the amount of renewable energy capacity added globally jumped by almost 50 percent, according to the International Energy Agency.
And with the rise of electric vehicles and heat pumps, similar gains are anticipated in the transportation sector and residential buildings.
Forecasting emissions is an inexact science. Greenhouse gas levels fell during the Covid-19 pandemic, then spiked as the world emerged from lockdown. Other wild cards, such as melting permafrost or huge wildfires, could further scramble projections. Nevertheless, the data suggests that after centuries of growth, humans are finally on the cusp of reducing the overall production of heat-trapping gases.
The decline in emissions will not be swift. Even if every government and business in the world made combating climate change a top priority, it would still take at least two decades, and an estimated $215 trillion, to make a full transition to an emissions-free world.
Doing so, the report said, would require the immediate adoption of what would essentially be a wartime approach to constructing renewable energy and subsidizing low-carbon technologies, and a set of strict regulatory measures designed to curb emissions-heavy modes of transportation, energy production and industry. For example, BloombergNEF projects that no new internal combustion engine vehicles could be sold after 2034.
In such a scenario, the BloombergNEF report forecasts that it may be possible to achieve net zero emissions by 2050, resulting in an average global temperature rise of 1.75 degrees above preindustrial levels.
3 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Protesters in China demand Xi Jinping step down, November 27, 2022
Unrest is growing in China over the country's strict COVID-19 measures. Fresh protests have broken out in major cities, with hundreds rallying at Beijing's elite Tsing-hua University, chanting 'we want freedom.' Many also held up blank sheets of paper in a symbolic protest against state censorship. More demonstrations have also been reported in Shanghai, following clashes with police overnight. Public anger has flared after a deadly apartment block fire, with many blaming an ongoing lockdown for hampering rescue efforts. Chinese officials have defended their zero-covid policy, despite the growing public backlash.
Deutsche Welle
Further reading:
AFP, via HKFP: Protests in Shanghai as anger mounts over China’s zero-Covid policy, November 27, 2022
BBC: China Covid: Protesters openly urge Xi to resign over China Covid curbs, November 27, 2022
The Guardian: Anti-lockdown protests spread in China as anger rises over zero-Covid strategy, November 27, 2022
Reuters: Blank sheets of paper become symbol of defiance in China protests, November 27, 2022
#Xi Jinping#Chinese Communist Party#china#COVID 19#Urumqi#tsinghua university#Beijing#shanghai#censorship#protest#surveillance#police#pandemic#politics#zero covid policy#Deutsche Welle#BBC#nanjing#zhengzhou#guangzhou#hong kong free press#Agence France Presse#Hong Kong#Russia#Moscow#Reuters
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Increased Surveillance by the China Government during the Global COVID-19 Pandemic Affects Online Communities?

In the wake of the global COVID-19 pandemic, governments worldwide, including China, intensified surveillance measures to curb the virus's spread. In this context, China's implementation of stringent surveillance, notably through Health Code Apps, has raised profound concerns about its impact on online communities. As facial recognition and data collection become intrinsic to daily life, the potential repercussions on digital spaces and the people within them demand careful examination. This discussion delves into the multifaceted consequences of increased surveillance by the Chinese government and its tangible effects on the dynamics of online communities.
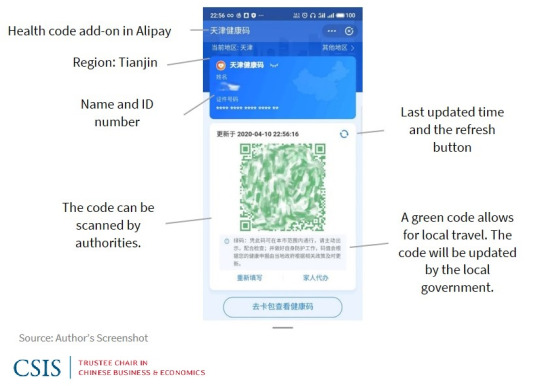

Privacy Erosion
In response to the global COVID-19 pandemic, various countries implemented measures to track and control the virus's spread, introducing tools such as contact tracing apps (Ojokoh et al., 2022), temperature checks (Qu & Lv, 2021) and travel restrictions (Burns et al., 2021). Simultaneously, In China, where stringent surveillance measures were already in place, the government leveraged technology to an even greater extent, using facial recognition and health QR codes to monitor citizens' movements. This involved the deployment of a series of applications known as "Health Code Apps," which have raised concerns about privacy erosion, particularly regarding the use of health code applications. Online communities are not immune to this erosion, as the data collected through these apps includes personal information, health status, and location details. This data is then utilized to assign one of three colours, indicating the user's health status (Ramos, 2020). However, Data is funnelled to entities like the provincial Big Data Bureau, Alibaba, and the telecommunications department, expanding the accessibility to user information, ranging from personal details to health status, location, and device specifics. This centralized model amplifies the risks of data aggregation and user re-identification, exemplified by the Beijing Health Bao system's data leak in December 2020. The incident exposed the photographs, ID numbers, and nucleic acid test information of celebrities, highlighting insufficient safeguards in place (Zhang, 2022). Online communities may find their members exposed to privacy breaches, leading to a chilling effect on open communication and expression within these digital spaces.

Potential for Abuse of Power:
The potential for the abuse of power in the context of surveillance, inadequate transparency and compliance measures is a significant concern for online communities as well. This concern is exemplified by recent events in Henan Province, where health code apps were allegedly manipulated to suppress protests related to potential losses in rural banks on the brink of collapse (Zhang, 2022). The legitimacy of these health code apps faced a setback as city officials marked over a thousand individuals as red, restricting their entry into Zhengzhou City and highlighting the vulnerability of such systems to misuse (Zhang, 2022). This incident underscores the potential for health code apps, initially designed for public health purposes, to transform into tools of surveillance, allowing government agencies to exert control under the guise of maintaining public health. The lack of stringent transparency requirements heightens the risk of these technologies being misused for purposes beyond their intended scope, which negatively impacts the freedom of expression within online communities. As governments exploit surveillance tools to monitor and influence online discussions, online communities may face challenges related to censorship and control, further emphasising the interconnected nature of surveillance concerns and their impact on digital spaces.
Technological Dependence:
Embracing extensive surveillance often involves a reliance on advanced technologies. In the case of Health Code Apps, facial recognition technology is integrated into residential area access control systems, permitting entry only to those with a green code (Ramos, 2020), which has implications for online communities. This reliance on advanced technologies may neglect more human-centric approaches to online interaction, potentially excluding or disadvantaging certain members of digital communities. As surveillance technologies become integral to online platforms, the balance between security measures and preserving the inclusivity and diversity of online communities becomes a critical consideration.
Trust Deficit:
The colour-coded system assigned by health code applications has far-reaching consequences for millions of users in their interactions within both physical and online communities. Requiring individuals to display their health codes in public transportation, shopping malls, markets, and other public places may contribute to a trust deficit between citizens and the online platforms they engage with (Jao et al., 2020). Users within online communities may question the motives behind such surveillance measures, especially if their personal information is shared without their knowledge. Rebuilding trust within online communities, once eroded by mandatory health code reliance, poses a considerable challenge, impacting the dynamics of digital social spaces.
