#Ancient Iberian Cultures
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo





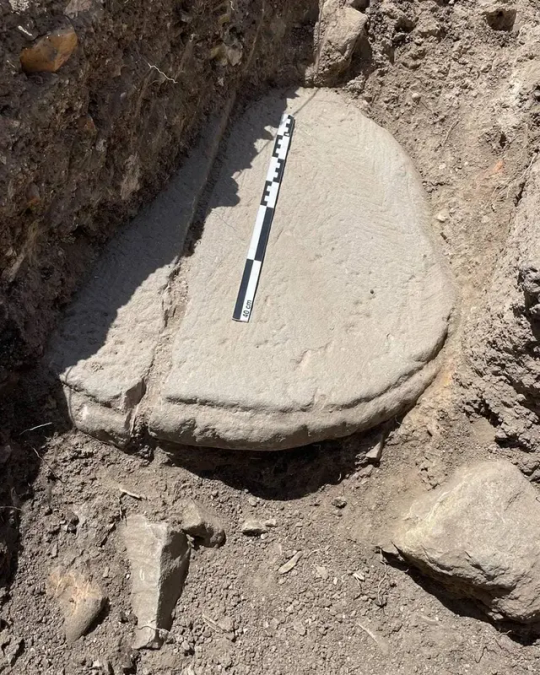
The archaeological site Iberian Citadel of Calafell (Penedès, Catalonia) was a fortified residence built by the Cessetani people (one of the Ancient Iberian peoples) and inhabited between the 6th and 2nd centuries BC. Its destruction was probably due to the Roman occupation.
A part of the archaeological site has been rebuilt in the original techniques to serve two purposes: one, it allowed archaeologists to research the building methods through experimental archaeology; and two, to show what an Ancient Iberian village from around the year 200 BC would look like. You can see the result in these photos: the foundations and lower part of the walls are made of stone to keep out the humidities from the ground, and the rest of wall is made of rammed earth, with ceilings using wooden beams and reed fences. The research focused on those elements that rarely leave a trace, for example the inclination of the roofs (when the walls and roofs are made of a material that doesn't resist the passage of time, like rammed earth) and water draining.
Photos from Enoturisme Penedès and Visit Calafell. You can find the results of the reseach in the article linked here.
#arqueologia#història#calafell#catalunya#ancient iberians#archeology#archaeology#antiquity#iberian#culture#history#historical#travel#europe#southern europe#protohistory#iron age#experimental archaeology#archaeological site#ancient iberian#ancient
88 notes
·
View notes
Text
Imagine discovering an #ancient #alphabet by sheer chance—a script that belonged to a long-lost civilization.
This is precisely what happened recently, shedding light on a forgotten culture that once thrived in what is now modern-day #Turkey.
The 20-centimeter (7.8-inch) #tablet was recently unearthed during an archaeological dig near the #Spanish town of #Guareña. Known as Casas del Turuñuelo, the site belongs to the late #Tartessian civilization that developed in the southwestern #Iberian Peninsula around 2,500 years ago.
When the Spanish National Research Council revealed the discovery on June 6, they simply explained that it depicted battling individuals who were identified as warriors.
The news caught the attention of Joan Ferrer i Jané, a computer scientist and expert in #Paleohispanic #languages at the University of Barcelona, who quickly realized the artifact was even more significant than the initial reports had suggested.
The newly found inscriptions promise to unlock secrets of the past, offering insights into the language, culture, and daily life of a people lost to history.
This remarkable find not only enriches our understanding of ancient civilizations but also sparks curiosity and excitement about the mysteries that still lie beneath the earth.
Read more at IFLScience.
https://www.iflscience.com/ancient-alphabet-of-a-long-lost-civilization-stumbled-upon-by-chance-74835
#ancient alphabet#ancient language#Turkey#Anatolia#Tartessian civilisation#Iberian Peninsula#Spanish National Research Council#ancient civilisation#extinct culture#Paleohispanic#University of Barcelona#language#culture#ancient civilizations#mysteries#translation#etymology
0 notes
Text

Genres: Heavy romance, Fall of your entire culture, Ancient history slice of life, Found family
Rating : 16+ for depictions of violence, mature themes and language. (List to be expanded on)
Summary
Life was once tranquil on the isolated coast of your city, surrounded by a loving family and promising prospects for success in your societal position. However, tranquility shattered as flames engulf your city, escape becomes the only viable option, if luck favors you enough to evade the soldiers blocking your path that is.
Yet, amidst the chaos, you realize that the existence of a stray and that of a Roman slave may not be so disparate.
If the gods truly have a plan for you, their track record thus far suggests they're not worthy of your trust either. But when a fate worse than death is upon your door, you really cant get picky can't you?
Features!
Assume the role of a member of an Iberian civilization dwelling along the coast.
Customize your protagonist's background as a warrior or a priest. Both with diferent odds on their favour.
Flee from the Romans (or choose otherwise) and embark on a quest to find a new place to call home.
Decide between preserving your culture from extinction or embracing the dawn of new societal norms, and confront the repercussions of your choices.
Engage in romantic pursuits with one of the available romance options. (Witch will be expanding as the game develops and progresses)
The RO´s Cast
Theodosius (Theo) Aurelius [He/Him]
Theo resembles his father´s features, tall, blond and with eyes coloured by the sea. He also has a cold temperament and a tendency to keep people at arm's length.
But being a powerful Roman family heir might make him a good ally. The truth is that you have no option but to please him or his father who bought you, all in hopes of a change of fortune. Or so you tell yourself, as the cold man shows you a mercy not proper of Romans. Maybe they are not as beastly as you thought after all?
Eon[He/Him]
Eon is a huge man, with signature red hair, heavily tanned skin and a green stare. So is his entire family, a mercenary group from the northern city of Numantine.
With a world of differences in between and a war that has shaken the safety of the entire peninsula, he is as good a bet on survival as it gets. But when the times can't seem rougher, this giant man offers a sweetness that you have rarely known amidst despair, maybe one strong enough to survive hunger?
Demo:
420 notes
·
View notes
Note
The most annoying thing about generic medieval fantasy slop is that most of it has basically nothing to do with real European history. Tolkien's stuff was based on folklore and myth from anglo-saxon England, so the omission of things like religion and social classes makes sense. But most modern DnD-like fantasy stuff is based on worlds that are much less mythical, and yet they're all exactly the same while having not much to do with real europe. There's no notable distinction between the names and languages of people from one country and another, they're all random european names that come from everywhere from Ireland to portugal to greece to Novgorod, with a few made up european-sounding names with no thought behind them. The exact way social stratification varied, like how some serfs from the HRE would be trained as knights and given valued positions as the emperor's Ministeriales; or the difference between serfs, free peasants who rent, free peasants who have common land, and gentry; or the antipathy between HRE Princes and the Free Cities' elites; or that the centralisation of the governments of the iberian crowns that was made possible by an increase in burghers who studied Roman Law and became Civil Servants; or how feudal lords didn't do much administration and were rarely even literate; is all completely ignored in favour of a worldbuilding-wise nonsensical stylistic mish-mash of anglo-saxon England, Arthurian Britain as imagined by the French, ancient-regime france and the late-medieval Hanse. I wanted to ask you something but I got lost in the rant, sorry
Don't matter, you can keep talking to me like that all night if you wish, in fact, feel free to get more comfortable over there
ahem
I'm very tired of the Middle Ages, even with well researched settings, I believe we reached a point of saturation. I do wonder when this omnipresence of the Middle Ages in fantasy came from, because while there are undertones of it in Tolkien for example, it doesn't scream Middle Ages (more of Arthurian and Anglo-Saxon legend though) I have a feeling there is more to this relatively Middle Ages obsession, because it's even widespread in pop-culture in a way that I feel other time periods aren't.
But what bothers me is the same as you Anon, the fact there is a lot of interesting things to explore about the Middle Ages, and instead it's treated as a shallow aesthetic, as a monolith that can be just used as decoration for your story. Because that's in fact my main complaint with worldbuilding, when cultures are treated as interchangeable monoliths, and then every setting is the same; and if your setting is generic and flat, it means that you could switch your characters to any other setting and that makes them generic and flat. And what is interesting about Middle Ages Europe is that people back then, like any past societies, had very different worldviews and very different ways of organizing their lives. You wouldn't just exchange a knight into a modern soldier or cop and it would be the same. The life of people back then was different, and I would expect a fantasy work inspired by that to reflect it.
Many don't seem to want to engage with that though. They want the aesthetics without any thought about the societies, culture, economics, dynamics that were there. And to be honest, at this point, those aesthetics are not even that compelling anymore.
87 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ancient human remains buried in Spanish caves were subsequently manipulated and utilized

Caves served as sites for burial and later modification of human remains for thousands of years in the Iberian Peninsula, according to a study published September 20, 2023, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Zita Laffranchi and Marco Milella of the University of Bern, Switzerland, and Rafael Martinez Sanchez, Universidad de Córdoba, Spain, and colleagues.
