#Born in Bihar
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
here's how armand can still be bengali
why do i think so? no other good reason than i am bengali myself and i want armand to be. (also assad zaman's family is from bangladesh. bengali solidarity!!!)
bengal: the region in south asia comprising present-day bangladesh and the indian states of west bengal, odisha, assam and parts of bihar.
armand said in the season one finale, that takes place in 2022, he is a 514 year old vampire. is it 514 years including or excluding his human years? let's go with including. that means armand would have been born in 1508.


now what was going on in india and bengal in 1508? well, the mughals hadn't come to india yet; it's still about two decades before babur makes his way here. delhi was under the rule of the lodi dynasty, the delhi sultanate was in its dying days. most of north india, mainly uttar pradesh and bihar was under the jaunpur sultanate. bengal was still it's own independent kingdom, called the bengal sultanate. alauddin hussain shah had just seized power and become the sultan of bengal in 1494, beginning the hussain shahi dynasty (they ruled in bengal till 1538 when the mughals captured the region).
india as a country did not exist yet. even it's conception would be a few centuries away still. the subcontinent was a collection of big and small kingdoms and sultanates, constantly warring amongst themselves, some ruled by hindu rulers others by muslims, each with their own distinct histories and cultures. bengal was one of the most prosperous and thriving among them. the bangla language and bengali culture was just beginning to develop.


vasco da gama had arrived in india in 1498, landing at kozhikode on the malabar coast. this began the arrival of the portugese in india, and soon other european colonialists followed. they soon set up their capital in goa, built forts all along the western coast and established trade through obtaining licenses and exclusive permits from local rulers. they first made their way to the bay of bengal region around 1516, with the first portugese representative- a guy called joao coelho- coming to chittagong (present day bangladesh). the first factory was set up in chittagong the next year.
the portugese traded in spices and cotton and fruits and muslin and also slaves. the european indian ocean slave trade began with the coming of the portugese in the early 16th century. slavery in south asian societies had obviously existed long before, and it was a deeply complex and diverse system of dependency and regimes of slavery. slavery of youth and children was also pretty prevalent: it would not be uncommon for poor, farming families to sell away themselves or their children to zamindars (landlords) and colonial overlords in desperation. there were many, many cases of young children being forced to get onboard ships where they'd be held agains their will and taken to europe, the americas or south-east asia. goa and lisbon were the two cities that linked the movement of goods and people between the indian and atlantic oceans, but goa wasn't the only place where enslaved children were traded in portugese india nor lisbon the only european they were taken to.
one of those kids might as well have been arun.


i know the brief glimpse at the talamasca files showed armand's origin to be in delhi but in this particular scene he clearly says that he was sent *to* delhi, thinking he was going to work on a merchant boat.
this is just a theory i have btw. armand could've been from maharastra or the deccan as well idk. anyway.
armand is a monster, a vicious, villanious creature of unfathomable powers and ferocity. but he is also so deeply tragic. he had been forcibly torn away from his people and his land. he has no memory of his family or his humanity. he has lived for over half a millenium. the india he might've known hasn't existed for centuries, and he never got to know the one that exists today. the bangla he might've spoken no one remembers anymore. he has nothing left of the human he was except that name.
further readings (STRONGLY SUGGESTED!!!):
267 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is so horrific.
———————
I have been following Siro’s story for 30 years, ever since I went to interview her and four other rural midwives in India’s Bihar state in 1996.
They had been identified by a non-governmental organisation as being behind the murder of baby girls in the district of Katihar where, under pressure from the newborns’ parents, they were killing them by feeding them chemicals or simply wringing their necks.
Hakiya Devi, the eldest of the midwives I interviewed, told me at the time she had killed 12 or 13 babies. Another midwife, Dharmi Devi, admitted to killing more - at least 15-20.
It is impossible to ascertain the exact number of babies they may have killed, given the way the data was gathered.
But they featured in a report published in 1995 by an NGO, based on interviews with them and 30 other midwives. If the report’s estimates are accurate, more than 1,000 baby girls were being murdered every year in one district, by just 35 midwives. According to the report, Bihar at the time had more than half a million midwives. And infanticide was not limited to Bihar.
Refusing orders, Hakiya said, was almost never an option for a midwife.
“The family would lock the room and stand behind us with sticks,” says Hakiya Devi. “They’d say: ‘We already have four-five daughters. This will wipe out our wealth. Once we give dowry for our girls, we will starve to death. Now, another girl has been born. Kill her.’
“Who could we complain to? We were scared. If we went to the police, we’d get into trouble. If we spoke up, people would threaten us."
The role of a midwife in rural India is rooted in tradition, and burdened by the harsh realities of poverty and caste. The midwives I interviewed belonged to the lower castes in India’s caste hierarchy. Midwifery was a profession passed on to them by mothers and grandmothers. They lived in a world where refusing orders of powerful, upper-caste families was unthinkable.
The midwife could be promised a sari, a sack of grain or a small amount of money for killing a baby. Sometimes even that was not paid. The birth of a boy earned them about 1,000 rupees. The birth of a girl earned them half.
The reason for this imbalance was steeped in India’s custom of giving a dowry, they explained. Though the custom was outlawed in 1961, it still held strong in the 90s - and indeed continues into the present day.
A dowry can be anything - cash, jewellery, utensils. But for many families, rich or poor, it is the condition of a wedding. And this is what, for many, still makes the birth of a son a celebration and the birth of a daughter a financial burden.
Siro Devi, the only midwife of those I interviewed who is still alive, used a vivid physical image to explain this disparity in status.
“A boy is above the ground - higher. A daughter is below - lower. Whether a son feeds or takes care of his parents or not, they all want a boy.”
The preference for sons can be seen in India’s national-level data. Its most recent census, in 2011, recorded a ratio of 943 women to every 1,000 men. This is nevertheless an improvement on the 1990s - in the 1991 census, the ratio was 927/1,000.
By the time I finished filming the midwives’ testimonies in 1996, a small, silent change had begun. The midwives who once carried out these orders had started to resist.
This change was instigated by Anila Kumari, a social worker who supported women in the villages around Katihar, and was dedicated to addressing the root causes of these killings.
Anila’s approach was simple. She asked the midwives, “Would you do this to your own daughter?”
Her question apparently pierced years of rationalisation and denial. The midwives got some financial help via community groups and gradually the cycle of violence was interrupted.
Siro, speaking to me in 2007, explained the change.
“Now, whoever asks me to kill, I tell them: ‘Look, give me the child, and I’ll take her to Anila Madam.’”
The midwives rescued at least five newborn girls from families who wanted them killed or had already abandoned them.
One child died, but Anila arranged for the other four to be sent to Bihar’s capital, Patna, to an NGO which organised their adoption.
The story could have ended there. But I wanted to know what had become of those girls who were adopted, and where life had taken them.
Anila’s records were meticulous but they had few details about post-adoption.
Working with a BBC World Service team, I got in touch with a woman called Medha Shekar who, back in the 90s, was researching infanticide in Bihar when the babies rescued by Anila and the midwives began arriving at her NGO. Remarkably, Medha was still in touch with a young woman who, she believed, was one of these rescued babies.
