#Blue Economy and Marine Pollution
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Blue Economy and Marine Pollution
It refers to the presentation, exploitation, and regeneration of the marine environment. It is used to describe a sustainability-based approach to coastal resources. Human activities pose a serious threat to the oceans, which is concerning, especially whe
Blue Economy and Marine Pollution: It refers to the presentation, exploitation, and regeneration of the marine environment. It is used to describe a sustainability-based approach to coastal resources. Human activities pose a serious threat to the oceans, which is concerning, especially when economic advantages are made at the expense of maintaining environmental sanity. Blue Economy Policy of…

View On WordPress
#Blue Bond#Blue Bond Economy#Blue Bond Policy of India#Blue Economy#Blue Economy and Marine Pollution#Blue Economy and Ocean Governance#blue economy means#Blue Economy policy#Blue Economy policy india vision#blue economy upsc#Details of Blue Economy policy#Gunter Pauli#India Blue Economy#India Blue Economy policy#Marine Pollution#maritime pollution#maritime pollution and associated challenges#Ocean Governance#professor Gunter Pauli#seven thematic areas#Sustainable Development Goals
1 note
·
View note
Text

Revitalizing the ocean economy with transformative sustainability innovation in urban planning and architectural design
Image: © Haptic Architects, Oslo Works, and BOGL
A waterside scheme spanning 45,000 sqm with features including Fjordarium—an aquarium with underwater galleries capturing the fjord’s marine life and anticipating its future. The facility is part of a wider knowledge hub of workspaces for marine industry and ocean tech businesses. Haptic Architects and Oslo Works reimagine a disused parking lot as a global centre for sustainable oceanic practices.
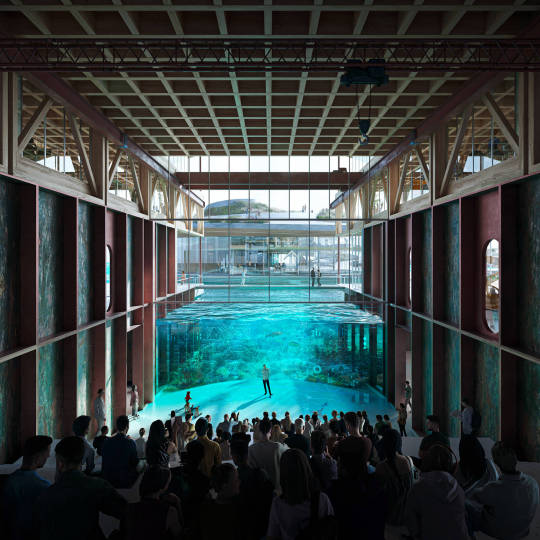

Fjordarium featuring underwater galleries that peek into the marine life of the fjord
The Fjord area is designed as the educational centre of the scheme and will house the Fjordarium. This building will provide an immersive visitor experience by offering a window directly into the fjord. The Fjordarium will encompass various facilities such as a restaurant, bar, gallery, event space, research laboratories, workspaces, and teaching rooms above and below the water level.

In collaboration with the Norwegian Institute for Water Research (NIVA), the design of the Fjordarium building has been created to safeguard marine biodiversity. The building, as per the design statement, will be engineered to withstand the fjord's waves and currents while maximising natural light penetration into the underwater areas. It will address the challenges and provide solutions for cleaning the heavily polluted fjord caused by agricultural waste. In partnership with We Are Human, the architects have conceived the Fjordarium as a destination that will seamlessly blend physical and virtual experiences. It will serve as a global learning platform, exploring the drivers of the new blue economy while promoting a shift towards environmental sustainability and a regenerative approach to oceans.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
























World Oceans Day
With oceans making up 66% of our Earth, it’s crucial we raise awareness about and tackle the threats facing these life-giving and life-containing bodies of water.
66% of the world is covered in a blanket of rich, vibrant blue, from its depths once came all life on the Earth, and it continues to house an immense amount of life. This blanket is the world’s oceans, and they serve as one of the most popular vacation spots in the world and play a vital role in the economy of countries worldwide. Across the briny deep massive amounts of cargo cross each year, and it still serves as the primary thoroughfare for trade. World Oceans Day celebrates the ocean and the important role it plays in our lives.
It’s a time for supporters of the oceans to focus on conversation and sustainability so that they can remain clean and usable. The animals deserve a happy and safe place to roam and live without having to worry about any destruction or man-made obstacles. It’s important to safeguard the oceans to help ensure a healthy home for all. One this day, people can come together to create a space for all to enjoy and appreciate, no matter where each person lives.
History of World Oceans Day
In 2008, the UN gathered and uniformly created World Oceans Day. It was first proposed in 1992 in Rio de Janeiro during the Earth Summit. The ocean has been an incredibly important part of human history, and this special was established with the intent of celebrating our connection to the sea and raising awareness about the various dangers it faces. There are nearly 200,000 identified species that live in the ocean, but the number of actual species that reside there is likely in the millions. It’s essential to ensure that they don’t have to worry about freely getting around and enjoying a healthy and safe home to reside.
Even with that being the case, there are still problems with overfishing, and the subsidies that are given for fishing in countries all around the world are causing depletion of the game species. These activities have led to efforts to restore the fishing industry being undermined, and the industry bringing in $50 billion a year less. It’s just one of the many factors that should have us all celebrating World Oceans Day and raising awareness about all the issues our big blue’s face.
There’s a global environmental catastrophe due to decades of overuse and a surge in single-use plastics. Plastic straws and bags are getting into the oceans and causing havoc. World Oceans Day is an opportunity to acknowledge and recognize the efforts that have been and are being made against plastic pollution. It’s enlightening and disheartening to know that today, 13,000,000 tons of plastic leaks into the ocean every year, which among other damage, kill 100,000 marine animals annually.
World Oceans Day Timeline
1987 Brundtland Report
This report, connected to The World Commission on Environment and Development (Brundtland Commission) notes that the ocean sector is lacking representation compared to other sectors.
1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro
Created as a way to celebrate the world’s shared ocean and raise awareness for the personal connection between humans and the ocean. This is where the concept for World Oceans Day was first proposed by the Canadian representatives.
2008 UN declares to recognize World Oceans Day
This year, after a four-year onsite and online petition drive, the UN General Assembly passes a Declaration that will officially recognize the day, beginning the following year.
2009 First World Oceans Day is celebrated
The inaugural World Oceans Day is observed with the theme “Our Oceans, Our Responsibilities.”
2016 World Oceans Day Youth Advisory Council is launched
Made up of 25 youth from all over the world, the Youth Advisory Council is created to develop and promote World Oceans Day.[5]
Why celebrate World Oceans Day?
It’s a good reminder to bring attention to the fact that oceans play a major role in everyday life all around the globe. The oceans provide a majority of the oxygen we breathe, so many consider them to be the lungs of our planet. The goal is to develop a worldwide movement of citizens to care better for the oceans. It’s an opportunity to inform and educate humans and the public of what our actions are doing to the ocean and what impact they have in the long run. It’s not only a day to celebrate the beauty, wealth, and promise of the ocean, but a chance to realize that they’re a critical part of the biosphere. They’re a significant source of food and medicines and simply can’t be ignored or mistreated any longer.
How to celebrate World Oceans Day
Start it off by a visit to the nearest ocean to restore a personal connection to the sea. Breathe deep and appreciate the beauty and serenity the ocean offers each day of the week. Invite family along, and while there, bring information about the ocean and what people really need to know about it to make visiting it a joy for years to come.
Pick a day to go to the ocean to clean up and help restore it instead of simply sitting by it. Gather friends and family and pitch in and pick up trash that surrounds the local beaches and oceans in the area. It’ll not only look nicer, but the wildlife in the area will benefit from these actions as well. Avoid single-use plastics, and instead pack a picnic lunch with reusable containers to enjoy after the hard work is complete. One may also consider organizing a fundraiser to aid preservation and restoration efforts at the local beach. With all the plastic waste coming off our beaches thanks to careless beach-goers, our ocean is awash with litter.
Use this as a time to increase one’s knowledge and explore the topic further. There are a variety of books and resources out there to help a person achieve this goal. Another idea is to gather a group of people and watch an ocean film on the topic to bring awareness to the concept of helping out the oceans.
There are plenty of activities and events that occur on World Oceans Day. Celebrate by choosing one or two to participate in and enjoy. Engage in the day’s events by piggybacking off of other ideas that people in the area have come up with instead of having to think of activities alone.
Source
#Vancouver#Burrard Inlet#Big Sur#Morro Bay#playa de las Catedrales#Albufeira#Atlantic Ocean#Spain#Portugal#travel#Miami Beach#Daytona Beach#seascape#landscape#original photography#World Oceans Day#WorldOceansDay#8 June#tourist attraction#USA#St. John's#Acadia National Park#Canada#Kalaloch Beach#Washington#Bandon#Oregon#Pacific Northwest#Point Arena Lighthouse#vacation
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why World Ocean Day?