In conclusion, the surge in surveillance by the Chinese government amid the global COVID-19 pandemic undeniably leaves a lasting imprint on online communities. The colour-coded system mandated by health code applications not only infiltrates public spaces but also infiltrates the very essence of digital interactions. This imposition triggers a tangible trust deficit within online communities as individuals question the motives behind these surveillance measures. Rebuilding trust within these virtual spaces, essential for vibrant and open communication, becomes a formidable challenge in the aftermath of mandatory health code reliance. The delicate equilibrium between bolstering security measures and safeguarding the inclusivity of online communities emerges as the linchpin for preserving the dynamic and diverse nature of these digital spaces. In essence, the impact of increased surveillance by the Chinese government is intimately intertwined with the well-being and resilience of online communities.
"Considering the implications of increased surveillance by the Chinese government during the global COVID-19 pandemic on online communities, we'd like to hear your perspective. How do you perceive the effects on privacy erosion, potential abuse of power, technological dependence, and the trust deficit within these digital spaces? Share your insights and cast your vote below."
Reference List
Burns, J., Movsisyan, A., Stratil, J. M., Biallas, R. L., Coenen, M., Emmert-Fees, K., Geffert, K., Hoffmann, S., Horstick, O., Laxy, M., Klinger, C., Kratzer, S., Litwin, T., Norris, S. L., Pfadenhauer, L. M., Von Philipsborn, P., Sell, K., Stadelmaier, J., Verboom, B., . . . Rehfuess, E. (2021). International travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review. The Cochrane Library, 2021(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd013717.pub2
Jao, N., Cohen, D., & Udemans, C. (2020). How China is using QR code apps to contain Covid-19. TechNode. https://technode.com/2020/02/25/how-china-is-using-qr-code-apps-to-contain-covid-19/
Ojokoh, B. A., Aribisala, B. S., Sarumi, O. A., Gabriel, A. J., Omisore, O. M., Taiwo, A. E., Igbe, T., Chukwuocha, U. M., Yusuf, T. A., Afolayan, A., Babalola, O., Adebayo, T., & Afolabi, O. (2022). Contact Tracing Strategies for COVID-19 Prevention and Containment: A scoping review. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 6(4), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6040111
Qu, J., & Lv, X. (2021). The response measures to the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak in China. Open Forum Infectious Diseases, 8(2). https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofab014
Ramos, L. F. (2020). Evaluating privacy during the COVID-19 public health emergency. The ACM Digital Library, 176–179. https://doi.org/10.1145/3428502.3428526
Zhang, X. (2022). Decoding China’s COVID-19 health code apps: the legal challenges. Healthcare, 10(8), 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10081479
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
A senior health official in Beijing has urged China's local leaders to find ways to boost the country's birth rate.
Yang Wenzhuang said officials must take active steps to tackle the detrimental effects of China's long-standing anti-population growth policy.
He also urged officials to "make bold innovations" in tackling the cost of childcare and education.
China reported in January that that its population had fallen for the first time in 60 years.
In 2022, there was just 6.77 births per 1,000 people in China, the lowest birth rate on record and down from 7.52 births in the previous year.
The country's strict one-child policy - which was implemented from 1980 to 2015 to respond to runaway population growth - has been blamed for the decline. Families that broke the rules were fined and, in some cases, even lost jobs.
The limit was increased nationally for married couples to two in 2016, and boosted further to three in 2021. But one province - Sichuan - has adopted even looser rules.
Mr Yang - who heads the country's Population Monitoring and Family Development department - said officials had to "firmly grasp the important window period of population development".
Speaking to a state-backed health magazine, Mr Yang said concerns about the cost of childcare were having a detrimental impact on population growth. He also identified challenges around money and career goals as causes for for the decline.
"Local governments should be encouraged to actively explore and make bold innovations in reducing the cost of childbirth, childcare and education" to promote the long-term balanced development of the population, Mr Yang said.
Mothers, your country needs you!
Some provinces have already begun implementing new measures to try to boost the birth rate, including giving money to sperm donors and giving unmarried couples who have children the same benefits as married couples.
In Sichuan, health authorities said they would allow unmarried couples to raise and family and enjoy benefits reserved for married couples. Previously there was a ban on single women registering a birth.
Authorities in the region also announced that couples would be allowed to have be allowed to have as many children as they want - a major reversal of the one -child poliy.
A shrinking population, falling birth rate and the prospect of a fast-aging population poses a long-term challenge to the world's second largest economy, which only recently dropped ultra-strict COVID-19 curbs.
A surging Indian economy also threatens to overtake China and push it down to third place.
In 2022, there was just 6.77 births per 1,000 people in China, the lowest birth rate on record and down from 7.52 births in the previous year.
The population on the other hand dropped by 850,000 people to 1.41175 billion, according to the National Bureau of Statistics. It was the first decline since 1961, the last year of China's Great Famine.
#nunyas news#see what happens if china bans abortion#wouldn't put it past them at all#be interesting to see the response in the western world too
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Leaked report on China's Covid crisis: 250 million people infected in 20 days of lifting curbs | World News
Leaked report on China’s Covid crisis: 250 million people infected in 20 days of lifting curbs | World News
Beijing: Almost 250 million people in China may have been affected by Covid-19 in just 20 days after the `zero-covid policy` was diluted in the first week of the month, according to radio Free Asia citing leaked government documents circulating on social media. In the 20-minute meeting of China`s National Health Commission, as per the leaked document look like, 248 million people were infected…
View On WordPress
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wednesday, November 13, 2024
Extreme weather cost $2tn globally over past decade, report finds (Guardian) Violent weather cost the world $2tn over the past decade, a report has found, as diplomats descend on the Cop29 climate summit for a tense fight over finance. The analysis of 4,000 climate-related extreme weather events, from flash floods that wash away homes in an instant to slow-burning droughts that ruin farms over years, found economic damages hit $451bn across the past two years alone. The report found a gradual upward trend in the cost of extreme weather events between 2014 and 2023, with a spike in 2017 when an active hurricane season battered North America. The US suffered the greatest economic losses over the 10-year period, at $935bn, followed by China at $268bn and India at $112bn. Germany, Australia, France and Brazil all made the top 10. When measured per person, small islands such as Saint Martin and the Bahamas saw the greatest losses.
Optimism and uncertainty at summit as Middle East awaits Trump’s return (BBC) As leaders of dozens of Arab and Islamic nations gather in the Saudi capital for a summit, there is widespread speculation about what a second Trump presidency will mean for the region. In sharp contrast to the fears voiced in Europe about Donald Trump’s famous unpredictability, Gulf Arab countries tend to view him as a force for stability. Writing in the officially approved Arab News opinion column, the prominent UAE business leader Khalaf al-Habtoor says: “In a Middle East where security is paramount, Trump’s focus on strengthening alliances and curbing extremist forces offers a way forward.” Here in Saudi Arabia, Trump is viewed much more favourably than Joe Biden. Through his son-in-law Jared Kushner, Trump enjoys warm relations with the de facto Saudi ruler, Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, known by his initials, MBS. The crown prince has never forgiven or forgotten Biden saying that Saudi Arabia needed to be made a pariah for its attitude to human rights.
