#Between-country prosperity divide
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
A local organization here has released a list of books that they feel are imperative to have in the time ahead. The list was not easily shareable, so I copy-pasted it here.
There is no need to read all of these, but one thing you can do that takes little effort is call your library and see if they have them in stock.
If you are moneyed, you can buy some copies and put them in little free libraries.
EDUCATING FOR ADVOCACY BOOK LIST
All books are written by authors from that culture
BOOKS FOR ADULTS
(2024) Be a Revolution: How Everyday People are Fighting Oppression and Changing the World - and How You Can, Too by Ijeoma Oluo
Each chapter discusses how someone is advocating for oppressed populations
and has examples of how others can do the same or similar.
(2024) The Message by Ta-Nehisi Coates
The author travels to Senegal, South Carolina and Palestine and grapples with deep questions and emotions.
(2023) Better Living Through Birding: Notes From a Black Man in the Natural World by Christian Cooper
A memoir of a Black man learning to claim space for himself and others like him.
(2022) Myth America: Historians Take On the Biggest Legends and Lies about Our Past Edited by Kevin M. Kruse and Julian E. Zelizer
The title explains it so well.
(2022) South to America: A Journey Below the Mason Dixon to Understand the Soul of a Nation by Imani Perry
History, rituals, and landscapes of the American South and why they must be understand it in order to understand America.
(2022) Memphis by Tara M. Stringfellow
Tells the story of 3 generations of a Southern Black family in Memphis.
(2021) How the Word is Passed: A Reckoning with the History of Slavery Across America by Clint Smith
An exploration of important monuments and landmarks in the USA that show
how slavery has been foundational in the development and history of our country.
(2021) The Sum of Us: What Racism Costs Everyone and How We Can Prosper Together by Heather McGhee
The title explains it.
(2021) The Seed Keeper by Diane Wilson
Historical fiction telling the story of several generations of a Dakota family
(2020) The Good Immigrant: 26 Writers Reflect on America edited by Nikesh Shukla and Chimene Suleyman
26 authors share their stories of living in the USA.
(2020) Caste: The Origins of Our Discontents by Isabel Wilkerson
Examines the unspoken caste system that has shaped America and shows how we continue to be defined in this way..
(2020) This Is What America Looks Like: My Journey from Refugee to Congresswoman
by Ilhan Omar
This title explains it.
(2019) The 1619 Project: A New Origin Story by Nikole Hannah Jones (among others)
Reframes our understanding of American history by placing slavery and its continuing legacy at the center of our national narrative.
(2019) Things are Good Now by Djamila Ibrahim
Stories of how migrants sort out their lives in foreign lands.
(2018) So You Want to Talk About Race by Ijeoma Oluo
An examination of race in America.
(2018) I’m Still Here by Austin Channing Brown
A memoir telling her journey of learning to love her blackness while navigating America's racial divide.
(2018) If They Come for Us by Fatimah Asghar
Poetry that captures the experience of being a Pakistani Muslim woman in contemporary America, while exploring identity, violence, and healing.
(2016) Stamped from the Beginning: The Definitive History of History of Racist Ideas in America by Ibram X. Kendi
Traces the history of Black America.
(2015) Between the World and Me by Ta-Nehisi Coates
A memoir, in the form of a letter to his young son, telling his personal experiences with racism and violence in the United States.
(2015) My Seneca Village by Marilyn Nelson
Poetry and information about Seneca Village – a multi-racial, multi-ethnic neighborhood in the center of Manhattan (Central Park ) that thrived in the mid-19th century.
(2014) An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States by Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz
Tells the 400+ years of US history, from the perspective of Indigenous peoples
(2013) Braiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom Scientific Knowledge, and the Teaching of Plants by Robin Wall Kimmerer
Explores the place of plants and botany in both Indigenous and Western life.
(2010) The Warmth of Other Suns: The Epic Story of America’s Great Migration by Isabel Wilkerson
Follows the stories of three Black Americans’ migration journeys from Mississippi, Florida and Louisiana.
(2010) The New Jim Crow: Mass Incarceration in the Age of Colorblindness
By Michelle Alexander
Explains how we haven’t ended, but have redesigned, the caste system in the U.S.
(1972) Lame Deer, Seeker of Visions by John (Fire) Lame Deer and Richard Erdoes
Told by Lame Deer, a Lakota medicine man, this memoir teaches the history of Indigenous people in the USA.
BOOKS FOR GRADES K-12
GRADES 7 - 12
(2021) Firekeeper’s Daughter by Angeline Boulley
The novel's main character is a young woman with a French mother and an Ojibwe father, who often feels torn between cultures.
(2021) The 1619 Project: Born on the Water by Nikole Hannah-Jones and Renée Watson
Illustrated by Nikkolas Smith
Tells the story and consequences of American slavery in verse.
(2020) Stamped: Racism, Antiracism, and You by Jason Reynolds and Ibram X. Kendi
Shorter and appropriate for middle and high schoolers.
(2020) All Boys Aren’t Blue by George M. Johnson
Series of personal essays about the author’s life growing up as a gay, black man.
(2020) Dictionary for a Better World: Poems, Quotes, and Anecdotes from A to Z by Irene Latham and Charles Waters Illustrated by Mehrdokt Amini
Explained in title.
(2020) Woke: A Young Poet’s Call to Justice by Mahogany L. Browne with Elizabeth Acevedo and Olivia Gatewood Illustrated by Theodore Taylor III
Poetry about fighting for racial justice through joy and passion.
(2020) Be Amazing: A History of Pride by Desmond Is Amazing Illustrated by Dylan Glynn
The history of Pride, with bold illustrations, focusing on the importance of embracing one’s own uniqueness and tuning out the haters.
(2020) Dear Justyce (Dear Martin #2) by Nic Stone
Continues the story of Justyce from Dear Martin in a series of flashbacks and letters.
(2020) Punching the Air by Ibi Zoboi and Yusef Salaam
A novel in verse about a boy who is wrongfully incarcerated.
(2019) Gender Queer: A Memoir by Maia Kobab
The author tells the story of life as a nonbinary person in graphic novel form.
(2019) An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States for Young People original book by Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz adapted by Debbie Rees and Jean Mendoza
Shorter and appropriate for middle and high schoolers
(2017) Sea Prayer by Khalad Hosseini Illustrated by Dan Williams
Written as a poetic letter, from father to son, this is a story of the journey of refugees.
(2017) Dear Martin (Dear Martin #1) by Nic Stone
A story of the realities of a Black teen living in America.
(2015) All American Boys by Jason Reynolds and Brendan Kiely
From the perspective of two teenage boys, one Black and one White, a story is told with the realization that racism and prejudice are still alive and well.
(2015) Beyond Magenta: Transgender and Nonbinary Teens Speak Out by Susan Kuklin
The author interviewed six transgender for gender-neutral young adults and lets
them tell their story.
(2011) Heart and Soul: The Story of America and African Americans written and illustrated by Kadir Nelson
The title explains it well
GRADES 4 - 6
(2023) An American Story by Kwame Alexander illustrated by Dare Coulter
Tells the story, poetically and honestly, about American slavery
(2023) Step by Step!: How the Lincoln School Marchers Blazed a Trail to Justice
by Debbie Rigaud and Carlotta Penn illustrated by Nysha Pierce
Tells the story of a group of Black mothers and children and their two-year march to integrate an Ohio elementary school.
(2022) Say Their Names by Caroline Brewer illustrated by Adrian Brandon
A young Black girl leads a #BlackLivesMatter protest march.
(2021) Stamped (For Kids): Racism, Antiracism, and You by Jason Reynolds and Ibram X. Kendi.
Shorter, more kid friendly version of Stamped from the Beginning.
(2021) Unspeakable: The Tulsa Race Massacre by Carole Boston Weatherford illustrated by Floyd Cooper
Traces the history of this African-American ‘Wall Street District’ and its destruction by White supremacists.
(2016). I Dissent: Ruth Bader Ginsburg Makes Her Mark by Debbie Levy illustrated by Elizabeth Baddeley
The life and work of RBG told in picture book form.
(2008) Silent Music: A Story of Baghdad written and illustrated by James Rumford
Ancient and recent history of Baghdad from the perspective of a young boy.
(2005) Show Way by Jacqueline Woodson illustrated by Hudson Talbott
Traces the history of the ‘show way’ quilt from slavery through freedom.
(2005) My Name is Bilal by Asma Mobin-Uddin illustrated by Barbara Kiwak
Muslim-American student experiencing religious prejudice.
(2005). Amelia to Zora: Twenty-Six Women Who Changed the World by Cynthia Chin-Lee Ilustrated by Megan Halsey and Sean Addy
An alphabet book that teaches about the extraordinary lives of 26 women.
(1978). The Other Way to Listen by Byrd Baylor and Peter Parnall
Helps children learn about indigenous cultures.
GRADES PRE-K - 3
(2023) These Olive Trees: A Palestinian Family’s Story written and illustrated by Aya Ghanameh
A story of a young girl and her family in Nablus, Palestine, 1967
(2020). Antiracist Baby by Ibram X. Kendi illustrated by Ashley Lukashvsky
Teaches young children how to be an antiracist.
(2016). When We Were Alone by David A. Robertson and Julie Flett
A young, indigenous girl learns about her grandmother’s experience in a
residential school.
(2013). A is for Activist by Innosanto Nagara (board book)
An ABC book that teaches children about being an activist.
646 notes
·
View notes
Text
DAY 6101
Jalsa, Mumbai Nov , 1, 2024/Nov 2 , Fri/Sat 12:08 am
🪔 ,
And the wishes to the Ef ..
November 02 .. birthday wishes to Ef Erlika from Indonesia 🇮🇩 .. Ef Abhijit Jagtab from Pune .. and .. Ef Dipagala Gala .. 🙏🏻❤️🚩
November 01 .. birthday wishes to Ef Vishan Lal 🪈 from Gurugram .. Ef Honey Aishu from Bangkok - Thailand 🇹🇭 .. Ef Nouranne Achraf from Egypt / France 🇪🇬🇫🇷 .. Ef Pankaj Shukla from Indore .. Ef Shubhra Rattan .. and Ef Somraj Mane from Kolhapur .. 🙏🏻❤️🚩
..
may this new year in your lives bring greater joy and prosperity ❤️🌹