Welcome to National Public School Kudlu! As we gather here on this special occasion of World Ocean Day, let us embark on a remarkable journey into the depths of the mighty blue that covers over 70% of our planet. Today, we celebrate the ocean—the life-giving force that sustains us, supports biodiversity, fuels our economy, and offers us countless adventures. Join us as we dive into the depths of knowledge and discover the significance of our magnificent oceans.
The Ocean's Purpose: Why It Matters:
Did you know that the ocean is responsible for producing at least 50% of the oxygen we breathe? That's right! Each breath we take is a gift from our vast and powerful ocean. Beyond oxygen production, the ocean also acts as a sanctuary for the Earth's remarkable biodiversity. It is home to millions of unique species, from the tiniest plankton to the majestic whales that grace our seas.
But the ocean's importance doesn't stop there. It serves as the primary source of protein for over a billion people worldwide. It nourishes our bodies and sustains coastal communities by providing an abundance of fish and seafood. Moreover, the ocean plays a significant role in our global economy. By 2030, an estimated 40 million people will be employed in ocean-based industries, contributing to the growth and prosperity of nations around the world.
Conserving the Ocean: Our Collective Responsibility:
Now that we understand the immense value of our oceans, it becomes our collective responsibility to conserve them. As members of National Public School Kudlu, we have the power to create positive change and protect the oceans for future generations. Here are some ways we can contribute:
Spread Awareness: Educate others about the importance of the ocean. Share your newfound knowledge with family, friends, and classmates. Inspire them to take action and become ocean ambassadors themselves.
Reduce Plastic Pollution: Plastic waste poses a severe threat to marine life and ecosystems. Say no to single-use plastics, recycle diligently, and participate in beach cleanup drives. Let's make a conscious effort to keep our oceans clean and free from harmful debris.
Conserve Water: The ocean and its inhabitants rely on freshwater sources. By conserving water in our daily lives, we can reduce the strain on these vital resources and ensure a healthier environment for both land and sea.
Support Sustainable Seafood: When choosing seafood, opt for sustainably sourced options. This decision helps protect ocean ecosystems and ensures the long-term viability of fish populations.
Conclusion: The Time for Action is Now!
As we celebrate World Oceans Day here at National Public School Kudlu, let us recognize the incredible role the ocean plays in our lives. From providing oxygen to sustaining biodiversity and supporting livelihoods, the ocean's significance cannot be overstated. We have a duty to preserve and protect this vast and remarkable ecosystem.
So, let's join hands, dear students, and take a pledge to conserve the ocean and keep our beaches clean. Together, we can make a difference. As we move forward, let us remember that our actions today shape the future of our oceans tomorrow.
Happy World Ocean Day! Let's dive into a brighter, bluer future!
#oceanday#worldoceanday#oceanday2023#ocean#oceanlofe#sea#oceans#nature#beach#protecttheoceans#environment#plasticpollution#saveourseas#beachcleanup#oceanlover#saveourocean#savetheocean#india#bangalore#bengaluru#schools#school#kids#children#classroom#teachers#Parents#family#nps#npskudlu
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unit 9 Blog Post
Imagine looking out at the ocean, stretching as far as the eye can see, powerful waves crashing against the shore. Now, consider that beneath this vast expanse lies an even greater mystery. One that’s baffling, beautiful, and filled with life we can barely comprehend. The most amazing thing I know about nature is that the ocean covers nearly 70 percent of Earth’s surface, yet over 95 percent remains unexplored (NOAA, n.d.). It’s as if we are living alongside another world entirely, right here on our planet.One of the most awe-inspiring aspects of the ocean is its biodiversity. Though we’ve cataloged 226,000 marine species, “the ocean may be home to 700,000 marine species, with likely not more than a million” (UNESCO, 2022). From the smallest plankton to the enormous blue whale - marine life is incredibly diverse.
The unknown ocean’s deep, dark recesses - places where sunlight never reaches - live bioluminescent organisms that create their own light, glowing in the blackness. The anglerfish, with its eerie glowing lure, and the giant squid, a creature that has inspired countless myths, are just two examples of life thriving in these hostile environments.he ocean is like a vast library, each layer and depth filled with secrets that tell the story of our planet. Some are clues to Earth’s ancient past; others are whispers of life forms that may have developed in ways we can only imagine. Artifacts from lost civilizations, remnants of ancient ecosystems, and fossils of creatures long extinct may be hidden in the depths, waiting to be discovered.
But perhaps the most astounding thing about the ocean is how it sustains life on Earth. The ocean is our planet’s most important support system. It impacts everyone: the air we breathe, food, transportation and commerce, weather, and climate change.
“Oceans are the lifeblood of the planet…” (Beck et al., 2019).
And yet, despite the ocean’s importance, it is in urgent need of protection. Our oceans face threats from climate change, pollution, acidification, and oxygen loss. This vast ecosystem regulates our climate by absorbing 25 percent of carbon emissions and 90 percent of excess heat, and it provides 50 percent of the oxygen we breathe (United Nations, n.d.). Additionally, it supports the global food supply, offering 15 percent of the world’s protein and serving as a primary food source for millions in developing countries (United Nations, n.d.). However, destructive practices, pollution, and rising temperatures damage marine ecosystems, endangering biodiversity, and threaten economies that rely on a healthy ocean. Protecting our ocean is essential for our planet’s future stability and our survival.
So, next time you look out over the ocean, remember that it is not just a beautiful, endless expanse. It’s an unknown world within our own: with secrets, mysteries, and wonders waiting to be discovered. The ocean is Earth’s last great frontier, and every wave hides something astonishing, calling us to explore. We must protect this undiscovered world, or we will never have the chance to explore it.


(Pictures taken by me at Ripley's Aquarium, Toronto.)
References:
Beck, L., Cable, T. T., & Knudson, D. M. (2019). Interpreting cultural and natural heritage: For A Better World. (pp.458). Sagamore Publishing.
NOAA (n.d.). Most of our ocean is unexplored. NOAA Ocean Exploration and Research: World Oceans Day. https://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/world-oceans-day/reason-1.html#:~:text=Given%20that%20the%20ocean%20is,of%20our%20ocean%20is%20unknown.
UNESCO (2022). What is Ocean Biodiversity. https://oceanliteracy.unesco.org/ocean-biodiversity/
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Detecting Microplastic Contamination with Nile Red
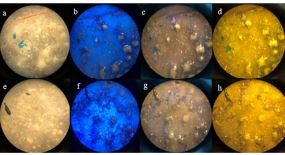
Abstract
This study delves into the evaluation of fluorescent lights staining microscopy and its efficiency in cross validation by comparison with light microscopy. Rapid detection of microplastics of various sizes can be distinguished in assessing coastal marine sediment. A development of a novel approach in rapid detection is employed for analysis of coastal marine sediment microplastic contamination, based on fluorescent tagging using Nile Red (NR), separated by density-based extraction using Zinc Chloride (ZnCl2) and filtration. The fluorescent staining tags onto microplastic to fluorescent, aides with excitation of blue light and color filters. Fluorescence excitation is detected using simple smartphone photography through a polarizer filter. Rapid detection using light microscopy allows fluorescent particles to be identified and counted in image-analysis. The study used a paired sample t-test to compare particle counts across five mesh sizes, revealing minimal too little to no significant differences between fluoresced and suspected MPs particles, indicating a novel detection process with greater selectivity and fluorescence intensity.

Introduction
The Philippines is an archipelagic country which consists of 7,641 islands and has an extensive and diverse coastline. It boasts as one of the longest coastlines in the world with a measure of approximately 36,000 kilometers (22,370 miles). This coastline encompasses a wide variety of features ranging from pristine beaches to rugged cliffs and rocky shores. These coastal areas play a crucial role in the country's culture, economy, and ecology as they provide habitat to numerous fish species, marine life, and migratory birds. It also serves as hubs for trade, tourism, and agriculture. However, with high level of tourism and recreational activities in the area such as fishing, swimming, sailing, and snorkeling may lead to have larger amount of plastic waste that can pollute and contaminate the marine environment (Chaisanguansuk et al., 2023)
Plastics and other synthetic, non-biodegradable pollutants, which are often referred to as “marine debris,” have been contaminating and polluting the world’s enclosed seas, coastal waters, and the wider open oceans for the past five or six decades (Gregory, 2009). The hazard posed by plastic waste is significant because it starves and suffocates wildlife, distributes invasive and possibly dangerous species, absorbs toxic chemicals, and breaks down into microplastics that can be ingested (Barnes et al., 2009). These microscopic particles, also known as microplastic which are smaller than 5 mm in size, are present in many different environments. It poses a threat to the ecosystem due to their small size (millimeters or less), it is accessible to a variety of organisms with the ability to cause both physical and toxicological harm (Law and Thompson, 2014). Microplastics can be swallowed by low-trophic feeders, filters, and deposits, as well as by detritivores and plankton-eating organisms. As a result, they can build up inside organisms and cause physical damage, like internal abrasions or blockages. Aside from the physical damage, microplastics can also leach into the environment, where they can cause cancer or endocrine disruption (Wright, 2013).
Even though microplastic contamination affects biota, the environment, and public health significantly, it is a difficult problem to solve since it is so pervasive, and the specific adverse consequences of both long-term and short-term exposure are unknown (Savuca, 2022). Because of the growing worries about the amount of marine plastic waste and the effects it has had on marine ecosystems, marine plastic debris pollution has been identified as a global concern (Mu et al., 2019).
This study serves as baseline studies in microplastic contamination in the coastal environment in sediments of Anda, Northwestern Pangasinan. This study generally aimed to identify the presence of microplastic contamination along the coastlines in sediments of Anda, Northwestern Pangasinan. Specifically, it aimed to detect microplastic contamination using Nile Red fluorescence along the coastlines in sediments of Anda, Northwestern Pangasinan and to assess the efficacy of Nile Red fluorescence in staining for rapid detection of microplastics along the coastline of Anda, Northwestern Pangasinan.
Source : Rapid detection of microplastic contamination using Nile red fluorescent tagging
0 notes
Text
WEEK 2 Climate Warriors
PART 1

Dr. Ayana Elizabeth Johnson is well-known for her work on climate change and ocean conservation and her contributions to science, policy, and activism. She has been a prominent voice in climate strategy talks even though color, marine biology, and environmental policy fields are historically male-dominated and less diverse. Ocean Collective and Urban Ocean Lab, two of her ventures that aim to promote sustainable ocean policies and urban-coastal management, are examples of her innovative multidisciplinary approach that combines academic study with real-world policy implications. Johnson's work in media, especially as co-host of "How to Save a Planet," helps to bring climate science to a broader audience and inspires them to take action.