As the Pandemic Deepened, Americans Kept Drinking More (NYT) Americans started drinking more as the Covid-19 pandemic got underway. They were stressed, isolated, uncertain—the world as they had known it had changed overnight. Two years into the disaster, the trend had not abated, researchers reported on Monday. The percentage of Americans who consumed alcohol, which had already risen from 2018 to 2020, inched up further in 2021 and 2022. And more people reported heavy or binge drinking. “Early on in the pandemic, we were seeing an enormous surge of people coming in to the clinic and the hospital with alcohol-related problems,” said Dr. Brian P. Lee, a hepatologist at Keck Medicine of the University of Southern California and the principal investigator of the study, published in Annals of Internal Medicine. Rates of heavy drinking and of alcohol-related liver disease had been rising steadily for decades before the pandemic struck. But alcohol-related deaths surged in 2020, with one study reporting a 25 percent increase in a single year, said Christian Hendershot, director of clinical research at U.S.C.’s Institute for Addiction Science.
Fire crews on both US coasts battle wildfires (AP) Fire crews battled small wildfires across the Northeast U.S. on Monday, including a blaze in New York and New Jersey that killed a parks employee over the weekend and postponed Veterans Day plans. The fire is one of several burning on the East Coast amid a lack of much rainfall since September. The East Coast fires were burning as much larger wildfires raged in California. Firefighters continued making progress against a wildfire northwest of Los Angeles in Ventura County that broke out Wednesday and quickly exploded in size due to dry, warm and gusty Santa Ana winds. The Mountain Fire in Ventura County prompted thousands of residents to flee their homes and was 41% contained as of Monday. The fire’s size remains around 32 square miles (about 83 square kilometers). In neighboring Nevada, authorities ordered the evacuation of hundreds of homes southwest of Reno and closed the main highway to Lake Tahoe after a wind-whipped wildfire erupted Monday and spread quickly through mountainside vegetation.
Haiti’s main airport shuts down as gang violence surges and a new prime minister is sworn in (AP) Haiti’s international airport shut down on Monday after gangs opened fire at a commercial flight landing in Port-Au-Prince, prompting some airlines to temporarily suspend operations as the country swore in a new interim prime minister who promised to restore peace. The Spirit Airlines flight headed from Fort Lauderdale, Florida, to Port-Au-Prince was just hundreds of feet from landing in Haiti’s capital when gangs shot at the plane striking a flight attendant, who suffered minor injuries, according to the airline, the U.S. Embassy and flight tracking data. The flight was diverted and landed in the Dominican Republic. Photos and videos obtained by The Associated Press show bullet holes dotting the interior of a plane.
Dutch tram set on fire while tensions are high after violence targeting Israeli fans (AP) Dozens of people armed with sticks and firecrackers set a tram on fire in Amsterdam on Monday, police said, while the city is facing tensions following violence last week targeting fans of an Israeli soccer club. Police said the fire was quickly extinguished and riot officers cleared the square. Images online showed people damaging property and setting firecrackers. Police said it was not clear who started the unrest and whether it was related to what happened last week. But they noted the tense atmosphere since five people were treated in the hospital and dozens detained Thursday following a Maccabi Tel Aviv-Ajax match. Reports of antisemitic speech, vandalism and violence have been on the rise in Europe since the start of the war in Gaza.
Russian glide bombs, drones and a ballistic missile kill 6, injure 30 in Ukraine (AP) Russian glide bombs, drones and a ballistic missile smashed into cities in southern and eastern Ukraine on Monday, officials said, killing at least six civilians and injuring about 30 others. Ukraine President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said that Russia has recently intensified strikes that have long tormented civilian areas, in an apparent effort to unnerve Ukrainians and wear down their willingness to keep up a war that is approaching its 1,000-day milestone. Both Russia and Ukraine are waiting to see how Washington will change its policy on the war after Donald Trump takes office as the U.S. president in January. The U.S. is the biggest provider of military help to Ukraine, but Trump has chided the Biden administration for giving Kyiv tens of billions of dollars of aid.
With new stealth fighter, China displays ambitions to challenge U.S. (Washington Post) China on Tuesday debuted its latest model of stealth fighter jet and foreshadowed an ambitious pipeline of advanced drones, as Beijing displayed its determination to match American military might by investing heavily in the latest tech and forging ever-closer bonds with partners like Russia. The maiden flight demonstration of the J-35A, a “fifth generation” fighter designed to evade radar detection and attack enemy targets at supersonic speeds, was the main attraction on the opening day of the Zhuhai air show on Tuesday. Chinese manufacturers have churned out huge numbers of ships, warplanes, missiles and drones to enforce Beijing’s sweeping territorial claims—and send a warning to the United States and its allies. Also on display were China’s efforts to present itself as an alternative to the United States when it comes to arms and as a reliable security partner for nations that share Beijing’s hostility toward the U.S.-led military alliance network. “By holding an air show of such proportion with such high publicity, China is definitely trying to [reach out to] like-minded countries in the ‘global south’ that are tired of western sanctions and don’t trust western technology,” said Collin Koh, a defense expert at the S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies in Singapore.
Driver rams his car into crowd in China, killing 35 (AP) A man who authorities said was upset over his divorce settlement rammed his car into a crowd of people exercising at a sports complex in southern China, killing 35 and severely injuring dozens of others, police said Tuesday. Police detained the 62-year-old man, who is being treated for wounds thought to be self-inflicted, shortly after the attack Monday night in the southern Chinese city of Zhuhai. The city is hosting the People’s Liberation Army’s annual aviation exhibition, which opened Tuesday, and searches for what happened were heavily censored for users behind China’s Great Firewall. Outside of the controls, however, videos circulated on the social media platform X. In several, dozens of people could be seen lying on the track at the sports complex, which is regularly used by hundreds of residents to run, play soccer or dance.
Ishiba survived a rare runoff to remain Japan’s prime minister but will face turmoil (AP) Japanese Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba, battered in parliamentary elections last month, has survived a rare runoff vote against the opposition to remain the country’s leader but he still faces turmoil ahead. One of his top priorities is dealing with the aftermath of a major corruption scandal in the long-ruling Liberal Democratic Party, in which dozens of lawmakers from the party are alleged to have pocketed profits from event ticket sales as kickbacks. Ishiba also now has a much-emboldened, opposition eager to push through policies long stymied by the LDP. Support ratings for his Cabinet have fallen to about 30%. Ishiba also faces challenges of restoring unity in his own party. A number of senior LDP lawmakers are waiting to overthrow him.