Anila told me that she had given all the girls saved by the midwives the prefix “Kosi” before their name, a homage to the Kosi river in Bihar. Medha remembered that Monica had been named with this “Kosi” prefix before her adoption.
The adoption agency would not let us look at Monica’s records, so we can never be sure. But her origins in Patna, her approximate date of birth and the prefix “Kosi” all point to the same conclusion: Monica is, in all probability, one of the five babies rescued by Anila and the midwives.
When I went to meet her at her parents’ home some 2,000km (1,242 miles) away in Pune, she said she felt lucky to have been adopted by a loving family.
“This is my definition of a normal happy life and I am living it,” she said.
Monica knew that she had been adopted from Bihar. But we were able to give her more details about the circumstances of her adoption.
Earlier this year, Monica travelled to Bihar to meet Anila and Siro.
Monica saw herself as the culmination of years of hard work by Anila and the midwives.
“Someone prepares a lot to do well in an exam. I feel like that. They did the hard work and now they’re so curious to meet the result… So definitely, I would like to meet them.”
Anila wept tears of joy when she met Monica. But Siro’s response felt different.
She sobbed hard, holding Monica close and combing through her hair.
“I took you [to the orphanage] to save your life… My soul is at peace now,” she told her.
But when, a couple of days later, I attempted to press Siro about her reaction, she resisted further scrutiny.
“What happened in the past is in the past,” she said.
But what is not in the past is the prejudice some still hold against baby girls.
Reports of infanticide are now relatively rare, but sex-selective abortion remains common, despite being illegal since 1994.
If one listens to the traditional folk songs sung during childbirth, known as Sohar, in parts of north India, joy is reserved for the birth of a male child. Even in 2024, it is an effort to get local singers to change the lyrics so that the song celebrates the birth of a girl.
While we were filming our documentary, two baby girls were discovered abandoned in Katihar - one in bushes, another at the roadside, just a few hours old. One later died. The other was put up for adoption.
Before Monica left Bihar, she visited this baby in the Special Adoption Centre in Katihar.
She says she was haunted by the realisation that though female infanticide may have been reduced, abandoning baby girls continues.
“This is a cycle… I can see myself there a few years ago, and now again there’s some girl similar to me.”
But there were to be happier similarities too.
The baby has now been adopted by a couple in the north-eastern state of Assam. They have named her Edha, which means happiness.
“We saw her photo, and we were clear - a baby once abandoned cannot be abandoned twice,” says her adoptive father Gaurav, an officer in the Indian air force.
Every few weeks Gaurav sends me a video of Edha's latest antics. I sometimes share them with Monica.
Looking back, the 30 years spent on this story were never just about the past. It was about confronting uncomfortable truths. The past cannot be undone, but it can be transformed.
And in that transformation, there is hope.
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
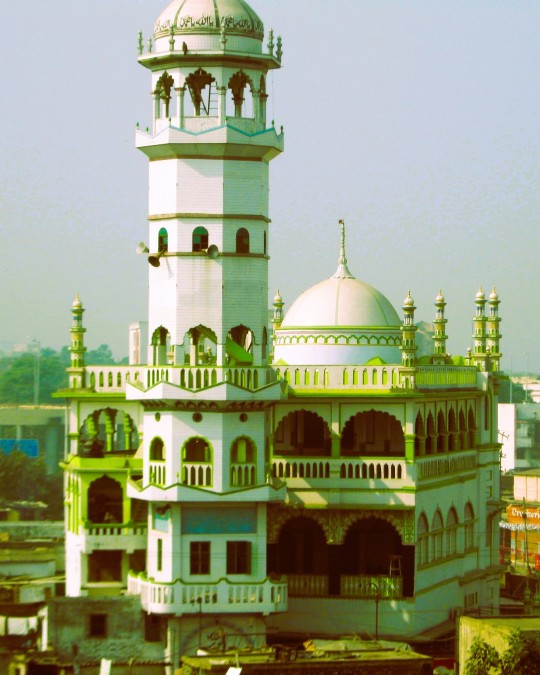

Jama Masjid Mosque, Patna, Bihar, India: Patna historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. Patna also serves as the seat of Patna High Court. The Buddhist, Hindu, and Jain pilgrimage centers of Vaishali, Rajgir, Nalanda, Bodh Gaya, and Pawapuri are nearby and Patna City is a sacred city for Sikhs as the tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh was born here. The modern city of Patna is mainly on the southern bank of the river Ganges. Wikipedia
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
Religious Imageries in JJK: The Conflicting Views of Shinto and Buddhism.
Disclaimer: This is not an explanation post, this is an observer post. I will try to sum up what I have observed so far.
Let's begin with the definition and history of both Shinto and Buddhism.
Shinto [神道]: Combined with the kanji of God/Kami (神) and Road /Michi(道), Shinto literally means The way of the God(s). It is the indigenous religion of Japan and is as old as Japan itself.
Shinto belief is polytheist and animistic as it has almost 8 million gods that are derived from nature and natural things. This religion revolves around "Kami". Kami can be manifested from anything, but the most important Kami are the natural ones.
Sun, Rain, Earth etc. The most important central Kami is Amaterasu the Kami of the Sun. The exact history of Shinto is untraceable but it was mentioned in the Yayoi Period (300 BCE to 300 CE) of text.
Shinto describes the world as a inhabitant of the human and the kami they worship. It describes the world as founded by the kami and once humans/ living beings pass away they become kami as well.
It is safe to say that Shinto belief described humanity as living being as a whole, where even after death they don't living. The idea of morality or immorality is also absent from it. The existence of Kami is the manifestation of humanity itself and not separated from human beings.
Fun Fact: Chinese indigenous religion 'Dao' has the same characters as Shinto's kanji. So it might be possible that Shinto actually comes from Chinese Daoism.
Buddhism: Buddhism is an Indian religion. It revolves around the teaching of Buddha. Buddha is no myth. Even though convoluted, early texts gives his name as "Gautama" and he lived around 5th to 6th Century BCE.
In India his name is mostly known as "Siddharth". He was born in Lumbini in present day Nepal and grew up in Kapilavastu. The border of India and Nepal, a town of the Ganges plain of present day Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
The most notable person who helped spread Buddhism around India so much that it was spread in the NEA and SEA is Emperor Asoka (304-232 BCE) from the Maurya Empire (322-180 BCE).
Buddhism circles around the suffering of human, the circle of life and Karma (deed). Where a soul is constant as it is being born in this world as human, it goes through the cycle of life (suffering) and it dies.
It also talks about Dharma as the ultimate truths, also that humans are born to fulfill a certain role. Moksha: The liberation from the earthly desire which should be the ultimate goal of a human being.
It also draws the line between God and humans as Gods are separated from the earthly matters and pushes the idea of Gods creating the universe and the creating the humanity.
The Mix of both Religion:
Though the idea of Shinto and Buddhism is pretty contradicting it existed with each other for centuries.