The use of caves as burial sites is a cultural phenomenon with a broad distribution in both space and time. In the southern Iberian Peninsula, this practice became particularly common starting around the 4th millennium BCE. Also common in the archaeological sites of this region is evidence of manipulation of buried human remains, although the cultural meaning behind this is largely unclear. Read more.
332 notes
·
View notes
Text

Moor or Moreno is a Spanish word that has several meanings, including "dark-skinned" or "brown-skinned". It can also refer to someone who has a dark complexion.
The Moors who rulled Spain..
Tariq ibn-Ziyad
In A.D. 711, a group of North African Muslims led by the Berber general, Tariq ibn-Ziyad, captured the Iberian Peninsula (modern Spain and Portugal). Known as al-Andalus, the territory became a prosperous cultural and economic center where education and the arts and sciences flourished.12 Dec 2019
Ancient African Kingdoms
Black history
81 notes
·
View notes
Text
As used, the term ‘precolonial’ Africa and the distortions it represents cannot illuminate our understanding of Africa and its history. More importantly, it is wrong to think of colonialism as a non-African phenomenon that was only brought in from elsewhere and imposed on the continent. Africa has given rise to a rich tapestry of diverse colonialisms originating in different parts of the continent. How are we to understand them? For example, if ‘precolonial Morocco’ refers to the time before France colonised Morocco, it must deny that the 800-year Moorish colonisation of the Iberian Peninsula, much of present-day France and much of North Africa was a colonialism. For, if it were, then ‘colonial Morocco’ must predate ‘precolonial Morocco’. I do not know how any of this helps us understand the history of Morocco. Similarly, a ‘precolonial’ Egypt that refers to Egypt before modern European imperialism would also deny Mohammed Ali’s colonial adventures at the head of Egypt in southern Europe and Asia Minor. Was ancient Egypt part of some precolonial formation? That strains credulity. To conceive of the history of Africa and Africans in terms only, or primarily, of their relation to modern European empires disappears the history of Africans as colonisers of realms beyond the continent’s land borders, especially in Europe and Asia. It is bad enough that the term distorts the history of African states’ involvement in overseas provinces. It is worse that it misdescribes the evolution of different African polities over time. The deployment of ‘precolonial Africa’ is undergirded by a few implausible assumptions. We assume either that there were no previous forms of colonialism in the continent, or that they do not matter. We talk as if colonialism was brought to Africa by Europe, after the 1884-85 Berlin West Africa Conference. But it takes only a pause to discover that this is false. African history is replete with accounts of empires and kingdoms. By their nature, empires incorporate elements of colonisation in them. If this be granted, Africa must have had its fair share of colonisers and colonialists in its history. When, according to the mythohistory (the founding myth of the empire) of Mali, Sundiata gathered different nations, cultures, political leaders and others to form the empire in the mid-13th century, he did not first seek the consent of his subjects. It was in the aftermath of their being subdued by his superior force that he did what Jean-Jacques Rousseau in the 18th century insisted all rulers should do if their rule is to escape repeated challenges and last for an appreciable length of time: turn might into right. Ethiopia, another veritable empire, is a multinational, multilingual, multicultural state whose members were not willing parties to their original incorporation into the polity. Whether you think of the Oromo or the Somali, many of their successor states within Ethiopia are, as I write this, still conducting anticolonial struggles against the Ethiopian state.