Israel Issues New Evacuation Warnings in Lebanon (NYT) The Israeli military issued new evacuation warnings for more than 20 towns and villages in southern Lebanon on Monday, and Hezbollah unleashed a large rocket barrage into northern Israel, the latest indications that the conflict showed few signs of abating. The widespread warnings across Lebanon’s south, the first in nearly a month, called on civilians to evacuate their homes immediately and move north above the Awali River, farther from the Israeli border. The river effectively demarcates southern Lebanon, which Israel invaded last month in a bid to destroy Hezbollah’s infrastructure and stop it from firing rockets and missiles into Israel. Repeated rounds of shuttle diplomacy over the past year, led by the Biden administration, have so far failed to contain the conflict between Israel and Hezbollah, which began last October when Hezbollah started its cross-border assaults in support of Hamas in Gaza. Officials say 3,200 people have been killed in Lebanon and more than a fifth of the population displaced.
Caught Between Wars, Syrian Refugees in Lebanon Return Home (NYT) When the civil war in Syria threatened his village more than a decade ago, a farmer and his family fled to neighboring Lebanon. The farmer, Ali Kheir Khallu, 37, found work there growing oranges and bananas. Life was hard, he said, but at least he felt safe. That feeling vanished last month as Israel ramped up its war with Hezbollah, the powerful Lebanese militia, heavily bombing sites that it said belonged to the group. When the bombs fell near Mr. Kheir Khallu’s house, he packed up his family, left behind the new lives they had built in Lebanon and fled back to Syria, where they are now struggling to start over, yet again. As the war in Lebanon expands, more than 1.2 million people—one-fifth of the population—have been displaced from their homes, the government says. While most have sought safety in other parts of Lebanon, more than 470,000 people, mostly Syrians, have crossed into Syria in the last six weeks, aid groups say.
0 notes
Text
Future of Coating Equipment Market: Trends and Predictions
The global coating equipment market was valued at USD 16.62 billion in 2021 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2022 to 2030. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for coatings in various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and construction. Coatings play a critical role in enhancing the durability, appearance, and performance of products across these industries. Despite a significant downturn in demand during the pandemic—caused by lockdowns and global restrictions to curb the spread of COVID-19—the industry is poised for recovery as governments ease restrictions and economic activities resume. Once the global economy stabilizes, the demand for coatings is expected to rebound.
A significant factor contributing to the market’s growth is the rising global demand for electric vehicles (EVs). Coatings are essential for EVs to protect against rust and corrosion, ensuring that the vehicles' surfaces remain intact and visually appealing. Moreover, the growing interest in coated electronic devices used in electric cars, including batteries, motors, and interior components, further strengthens the demand for coating solutions. As the automotive industry moves toward sustainability and electrification, coating technologies become increasingly important in meeting the functional and aesthetic demands of modern vehicles.
Governments worldwide are supporting the transition to electric-powered vehicles through a variety of subsidies and incentives, such as tax breaks for electric car buyers, funding for the installation of charging stations, and budget allocations for advanced battery development. These initiatives, combined with the growing focus on environmental sustainability and reducing carbon footprints, are expected to significantly boost the demand for coating equipment over the forecast period.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Coating Equipment market
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region led the global coating equipment market in 2021, capturing 45.3% of the market share. Several key factors contribute to this dominance, including robust industrial development, a growing construction sector, and an expanding automotive industry. The region's high population growth further increases demand for diverse products that require coating applications, such as automobiles, industrial machinery, and consumer goods. Additionally, the demand for coatings with better efficiency, driven by the need for more durable, sustainable, and high-performance products, is expected to fuel the market’s growth over the forecast period.
Governments in the Asia Pacific are heavily investing in infrastructure development, which further boosts the need for coatings in construction projects, including residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. This trend is anticipated to create strong demand for coating solutions, particularly in fast-developing economies such as China, India, and Southeast Asia.
Europe
In Europe, the coating equipment market is expected to see significant growth, primarily driven by efficiency improvements in existing buildings and renovations. As older buildings are retrofitted with more energy-efficient solutions, there is an increasing need for advanced coatings that improve durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetics. The region's emphasis on sustainability and green building standards plays a key role in this trend.
Additionally, the planning of public-private partnership (PPP) projects across Europe, including road construction, hospital development, schools, and airports, is expected to further drive the demand for coatings. These infrastructure projects often require coatings for protection, aesthetics, and to meet environmental regulations. This growing focus on both infrastructure expansion and energy-efficient renovations is poised to stimulate demand for coating technologies throughout the forecast period.
North America
In North America, the United States held the largest share of the market, accounting for 57.5% of the coating equipment industry in 2021. The U.S. market is driven by substantial government investments aimed at increasing industrial employment and stimulating manufacturing growth. These investments, particularly in advanced manufacturing and infrastructure projects, create a favorable environment for the adoption of coating equipment.
Moreover, the automotive sector in North America is experiencing a surge in demand for coating solutions due to the growing production of electric vehicles (EVs). Coatings are essential in the automotive industry, especially for vehicles like electric cars, which require special coatings for enhanced performance, durability, and appearance. The presence of major automotive manufacturers such as General Motors, Ford, and Tesla, as well as key automotive OEMs in the region, continues to drive demand for advanced coating technologies. Additionally, government incentives for electric vehicle production are expected to accelerate the demand for coating equipment tailored for these vehicles.
Browse through Grand View Research's Paints, Coatings & Printing Inks Industry Research Reports.
• The global hydrophobic coating market was valued at USD 2.06 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5% from 2024 to 2030.
• The global nanocoatings market size was valued at USD 12.86 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.4% from 2024 to 2030.
Key Companies & Market Share Insights
The coating equipment market is highly competitive, with several prominent players dominating the industry. These companies are focused on advancing technological capabilities and developing innovative solutions to meet the evolving needs of consumers. Leading market players are investing in automated systems, advanced coating equipment, and various specialized components like hand sprays and trolleys to cater to diverse application requirements. Additionally, mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships are key strategies for companies looking to enhance their technical expertise and expand their product offerings
Key Coating Equipment Companies
Some prominent players in the global coating equipment market include:
• Nordson Corporation
• Gema Switzerland GmbH
• J. Wagner GmbH
• ANEST IWATA Corporation
• Carlise Companies Inc
• IHI Ionbond AG
• Statfield
• SAMES KREMLIN
• The Eastwood Company
• Graco Inc
• RED LINE INDUSTRIES LIMITED
• Pittsburgh Spray
• Reliant Finishing Systems
• ANEST IWATA USA, Inc.
• IHI HAUZE B.V.
Order a free sample PDF of the Coating Equipment Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
#Coating Equipment Market#Coating Equipment Market Analysis#Coating Equipment Market Report#Coating Equipment Industry#Coating Equipment Market Regional Insights
0 notes
Text
People In China Are Demanding The End Of Strict COVID Restrictions After 10 People Died In A Fire
Protests are continuing in China against strict COVID lockdown restrictions after a deadly apartment fire brought some people closer to a breaking point. Across the country, demonstrators took to the streets — a mass movement that is rare in China — and defied laws designed to curb the spread of COVID-19. Some appeared with sheets of blank white paper, in place of traditional protest signs, as a…
0 notes
Text
Picture this scenario. It’s 2028, and U.S. intelligence services have assessed that the Chinese military is preparing a full-scale invasion of Taiwan to make good on Chinese President Xi Jinping’s pledge to “reunify” the island with the mainland. In a desperate attempt to deter the attack, Washington leads G-7 efforts to threaten Beijing with massive economic sanctions. The stakes are high, but there is a catch: China has likely priced in the costs of U.S. sanctions in its invasion calculations. And if the current trajectory of U.S.-Chinese economic and financial disengagement is any indication, U.S. leverage over Beijing will have substantially waned by 2028.