Conservation of marine ecosystems is at the heart of Johnson's creative solutions, essential to a more comprehensive approach to climate change. To make communities more resistant to climate change, she pushes for more sustainable fishing practices, less plastic pollution, and incorporating blue carbon habitats. As a leader, she exemplifies the current trend toward women taking the lead in developing environmentally friendly policies and programs that are both effective and equitable since the effects of climate change disproportionately impact them. Johnson’s work highlights the importance of interdisciplinary approaches and varied viewpoints in solving global climate problems.
PART 2

Kenyan engineer and businessman Nzambi Matee started Gjenge Makers, a social company that turns plastic waste into stronger and lighter bricks than regular concrete bricks. Her project addresses the big problem of plastic waste in cities and provides affordable and long-lasting building materials that could help struggling areas find homes. Not only does her business create jobs in the area, but it also helps the economy by creating jobs in waste collecting and brick-making.

Matee's business has clear environmental and economic benefits, but it meets problems like how to make it bigger, getting approval from regulators, and finding a market for it. This is because the construction industry is usually reluctant to switch from using traditional materials. It's possible that the mass media doesn't cover these kinds of creative solutions because they're too busy with more significant, more immediate stories, don't understand the technical details, or prefer more shocking stories. Using lobbying in the media and social media to raise awareness could help these important environmental innovations get more attention and have a more significant effect.
PART 3
1. The Key Quote and What It Means

Melissa Hornbein said, "Judge Seeley understood not only the legal issues but also the complex scientific issues surrounding the climate crisis as well as clearly how these particular plaintiffs were affected." This statement hits home because it shows how personally and deeply the judge understood the case. This ruling is significant because it shows that the law can and should protect people's rights to a healthy environment and hold governments responsible for the scientific facts of climate change. It gives young activists more power and sets a positive example for future environmental lawsuits. This shows how powerful combining scientific knowledge with legal action can be.
2. An essential part of the state constitution

A vital part of Montana's Constitution that guarantees a "clean and healthy environment" was the key to the court's win. This promise was the most critical part of the case; it gave a clear standard against which the state's policies were judged and found to be lacking. The young claimants used this constitutional right as a solid basis to say that their government's actions (or lack of actions) on climate change were bad policies and violations of the Constitution that affected real lives.
3. Why young women are taking the lead on climate change

Young women are becoming more active in the climate movement. This may be because they have a unique view of the future and a solid duty to care for and protect their communities. Many young women were aware of social and environmental justice problems as kids. Many also see climate change as an immediate threat that worsens existing inequality. Their leadership is marked by passion and a potent mix of understanding and realism that drives them to find natural ways to make the world more sustainable.
4. Effects on youth climate activism around the world