145 notes
·
View notes
Note
Imo there is not enough Valyria content out there so I would LOVE to see your thoughts/headcanons on what the geography, city, fashion, etc. looked like
okay this ones a little difficult because even though Valyria is clearly inspired by Rome, I don't like roman (aka greek) architecture for them it just doesn't really fit to me. Honestly its hard to assign any real life inspo because the existence of dragons would have had some major impact on the society as a whole, architecture included
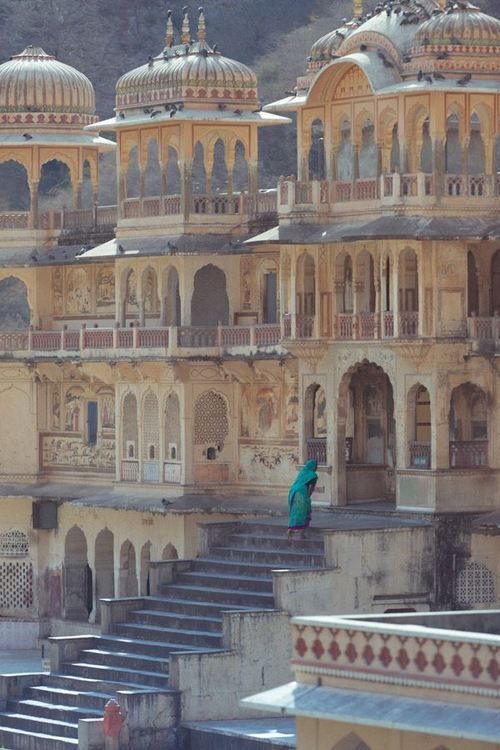
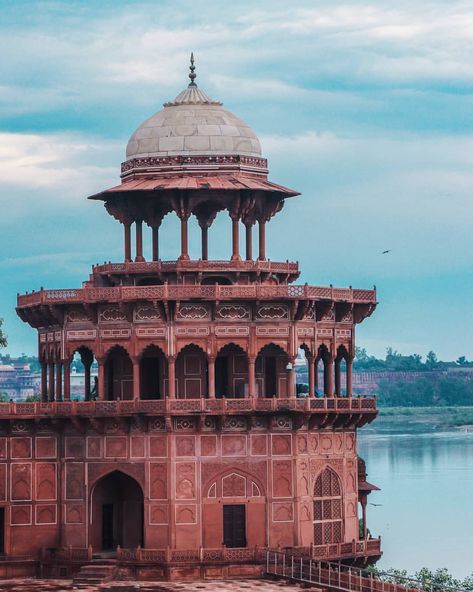
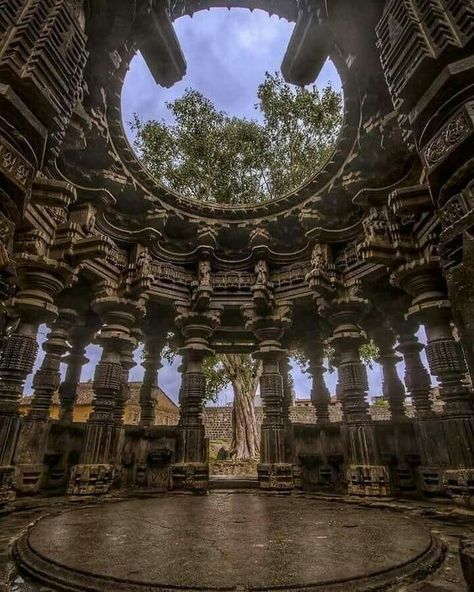
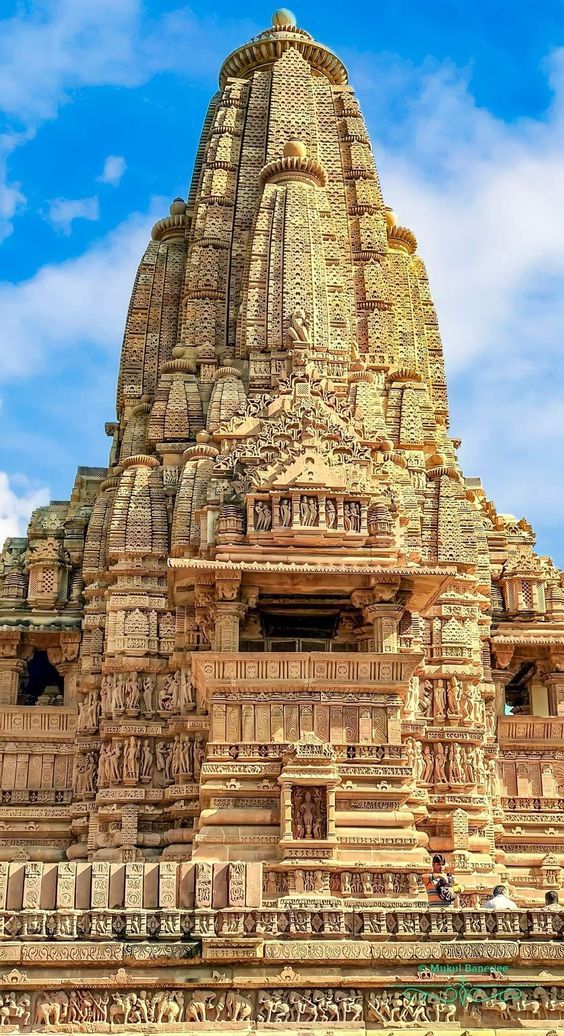
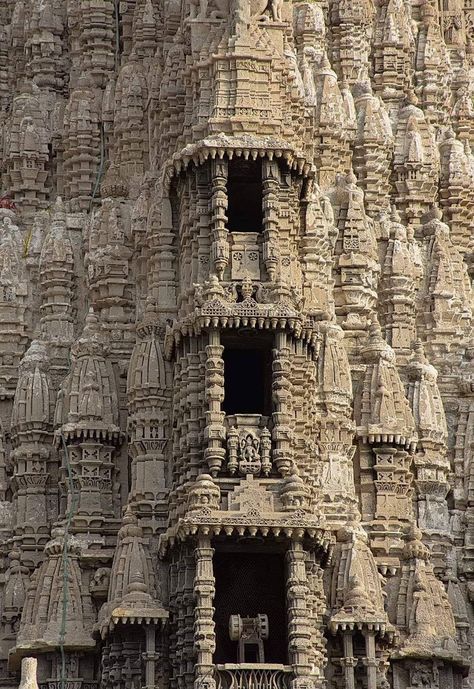
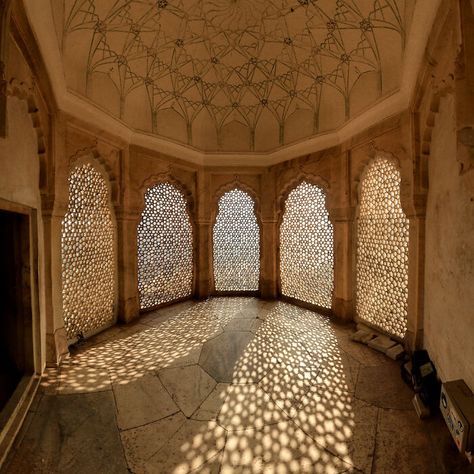
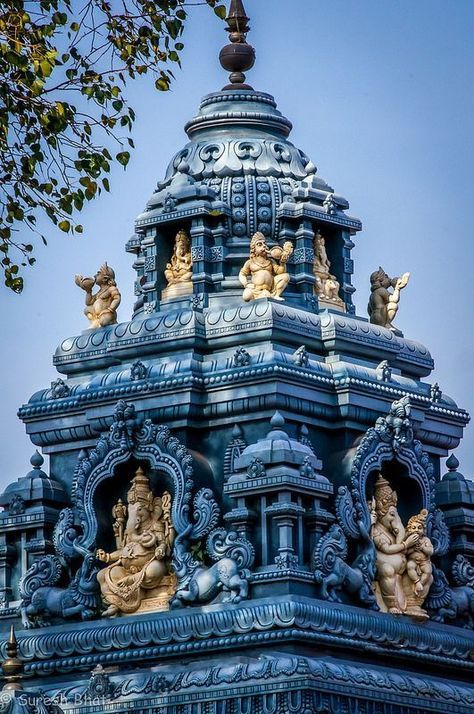








However, if I had to pick a type to ascribe to Old Valyria, my first choice would be a twist on Hindu architecture. I am absolutely obsessed with the sheer amount of details on the buildings (especially the Meenaskshi Temple at the bottom, everyone please go look at more pictures of it it's gorgeous). It's incredibly complex but also tends to be very symmetrical, the styles perfected over hundreds and hundreds of years. I also really love the idea of the spaces being open and well lit, it fits well.
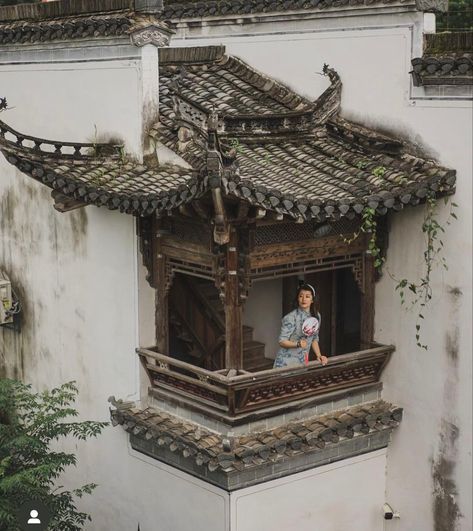






Another alternative is traditional Chinese architecture, with the added bonus of dragon motifs that are already there :D Another type of architecture with an intense focus on details, symmetry, and how the design of a space affects a person. Architecture is a reflection of where a society is in their development, and I find that this could be a good inspiration for Valyria, an advanced culture with the excess time and resources to build things like these.
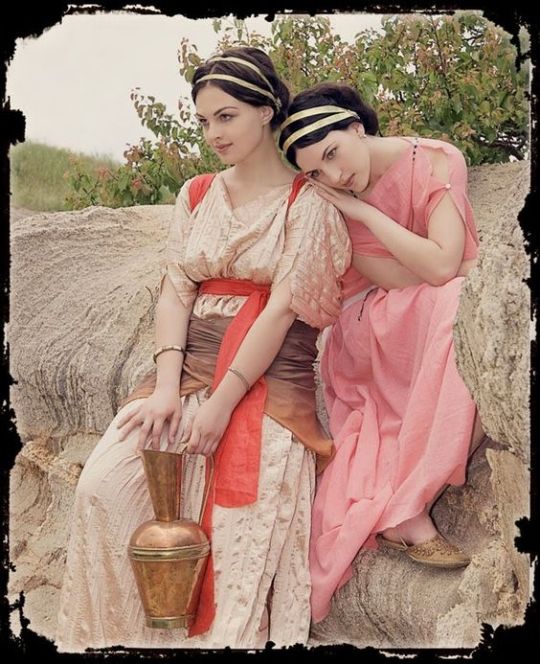
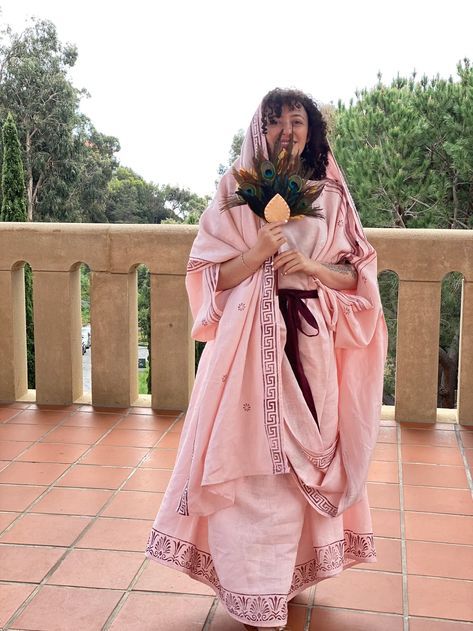
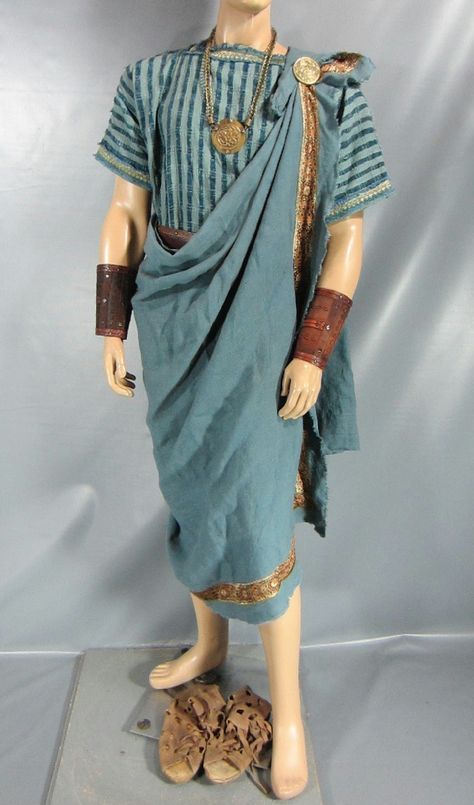
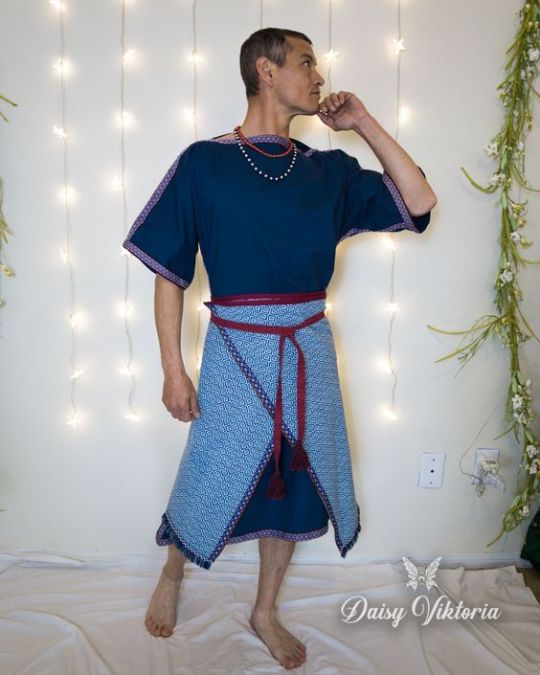
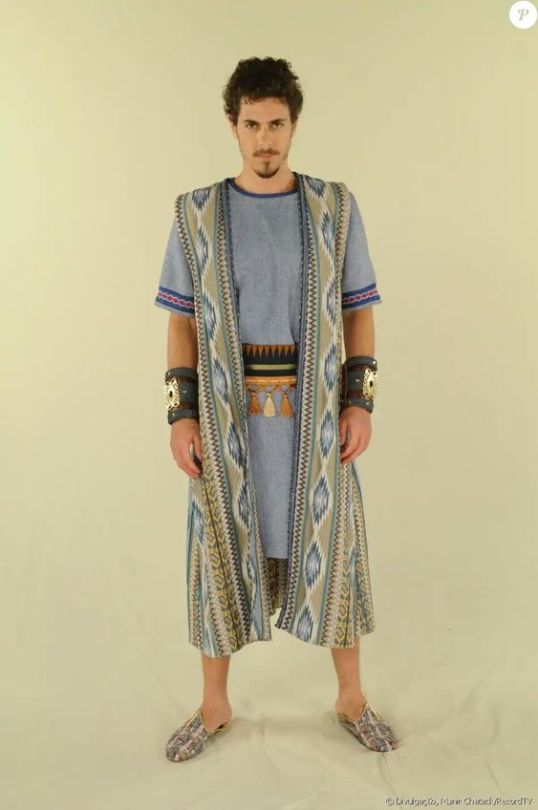
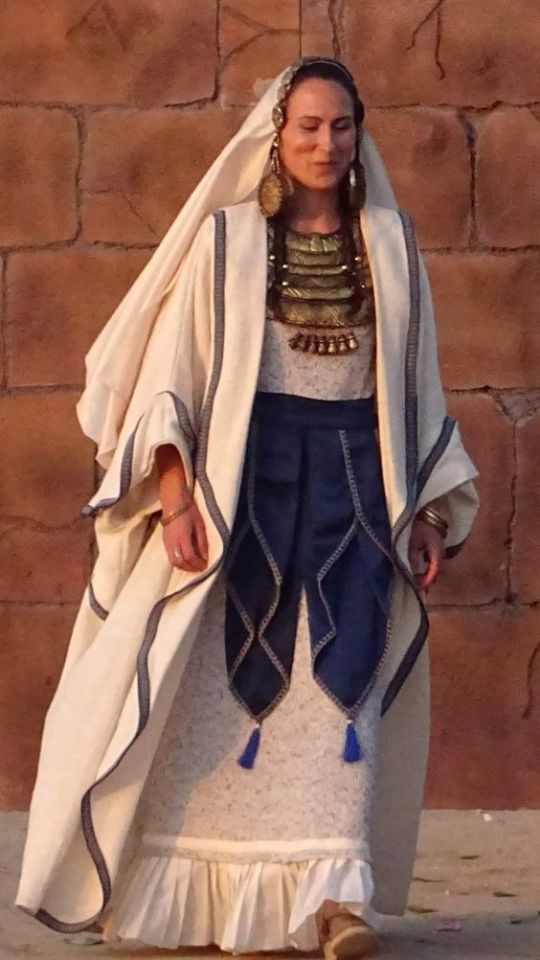
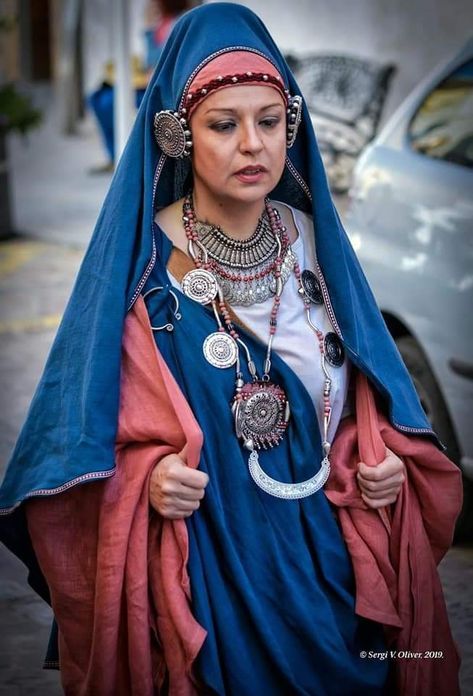








Woof okay clothing is all over the place I need to brainstorm and tighten my focus on different inspos (also I wish I could draw well so I can blend these styles properly but alas...anyways we ball). The main thing is mediterranean cultures I know that much. The Iberian Peninsula, Rome, Greece, the Minoans, Malta, Cyprus, etc etc all the ancient clothing and traditional costumes from around the Mediterranean Sea. Valyria was in a warmer, damper climate, meaning lots of loose fabric that could let air through but wouldn't weigh you down. Also doubling as shields from the sun. You get the gist I use this type of clothing all the time.
Okay Random Cultural Things Time
Art and literature? honestly really important because while yes this was a conquering civilization, they needed their exploits to live on in wall frescoes and written epics and dramatic pantomimes. I think they were literate, and probably spread written Valyrian to all the colonies, so that they were easily assimilated. People particularly fond of their dragons had pictures of them made and statues sculpted so that they would live on after their death.