Any signal of an impending Chinese invasion of Taiwan would send G-7 policymakers into overdrive. Alongside a possible military response, G-7 allies would likely threaten sanctions as part of a deterrence package. On sanctions, the worry for Beijing could be the extent to which other major economies will join Washington’s efforts. Among U.S. allies and partners, the stance of the European Union would probably be the one that matters most to Beijing. Trade with the EU accounts for China’s largest trade surplus—more than the surplus with the United States and roughly equal to China’s surplus with all developing economies put together.
Sanctions deterrence is hard to get right. For it to succeed, Chinese leaders would have to be convinced that the costs associated with an invasion would be painfully higher than what they have already factored in. This would not be easy, as Chinese policymakers know that an aggression against Taiwan would come at a very high price; economists reckon that a conflict over the island could shave up to 10 percent off global GDP growth, a hit nearly twice as high as that caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
This is precisely why EU sanctions threats could be critical in the run-up to a Taiwan conflict. Ahead of an invasion of Taiwan, Beijing would fully price in the costs associated with retaliatory sanctions from the United States and several key U.S. partners, including Britain, Canada, and Japan. However, Chinese leaders would likely assume that they could prevent the EU from joining in. They may believe in their continued ability to exploit divisions among EU member states, for instance by getting support from Beijing’s European partners. Hungary, which received nearly half of all Chinese foreign direct investment in Europe last year, would be a main suspect. Precisely because Beijing believes it can avoid a major economic and financial rupture with Europe, EU sanctions threats could thus prove game-changing, as they would do exactly what sanctions deterrence is supposed to achieve: substantially change Beijing’s cost-benefit calculation for an invasion.
History shows that European policymakers have a tendency to hope for the best, rather than prepare for the worst. That makes serious EU planning for a Taiwan contingency unlikely in the coming years. Were an invasion scenario to materialize, European policymakers would need to quickly decide whether to go down the sanctions road and assess which economic statecraft measures are the likeliest to sway Beijing’s thinking. The Western sanctions toolkit relies on three tools: financial sanctions that leverage the preeminence of G-7 currencies in global trade, export controls that deprive adversaries of access to top-notch technology in a bid to degrade their military capabilities, and trade measures that curb the export revenues of foes through tariffs or import bans. However, recent developments suggest that by 2028 the traditional Western sanctions toolkit may have become mostly ineffective against Beijing.
Start with financial sanctions. In recent months, Chinese firms have crossed a symbolic threshold: They now invoice the majority of their cross-border trade in renminbi, up from 0 percent in 2010—a prerequisite if China is to eventually avoid Western-controlled financial channels. By 2028, Chinese firms will likely use the renminbi even more than they already do, partly shielding their transactions from Western financial sanctions. What’s more, the inconvenient truth for EU policymakers is that China cares more about its access to the U.S. dollar than to the euro, in which less than 3 percent of China’s global payments are denominated. Finally, China is doubling down on efforts to develop CIPS, its homegrown alternative to SWIFT, the global payments system based in Belgium that connects all of the world’s banks. If China’s transactions are denominated in renminbi and do not go through SWIFT, they become mostly immune to Western financial sanctions. The upshot? Threats of cutting Chinese access to SWIFT or the euro are unlikely to change China’s calculus.
European export controls are similarly unlikely to make much of an impression on China. Over the past several years, Washington has relied on such measures to prevent Chinese firms from closing the technology gap with their U.S. counterparts. So far, the results have been mixed. Despite stringent export controls on semiconductors, for instance, China still manages to make headway in the field. Just last year, Chinese firms manufactured a top-notch 7-nanometer chip. They also appear to be on track to produce 5-nanometer chips this year, suggesting that U.S. export controls are slowing—but not halting—Chinese progress. What’s more, EU policymakers would probably struggle to identify even one sector where European firms hold a substantial technological advantage. In the global tech race, the two leading actors are the United States and China, not Europe. Finally, export controls are unlikely to meaningfully degrade China’s ability to wage war, not least because Chinese leaders will probably want to make sure they have closed the tech gap before invading Taiwan, the world leading manufacturer of microchips.
For Western policymakers, another intriguing trade measure would entail restricting Beijing’s access to critical imports. Leaving food and feedstocks aside, energy could be a priority sector for such measures. Beijing imports 70 percent of its oil consumption, for example. Chinese leaders would likely build large commodity stockpiles before initiating a military conflict, but these would not last forever. The G-7 has a couple of aces up its sleeve to curb China’s oil supplies. First, two G-7 members—the United States and Canada—jointly produce nearly 30 percent of the world’s oil. Second, China’s largest current oil supplier, Russia, would probably struggle to come to Beijing’s rescue, since Russian oil production is likely to drop in the coming years as Western sanctions curb Moscow’s ability to develop new fields. Iran, another member of China’s coalition, would be of little help to Beijing as well. Tehran’s crude production is only 4 percent of global output.
With financial sanctions and export controls out of the equation for the EU, the bloc’s policymakers would still have one option to try to alter China’s calculus around Taiwan: trade measures. EU tariffs or import bans would leverage a fundamental flaw in China’s economic model. Each year, Chinese firms churn out as much in manufactured goods as their counterparts in the United States and the EU combined. Yet the country’s reliance on exports as a driver of growth is also its Achilles’ heel. Exports account for nearly 20 percent of China’s GDP, supporting the livelihoods of at least 100 million Chinese citizens. Despite Beijing’s efforts to deepen trade ties to emerging economies, the EU remains the primary destination for Chinese exports. This gives EU policymakers a valuable card to play: leveraging access to the EU market.
Blanket bans on all Chinese imports would be hugely painful for Europe, since many industrial firms rely on Chinese intermediary inputs and machinery to operate. Instead, the EU could target imports of non-critical consumer goods. EU import bans targeting Chinese goods in just two sectors—electronic and electrical gear, such as kettles, phones, and fridges; and low-end goods, such as clothes, footwear, and toys—could deal a blow to the Chinese economy. If all G-7 economies are in, such import bans could slash China’s exports by a massive 20 percent.
Three data points suggest that the bloc will retain substantial leverage over Beijing by 2028. First, EU imports from China grew by a whopping 41.9 percent between 2019 and 2023, highlighting how Chinese exporters are not keen to cut ties to the EU. Second, the bloc remains a huge customer for Chinese tech firms; the EU’s reliance on Chinese-made technology-intensive goods is rising steadily. Third, at $8.1 billion, German foreign direct investment in China was higher during only the first six months of 2024 than in all of 2023. This all stands in stark contrast with the United States, which is doubling down on efforts to cut economic ties to China. Since 2019, U.S. imports from China have dropped by nearly 5 percent, even as overall U.S. imports were up by nearly 24 percent.