Govardhan Pooja ... नमस्कार 🙏
and the festivities continue .. as do all the rituals .. and among all this Australia declares the month of October as a heritage month of Hindu festivities .. grace and divine blessings ..
But the intimacy of soft celebrations and the adherence to the control of many environmental obligations is revered .. as another year of the year of Lights ends , to another day of light ..
The intrigue of religious festivities .. their time and date and occasion still brings a wonder to many .. indeed to a great many .. and the readings of our Ef Sudhir and his dedicated research on the subject does evoke curiosity .. and awareness ...
The Calendar
There are two lunar calendars in the Jyotish Shastra… One is Purnaant and the other is Amaant…
There's a gap of 15 days between the two, although the order of the months are the same…
For instance, Deepavali's Lakshmi puja is on Purnaant Kartik Amavasya… while the same day is Amaant Ashwin Amavasya in some states…
So, the festival has a different reason in each region, and one common reason at the national level…
Like, the South, where the Lakshmi puja night of diwali is to recall the victory of Krishna over Narakaasur… In the North, it's for the return of Shri Ram to Ayodhya…
The concept of a civilisation made of many cultures dates back to the Treta Yug…
Diwali is celebrated for different days in different places… One day, three days, five days and eleven days… depending on the local history…
Yes… the different calendars, different cultures, but the same festivals, and the same civilisation…
You know, what… I think it's always an advantage when we do something that has no precedence… when there is nothing to refer…
This organisation of a nation is first envisaged in the chronicles of the satyug… each kingdom was called a country… group of countries was a region… the collective of regions was called a nation…
In Hindi - देश, प्रदेश तथा राष्ट्र…
What calendar do I follow?
I follow Rishi Varāhamihira's Brihat Samhita… In that, there is no need of dividing time into months and years…
The movements of cosmic objects don't need a calendar to have months and years… Only days are enough… Just count the days from a no-moon or a new-moon… the patterns are measurable and predictable…
Like,
The diwali always happens on the same no-moon night… regardless of which month in which state…
Thus, all the differences are dissolved in the universal medium… 🙂
About the light…
Darkness is not displaced by light… darkness is eliminated by light…
तमसो मा ज्योतिर्गमय।
Easiest way to do it is: Use one lamp to light the next… A series of lamps… Hence, Deepavali… Deep + Aavali - strings of light…
एक ब्रह्म है… एक सत्य है… एक ही है परमात्मा… प्राणों से प्राण मिलाते चलो.
my obsessed gratitude ..
my love and regard ...

Amitabh Bachchan
108 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Five Nations of Shukweso (Part 1)

The Union of the Shukwoto States




A Tribal and City State Confederation of Shukwoto-Speaking States in the Northeastern Region of Shukweso. It comprises of 8 States:
The Principality of Nkaibo
The Shezōbwe State
The Hezawe Community
The Chamazuteni State
The Bekuwōwe State
The Kingdom of the Befōdji
The Deyōshu City State
The Ofami State
The government contains:
A National Congress acting as its legislature comprising of 15 Representatives from each State. Name: The National Congress (Bezokwōdji)
An executive council of the 8 State Level Heads. Name: The Servants of Ngozimenhaza (Ngozidji)
Judicial Elected Monarch who mediates between the states and acts as Chief Diplomat of the Union. Name: Judge of the 8 States (Mdomōwe p'Kayembi Kashukwa)
The People's Democratic Republic in Chukwezi