Young climate activists worldwide can take heart from the outcome of the Held v. Montana case, which shows that their views can make a big difference. Not just one U.S. state won this case. It shows young people everywhere that the legal system can be a powerful tool in the fight for a sustainable world. As word of this story grows, it could lead to a flood of legal challenges led by young people worldwide. This could change how countries deal with the urgent needs of climate change. Teenagers can make a difference if they speak out, act, and demand that people be held responsible.
References
‘Gamechanger’: judge rules in favor of young activists in US climate trial | Montana | The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2023/aug/14/montana-climate-trial-young-activists-judge-order
Human Rights and Climate Change: An Introduction – American University International Law Review. https://auilr.org/2024/01/08/human-rights-and-climate-change-an-introduction/
Goodmark, L. S. (2004). Law is the Answer? Do We Know That For Sure? Questioning the Efficacy of Legal Interventions for Battered Women. https://core.ac.uk/download/56356203.pdf
0 notes
Text
What Are the Flaws With A Hydrogen Economy?
Note: This was written in late 2020 and is overdue an update.
Abstract
Climate change is already having substantial societal and ecological impacts and these are projected to worsen this century. Solutions are framed within a dominant narrative of a 'net zero' or 'carbon neutral' world, which has led to speculation of a potential ‘hydrogen economy’, where the gas is presented as a green technology and a clean burning fuel.
Many of the media stories, institutional and academic studies are very favourable towards the idea of a hydrogen economy and a critical evaluation of its downsides is lacking. Many idealists view a world powered by green hydrogen made from renewable energy as a step forward. Yet, most hydrogen is currently manufactured from fossil fuels and green hydrogen is 3-4 times the cost. Many analyses overlook some of the key limitations of hydrogen, notably the poor energy efficiency of its applications, difficulties with storage and distribution, it’s role as an indirect greenhouse gas and its potential stratospheric impacts.
Many of these issues were raised well over a decade ago and are now being conveniently overlooked, despite the challenges not having been overcome. In addition, the huge expectations placed on renewable energy and hydrogen in future scenarios often fail to consider the resource implications these technologies are constrained by and the ecological impacts from increased mining of key metals. A hydrogen-powered world is now being promoted by many companies who have played damaging roles in our current fossil fuel economy, amongst them are oil and gas, automobile and aviation companies who seek an extension to the industrial growth that has wrecked our biosphere. Carbon Capture and Storage is offered in place of ‘Keep It In The Ground’ as climate-wrecking mega-corporations attempt to rebrand their businesses as net zero.
One of the principal problems is that the public are being sold a 'Green Hydrogen' future, which is low carbon and clean burning, whereas what they will get, is 'Blue Hydrogen' i.e. Hydrogen with Carbon Capture and Storage or perhaps 'Grey Hydrogen' if CCS plans become unviable, both of which are more greenhouse gas intensive and ecologically damaging than the alternative of sticking and eventually phasing out methane.
In addition there are the dangers of Carbon Capture and Storage, which include earthquakes from induced seismicity and the potential risks of asphyxiation from leaking CO2 pipes and the poisoning of marine ecosystems.
This greenwash is business as usual. We need to be wary of climate-centric solutions which threaten the integrity of other planetary boundaries. A much smaller niche role for green hydrogen coupled to a less energy intensive future is suggested as an alternative solution.
Introduction
Greenhouse gas emissions must be drastically reduced in order to combat climate change (IPCC, 2014). Fossil fuel combustion is also accompanied by increased air pollution. This has led to speculation of a potential ‘hydrogen economy’, which presents hydrogen as a green technology and a clean burning fuel (Brandon and Kurban, 2017). However, 96% of hydrogen is currently made from fossil fuels in processes which also emit carbon dioxide, fuelling climate change (Nikolaidis and Poullikkas, 2017). Hydrogen can also be made from renewable energy by electrolysis, so-called green hydrogen. However, this process is currently around three to four times more expensive than steam methane reformation (SMR), the dominant approach at present. SMR can be coupled to carbon capture and storage (CCS) which could theoretically reduce emissions. However, there are currently only two large-scale production facilities in the world that have adopted this method (Global CCS Institute, 2019). CCS is unproven to work effectively and safely at scale and to date it has mostly been used to exploit more fossil fuels. Placing our faith in this route represents a large gamble for humanity.
A number of think tanks have recently touted the benefits of hydrogen (Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2019; International Energy Agency, 2019; Hydrogen Council, 2020). Consequently, hydrogen has been the subject of recent media stories (Clarke, 2020; Harrabin, 2020; Jolly, 2020; Hannan, 2020; Coman, 2020). The fossil fuel industry have been keen to promote hydrogen with CCS in order to maintain demand in a decarbonising economy, but their ‘solutions’ look very much like business as usual. Continued methane production also increases the likelihood of unconventional exploitation techniques, such as fracking and coal bed methane, which are known to pollute water and cause earthquakes (Concerned Health Professionals of New York and Physicians for Social Responsibility, 2019). The UK aims to achieve a carbon neutral economy by 2050 (UK Government, 2019) and one of the solutions that has been proposed is hydrogen (Committee on Climate Change, 2018; Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2019; National Infrastructure Commission, 2020; Oxford Institute for Energy Studies, 2020).
Most hydrogen is currently used for oil refining and to make ammonia for fertilisers. Potential uses that have been proposed for hydrogen are as a transport fuel, for heating buildings and for power generation, although it’s unclear, which if any of these pathways will play a major role in any future economy (Brandon and Kurban, 2017; Committee on Climate Change, 2018). Surplus renewable energy could also be used to make hydrogen that acts as an energy store, helping to balance intermittency. Alternatively, the hydrogen could be converted to methane, a solution referred to as power-to-gas, although the multiple steps in the process result in a low overall efficiency (Götz et al, 2016).
Hydrogen can be used in fuel cells or combusted directly to produce energy. The main product of either process is water and no greenhouse gas emissions are produced. Fuel cells use hydrogen to make electrical energy with zero emissions. However, if hydrogen is combusted in a gas turbine or hydrogen boiler, the process also produces nitrogen oxides (NOx), which contribute to air pollution. Air pollution is estimated to cause 40,000 annual deaths in the UK (RCP & RCPCH, 2016) and 456,000 in the EU (European Environment Agency, 2019). Increased atmospheric hydrogen due to leakage could lead to stratospheric ozone depletion and it’s also an indirect greenhouse gas, albeit with a low climate impact (Tromp, 2003; Schultz et al, 2003; Warwick et al, 2004; Derwent et al, 2020).
In addition to its environmental impacts, a number of key limitations are often overlooked when considering hydrogen as an energy carrier. There are substantial challenges with storage and distribution and production inefficiencies along each of the pathways to hydrogen means that better alternatives are available (Kreith and West, 2004; Bossel, 2006; Page and Krumdiek, 2009; Balat and Kirtay, 2010). We should be wary of viewing hydrogen as a silver bullet. These limitations manifest themselves as increased costs, which means that hydrogen will require political support and financial incentives in order to scale to the point at which it can be competitive. Pursuing the hydrogen economy to this degree means following a path of increased industrialisation, which will lead to further ecological degradation. Further, the extent to which many climate solutions are dependent on renewable energy is likely to be limited by the degree to which these technologies can be scaled up. A key constraint here will be the depletion of critical metals which are required for solar PV, wind energy, battery, fuel cell and electrolysis technologies (Kleijn and van der Voet, 2010; Watari et al, 2018; Valero et al, 2018; Heffernan, 2019). Rather worryingly, the embodied energy problem does not seem to be widely understood. All materials have an ecological footprint which comes from the mining of materials and their manufacture and distribution. Framing renewable energy as a ‘zero carbon’ solution merely shows how extensive scientific illiteracy is within the green and climate movements. Sadly, this often extends to the academic literature.
Relying on renewable energy for all our electricity, heating and transport energy requirements alongside expectations of future economic growth represent unrealistic expectations. Modern lifestyles centred on affluence and overconsumption have transgressed planetary boundaries and paths towards a sustainable future should embrace a degrowth economy (Steffen et al, 2015; Kallis, 2018; Wiedmann et al, 2020). Proposed climate solutions should be considered within the wider framework of respecting these planetary boundaries.
References
Amrose, J. (2020) Shell unveils plans to become net-zero carbon company by 2050 net zero carbon target for 2050. The Guardian, 16th April [online] Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/ business/2020/apr/16/shell-unveils-plans-to-become-net-zero-carbon-company-by-2050 [Accessed: 04/07/2020]
Balat, M., Kirtay, E. (2010) Major Technical Barriers to a “Hydrogen Economy.” Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects 32, 863–876.
Bossel, U. (2006) Does a Hydrogen Economy Make Sense? Proceedings of the IEEE 94, 1826– 1837.
Brandon, N.P., Kurban, Z. (2017) Clean energy and the hydrogen economy. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 375, 20160400.
Burridge, T. (2019) All aboard Britain’s first hydrogen train. BBC, 20th June [online] Available at: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-48698532 [Accessed: 01/07/2020]
Coman, J. (2020) Can a hydrogen boom fuel a green recovery for Britain? The Guardian, 19th July [online] Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2020/jul/19/can-a-hydrogen-boom- fuel-a-green-recovery-for-britain [Accessed: 20/07/2020]
Concerned Health Professionals of New York and Physicians for Social Responsibility (2019) Compendium of Scientific, Medical, and Media Findings Demonstrating Risks and Harms of Fracking (Unconventional Gas and Oil Extraction) Sixth Edition [online] Available at: http:// concernedhealthny.org/compendium/ [Accessed: 03/07/2020]
Clarke, S. (2020) Is hydrogen the solution to net zero home heating? The Guardian, March 21st [online] Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/science/2020/mar/21/is-hydrogen-the-solution- to-net-zero-home-heating [Accessed: 01/07/2020]
Committee on Climate Change (2018) Hydrogen in a low-carbon economy [online] Available at: https://www.theccc.org.uk/publication/hydrogen-in-a-low-carbon-economy/ [Accessed: 01/07/2020]
Derwent, R.G., Stevenson, D.S., Utembe, S.R., Jenkin, M.E., Khan, A.H., Shallcross, D.E. (2020) Global modelling studies of hydrogen and its isotopomers using STOCHEM-CRI: Likely radiative
forcing consequences of a future hydrogen economy. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 45, 9211–9221.
European Environment Agency (2019) Air Quality in Europe - 2019 report [online] Available at: https://www.eea.europa.eu//publications/air-quality-in-europe-2019 [Accessed: 01/03/2020]
Global CCS Institute (2019) Global Status of CCS 2019 [online] Available at: https:// www.globalccsinstitute.com/resources/global-status-report/ [Accessed: 15/04/2020]
Götz, M., Lefebvre, J., Mörs, F., McDaniel Koch, A., Graf, F., Bajohr, S., Reimert, R., Kolb, T. (2016) Renewable Power-to-Gas: A technological and economic review. Renewable Energy 85, 1371– 1390.
Hannan, D. (2020) Britain can lead the world in transmuting water into fuel [online] Available at: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2020/07/18/britain-can-lead-world-transmuting-water-fuel/ [Accessed: 21/07/2020]
Harrabin, R. (2020) Is the hydrogen tech 'revolution' hope or hype? BBC, 1st July [online] Available at: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-53238512 [Accessed: 01/07/2020]
Heffernan, O. (2019) Seabed mining is coming — bringing mineral riches and fears of epic extinctions. Nature 571, 465–468.
Hydrogen Council (2020) Path to hydrogen competitiveness [online] Available at: https:// hydrogencouncil.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Path-to-Hydrogen-Competitiveness_Full- Study-1.pdf [Accessed: 27/06/2020]
Institution of Engineering and Technology (2019) Transitioning to hydrogen [online] Available at: https://www.theiet.org/impact-society/sectors/energy/energy-news/transitioning-to-hydrogen- assessing-the-engineering-risks-and-uncertainties/ [Accessed: 01/07/2020]
International Energy Agency (2019) The future of hydrogen [online] Available at: https:// www.iea.org/reports/the-future-of-hydrogen [Accessed: 01/07/2020]
IPCC (2014) IPCC Fifth Assessment Report [online] Available at: https://www.ipcc.ch/assessment- report/ar5/ [Accessed: 01/07/2020]
Jolly, J. (2020) Hydrogen fuel bubbles up the agenda as investments rocket. The Guardian, 28th June [online] Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2020/jun/28/hydrogen-fuel- bubbles-up-the-agenda-as-investments-rocket [Accessed: 01/07/2020]
Kallis, G., Kostakis, V., Lange, S., Muraca, B., Paulson, S., Schmelzer, M. (2018) Research On Degrowth. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 43, 291–316.
Kleijn, R., van der Voet, E. (2010) Resource constraints in a hydrogen economy based on renewable energy sources: An exploration. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 14, 2784–2795.
Kreith, F., West, R. (2004) Fallacies of a Hydrogen Economy: A Critical Analysis of Hydrogen Production and Utilization. Journal of Energy Resources Technology 126, 249–257.
Murray, J. (2020) Zero-carbon hydrogen injected into gas grid for first time in groundbreaking UK trial. The Guardian, 24th January [online ] Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/ 2020/jan/24/hydrogen-uk-gas-grid-keele-university [Accessed: 01/07/2020]
National Infrastructure Commission (2020) Net Zero: Opportunities for the power sector [online] Available at: https://www.nic.org.uk/publications/net-zero-opportunities-for-the-power-sector/ [Accessed: 01/07/2020]
Nikolaidis, P., Poullikkas, A. (2017) A comparative overview of hydrogen production processes. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 67, 597–611.
Page, S., Krumdieck, S. (2009) System-level energy efficiency is the greatest barrier to development of the hydrogen economy. Energy Policy 37, 3325–3335.
Royal College of Physicians and Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health (2016) Every breath we take, the life long impact of air pollution [online] Available at: https:// www.rcplondon.ac.uk/projects/outputs/every-breath-we-take-lifelong-impact-air-pollution [Accessed: 01/03/2020]
Schultz, M.G., Diehl, T., Brasseur, G.P., Zittel, W. (2003) Air Pollution and Climate-Forcing Impacts of a Global Hydrogen Economy. Science 302, 624–627.
Steffen, W., Richardson, K., Rockström, J., Cornell, S.E., Fetzer, I., Bennett, E.M., Biggs, R., Carpenter, S.R., Vries, W. de, Wit, C.A. de, Folke, C., Gerten, D., Heinke, J., Mace, G.M., Persson, L.M., Ramanathan, V., Reyers, B., Sörlin, S. (2015) Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 347, 1259855. Tromp, T.K. (2003) Potential Environmental Impact of a Hydrogen Economy on the Stratosphere. Science 300, 1740–1742.
Valero, A., Valero, A., Calvo, G., Ortego, A. (2018) Material bottlenecks in the future development of green technologies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 93, 178–200.
Warwick, N.J., Bekki, S., Nisbet, E.G., Pyle, J.A. (2004) Impact of a hydrogen economy on the stratosphere and troposphere studied in a 2-D model. Geophysical Research Letters 31, L05107.
Watari, T., McLellan, B.C., Ogata, S., Tezuka, T. (2018) Analysis of Potential for Critical Metal Resource Constraints in the International Energy Agency’s Long-Term Low-Carbon Energy Scenarios. Minerals 8, 156.
Wiedmann, T., Lenzen, M., Keyßer, L.T., Steinberger, J.K. (2020) Scientists’ warning on affluence. Nature Communications 11, 3107.
0 notes
Text
Marine Electronics Applications: Transforming Maritime Industries and Market Trends