In the run-up to a Chinese aggression against Taiwan, Europe’s stance could well matter more than both China and the EU currently assume. But making use of this leverage would be no easy feat for the bloc, considering that member states have widely diverging stances over their economic relationships with China. One need only look at current intra-EU fights over electric vehicle tariffs to guess that EU member states have widely diverging views regarding the threat that China poses—or does not pose—to Europe.
But at the same time, the EU’s handling of the European debt crisis, the COVID-19 pandemic, and Russia’s war in Ukraine have shown that the bloc is capable of getting its act together when faced with catastrophe. Given that Europe’s stance could matter far more than it thinks, now would be a good time for the EU and member governments to start planning their response to a Taiwan crisis.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS) Market,Industry Forecast, 2024–2030.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market Overview
Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS) Market Size is forecast to reach $ 80,000 Million by 2030, at a CAGR of 30% during forecast period 2024–2030. The emerging demand for carbon dioxide injection technologies for Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) and stringent government standards for greenhouse gas emissions are the key factors driving the market growth. Carbon Capture and Storage or Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) is a technology to combat climate change in which Carbon dioxide (CO2) is captured and then transported where it is stored permanently across depleted hydrocarbon fields and deep saline aquifer formations. The goal of carbon capture and storage is to keep CO2 emissions out of the atmosphere as increased levels of CO2 is the main culprit behind the Greenhouse effect and global warming which has a detrimental effect not only on the environment and also on the economy as a whole.
Request Sample:

When the COVID-19 pandemic hit, many end use industries like Chemical plants, Iron and Steel, Fertilizer and other industries scaled back production and many were shut down due to lockdowns. In early 2020, investing huge capital for Carbon Capture and Storage projects took a backseat for a while as industries struggled to make profits. For instance, in March 2020 Petra Nova CCS Facility, USA paused all Carbon Capture and Storage operations. On the other hand, as human activities were brought to a complete standstill, the levels of CO2 also decreased. According to the Global Carbon Project, in April 2020, daily global emissions decreased by 17% when compared with the mean 2019 levels. This made people more conscious of the efforts to reduce CO2 emissions and push for clean technologies to combat climate change which in turn boosts the Carbon Capture and Storage market.
Inquiry Before Buying:
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market Report Coverage
The report: “Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market — Forecast (2024–2030)”, by IndustryARC, covers an in-depth analysis of the following segments of the Carbon Capture and Storage Market.
By Capture Technology: Post Combustion Capture, Pre-Combustion Capture, Oxyfuel Combustion and Industrial Separation
By Storage Technology: Geological Storage, Deep Ocean Storage, and Enhanced Oil Recovery (EO
By End-Use Industry: Power Generation, Iron and Steel, Oil and Gas, Chemicals, Cement and Concrete, Biofuels, Fertilizers, Textiles, Food and Beverages, Paper and Pulp, and Others
By Geography: North America (USA, Canada, and Mexico), Europe (UK, Germany, France, Italy, Netherlands, Spain, Russia, Belgium, and Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand, Indonesia, Taiwan, Malaysia, and Rest of APAC), South America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Chile, and Rest of South America), Rest of the World (Middle East and Africa)
Key Takeaways
North America dominates the CCS market, with USA having the lion’s share of operational or under construction schemes of CCS plants.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that we need a carbon capture and storage industry capable of capturing 7,000 million tons of carbon dioxide per year and storing it underground by 2050. So, the future of the global CCS industry looks promising.
There has been an increase in Global warming and CO2 emissions post lockdowns. This is leading to an increase in demand to curb emissions, which is increasing the demand for carbon capture and consecutively driving the market growth.
The major opportunity for this market is growing climate change awareness and development of clean and green mitigation technologies. Furthermore, it is also an opportunity for this market to develop advanced technology for safe and long-term storage of CO2.
Figure: Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market Revenue Share, By Capture Technology, 2020 (%)
For More Details on This Report — Request for Sample
Schedule a Call:
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market Segment Analysis — By Capture Technology
Pre-combustion, post-combustion, oxy-fuel combustion, and industrial separation are some of the widely used capture technologies. The post-combustion capture segment held the largest share of 55.6% in the CCS market in 2020. In post combustion capture CO2 is removed after combustion of fossil fuels in power plants. CO2 is captured from flue gases at power stations or other point sources. The technology is currently used in other industrial applications as well. Post combustion capture is most popular in research because PCC can be typically built into existing industrial plants and power stations (retro-fitting) without significant modifications to the original plant. Post Combustion Capture offers high operational flexibility (partial retrofit, zero to full capture operation) and it can match market conditions for both existing and new power stations. Renewable technologies can be integrated in this process, in particular, Post Combustion Capture allows the use of low-cost solar thermal collectors to provide the necessary heat to separate CO2 from sorbents, effectively reducing the loss of electrical output caused by capture.
Oxy-fuel combustion is the fastest growing capture technology in the Carbon Capture and Storage market in 2020 and is growing at a CAGR of 41.0% during 2024–2030. Oxy-fuel combustion is the process of combusting hydrocarbon fuel in the presence of high purity oxygen. Generally, oxy-fuel combustion recycles flue gas to achieve a lower flame temperature, which makes it a highly efficient energy-saving combustion technology. Due to the large quantity of high purity oxygen required for this process, cryogenic air separation is currently the technology of choice for oxygen production. As demand for highly efficient and effective capture technologies increases, Post-combustion Capture and Oxy-fuel Combustion are expected to dominate the market during the forecast period.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market Segment Analysis — By Storage Technology
The last and the most critical step in CCS is permanent storage of CO2. Geological Storage, Deep Ocean Storage and Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) are some of the storage technologies used. The EOR segment held the largest share of 70.0% in the CCS market in 2020. Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) is a process of extraction of crude oil from an oil field that otherwise cannot be recovered. Due to the physics of fluid flow, about two-thirds of conventional crude oil discovered in oil fields remains unproduced — primary oil recovery produces only about 10% of the reservoir’s original oil in place, with secondary recovery techniques increasing original oil in place production to approximately 20 to 40%. Tertiary (EOR) techniques prolong the life of producing fields, ultimately leading to recovery of 30 to 60% of the original oil in place. The United States Department of Energy (DOE) has estimated that full use of next generation CO2-EOR in the country could generate an additional 240 billion barrels of recoverable oil resources. Developing this potential would depend on the availability of commercial CO2 in large volumes, which could be made possible by widespread use of carbon capture and storage. Geological storage is the fastest growing storage technology segment in the Carbon Capture and Storage market in 2020 and is growing at a CAGR of 33.1% during 2024–2030. Geological Storage involves injecting CO2 as a supercritical fluid and injecting it into geological formations like saline aquifers or deep unminable coal beds 800 meters or more below the Earth’s crust. According to the Global CCS institute, as of June 2021, 26 commercial CCS facilities with a total capacity of 40 million tons per annum (Mtpa) are operating, 3 more are in construction, 13 are in advanced development and approximately 21 are in early development. Each of these facilities is or will permanently store hundreds of thousands of tons of CO2 per year, and several store more than one million tons of CO2 each year. Five of the 21 operating facilities use dedicated geological storage.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market Segment Analysis — By End Use Industry
Industries produce about 8 billion tons of CO2 emissions annually. Chemical, Iron and steel and cement industries are responsible for 70% of these emissions due to the nature of their processes and high temperature heat requirements. The only feasible option for mitigation is to remove CO2 after production using CCS. The Oil and gas segment held the largest share of 62.8% in the Carbon Capture and Storage market in 2020. The rising demand for crude oil and natural gas across various industries has driven the growth of the oil and gas industry. The rising investments in the oil industry to meet growing energy requirements with the focus on lowering greenhouse gas emissions will significantly stimulate the implementation of carbon capture and storage projects. The fastest growing end use industry segment in the Carbon Capture and Storage market in 2020 is biofuels which is growing at a CAGR of 43.2% during 2024–2030. This segment is growing fast owing to its popularity as a negative emission technology- Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS). BECCS is the process of extracting bioenergy from biomass and capturing and storing the CO2 thereby removing the atmospheric CO2. Biogenic CO2 is typically counted as a net-zero emission in most Greenhouse gas accounting schemes. This makes it a very low-cost CO2 source for capture. Thus, favoring the CCS market.