Even though Buddhism entered in japan in Yayoi Period (250-538 AD), it became popular in Asuka Period (538-710) due to buddhist sect taking the rein of the country. Initially Buddhism and Shinto coexisted and even mixed with each other. It was called Shinbutsu-Shougou. However, later it was forcefully separated by Japanese nationalists in Meiji Era (1868-1912) and Shinto became the state religion of Japan with the Emperor being worshipped as Kami the descendants of Amaterasu.
Cursed Spirit: The reason I am writing this is not because the obvious depiction of buddha, Buddhist shrines and mention of clans and sects etc. What caught my interest was that the idea of "Cursed Spirit".
The textbook explanation of Cursed Spirit is that the reaction of human emotions but as we see it is actually the manifestation of human existence. As long as humans will exist, curses will also exist.
Which pretty much resembles the idea of Kami.
The timeline: The golden era of jujutsu was Heian Era which historically existed between 794-1185 AD. Almost a century after Buddhism was introduced in Japan. Also in that era Sukuna rose up as the king of curses. Which may indicate the clans existed even before and Sukuna existed throughout.
Characters like Kenjaku and Tengen their birth and living timeline are unknown but they might just as be as old as Japan, like Shinto.
Getou and Megumi are the only two people who can control curses as Shikigami. Which is another japanese Shinto belief that has also been associated with "Curses" during Heian Era.
The people who used to control Shikigami were called Onmyoji (Yin-Yang Master).
Both of them were either antagonised or villfied by the jujutsu society at one point.
Also the most important part that made me think about this is...Sukuna's domain.

This resembles an average Shinto shrine...

The Tori is missing.
Insanity.
Anyways. I am not saying that Gege is making one religion look bad and another look good. It's not true and actually far from it. Though contradiction, Gege shows the good and bad of both sides. Kenjaku is bad and the higher ups are as worse as him.
Personally I think this is a battle of belief of the world with a main character emerges with no beliefs at all. Itadori Yuuji hates Sukuna but not by the virtue of being Gojo's student but his own opinion about him. In the latest chapter he says "Human beings are not a tool, so nobody's existence is premediated." Which contradicts the idea of "Dharma".
The message might be "If you want to change the world, you have to diverge from the existing path and forge your own."
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Heroes
Amitabh Parashar BBC Eye Investigations
Midwife Siro Devi is clinging to Monica Thatte, sobbing. Monica, in her late 20s, has returned to her birthplace - the Indian town where Siro has delivered hundreds of babies.
But this is no straightforward reunion. There is a painful history behind Siro's tears. Shortly before Monica was born, Siro and several Indian midwives like her were regularly pressured to murder newborn girls.
Monica, evidence suggests, is one they saved.
I have been following Siro’s story for 30 years, ever since I went to interview her and four other rural midwives in India’s Bihar state in 1996.
They had been identified by a non-governmental organisation as being behind the murder of baby girls in the district of Katihar where, under pressure from the newborns’ parents, they were killing them by feeding them chemicals or simply wringing their necks.
Hakiya Devi, the eldest of the midwives I interviewed, told me at the time she had killed 12 or 13 babies. Another midwife, Dharmi Devi, admitted to killing more - at least 15-20.
It is impossible to ascertain the exact number of babies they may have killed, given the way the data was gathered.
But they featured in a report published in 1995 by an NGO, based on interviews with them and 30 other midwives. If the report’s estimates are accurate, more than 1,000 baby girls were being murdered every year in one district, by just 35 midwives. According to the report, Bihar at the time had more than half a million midwives. And infanticide was not limited to Bihar.
Refusing orders, Hakiya said, was almost never an option for a midwife.
“The family would lock the room and stand behind us with sticks,” says Hakiya Devi. “They’d say: ‘We already have four-five daughters. This will wipe out our wealth. Once we give dowry for our girls, we will starve to death. Now, another girl has been born. Kill her.’
“Who could we complain to? We were scared. If we went to the police, we’d get into trouble. If we spoke up, people would threaten us."

Amitabh watching the extraordinary interviews he did with the midwives in the 90s
The role of a midwife in rural India is rooted in tradition, and burdened by the harsh realities of poverty and caste. The midwives I interviewed belonged to the lower castes in India’s caste hierarchy. Midwifery was a profession passed on to them by mothers and grandmothers. They lived in a world where refusing orders of powerful, upper-caste families was unthinkable.
The midwife could be promised a sari, a sack of grain or a small amount of money for killing a baby. Sometimes even that was not paid. The birth of a boy earned them about 1,000 rupees. The birth of a girl earned them half.
The reason for this imbalance was steeped in India’s customof giving a dowry, they explained. Though the custom was outlawed in 1961, it still held strong in the 90s - and indeed continues into the present day.
A dowry can be anything - cash, jewellery, utensils. But for many families, rich or poor, it is the condition of a wedding. And this is what, for many, still makes the birth of a son a celebration and the birth of a daughter a financial burden.
Siro Devi, the only midwife of those I interviewed who is still alive, used a vivid physical image to explain this disparity in status.

Siro has worked as a midwife since she was a child
“A boy is above the ground - higher. A daughter is below - lower. Whether a son feeds or takes care of his parents or not, they all want a boy.”
The preference for sons can be seen in India’s national-level data. Its most recent census, in 2011, recorded a ratio of 943 women to every 1,000 men. This is nevertheless an improvement on the 1990s - in the 1991 census, the ratio was 927/1,000.

Anila Kumari (second left), a social worker, led sessions in the 1990s to nudge the midwives into a different approach
By the time I finished filming the midwives’ testimonies in 1996, a small, silent change had begun. The midwives who once carried out these orders had started to resist.
This change was instigated by Anila Kumari, a social worker who supported women in the villages around Katihar, and was dedicated to addressing the root causes of these killings.
Anila’s approach was simple. She asked the midwives, “Would you do this to your own daughter?”
Her question apparently pierced years of rationalisation and denial. The midwives got some financial help via community groups and gradually the cycle of violence was interrupted.
Siro, speaking to me in 2007, explained the change.
“Now, whoever asks me to kill, I tell them: ‘Look, give me the child, and I’ll take her to Anila Madam.’”
The midwives rescued at least five newborn girls from families who wanted them killed or had already abandoned them.
One child died, but Anila arranged for the other four to be sent to Bihar’s capital, Patna, to an NGO which organised their adoption.
The story could have ended there. But I wanted to know what had become of those girls who were adopted, and where life had taken them.
#Indian midwives#Heroes#Infanticide#India#Bahir state#district of Katihar#Men wanted their daughters dead but did want to commit murder themselves#Anila Kumari
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Portrait of an Indian Lady, traditionally called the Bibi of John Wombwell (d. 1795), Arthur William Devis
In Calcutta [Arthur William Devis] quickly established himself as one of the leading European painters in India, painting portraits of a number of the most eminent figures among the British community, including Warren Hastings, the Governor-General. [...]