A Prosperous Socialist Republic in Southwestern Shukweso. The nation is divided into 5 Provinces and 1 Autonomous Region.
The Provinces:
Shakwo State
Kochukwe State
Shanwo State
Shafashkezi State
Kolamazu State
The Autonomous Region:
The Kozēyishāzo Autonomous Region
The country is governed by an alliance of Unions, Guilds, Trade Syndicates, Mass Organizations, and Ethnic and Regional Councils forming the Chukwezi People's Democratic Union
They meet in the National People's Assembly where delegates are elected and recalled by their constituents. They assign agencies and administrative duties to specific unions, syndicates, mass organizations, and ethnic and regional councils for the purpose of building and executing policy. They make decisions built on consensus and, if divided issue referendums to the people.
36 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The Invasion of Poland in 1939
The leader of Nazi Germany Adolf Hitler (1889-1945) ordered the invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939. Hitler's refusal to withdraw brought a declaration of war from Britain and France on 3 September, and so began the Second World War (1939-45). The USSR invaded eastern Poland on 17 September, and the country was divided and occupied by two totalitarian regimes.
Warsaw after the German Invasion, 1939
Imperial War Museums (CC BY-NC-SA)
Hitler's Aggressive Foreign Policy
To understand why Poland became the country Britain and France decided to go to war over, it is necessary to trace the path of Germany's expansion from 1935. Adolf Hitler gained power in 1933, and two years later, he began a series of land grabs, each time using a combination of military manoeuvres, diplomacy, and bluff to convince world leaders that each new step into neighbouring territory would be his last. Hitler had promised the German people he would regain the territories lost after the First World War (1914-18) in the humiliating Treaty of Versailles (1919). Hitler said Germany needed Lebensraum ('living space') for its people, that is, new lands where they could prosper.
In March 1935, Hitler took back the coal-rich Saar region on Germany's western border, an area that had been governed by the League of Nations (the forerunner of today's United Nations) since the end of WWI. In March 1935, voters in the Saar decided overwhelmingly to rejoin Germany. Hitler, encouraged by the lack of an effective international response to Japan's invasion of Chinese Manchuria in 1931 and Italy's invasion of Abyssinia (Ethiopia) in 1935, next occupied the Rhineland, an area between Germany and France which the Versailles Treaty had stipulated must remain demilitarised. German troops entered the Rhineland in March 1936. Hitler then formally repudiated the Treaty of Versailles and embarked on a programme of rearmament. In 1936, he made an alliance with Italy, the Rome-Berlin Axis. In March 1938, Hitler occupied Austria, the country of his birth. The Anschluss ('fusion') with Austria was later endorsed by a plebiscite.
Next, Hitler wanted the Sudetenland, a neighbouring region of Czechoslovakia that had a German-speaking majority. Even though France and the USSR had signed a treaty in 1935 promising to protect Czechoslovakia from outside aggression, neither was willing to go to war when it came to the crunch. The majority of the population of Britain, like in France, was against the idea of a war and even against the policy of rearmament. At the Munich Conference of September 1938, Britain, France, Italy, and Germany met. In the Munich Agreement, the four powers agreed the Sudetenland would be handed over to Germany. The governments of Czechoslovakia and the USSR had no say in the matter. Hitler had promised to respect what remained of Czechoslovakia, but this he did not do, instead, he promoted the separation of Slovakia and invaded Bohemia and Moravia in March 1939. In the same month, Germany seized Memelland in Lithuania. In April, the fascist dictator in Italy, Benito Mussolini (1883-1945), occupied Albania. It was now clear to even the most naive of diplomats that nothing Hitler or Mussolini signed could ever be trusted.
Europe on the Eve of WWII, 1939
Simeon Netchev (CC BY-NC-ND)
Continue reading...
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
To the people with hate in their heart: I’m not a political person, but I need to say something. . . There are so many people driven by hatred in this country because of the media’s constant baiting against anything at ALL that can divide people. Race, Trump, all of it. It’s absolutely sickening.
An innocent person died today in the crossfire.
And someone in my feed recently posted that Trump is for abortion now - apparently it was yet another person who has been watching mainstream media and being fed twisted words and lies. What he ACTUALLY SAID was that he wants the authority about killing babies to go to each individual state instead of a nationwide laws like you would find in a DICTATORSHIP like we have NOW!!!!! (It is absolutely ironically that the media likes to call Trump a dictator - the one who fights for the power to go back k to the people. It is absolutely astonishing .
Why do you think this man has been under so much attack when all he wants to do is put the power back k into the hands of the people?
The evil people in government (both republican and democrat and everything in between) is terrified of losing their control and MONEY!! That’s why!!!
Right now we are starving because they want us under their thumb. They want socialism like third world countries.
We had 4 years of good times and groceries and homes, etc - now no one can afford anything.
WAKE UP PEOPLE.
WE DO NOT DESERVE IT BUT GOD THIS MAN BUT HE PROTECTED THIS MAN TODAY!!!!
He left a GOOD AND PROSPEROUS LIFE TO HELP US.
Btw, I don’t know the last time maybe that you read Isaiah 45 - but check it out sometime.
His Immediate response in this horrific situation - where he could have easily died - is the kind of guy I want on my side. He did not cower or even stumble, he thought quick and he showed strength and composure and integrity. This is a picture of strength. This is a picture of a leader.

63 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dear Friend,
When I was a teenager, I told my dad I wanted to be an actor. In response, he gave me the only piece of advice he ever offered me—“Learn to play the accordion.” And he was serious. He said, “You can always make a living with an accordion.”
Because I ignored his advice, I never found out if he was right. Instead, I’ve lived 80 creative years pursuing acting and photography, and working as a director and poet.
If I had listened to my father, and hadn’t done any of those things, chances are you wouldn’t have recognized my name and you wouldn’t be reading this. Now that you are, I’d like to ask you to consider what I have to say. I reach out to you as someone who is troubled to see the conflict between Israelis and Palestinians continue apparently without an end in sight.
In fact, there is an end in sight. It’s known as the two-state solution—a secure, democratic Israel as the Jewish State alongside an independent Palestinian state. Even Israel’s nationalist Prime Minister Binyamin Netanyahu, has come to see this as the shape of the future. The problem is how to reach that end point. It’s something we should be concerned about—not only as world citizens, but as Americans.
You might recall the episode in the original Star Trek series called, “Let That Be Your Last Battlefield.” Two men, half black, half white, are the last survivors of their peoples who have been at war with each other for thousands of years, yet the Enterprise crew could find no differences separating these two raging men.
But the antagonists were keenly aware of their differences—one man was white on the right side, the other was black on the right side. And they were prepared to battle to the death to defend the memory of their people who died from the atrocities committed by the other.
The story was a myth, of course, and by invoking it I don’t mean to belittle the very real issues that divide Israelis and Palestinians. What I do mean to suggest is that the time for recriminations is over. Assigning blame over all other priorities is self-defeating. Myth can be a snare. The two sides need our help to evade the snare and search for a way to compromise.
This is the message that Americans for Peace Now seeks to spread. I’m a strong supporter of APN and the work it does. It is a leading voice for Americans who support Israel and know that a negotiated peace will ensure Israel’s security, prosperity, and continued viability as a Jewish and democratic state.
The Middle East is only getting more tumultuous. The upheavals throughout the region show that what happens in the Middle East can’t help but affect us in the United States. This year, we’ve seen oil prices rise sharply and America become involved militarily in Libya. The cost to American lives and our economy continues to rise at a time when unemployment and deficits are sapping our country’s strength.
“If we can solve the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, then that will make it easier for Arab states and the Gulf states to support us when it comes to issues like Iraq and Afghanistan. It will also weaken Iran, which has been using Hamas and Hezbollah as a way to stir up mischief in the region.”
Those are the words of candidate Barack Obama in 2008. And although they’re just as accurate today, time has not stood still.
We’ve also seen a marked increase in violence: a Jewish family was murdered in the West Bank and a woman was killed in a bus bombing in Jerusalem. A rocket attack on southern Israel from the Hamas-controlled Gaza Strip resulted in a school bus being hit and a teen died of his wounds. Israel, in turn, has retaliated. We need strong American leadership now to pivot from the zero-sum mentality of violence to an attitude that focuses on the parties shared interests: security and prosperity.
If you’ve learned something from this letter, I’ve succeeded in my preliminary task. Now I ask for your support to continue APN’s educational efforts in this country—to spread the message that there is a peace solution, and to let Congress and the White House know it’s preferable for America to be part of the solution than to be drawn into another conflict.
There is a sizable number of influential voices in Israel saying the same thing. In April, a group of 50 prominent Israelis, including the former heads of the Mossad (Israel’s CIA), the Shin Bet (its FBI), and the military, issued a call for two states for two nations. Their plan includes a Palestinian state alongside Israel with agreed-upon land swaps. The Palestinian-populated areas of Jerusalem would become the capital of Palestine; the Jewish-populated areas the capital of Israel.
These experts are not naïve. They know that even if the Palestinian pragmatists of Fatah reconcile with Hamas, there will be extremists who will try to sabotage any future peace deal. They know how to deal with violent extremists. These people were entrusted with Israel���s security and are saying that the work they did alone isn’t enough to bring Israel security. We cannot know yet what this unification of Hamas with Fatah means and we have to wait and see what emerges. Regardless, the principle of establishing two independent states, one Jewish and the other Palestinian, is still critical in this region for both Israel and the Palestinian people. That is the goal, to support the rational and moderate course.
Their action plan echoes the 348 senior Israeli reserve army officers and combat soldiers who came together in 1978 to urge their government to sign a peace treaty with Egypt. They formed Shalom Achshav, Israel’s Peace Now movement which APN provides nearly 50 percent of their funding.
Peace Now’s activities and programs—such as Settlement Watch, the ongoing monitoring of settlement construction on the West Bank—keeps peace on the world’s agenda. Peace Now gathers and publishes detailed information on settlements and is widely cited in Israeli and international media as the foremost authority on settlements. Peace Now is likewise well known for mobilizing demonstrations and organizing grassroots pro-peace activities. Innovations include an interactive online map of the settlements, “Facts on the Ground,” also available as an app for iPhone and iPad developed by APN applying Peace Now’s courageous work.
Like those Israelis who issued the peace plan, the members of Peace Now have their boots on the ground. They serve in Israel’s military reserves and see every day what life is like without a negotiated peace with the Palestinians.
That’s why I’m a supporter of APN and Peace Now.
I hope you’ll join me, and lend your voice to the influential and credible peace lobby that exists here as well as in Israel. Please give the tax-deductible contribution you can afford.
Dare I say it? It’s the logical thing to do.
Leonard Nimoy
5/11/2011