The global marine electronics market is a rapidly evolving sector that encompasses a wide range of electronic systems and devices used in maritime operations. These technologies enhance navigation, communication, safety, and operational efficiency across various types of vessels, from commercial ships and leisure boats to military and research vessels. As maritime industries continue to embrace digitalization and technological advancements, the demand for sophisticated marine electronics is on the rise.
Get a Deeper Understanding of the Industry by Visiting: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/marine-electronics-market-5282209.html
Industry Trends
Integration of Advanced Technologies:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: These technologies are being integrated into marine electronics for predictive maintenance, automated navigation, and improved decision-making.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT-enabled devices allow for real-time data collection and communication between various onboard systems, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and safety.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Used in training and simulation, AR and VR provide immersive environments for crew training and navigation simulations.
Increased Focus on Cybersecurity:
As vessels become more connected, cybersecurity has become a critical concern. Companies are investing in robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and systems from cyber threats.
Sustainability and Environmental Regulations:
The push for greener shipping solutions is driving the development of energy-efficient marine electronics. Systems that optimize fuel consumption and reduce emissions are gaining popularity.
Growth of Autonomous Vessels:
Autonomous and remotely operated vessels are on the rise, requiring advanced sensor systems, navigation technologies, and control systems to operate safely and efficiently.
Enhanced Connectivity:
The demand for high-speed internet and reliable communication systems at sea is growing. Satellite communication and 5G technologies are being deployed to meet these needs.
Opportunities
Expansion in Emerging Markets:
Emerging economies are investing in maritime infrastructure and fleet modernization, presenting opportunities for marine electronics manufacturers to tap into new markets.
Retrofit and Upgrade Market:
Older vessels are being retrofitted with modern electronics to improve efficiency, safety, and compliance with new regulations, creating a significant market for upgrades.
Blue Economy Initiatives:
Governments and organizations focusing on sustainable ocean economies are investing in technologies that support marine conservation, resource management, and pollution control, driving demand for advanced marine electronics.
Defense and Security Applications:
Increased maritime security threats and the need for advanced surveillance systems offer opportunities for growth in the defense sector, with a focus on radar, sonar, and communication technologies.
Recreational Boating:
The rising popularity of recreational boating and yachting is driving demand for sophisticated onboard electronics, including navigation systems, entertainment, and connectivity solutions.
Get Thorough Information in Our PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=5282209
Market Dynamics
Technological Advancements:
Continuous innovation in electronic components, sensors, and software is driving market growth by enhancing the capabilities and reliability of marine systems.
Regulatory Compliance:
Compliance with international maritime regulations, such as SOLAS (Safety of Life at Sea) and MARPOL (Marine Pollution), is a key driver for adopting advanced marine electronics.
Economic Factors:
Fluctuations in global trade, oil prices, and economic conditions can impact the shipping industry, influencing the demand for marine electronics.
Supply Chain Challenges:
The global supply chain for electronic components is complex and can be affected by geopolitical tensions, raw material shortages, and manufacturing disruptions, impacting the marine electronics market.
Competitive Landscape:
The market is highly competitive, with numerous players offering a wide range of products. Companies are focusing on innovation, strategic partnerships, and customer service to differentiate themselves.
Partnerships
Collaborations with Shipbuilders:
Partnerships with shipbuilders enable the integration of advanced electronics into new vessel designs, ensuring compatibility and streamlined installations.
Alliances with Technology Firms:
Collaborating with technology companies specializing in AI, IoT, and cybersecurity can enhance product offerings and improve system capabilities.
Research and Development Partnerships:
Joint ventures with research institutions and universities drive innovation and accelerate the development of cutting-edge marine technologies.
Cross-Industry Partnerships:
Collaborations with other industries, such as telecommunications and defense, allow for the exchange of expertise and technology transfer, leading to the development of innovative marine solutions.
Government and Regulatory Bodies:
Working with governments and regulatory bodies to ensure compliance and stay ahead of regulatory changes can provide a competitive advantage and build trust with customers.
Discover All the Steps in Our Detailed Sample: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/requestsampleNew.asp?id=5282209
Key Companies
Raymarine (FLIR Systems):
Raymarine specializes in marine electronics for recreational boating and light commercial marine markets, offering radar, navigation, and communication systems.
Furuno Electric Co., Ltd.:
A leader in marine electronics, Furuno provides a wide range of products, including radar, fish finders, and navigation systems, known for their reliability and innovation.
Garmin Ltd.:
Garmin offers advanced navigation systems, communication devices, and marine sensors for both recreational and commercial vessels, focusing on user-friendly interfaces and robust performance.
Navico Group (Simrad, Lowrance, B&G):
Navico, under its brands Simrad, Lowrance, and B&G, provides a comprehensive range of marine electronics for commercial and leisure markets, emphasizing integration and connectivity.
Kongsberg Maritime:
Kongsberg Maritime delivers cutting-edge marine electronics solutions for the commercial shipping, offshore, and defense sectors, including integrated bridge systems and autonomous vessel technologies.
Northrop Grumman Corporation:
Northrop Grumman offers advanced electronic warfare and navigation systems for defense applications, focusing on enhancing situational awareness and security.
Thales Group:
Thales provides innovative marine electronics for navigation, communication, and surveillance, catering to both civilian and military markets with a focus on security and reliability.
The global marine electronics market is poised for significant growth, driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for connectivity, and the need for enhanced safety and efficiency in maritime operations. Key industry players are leveraging innovation, strategic partnerships, and a focus on sustainability to address emerging opportunities and challenges. As the maritime industry continues to embrace digitalization and automation, marine electronics will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of navigation, communication, and operational excellence at sea.
About MarketsandMarkets™
MarketsandMarkets™ has been recognized as one of America's best management consulting firms by Forbes, as per their recent report.
MarketsandMarkets™ is a blue ocean alternative in growth consulting and program management, leveraging a man-machine offering to drive supernormal growth for progressive organizations in the B2B space. We have the widest lens on emerging technologies, making us proficient in co-creating supernormal growth for clients.
Earlier this year, we formally transformed into one of America's best management consulting firms as per a survey conducted by Forbes.
The B2B economy is witnessing the emergence of $25 trillion of new revenue streams that are substituting existing revenue streams in this decade alone. We work with clients on growth programs, helping them monetize this $25 trillion opportunity through our service lines - TAM Expansion, Go-to-Market (GTM) Strategy to Execution, Market Share Gain, Account Enablement, and Thought Leadership Marketing.
Built on the 'GIVE Growth' principle, we work with several Forbes Global 2000 B2B companies - helping them stay relevant in a disruptive ecosystem. Our insights and strategies are molded by our industry experts, cutting-edge AI-powered Market Intelligence Cloud, and years of research. The KnowledgeStore™ (our Market Intelligence Cloud) integrates our research, and facilitates analysis of interconnections through applications, helping clients look at the entire ecosystem and understand the revenue shifts in their industry.
To learn more, visit www.MarketsandMarkets™.com or follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn and Facebook.
Contact: Mr. Rohan Salgarkar MarketsandMarkets™ INC. 630 Dundee Road Suite 430 Northbrook, IL 60062 USA: +1-888-600-6441 Email: [email protected]
#Marine Electronics#Marine Electronics Market#Marine Electronics Industry#Global Marine Electronics Market#Marine Electronics Market Companies#Marine Electronics Market Size#Marine Electronics Market Share#Marine Electronics Market Growth#Marine Electronics Market Statistics
0 notes
Text
India's Blue Economy: Sailing Towards Sustainable Growth and Security

The World Bank defines the blue economy as the sustainable use of ocean resources to benefit economies, livelihoods and an overall Marine ecosystem. Gunter Pauli introduced the concept in his 2010 book- “The Blue economy:10 Years, 100 Innovations, 100 Million Jobs.”Blue Economy advocates the greening of ocean development strategies for higher productivity and conservation of the ocean’s health. It encompasses coastal tourism, water desalination, renewable energy, fishing and aquaculture, deep sea mining, waste management, marine genetic sources and biotechnology. It focuses on integrating development measures of the ocean economy with a suitable business model, keeping the idea of social inclusion and environmental sustainability at its core. This is reflected in the Sustainable Development Goals, which call for the conservation and sustainable use of the ocean, seas and marine resources (SDG 14). Today, the marine ecosystem faces an unprecedented threat: climate change, pollution, and overexploitation; there is a need for all-around action to safeguard the health and resilience of ocean resources.
.
Estimated to be worth 1.5 US Trillion dollars per year globally, it provides 30 million jobs and is a vital protein source to over 3 billion people worldwide. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has predicted that the ocean economy may double to 3 Trillion. Although eclipsed by the boom in the green economy, it has great potential for boosting economic growth by opening opportunities for income generation. Oceans cover three-quarters of the earth's surface. They play a significant role in protecting biodiversity, keeping the planet at an optimum average Temperature and absorbing about 30 percent of global Carbon Dioxide emissions. At least 3-5 percent of the global GDP is from oceans. It can support food security and diversification to address new resources for energy. According to research commissioned by the high-level panel for a sustainable ocean economy, 1 US Dollar invested in key ocean activities yields five times, i.e., 5 US Dollars in return, often more. The net value of ocean assets, also known as natural capital, is estimated at 24 Trillion US Dollars.
Regarding the Indian Subcontinent, the blue economy presents an unprecedented opportunity, be it fulfilling national socio-economic interests or connectivity with neighbours. It can play a vital role in livelihood generation, building energy security, and improving coastal communities' health and living standards. India has a coastline over 7,500 km long spread across nine coastal states, 12 major and 200 minor ports. 95 Percent of the Country’s business is supported by the blue economy via transportation, contributing to approximately 4 percent of the GDP. The Indian Ocean is a significant trade conduit, with around 80 per cent of global oil trade. Better connectivity in the region will optimise transport costs and reduce maritime wastage of resources, thereby boosting trade sustainability.
The recent presentation of the interim budget emphasised promoting “Blue Economy 2.0.” It included introducing schemes focused on restoration and adaptation measures and an integrated and multi-sector strategy. Central to the scheme are restoration and adaptation. This involves restoring degraded coastal ecosystems and implementing strategies to tackle threats of rising sea levels and extreme weather conditions. These efforts will prove crucial for preserving biodiversity, protecting coastal communities and maintaining ecosystem services provided by marine habitats. Blue Economy 2.0 focuses on expanding coastal and mariculture to cater to the growing demand for seafood while reducing the pressure on wild fish stocks. Sustainable aquaculture promotion and integration with tourism and renewable energy sectors provide opportunities to coastal communities, ensuring the long-term viability of marine resources. Blue Economy 2.0 recognises the interdependence of various sectors and the need for coordinated action across government, industries and society. Fostering this collaboration will harness stakeholders' integrated efforts to achieve sustainable development goals in India’s Coastlines.
The government of India has taken various measures to promote the idea of investing in the Blue Economy. The Deep Ocean Mission was developed to harness living and non-living resources from deep oceans. The India-Norway Task Force on Blue Economy for Sustainable Development was inaugurated jointly by both countries in 2020 to develop joint initiatives. The Sagarmala project was a strategic initiative for port-led development through extensive use of IT services and modernisation of ports. The O-Smart scheme aims to regulate the use of oceans and marine resources for sustainable development. Lastly, India has a national fisheries policy for promoting the blue growth initiative, which focuses on the sustainable utilisation of fisheries wealth from marine and aquatic resources.
This blue economy promotion comes with its challenges. There are constant threats of sea-borne terror, piracy, robbery, maritime terrorism, illicit crude oil trade, trafficking, and smuggling. Natural disasters like tsunamis, cyclones, hurricanes, etc, happen on an annual basis, resulting in leaving people stranded and property worth millions destroyed. There are man-made problems like oil spills and climate change issues that risk disturbing the maritime eco-balance. Due to climate change issues, rising average sea temperatures threaten marine life, habitats, and interdependent communities. Marine pollution is untreated sewage, agricultural runoff, and marine debris. Illegal and unregulated extraction of marine resources is yet another issue that needs earnest mitigation policies.
With its vast maritime interests, the Blue economy is pivotal in strengthening India's economic growth. What is the way forward then? India should go forward with the Gandhian approach of balancing economic growth with sustainability for long-term growth, employment generation, equity and environmental protection. “Blue Investment” could be the next GDP Multiplier on the condition that sustainability and socio-economic growth are its pedestals. India should consider these water bodies a global stage for advocating socio-economic diplomacy. Focus on Marine technological centres and shipping & Communication services will help the creation hub for R&D purposes. A practical approach will foster a robust Indian Ocean security strategy, which will, in turn, address any humanitarian crisis and natural disasters.
-AYUSH RAJ
0 notes
Text
MJ: Research
Plastic Pollution Facts and Figures
1 in 3 fish caught for human consumption now contains plastic