Sports and entertainment also pretty big as well. Valyrians were a highly competitive people To Me so I think that riding, swimming, wrestling, racing, and other games were popular with the people, even those in the higher classes. Also fuck it I bet they raced their dragons. A really tall amphitheater where rich men lost money as they watched dragons circle around the ring. Or fight in midair, if the dragon riders were prisoners or sentenced to death.
As for religion, the Valyrians worshipped the gods that gave them dragons, but also tolerated the other faiths of the places the conquered, just in order to ease tensions (and because they had no dragons so why would they worship dragon gods). I like the idea of Roman household gods, with small altars in every home. Statues of the gods of the home, along with any gods a particular family might favor, along with ancestor veneration and dragon veneration. Dragon skulls and dragon masks on the walls baby!
#woah this was really long#spent my entire women and gender studies class doing this sorry Judith butler#asoiaf worldbuilding
100 notes
·
View notes
Text
by Mark Oppenheimer
Black Classic also offers numerous books by the late Hunter College historian John Henrik Clarke (1915-1998), who shared Welsing’s homophobia. Clarke’s detractors often mention his antisemitism, but his homophobia is sometimes overlooked. On YouTube, you can see him cheered on as he tells an audience that Africans “had a healthy attitude toward things other people made unhealthy and made filthy and dirty.” Scornfully, he denies the possibility of gay Africans in antiquity. “Show me one case of sexual deviation before the coming of foreigners!” Elsewhere, Clarke, who blamed the “Jewish educational mafia” for multiculturalism, wrote an introduction to an edition of Michael Bradley’s 1978 book The Iceman Inheritance, which argues that white people are genetically predisposed to higher levels of racism and aggression than other groups, and speculates that Jews might be the ultimate “Neanderthal-Caucasoids.”
He also wrote the foreword to Bradley’s 1992 work Chosen People from the Caucasus: Jewish Origins, Delusions, Deceptions and Historical Role in the Slave Trade, Genocide and Cultural Colonization. This last work argues that the people known as Jews today are descended from eighth-century converts to Judaism, having usurped the tradition from a group that had been practicing Judaism for more than two millennia; these late-arriving Jews, including today’s Ashkenazi Jews, have uniquely high levels of Neanderthal aggression, which has helped them dominate other groups.
In 2001, Clarke told an interviewer that “the European uses this religion”—Judaism—“as the handmaiden of his imperial desires. I strictly mean the Europeans who answer to the word Jew. He reads the word Jew into ancient history, where the word didn’t exist. When the European Jew didn’t exist.” In an interview you can find online, Clarke told an audience, “If Jews want to dominate something, it’s very easy to dominate us. So that’s what they do.”
The idea that “white” Jews, whether Ashkenazi, Sephardi (Iberian), or Mizrahi (Middle Eastern and North African), are somehow impostors or usurpers—with the “real” Jews coming from the Nile River Valley or other parts of Africa—is a poisonous myth deployed to subvert the ancient connection of the Jewish people to the land of Israel. It’s a lie presented as a given within a certain strain of Afrocentric thought, and embraced not only by Clarke but by the aforementioned “Dr. Ben”—Yosef A.A. ben-Jochannan—who, like Clarke, is well-represented in the offerings of Black Classic Press, which publishes 12 ben-Jochannan titles. These include We the Black Jews: Witness to the “White Jewish Race” Myth and African Origins of the Major “Western Religions.”