#i'm gonna start rbing this every time a star trek blog is antisemitic to me for i/p reasons. leonard nimoy would be deeply disappointed in#some of the stuff y'all are saying. have some compassion for your fellow humans#peace activism#leonard nimoy#radical compassion#eretz yisrael#this letter made a tangible difference when it was published and helped direct a lot of money towards apn and peace now#long post#jewish star trek
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Socialism: Utopian and Scientific - Part 19
[ First | Prev | Table of Contents | Next ]
Already in his Geneva letters, Saint-Simon lays down the proposition that “all men ought to work”. In the same work he recognizes also that the Reign of Terror was the reign of the non-possessing masses.
“See,” says he to them, “what happened in France at the time when your comrades held sway there; they brought about a famine.” [Lettres d’un habitant de Genève à ses contemporains, Saint-Simon, 1803]
But to recognize the French Revolution as a class war, and not simply one between nobility and bourgeoisie, but between nobility, bourgeoisie, and the non-possessors, was, in the year 1802, a most pregnant discovery. In 1816, he declares that politics is the science of production, and foretells the complete absorption of politics by economics. The knowledge that economic conditions are the basis of political institutions appears here only in embryo. Yet what is here already very plainly expressed is the idea of the future conversion of political rule over men into an administration of things and a direction of processes of production – that is to say, the “abolition of the state”, about which recently there has been so much noise.
Saint-Simon shows the same superiority over his contemporaries, when in 1814, immediately after the entry of the allies into Paris, and again in 1815, during the Hundred Days’ War, he proclaims the alliance of France and England, and then of both of these countries, with Germany, as the only guarantee for the prosperous development and peace of Europe. To preach to the French in 1815 an alliance with the victors of Waterloo required as much courage as historical foresight.