More so than most European artists working in India, however, with the possible exception of Renaldi, Devis’s work in India demonstrates a clear interest in the native population of the Subcontinent – a sensibility that some historians have credited to his experiences in the Pellew Islands. Whilst principally based in Calcutta, he made frequent trips out into the surrounding country to sketch Indian villagers at work. In the autumn of 1786 he travelled as far as Patna, on the south bank of the Ganges in the north eastern state of Bihar. There he made studies of local people engaged in their traditional industries, including paper and saltpetre making, as well as the weaving of stripped cotton carpets, known as satringis, for which Patna was famous. It may be to this trip that the present portrait relates, particularly with the richly stripped textiles of the lady’s divan and the notable cusped archway in the background, typical of India’s northern cities. [...]
Reclining on a richly cushioned divan, wearing a saffron coloured sari and sumptuous jewels, the unknown Indian lady depicted in this portrait is clearly somebody of noble birth and high social status. At her side is a gilt stemmed cup overflowing with jewels, while a bihishti lays the dust in the courtyard beyond. It is a scene of opulent leisure and casual refinery. The composition closely relates to a portrait of Anne Heatly, probably the bibi of Suetonius Grant Heatly, an American born East India Company official who held positions at Chotanagpur, Palamu and Purina. Both paintings share the same compositional elements, including the red bolster and cushions with their green and yellow stripped bordering; the tazza like cup with its hanging pearls; the archway and the background figures; whilst the sitter’s themselves share the same heavy-lidded eyes; soft, flowing drapery and elegantly reclining pose. The portrait of Anne Heatly, which appeared at auction in 2006, was also previously given to Charles Smith. However, following subsequent cleaning and restoration, it has also now been correctly identified as being by Devis. The two paintings, almost mirror images of each other, save for the difference in format (the portrait of Heatly being in landscape), clearly belong to the same moment in the artist’s career.
Whilst the sitter in the present portrait remains unknown, as Mildred Archer noted, she is too confident in her poise to be an orthodox Muslim woman of rank – who would not have allowed herself to be painted in public – and is most likely the bibi of another high-ranking British official. The term bibi has its roots in the Indian word for ‘princess’ and served as a personalised or intimate reference to the women who first formed relationships with European traders in the seventieth century who were, in fact, mostly princesses of Indian royal families. Young women taken from the royal zenana – sisters, nieces, daughters of the ruling nawab or his brothers – and given in arranged marriages to important European officials, they played an important role in strengthening the diplomatic alliances between a reigning nawab and powerful Company representatives that promoted the political and economic interests of both parties (much in the same way that European royal courts use arranged marriage as a means of strengthening diplomatic ties). Well educated at home by elderly scholars, these noblewomen were literate, often able to speak and read several languages and regional dialects, and schooled in the study of mathematics, history, the natural sciences and medicine. In many cases these marriages produced genuinely happy unions, with the multi-racial offspring they produced further helping to knit the Indian and European communities together.
The custom of high-ranking British Company officials taking an aristocratic Indian mistress continued as both a social and political necessity well into the eighteenth century, to which a number of known portraits of the mistresses of British officials by the likes of Zoffany, Renaldi and James Wales attest. The practice was finally ended by the Marquess Wellesley when he was Governor-General in the 1790s, following which the British and Indian communities became increasing segregated through the course of the nineteenth century.
[Text from Sotheby's]
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The murder of a politician in a bustling area in India's Mumbai city has sent shockwaves across the country.
Baba Ziauddin Siddique, 66, was shot on Saturday night near his carwhile he was leaving his son's office. He died later in hospital.
The killing of Siddique, an influential politician who was part of the coalition governing Maharashtra state - of which Mumbai is the capital - has set off a political blame-game.
The motive for the murder is not clear yet, but for many it has brought back memories of the 1990s, when politicians and film stars were frequently targeted by Mumbai's underworld.
Police have arrested three people so far and say investigations are continuing. Local media reports say the arrested men are part of a notorious gang whose leader is currently in jail.
Who was Baba Siddique?
Born in the eastern state of Bihar, Siddique migrated to Mumbai at the age of five with his father, a watchmaker.
He started his political career in the 1980s as a student leader with the Congress party, soon leading its youth wing in Mumbai. He then entered local council politics before being elected to the state’s legislature three times in a row and becoming a minister in 2004 for about four years.
In February, he left the Congress to join the Nationalist Congress Party which, along with Prime Minister Narendra Modi's Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and the Shiv Sena, currently governs state.
Apart from his political activities, Siddique also made headlines for his glitzy iftar parties held during the Muslim holy month of Ramadan which were attended by top Bollywood stars.
It was at his iftar party in 2013 that superstars Salman Khan and Shahrukh Khan ended their much-discussed rift with a hug - that propelled "the annual Siddique affair into a must-watch event on the city’s social calendar", Midday newspaper wrote in 2016.
How was Siddique killed?
The politician was shot outside his son’s office as he was about to enter his car in the busy Bandra area.
Police said three shooters fired six-seven rounds, hitting Siddique's abdomen and chest, and fled the scene. A bystander was also injured as a stray bullet hit his leg.
Investigators said they had recovered two pistols and 28 live rounds of ammunition from the arrested men.
Siddique had three police guards - local media reported his security was upgraded days ago - but the suspects reportedly distracted them by setting off a "smoke firecracker".
What is the state of the investigation?
Police have been granted custody of the arrested men for a week. They say they are on the lookout for their accomplices.
“We have set up 15 teams and investigation is on to identify who provided logistical support to the shooters,” senior police official Datta Nalawade said.
While the police have not confirmed it, several reports citing sources have linked the arrested men with the notorious Bishnoi gang. The gang's leader Lawrence Bishnoi is an accused in several cases and is currently in a high-security prison in Gujarat state.
Within hours of the shooting, a man claiming to be a member of the gang posted on Facebook that they were behind Siddique’s killing. Police have not yet confirmed the authenticity of the post.
Though Bishnoi has been in jail since 2015, he frequently makes news. Many social media accounts claiming to belong to him or his associates have often posted his selfies from jail. He even gave interviews to a TV channel in 2022, prompting an investigation.
Many of the reports on Bishnoi are based on police sources and it’s not clear how he conducts the gang's operations while in prison.
The gang's name popped up in connection with the murder of Punjabi rapper Sidhu Moosewala in 2022.
In April, police arrested two gang members for allegedly firing shots outside the apartment of actor Salman Khan in Mumbai.
On Monday, the Canadian police also said it believed the Bishnoi group had connections to Indian government agents who were using the gang to target Sikh separatists on their soil. India has not officially responded to the police claims.
What else has happened?
Siddique’s killing is the first major assassination of a politician in Mumbai since the 1990s when high-profile killings of politicians, businessmen and Bollywood celebrities by criminal gangs of the Mumbai underworld were not uncommon.
Local media reports said he had received a death threat two weeks ago, which led to his security being upgraded.
His killing within days of that has put the state government on the backfoot, with Maharashtra set to hold assembly elections soon.
Congress president Mallikarjun Kharge called the murder “a complete failure of law and order in Maharashtra”, and Delhi's former chief minister Arvind Kejriwal said the incident had scared not only the people of Maharashtra “but the entire country”.