In 2015, shortly after ben-Jochannan’s death at 96, The New York Times reported that for decades he had deceived employers about his credentials, telling Cornell and other institutions that he had degrees from Cambridge, in England, and the University of Puerto Rico at Mayagüez. Neither school had a record of his enrollment. “ ‘People condemn me for not being an intellectual of the Ph.D. type,’ Mr. Ben-Jochannan once said, reacting to questions later raised about his résumé,” the Times wrote. “While he used the ‘white man’s credential’ to go ‘certain places,’ Mr. Ben-Jochannan said, he refused to ‘let the white man certify’ his work.”
As far as I can tell, Coates has nowhere discussed the allegations against ben-Jochannan, his longtime intellectual partner—and a writer who remains a source of revenue for the press. To the contrary, Coates has always spoken of ben-Jochannan with reverence. “In 1978, when we started publishing, three elders were inspirations and gave their support—John G. Jackson, John Henrik Clarke, and Yosef ben-Jochannan,” writes Coates on the Black Classic website. “His books have revolutionized the way Black people relate to Africa and the Nile Valley.” After ben-Jochannan’s death, Coates told the Times, “I consider Dr. Ben the greatest of the self-trained historians.” Ta-Nehisi told the Times that ben-Jochannan’s example “runs through everything I do.”
Along with Clarke and ben-Jochannan, one of the authors best represented in Black Classic’s offerings remains Tony Martin. The Jewish Onslaught may be gone from the website, but several of his other books are still there, including a pamphlet, published in 1998, containing the text of a lecture given in Trinidad called The Progress of the African Race Since Emancipation and Prospects for the Future. Although largely about the Afro-Caribbean experience, Martin takes time to explain that “[p]seudo-scientific racism had been around since at least the 4th or 5th century AD when the Jewish holy book, the Talmud, pioneered the notion that Africans were recipients of the curse of Ham.” The Talmud makes no connection between Noah’s son Ham and Africa—that is a later, mainly Christian tradition, seen in early church theologians like Eusebius of Caesarea (CE 260-340) and Bede (CE 673-735).
But Martin, though a professor at Wellesley for many years, isn’t making a scholarly argument. He is making an indictment. This is also what he is doing when he writes:
“When President Clinton becomes president, he goes to Geneva and he bows down before the World Jewish Congress. When the African American woman Myrlie Evers-Williams became head of the NAACP the other day, she went straight to Geneva and bowed down before the World Jewish Congress.” This is fiction, of course—neither of them went to Geneva to genuflect before Jews—but hardly surprising coming from Martin, who elsewhere in his pamphlet calls the World Jewish Congress “a body organized on a racial or religious or whatever-the-Jews-are basis.”
One has to ask: Why is Coates selling this?
#w paul coates#national book award#antisemitism#the jewish onslaught#national book foundation#black classic press
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ancient Roman Forum Unearthed in Spain
A Spanish Farmer Long Believed a Roman Forum Once Stood on His Land. He’s Now Proven Right
Researchers have identified the Roman ruins in Ubrique as a large venue for public gathering.
In the late 1700s, Juan Vegazo, a farmer and amateur historian in Ubrique, in the southern Spanish province of Cadiz, had a grand theory: buried within the rock and dirt of a nearby hill lay the remains of an ancient Roman forum.
News from the excavations at Pompeii was reviving interest in Roman culture across Europe and inspired Vegazo to buy up the limestone hills and begin excavating. He uncovered inscriptions related to second century emperors, a name for the city, Ocuri, and laid the foundations for future archaeologists to uncover defensive walls, baths, and a mausoleum.
Still, Vegazo’s vision of the past remained incomplete. Until now. More than 300 years on, Vegazo has been vindicated by a team of archaeologists from the University of Granada. In coordination with the town of Ubrique, researchers have uncovered architectural elements in Ocuri that point to a large, public forum that would have served as place of gathering, socializing, and speechmaking. The finding infers that Ocuri was larger and more significant than previously believed.


Key to the discovery is a 50-foot-long wall that is believed to have enclosed the Roman forum as well as architectural elements of large and public buildings. Among these buildings is a large ceremonial site, as offered by the discovery of a monumental altar, column shafts and bases, and statue pedestals. Researchers believe the site supported religious practices related to water that mixed Roman and local customs.
“The excavations outline a space that is crucial for understanding the arrival and consolidation of the Romans in the southern Iberian Peninsula, as well as their hybridization with the communities that had already settled in the area,” the University of Granada’s Department of Prehistory and Archaeology said in a statement.



With its strategic hilltop position, it’s long been believed that a settlement pre-dated the Romans with researchers suggesting the absorption was both physical and cultural. Researchers now believe the site was inhabited until the end of the 4th century C.E. based on coins that were discovered—in particular, one marked with a Christogram, which is among the earliest forms of Christian iconography and was deployed by Constantine I in 312 C.E.
This continued presence in the southern reaches of Hispania, as the territory was known following its annexation in 19 C.E., was partly due to the trade advantages it offered, as it connected the coast to the interior parts of the province. Along with showing Ocuri’s size, the discovery of North African goods, including ceramics, suggests a strong and enduring (through the late 3rd century at least) economic links across the peninsula.
Aside from Roman discoveries, researchers also found evidence of medieval defensive structures.
By Richard Whiddington.

#Ancient Roman Forum Unearthed in Spain#Ubrique#Ocuri#ancient roman ruins#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#roman history#roman empire
23 notes
·
View notes
Note
Child of Venus (or alternatively a legacy) Tim Drake.
First really quickly going to run down some very basic history quickly.
Roman Venus comes from the Greek Aphrodite, who comes from the Western Semitic goddess Astarte, who is known by the ancient Mesopotamian as Ishtar and earlier Ianna.
This is an extreme overview of thousands of years of history, but it conveys my point. I want to explore all of these aspects quickly before I get into my thoughts on how this connects. (Also, like an extreme basic rundown of things that people might not know)
Ianna - is the goddess of love and war (along with several other fields) but is also heavily associated with divine law and political power. An interesting fact is that she was actually a three-form goddess. She went from a fairly localised deity to one of the most venerated deities across Mesopomeia. When the Assyrians took over, she became the highest deity, even above their national ones. She was so popular and essential that she is alluded to in Hebrew text. She didn’t experience a proper decline until the period between the 1st century CE and the sixth century CE when Christianity became widespread. She was in more myths than any other Sumerian deity. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inanna
Astarte - is the goddess of these associated combinations: war, royal power, healing, and hunting (and several others). The travels, trade, and colonisation of the people would end with her being worshipped and an accepted deity in many places, from Egypt to the Iberian peninsula. She is considered to be the equivalent of Isis in some schools of thought. Her worship would land in Cyprus, where she could have merged with a local goddess and would slowly go to mainland Greece during the late Mycenean era or the following post-Broze age collapse. In the Greek classical period, she was occasionally equated with Aphrodite through (what a great many Polythetsic cultures did) the practice of synchronising deities. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Astarte
Aphrodite - is the goddess of love, beauty, and passion (along with the others everyone knows). She is one of the twelve Olympians and is one of the most widely celebrated and worshipped deities in the Hellenic world. Some of her other epithets were Eleemon (the merciful) and Enoplios (armed). She was called Tymborychos (gravedigger) along with the previously discussed Areia (the warlike) in one of her darker, more violent natures. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aphrodite# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aphrodite_Areia
Venus - is the goddess of desire, prosperity, and victory. She is the ancestor of the Roman people through her son, and Julius Ceaser claimed to have been her ancestor. A couple of the epithets I want to highlight for a moment are Fleix (lucky), Genetrix (the mother), Physica Pompeiana (Pompeii’s protective goddess), Verticordia (charger of hearts), and Victrix (victorious) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Venus_(mythology)
Okay, now let's move on to my thoughts because this consumed my brain so much that I needed to grab my computer and write it down.
The Thoughts!
I’ll start with the child of Venus and then do the legacy version.
Janet and Venus. Imagine if, on one of the important archaeology trips, Janet comes across something important to Venus. It could be anything, whether it be the start of new ruins of a worship spot or a statue. Venus appreciates Janet's respect towards the findings and wants to know more about Janet. (There is also the fact that there is an extreme difference between the number of men and women in archaeology, especially field archaeology.) The two of them share a conversation where Janet shows interest in the history of Venus, and Venus herself drops the idea that the history behind Venus and the goddesses that precede her is also enjoyable. It was a test. Janet takes this information, wanting to have another conversation with the woman and learns as much as possible. Realising that she can do more field research, she sets it up. Venus appreciates this, and he wonders whether Tim is just the kid of Janet and Venus or if he has a three-parent setup. Tim exists.
Did Venus more or less give Janet a quest? Yes. Does Janet regret it? No. It is a very cute and tragic set-up because to be favoured by the gods is to be doomed by them. You could change up their death a bit, too. To match the tragedy vibe.