90% of made from fossil fuels

2.5toness of carbon dioxide is generated by producing 1 tonne of plastic

Plastic pollution in numbers
8 million pieces of plastic make their way into the ocean every day (OSPAR, 2009)
12millions tonnes of plastic is dumped into the ocean every year
80% of all studies on marine debris are plastic( IUCN)
5.25% trillion macro and microplastics may now be floating in the open ocean, weighing up to 269, 000 tonnes (Eriksen, 2014)
Every year, 100,000 marine mammals and turtles and 1 million sea birds are killed by marine plastic pollution. (UK Government, 2018)
How much plastic pollution is there?
Every year, a staggering 12 million tons of plastic pollution infiltrates the ocean. Of this amount, 9.5 million tons originate from land-based sources, while 1.75 million tons are directly discarded into the sea by the fishing and shipping industries.
In the ocean, an estimated 51 trillion tiny plastic fragments exist, collectively weighing 269,000 tons. This mass equates to the weight of approximately 1,345 adult blue whales, and it surpasses the number of stars in our galaxy by 500-fold.
How long does plastic last?
Plastic possesses strength, flexibility, and durability, attributes that render it highly functional. However, these very qualities also render it resistant to breakdown. In marine environments, a plastic bottle can endure for up to 450 years, gradually breaking into smaller fragments that persist indefinitely. Every piece of plastic ever manufactured remains in existence in some capacity, and our current consumption of plastic is surpassing previous records.
What harm does plastic pollution do to the environment?
The impact of plastic pollution on wildlife, including fish, dolphins, seabirds, and seals, is dire, often leading to fatal consequences. These creatures can become ensnared in plastic debris or ingest it mistakenly, posing grave threats to their health and survival.
Numerous distressing incidents serve as stark reminders of this issue. For instance, the sight of deceased albatrosses in the Midway Atoll, their stomachs filled with plastic waste, paints a grim picture. Similarly, the discovery of a malnourished whale off the coast of Norway, its stomach containing 30 plastic bags and large quantities of plastic packaging, highlights the pervasive nature of this problem.
Plastic pollution doesn't affect me directly though, does it?
As seafood increasingly contains plastic, the pertinent query shifts from whether we ingest plastic to assessing its impact on our well-being. Plastic in seawater acts as a sponge for harmful chemicals like PCBs and DDTs, notorious for their association with endocrine disruption and certain cancers. This peril amplifies as plastic ascends the food chain. Alarmingly, microplastics have infiltrated human bloodstreams and unsettlingly traverse from mothers to unborn children through the placenta.
The beach, a sanctuary for connecting with nature, loses its essence when marred by plastic debris. Given the substantial contribution of coastal tourism, valued at £5.5 billion to the UK economy, many rely on pristine shores for their livelihoods.
Even for those who abstain from consuming seafood or visiting beaches, the ubiquitous inhalation of air remains unavoidable. Notably, marine flora produces a staggering 70% of the indispensable oxygen we rely on for sustenance.
0 notes
Photo
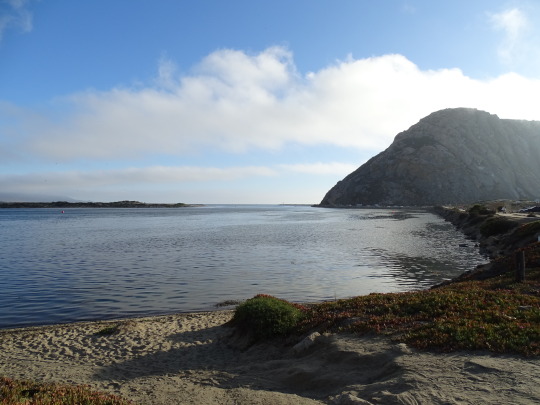
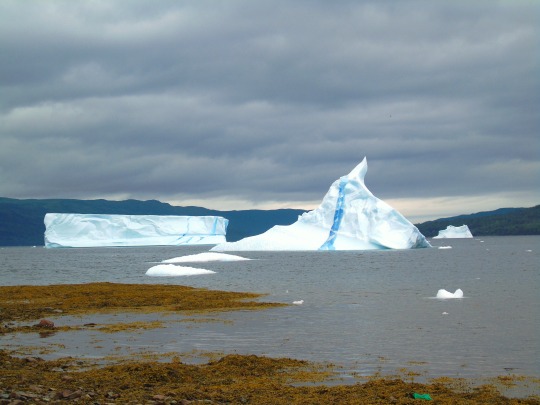
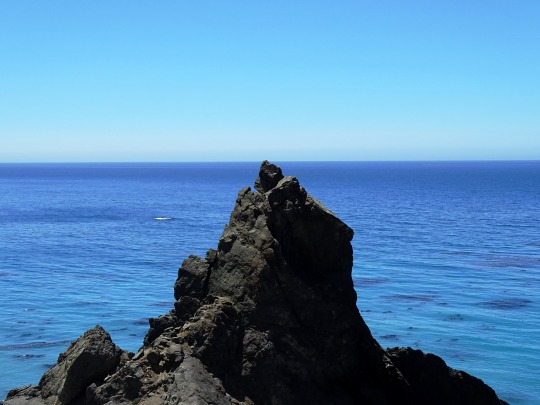
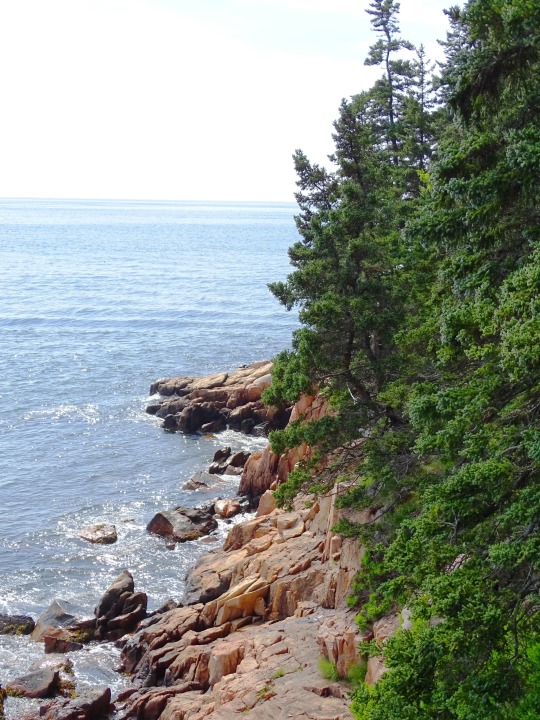