Chief Minister of Maharashtra Eknath Shinde has defended his government.
“[The culprits] will not be spared no matter who they are, be it the Bishnoi gang or any underworld gang… Those who are receiving threats, their safety is the state government’s responsibility and it will fulfil its responsibility,” he said.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mod 3: Gymnosperms
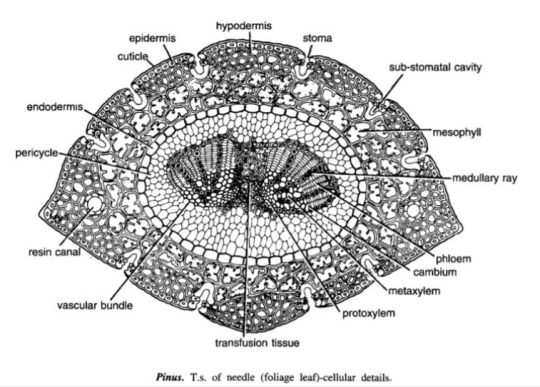
Pinus Needle T.S.
It is circular in outline in P. monophylla, semicircular in P. sylvestris and triangular in P. longifolia, P. roxburghii, etc.
Outermost layer is epidermis, which consists of thick-walled cells. It is covered by a very strong cuticle.
Many sunken stomata are present on the epidermis.
Each stomata opens internally into a substomatal cavity and externally into a respiratory cavity or vestibule.
Below the epidermis are present a few layers of thick-walled sclerenchymatous hypodermis. It is well developed at ridges
In between the hypodermis and endodermis is present the mesophyll tissue.
Cells of the mesophyll are polygonal and filled with chloroplasts. Many peg-like infoldings of cellulose also arise from the inner side of the wall of mesophyll cells.
Few resin canals are present in the mesophyll, adjoining the hypodermis. Their number is variable but generally they are two in number.
Endodermis is single-layered with barrel-shaped cells and clear casparian strips.
Pericycle is multilayered and consists of mainly parenchymatous cells and some sclerenchymatous cells forming T-shaped girder, which separates two vascular bundles. Transfusion tissue consists of tracheidial cells.
Two conjoint and collateral vascular bundles are present in the center. These are closed but cambium may also be present in the sections passing through the base of the needle.
Xylem lies towards the angular side and the phloem towards the convex side of the needle.
Idk where to find xeric nature info
Williamsoniaceae
Occurrence of Williamsonia
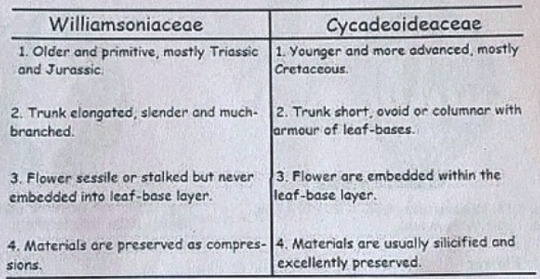
Williamsonia belongs to family Williamsoniaceae of Bennettiales.
It has been reported from Upper Triassic period but was more abundant in Jurassic.
This was earlier discovered under the name Zamia gigas by Willamson in 1870 but has now been named as Williamsonia.
Professor Birbal Sanhi (1932) described W. sewardiana from Rajmahal Hills of Bihar (India).
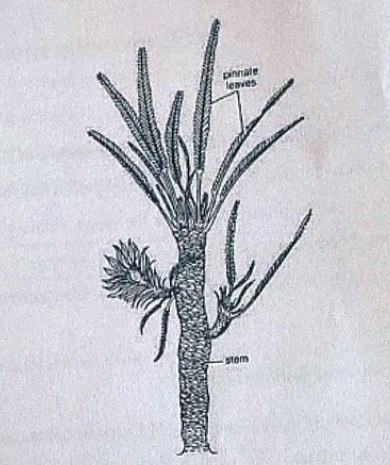
External Features of Williamsonia
Williamsonia resembled Cycas in appearance, but its best-knows species is W. sewardiana. The plant had an upright, branched, and stout stem covered by persistent leaf bases.
A terminal crown of pinnately compound leaves was present. For the stem genus Bucklandia, Sharma (1991) opined that features of leaf bases such as their shape, size and arrangement pattern are of taxonomic significance.
He observed that leaves in Williamsoniaceae show syndetocheilic stomata with rachis possessing collateral endarch vascular bundles.
Reproduction in Williamsonia
The fructifications of Williamsonia were large and attained a diameter of about 12 cm.
They were borne on a peduncle.
Many spirally arranged bracts were present around the base of the floral axis.
In W. gigas the cones were present among the crown of leaf bases while in W. sewardinia they were present on the short lateral branches.
Williamsonia plants were unisexual.
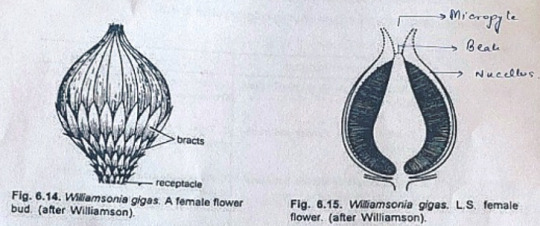
Female Flower
The female 'cones' of W. gigas and W. sewardiana have been investigated in detail. Instead of 'strobili' or 'cones', Sporne (1965) proposed to use the term 'flower'.
The conical receptacle was surrounded by many perianth-like bracts. The ovules were stalked.
The apex of the receptacle was naked and sterile. The nucellus was surrounded by a single vascularize integument, which was fused with the nucellus. The nucellus had a well-marked beak and a pollen chamber. In young ovules the micropylar canal was long and narrow.
In mature ovules, the canal widened because of the formation of nucellar plug and disappearance of interlocking cells. In the apical part of the endosperm, Sharma (1979) observed 2 or more archegonia.
Male Flower
Male flowers consisted of a whorl of microsporophyll's which were united to form a more or less cuplike structure. In majority of the investigates species the sporophylls were un-branched but in some species they were also pinnately branched.
Sitholey and Bose discovered W. santalensis from Upper Gondwana, and observed that microsporophyll's in the species were bifid.
One of the branches of microsporophyll was fertile while the other was sterile. The fertile part has finger-like structures called synangia. Each synangium had two rows of chambers enclosing microsporangia.
The fertile branch of the bifid sporophyll possessed many purse-like capsules, in each of which there were present many monocolpate pollen grains.

Cycadeoideaceae
Classification:
Division - Cycadeoidophyta
Order - Cycadeoideales
Family - Cycadeoideaceae
Genus - Cycadeoidea
Introduction:
Cycadeoidea is the only genus of family Cycadeoidaceae, represented by thirty species. They are entirely extinct and resemble cycads in the outward stumpy appearance of trunk and an apical crown of pinnate compound leaves. This fossil group of plants flourished during the Triassic to Cretaceous periods of the Mesozoic era. They are reported from various places in the world, in India the Cycadeoidales are found in Rajmahal Hills in Bihar. The petrified trunks of C. entrusca are the oldest fossil ever collected by man.