Tim grows up learning all about his parent's work. It may not have been his favourite, but he listened and learned. Tim, sent to boarding schools and in the comics, always saw school as a necessity but something secondary—Tim, who was often separate from his parents. What if when Dick Grayson’s parents died (Monster attack?), his parents realised just how dangerous the world is, and they sent him to different boarding schools to try and keep him safe. It could also explain some of Jack’s attitude. Knowing that Tim isn’t truely his. Knowing the reality that fate could hand his son. Explain why he often sits back to parenting, knowing that his son could die in tragedy young, but also why he clings sometimes. Why will he hammer down on parenting when he realises that he can’t protect his kid and his kid could die?
Now onto Tim. Tim loves his city so much. Tim goes back to Gotham even when his whole family moves. Tim would do anything for Gotham. That is Passion and Love. That is dedication. Tim, who becomes Robin. Who must go through a much longer trail and training before becoming Robin properly? He who trained under Shiva, who Shiva sees potential for. He who chooses an unconventional weapon. One that does not quickly kill but requires skill and ability to use. (He is fighting a war in Gotham but also loves Gotham. He hurts and helps. He causes pain, and he saves. He brings himself to ruin to help his loved ones in his beloved city and make something better for the world he lives in.)
Tim finds himself victorious most of the time but sometimes has to rely a bit on luck. He is Robin, a protector of Gotham. Tim, by the way of being Robin, is trying to create a better Gotham. Tim is the one who created the Batfamily as we know it. He often gets people to work together that do not work together very well.
He is also well-travelled because he is Robin and a hero in general. He has been on multiple teams and has worked alone, and despite seeing what the world (the universe) has to offer, he is still from Gotham and will belong to Gotham.
But tragedy follows him, and he ends up in front of the graves of his loved ones more often than not. His parents, his friends, and those he feels he has failed. Even with the best of intentions, people still die and leave, and generally, being Robin creates a tragedy.
Tim being the first Roman in the family could be very alienating and make him feel like he has to prove himself, but also the idea that he would have to work harder to prove he can fight and be here, and people still underestimate him? Venus may have been significant, but people have inherent biases. No one would assume a child of Venus would be a skilled warrior despite the history of war. However, the opposite is how people would think he only got this far because of how important of a goddess his mother is. That he didn’t have to put in the hard work because he wasn’t expected to.
I have many more thoughts, but they generally vibe without a coherent statement. If I find words for them, I’ll send another annon.
~~~
The Legacy idea
One of the Drakes is a child of Venus who is doing archaeology because it is part of the quest their mother sent them on. They are constantly travelling because staying in one place could have put their son in even more danger. If you still wanted Tim to be tied to Athena, you could have the other parent be a child or a legacy of Athena.
Annon AK
(btw if you guys are interested in aphrodite lore, i really enjoyed Overly Sarcastic Production’s video on her! theyve also done one on Dionysus, Hermes and Hades/Persephone - plus a ton of other myths and classics :))
Honestly i am so in love with aphrodite/venus child tim (no pun intended). while yes athena fits him in terms of intellect and wit- tim is more so defined by his love- for his friends, family, gotham itself. (and thank you @pooky-chan for telling me abt aphrodite tim, i feel like his love is such an underused part of his character.)
i think actually going into janet and jack's relationship with venus is super interesting! i hadn't really thought about how their birth/godly parent would effect any of their family dynamic at all.
tbh everything youve said is really great! i definitely couldn't have gone in that much detail for his background. thank you for sharing :D
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
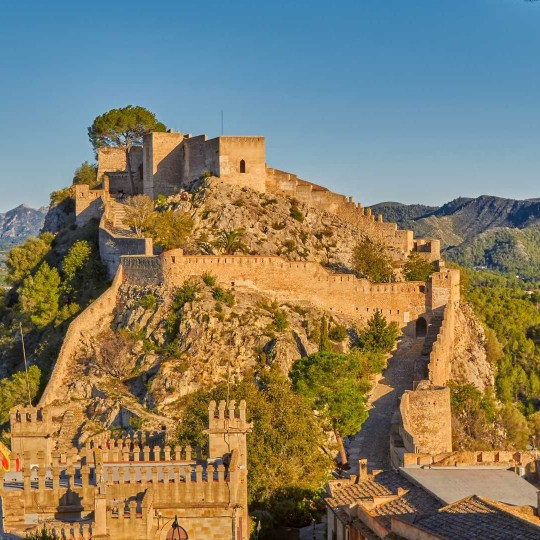
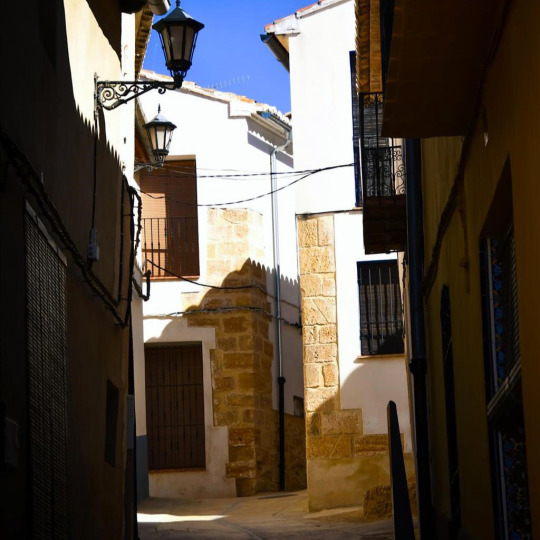
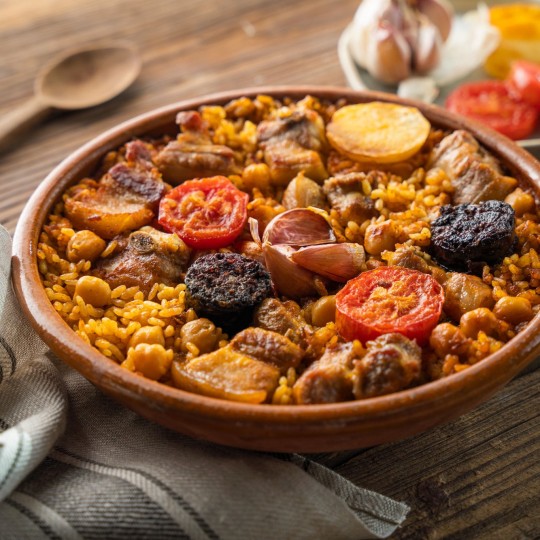
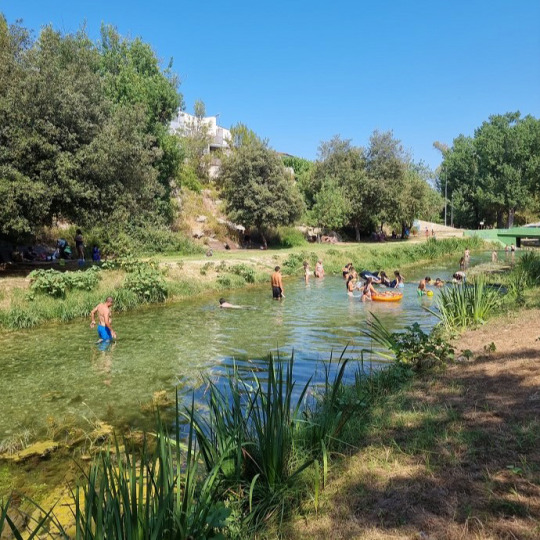
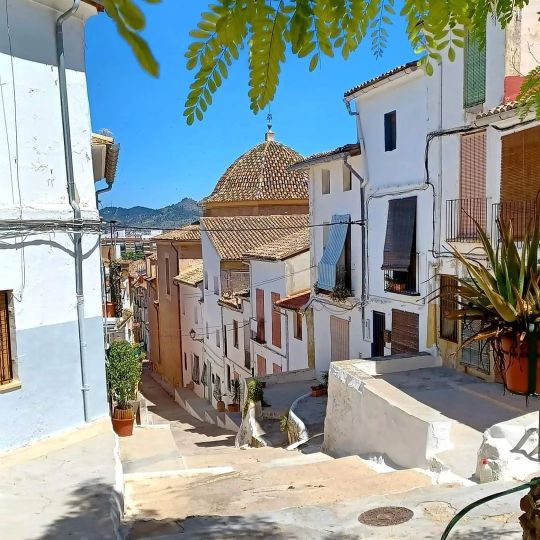









De Salses a Guardamar i de Fraga a l’Alguer: les comarques de parla catalana una a una. 65/88: la Costera (Central Valencian Country).
La Costera is a shire whose capital city is Xàtiva.
The inhabitants of Xàtiva are known with the nickname "socarrats" (which means "burned"). Xàtiva had been the main city in this area for a very long time, it had officially been given the title of city in the year 1347 and by the 1700s it was the second most populated city in all the Kingdom of València (second only to València itself). But its inhabitants had to face a particular cruelty from king Philip V.
