#BIG OIL
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Source


Source
Make them pay
#hawaii#politics#us politics#government#big oil#ban fossil fuels#environmentalism#environment#news#the left#progressive#current events#climate activism#climate justice#climate change
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
#vermont#usa#good news#climate litigation#global climate change#big oil#fossil fuels#environmentalism#science
865 notes
·
View notes
Text

1K notes
·
View notes
Text

[source]
guess who's sucking Big Oil's dick hard enough to actively allow a genocide
#look I'm not sure who I want to rip to fucking shreds the most at this point but THERE IS A LIST#palestine#israel#big oil#IT'S ALWAYS ABOUT FUCKING OIL#IRAQ WAS THE SAME#arabs' lives don't matter to them because all they care about is big oil's bribes and campaign money
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - January 22-28
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles!
1. Sunfish that got sick after aquarium closed has recovered — thanks to human cutouts

“A solitary sunfish […] appeared unwell days after the facility closed last month for renovations. As a last-ditch measure to save the popular fish, its keepers hung their uniforms and set up human cutouts outside the tank. The next morning, the sunfish ate for the first time in about a week and has been steadily recovering[….]”
2. Costco stands by DEI policies, accuses conservative lobbyists of 'broader agenda'

“[Each of the board of directors and 98% of shareholders voted to reject a measure against DEI.] Costco's board wrote that “our commitment to an enterprise rooted in respect and inclusion is appropriate and necessary[….]””
3. Nearly $37 Million Will Support Habitat Restoration in Coastal Louisiana

“The project will restore nearly 380 acres of marsh and construct more than 7,000 feet of terraces in St. Bernard Parish. […] Coastal wetlands help protect communities [… from] wind, waves, and flooding[… and] support a statewide seafood industry valued at nearly $1 billion per year.”
4. Cooling green roofs seemed like an impossible dream for Brazil's favelas. Not true!

“[… A Brazilian nonprofit] teaches favela residents how to build their own green roofs as a way to beat the heat without overloading electrical grids[…,] dampen noise pollution, improve building energy efficiency, prevent flooding by reducing storm water runoff and ease anxiety.”
5. Bacteria found to eat forever chemicals -- and even some of their toxic byproducts
“"Many previous studies have only reported the degradation of PFAS, but not the formation of metabolites. We not only accounted for PFAS byproducts but found some of them continued to be further degraded by the bacteria," says the study's first author[….]”
6. A father and daughter’s to turn oil data into life-saving water

“The aquifer [discovered through oil-owned seismic data], it turned out, was vast enough to provide water for 2 million people for more than a century.”
7. Trump’s funding pause won’t impact federal student loans, Pell Grants
“[… T]he temporary pause will not impact “assistance received directly by individuals,” including federal direct student loans and Pell Grants, which are government subsidies that help low-income students pay for college.”
8. In Uganda, a women-led reforestation initiative fights flooding, erosion

“[… T]he Kasese municipality has established nurseries to provide free tree seedlings, particularly to women, to support reforestation efforts. [… They] plant Ficus trees near their homesteads to provide shade and help control erosion, and Dracaena trees on their fields to retain soil moisture.”
9. [A Texas school board] votes yes to provide low-cost housing to staff at no cost to the district

“The program will include 300 homes[…] only a short commute to campuses. […] Rent will be determined on a sliding scale based on their salaries, with those making less receiving a larger discount. The proposed community would include amenities, like childcare facilities[….]”
10. Heat pumps keep widening their lead on gas furnaces

“Americans bought 37% more air-source heat pumps than the next-most-popular heating appliance, gas furnaces, during the first 11 months of the year. That smashes 2023’s record-setting lead of 21%.”
January 15-21 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#fish#sunfish#mola mola#aquarium#us politics#costco#dei#diversity equity and inclusion#louisiana#habitat restoration#green infrastructure#brazil#global warming#science#forever chemicals#recycling#water#water scarcity#big oil#student loans#federal aid#reforestation#gardening#low income#affordable housing#housing#school#heat pump installation
136 notes
·
View notes
Text
188 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trickle-down Karma, anyone? 🤨