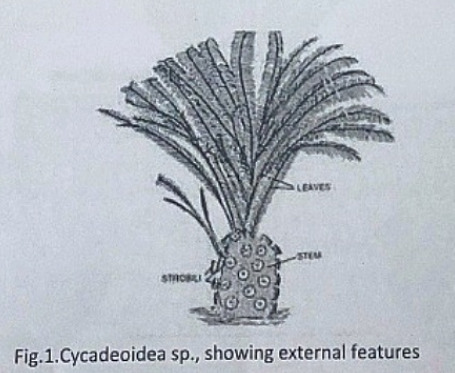
External Features:
The genus Cycadeoidea had a short, branched, or unbranched spherical, conical, or irregular trunk. The diameter of the trunk is 50cm and the highest rarely reached a meter except in C. jenneyana, it attended the height of several meters. These trunks are covered by rhomboidal leaf bases having multicellular hairs in between. Crown of 10ft long pinnate compound leaves are present at the top.
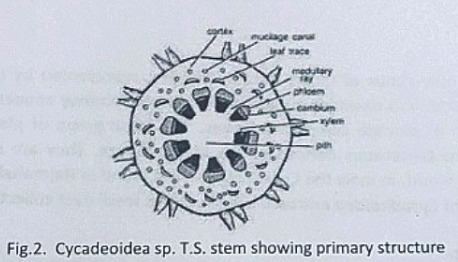
Anatomy of Stem:
The transverse section of the stem shows roughly a circular outline. The epidermis is not very distinct due to the presence of heavy armor of leaf bases. The cortex is parenchymatous and traversed by mucilage canals and numerous leaf traces. The primary vascular structure consists of a ring of endarch, collateral, conjoint, and open vascular bundles encircling the pith. Pith is wide and parenchymatous. A ray-like extension passes between the vascular bundles that make their appearance discrete.
There is a cambium ring with a thin zone of secondary wood. The secondary wood encircles the primary xylem and consists of tracheids with scalariform and bordered pits. The secondary medullary rays traverse the secondary xylem and secondary phloem.
The C-shaped leaf traces arise singly from the primary vascular strand and entering the cortex divided into several masarch strands and enters straight into the leaf.
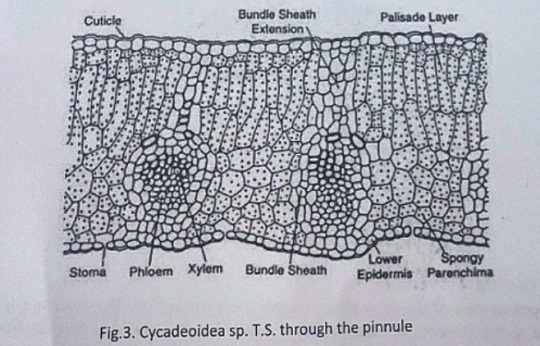
Anatomy of Leaf:
The pinnules show xerophilous structure. The upper and lower epidermis is heavily cutinized and thick walled. The mesophyll cells are distinguished into palisade and spongy parenchyma. The vascular bundles are mesarch and surrounded by bundle sheath.
Reproduction:
The reproductive structure is represented by flowers. In most of the species, the flowers are bisexual and arise in the axil of each leaf.
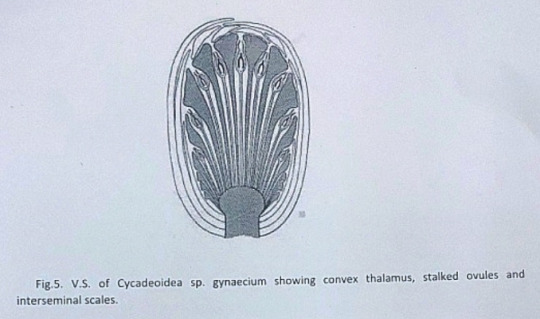
Structure of Flower:
The flowers are bisporangiate, stalked, and partially sunken in the leaf base armor. Rach such mature flower is 5-10cm in diameter and 10cm long. From the base of such flowers about 100 to 150 hairy bracts arise in close spiral little below the apex. These bracts formed a perianth like structure and protect the megasporangiate and microsporangiate parts of a flower. The microsporophyll or androecium forms a whorl united at the base into a sheath. The megasporophyll or gynaecium consists of numerous stalked ovules born around a central receptacle. Between the ovules, interseminal scales with expanded tips are present. These expanded tips fused to form a continuous surface with pores, through which the micropyle of ovules extended. The vascular supply of flowers consists of many branches from leaf traces.
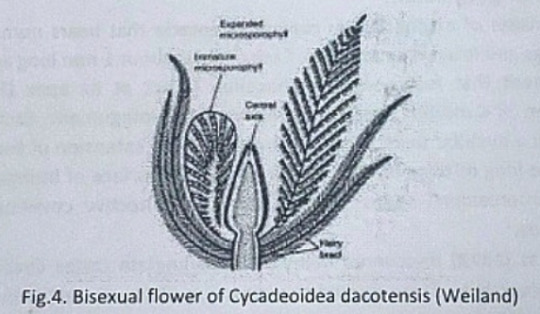
Microsporophyll or Androecium:
The microsporophyll is 10-12cm long, consists of a central rachis bearing numerous pinnae. The pinnae bear two rows of bean-shaped shortly stalked pollen capsules or synangia. These pollen capsules are born on the trabeculae within the fertile region of microsporophyll. A line of dehiscence is also visible at the base of each microsporophyll. This suggest that the entire microsporophyll might have been shed as a unit. The pollen capsule or synangia measures about 3.5x2.5mm and its wall is several layers thick, the outer layer made up of palisade like cells, and the inner layer is made up of thin-walled cells followed by a tapetum. The tapetum was not demarcated. A ring of microsporangia arranged around the periphery of each synangium. The microsporangia dehisce longitudinally and release the microspores into the synangial cavity. At maturity, the synangia liberate these microspores outside by an apical opening that splits into two valves. The liberated microspores or pollens are oval, measures up to 68µ that represents the male gametophytes. Pollen grains of Cycadeoidea are multicellular.
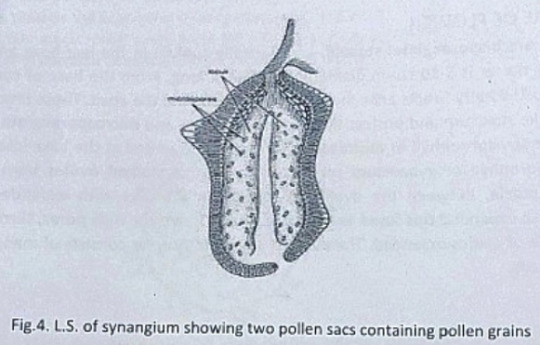
Megasporophyll or Gynoecium
The gynoecium consists of a spherical or conical receptacle that bears numerous stalked orthotropous ovules and interseminal scales. Each ovule is about 1mm long and consists of the single integument that fused with the nucellus except at its apex.