During the War of the Spanish Succession (1701-1715), the Castillian (Spanish) army militarily occupied the Kingdoms of València, Aragon, Catalonia, and Mallorca. The invader king, Philip V, ended their independence and incorporated them by "right of conquest" to Spain, abolishing their historical forms of government and historical laws, forbidding the use of the Catalan-Valencian language in all official settings, imposing the use of Spanish, forbid many of our culture's holidays, closed down universities, publicly executed thousands and inflicted public humiliations and exile on more, and imposed extremely high taxes to pay for their homeland's militarization. At that moment, the Spanish army started a period that historians have labelled "military terrorism", where they did everything in their hand to impose a state of terror and psychological punishment on the conquered population. Among the punishments, there were massacres, mass deportations, and public torture. More than 30 Catalan towns and cities were burned to the ground, the larger of which was Xàtiva.
The people of Xàtiva had resisted the advancement of the Bourbon army (the Castillian and French armies) but in the end they couldn't resist the much superior artillery brought from France. As a punishment for their resistance, the whole city was set on fire and burned to the ground, the city's name was changed from Xàtiva to the Spanish name "Nueva Colonia de San Felipe" ("New Colony of Saint Philip"), many of its inhabitants were killed and had all their belongings taken (they were sentenced to death without a trial; the Spanish army even killed 73 people -many of whom were women and children- who were praying in a church all at once) and more than 300 Xativan families were deported to Castilla-La Mancha (Spain). Philip V's orders were: "demolish all of Xàtiva, don't leave any building standing, not even the churches". They also destroyed all the literary and artistic works as well as historical documents that were made by these people he considered rebels. Instead, they built a monument "designed to commemorate the future ages of the chastisement of rebellious people".
The fire that consumed this big city and burned it to the ground, an event amplified by the Spanish Bourbonic propaganda as a way of saying "look what happens to rebels: submit and don't dare to try any resistance", has remained in the memory of the people of this area. For this reason, the inhabitants of Xàtiva are still jokingly called "burned ones". This is referenced in the iconic Valencian traditional song Malaguenya de Barxeta, with the line "I come from the heart of the Costera, the town of the burned ones, where my Valencian Country is reborn from the ashes" (vinc del cor de la Costera / del poble dels socarrats. / D'allà on renaix de les cendres / el meu País Valencià.)
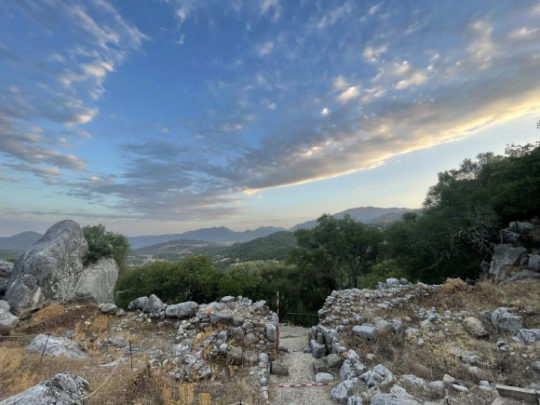
Besides the tragic history of the Xàtiva Extermination, the Costera shire has many more historical sites. It's also interesting to highlight the Montesa castle, built by the Order of Montesa (the successors of the Knights Templar); as well as the Ancient Iberian site of La Bastida de les Alcusses (5th-4th centuries BC).
Photos from Comunitat Valenciana, Turisme La Costera, Arroz Dacsa, Valencia Bonita, munozmontell/xativafotosoficial, ninosenmochila, Enrique Íñiguez Rodríguez/Wikimedia. More information about Xàtiva's destruction can be found in this article (in Spanish).
#comarques#la costera#país valencià#xàtiva#història#guerra de successió#history#war of the spanish succession#war history#imperialism#spanish history#europe#european history#castle#montesa#castles#18th century#1700s#early modern history
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

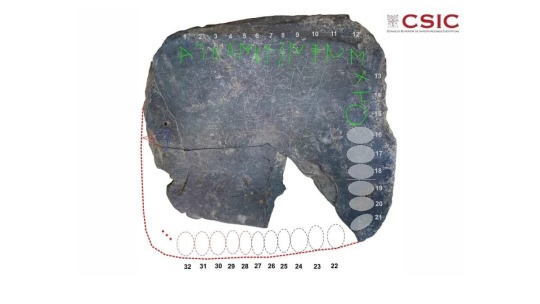
they just discovered an alphabet in the el turuñuelo tartessic site !!!!! this is huge !!!!!!
the tartessic culture is the oldest in the iberian peninsula, located in the southwestern corner of the peninsula and dated to around the 9th century BCE to the 5th/4th century BCE. in this map you can see in the brightest red the core of the culture, in darker red the dispersion to the north in later centuries, and in light red its cultural sphere, which spanned almost half of the peninsula.

if you are interested in the culture, i have a post about them.
el turuñuelo is an archaeological site located in guareña (guadajoz), in the northernmost point of the tartessos culture. it is with no doubt the singlemost important tartessic archaeological site, and i would even go on to say it is the biggest archaeological discovery of this century - at least in europe.
it was discovered in 2015, and it is a sanctuary or some sort of temple complex, which at first made the news because of its incredible state of preservation: a complete set of stairs and the remains of a horse hecatomb with at least 17 complete bodies were found in 2017.
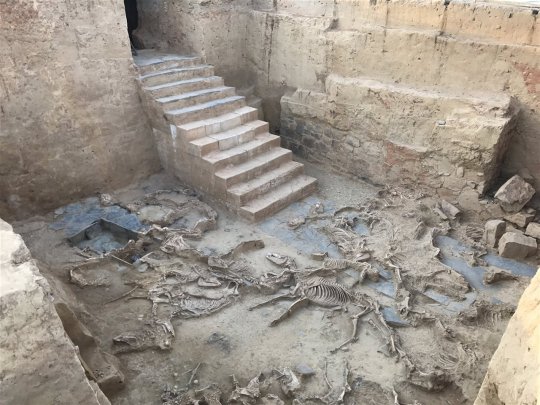

it already was the most important tartessic archaeological site just because of that (there are very few tartessic sites and most of them are not very well preserved), but after the excavations halted during covid, these last few years they returned to the site and they have made amazing discoveries. the most well-known and televised one, that made it to the news and i got to see when they set up an exposition about them last summer, are the faces of el turuñuelo in 2023, the first ever representation of tartessians by tartessians. i made a post about them, if you are interested.

this year they not only found a large collection of tartessic ceramic - which lets us know that the temple was also an artisan and probably commercial center as well, as it was usual in ancient religious centers - but just a few days ago they discovered a slate plaque with human figures, that seem to be a sort of trial drawings made by some artisan

if they seem familiar, that's because it is in one of these plaques where the alphabet has been able to be traced down, being able to be confirmed only today (11/06/2024). this is only the third southwestern paleohispanic alphabet ever founded - an alphabet derived from the phoenician one - and the most recent. it is also distinct from the other two previously discovered ones, seeing some sort of dialectalism in the way this alphabet (or set of alphabets) worked. more importantly, it is the first one to note a tartessic language, which we know was not indoeuropean in nature and also distinct from the iberian languages of the mediterranean coast. this was a distinct language or languages.
this is very exciting not only because we have a tartessic alphabet, but also because we know from greek authors like strabo that tartessians were known to be scholars that had large libraries with all sorts of knowledge of the past. we also know that the greeks interacted with the tartessians. so. it is possible that, if el turuñuelo had one of these archives that strabo talked about, that more writting can be salvaged and not only that, we could find a bilingual text in tartessian and greek that could act as a rosetta stone to finally descipher tartessian, the oldest known language in the iberian peninsula.
i cannot wait to see what el turuñuelo brings us next, it's so very exciting !!!!!!!
#archaeology#tartessos#spain#turuñuelo#i'm so fucking excited man#el turuñuelo is the gift that keeps on living#and not only that#they started to excavate el turuñuelo because they did a survey beforehand and found a series of tumuli along the guareña valley#and fixated in el turuñuelo just cause#but there's more sites like el turuñuelo waiting to be excavated#IMAGINE WHAT WE'LL GET IN THE NEXT YEARS
38 notes
·
View notes
Text


🌿 Romeo & Jamil - Gay Love Story in Andalusia 1100 AD 💖 🎶 Watch the Video: https://youtu.be/3iBkzEKmg2M
Around the year 1100, Europe was deeply divided. While the north was dominated by religious rigor and feudal violence, the southern Iberian Peninsula—Al-Andalus—was experiencing a remarkable period of cultural and intellectual flourishing.
🔸 In cities like Córdoba, Seville, and Granada, the Almoravids, a Berber dynasty from North Africa, had unified Al-Andalus under their rule. Though religiously conservative, they proved remarkably tolerant in practice—allowing Muslims, Christians (Mozarabs), and Jews to coexist in relative peace.
🔸 Between the Islamic south and the Christian kingdoms in the north, there was no open war at this time—more a tense equilibrium, a kind of "cold peace".