If in Saint-Simon we find a comprehensive breadth of view, by virtue of which almost all the ideas of later Socialists that are not strictly economic are found in him in embryo, we find in Fourier a criticism of the existing conditions of society, genuinely French and witty, but not upon that account any the less thorough. Fourier takes the bourgeoisie, their inspired prophets before the Revolution, and their interested eulogists after it, at their own word. He lays bare remorselessly the material and moral misery of the bourgeois world.
He confronts it with the earlier philosophers’ dazzling promises of a society in which reason alone should reign, of a civilization in which happiness should be universal, of an illimitable human perfectibility, and with the rose-colored phraseology of the bourgeois ideologists of his time. He points out how everywhere the most pitiful reality corresponds with the most high-sounding phrases, and he overwhelms this hopeless fiasco of phrases with his mordant sarcasm.
Fourier is not only a critic, his imperturbably serene nature makes him a satirist, and assuredly one of the greatest satirists of all time. He depicts, with equal power and charm, the swindling speculations that blossomed out upon the downfall of the Revolution, and the shopkeeping spirit prevalent in, and characteristic of, French commerce at that time. Still more masterly is his criticism of the bourgeois form of the relations between sexes, and the position of woman in bourgeois society. He was the first to declare that in any given society the degree of woman’s emancipation is the natural measure of the general emancipation.
But Fourier is at his greatest in his conception of the history of society. He divides its whole course, thus far, into four stages of evolution – savagery, barbarism, the patriarchate, civilization. This last is identical with the so-called civil, or bourgeois, society of today – i.e., with the social order that came in with the 16th century. He proves “that the civilized stage raises every vice practiced by barbarism in a simple fashion into a form of existence, complex, ambiguous, equivocal, hypocritical” – that civilization moves “in a vicious circle”, in contradictions which it constantly reproduces without being able to solve them; hence it constantly arrives at the very opposite to that which it wants to attain, or pretends to want to attain, so that, e.g., “under civilization poverty is born of superabundance itself”. [Théorie de l’unite universelle, Fourier, 1843 and Le nouveau monde industriel et sociétaire, ou invention du procédé d'industrie attrayante et enaturelle distribuée en séries passionnées, Fourier, 1845]
[ First | Prev | Table of Contents | Next ]
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump Issues Executive Order Aimed At Deporting Anti-Israel Protesters
by blueapples | Jan 31, 2025
Last spring, a wave of protests across college campuses nationwide against Israel’s war in Gaza became the focal point of the growing cultural schism further dividing American society. The dichotomy between supporters and opponents of those protests immediately parlayed into the 2024 election cycle, with rightwing politicians seizing upon the opportunity to use the chaos in order to chip away at the crumbling foundation that the Biden administration’s re-election hopes rested upon. Smelling blood in the water, Biden’s opponents used the protests as evidence of the incumbent’s anti-American ideals manifesting on the nation’s soil and vowed to take swift action against the participants.
As is often the case, the right inextricably tied the interests of the US to those of Israel by categorizing the protesters critical of the genocidal war effort led by the Netanyahu regime as terrorists who were able to find safe haven in the US due to policies of the Biden administration like DEI and open borders that were rooted in Cultural Marxism. Proposed legislation aimed at purging students on visas involved in the protests due to their political leanings gained momentum but ultimately did not achieve any impact. However, an Executive Order signed by the Trump Administration realizes the goal of that reactionary response to those protests and carries the same concerns about its constitutionality and the chaos that enveloped the country across college campuses last spring being used as a catalyst to infringe upon the right to free speech.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
August 20, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Aug 21, 2024
At Chicago’s United Center today, the delegates at the Democratic National Convention reaffirmed last week’s online nomination of Kamala Harris for president. The ceremonial roll-call vote featured all the usual good natured boasting from the delegates about their own state’s virtues, a process that reinforces the incredible diversity and history of both this land and its people. The managers reserved the final slots for Minnesota and California—the home states of Democratic vice presidential candidate Tim Walz and presidential candidate Kamala Harris, respectively—to put the ticket over the top.
When the votes had been counted, Harris joined the crowd virtually from a rally she and Walz were holding at the Fiserv Forum in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Last month the Republicans held their own national convention in that venue, and for Harris to accept her nomination in the same place was an acknowledgement of how important Wisconsin will be in this election. But it also meant that Trump, who is obsessed with crowd sizes, would have to see not one but two packed sports arenas of supporters cheer wildly for her nomination.
He also had to contend with former loyalists and supporters joining the Democratic convention. His former press secretary, Stephanie Grisham, told the Democratic convention tonight that when the cameras are off, “Trump mocks his supporters. He calls them basement dwellers.” Grisham endorsed Harris, saying: “I love my country more than my party. Kamala Harris tells the truth. She respects the American people and she has my vote.”
Trump spoke glumly to a small crowd today at the Livingston County Sheriff’s Office in Howell, Michigan.
It was almost exactly twenty years ago, on July 27, 2004, that 43-year-old Illinois state senator Barack Obama, who was, at the time, running for a seat in the U.S. Senate, gave the keynote address to that year’s Democratic National Convention. It was the speech that began his rise to the presidency.
Like the Democrats who spoke last night, Obama talked in 2004 of his childhood and recalled how his parents had “faith in the possibilities of this nation.” And like Biden last night, Obama said that “in no other country on earth, is my story even possible.” The nation’s promise, he said, came from the human equality promised in the Declaration of Independence.
“That is the true genius of America,” Obama said, “a faith in the simple dreams of its people, the insistence on small miracles.” He called for an America “where hard work is rewarded.” “[I]t's not enough for just some of us to prosper,” he said, “[f]or alongside our famous individualism, there's another ingredient in the American saga.”
He described that ingredient as “[a]belief that we are connected as one people. If there's a child on the south side of Chicago who can't read, that matters to me, even if it's not my child. If there's a senior citizen somewhere who can't pay for her prescription and has to choose between medicine and the rent, that makes my life poorer, even if it's not my grandmother. If there's an Arab American family being rounded up without benefit of an attorney or due process, that threatens my civil liberties. It's that fundamental belief—I am my brother's keeper, I am my sister's keeper—that makes this country work. It's what allows us to pursue our individual dreams, yet still come together as a single American family. ‘E pluribus unum.’ Out of many, one.”
Obama emphasized Americans’ shared values and pushed back against “those who are preparing to divide us, the spin masters and negative ad peddlers who embrace the politics of anything goes.” He reached back into history to prove that “the bedrock of this nation” is “the belief that there are better days ahead.” He called that belief “[t]he audacity of hope.”
Almost exactly twenty years after his 2004 speech, the same man, now a former president who served for eight years, spoke at tonight’s Democratic National Convention. But the past two decades have challenged his vision.
When voters put Obama into the White House in 2008, Republicans set out to make sure they couldn’t govern. Mitch McConnell (R–KY) became Senate minority leader in 2007 and, using the filibuster, stopped most Democratic measures by requiring 60 votes to move anything to a vote.
In 2010 the Supreme Court handed down the Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission decision, declaring that corporations and other outside groups could spend as much money as they wanted on elections. Citizens United increased Republican seats in legislative bodies, and in the 2010 midterm elections, Republicans packed state legislatures with their own candidates in time to be in charge of redistricting their states after the 2010 census. Republicans controlled the key states of Florida, Wisconsin, North Carolina, Ohio, and Michigan, as well as other, smaller states, and after the election, they used precise computer models to win previously Democratic House seats.
In the 2012 election, Democrats won the White House decisively, the Senate easily, and a majority of 1.4 million votes for House candidates. Yet Republicans came away with a thirty-three-seat majority in the House of Representatives. And then, with the 2013 Shelby County v. Holder decision, the Supreme Court gutted the Voting Rights Act, making it harder to protect Democratic voters.
As the Republicans skewed the mechanics of government to favor themselves, their candidates no longer had to worry they would lose general elections but did have to worry about losing primaries to more extreme challengers. So they swung farther and farther to the right, demonizing the Democrats until finally those who remain Republicans have given up on democracy altogether.
Tonight’s speech echoed that of 2004 by saying that America’s “central story” is that “we are all created equal,” and describing Harris and Walz as hardworking people who would use the government to create a fair system. He sounded more concerned today than in 2004 about political divisions, and reminded the crowd: “The vast majority of us do not want to live in a country that’s bitter and divided,” he said. “We want something better. We want to be better. And the joy and the excitement that we’re seeing around this campaign tells us we’re not alone,” he said.
And then, in his praise for his grandmother, “a little old white lady born in a tiny town called Peru, Kansas,” and his mother-in-law, Marion Robinson, a Black woman from the South Side of Chicago, he brought a new emphasis on ordinary Americans, especially women, who work hard, sacrifice for their children, and value honesty, integrity, kindness, helping others, and hard work.
They wanted their children to “do things and go places that they would’ve never imagined for themselves.” “Whether you’re a Democrat or a Republican or somewhere in between,” he said, “we have all had people like that in our lives:... good hardworking people who weren’t famous or powerful but who managed in countless ways to leave this country just a little bit better than they found it.”
If President Obama emphasized tonight that the nation depends on the good will of ordinary people, it was his wife, former first lady Michelle Obama, who spoke with the voice of those people and made it clear that only the American people can preserve democracy.
In a truly extraordinary speech, perfectly delivered, Mrs. Obama described her mother as someone who lived out the idea of hope for a better future, working for children and the community. “She was glad to do the thankless, unglamorous work that for generations has strengthened the fabric of this nation,” Mrs. Obama said, “the belief that if you do unto others, if you love thy neighbor, if you work and scrape and sacrifice, it will pay off. If not for you, then maybe for your children or your grandchildren.”
Unlike her husband, though, Mrs. Obama called out Trump and his allies, who are trying to destroy that worldview. “No one has a monopoly on what it means to be an American,” she said. “No one.” “[M]ost of us will never be afforded the grace of failing forward,” she said. “We will never benefit from the affirmative action of generational wealth. If we bankrupt a business…or choke in a crisis, we don't get a second, third, or fourth chance. If things don't go our way, we don't have the luxury of whining or cheating others to get further ahead…we don't get to change the rules so we always win. If we see a mountain in front of us, we don’t expect there to be an escalator waiting to take us to the top. No, we put our heads down. We get to work. In America, we do something."
And then Mrs. Obama took up the mantle of her mother, warning that demonizing others and taking away their rights, “only makes us small.” It “demeans and cheapens our politics. It only serves to further discourage good, big-hearted people from wanting to get involved at all. America, our parents taught us better than that.”
It is “up to us to be the solution that we seek.” she said. She urged people to “be the antidote to the darkness and division.” “[W]hether you’re Democrat, Republican, Independent, or none of the above,” she said, “this is our time to stand up for what we know. In our hearts is right. Not just for our basic freedoms, but for decency and humanity, for basic respect. Dignity and empathy. For the values at the very foundation of this democracy.”
“Don’t just sit around and complain. Do something.”
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Letters From An American#Heather Cox Richardson#politcal history#grace#poetry#Democratic National Convention#The Obamas#history#American History#Citizens United
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
As speculation mounts over possible negotiations to end the Russian invasion of Ukraine, it is important to understand the nature of the war unleashed by Vladimir Putin almost three years ago. Crucially, this is not a conventional war for land that can be resolved by offering limited territorial concessions. Putin’s goals are far more ambitious. He is waging the current war in order to undermine the existing international security architecture and replace it with a new world order where a handful of great powers are able to dominate their neighbors.
Since launching the full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, Putin has repeatedly outlined his vision for a “multipolar world order” that would reverse the verdict of the Cold War and create a world divided into spheres of influence. By challenging the sanctity of borders with his invasion of Ukraine, Putin aims to remove a central pillar of today’s global security system and normalize the use of military force in international affairs. If his efforts are perceived as successful, this will set a disastrous precedent that will embolden authoritarian regimes around the world.
Putin’s dream of establishing a new world order is reflected in his push for bilateral talks with the United States to discuss the fate of Ukraine and Europe without Ukrainian or European participation. He wants to demonstrate that sovereignty is negotiable and convey the message that some nations are more equal than others. The consequences of this approach could be catastrophic for both Ukraine and Europe as a whole.
The world order Putin hopes to usher in would be governed by the laws of the geopolitical jungle and defined by insecurity and aggression. Armed conflicts would proliferate around the world as previously accepted rules of international relations were replaced by the overriding principle that “might is right.” The unprecedented global economic prosperity of the past three decades would also be threatened amid mounting barriers to trade and record levels of defense spending. The only obvious beneficiaries would be nations like Russia that seek to embrace revisionist or expansionist agendas.
The international security situation is now so grave and has escalated to such a level that it can no longer be resolved by appeasing Russia or seeking some kind of compromise peace. Instead, Russia must lose in Ukraine, and must be seen to lose.
At present, that is not the case. On the contrary, Putin is more confident than ever of victory and sees no reason to end the war. He is projecting strength around the world and is successfully building a coalition of fellow authoritarian powers including China, Iran, and North Korea, who all provide support for the war in Ukraine and share Moscow’s objective of overthrowing the current world order.
On the home front, Putin has succeeded in shifting the Russian economy onto a wartime footing, and has found new partners to compensate for the collapse in ties with the West. He is openly preparing for a long war and is counting on a lack of Western resolve to confront him.
In order to stop the war, Putin must be persuaded that continuing the invasion of Ukraine will lead to disaster for Russia. This requires a range of measures designed to weaken Russia’s position both economically and militarily.
Russia’s economic outlook is already worsening as a result of the war and could become far more serious if Western leaders take the necessary steps. There is an obvious need for greater coordination between the United States, UK, EU, and other countries engaged in sanctioning the Russian war effort. Implementation of existing sanctions remains inadequate, while tougher measures are needed to target intermediaries.
Economic hardships alone will not bring Putin to the negotiating table. He must also be forced to confront the prospect of military defeat. This will require a major shift in thinking among Ukraine’s partners. At present, Ukraine finds itself forced to fight a defensive war of attrition with the aim of inflicting unacceptable losses on the invading Russians. However, Putin clearly has a very high tolerance for losses, and can also call upon huge untapped reserves of manpower to replenish the depleted ranks of his army. If the current war of attrition continues, Russia will eventually and inevitably win.
Instead, Ukraine must be equipped to defeat Russia on the battlefield. The Ukrainian military has repeatedly demonstrated its ability to beat Russia, but currently lacks the military capabilities to turn local victories into a war-winning position. This needs to change.
Western fears of escalation mean Kyiv is still being denied a wide range of weapons and faces restrictions on its ability to defend itself. As a result of this overly cautious approach, the Kremlin is able to wage a total war against Ukraine with little fear of major counterattacks inside Russia. Putin also enjoys overwhelming advantages in firepower, including a far larger and more advanced air force. No NATO member state would even consider fighting a war without adequate air power, but that exactly what Ukraine is currently being expected to do.
So far, the West has been arming Ukraine to survive. Putin will not end the invasion until he becomes convinced that Western leaders are determined to arm Ukraine for victory. Ukraine’s military requirements are well known. All that is missing is the requisite political will to act. This means providing fighter jets, long-range missiles, armor, and artillery in large quantities along with dramatically enhanced drone and electronic warfare capabilities.
By supplying Ukraine with sufficient military aid, the West could finally oblige Putin to rethink the current war while also creating a powerful deterrence force capable of preventing further Russian aggression. Anything less will merely create a pause in hostilities that Putin will use to rearm and prepare for the next phase of his war against the West. The price of stopping Russia in Ukraine is high, but it will be dwarfed by the costs of a new authoritarian world order if Putin’s invasion is allowed to succeed.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
About the past of the islands /sobre el pasado de las islas
Advertencia: Estos no son mis ideales, solo es para profundizar en la historia y los problemas de aquellas épocas y acercarme lo más que puedo al mundo real. :")
Warning: These are not my ideals; this is only to deepen the story and the issues of those times and get as close as possible to the real world. :")