According to Lignier, in C. morieri, nucellus is free from the integument. Each ovule has a pollen chamber and a nucellar beak. This nucellar beak is the extension of the integument. The ovules also have long micropyle, extended from the flat surface of interseminal scales. The fused tips of interseminal scales form an external protective covering or pericarp surrounding the seeds.
Crepet and Delevoryas discovered many of bisporangiate cones from the Cretaceous of black hills. They studied the structure of these ovules in detail. These ovules are urn-shaped and resemble with the ovules of C. wellsii. According to them the micropyle of these ovules are funnel-shaped due to the constriction below the flaring. The inner wall of the micropyle is lined with large cells, considered to be epidermal cells. The integument has three distinct layers. The outer fleshy layer of radially elongated cells, the middle stony layer made up of thick-walled cells, and the inner layer is fleshy.
The young nucellus is made up of thin-walled cells. The cells at the micropylar end are much elongated (80µ long) in comparison to the cells of the chalazal end. The cell at the nucellar tip is pointed up tp whereas cells on either side are bend outward to give the nucellus a distinct shape.
Crepet and Delevoryas reported a linear tetrad or row of three cells in the center of the nucellus.
The seeds are somewhat elongated or oval and possessed two cotyledons.
#exam season#send help#biology#notes#science#botany#gymnosperms#pines#pine trees#pine needles#plants#plant science#plant biology#nature#long post
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
George Orwell being born in Motihari Bihar is my favourite fun fact
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
i have been seeing posts and videos about suzani embroidery in connection to palestine and it didn't strike me earlier but sounded familiar. is it connected to sujani embroidery (bihar)?
from what i can understand they are both ritually made by women of the household, often mother's when a child is born, and while sujani layers fabrics together suzani is created in different pieces and out together.
is there an actual connection between the two or is it one of those funny coincidences?
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

🔷🔹Al-Mufaddal Ibn Amr reported that Imam Sadiq, peace be upon him, said: “Do you know what is the shirt of Yousuf?” He said: “No”. The Imam said: “When fire was set in order to burn Ibrahim, peace be upon him, Jibraeel brought him this shirt and put it on him. Thus, he wasn’t affected by heat or cold. When his death approached, he put it in an amulet and gave to Ishaq, peace be upon him, who passed it on to Ya’qoub, peace be upon him, and Ya’qoub passed it on to Yusuf, peace be upon him, when he was born. It was with him when all those events happened to him. So, when Yusuf, peace be upon him, brought it out of the amulet in Egypt, Ya’qoub was able to smell it. This is what Allah said about { I do indeed feel the smell of Yusuf, if only you think me not a dotard}; it is the shirt that was brought down from heaven”. He said: “May I be sacrificed for your sake, with whom is this shirt now?” He, peace be upon him, said: “With people worthy of it. It will be with our Qa’im (Rising One) when he rises. Every knowledge or other than knowledge inherited by each prophet reaches the household of Mohamad, peace be upon him & his family.
📚Bihar al-Anwar, vol.52, p.327.
#imammahdi #yamahdi #YaMahdi #yamahdiadrikna
1 note
·
View note
Text
Happy Birthday 🎂 🥳 🎉 🎈 🎁 🎊 To You
The Indian Halle Berry 🇮🇳🧡🤎 Of My Dreams
Hailing All The Way From India 🇮🇳
She was born on 18 July 1982 in Jamshedpur, Bihar (present-day Jharkhand), to Ashok and Madhu Chopra, both physicians in the Indian Army.
She is an Indian actress and producer. The winner of the Miss World 2000 pageant, She is one of India's highest-paid actresses and has received numerous accolades, including two National Film Awards and five Filmfare Awards. In 2016, the Government of India honoured her with the Padma Shri, and Time named her one of the 100 most influential people in the world. In the next two years, Forbes listed her among the World's 100 Most Powerful Women, and in 2022, she was named in the BBC 100 Women list.
On Instagram, She is the most-followed Indian actor.
Please Wish This Amazing & Extraordinary Indian Born 🇮🇳🧡🤎 Actress Of Remarkable Acting & Beauty
A Very Happy Birthday 🎂 🥳 🎉 🎈 🎁 🎊
You Know Her & If You Dont, You Will Learn To Love Her Like I Do 😊🧡
The 1 & Only
MS. PRIYANKA CHOPRA AKA THE INDIAN HALLE BERRY 🇮🇳🧡🤎 #PriyankaChopra

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Madhusudan Das
Madhusudan Das
Madhusudan Das (28 April 1848 – 4 February 1934) was an Indian lawyer and social reformer, who founded Utkal Sammilani in 1903 to campaign for the unification of Odisha along with its.. social and industrial development. He was one of the prominent figure, helping in the creation of Orissa Province (present-day Odisha, India), which was established on 1 April 1936. He was also the first graduate and advocate of Orissa. He is also known as Kulabruddha (Grand Old Man),
MADHUSUDAN DAS ALL ODIA BOOK AVAILABLE Madhu Babu, and Utkal Gouraba (Pride of Utkal). In Odisha, his birthday is celebrated as the Lawyers' Day on 28 April.
Family-
Madhusudan Das was born 28 April 1848 at Satyabhamapur, 20 kilometres (12 mi) from Cuttack during the Company rule in India in a Zamindari Karana family.His father was Choudhury Raghunath Das and his mother, Parvati Devee. They had initially named him Gobindaballabh. He had two elder sisters and a younger brother named Gopalballabh. Gopalballabh was a Magistrate at Bihar Province and the father of Ramadevi Choudhury. He was converted to Christianity that caused him boycotted in the village which he had to quit to erect a small house at the end of the village. The house was known as ‘Madhukothi’ or ‘Balipokharikothi’, later on used as the state office of the Kasturba National Memorial Trust, in a part of which was running the Anganabadi, Balbadi. Madhusudan had adopted two Bengali girls; Sailabala Das and Sudhanshubala Hazra. Sailabala was an educationist who had been trained in England, and in whose name the famous Sailabala Women's College of Cuttack was founded.Sailabala was Bengali, and her parents had left her in the care of Madhusudan Das and his wife Soudamini Devi at Calcutta. In 1864, he passed Matriculation from Cuttack and thereafter he was inclined to become a teacher and began his career as a teacher at Balasore for three years. The year 1866 was the year of a acute famine in Odisha, called the "Naanka Durviksha" When more than one lakh people died of hunger. This year he converted himself to Christian and changed his name as Madhusudan Das from his earlier name of Gobinda Ballav Choudhury.