World Oceans Day
With oceans making up 66% of our Earth, it’s crucial we raise awareness about and tackle the threats facing these life-giving and life-containing bodies of water.
66% of the world is covered in a blanket of rich, vibrant blue, from its depths once came all life on the Earth, and it continues to house an immense amount of life. This blanket is the world’s oceans, and they serve as one of the most popular vacation spots in the world and play a vital role in the economy of countries worldwide. Across the briny deep massive amounts of cargo cross each year, and it still serves as the primary thoroughfare for trade. World Oceans Day celebrates the ocean and the important role it plays in our lives.
It’s a time for supporters of the oceans to focus on conversation and sustainability so that they can remain clean and usable. The animals deserve a happy and safe place to roam and live without having to worry about any destruction or man-made obstacles. It’s important to safeguard the oceans to help ensure a healthy home for all. One this day, people can come together to create a space for all to enjoy and appreciate, no matter where each person lives.
History of World Oceans Day
In 2008, the UN gathered and uniformly created World Oceans Day. It was first proposed in 1992 in Rio de Janeiro during the Earth Summit. The ocean has been an incredibly important part of human history, and this special was established with the intent of celebrating our connection to the sea and raising awareness about the various dangers it faces. There are nearly 200,000 identified species that live in the ocean, but the number of actual species that reside there is likely in the millions. It’s essential to ensure that they don’t have to worry about freely getting around and enjoying a healthy and safe home to reside.
Even with that being the case, there are still problems with overfishing, and the subsidies that are given for fishing in countries all around the world are causing depletion of the game species. These activities have led to efforts to restore the fishing industry being undermined, and the industry bringing in $50 billion a year less. It’s just one of the many factors that should have us all celebrating World Oceans Day and raising awareness about all the issues our big blue’s face.
There’s a global environmental catastrophe due to decades of overuse and a surge in single-use plastics. Plastic straws and bags are getting into the oceans and causing havoc. World Oceans Day is an opportunity to acknowledge and recognize the efforts that have been and are being made against plastic pollution. It’s enlightening and disheartening to know that today, 13,000,000 tons of plastic leaks into the ocean every year, which among other damage, kill 100,000 marine animals annually.
World Oceans Day Timeline
1987 Brundtland Report
This report, connected to The World Commission on Environment and Development (Brundtland Commission) notes that the ocean sector is lacking representation compared to other sectors.
1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro
Created as a way to celebrate the world’s shared ocean and raise awareness for the personal connection between humans and the ocean. This is where the concept for World Oceans Day was first proposed by the Canadian representatives.
2008 UN declares to recognize World Oceans Day
This year, after a four-year onsite and online petition drive, the UN General Assembly passes a Declaration that will officially recognize the day, beginning the following year.
2009 First World Oceans Day is celebrated
The inaugural World Oceans Day is observed with the theme “Our Oceans, Our Responsibilities.”
2016 World Oceans Day Youth Advisory Council is launched
Made up of 25 youth from all over the world, the Youth Advisory Council is created to develop and promote World Oceans Day.
Why celebrate World Oceans Day?
It’s a good reminder to bring attention to the fact that oceans play a major role in everyday life all around the globe. The oceans provide a majority of the oxygen we breathe, so many consider them to be the lungs of our planet. The goal is to develop a worldwide movement of citizens to care better for the oceans. It’s an opportunity to inform and educate humans and the public of what our actions are doing to the ocean and what impact they have in the long run. It’s not only a day to celebrate the beauty, wealth, and promise of the ocean, but a chance to realize that they’re a critical part of the biosphere. They’re a significant source of food and medicines and simply can’t be ignored or mistreated any longer.
How to celebrate World Oceans Day
Start it off by a visit to the nearest ocean to restore a personal connection to the sea. Breathe deep and appreciate the beauty and serenity the ocean offers each day of the week. Invite family along, and while there, bring information about the ocean and what people really need to know about it to make visiting it a joy for years to come.
Pick a day to go to the ocean to clean up and help restore it instead of simply sitting by it. Gather friends and family and pitch in and pick up trash that surrounds the local beaches and oceans in the area. It’ll not only look nicer, but the wildlife in the area will benefit from these actions as well. Avoid single-use plastics, and instead pack a picnic lunch with reusable containers to enjoy after the hard work is complete. One may also consider organizing a fundraiser to aid preservation and restoration efforts at the local beach. With all the plastic waste coming off our beaches thanks to careless beach-goers, our ocean is awash with litter.
Use this as a time to increase one’s knowledge and explore the topic further. There are a variety of books and resources out there to help a person achieve this goal. Another idea is to gather a group of people and watch an ocean film on the topic to bring awareness to the concept of helping out the oceans.
There are plenty of activities and events that occur on World Oceans Day. Celebrate by choosing one or two to participate in and enjoy. Engage in the day’s events by piggybacking off of other ideas that people in the area have come up with instead of having to think of activities alone.
World Oceans Day FAQs
When is World Oceans Day?
World Oceans Day has taken place on June 8 every year since 2009, with the inaugural theme of Our Oceans, Our Responsibilities.
What is the importance of World Oceans Day?
The purpose of this day is to develop a worldwide movement of citizens for the ocean while mobilizing people and raising awareness.
What is the World Oceans Day theme?
Each year, the theme for World Oceans Day changes, with past themes including Oceans & People, Healthy Oceans–Healthy Planet, Our Oceans–Our Future, and Innovation for a Sustainable Ocean.
Who started World Oceans Day?
World Oceans Day was first suggested by Canada in 1992 at the Earth Summit in Rio. After years of petitions, the UN officially recognizes the day.
How to help with World Oceans Day?
This day can be observed by getting involved in education, reducing carbon footprints, minimizing the use of plastic and making sustainable seafood choices.
Source
#Mussel Rock Park#Morro Rock State Preserve#Morro Bay#Pacific Ocean#Big Sur#California#West Coast#Atlantic Ocean#As Catedrais Beach#Spain#Albufeira#Portugal#Miami Beach#Acadia National Park#iceberg#Green Bay#King's Point#Newfoundland#Canada#seascape#landscape#cityscape#travel#vacation#World Oceans Day#WorldOceansDay#8 June#Maine#Florida#East Coast
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blue Economy Ecosystem and Framework in India
Written By: Jagriti Shahi


Figure: Market Growth of India's Blue Economy in 5 Years (2018-2023)
This table would include various key sectors within the Blue Economy and their estimated market growth rates over the past 5 years (2018-2023
Fisheries and Aquaculture
The fisheries sector is a cornerstone of India's Blue Economy, providing livelihoods to millions of people. India is not only one of the largest consumers of fish globally but is also a major exporter. Embracing sustainable practices in fisheries and promoting responsible aquaculture is imperative for ensuring the long-term viability of this industry. Initiatives that focus on modernizing fishing techniques, promoting aquaculture, and ensuring the well-being of coastal communities contribute to a more sustainable and resilient Blue Economy.
Fisheries:
Economic Importance: Fisheries contribute substantially to the global economy, generating income for millions of people engaged in fishing and related activities. Fish and seafood products are among the most traded commodities internationally, fostering economic growth and employment.
Food Security: Fish is a vital protein source, especially for communities in coastal regions and developing countries. The accessibility of fish as a food source makes it a critical element in addressing malnutrition and ensuring food security.
Sustainable Practices: Overfishing, illegal fishing, and bycatch pose significant challenges to the sustainability of fisheries. Sustainable fishing practices, such as catch quotas, size limits, and marine protected areas, are essential to prevent the depletion of fish stocks and maintain healthy ecosystems.
Technology and Innovation: Technology, including satellite tracking and data analytics, plays a role in fisheries management. Innovations like selective fishing gear and fishery monitoring systems help reduce bycatch and enable more sustainable fishing practices.
Aquaculture:
Growing Importance: Aquaculture, or the farming of fish and other aquatic organisms, has become increasingly important in meeting the growing demand for seafood. It provides a controlled environment for the breeding and harvesting of various species.
Diversification of Species: Aquaculture allows for the cultivation of a wide range of species, including fish, shrimp, mollusks, and seaweed. This diversification contributes to resilience in the face of environmental changes and market demands.
Environmental Concerns: While aquaculture has many benefits, it also raises environmental concerns. Issues such as water pollution, habitat degradation, and the use of antibiotics and chemicals can have negative impacts. Sustainable aquaculture practices aim to address these concerns by promoting responsible farming methods.
Certification and Standards: Certification programs, such as those by the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) and Best Aquaculture Practices (BAP), help consumers identify products from responsibly managed aquaculture operations. These programs set standards for environmental and social responsibility in the industry.

Figure: Growth Comparison of Fisheries and Aquaculture in India (2018-2023)
Key Insights:
Aquaculture outpaces Fisheries: While both sectors contribute significantly to India's Blue Economy, Aquaculture exhibits a deutlich stronger growth trajectory compared to traditional Fisheries.
Factors behind Aquaculture's Growth: Several factors contribute to Aquaculture's higher growth rate, including rising demand for fish and seafood, government initiatives promoting sustainable aquaculture practices, and advancements in technology like fish farming techniques.
Fisheries facing challenges: Fisheries growth remains modest due to issues like overfishing, resource depletion, and climate change impacts. This emphasizes the need for sustainable fishing practices and conservation efforts.
Sustainable Practices:
Ecosystem-Based Management: Adopting an ecosystem-based approach considers the entire ecosystem when managing fisheries. This approach aims to maintain the health of marine ecosystems, prevent overfishing, and protect biodiversity.
Community Engagement: Involving local communities in fisheries management and aquaculture projects is essential for sustainable practices. Community-based approaches empower local stakeholders and promote responsible resource use.
Research and Innovation: Continued research and innovation are critical for the development of sustainable practices. This includes the use of technology, improved breeding techniques, and the development of alternative feeds in aquaculture.
In conclusion, fisheries and aquaculture are vital to global food systems, economies, and ecosystems. Ensuring the sustainability of these practices is not only a responsibility but also a necessity for future generations. By embracing sustainable approaches, addressing challenges, and fostering international cooperation, the fisheries and aquaculture sectors can thrive while preserving the health of our oceans.