In this universe, objects, animals, and anthropomorphic beasts are widely despised across most of the world. This is because, since the beginning of time, when these races first began to appear, they were deemed products of evil. To humans, it was unnatural to see objects come to life, so they were associated with dark magic and demons.
Even in places with different religions, these beings were shunned. Over time, most belief systems established rituals or methods to "redeem" their supposed dark nature, seeking divine forgiveness. One practice that endured was the use of gloves. In ancient times, anthropomorphic objects could be born with deformities, such as having more or fewer fingers than usual. To conceal these anomalies and show respect to God, they began covering their hands, extending the custom to any other strange feature.
This form of racism or speciesism persisted in nearly every country—except for the Inkwell Islands. Long ago, these lands were not called that; in fact, they were abandoned islands, unknown to the rest of the world. The original inhabitants were divided into very distinct tribes, but due to the hardships brought by droughts, they chose to unite and explore their surroundings. Over time, this led to an alliance between all species, fostering acceptance and a greater openness to learning about each other's origins and customs.
When the ancient Lucifer discovered these islands, he was intrigued by how well their inhabitants coexisted, in stark contrast to the rest of the world. Perhaps this drew him to help the tribes prosper. He taught them the importance of independence as beings, free from the need to depend on gods. Even so, he never interfered with their rituals to honor certain aspects of nature, as he understood that these practices made them grateful for what was essential.
Lucifer learned much from them, and they, in turn, learned from him—whether in various arts, magic, or philosophy. As this society flourished, the once-separate tribes united under a single name for the collection of islands: "Aeterna." To better organize their growing civilization, they divided themselves into aquerales, administrative sections that helped maintain order and progress. The people of Aeterna came to be known as Aeternians.
However, when Lucifer was mortally wounded and imprisoned in a crystal as punishment for teaching magic to mortals, the islands suffered great devastation due to the angels' attack. To protect themselves, the Aeternians cast a powerful spell that hid the islands from God's sight and relocated them elsewhere.
Over time, the islands were rediscovered by foreign explorers, who were amazed by their rich flora and fauna. Eager to exploit these resources, they attempted to seize the fertile lands, as much of the islands remained barren and lifeless. However, after witnessing the Aeternians’ magic, they grew fearful and sought alternative ways to benefit from the land without direct conflict.
A deal was made: the Aeternians would provide natural resources in exchange for the foreigners helping to restore the islands, building larger and more livable settlements for everyone. However, as time passed, this agreement became distorted. Eventually, the self-proclaimed kings pushed the Aeternians into the protected regions while they took control of the rest of the land.
All of this happened under the rule of the reigning kings, a system of power that lasted for generations due to the islands' geographical isolation from the rest of the world.