#ronald reagan#jimmy carter#solar panels#white house#pacific palisades#wildfires#climate change#big oil#fossil fuels#that's what you get#karma
122 notes
·
View notes
Text
"On his first day in office, Trump issued an executive order resurrecting a committee — nicknamed the God Squad — that hasn't met in decades. Its purpose is to decide which species live or die — so that corporations can drill, mine and log the public lands that sustain the wild legacy belonging to all of us.
Doug Burgum, Trump's pick to lead the Interior Department and a cheerleader for Big Oil, will also chair that committee, which can overrule the Endangered Species Act. It will meet at least four times a year, and we know what to expect from those meetings: illegal workarounds so more oil wells can be built in the homes of rare and vulnerable animals and plants.
The anti-nature agenda of the new administration must be blocked, and the Center for Biological Diversity is already in court to do it.
Please help us fight back with a gift to the Future for the Wild Fund "
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
New research has found that a complex form of air pollution from Alberta's oilsands has gone largely unreported — and the impacts to downwind habitats are "entirely unknown."
The peer-reviewed study, led by researchers with Environment Canada and Yale University, investigated the fate of carbon pollution from the industry by measuring plumes of pollution pumped out from industrial sites in northern Alberta.
Alberta government officials say the research is part of their ongoing efforts to better understand gas-phase organic carbon, a volatile source of oilsands contamination.
Critics say the findings are another blot on Alberta's environmental record that demands immediate action from the provincial regulator. [...]
Continue Reading.
Tagging: @newsfromstolenland, @abpoli
97 notes
·
View notes
Text

#Supreme Court#Corruption#Bribery#Uncle Thomas#Deadbeat Billionaires#Tax The Rich#CHEVRON#Big Oil#Big Pharma#Robert Reich
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Uriel Araujo
In an underreported but hugely important development, the United States is now claiming a vast portion of the ocean floor, twice the size of California. According to the U.S. Department of State (DOS) Media Note released on December 19, the area “is approximately one million square kilometers spread across seven regions” and “holds many resources.”
264 notes
·
View notes
Text

#socialism#communism#democrats#new world order#climate change#republicans#wef#biden#trump#nwo#climate change hoax#big oil#carbon footprint#global warming
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
TIL: There are a decent amount of laws limiting drilling for oil in specifically the “Gulf of Mexico” suddenly it makes sense why Trump has been so hung up on renaming it to the “Gulf of America”. The laws can be updated easily by Congress…
#us politics#trump#anti capitalism#climate crisis#climate change#big oil#gulf of mexico#gulf of america#follow the money#even the stupid things are nefarious
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
New Oil From My Facility
My new oil is fun, sticky, slick, funny, awesome, yummy, interesting, super interesting, Turing complete, gay, interesting, quality, and quality, and interesting!
I am giving away free samples for $240.55!
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Good News - May 22-28
Like these weekly compilations? Support me on Ko-fi or $Kaybarr1735! Also, if you tip me on Ko-fi or CashApp (and give me some way to contact you if it doesn’t automatically), at the end of the month I'll send you a link to all of the articles I found but didn't use each week - almost double the content!
1. Scientists Invent Healthier More Sustainable Chocolate

“The new chocolate recipe from researchers at ETH Zurich uses more materials from the cocoa pod that are usually discarded, including more of the pulp as well as the inner lining of the husk, known as the endocarp. […] The resulting chocolate also [was “deliciously sweet” and] had 20% more fibre and 30 percent less saturated fat than average European dark chocolate[, and] it could enable cocoa farmers [to] earn more from their crops.”
2. Vermont Is Coming for Big Oil, Making It Pay for Decades of Climate Pollution

“Legislators in Montpelier are on the brink of enacting the "Climate Superfund Act," modeled after the federal Superfund law, that seeks to make oil, gas and coal companies pay for damages linked to historical greenhouse gas emissions. […] Companies would be held liable for the costs associated with […] floods and heat waves, along with losses to biodiversity, safety, economic development and anything else the treasurer deems reasonable[, that were caused by their emissions].”
3. Important bird habitat now protected in the Rocky Mountain Trench
“Grassland-reliant species in the Rocky Mountain Trench now have more protected habitat thanks to a new [270-hectare] conservation area near Cranbrook. […] About one-third of the Skookumchuck Prairie Conservation Area is forested[…,] Most of the site is a dry grassland[…, and] Three hectares of wetlands add to the landscape diversity and offer crucial benefits to wildlife and water systems in the area. This conservation gem also provides habitat for endangered American badger and excellent winter range for elk, mule deer and white-tailed deer.”
4. Lemur Week marked by 70th breeding success