Buy Now :
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market Segment Analysis — By Geography
North America held the largest share in the CCS market in 2020 up to 54.0%. The US already had the highest number of operational CCS facilities and continued its lead in the global CCS projects with 12 of the 17 new commercial facilities added to the list projects in 2020. According to industry insights, North America will witness substantial growth on account of the increasing energy demands. For instance, the primary energy produced from fossil fuels in the US accounted for 79% of the total primary energy production in 2020 according to the IEA. Hence, there is a need to upgrade the conventional systems with effective emission control technologies like CCS to achieve the minimum emission rate. This contributes to the regional market growth. Projects were announced in the following end use industries — cement manufacturing, coal and gas-fired power plants, waste-to-energy plants, ethanol facilities and chemical production. These new projects are mainly due to incentives from the government as well as the DOE. Stringent regulatory standards by the government to decrease the greenhouse gas emissions will further boost the demand for carbon capture and storage technology in the region.
The APAC region is the fastest growing region and is growing at a CAGR of 44.3% during 2024–2030. In the Asia Pacific region commitments to reach net-zero emissions saw significant support over the last year from both, governments and businesses, which is spearheading CCS investment and driving the growth of the market. Increasing industrialization rate coupled with the growing investment toward expansion of manufacturing facilities has raised the deployment of CCS projects. Rapid deployment of gas and coal power plants in to cater to the growing demand for energy will accelerate the Asia Pacific market growth. For instance, in June 2021 Japan proposed $10 billion in government funding for low carbon projects overseas, particularly in Asia with the aim of offsetting the environmental impacts as it stays dependent on oil and gas imports to maintain energy security. Rising awareness regarding emission control along with ongoing industrial and commercial expansion will boost the market.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market Drivers
Global Aim for Net Zero
There has been a tremendous growth in the renewable energy sources sectors but climate experts and scientists believe that this alone will not result in zero carbon emissions. CCS plays a vital role in ridding the existing energy sources of greenhouse gas emissions and one step closes to net zero. The CCS technologies available today can absorb more than 90% of CO2 generated by fossil fuel power stations and industrial plants. According a report, the International Energy Agency declares that without CCS it will be impossible to achieve the ambition of the Paris Agreement. Many countries have begun adopting CCS to put them on the right track to net zero. A Norwegian Company, Equinor’s “Hydrogen to Humber (H2H) Saltend” project will provide blue (zero emission) hydrogen from natural gas with carbon capture and storage technology for the Humber region in UK. The project is one of many steps toward realizing the 2019 UK law committing to net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. Such projects act as drivers for the CCS market during the forecast period.
Role of Power Generation Industry
The expeditious decarbonization of power generation industry is of utmost importance in achieving net-zero emissions as electricity generation is one of the largest sources of CO2 emissions globally. The demand for electricity is forecast to increase significantly. CCS equipped power plants will help ensure that the low carbon grid of the future is resilient and reliable. CCS is also essential for reducing emissions from the existent world-wide fossil fuel power plants. Globally, there is approximately 2,000 Giga Watts (GW) of operating coal-fired capacity, with over 500 GW of new capacity expected by 2030. Over 200 Gigatons of new capacity is already under construction. Without CCS retrofit or early retirement, coal and gas-fired power stations, both current as well as under construction, will continue emitting CO2 at rates that will consume 95% of the IEA’s Sustainable Development Scenario carbon budget by 2050. Retrofitting fossil fuel power generation plants with CCS can be a cost-effective option which means economies that are heavily dependent on coal such as China, India, and Southeast Asian countries can continue using it while moving toward a low-carbon economy, thereby transitioning towards zero emission. Thus, the growth in power generation also fuels the growth of CCS market.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market Challenges
High Cost of Carbon Capture and Storage
Incorporating CCS technologies increases costs including capital investment in equipment technology, operating costs and transportation costs without providing additional revenue. The high cost of carbon capture and storage has kept the technology from entering mainstream use. Climate policies like carbon pricing are still not strong enough to make CCS economically attractive. For Carbon capture alone the cost varies from $15–120 per ton of CO2. Some CO2 capture technologies are commercially available now, while others are still in development, and this further contributes to the large range in costs. This challenge can be offset by government economic packages and incentives.
Environmental Considerations
The main critique towards CCS is that it may strengthen dependency on non-renewable fossil fuels and coal mining instead of adopting renewable energy solutions. Another concern is regarding the possible leaks in storage. Other concerns are explosions, earthquakes or any ecosystem side-effects. Such factors have become the major challenge of CCS which constrains the growth of the market.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market Landscape
Technological advancements, partnerships, and R&D activities are key strategies adopted by players in the Carbon Capture and Storage market. Carbon Capture and Storage market top companies are General Electric Company, Royal Dutch Shell PLC, Aker Solutions ASA, Fluor Corporation, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd, Halliburton Company, Siemens AG, Total S.A., Equinor ASA, ADA-ES, Inc, Exxon Mobil Corporation and Schlumberger Limited among others.
Acquisitions/Technology Launches
In June 2021, Northern Lights, Total Energies, Oxy Low Carbon Ventures, South Pole, Perspectives and Carbon Finance Labs announced the launch of the CCS+ Initiative which focus on advancing carbon accounting for a range of carbon capture, utilization, storage, and removal technologies that are underpinned by robust cradle-to-grave life cycle assessments (LCA) and rigorous verification standards to ensure environmental integrity.
In February 2020 Chevron Technology Ventures partnered with WAVE Equity Partners, and Marubeni Corporation by investing $16 million in Carbon Clean Solutions. Carbon Clean Solutions Limited is developing a carbon capture system that can be shipped to remote sites, where it will remove carbon dioxide at a price of $30 per ton.