Political career--
Known as 'Madhu Babu' by the common people, he worked for the political, social and economical upliftment of the people of Orissa and worked as a lawyer, journalist, legislator, politician and social reformer. He founded Utkal Sammilani which brought a revolution in the social and industrial development of Orissa. He was elected as a member of the legislative council of Bihar and Orissa Province and under the Diarchy scheme of Government of India Act, 1919, he was appointed as Minister for Local Self-Government, Medical Public Health, Public Works in 1921. He was the first Odia to become a member of both the legislative council and the Central Legislative Assembly of India. He founded Utkal Sammilani (Utkal Union Conference) which laid the foundation of Odia nationalism. Utkal Sammilani spearheaded the demand for unification of Odia speaking areas under a single administration. This led to the formations of state of Odisha on 1 April 1936. He was also the first Odia to travel to England. He founded the Utkal Tannery in 1905, a factory producing shoes and other leather products. In 1897 he founded the ODISHA Art Ware Works. With his support, the Tarakasi(filigree) work of silver ornaments achieved commendable feet.
Contribution to literature--
As a writer and poet, patriotism was always at the forefront of his mind, and that was reflected in all of his literary works. He penned a number of articles and poems in both English and Odia. Some of his important poems are "Utkal Santan", "Jati Itihash" and "Jananira Ukti". He was also an influential speaker in Odia, Bengali and English.
Last years--
He died on 4 February 1934 at the age of 85.
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo




Women’s History Month: Nonfiction Recommendations
Sisters of Mokama by Jyoti Thottam
New York Times editor Jyoti Thottam’s mother was part of an extraordinary group of Indian women. Born in 1946, a time when few women dared to leave their house without the protection of a man, she left home by herself at just fifteen years old and traveled to Bihar - an impoverished and isolated state in northern India that had been one of the bloodiest regions of Partition - in order to train to be a nurse under the tutelage of the determined and resourceful Appalachian nuns who ran Nazareth Hospital. Like Thottam’s mother’s journey, the hospital was a radical undertaking: it was run almost entirely by women, who insisted on giving the highest possible standard of care to everyone who walked through its doors, regardless of caste or religion.
Fascinated by her mother’s story, Thottam set out to discover the full story of Nazareth Hospital, which had been established in 1947 by six nuns from Kentucky. With no knowledge of Hindi, and the awareness that they would likely never see their families again, the sisters had traveled to the small town of Mokama determined to live up to the pioneer spirit of their order, founded in the rough hills of the Kentucky frontier. A year later, they opened the doors of the hospital; soon they began taking in young Indian women as nursing students, offering them an opportunity that would change their lives. One of those women, of course, was Thottam’s mother.
In Sisters of Mokama, Thottam draws upon twenty years’ worth of research to tell this inspiring story for the first time. She brings to life the hopes, struggles, and accomplishments of these ordinary women - both American and Indian - who succeeded against the odds during the tumult and trauma of the years after World War II and Partition. Pain and loss were everywhere for the women of that time, but the collapse of the old orders provided the women of Nazareth Hospital with an opening - a chance to create for themselves lives that would never have been possible otherwise.
The Code Breaker by Walter Isaacson
When Jennifer Doudna was in sixth grade, she came home one day to find that her dad had left a paperback titled The Double Helix on her bed. She put it aside, thinking it was one of those detective tales she loved. When she read it on a rainy Saturday, she discovered she was right, in a way. As she sped through the pages, she became enthralled by the intense drama behind the competition to discover the code of life. Even though her high school counselor told her girls didn’t become scientists, she decided she would.
Driven by a passion to understand how nature works and to turn discoveries into inventions, she would help to make what the book’s author, James Watson, told her was the most important biological advance since his codiscovery of the structure of DNA. She and her collaborators turned a curiosity of nature into an invention that will transform the human race: an easy-to-use tool that can edit DNA. Known as CRISPR, it opened a brave new world of medical miracles and moral questions.
After helping to discover CRISPR, Doudna became a leader in wrestling with these moral issues and, with her collaborator Emmanuelle Charpentier, won the Nobel Prize in 2020. Her story is an “enthralling detective story” (Oprah Daily) that involves the most profound wonders of nature, from the origins of life to the future of our species.
The Doctors Blackwell by Janice P. Nimura
Elizabeth Blackwell believed from an early age that she was destined for a mission beyond the scope of "ordinary" womanhood. Though the world at first recoiled at the notion of a woman studying medicine, her intelligence and intensity ultimately won her the acceptance of the male medical establishment. In 1849, she became the first woman in America to receive an M.D. She was soon joined in her iconic achievement by her younger sister, Emily, who was actually the more brilliant physician.
Exploring the sisters’ allies, enemies, and enduring partnership, Janice P. Nimura presents a story of trial and triumph. Together, the Blackwells founded the New York Infirmary for Indigent Women and Children, the first hospital staffed entirely by women. Both sisters were tenacious and visionary, but their convictions did not always align with the emergence of women’s rights - or with each other. From Bristol, Paris, and Edinburgh to the rising cities of antebellum America, this richly researched new biography celebrates two complicated pioneers who exploded the limits of possibility for women in medicine. As Elizabeth herself predicted, "a hundred years hence, women will not be what they are now."
The Queens of Animation by Nathalia Holt
From Snow White to Moana, from Pinocchio to Frozen, the animated films of Walt Disney Studios have moved and entertained millions. But few fans know that behind these groundbreaking features was an incredibly influential group of women who fought for respect in an often ruthless male-dominated industry and who have slipped under the radar for decades.
In The Queens of Animation, bestselling author Nathalia Holt tells their dramatic stories for the first time, showing how these women infiltrated the boys' club of Disney's story and animation departments and used early technologies to create the rich artwork and unforgettable narratives that have become part of the American canon. As the influence of Walt Disney Studios grew - and while battling sexism, domestic abuse, and workplace intimidation - these women also fought to transform the way female characters are depicted to young audiences.
With gripping storytelling, and based on extensive interviews and exclusive access to archival and personal documents, The Queens of Animation reveals the vital contributions these women made to Disney's Golden Age and their continued impact on animated filmmaking, culminating in the record-shattering Frozen, Disney's first female-directed full-length feature film.
#women's history month#women's history#nonfiction#nonfiction books#Library Books#Book Recommendations#book recs#Reading Recs#reading recommendations#Want To Read#to read#TBR pile#tbr#Booklr#book tumblr#book blog#library blog
4 notes
·
View notes
Note
YESS i am
i was born and brought up in delhi tho
my mom's from kolkata and baba's from bangladesh
Woah I'm born and brought up in Calcutta, my mum's completely Bengali but my Dad hails from Bihar and Bengal both<3
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Biography of Physics Wallah

Alakh Pandey (Physics Wallah). Alakh Pandey is an Indian educator and motivational speaker which is commonly known as (physics wallah) and also he is the co-founder of physics wallah .he started his YouTube channel in 2016 by the name (physics wallah) the aim was to improve the quality of Indian education and made education affordable to students in India. Alakh Pandey made a significant role in the field of education in India. He was born on 7 November 1991 in Sasaram, Bihar Alakh Pandey is known as the face among student who is preparing the competitive exams like JEE, IIT, NEET, and other engineering and medical entrance exams. Alakh Pandey completed his schooling at D.A.V public school in Sasaram, Bihar after completing the school he register his name for IIT – BOMBAY to attempt his undergraduate degree in mechanical engineering. He dropped out his college in his third year to teach physics at the institute of Kanpur.
6 notes
·
View notes