Figure: Recent growth in India's maritime tourism
India's coastal regions boast rich cultural and natural heritage, offering significant potential for maritime tourism. From pristine beaches to historical maritime sites, there is a wealth of untapped opportunities. Responsible tourism practices, including eco-friendly initiatives and community engagement, can help leverage this potential, providing economic benefits while preserving the beauty of coastal ecosystems.
Cruise Tourism: Cruise tourism is a major component of maritime tourism, with passengers exploring different destinations along coastal areas or island-hopping. The cruise industry provides opportunities for local businesses, tour operators, and port communities.
Eco-Tourism and Sustainable Practices: The growing interest in eco-friendly travel has led to the development of sustainable maritime tourism practices. Eco-tourism initiatives, such as wildlife tours, bird watching, and guided nature walks, cater to environmentally conscious travelers.
Cultural and Heritage Tourism: Coastal regions often have a rich maritime heritage, including historic ports, lighthouses, and maritime museums. Cultural and heritage tourism allows visitors to immerse themselves in the maritime history and traditions of a particular area.
Adventure Tourism: The thrill of water-based adventure activities, such as kayaking, parasailing, and jet-skiing, attracts adventure enthusiasts. Coastal destinations with diverse landscapes offer opportunities for a wide range of exciting experiences.
Port Development:
Efficient and modern ports are crucial for facilitating trade and commerce. India has been actively investing in the development and upgradation of its ports through initiatives like the Sagarmala program. The program aims to harness the potential of India's coastline and waterways for economic development, job creation, and improving maritime logistics.
Trade Facilitation: Ports serve as key nodes in the global supply chain, facilitating the movement of goods between countries. Efficient ports contribute to the seamless flow of imports and exports, reducing logistics costs and enhancing international trade.
Economic Growth: Well-developed ports stimulate economic growth by attracting investments, generating employment opportunities, and fostering the development of related industries. Ports are often major contributors to a nation's GDP.
Connectivity: Ports play a crucial role in connecting landlocked regions to international markets. Improved port infrastructure enhances connectivity between coastal and inland areas, promoting regional development and reducing transportation costs.
Logistics Efficiency: Modernized ports with advanced infrastructure, technology, and logistics systems contribute to streamlined cargo handling processes. This efficiency reduces turnaround times for ships, increases cargo throughput, and enhances overall port performance.
Offshore Wind Energy: Offshore wind energy is a key component of the Blue Economy, harnessing the power of wind over the open seas. Offshore wind farms can provide a substantial and sustainable source of electricity.
Tidal and Wave Energy: Tidal and wave energy represent forms of marine renewable energy that tap into the kinetic energy generated by tides and waves.
Floating Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Arrays: Floating solar PV arrays involve placing solar panels on the surface of bodies of water, such as lakes or coastal areas.
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC: OTEC harnesses the temperature difference between the warm surface waters and the cold deep ocean waters to produce electricity.
Blue Revolution Scheme: Aims to increase fish production and income of fishers through subsidies on fish seed, feed, and infrastructure.
Sagarmala Programme: Develops port infrastructure and coastal economic zones to boost maritime trade and logistics.
National Livestock Mission: Provides subsidies for setting up and modernizing aquaculture farms.
National Clean Energy Mission: Promotes investments in renewable ocean energy technologies like offshore wind and tidal power.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY): Launched in 2020, PMMSY is a flagship scheme for the holistic development of the fisheries sector in India. It aims to Increase fish production and productivity, Improve the socio-economic status of fishers and fish farmers, Create employment opportunities in the fisheries sector.
0 notes
Text
Column: Prospect of PBAT Administration -FY2024 Budget by Kenny Odugbemi


President Bola Ahmed Tinubu a.k. PBAT
Reflection from the past administration
Goodluck. Jonathan left $15bn, but PMB after 2years squandered this with net of -$17bn GEJ made impressive impact in upgrading our infrastructure at mega level above $1b these includes International Airport Abuja& Lagos including major thousands of km of federal roads But PMB never complete any mega projects bit plunge our economy to incur total debt of N77trn at hand over what a financial wrecklessness Fy 2024 bench marked against Fy2023 with the following positive percentage progression Budget 34% Revenue 88.3% Borrowing 79.69% Debt expenditure 34% Recurrent expenditure 17.95% Capital expenditure 77.55% Budget deficit 14% Tax:GDP 45% Fy 2024 Sectoral allocation Defence 12% Education 4% Health/Social services 3% Police 3.4© Agric 1.2% Power 0.31% Note Budget revenue =Budget deficit We shall be leveraging on borrowed fund to implement our capital projects through FDI inflow to execute our proposed strategic projects across all sectors through invoice financing Opportunities PH refinery will commence operation by the end of December We are witnessing emergence of several Modular refineries to produce base oil,LPG terminal, methanol plant, Gas processing, We are having over 60000lpd to augement imported PMS The petroleum processing by products such as polypropylene key ingredients used to produce Resins, plastics, aluminum coke used to produce can for beverages As of today, We have direct investment by Son of a Billionaire to a acquire aluminum cans production here in Nigeria Climate change (Carbon emissions) We have reliable information that Federal government sponsored 422 delegates out of reported 1,147 delegates at huge cost of $80m This expenditure has received wider condemnation in view of our depressed economy China is a major polluter of our environment who will now be paying billion s of dollars as reparations for the depletion of ozone layers We now have a tragedy of common leading to disappearance of our global environment Advantages of participation We might be awarded with Carbon credit running in billions of dollar Knowledge reward on climate change impact Pledge of electric busses by many donor, we shall be receiving first tranch of 100 electric buses We signed billion dollar contract in power, aviation, solid mineral, ecological support,and environmental pollution Our liberal nature has helped us to socialize to support drive for credit rewards Conclusion We shall have return on investment in these form Reparations Tragedy of common pledge We need to establish all inclusive Mineral resources Commission cutting across mineral deposits which includes and not limited to the following Gold Copper Bitumen Magnite Lithium Phosphate etc Other anticipated diverse revenue resources such as Marine &Blue economy ($296bn) Creative art Tourism Digital innovations Steel development Fy 2024 budget will give more emphazy on Security Poverty reduction and human capacity development We expect strategic investment across all sectors education, power,trade and investments etc There is a promise to carry out major review of our fiscal responsibility act 2007 Encouragement of public participation act to reflect true need of Nigeria populace Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Sea, and Seamless Web Designers in Tampa
The sea, with its vastness and mysterious depths, has captivated human imagination for centuries. Its rhythmic waves, diverse marine life, and endless horizons evoke a sense of awe and wonder. Similarly, in the world of digital landscapes, seamless Web designers in Tampa navigate the boundless possibilities of the internet with creativity and expertise. Tampa, a vibrant city on the gulf coast of Florida, serves as the backdrop for a community of web designers dedicated to crafting online experiences that seamlessly mirror the fluidity of the sea. Like skilled sailors navigating the vast ocean, these designers skillfully navigate the complexities of web development, ensuring that websites are not only visually appealing but also function seamlessly. In this convergence of natural beauty and digital innovation, Tampa's Seamless Web Designers stand as artisans, weaving the threads of creativity and functionality into a harmonious online tapestry.
Introduction to the Sea
The sea, a vast web designers in Tampa expanse of saltwater covering more than 70% of earth's surface, holds a mysterious allure that has captivated human beings for centuries. Its deep blue hues and rhythmic waves create a mesmerizing canvas that has inspired art, literature, and exploration throughout history. The sea is not merely a physical entity but a symbol of boundless possibilities, a source of life, and a reflection of the planet's dynamic nature.
Marine Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Beneath the surface of the sea lies a rich tapestry of marine biodiversity and ecosystems. Coral reefs, teeming with colorful fish and intricate organisms, create underwater wonderlands. From the microscopic plankton to the majestic whales, the sea sustains an incredible variety of life. These diverse ecosystems play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the global environment, supporting fisheries, and contributing to the overall health of the planet.
Cultural Significance of the Sea
The sea has profoundly influenced human culture, shaping traditions, economies, and lifestyles across the globe. Coastal communities have relied on the sea for sustenance, trade, and transportation for centuries. Maritime folklore and myths often center around the sea, depicting it as both a provider and a formidable force that demands respect. The sea's influence is not only practical but deeply embedded in the cultural fabric of societies worldwide.
Challenges Facing the Oceans
Despite its beauty and importance, the sea faces numerous challenges in the modern era. Climate change, overfishing, pollution, and habitat destruction pose significant threats to marine ecosystems. Rising sea levels and the acidification of oceans further exacerbate these issues. Addressing these challenges requires global cooperation, sustainable practices, and a collective commitment to preserving the health and integrity of the world's oceans.
Seamless Web Designers in Tampa
In the vibrant city of Tampa, a hub of innovation and creativity, seamless web designers play a crucial role in shaping the online presence of businesses and individuals. These professionals, armed with technical expertise and artistic flair, craft websites that seamlessly blend form and function. From user-friendly interfaces to visually stunning layouts, web designers in Tampa are adept at creating digital spaces that not only captivate visitors but also enhance the overall user experience.
Navigating Trends in Web Design
The field of web design is dynamic, with trends constantly evolving to meet the changing needs and preferences of users. Tampa's seamless web designers stay at the forefront of these trends, incorporating responsive design, intuitive navigation, and visually engaging elements into their projects. Keeping abreast of technological advancements, they ensure that websites are not only aesthetically pleasing but also optimized for performance across various devices and platforms.
Local Impact and Global Reach
While Tampa's seamless web designers contribute significantly to the local business landscape, their impact extends far beyond city limits. In an interconnected digital world, the websites they create have the potential to reach a global audience. This intersection of local expertise and global reach highlights the importance of skilled web designers in facilitating the online success of businesses, fostering innovation, and contributing to the ever-expanding digital ecosystem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the sea has long been a source of inspiration, awe, and sustenance for human civilizations throughout history. Its vastness, beauty, and dynamic nature serve as a metaphor for life's constant change and evolution. As we contemplate the sea, we are reminded of the interconnectedness of all living things and the need for environmental stewardship to ensure its preservation for future generations.
0 notes