Key Market Players:
The Top 5 companies in the Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS) Market are:
Aker Carbon Capture
Equinor ASA
Shell Plc
Exxon Mobil Corporation
TotalEnergies
For more Chemicals and Materials Market reports, please click here
0 notes
Text
The Short-Acting Insulin Market To Grow At Highest Pace Owing To Increasing Prevalence Of Diabetes

The short-acting insulin market comprises human insulin, insulin lispro, insulin aspart, and insulin glulisine. Short-acting insulin helps patients with diabetes to manage their blood sugar level within a few hours after injection. It is commonly used before or during meals or when blood sugar level is high. The increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide has significantly boosted the demand for short-acting insulin for effective management and treatment of the disease.
The Short-Acting Insulin Market is estimated to be valued at US$ 9.5 Bn in 2024 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 5.1% over the forecast period 2024-2031.
Key Takeaways
Key players operating in the short-acting insulin are Eli Lilly and Company, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Biocon, and Adocia.
Eli Lilly and Company is a global leader in diabetes care with prominent products such as Humalog and Admelog. Novo Nordisk is one of the leading pharmaceutical companies in diabetes care with short-acting insulin products such as NovoRapid and Fiasp.
The growing incidence of diabetes due to obesity, lack of physical activity, and unhealthy lifestyles has spurred the demand for short-acting insulin worldwide. According to the International Diabetes Federation, approximately 537 million adults were living with diabetes in 2021, and the number is expected to rise to 643 million by 2030 and 784 million by 2045.
Technological advancements in drug delivery systems have led to the development of novel short-acting insulin formulations for improved efficacy and patient compliance. For instance, Fiasp by Novo Nordisk is an ultra-fast-acting insulin aspart indicated for adults with diabetes.
Market Trends
Growing popularity of pre-filled insulin pens - Pre-filled insulin pens offer convenience of use and accurate dose delivery compared to vials and syringes. This is encouraging more patients and healthcare providers to shift from conventional vials to pre-filled insulin pens.
Growing demand for human insulin analogs - Second-generation human insulin analogs mimicking rapid-acting insulin have demonstrated faster absorption and onset of action. Hence, they are gaining traction over conventional human insulins.
Market Opportunities
Smart insulin delivery devices - Integration of connectivity features in insulin pumps and pens can help synchronize insulin delivery with daily activities and meals. This represents a lucrative avenue.
Emerging economies in Asia - Countries like China, India, Indonesia, and Vietnam are expected to fuel future demand growth owing to increasing diabetes prevalence and enhanced access to treatment options.
In conclusion, the Short-Acting Insulin Market is expected to grow notably in the forecast period owing to the rising prevalence of diabetes worldwide along with technological developments for convenient and more efficient insulin therapies.
Impact Of COVID-19 On Short-Acting Insulin Market Growth
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the growth of the Short-Acting Insulin Market. During the initial months of the pandemic, several nations imposed strict lockdowns and social distancing measures to curb the spread of the virus. This led to disruptions across the healthcare sector and supply chain networks. Many diabetic patients faced challenges in regularly accessing insulin therapy and management services during this period. It became difficult for patients to physically visit hospitals or clinics for insulin injections or consultations with doctors. Telehealth and remote monitoring emerged as viable options to ensure continuity of care. However, not all patients had access to these virtual healthcare platforms.
With lockdowns being gradually lifted in many countries post mid-2020, the short-acting insulin market is recovering. Healthcare systems have implemented new protocols and guidelines to minimize infection risks while delivering services. Insulin manufacturers ramped up production to meet any surge in demand. Governments also focused on strengthening supply chains and ensuring uninterrupted availability of diabetes treatment and management products. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for innovative insulin delivery methods like pens, pumps and wearable devices. It also emphasized the importance of personalized therapy and glucose monitoring technology. In the coming years, the market is expected to grow backed by increasing diagnosis rates, growing awareness about diabetes self-management, and advances in insulin therapy products.
Geographical Regions With Highest Short-Acting Insulin Market Value
North America represented the largest short-acting insulin market in terms of value in 2024. This is attributed to the rising prevalence of diabetes, growing obesity rates, availability of advanced treatment options and high healthcare spending in the US and Canada. Europe held the second position driven by increasing government focus on noncommunicable diseases and presence of major market players. Asia Pacific is projected to be the fastest growing regional market between 2024-2031 backed by growing awareness, expanding patient reach of key players and rising healthcare investments in countries like China and India.
Fastest Growing Regional Market For Short-Acting Insulin
Asia Pacific is poised to be the fastest growing regional market for short-acting insulin during the forecast period from 2024 to 2031. This can be attributed to factors like rising diabetes prevalence, growing medical expenditures, increasing focus on prevention and management of chronic diseases, improving access to diagnosis and treatment services, and expansion initiatives by leading manufacturers. Furthermore, adoption of technologies like smartphones and smart insulin pens is supporting diabetes care in the region. Asia Pacific countries such as China, India and Indonesia offer lucrative growth opportunities for market players due to rising healthcare infrastructure, surge in medical tourism and rapidly increasing patient pool.
Get more insights on this topic: https://www.trendingwebwire.com/advanced-technologies-are-estimated-to-drive-growth-in-the-short-acting-insulin-market/
Author Bio:
Money Singh is a seasoned content writer with over four years of experience in the market research sector. Her expertise spans various industries, including food and beverages, biotechnology, chemical and materials, defense and aerospace, consumer goods, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/money-singh-590844163 )
What Are The Key Data Covered In This Short-Acting Insulin Market Report?
:- Market CAGR throughout the predicted period
:- Comprehensive information on the aspects that will drive the Short-Acting Insulin Market's growth between 2024 and 2031.
:- Accurate calculation of the size of the Short-Acting Insulin Market and its contribution to the market, with emphasis on the parent market
:- Realistic forecasts of future trends and changes in consumer behaviour
:- Short-Acting Insulin Market Industry Growth in North America, APAC, Europe, South America, the Middle East, and Africa
:- A complete examination of the market's competitive landscape, as well as extensive information on vendors
:- Detailed examination of the factors that will impede the expansion of Short-Acting Insulin Market vendors
FAQ’s
Q.1 What are the main factors influencing the Short-Acting Insulin Market?
Q.2 Which companies are the major sources in this industry?
Q.3 What are the market’s opportunities, risks, and general structure?
Q.4 Which of the top Short-Acting Insulin Market companies compare in terms of sales, revenue, and prices?
Q.5 Which businesses serve as the Short-Acting Insulin Market’s distributors, traders, and dealers?
Q.6 How are market types and applications and deals, revenue, and value explored?
Q.7 What does a business area’s assessment of agreements, income, and value implicate?
*Note: 1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research 2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it
#Short-Acting Insulin Market Trend#Short-Acting Insulin Market Size#Short-Acting Insulin Market Information#Short-Acting Insulin Market Analysis#Short-Acting Insulin Market Demand
0 notes
Text
Hit Chinese Video Game, ‘Wukong’ Seeks to Curb ‘Negative Discourse’
Black Myth: Wukong tried to forbid influential overseas streamers from discussing “feminist propaganda,” Covid-19 and China’s video game industry policies. source https://www.nytimes.com/2024/08/20/world/asia/chinese-videogame-wukong-censorship.html
0 notes