En este universo, los objetos, animales y bestias antropomórficas son mal vistas en casi todos los lugares del mundo. Principalmente porque, desde el inicio de los tiempos, cuando estas razas comenzaron a aparecer, fueron tachadas como productos del mal. No era natural para los humanos ver cómo los objetos cobraban vida, y se consideró como resultado de la magia oscura de los demonios.
Incluso en lugares con diferentes religiones, estos seres eran rechazados. Con el tiempo, en la mayoría de las religiones se comenzaron a exigir rituales o formas de “purificación” para “recompensar” su naturaleza oscura, bajo la idea de buscar el perdón divino. Una de las prácticas que perduró fue el uso de guantes, ya que, en el caso de los objetos, podían presentar deformidades, como nacer con menos o más dedos. Por ello, cubrían sus manos con guantes para ocultar estas anomalías como un gesto de respeto hacia Dios. También se cubrían cualquier parte bestial o anómala de su cuerpo.
Este tipo de racismo o especismo prevaleció en casi todos los países, excepto en las islas Inkwell. Estas, en un principio, no se llamaban así. Eran unas islas abandonadas y desconocidas para el resto del mundo. Sus habitantes originales estaban divididos en tribus muy diferentes entre sí, pero la precariedad causada por las sequías los llevó a unirse para explorar las islas vecinas. Esto dio lugar a una alianza entre todas las especies, fomentando una mayor aceptación y apertura para entender sus orígenes y costumbres.
Cuando el antiguo Lucifer encontró estas islas, se sintió intrigado al ver cómo todos los habitantes convivían en armonía, a diferencia del resto del mundo. Tal vez por esto decidió ayudar a las tribus a prosperar. Les enseñó la importancia de su independencia como seres, de no depender de dioses. Aun así, nunca intervino en los rituales que tenían para honrar ciertos aspectos de la naturaleza, ya que estos los hacían agradecidos por lo indispensable.
Lucifer aprendió mucho de ellos, y ellos de él. Compartieron conocimientos en diversas artes, magia y filosofía. A medida que esta sociedad prosperaba, las tribus se unieron en una sola comunidad, que nombraron “Aeterna”, en honor al conjunto de islas. Para organizarse, se clasificaron en aquerales, un sistema que les permitía mantener el control de su sociedad.
Sin embargo, cuando Lucifer fue herido de muerte y encerrado en un cristal como castigo por enseñar magia a los mortales, las islas quedaron gravemente dañadas tras el ataque de los ángeles. No obstante, las islas fueron ocultadas gracias a un poderoso hechizo que las mantuvo fuera de la vista de Dios, reubicándolas en otro lugar.
Después de mucho tiempo, las islas fueron redescubiertas por exploradores extranjeros que quedaron maravillados por la fauna y flora del lugar. Estos intentaron explotar sus recursos naturales, pero solo las áreas habitadas por los Aeternitas eran fértiles, mientras que el resto de las islas estaban desoladas e infértiles. Los extranjeros intentaron tomar las tierras fértiles por la fuerza, pero se atemorizaron al descubrir la magia que poseían los Aeternitas. Así que buscaron otras alternativas: un acuerdo de paz. Según este trato, los Aeternitas proporcionarían recursos naturales, y a cambio, los extranjeros repararían las tierras infértiles, construyendo residencias más grandes y habitables para todos.
Sin embargo, con el tiempo, este acuerdo se distorsionó. Los autoproclamados reyes excluyeron a los Aeternitas de las mejores tierras, confinándolos únicamente a las áreas que protegían.
Todo esto ocurrió bajo el régimen de los reyes de aquel momento, un sistema que perduró por generaciones debido a lo aisladas que estaban las islas del resto del mundo.
#lil lucifer au#cuphead#lucifer#casino cups au swap#casino cups#casino cups swap#inkwell#lil lucifer#el pasado de lucifer#lucifer's past
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
1890s America and Red Dead Redemption
Part One: Violent Delights and Violent Ends
-----
The latter half of the 1800s was a time characterized by struggle. Off the back of the Civil War, a country divided in not two but four by the rising industry to the east and the stubborn pastoralism of the west. The southern portion of the country beaten down, burned and disgraced, and the northern portion rolling in gold and prosperity. Whether they knew it or not, the common American had their life ultimately shaped by these divisions.
As the opening lines of Red Dead Redemption 2 state: "The age of outlaws and gunslingers was at its end" (Rockstar, 2018). Yet contrary to the following text, America was far from becoming a "land of laws". Laws for the poor, perhaps, but the wealthy still thrived and skirted just beyond the boundaries of human decency.
From the 1870s to the 1920s, miners and railroad workers unionized and carried out often violent protests in the hopes of gaining better working conditions. The poor had little but their fists, and they had no qualms about using them. It is in this turmoil we find Dutch Van Der Linde with his Robin Hood-esque visions of a crumbling elite and prospering poor. The struggle between workers and their iron-fisted overseers was bloody, and Dutch would not have it any other way. Those he took under his wing were the beaten down lowest tiers of society. How could they not see him as a shining idol of American idealism? What he wants, what he fights for, it is for them. Outcasts with nowhere else to turn, given a cause and a home and something that perhaps felt real to them for the first time in a long time.
Race is a topic not wholly explored, but touched on certainly within the game. Tensions rose as racial divisions were made even clearer, black Americans fighting for their own foothold in a world that has just opened up to them and their children. Lenny Summers is the first in generations to be born free of slavery. Javier comes from a country that has been terrorized by colonialism and corruption, yet he still dreams of returning. 1890s Mexico (and what we see in RDR1) is a topic of its own, though the spirit of people downtrodden by colonialism is echoed throughout both games. Sean, who was chased from the country his father fought for. Whose father was killed in his own bed, likely in the same room as his son. Violence in this world is inescapable, a swirling vortex that consumes everything in its path.
Dutch embraced this, as many leaders of the past and future have. If you cannot fight with peace, then sticks and stones make for much better conversation. I can't say I disagree with him, in all honesty, and that is what makes him so fascinating. He's right. He has a point, a cause. What went so wrong? Do heroes not get a happy ending?
In 1892, railroad employees of Carnegie Steel in Pennsylvania's Homestead plant went on strike when chairman Henry Frick cut their pay dramatically. 300 agents of the Pinkerton detective agency arrived, escalating tensions. Violence erupted, the Pennsylvania national guard was called. Sixteen men were killed.
Leviticus Cornwall is Andrew Carnegie, Andrew Carnegie is Leviticus Cornwall. The Pinkertons are rightful villains in our narrative, the gang is a thorn in their side which must be cut free. Law and order, right? Dutch was right, his killing of Cornwall was arguably deserved. Yet what makes it so wrong?
Dutch's actions are selfish, in the end. Not because he doesn't care for the people around him, as I believe he truly does. He sees things getting worse and worse and only digs in his heels. Dutch is the American Dream. The bloody messiah to the poor and disadvantaged. He guts them the same as any railroad magnate. Power corrupts, this is what we learn. Power and vitriol and paranoia. The people left struggling in his wake are the common folk who get caught in the crossfire, used and abused only to prove a point. They know nothing but violence, and who is to tell them otherwise? Even Arthur in his end of life maturation cannot pry himself free. He kills and kills and in the end he dies for it. Even John, who tried to leave it behind. Even Sadie, who was ruined by it, embraced it in the end.
The American dream is indecipherable from the American nightmare. They are lovers and companions. There is nothing to do but fight, and even then you have no hope of winning. It's a beautiful tragedy, is it not? All these people who never had a chance, yet who tried anyway. Workers who gained little and lost everything still took their signs and marched for what was right. Black Americans who were beaten down again and again still got up each and every day and did whatever it was they had to do. Native Americans, who were nearly erased. Who still cling to their heritage and claw back what has been stolen. Red Dead Redemption is about the small people. The forgotten in the annals of American history.
24 notes
·
View notes
Note
really intrigued by ur masters program. could u tell us more abt it? what sort of reading did u do, ur thesis etc etc
for sure!! i studied comparative social policy, which is essentially a study of the history of welfare state development - policies which are 'social', i.e. in that they are designed to support people. think things like pensions, welfare benefits, healthcare, poverty-reduction, things like that!
more under the cut :)
the programme i studied had a focus on OECD countries, which are generally divided into 3 types of welfare states: (1) liberal welfare states, which tend to be anglosphere countries, so the uk, ireland, australia and new zealand - some models include the US, and some don't because the US is an outlier in that... it just doesn't have a lot of the welfare benefits that other anglosphere countries have (think free healthcare, guaranteed maternity leave) on a federal level. (2) is social-democratic welfare states, which tend to be more generous and universal (nordic countries), and finally (3) conservative welfare states, countries like germany and france where welfare rights have a history of being linked to class struggle and workers rights, and are more likely to be linked to your occupation.
this isn't an all-encompassing model and there have been many attempts to update it to include asian/african/latin american welfare states (this is an extremely eurocentric model) and add nuance to the conversation, but just a general overview of the types of stuff we discussed!
in terms of things i studied specifically, i focused on gender and poverty as my two options, looking at ways that welfare states can alleviate/worsen poverty and gender inequality. it was really fascinating stuff but ultimately hampered by the fact that oxford is an extremely old fashioned organisation and didn't have much in the way of diversity in reading lists.. so it had to be found by myself lmao
as for my dissertation, i compared the levels of generosity in welfare benefit allocation between the united kingdom and the republic of ireland. the uk introduced restrictive welfare legislation which prevented the majority of non-european immigrants from accessing welfare (known as no recourse to public funds) in 1995, but ireland didn't until 2007, so i wanted to know why that was. ultimately i found it was because of 2 things: 1. differing levels of economic prosperity - ireland's economy was stratospheric before the 2008 crash, and the uk not so much. ireland didn't want to introduce deterrent legislation to prevent immigrants coming to ireland because they needed immigrants to join the labour force. and (2) the rhetoric of public debate in the uk was much more harshly anti-immigrant than in ireland, thanks to thatcherism (lol). ireland wasn't exactly Positive about immigration, but political debate had a lot more to do with the economy and appeals to emotion vs in the uk the rhetoric was much more fiercely us vs them, if that makes sense. it was an interesting project!!
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

a terra incognita introduction
cast: jake ✗ fem.reader
synopsis: as the world entered the middle of the 21st century, many things have changed for the better or for worse in the newly united korea peninsula: the preparation for the succession of the new conglomerates of the past decade, the uprising of deviant androids, and the new layer of life shield by walls of codes. in the middle of it, two beings are trying to understand each other and the situation of the world they live in; an unknown territory
genre: cyberpunk, cyber noir, psychological thriller, science fiction, dystopian future, politics and philosophies regarding artificial intelligence and humanity, romance, drama, angst, mature content (war and revolution, explicit smut)
based on: video game cyberpunk 2077 (2020) and detroit: become human (2018), anime serial experiments lain (1998), and tv show succession (2018-2023)
masterlist

united korea
the united republic of korea (known as "united korea") is an east asia nation on the korean peninsula. as a result of the reunification agreement back in 2025 of the former north and south korea, the state has now prospered in terms of sociopolitical and economic issues from the korean war. it now excels technologically as one of the firsts in the world to introduce commercialized androids along with other east asian countries such as japan and china. in the aftermath of the social media collapse and the cyber world war of 2027-2030, the private conglomerates of the state have released a new way to connect to the information superhighway.
FLAG