“A wildlife park has celebrated its 70th lemur breeding success ahead of a week raising money to help save the endangered primates. […] The park's open-air Madagascar exhibit is home to 31 free-roaming lemurs and was officially opened in 2008. […] Females are only sexually receptive for just one or two days a year, leaving a small window of opportunity for males to father offspring. […] The two playful siblings, one female and one male, were born to father Bernard and mother Hira.”
5. Innovative material for sustainable building
“Researchers introduce a polymer-based material with unique properties. This material allows sunlight to enter, maintains a more comfortable indoor climate without additional energy, and cleans itself like a lotus leaf. The new development could replace glass components in walls and roofs in the future.”
6. Isle of Wight eagles don't pose threat to lambs as feared

“While there had previously been fears that the eagles would feed on livestock, such as lambs, the project has found no evidence of this. [… “W]hite-tailed eagles effectively steal meals from other predatory birds[, which is] a really important ecological role that had been lost within the landscape and is being restored.” [… The birds’] population was boosted by a chick last year – the first time the species has bred in England in 240 years.”
7. Breakthrough discovery uses engineered surfaces to shed heat
“Cheng's team has found a way to lower the starting point of the [Leidenfrost] effect by producing a surface covered with micropillars. […] The discovery has great potential in heat transfer applications such as the cooling of industrial machines and surface fouling cleaning for heat exchangers. It also could help prevent damage and even disaster to nuclear machinery.”
8. New malaria vaccine delivered for the first time
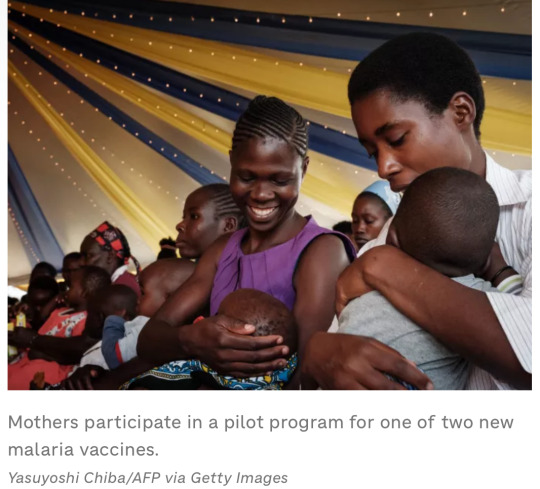
“A total of 43,000 doses arrived by air today from UNICEF, and another 120,000 are scheduled to show up in the coming days. […] They're the first vaccines designed to work against a human parasite. […] Across four African countries, these trials showed a 75% reduction in malaria cases in the year following vaccination of young children. […] The Serum Institute of India, who will be manufacturing the new vaccine, says a hundred million doses will likely be available to countries by the middle of next year.”
9. Urban gardening may improve human health: Microbial exposure boosts immune system
“"One month of urban indoor gardening boosted the diversity of bacteria on the skin of the subjects and was associated with higher levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines in the blood. The group studied used a growing medium with high microbial diversity emulating the forest soil," [… whereas] the control group used a microbially poor peat-based medium. [… N]o changes in the blood or the skin microbiota were seen. […] “This is the first time we can demonstrate that meaningful and natural human activity can increase the diversity of the microbiota of healthy adults and, at the same time, contribute to the regulation of the immune system."”
10. Cities Are Switching to Electric Vehicles Faster Than Individuals
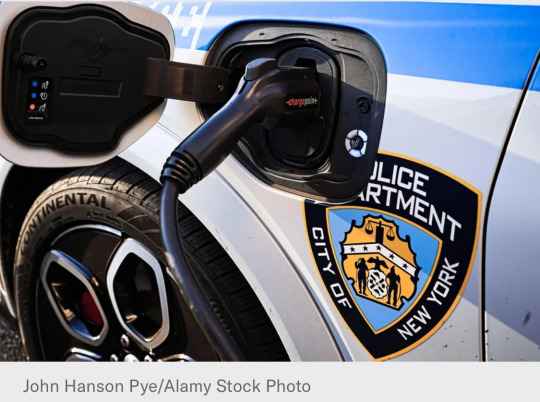

“[M]ost large cities have adopted some kind of climate goal, and some of them are buying EVs for their municipal fleets at a faster rate than the general public. And that progress could speed up as more EVs enter the market and as cities get educated about grant funding and tax incentives that were passed over the last four years.”
May 15-21 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#chocolate#sustainability#farming#health#vermont#big oil#oil companies#climate change#cooling#technology#nuclear#malaria#vaccine#africa#unicef#eagles#livestock#england#birds#electric vehicles#glass#energy efficiency#habitat#conservation#lemur#zoo#gardening#urban gardening
351 notes
·
View notes