📚 Córdoba: A Beacon of Knowledge
Córdoba was considered one of the most advanced cities in Europe, with libraries, medical schools, translation centers, and breathtaking mosques. Its legendary library reportedly held over 400,000 manuscripts—an unimaginable number for the time.
➤ Ironically, the conservative Almoravids helped preserve and translate ancient Greek philosophy into Latin, particularly works by Aristotle and Plato, which would later inspire the European Renaissance.
Alongside science, poetry, music, and courtly culture flourished—full of sensual and aesthetic sophistication. The muwashshaha, a poetic form blending Arabic and Romance language elements, is just one example of this cultural fusion.
💗 Homoerotic Expression in Andalusian Culture
An often overlooked but fascinating aspect of this era is the presence of homoerotic relationships and culture.
Islamic law officially forbade same-sex intercourse, but romantic affection between men—especially in literature and poetry—was widespread and deeply rooted.
➤ Poets like Ibn Hazm, al-Muʿtamid, and Ibn Quzmān wrote about the beauty of young men with a candidness that would be unthinkable in many Islamic societies today.
➤ Ibn Hazm’s classic work “Tawq al-Hamama” (The Ring of the Dove) explores both heterosexual and homosexual love with remarkable sensitivity.
The contradiction between religious doctrine and cultural practice created a kind of tolerated ambiguity: homoerotic themes were acceptable—as long as they remained poetic, symbolic, and discreet.
Even under the stricter Almoravid regime, this tradition persisted, revealing just how deeply embedded homoerotic aesthetics were in the culture of Al-Andalus.
🛡️ Christian Spain: Repression and Hypocrisy
In contrast, Christian northern Spain was far more rigid. Homosexuality was often punished harshly by both church and state.
And yet, close male bonds flourished within monasteries and knightly orders—relationships often disguised as "brotherly love" that may have had deeper layers.
The ideology of the Reconquista further stigmatized anything perceived as “Moorish,” even when those cultural practices were secretly admired or emulated.
🌍 Bridging the Divide
The idea that in 1111, two young men—a Christian from the north and a Muslim scholar’s son from the south—could form a bond, is not just poetic. It’s historically plausible.
➤ Encounters did happen—along trade routes, in border zones, through diplomacy, or even educational exchanges. Christians did sometimes study in Al-Andalus despite the tensions.
Figures like Ibn ʿAmmār, or certain noble intermediaries between the two worlds, show that cross-cultural friendships and romances weren’t mere fantasy—they were part of history.
✨ A Complex Legacy
Al-Andalus was no utopia. Political power struggles, inequality, and religious tension existed. But for a brief time, it was a place where knowledge, art, and human connection transcended barriers.
The fact that homoerotic poetry and aesthetics flourished in such a conservative religious context reminds us that medieval history was far more nuanced and layered than many modern narratives suggest.
Text supported by Claud 3.7 Sonnet, GPT4o Images: FLUX1.1 Image to video: Kling AI 1.6, Hailuo Minimax Sound: SUNO AI v4.5
#AlAndalus#LGBT#lovestory#MedievalRomance#HistoricalFiction#ArabSpain#aiart#aianimation#musicvideo#ArabicPoetry#OldSpanish
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Language Goals 2024

{Chinese (Mandarin)}
Go through the Peking University lectures from HSK1 to HSK4
Go through the HSK official textbooks from HSK2 to HSK4
Watch more Chinese dubs in order to better my listening comprehension
{French}
Go to France for a 2 week long French culture and language intensive course
Revise my B2 notes and start delving into C1 material
Read at least 5 books in French
{Spanish}
Revise my B1 and B2 material + exercises
Improve on my daily exposure to European Spanish
Read at least 5 books in Spanish
{Russian}
Recover my Russian by picking up B1 and B2 textbooks
Better my weekly exposure to Russian (audio and translations)
Read at least 2 books in Russian
{Italian}
Do my university exam and pass with a decent grade
Revision + exercises from B1-B2 level textbooks
Translate/read Italian everyday for 20 minutes
Improve my Italian exposure by listening to podcasts daily
{Latin}
Pick up Latin again (study on a weekly basis)
Finish the ‘Reading Latin: Grammar and exercises’ series
{Catalan}
Read ‘Complete Catalan’
Delve more into the history of the language
{Galician}
Read a Galician Grammar and Vocabulary textbook
Read ‘A companion to Galician Culture’
{Others…}
Read ‘Origen y Gramática del Romance Andalusí’ and delve more into the history of Mozarabic and dialects spoken during the Andalusian Period throughout different Iberian regions
Maybe start studying Greek or Ancient Greek… Highly depends on how my summer studying will be structured.
These are quite ambitious goals but I do hope to be able to at lest cover 70% of what is present within this list (depending upon my university’s workload…of course…).
#classic academia#dark academia#study#studyblr#aesthetic#studyspo#langblog#langblr#language#studyspiration#study hard#study blog#study motivation#study aesthetic#studygram#studyinspo#study goals#uni#university#dark academism#dark academic aesthetic#chaotic academia#academia aesthetic
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
Deep dives into folklore: Portuguese folklore

Portuguese folklore, a mesmerizing mosaic of myths and legends, serves as a profound testament to the cultural heritage of the nation. Woven over centuries, this intricate tapestry reflects the dynamic interplay of historical influences, blending the legacies of Phoenicians, Romans, Moors, Celts, and Christians. Rooted in a diverse historical landscape, Portuguese folklore encapsulates the essence of the country's identity, encapsulating the collective imagination of its people. As we embark on a deep dive into this mystical realm, we unveil the stories, characters, and cultural significance that have endured through the ages, illuminating the captivating spirit of Portugal's folklore.
Portuguese folklore has deep roots in the country's history, blending influences from various civilizations that have shaped the region over millennia. Phoenician, Roman, Moorish, and Celtic influences, among others, have contributed to the diverse range of myths and legends that make up Portugal's folklore.
One of the earliest influences on Portuguese folklore is the Roman presence in Lusitania. The Romans introduced their own deities and myths, blending with the existing indigenous beliefs. As Christianity took root in the region, a symbiotic relationship developed between pagan and Christian elements, resulting in a unique blend of folklore that reflects Portugal's cultural identity.
The Lusitanian Mythical Heritage:
Before Roman rule, the Lusitanians, an ancient Celtic people, had their own pantheon of deities and mythical beings. The god Bandua, associated with war and protection, and the goddess Ataegina, linked to fertility, are examples of Lusitanian figures that persisted in local folklore.
The Moura Encantada:
The Moura Encantada, or the Enchanted Moorish Maiden, is a prominent figure in Portuguese folklore. These mythical beings are often beautiful women with magical powers, dwelling in hidden places or trapped in enchantments. Stories of love, loss, and magical intervention surround the Moura Encantada, emphasizing themes of fate and destiny.
The Lobo Ibérico (Iberian Wolf):
Wolves hold a significant place in Portuguese folklore, symbolizing both danger and wisdom. The Lobo Ibérico is a recurring motif, representing the untamed wilderness and the struggle for survival. Folk tales often feature wolves as shape-shifters or mystical guardians, embodying the complex relationship between humans and nature.
The Barco da Roda (Wheelbarrow Boat):
Coastal regions of Portugal have tales of the Barco da Roda, a phantom boat that appears during storms. Believed to be a harbinger of doom, this spectral vessel is associated with the souls of the deceased. The folklore surrounding the Barco da Roda reflects the maritime culture and the inherent connection between the Portuguese people and the sea.
Portuguese folklore serves as a mirror reflecting the collective consciousness of the nation. It embodies the struggles, triumphs, and enduring spirit of the Portuguese people. The fusion of pagan and Christian elements in folklore illustrates the adaptive nature of Portugal's cultural identity.
Festivals and celebrations often incorporate folklore, with traditional dances, music, and costumes bringing mythical characters to life. The Feast of São João, celebrated across Portugal, features rituals and customs that trace their roots to ancient solstice celebrations, merging pre-Christian traditions with Christian elements.
In conclusion, Portuguese folklore is a captivating journey through the cultural tapestry of a nation. Its origins in diverse historical influences, the presence of mythical figures like the Moura Encantada and the Lobo Ibérico, and its cultural significance in festivals and celebrations all contribute to the richness of Portugal's folklore. Through the ages, these stories have been passed down, evolving and adapting while preserving the essence of Portugal's enchanting heritage.
Taglist (reply or reblog to be added): @axl-ul @crow-flower @thoughts-fromthevoid @alderwoodbooks @harleyacoincidence @tuberosumtater @sonic-spade @theonlygardenia @holymzogynybatman @nulliel-tres @w0rkah0licz @sylvanthorn @tigertaurus22 @profiterole-reads @mathias-musings @1899adgg1997tbmd @grimmparanormalinvestigations
#writeblr#writers of tumblr#writing#bookish#booklr#fantasy books#creative writing#book blog#ya fantasy books#ya books#deep dives into folklore#deep dives#folklore#mythology#portuguese#portuguese folklore
38 notes
·
View notes