(flag link to r/alternatehistory on reddit)
INFORMATION
capital cities: neo seoul | neo pyongyang
population: 65.5 million
language: korean | english | japanese | chinese
>> HISTORY
>> GEOGRAPHY
>> GOVERNMENT
>> SOCIETY
>> ECONOMY
>> MILITARY
>> MAJOR CITIES
neo seoul
one of the capital cities of united korea and the former capital of south korea, neo seoul is a metropolis for the state's bustling life from the most traditional to the most modern. neo seoul is known for six districts that are divided by the han river flowing in the middle, known as the division of north seoul and south seoul
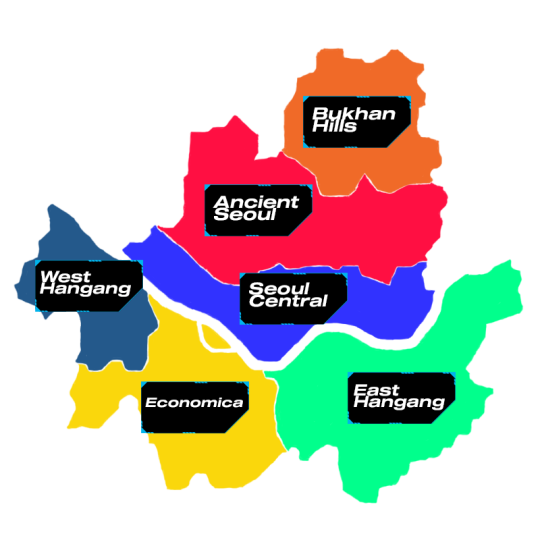
north seoul encapsulates the traditional side of neo seoul and the center for the city's and state's government administration
south seoul lies the center of neo seoul's economy where conglomerates build their headquarters. a distinct living cost gap can be seen to compare those living in the north and those in the south where it is connected to incheon, a major city of transportation with its international seaports and airport
neo pyongyang
one of the capital cities of united korea and the former capital of north korea, neo pyongyang is the capital of the parliament of united korea. it's located on the taedong river kilometers upstream from the yellow sea. it is known as the city where the declaration of unification was signed along with its establishment as half of the capitals of the unified countries. much of the population of neo pyongyang are citizens coming from the southern of the peninsula as they migrate to fill in the spaces and utilize materials. it is also a growing industrial hub where conglomerates built their factories, along with kaesong.
with the rise of deviancies from androids made by shim laboratories, journalists have made observations and assume that neo pyongyang is the main hub of the rebellion between androids and their creator (as one human equates to two androids), creating unrest between the two parties. yet, they also say that neo pyongyang is a better refuge for deviant androids than neo seoul.

taglist: @raeyunshm @endzii23 @fluffyywoo @camipendragon @hiqhkey @wccycc @cha0thicpisces @y4wnjunz @yeehawnana @beansworldsstuff @kimipxl @blurryriki @reallysmolrenjun @frukkoneeeeg
© writingmochi on tumblr, 2021-2025. all rights reserved
#enhypen imagines#enhypen smut#enhypen x reader#enhypen scenarios#enhypen angst#enhypen fanfiction#jake x reader#rsc: t.i.#cr: jake#cs: enhypen#sc: regina
37 notes
·
View notes
Photo

India overtakes China to become world’s most populous country (Hannah Ellis-Petersen, The Guardian, April 24 2023)
“It is also the first time since 1950, when the UN first began keeping global population records, that China has been knocked off the top spot.
China’s population decline follows decades of strict laws to bring the country’s booming birthrate under control, including the introduction of a one-child policy in the 1980s.
This included fines for having extra children, forced abortions and sterilisations.
While initially highly effective in controlling the population, these policies became a victim of their own success, and the country is now grappling with an ageing population in steep decline, which could have severe economic implications.
Part of the problem is that because of a traditional preference for boys, the one-child policy led to a massive gender imbalance.
Men now outnumber women by about 32 million. “How can the country now shore up birth rates, with millions of missing women?” asks Mei Fong, the author of One Child, a book about the impact of the policy.
Recent policies introduced in China trying to incentivise women to have more children have done little to stimulate population growth.
Women still have only 1.2 children and the population is expected to fall by almost 10% in the next two decades.
According to projections, the size of the Chinese population could drop below 1 billion before the end of the century.
In India, the population has grown by more than a billion since 1950. Though growth has now slowed, the number of people in the country is still expected to continue to rise for the next few decades, hitting its peak of 1.7 billion by 2064. (…)
India’s demography is far from uniform across the country.
One third of predicted population growth over the next decade will come from just two states, Bihar and Uttar Pradesh, in the north of the country, which are some of India’s poorest and most agricultural states.
Uttar Pradesh alone already has a population of about 235 million, bigger than Nigeria or Brazil.
Meanwhile states in India’s south, which is more prosperous and has far higher rates of literacy, population rates have already stabilised and have begun to fall.
In the next decade, states in the southern states such as Kerala and Tamil Nadu are likely to start grappling with an ageing population, and by 2025, one in five people in Kerala will be over 60.
The divide in population growth between India’s north and south could also have political implications.
After 2026, India’s electoral lines are due to be revised and redrawn based on census data, in particular relating to the number of people in constituencies.
Many politicians in southern states have expressed concern that their successes in bringing down population numbers, through education programmes, family planning and high literacy, could result in a reduction in their political representation in parliament, and a further political domination of the northern states that continue to have a population boom.
Currently the average age in India is just 29, and the country will continue to have a largely youthful population for the next two decades.
A similar “demographic dividend” proved highly useful in China, leading to an economic boom, particularly in manufacturing.
While India has one of the world’s fastest-growing economies in the world, and recently overtook the UK as the fifth-largest, experts have stressed that the country needs more investment in education and employment to seize the opportunity presented by a young population over the next few decades.
India continues to struggle with high youth unemployment and less than 50% of working-age Indians are in the workforce.
The figure for women is even lower, with just 20% of women participating in the formal labour market, a figure that is decreasing as India develops.”
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
Celebrating Cultural Diversity: A Filipino Perspective
Culture is a perfect manifestation of the art of what it means to be a human being living in this world. It illustrates the way of life of every person in a community, tribe, or country. Culture isn’t something that can be described with just a few words; I believe that to fully grasp it, one must be a part of the flow and actively get involved. Tradition and culture are inseparable. One cannot exist without the other. But the most important element is the people themselves who shape the culture and tradition that have existed up until today.
As a Filipino, our culture comprises many wonderful aspects that amaze me every time I think about them. One cultural custom that I find fascinating is our resilience: our ability to get up after a downfall and smile in any situation or with any person we interact with. This world is not always sunny, but we Filipinos always find it in our hearts to dance in the middle of the storm, and that is truly beautiful. Another cultural value that I am most proud of is our faith in God. I don’t want to sound biased, but this is the truth. This quality is the foundation of our resilience. We survive and prosper because we never lose hope. We get up each day with the thought, “This is just a bad day but never an awful life. God will send me His divine grace to help me get by.” Once again, I am proud to be a Filipino, and living in this society while engaging in this culture gives me a unique identity worthy of being known.
As I have stated in the previous paragraph, I greatly appreciate our own culture. But just like all other traditions, nothing is perfect. There are no superior or inferior values and heritage, but if I had to alter two specific norms in our country, perhaps it would be gossiping and the crab mentality. I want to change these aspects because they can cause more negative effects than positive ones. These traits can be self-destructive and may badly affect others as well. As a concerned citizen, I suggest that changing them is the right thing to do for the betterment of the community, to keep the lifestyle of everybody in harmony.
Culture is undeniably diverse. Many kinds of ethnicities, races, and nationalities are spread out all over the globe. As I continue my journey in life, meeting individuals with different cultures and philosophies is part of it. There are no specific steps to flawlessly communicate with people who practice unfamiliar traits and values, but I can strive to be more empathetic, open-minded, and sensitive in dealing with them. I believe that our differences are not the reason we are divided, nor why there are conflicts. The true reason behind societal divergence is our lack of capacity to accept new ideas and ways of living.
Every person is a complex being, and as we live together in this world, certain issues like conflicts and misunderstandings between countries or in a community are almost impossible to avoid. But this must not always be the case, because after all, we are breathing the same air, and we are under the same sky. Our goal is to be at peace amidst diversity, not at war.
Written by: Amaranthine Briar / Akahana
𝐋𝐞𝐭𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐬 𝐭𝐨 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐔𝐧𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐫𝐬𝐞
Content Copyright © Rose R. Sales All rights reserved.
7 notes
·
View notes